Genome-Wide Analysis of the PIN Auxin Efflux Carrier Gene Family in Coffee
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Genome-Wide Identification of PIN in Coffee Species
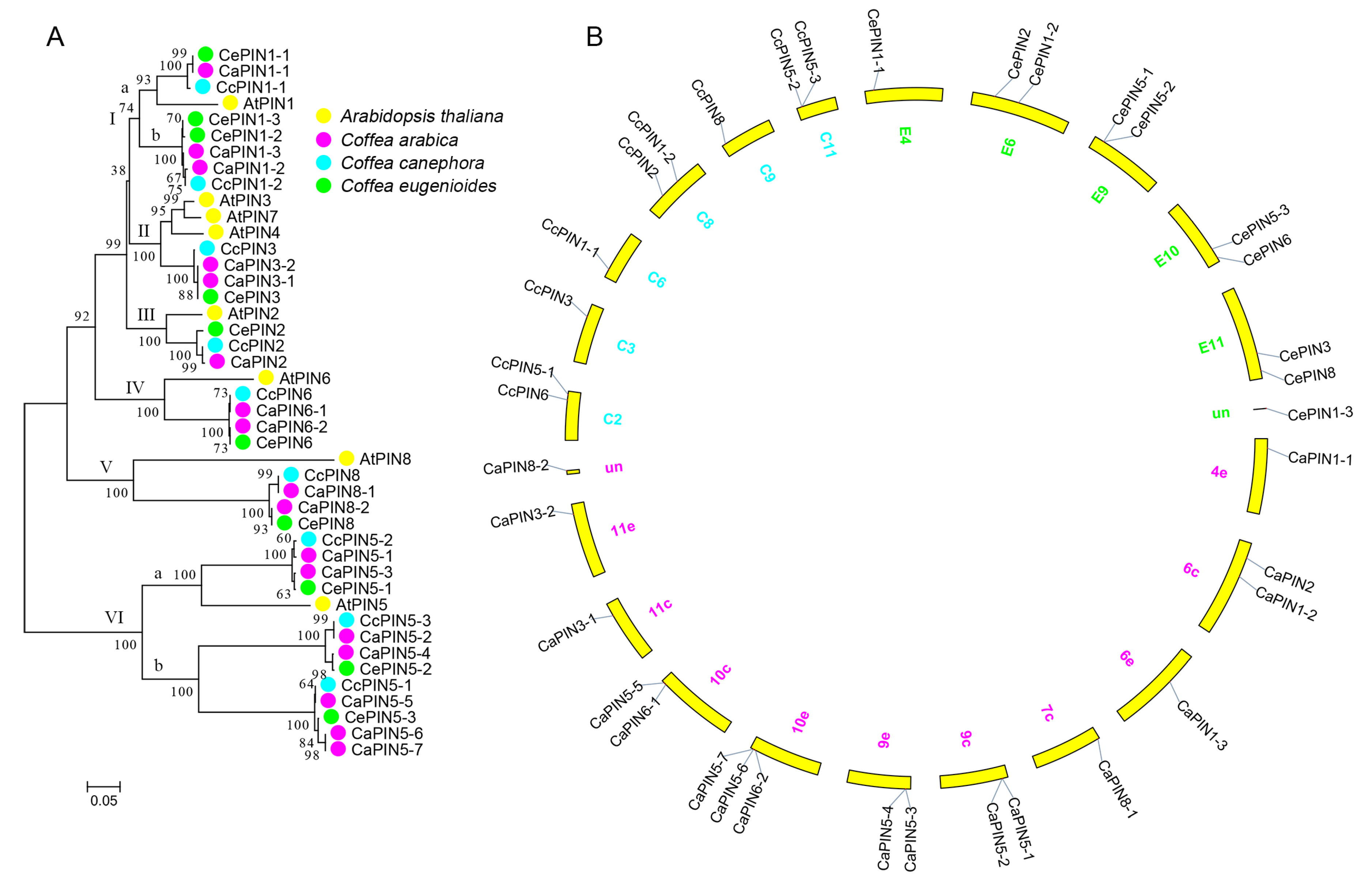
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of Coffee PIN
2.3. Cis-Element Prediction and Gene Structure Analysis of Coffee PIN
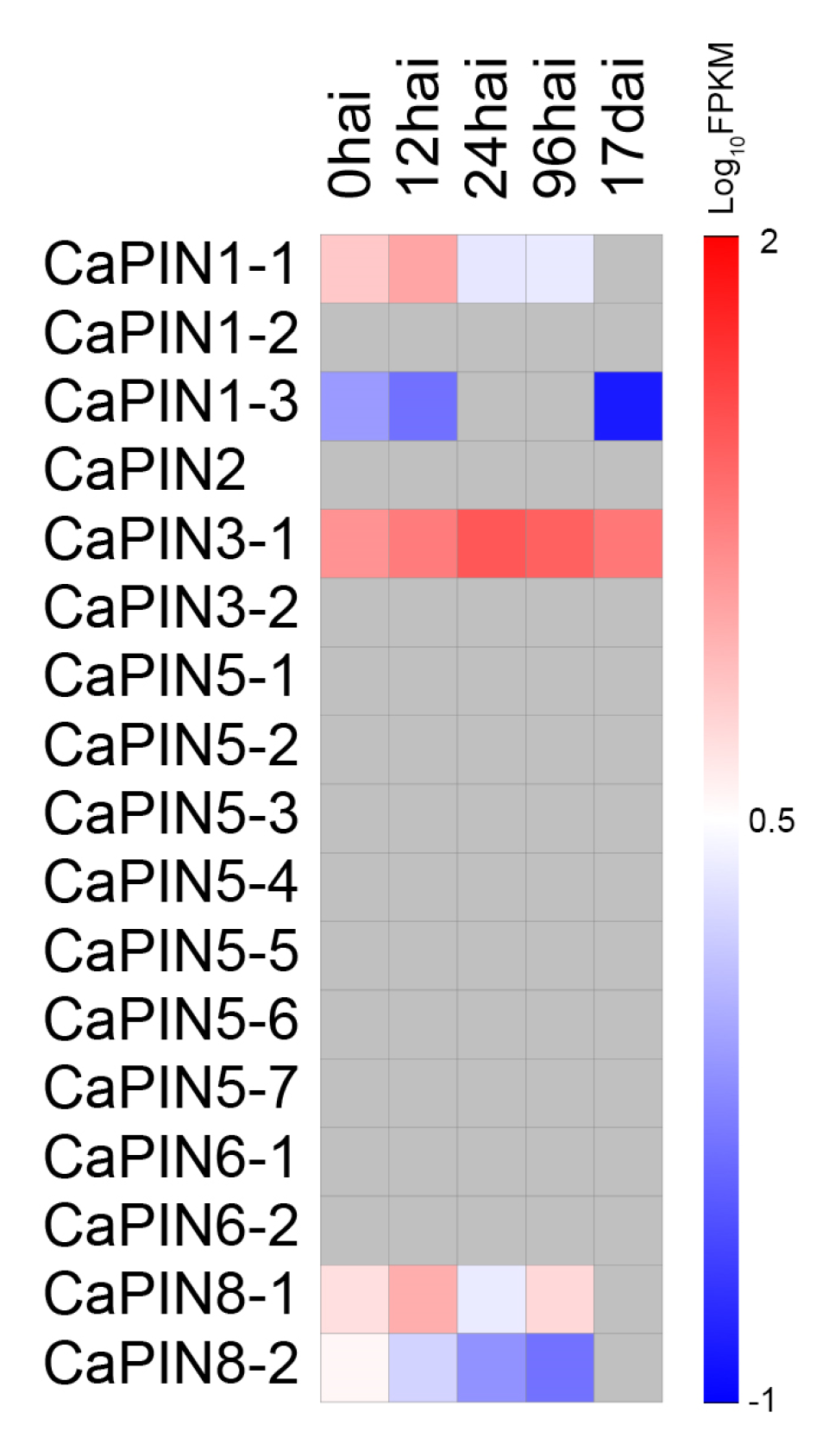
2.4. In Silico Expression of Coffee PINs under Biotic Stress
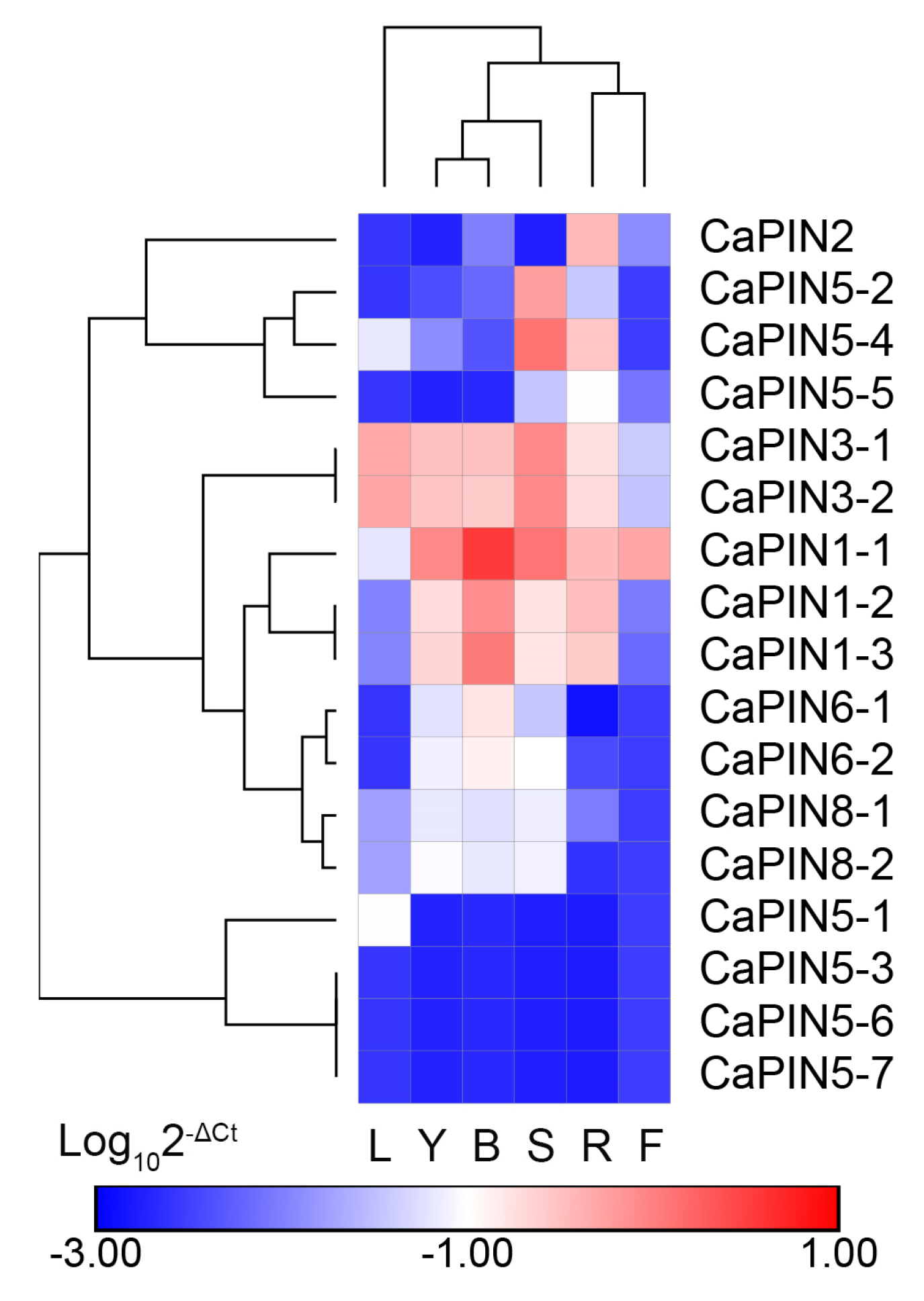
2.5. Expression Profiles of Coffee PINs in Different Coffee Tissues
3. Discussion
3.1. Evolution of the Coffee PINs
3.2. Candidate Regulators in the Coffee PIN family
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sequence Retrieval and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.2. Cis-Element and Gene Structure Analysis
4.3. Plant Materials and RNA Extraction
4.4. Expression Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weijers, D.; Friml, J. SnapShot: Auxin signaling and transport. Cell 2009, 136, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adamowski, M.; Friml, J. PIN-dependent auxin transport: Action, regulation, and evolution. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Finet, C.; Jaillais, Y. AUXOLOGY: When auxin meets plant evo-devo. Dev. Biol. 2012, 369, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krecek, P.; Skupa, P.; Libus, J.; Naramoto, S.; Tejos, R.; Friml, J.; Zazímalová, E. The PIN-FORMED (PIN) protein family of auxin transporters. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.J.; Luo, J. The PIN-FORMED Auxin Efflux Carriers in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Z.; Wang, B.; Moreno, I.; Duplakova, N.; Simon, S.; Carraro, N.; Reemmer, J.; Pencik, A.; Chen, X.; Tejos, R.; et al. ER-localized auxin transporter PIN8 regulates auxin homeostasis and male gametophyte development in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mravec, J.; Skupa, P.; Bailly, A.; Hoyerova, K.; Krecek, P.; Bielach, A.; Petrasek, J.; Zhang, J.; Gaykova, V.; Stierhof, Y.D. Subcellular homeostasis of phytohormone auxin is mediated by the ER localized PIN5 transporter. Nature 2009, 459, 1136–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S.; Skupa, P.; Viaene, T.; Zwiewka, M.; Tejos, R.; Klima, P.; Carna, M.; Rolcik, J.; De Rycke, R.; Moreno, I.; et al. PIN6 auxin transporter at endoplasmic reticulum and plasma membrane mediates auxin homeostasis and organogenesis in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2016, 211, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakusová, H.; Abbas, M.; Han, H.; Song, S.; Robert, H.S.; Friml, J. Termination of shoot gravitropic responses by auxin feedback on PIN3 polarity. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 3026–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rigo, G.; Ayaydin, F.; Tietz, O.; Zsigmond, L.; Kovacs, H.; Pay, A.; Salchert, K.; Darula, Z.; Medzihradszky, K.F.; Szabados, L.; et al. Inactivation of plasma membrane-localized CDPK-RELATED KINASE5 decelerates PIN2 exocytosis and root gravitropic response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 1592–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosquete, M.R.; Waidmann, S.; Kleine, V.J. PIN7 auxin carrier has a preferential role in terminating radial root expansion in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xi, W.; Gong, X.; Yang, Q.; Yu, H.; Liou, Y.C. Pin1At regulates PIN1 polar localization and root gravitropism. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haga, K.; Sakai, T. PIN auxin efflux carriers are necessary for pulse-induced but not continuous light-induced phototropism in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zadnikova, P.; Petrasek, J.; Marhavy, P.; Raz, V.; Vandenbussche, F.; Ding, Z.; Schwarzerova, K.; Morita, M.T.; Tasaka, M.; Hejatko, J.; et al. Role of PIN-mediated auxin efflux in apical hook development of Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 2010, 137, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okada, K.; Ueda, J.; Komaki, M.K.; Bell, C.J.; Shimura, Y. Requirement of the auxin polar transport system in early stages of Arabidopsis floral bud formation. Plant Cell 1991, 3, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pahari, S.; Cormark, R.D.; Blackshaw, M.T.; Liu, C.; Erickson, J.L.; Schultz, E.A. Arabidopsis UNHINGED encodes a VPS51 homolog and reveals a role for the GARP complex in leaf shape and vein patterning. Development 2014, 141, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, A.; Takahashi, M.; Shibasaki, K.; Wu, S.; Inaba, T.; Tsurumi, S.; Baskin, T.I. Gravitropism of Arabidopsis thaliana roots requires the polarization of PIN2 toward the root tip in meristematic cortical cells. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 1762–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vieten, A.; Vanneste, S.; Wisniewska, J.; Benková, E.; Benjamins, R.; Beeckman, T.; Luschnig, C.; Friml, J. Functional redundancy of PIN proteins is accompanied by auxin-dependent cross-regulation of PIN expression. Development 2005, 132, 4521–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Maere, S.; Lee, E.; Van, I.G.; Xie, Z.; Xuan, W.; Lucas, J.; Vassileva, V.; Kitakura, S.; et al. A coherent transcriptional feed-forward motif model for mediating auxin-sensitive PIN3 expression during lateral root development. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willige, B.C.; Chory, J. A current perspective on the role of AGCVIII kinases in PIN-mediated apical hook development. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friml, J.; Benková, E.; Blilou, I.; Wisniewska, J.; Hamann, T.; Ljung, K.; Woody, S.; Sandberg, G.; Scheres, B.; Jürgens, G.; et al. AtPIN4 mediates sink-driven auxin gradients and root patterning in Arabidopsis. Cell 2002, 108, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cazzonelli, C.I.; Vanstraelen, M.; Simon, S.; Yin, K.; Carron-Arthur, A.; Nisar, N.; Tarle, G.; Cuttriss, A.J.; Searle, I.R.; Mathesius, J.; et al. Role of the Arabidopsis PIN6 auxin transporter in auxin homeostasis and auxin-mediated development. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ditengou, F.A.; Gomes, D.; Nziengui, H.; Kochersperger, P.; Lasok, H.; Medeiros, V.; Paponov, I.V.; Nagy, S.K.; Nádai, T.V.; Mészáros, T.; et al. Characterization of auxin transporter PIN6 plasma membrane targeting reveals a function for PIN6 in plant bolting. New Phytol. 2017, 217, 1610–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dal Bosco, C.; Dovzhenko, A.; Liu, X.; Woerner, N.; Rensch, T.; Eismann, M.; Eimer, S.; Hegermann, J.; Paponov, I.A.; Ruperti, B.; et al. The endoplasmic reticulum localized PIN8 is a pollen-specific auxin carrier involved in intracellular auxin homeostasis. Plant J. 2012, 71, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I. A showcase of future plant biology: Moving towards next-generation plant genetics assisted by genome sequencing and systems biology. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forestan, C.; Farinati, S.; Varotto, S. The Maize PIN Gene Family of Auxin Transporters. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, P.; Zhao, P.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiao, H.; Yu, J.; Xiao, G. The PIN gene family in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum): Genome-wide identification and gene expression analyses during root development and abiotic stress responses. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Zheng, H.; Chen, J.; Lu, M. A survey of Populus PIN-FORMED family genes reveals their diversified expression patterns. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2437–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, D.; Song, J.; Wang, R. Characterization of the Auxin Efflux Transporter PIN Proteins in Pear. Plants 2020, 9, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sańko-Sawczenko, I.; Łotocka, B.; Czarnocka, W. Expression Analysis of PIN Genes in Root Tips and Nodules of Medicago truncatula. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, C.; Bai, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, M.; Jiang, D.; Qi, Y. Expression profile of PIN, AUX/LAX and PGP auxin transporter gene families in Sorghum bicolor under phytohormone and abiotic stress. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2954–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chai, C.; Valliyodan, B.; Maupin, C.; Annen, B.; Nguyen, H.T. Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of the PIN auxin transporter gene family in soybean (Glycine max). BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Qin, G.; Si, P.; Luo, Z.; Gao, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Wei, P.; Xia, Q.; Lin, F.; et al. Analysis of Nicotiana tabacum PIN genes identifies NtPIN4 as a key regulator of axillary bud growth. Physiol. Plant. 2017, 160, 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Wang, D.; Zhang, C.; Kong, N.; Ma, H.; Chen, Q. Comparative Analysis of the PIN Auxin Transporter Gene Family in Different Plant Species: A Focus on Structural and Expression Profiling of PINs in Solanum tuberosum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, W.; Huang, Z.A.; Cho, M.; Yu, Q.; Wu, C.; Yu, C. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the CaLAX and CaPIN gene families in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) under various abiotic stresses and hormone treatments. Genome 2018, 61, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Guyot, R.; De Kochko, A.; Byers, A.; Navajas-Pérez, R.; Langston, B.J.; Dubreuil-Tranchant, C.; Paterson, A.H.; Poncet, V.; Nagai, C.; et al. Micro-collinearity and genome evolution in the vicinity of an ethylene receptor gene of cultivated diploid and allotetraploid coffee species (Coffea). Plant J. 2011, 67, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.C.; Pedersen, B.; Freeling, M. Following tetraploidy in an Arabidopsis ancestor, genes were removed preferentially from one homeolog leaving clusters enriched in dose-sensitive genes. Genome Res. 2006, 16, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woodhouse, M.R.; Schnable, J.C.; Pedersen, B.S.; Lyons, E.; Lisch, D.; Subramaniam, S.; Freeling, M. Following tetraploidy in maize, a short deletion mechanism removed genes preferentially from one of the two homologs. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunter, N. Meiotic Recombination: The Essence of Heredity. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a016618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, B.; Cao, J.F.; Hu, G.J.; Chen, Z.W.; Wang, L.Y.; Shangguan, X.X.; Wang, L.J.; Mao, Y.B.; Zhang, T.Z.; Wendel, J.F.; et al. Core cis-element variation confers subgenome-biased expression of a transcription factor that functions in cotton fiber elongation. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 1061–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Hu, R.; Palla, K.J.; Tuskan, G.A.; Yang, X. Advances and perspectives on the use of CRISPR/Cas9 systems in plant genomics research. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2016, 30, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tennessen, J.A.; Wei, N.; Straub, S.C.K.; Govindarajulu, R.; Liston, A.; Ashman, T.L. Repeated translocation of a gene cassette drives sex-chromosome turnover in strawberries. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2006062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y. Essential Roles of Local Auxin Biosynthesis in Plant Development and in Adaptation to Environmental Changes. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacete, L.; Mélida, H.; Miedes, E.; Molina, A. Plant cell wall-mediated immunity: Cell wall changes trigger disease resistance responses. Plant J. 2018, 93, 614–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottani, S.; Zabet, N.R.; Wendel, J.F.; Veitia, R.A. Gene Expression Dominance in Allopolyploids: Hypotheses and Models. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCBI. Available online: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/ (accessed on 7 July 2020).
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ProtParam Tool. Available online: Web.expasy.org/protparam/ (accessed on 7 July 2020).
- Yu, C.S.; Chen, Y.C.; Lu, C.H.; Hwang, J.K. Prediction of protein subcellular localization. Proteins 2006, 64, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; Von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DNAMAN-Bioinformatics Solutions. Available online: www.lynnon.com (accessed on 7 July 2020).
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Wang, B.; Xi, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, C.; Zheng, J.; Gao, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Wu, W.; et al. Transcriptome comparison reveals distinct selection patterns in domesticated and wild Agave species, the important CAM plants. Int. J. Genom. 2018, 2018, 5716518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools—An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Peer, Y.V.D.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequence Read Archive. Available online: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra (accessed on 7 July 2020).
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3—New capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Xiao, M.; Xi, J.; He, C.; Zheng, J.; Chen, H.; Gao, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, W.; Liang, Y.; et al. De novo transcriptome assembly of Agave H11648 by Illumina sequencing and identification of cellulose synthase genes in Agave species. Genes 2019, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| ID | NCBI Accession | Chromosome Location | Coding Sequence (bp) | Predicted Protein (aa) | Molecular Weight | pI | CELLO Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaPIN1-1 | LOC113742499 | Chr4e:5319931-5324277(+) | 1809 | 602 | 66,068.52 | 8.78 | PlasmaMembrane (4.325) |
| CaPIN1-2 | LOC113692256 | Chr6c:19755675-19759117(−) | 1800 | 599 | 64,648.69 | 9.11 | PlasmaMembrane (4.541) |
| CaPIN1-3 | LOC113695379 | Chr6e:18475803-18479240(−) | 1800 | 599 | 64,660.77 | 9.06 | PlasmaMembrane (4.613) |
| CaPIN2 | LOC113691530 | Chr6c:8677641-8680633(+) | 1857 | 618 | 67,154.96 | 9.04 | PlasmaMembrane (4.413) |
| CaPIN3-1 | LOC113716800 | Chr11c:28762761-28766913(+) | 1995 | 664 | 71,668.43 | 7.71 | PlasmaMembrane (3.822) |
| CaPIN3-2 | LOC113719107 | Chr11e:36778779-36782931(+) | 1995 | 664 | 71,668.43 | 7.71 | PlasmaMembrane (3.822) |
| CaPIN5-1 | LOC113708749 | Chr9c:3275956-3277726(+) | 1074 | 357 | 39,130.15 | 7.66 | PlasmaMembrane (4.154) |
| CaPIN5-2 | LOC113708750 | Chr9c:3294659-3297259(+) | 1077 | 358 | 39,279.26 | 7 | PlasmaMembrane (4.359) |
| CaPIN5-3 | LOC113709610 | Chr9e:2787073-2799648(+) | 1074 | 357 | 39,084.12 | 7.66 | PlasmaMembrane (4.072) |
| CaPIN5-4 | LOC113709696 | Chr9e:2809701-2812402(+) | 1077 | 358 | 39,286.23 | 6.95 | PlasmaMembrane (4.384) |
| CaPIN5-5 | LOC113714408 | Chr10c:43832409-43834939(+) | 1089 | 362 | 40,211.78 | 7.99 | PlasmaMembrane (4.578) |
| CaPIN5-6 | LOC113712046 | Chr10e:38622577-38625089(+) | 1089 | 362 | 40,315.95 | 7.99 | PlasmaMembrane (4.577) |
| CaPIN5-7 | LOC113712037 | Chr10e:38697672-38700185(+) | 1089 | 362 | 40,315.95 | 7.99 | PlasmaMembrane (4.577) |
| CaPIN6-1 | LOC113713240 | Chr10c:42560611-42566696(+) | 1635 | 544 | 59,358.58 | 8.67 | PlasmaMembrane (4.589) |
| CaPIN6-2 | LOC113710898 | Chr10e:37414288-37421605(+) | 1644 | 547 | 59,627.88 | 8.52 | PlasmaMembrane (4.621) |
| CaPIN8-1 | LOC113698547 | Chr7c:901163-904039(−) | 1080 | 359 | 38,908.26 | 9.02 | PlasmaMembrane (4.057) |
| CaPIN8-2 | LOC113722850 | NW_020850478.1:2088684-2091128(−) | 1080 | 359 | 38,862.37 | 8.89 | PlasmaMembrane (3.982) |
| CcPIN1-1 | Cc04_g06290 | Chr6:4778381-4782838(+) | 1809 | 602 | 66,017.47 | 8.78 | PlasmaMembrane (4.238) |
| CcPIN1-2 | Cc06_g19880 | Chr8:22061777-22064841(−) | 1800 | 599 | 64,662.72 | 9.11 | PlasmaMembrane (4.560) |
| CcPIN2 | Cc06_g12940 | Chr8:10631952-10634716(+) | 1857 | 618 | 67,168.99 | 9.04 | PlasmaMembrane (4.450) |
| CcPIN3 | Cc11_g08680 | Chr3:26054971-26059237(+) | 1998 | 665 | 71,838.64 | 7.71 | PlasmaMembrane (3.852) |
| CcPIN5-1 | Cc10_g14830 | Chr2:25683429-25685861(+) | 1089 | 362 | 40,211.78 | 7.99 | PlasmaMembrane (4.578) |
| CcPIN5-2 | Cc09_g03470 | Chr11:2994318-2996247(+) | 1074 | 357 | 39,132.12 | 7.66 | PlasmaMembrane (4.147) |
| CcPIN5-3 | Cc09_g03480 | Chr11:3012816-3015442(+) | 1077 | 358 | 39,279.26 | 7 | PlasmaMembrane (4.359) |
| CcPIN6 | Cc10_g12950 | Chr2:22666072-22671714(−) | 1635 | 544 | 59,372.6 | 8.67 | PlasmaMembrane (4.596) |
| CcPIN8 | Cc07_g03020 | Chr9:2053274-2055299(−) | 1080 | 359 | 38,908.26 | 9.02 | PlasmaMembrane (4.057) |
| CePIN1-1 | LOC113768376 | Chr4:4999933-5004212(+) | 1809 | 602 | 66,068.52 | 8.78 | PlasmaMembrane (4.325) |
| CePIN1-2 | LOC113775722 | Chr6:26100829-26104135(−) | 1800 | 599 | 64,602.73 | 9.05 | PlasmaMembrane (4.549) |
| CePIN1-3 | LOC113759196 | NW_020864866.1:1155-4437(+) | 1800 | 599 | 64,616.75 | 9.05 | PlasmaMembrane (4.566) |
| CePIN2 | LOC113776283 | Chr6:12410330-12413098(+) | 1845 | 614 | 66,772.54 | 9.03 | PlasmaMembrane (4.414) |
| CePIN3 | LOC113751527 | Chr11:38612643-38616661(+) | 1986 | 661 | 71,315.05 | 7.71 | PlasmaMembrane (3.858) |
| CePIN5-1 | LOC113783693 | Chr9:5448811-5450798(+) | 1074 | 357 | 39,098.15 | 7.66 | PlasmaMembrane (4.085) |
| CePIN5-2 | LOC113783723 | Chr9:5460896-5463464(+) | 1077 | 358 | 39,300.26 | 6.95 | PlasmaMembrane (4.393) |
| CePIN5-3 | LOC113750662 | Chr10:31456928-31459384(−) | 1089 | 362 | 40,293.93 | 7.99 | PlasmaMembrane (4.574) |
| CePIN6 | LOC113750213 | Chr10:36854392-36860603(−) | 1620 | 539 | 59,223.7 | 8.64 | PlasmaMembrane (4.611) |
| CePIN8 | LOC113754254 | Chr11:48522325-48524966(+) | 1080 | 359 | 38,879.22 | 9.02 | PlasmaMembrane (3.985) |
| ID | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | Product Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| CaPIN1-1 | TTTTGATGGGGCTATGAAGC | TCTCTGGACTCCATCCATCC | 155 |
| CaPIN1-2 | GGGTATCCGGATCAATCCTT | AATTGTTTGCCCTCATGGAC | 173 |
| CaPIN1-3 | AGGCAATCCCAGGGACTTAT | TTTTGGCCTTTTGGGTGTAG | 211 |
| CaPIN2 | GTTCAGGCATCAACCGTTTT | TTCCAAGCTTCCATTTTTGG | 182 |
| CaPIN3-1 | GGTTGAGTCCGACGTTGTTT | ACCCTCTTGGCGTAGGATTT | 221 |
| CaPIN3-2 | TGGCTCTTCAGCCAAAGATT | TTTGGCAAACACAAATGGAA | 191 |
| CaPIN5-1 | TATTGCGATGTATTAGTACACC | GTACTGTTGAAGAGGTGTTCCG | 141 |
| CaPIN5-2 | GCCCTTTAATCCACAACACG | ATCGAATGCTCTTCCCGATA | 238 |
| CaPIN5-3 | ATTCGAAATAAAAGTGGTGT | TTACTTTGAGTGGATAGCAA | 199 |
| CaPIN5-4 | TCACTACAAATAACAATTGCT | GTAGCTTATATTGTAAAGTGT | 153 |
| CaPIN5-5 | AATTATTTTACCCTTTCCTCC | AAATGAGGCTATGGATTGTGG | 175 |
| CaPIN5-6 | TAGGAGGGGGCCAATTTTAT | TAAACCACGGCAGGCTAAGT | 180 |
| CaPIN5-7 | TGCATAGCTGGCTTGATTTG | CTTAAAGCCATCCCGAACAA | 197 |
| CaPIN6-1 | TGTAGTATACGTAACACGCTA | ACTTTATTATTCAACCCAACC | 146 |
| CaPIN6-2 | TGTCGTTCTCTTTTGTGGTTG | GGAAGGAAGCCAACAAAGGAC | 205 |
| CaPIN8-1 | AAATTGTCGCCGAATTTCAC | TGCACCAAATTTATCGTTCG | 196 |
| CaPIN8-2 | TGAAGACAGGAGGTGTCGTG | GGATTGCCAAATCTGCATCT | 225 |
| Protein phosphatase | ATGTGGACCGAGGAAAACAG | AGGGCAGCTACAGGAAGACA | 214 |
| Tubulin | AAGTACTCCGGCGACTCAGA | GGCGGAAGATCTGACCATAA | 157 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Bai, X.; Guo, T.; Xie, Z.; Laimer, M.; Du, D.; Gbokie, T., Jr.; Zhang, Z.; He, C.; Lu, Y.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of the PIN Auxin Efflux Carrier Gene Family in Coffee. Plants 2020, 9, 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9091061
Huang X, Bai X, Guo T, Xie Z, Laimer M, Du D, Gbokie T Jr., Zhang Z, He C, Lu Y, et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of the PIN Auxin Efflux Carrier Gene Family in Coffee. Plants. 2020; 9(9):1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9091061
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xing, Xuehui Bai, Tieying Guo, Zhouli Xie, Margit Laimer, Dengxiang Du, Thomas Gbokie, Jr., Zhirun Zhang, Chunping He, Ying Lu, and et al. 2020. "Genome-Wide Analysis of the PIN Auxin Efflux Carrier Gene Family in Coffee" Plants 9, no. 9: 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9091061
APA StyleHuang, X., Bai, X., Guo, T., Xie, Z., Laimer, M., Du, D., Gbokie, T., Jr., Zhang, Z., He, C., Lu, Y., Wu, W., & Yi, K. (2020). Genome-Wide Analysis of the PIN Auxin Efflux Carrier Gene Family in Coffee. Plants, 9(9), 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9091061






