On Optimal Multi-Sensor Network Configuration for 3D Registration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Optimal Multi-Sensor Configuraion
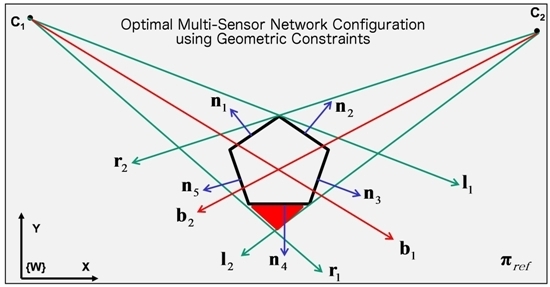
2.1. Edge Visibility Criteria and Camera Configuration
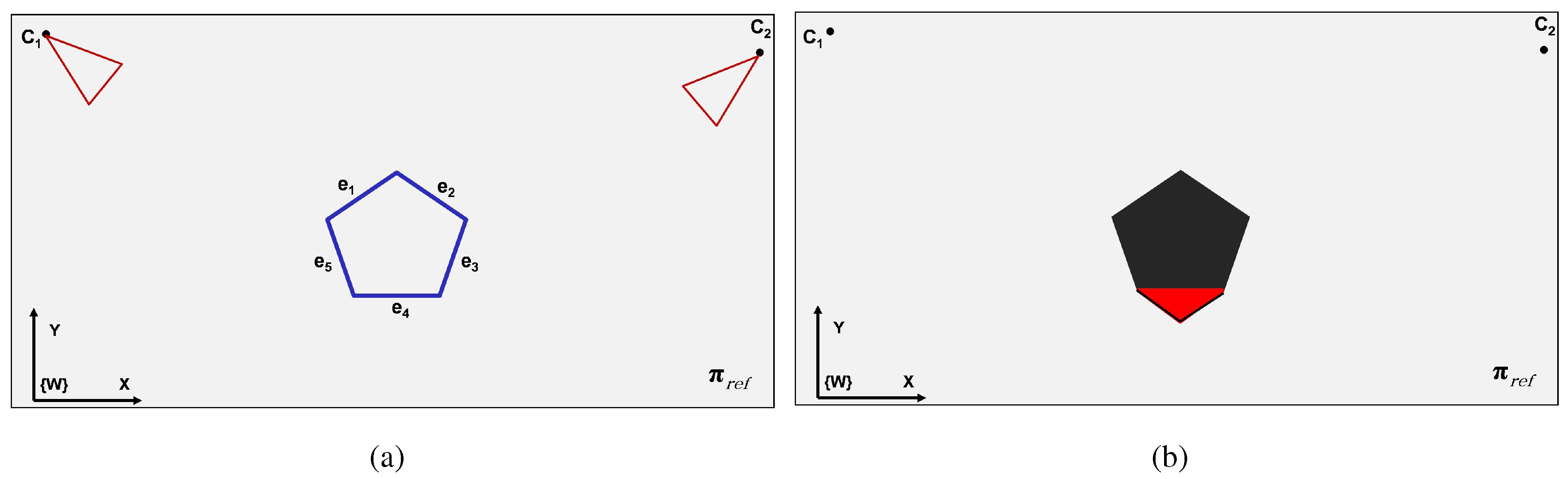
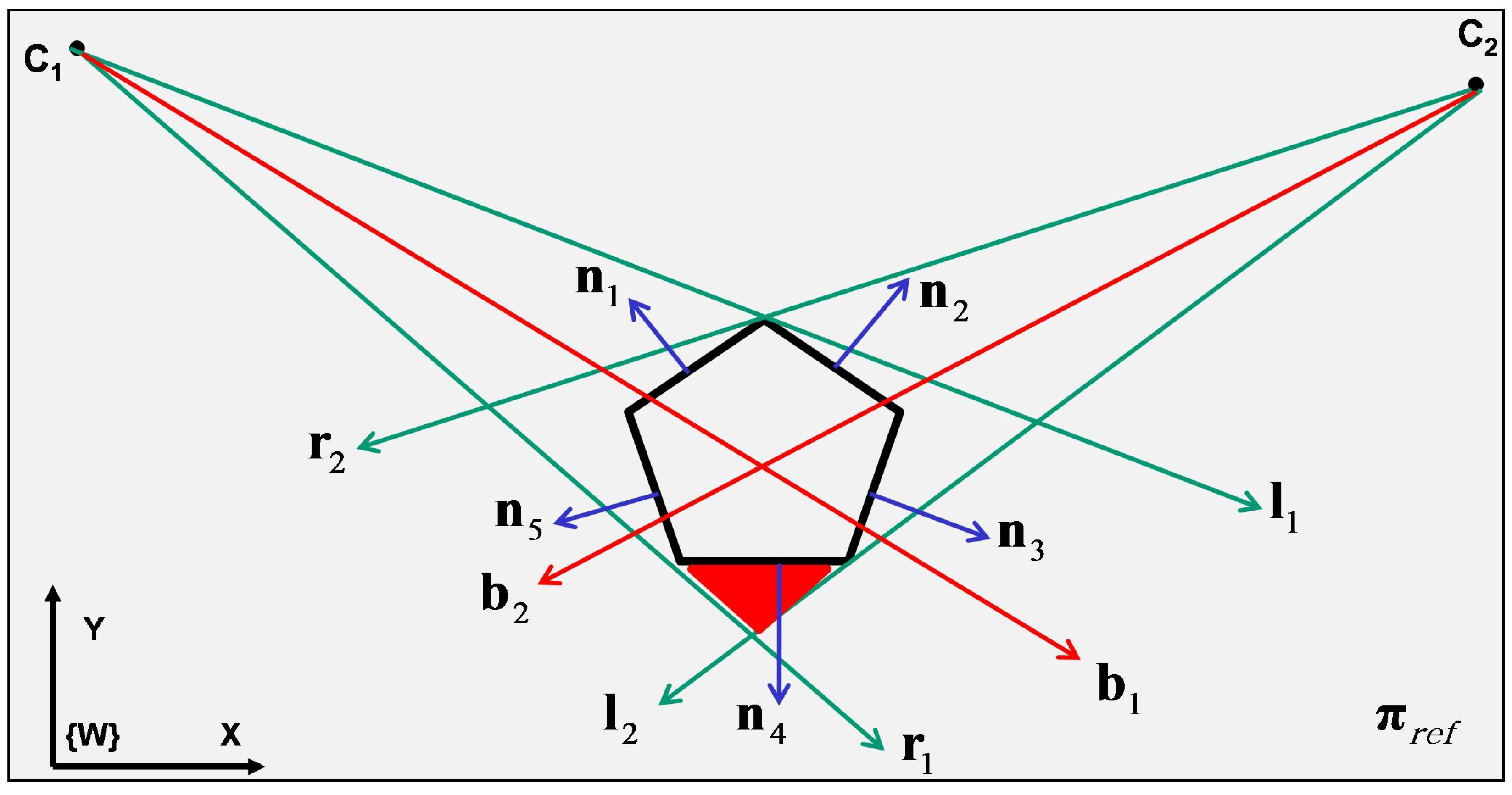
| ALGORITHM 1: Criteria to check the edges visibility for a given polygon. k is number of polygon’s edges and is the j’th edge. is the normal vector corresponding to . is the bisecting vector for camera i. Each edge is checked and will be labelled as either ‘visible’ or ‘invisible’. Labelled as ‘invisible’ for an edge means that it is invisible for all the cameras. |
 |
2.2. Optimal Camera Placement Using Genetic Algorithm
| Chromosome | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gene(1) | gene(2) | ... | gene() | ||||||||||||
| fov | cost | fov | cost | ... | fov | cost | |||||||||
| ALGORITHM 2: Algorithm to generate a valid gene. is the matrix of vertices of the polygon. max_fov is the maximum possible FOV for each gene (camera) and ‘space’ is the search space. Having these as the inputs, the algorithm generates a valid gene with its properties. The position of each gene signifies the position of the corresponding camera. The function getTangentsToPolygon(V,p) receives the matrix of the vertices of the polygon () and the position () of the camera (gene) and returns two vectors ( and ) which are tangents to the given polygon. Then, the angular bisecting vector is stored in . This bisecting vector will be used to compute the cost value of the gene. It can be also interpreted as the looking direction of the camera. Then the generated gene is returned as the result of the function createGene() |
 |

| ALGORITHM 3: Algorithm to generate a chromosome. is the matrix of vertices of the polygon. indicates the chromosome’s length or in other words the number of cameras. max_fov is the maximum possible FOV for each gene (camera) and ‘space’ is the search space. Given these as inputs, the algorithm generate a chromosome with genes and returns it (using Algorithm 2). |
 |
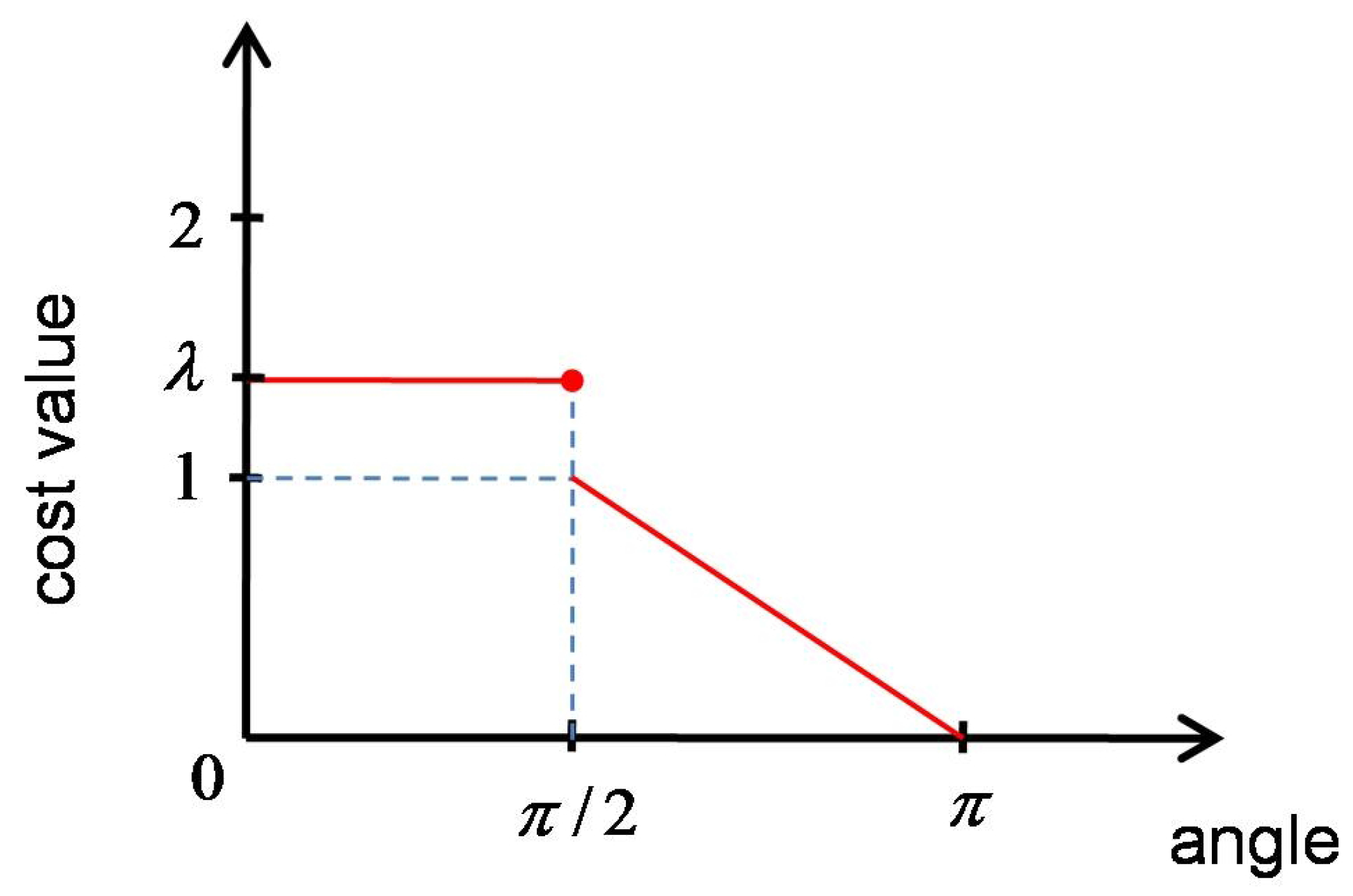
| ALGORITHM 4: Algorithm to compute the cost of a chromosome and its genes. The inputs are , the vertices’s matrix and chromosome. The cost value among each individual gene in the chromosome and each edge of the polygon is computed using the Equation (1). The cost value gets penalized for the genes which are visiting an edge that was previously visited by an antecedent gene of the chromosome (line 0-0). The penalty value is obtained using Equation (2). |
 |

| ALGORITHM 5: Genetic algorithm to search for an optimal solution for camera placement problem. |
 |
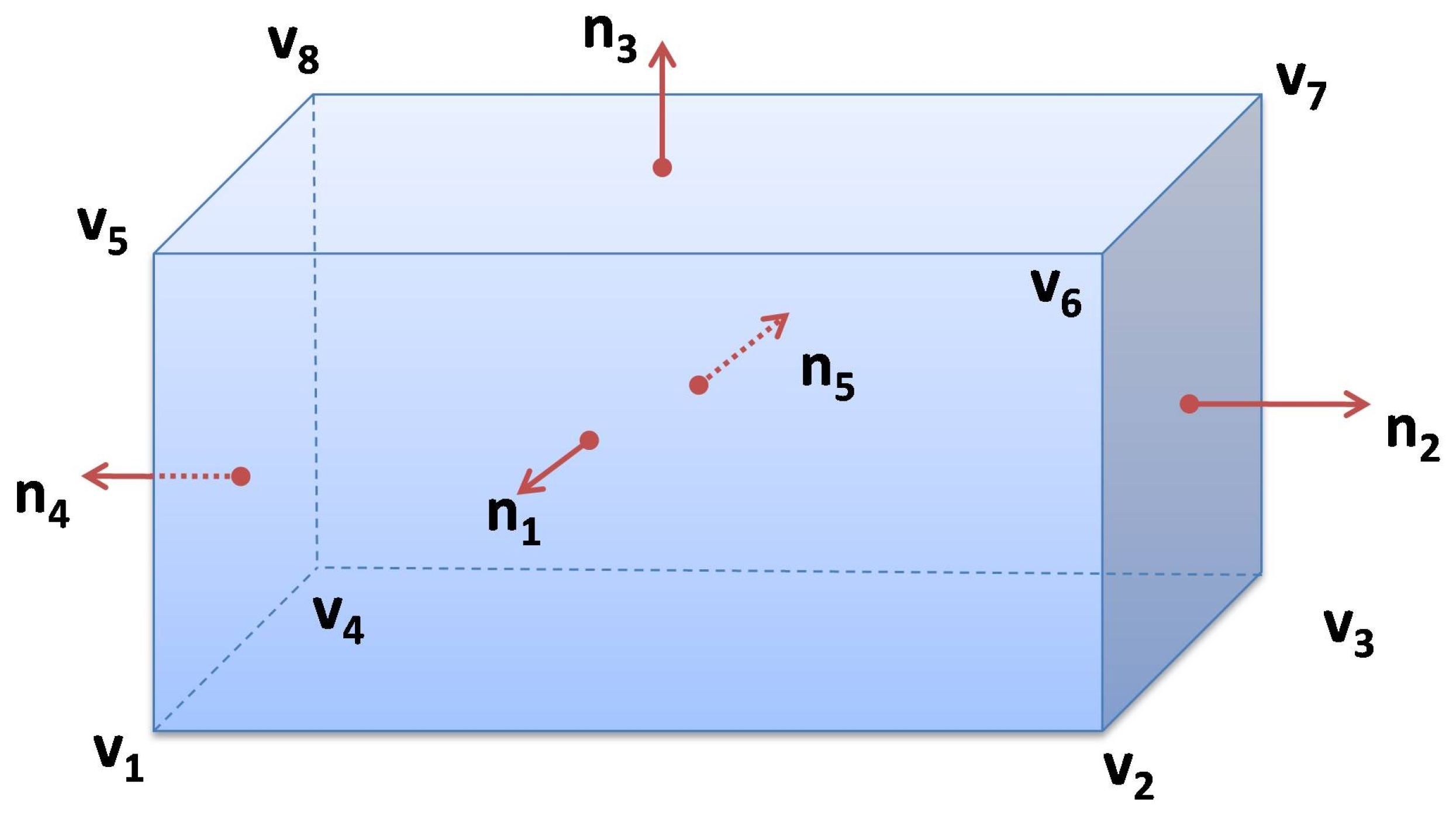
3. Camera Placement Optimization Using GAs
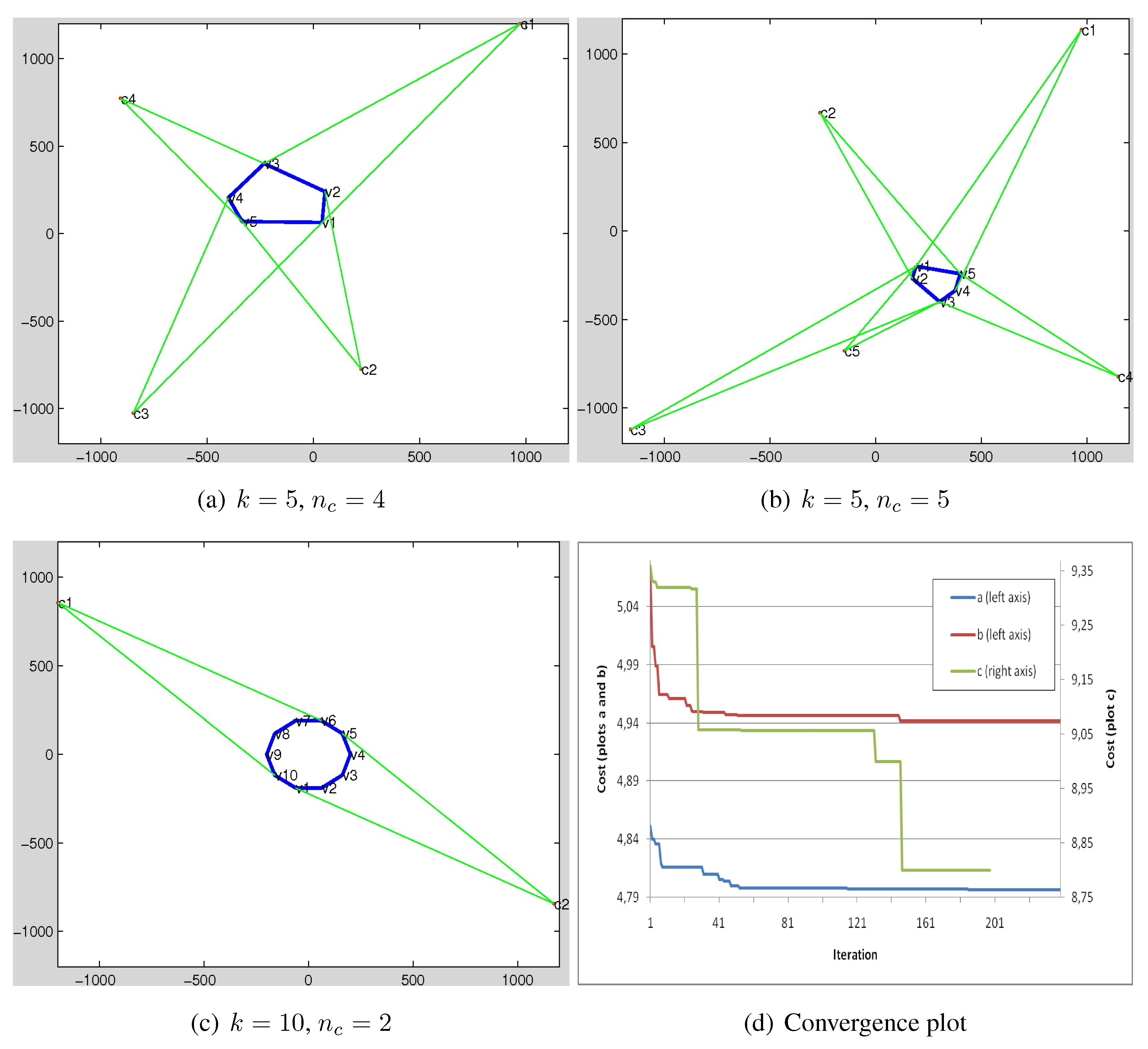
3.1. Simulation


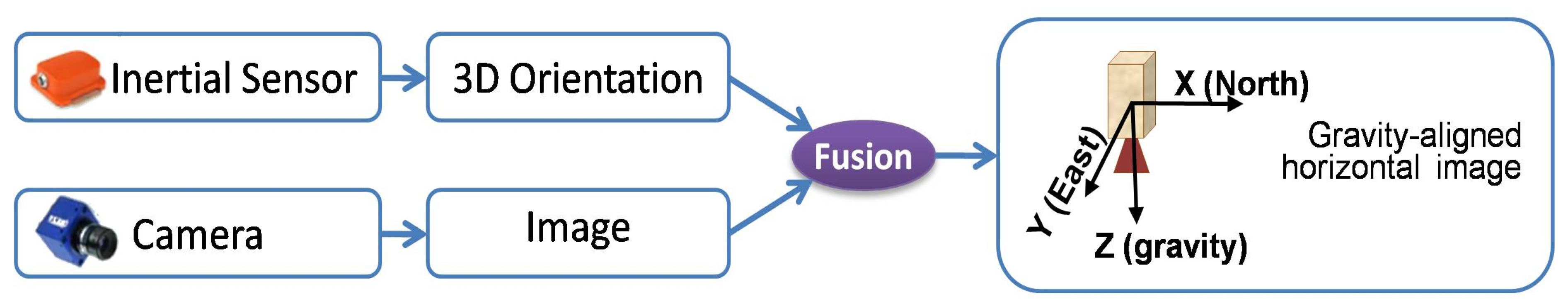
3.2. Application in 3D Registration for Human Movement Analysis


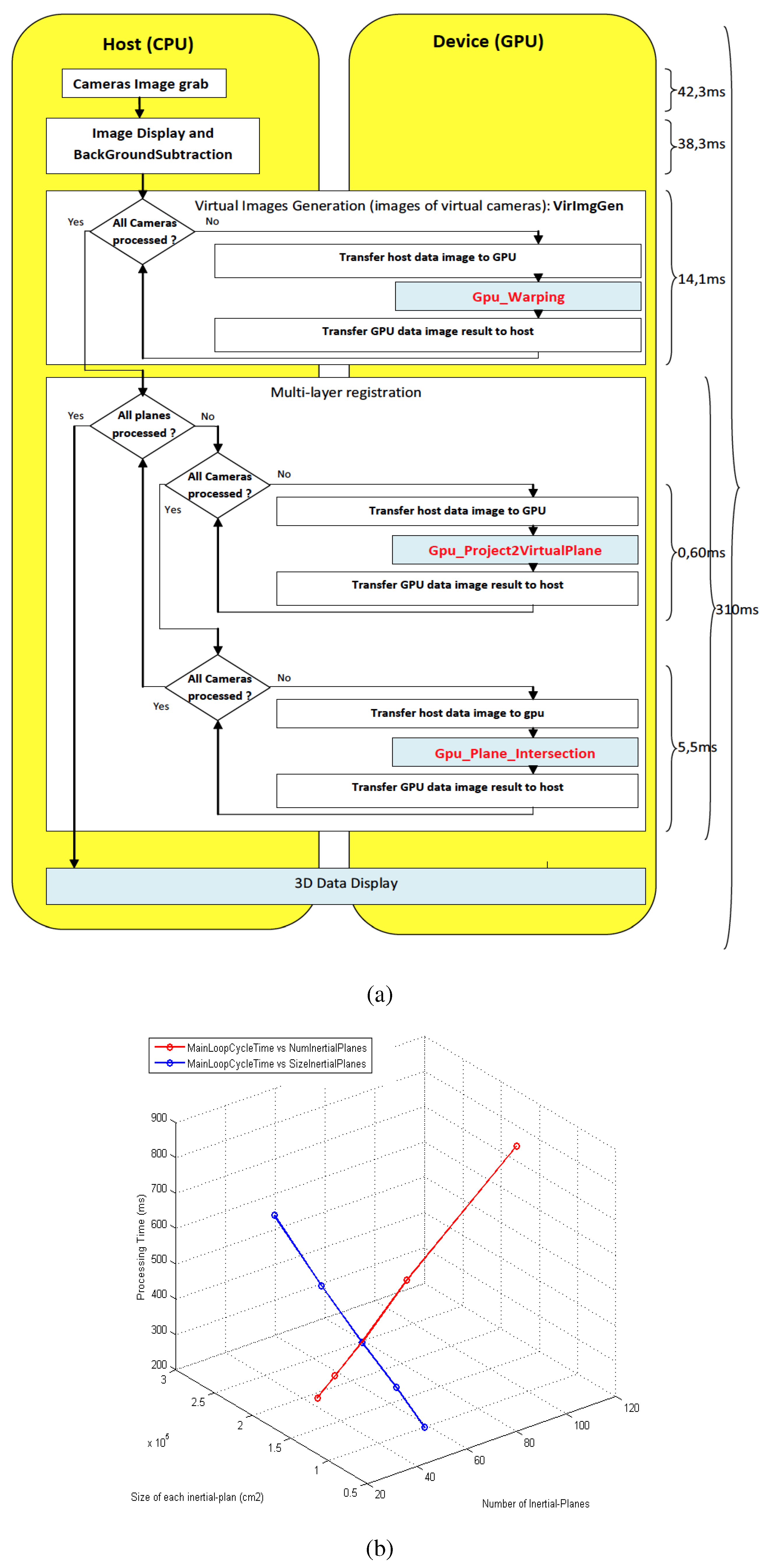


4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aliakbarpour, H.; Freitas, P.; Quintas, J.; Tsiourti, C.; Dias, J. Mobile Robot Cooperation with Infrastructure For Surveillance: Towards Cloud Robotics. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Recognition and Action for Scene Understanding (REACTS) in the 14th International Conference of Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns (CAIP), Malaga, Spain, 1–2 September 2011.
- Blasch, E.; Bosse, E.; Lambert, D.A. High-Level Information Fusion Management and Systems Design; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Blasch, E.; Plano, S. JDL Level 5 fusion model: User refinement issues and applications in group tracking. SPIE Proc. 2002, 4729, 270–279. [Google Scholar]
- Lohweg, V.; Mönks, U. Sensor fusion by two-layer conflict solving. In Proceedings of the 2010 2nd International Workshop on Cognitive Information Processing (CIP), Elba, Italy, 14–16 June 2010; pp. 370–375.
- Aliakbarpour, H.; Ferreira, J.F.; Khoshhal, K.; Dias, J. A Novel Framework for Data Registration and Data Fusion in Presence of Multi-Modal Sensors. In Emerging Trends in Technological Innovation; Springer: Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 314, pp. 308–315. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, S.; Yin, X.; Wu, H.; Jin, M.; Gu, X.D. Deterministic Greedy Routing with Guaranteed Delivery in 3D Wireless Sensor Networks. Axioms 2014, 3, 177–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, M.; Koutsoukos, X. Collaborative 3D Target Tracking in Distributed Smart Camera Networks for Wide-Area Surveillance. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2013, 2, 316–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M. Probabilistic Framework for Sensor Management. Ph.D. Thesis, Fakultät für Informatik, Universität Karlsruhe, Karlsruhe, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bhanu, B.; Ravishankar, V.C.; Roy-Chowdhury, A.K.; Aghajan, H.; Terzopoulos, D. Distributed Video Sensor Networks; Springer: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, H.; Jin, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xia, S. Cut-and-Sew: A Distributed Autonomous Localization Algorithm for 3D Surface Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking and Computing (MobiHoc’13), Bangalore, India, 29 July–1 August 2013; pp. 69–78.
- Zhou, H.; Xia, S.; Jin, M.; Wu, H. Localized and Precise Boundary Detection in 3D Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. (TON) 2015. To appear. [Google Scholar]
- Kavi, R.; Kulathumani, V. Real-Time Recognition of Action Sequences Using a Distributed Video Sensor Network. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2013, 2, 486–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, D.S.; Yang, C.K. Optimal Configuration of Redundant Inertial Sensors for Navigation and FDI Performance. Sensors 2010, 10, 6497–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.K.; Shim, D.S. Best Sensor Configuration and Accommodation Rule Based on Navigation Performance for INS with Seven Inertial Sensors. Sensors 2009, 9, 8456–8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Dong, J.; Landry, R.J.; Chen, D. A Novel Optimal Configuration form Redundant MEMS Inertial Sensors Based on the Orthogonal Rotation Method. Sensors 2014, 14, 13661–13678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, M. An Introduction to Genetic Algorithms; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, P.K.; Mahajan, A. A genetic algorithm-based approach to calculate the optimal configuration of ultrasonic sensors in a 3D position estimation system. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2002, 41, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglar, M.; Gromada, M.; Stachowicz, F.; Trzepiecinski, T. Optimal configuration of piezoelectric sensors and actuators for active vibration control of a plate using a genetic algorithm. Acta Mech. 2015, 226, 3451–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; O’Connor, I. iMASKO: A Genetic Algorithm Based Optimization Framework for Wireless Sensor Networks. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2013, 2, 675–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Zhang, P.; Chen, X.; Cai, M.; Yang, D. Genetic Algorithm (GA)-Based Inclinometer Layout Optimization. Sensors 2015, 15, 9136–9155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Guo, L.; Duan, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, H. Dynamic Deployment of Wireless Sensor Networks by Biogeography Based Optimization Algorithm. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2012, 1, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliakbarpour, H.; Aliakbarpour, H.; Naseh, H. 3D Reconstruction of Human/Object Using a Network of Cameras and Inertial Sensors; Scholar’s Press: Saarbrucken, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Aliakbarpour, H.; Palaniappan, K.; Dias, J. Geometric exploration of virtual planes in a fusion-based 3D registration framework. In Proceedings of the SPIE Conference Geospatial InfoFusion III (Defense, Security and Sensing: Sensor Data and Information Exploitation), Baltimore, MD, USA, April 2013; Volume 8747.
- Aliakbarpour, H.; Dias, J. IMU-Aided 3D Reconstruction based on Multiple Virtual Planes. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 1–3 December 2010; pp. 474–479.
- Aliakbarpour, H.; Dias, J. Volumetric 3D reconstruction without planar ground assumption. In Proceedings of the 5th ACM/IEEE Internaltional Conference Distributed Smart Cameras, Ghent, Belgium, 22–25 August 2011.
- Aliakbarpour, H.; Dias, J. Multi-Resolution Virtual Plane Based 3D Reconstruction Using Inertial-Visual Data Fusion. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISAPP), Vilamoura, Portugal, 5–7 March 2011.
- Aliakbarpour, H.; Dias, J. Inertial-Visual Fusion For Camera Network Calibration. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Conference on Industrial Informatics, Caparica, Lisbon, Portugal, 26–29 July 2011; pp. 422–427.
- Aliakbarpour, H.; Dias, J. Human Silhouette Volume Reconstruction Using a Gravity-Based Virtual Camera Network. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Information Fusion, Edinburgh, UK, 26–29 July 2010.
- Aliakbarpour, H.; Dias, J. Three-dimensional reconstruction based on multiple virtual planes by using fusion-based camera network. IET J. Comput. Vis. 2012, 6, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliakbarpour, H. Exploiting Inertial Planes for Multi-Sensor 3D Data Registration. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Aliakbarpour, H.; Almeida, L.; Menezes, P.; Dias, J. Multi-Sensor 3D Volumetric Reconstruction Using CUDA. J. 3D Res. 2011, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aliakbarpour, H.; Prasath, V.B.S.; Dias, J. On Optimal Multi-Sensor Network Configuration for 3D Registration. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2015, 4, 293-314. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan4040293
Aliakbarpour H, Prasath VBS, Dias J. On Optimal Multi-Sensor Network Configuration for 3D Registration. Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks. 2015; 4(4):293-314. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan4040293
Chicago/Turabian StyleAliakbarpour, Hadi, V. B. Surya Prasath, and Jorge Dias. 2015. "On Optimal Multi-Sensor Network Configuration for 3D Registration" Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks 4, no. 4: 293-314. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan4040293
APA StyleAliakbarpour, H., Prasath, V. B. S., & Dias, J. (2015). On Optimal Multi-Sensor Network Configuration for 3D Registration. Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks, 4(4), 293-314. https://doi.org/10.3390/jsan4040293