Strigolactone Signaling Genes Showing Differential Expression Patterns in Arabidopsis max Mutants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
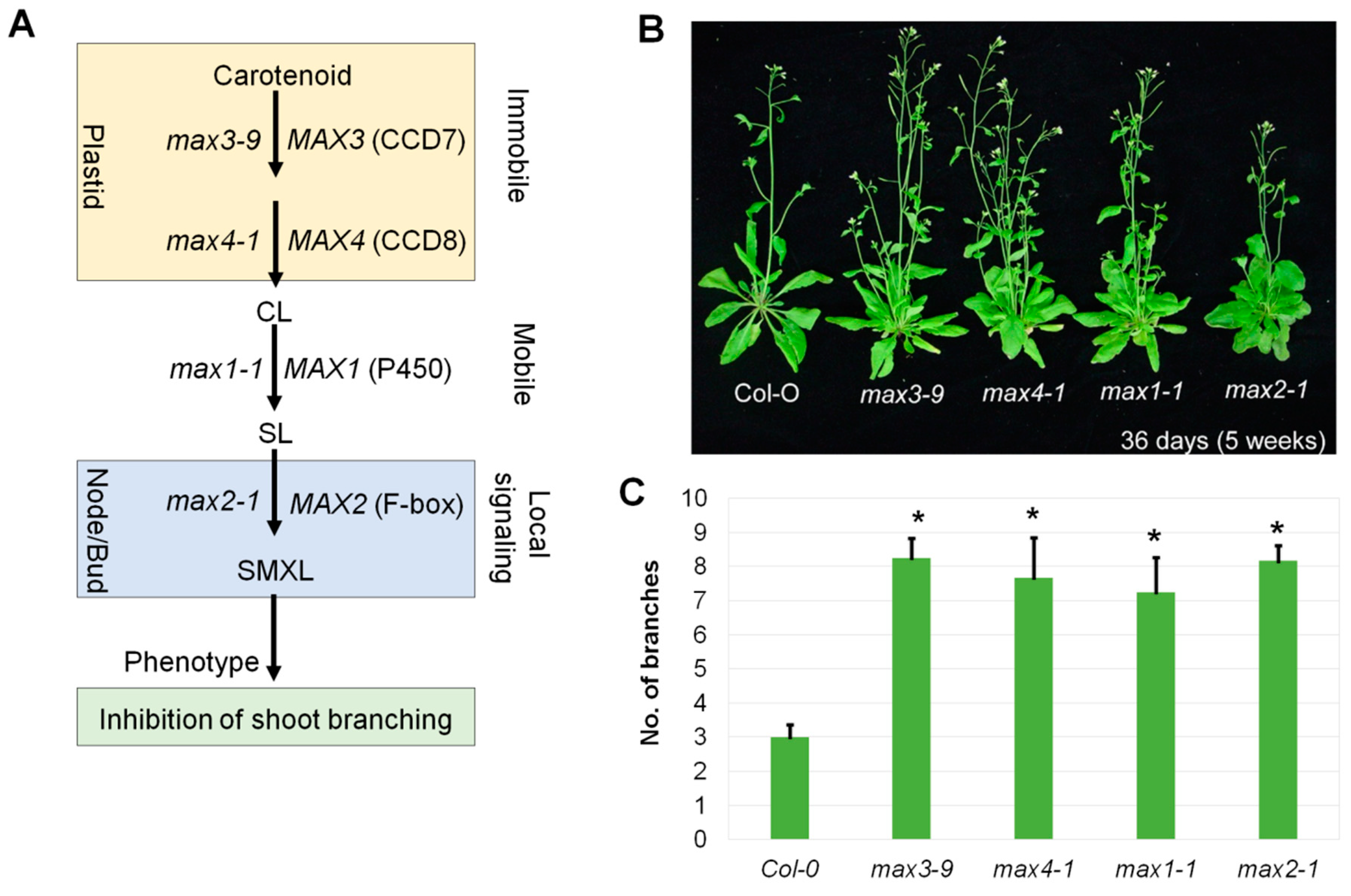
2.1. The Branched Phenotype of max Mutants and Strigolactone Signaling
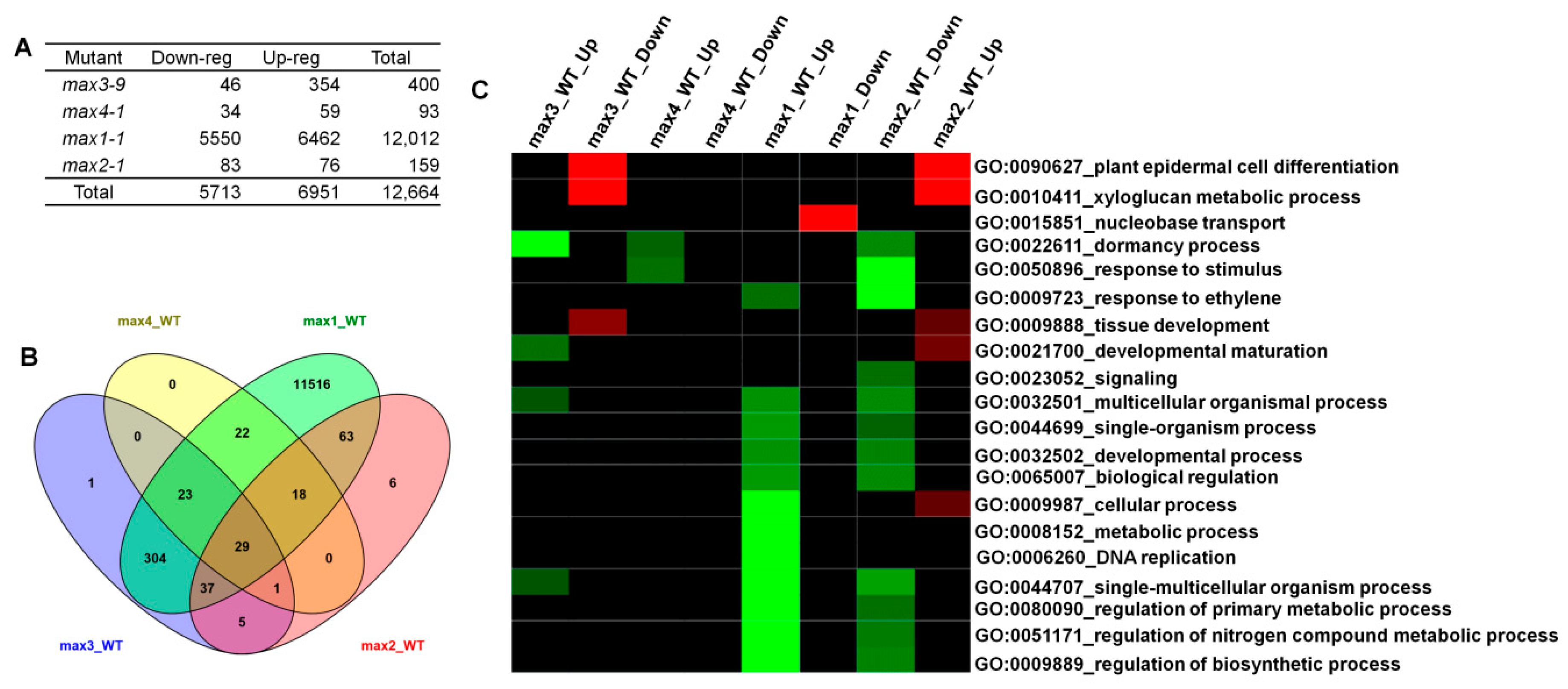
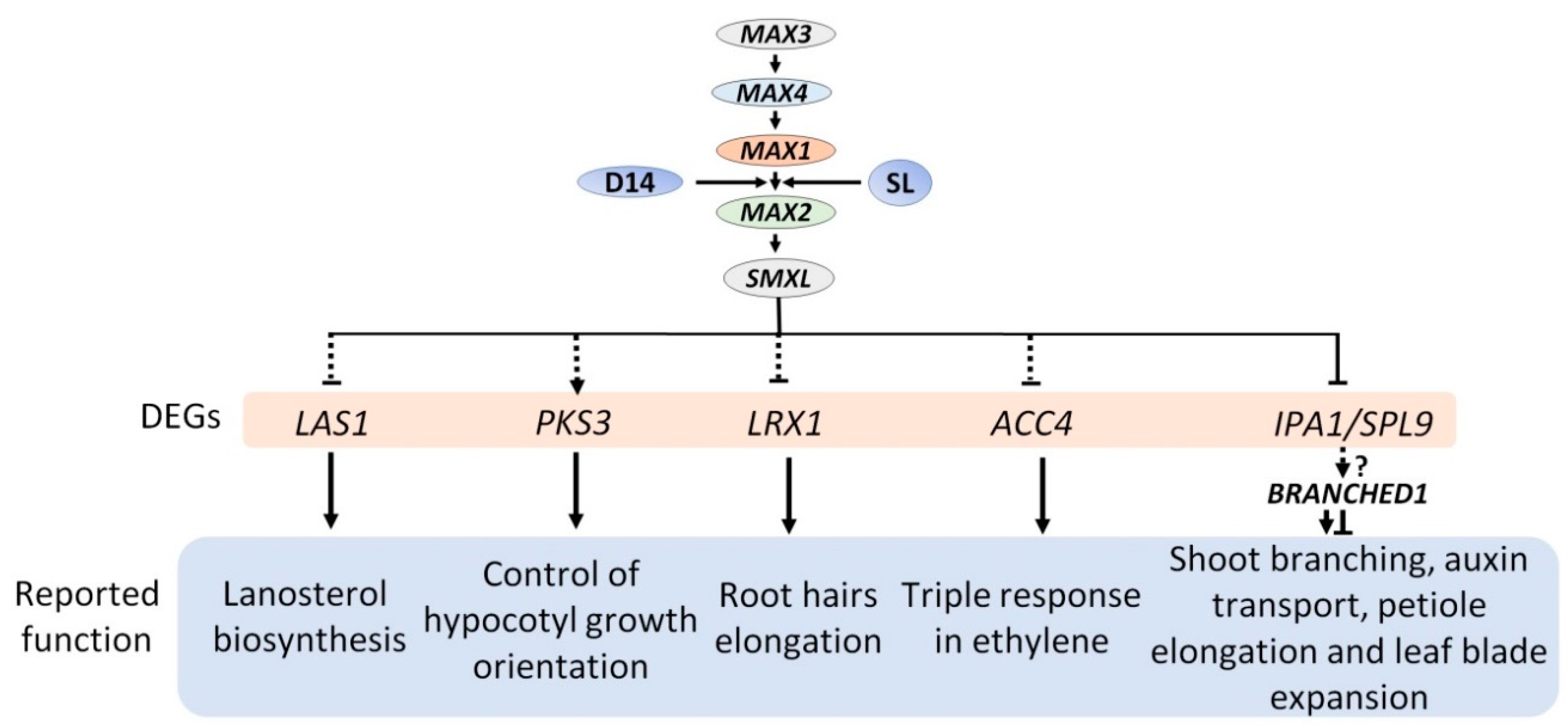
2.2. Microarray Analysis Revealed Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) in max Mutants and the Role of Those Genes in the Biological Process
2.3. Strigolactone Metabolism-Related Genes Showed Differential Expression Pattern in the max Mutant
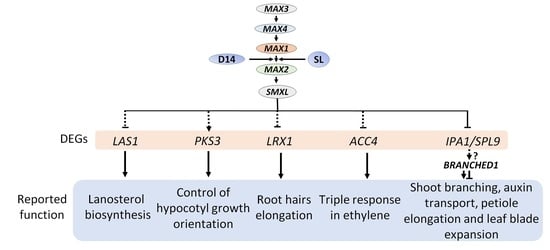
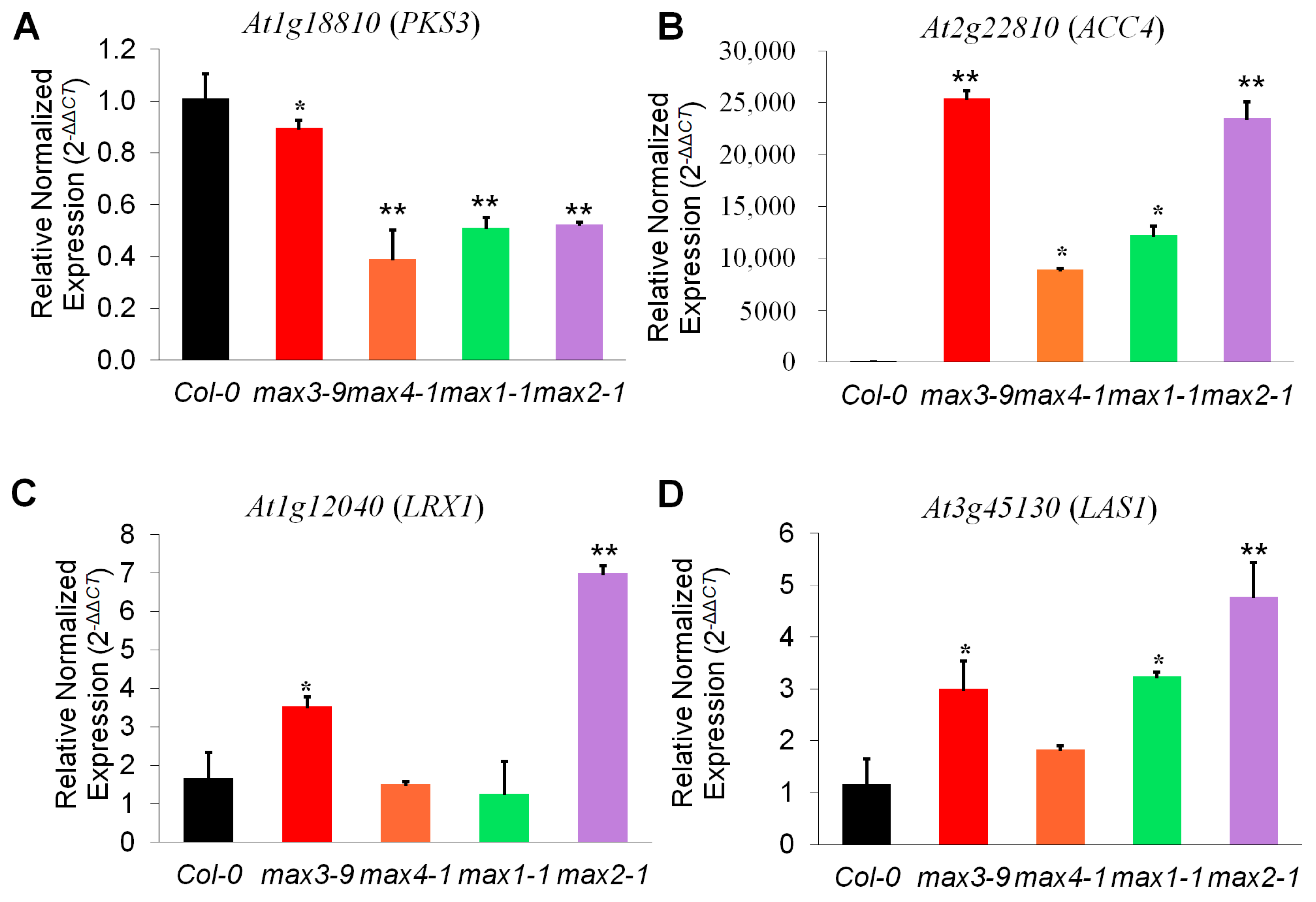
2.4. Expression Analysis Revealed Candidate Genes Involved in Downstream SL Pathway
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
3.2. Microarray Hybridization and Data Analysis
3.3. Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCD7 | CAROTENOID CLEAVAGE DIOXYGENASE 7 |
| CCD8 | CAROTENOID CLEAVAGE DIOXYGENASE 8 |
| SL | STRIGOLACTONE |
| IPA1 | IDEAL PLANT ARCHITECTURE 1 |
| ABI4 | ABA INSENSITIVE 4 |
| ACC4 | AMINOCYCLOPROPANE-1-CARBOXYLATE SYNTHASE 4 |
| LRX1 | LEUCINE-RICH REPEAT/EXTENSIN 1 |
| LAS1 | LANOSTEROL SYNTHASE 1 |
| PKS3 | PROTEIN KINASE 3 |
| GO | GENE ONTOLOGY |
References
- Xie, X.; Yoneyama, K.; Yoneyama, K. The strigolactone story. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2010, 48, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, C.E.; Whichard, L.P.; Turner, B.; Wall, M.E.; Egley, G.H. Germination of Witchweed (Striga lutea Lour.): Isolation and Properties of a Potent Stimulant. Science 1966, 154, 1189–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwmeester, H.J.; Matusova, R.; Zhongkui, S.; Beale, M.H. Secondary metabolite signalling in host-parasitic plant interactions. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Ruyter-Spira, C.; Bouwmeester, H. The interaction between strigolactones and other plant hormones in the regulation of plant development. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutjahr, C.; Parniske, M. Cell and developmental biology of arbuscular mycorrhiza symbiosis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2013, 29, 593–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, K.; Matsuzaki, K.; Hayashi, H. Plant sesquiterpenes induce hyphal branching in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Nature 2005, 435, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besserer, A.; Becard, G.; Jauneau, A.; Roux, C.; Sejalon-Delmas, N. GR24, a synthetic analog of strigolactones, stimulates the mitosis and growth of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Gigaspora rosea by boosting its energy metabolism. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Pandya-Kumar, N.; Kapulnik, Y.; Koltai, H. Strigolactone signaling in root development and phosphate starvation. Plant Signal. Behav. 2015, 10, e1045174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneyama, K.; Xie, X.N.; Kim, H.I.; Kisugi, T.; Nomura, T.; Sekimoto, H.; Yokota, T.; Yoneyama, K. How do nitrogen and phosphorus deficiencies affect strigolactone production and exudation? Planta 2012, 235, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Roldan, V.; Fermas, S.; Brewer, P.B.; Puech-Pages, V.; Dun, E.A.; Pillot, J.P.; Letisse, F.; Matusova, R.; Danoun, S.; Portais, J.C.; et al. Strigolactone inhibition of shoot branching. Nature 2008, 455, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umehara, M.; Hanada, A.; Yoshida, S.; Akiyama, K.; Arite, T.; Takeda-Kamiya, N.; Magome, H.; Kamiya, Y.; Shirasu, K.; Yoneyama, K.; et al. Inhibition of shoot branching by new terpenoid plant hormones. Nature 2008, 455, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agusti, J.; Herold, S.; Schwarz, M.; Sanchez, P.; Ljung, K.; Dun, E.A.; Brewer, P.B.; Beveridge, C.A.; Sieberer, T.; Sehr, E.M.; et al. Strigolactone signaling is required for auxin-dependent stimulation of secondary growth in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20242–20247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamiaux, C.; Drummond, R.S.M.; Janssen, B.J.; Ledger, S.E.; Cooney, J.M.; Newcomb, R.D.; Snowden, K.C. DAD2 Is an alpha/beta Hydrolase Likely to Be Involved in the Perception of the Plant Branching Hormone, Strigolactone. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 2032–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapulnik, Y.; Delaux, P.M.; Resnick, N.; Mayzlish-Gati, E.; Wininger, S.; Bhattacharya, C.; Sejalon-Delmas, N.; Combier, J.P.; Becard, G.; Belausov, E.; et al. Strigolactones affect lateral root formation and root-hair elongation in Arabidopsis. Planta 2011, 233, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapulnik, Y.; Resnick, N.; Mayzlish-Gati, E.; Kaplan, Y.; Wininger, S.; Hershenhorn, J.; Koltai, H. Strigolactones interact with ethylene and auxin in regulating root-hair elongation in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 2915–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorefan, K.; Booker, J.; Haurogne, K.; Goussot, M.; Bainbridge, K.; Foo, E.; Chatfield, S.; Ward, S.; Beveridge, C.; Rameau, C.; et al. MAX4 and RMS1 are orthologous dioxygenase-like genes that regulate shoot branching in Arabidopsis and pea. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.W.; Xue, L.G.; Xu, S.J.; Feng, H.Y.; An, L.Z. Mediators, Genes and Signaling in Adventitious Rooting. Bot. Rev. 2009, 75, 230–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, A.; Mason, M.G.; De Cuyper, C.; Brewer, P.B.; Herold, S.; Agusti, J.; Geelen, D.; Greb, T.; Goormachtig, S.; Beeckman, T.; et al. Strigolactones Suppress Adventitious Rooting in Arabidopsis and Pea. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 1976–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruyter-Spira, C.; Kohlen, W.; Charnikhova, T.; van Zeijl, A.; van Bezouwen, L.; de Ruijter, N.; Cardoso, C.; Lopez-Raez, J.A.; Matusova, R.; Bours, R.; et al. Physiological Effects of the Synthetic Strigolactone Analog GR24 on Root System Architecture in Arabidopsis: Another Belowground Role for Strigolactones? Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowden, K.C.; Simkin, A.J.; Janssen, B.J.; Templeton, K.R.; Loucas, H.M.; Simons, J.L.; Karunairetnam, S.; Gleave, A.P.; Clark, D.G.; Klee, H.J. The Decreased apical dominance1/Petunia hybrida CAROTENOID CLEAVAGE DIOXYGENASE8 gene affects branch production and plays a role in leaf senescence, root growth, and flower development. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 746–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, P.B.; Koltai, H.; Beveridge, C.A. Diverse Roles of Strigolactones in Plant Development. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, Y.; Yamaguchi, S. Strigolactone biosynthesis and perception. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapulnik, Y.; Koltai, H. Strigolactone Involvement in Root Development, Response to Abiotic Stress, and Interactions with the Biotic Soil Environment. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldie, T.; McCulloch, H.; Leyser, O. Strigolactones and the control of plant development: Lessons from shoot branching. Plant J. 2014, 79, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Babili, S.; Bouwmeester, H.J. Strigolactones, a Novel Carotenoid-Derived Plant Hormone. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2015, 66, 161–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, E.L.; Alder, A.; Hunn, S.; Ferguson, J.; Lehtonen, M.T.; Scheler, B.; Kerres, K.L.; Wiedemann, G.; Safavi-Rizi, V.; Nordzieke, S.; et al. Strigolactone biosynthesis is evolutionarily conserved, regulated by phosphate starvation and contributes to resistance against phytopathogenic fungi in a moss, Physcomitrella patens. New Phytol. 2017, 216, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, P.D.; Bramley, P.M. The biosynthesis and nutritional uses of carotenoids. Prog. Lipid Res. 2004, 43, 228–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moise, A.R.; Al-Babili, S.; Wurtzel, E.T. Mechanistic Aspects of Carotenoid Biosynthesis. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 164–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisar, N.; Li, L.; Lu, S.; Khin, N.C.; Pogson, B.J. Carotenoid Metabolism in Plants. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.H.; Strack, D. Carotenoids and their cleavage products: Biosynthesis and functions. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 663–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, A.; Jamil, M.; Marzorati, M.; Bruno, M.; Vermathen, M.; Bigler, P.; Ghisla, S.; Bouwmeester, H.; Beyer, P.; Al-Babili, S. The Path from beta-Carotene to Carlactone, a Strigolactone-Like Plant Hormone. Science 2012, 335, 1348–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, N.; de Saint Germain, A.; Pillot, J.P.; Boutet-Mercey, S.; Dalmais, M.; Antoniadi, I.; Li, X.; Maia-Grondard, A.; Le Signor, C.; Bouteiller, N.; et al. The Pea TCP Transcription Factor PsBRC1 Acts Downstream of Strigolactones to Control Shoot Branching. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbull, C.G.N.; Booker, J.P.; Leyser, H.M.O. Micrografting techniques for testing long-distance signalling in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2002, 32, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booker, J.; Auldridge, M.; Wills, S.; McCarty, D.; Klee, H.; Leyser, O. MAX3/CCD7 is a carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase required for the synthesis of a novel plant signaling molecule. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booker, J.; Sieberer, T.; Wright, W.; Williamson, L.; Willett, B.; Stirnberg, P.; Turnbull, C.; Srinivasan, M.; Goddard, P.; Leyser, O. MAX1 encodes a cytochrome P450 family member that acts downstream of MAX3/4 to produce a carotenoid-derived branch-inhibiting hormone. Dev. Cell 2005, 8, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auldridge, M.E.; Block, A.; Vogel, J.T.; Dabney-Smith, C.; Mila, I.; Bouzayen, M.; Magallanes-Lundback, M.; DellaPenna, D.; McCarty, D.R.; Klee, H.J. Characterization of three members of the Arabidopsis carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase family demonstrates the divergent roles of this multifunctional enzyme family. Plant J. 2006, 45, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stirnberg, P.; van de Sande, K.; Leyser, H.M.O. MAX1 and MAX2 control shoot lateral branching in Arabidopsis. Development 2002, 129, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Stirnberg, P.; Furner, I.J.; Leyser, H.M.O. MAX2 participates in an SCF complex which acts locally at the node to suppress shoot branching. Plant J. 2007, 50, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Haq, B.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Rehman, N.U.; Wang, J.J.; Li, P.H.; Li, D.Q.; Zhao, J. Functional characterization of soybean strigolactone biosynthesis and signaling genes in Arabidopsis MAX mutants and GmMAX3 in soybean nodulation. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, R.X.; Qian, Q.; Yan, M.X.; Meng, X.B.; Fu, Z.M.; Yan, C.Y.; Jiang, B.; Su, Z.; Li, J.Y.; et al. DWARF27, an Iron-Containing Protein Required for the Biosynthesis of Strigolactones, Regulates Rice Tiller Bud Outgrowth. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 1512–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, M.; Al-Babili, S. On the substrate specificity of the rice strigolactone biosynthesis enzyme DWARF27. Planta 2016, 243, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, M.; Hofmann, M.; Vermathen, M.; Alder, A.; Beyer, P.; Al-Babili, S. On the substrate- and stereospecificity of the plant carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase 7. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 1802–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, S.; Sado, A.; Tanaka, K.; Kisugi, T.; Asami, K.; Ota, S.; Kim, H., II; Yoneyama, K.; Xie, X.; Ohnishi, T.; et al. Carlactone is converted to carlactonoic acid by MAX1 in Arabidopsis and its methyl ester can directly interact with AtD14 in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18084–18089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, P.B.; Yoneyama, K.; Filardo, F.; Meyers, E.; Scaffidi, A.; Frickey, T.; Akiyama, K.; Seto, Y.; Dun, E.A.; Cremer, J.E.; et al. LATERAL BRANCHING OXIDOREDUCTASE acts in the final stages of strigolactone biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 6301–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Li, X.L.; Lu, Z.F.; Meng, X.B.; Wang, Y.H.; Smith, S.M.; Li, J.Y. Strigolactone Signaling in Arabidopsis Regulates Shoot Development by Targeting D53-Like SMXL Repressor Proteins for Ubiquitination and Degradation. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 3128–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalma-Weiszhausz, D.D.; Warrington, J.; Tanimoto, E.Y.; Miyada, C.G. The affymetrix GeneChip platform: An overview. Methods Enzym. 2006, 410, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, G.K. Linear models and empirical bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2004, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, Y.; Sado, A.; Asami, K.; Hanada, A.; Umehara, M.; Akiyama, K.; Yamaguchi, S. Carlactone is an endogenous biosynthetic precursor for strigolactones. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, E.M.; Lin, W.C.; Husbands, A.Y.; Yu, L.F.; Jaganatha, V.; Jablonska, B.; Mangeon, A.; Neff, M.M.; Girke, T.; Springer, P.S. Arabidopsis LATERAL ORGAN BOUNDARIES negatively regulates brassinosteroid accumulation to limit growth in organ boundaries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21146–21151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundappan, I.; Bennett, T.; Morffy, N.; Liang, Y.Y.; Stang, J.P.; Abbas, A.; Leyser, O.; Nelson, D.C. SMAX1-LIKE/D53 Family Members Enable Distinct MAX2-Dependent Responses to Strigolactones and Karrikins in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 3143–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.J.; Yu, Y.W.; Li, S.H.; Wang, J.; Tang, S.J.; Huang, R.F. Abscisic Acid Antagonizes Ethylene Production through the ABI4-Mediated Transcriptional Repression of ACS4 and ACS8 in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchisaka, A.; Yu, G.X.; Jin, H.L.; Alonso, J.M.; Ecker, J.R.; Zhang, X.M.; Gao, S.; Theologis, A. A Combinatorial Interplay Among the 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-Carboxylate Isoforms Regulates Ethylene Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 2009, 183, 979–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.P.; Wang, X.N.; Li, N.N.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Mu, S.C.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X. Functional Analysis of MAX2 in Phototropins-Mediated Cotyledon Flattening in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, K.P.; Luo, Q.; He, S.B.; Lu, X.D.; Yang, H.Q. Strigolactone-Regulated Hypocotyl Elongation Is Dependent on Cryptochrome and Phytochrome Signaling Pathways in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demarsy, E.; Schepens, I.; Okajima, K.; Hersch, M.; Bergmann, S.; Christie, J.; Shimazaki, K.; Tokutomi, S.; Fankhauser, C. Phytochrome Kinase Substrate 4 is phosphorylated by the phototropin 1 photoreceptor. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 3457–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.C.; Scaffidi, A.; Dun, E.A.; Waters, M.T.; Flematti, G.R.; Dixon, K.W.; Beveridge, C.A.; Ghisalberti, E.L.; Smith, S.M. F-box protein MAX2 has dual roles in karrikin and strigolactone signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8897–8902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diet, A.; Link, B.; Seifert, G.J.; Schellenberg, B.; Wagner, U.; Pauly, M.; Reiter, W.D.; Ringli, C. The Arabidopsis root hair cell wall formation mutant lrx1 is suppressed by mutations in the RHM1 gene encoding a UDP-L-rhamnose synthase. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 1630–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolesnikova, M.D.; Xiong, Q.B.; Lodeiro, S.; Hua, L.; Matsuda, S.P.T. Lanosterol biosynthesis in plants. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2006, 447, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohyama, K.; Suzuki, M.; Kikuchi, J.; Saito, K.; Muranaka, T. Dual biosynthetic pathways to phytosterol via cycloartenol and lanosterol in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, B.; Huang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Mou, Z.; Li, J. Increased expression of MAP KINASE KINASE7 causes deficiency in polar auxin transport and leads to plant architectural abnormality in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.K.; Yu, J.; Lee, K.M.; Son, M.; Min, K.; Lee, Y.W.; Kim, K.H. Genome-wide expression profiling shows transcriptional reprogramming in Fusarium graminearum by Fusarium graminearum virus 1-DK21 infection. BMC Genom. 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Workman, C.; Jensen, L.J.; Jarmer, H.; Berka, R.; Gautier, L.; Nielser, H.B.; Saxild, H.H.; Nielsen, C.; Brunak, S.; Knudsen, S. A new non-linear normalization method for reducing variability in DNA microarray experiments. Genome Biol. 2002, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh-Thu, P.T.; Hwang, D.J.; Jeon, J.S.; Nahm, B.H.; Kim, Y.K. Transcriptome analysis of leaf and root of rice seedling to acute dehydration. Rice 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeeberg, B.R.; Feng, W.M.; Wang, G.; Wang, M.D.; Fojo, A.T.; Sunshine, M.; Narasimhan, S.; Kane, D.W.; Reinhold, W.C.; Lababidi, S.; et al. GoMiner: A resource for biological interpretation of genomic and proteomic data. Genome Biol. 2003, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, S.; Kim, J.S.; Jun, K.M.; Lee, S.B.; Kim, M.S.; Nahm, B.H.; Kim, Y.K. Analysis of Genes with Alternatively Spliced Transcripts in the Leaf, Root, Panicle and Seed of Rice Using a Long Oligomer Microarray and RNA-Seq. Mol. Cells 2017, 40, 714–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meur, N.L.; Gentleman, R. Analyzing biological data using R: Methods for graphs and networks. Methods Mol Biol. 2012, 804, 343–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, S.C.; Beveridge, C.A. IPA1: A direct target of SL signaling. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1191–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, M.; Kim, I.; Kim, Y.-K.; Heo, J.B.; Suh, M.C.; Kim, H.U. Strigolactone Signaling Genes Showing Differential Expression Patterns in Arabidopsis max Mutants. Plants 2019, 8, 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8090352
Kumar M, Kim I, Kim Y-K, Heo JB, Suh MC, Kim HU. Strigolactone Signaling Genes Showing Differential Expression Patterns in Arabidopsis max Mutants. Plants. 2019; 8(9):352. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8090352
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Manu, Inyoung Kim, Yeon-Ki Kim, Jae Bok Heo, Mi Chung Suh, and Hyun Uk Kim. 2019. "Strigolactone Signaling Genes Showing Differential Expression Patterns in Arabidopsis max Mutants" Plants 8, no. 9: 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8090352
APA StyleKumar, M., Kim, I., Kim, Y.-K., Heo, J. B., Suh, M. C., & Kim, H. U. (2019). Strigolactone Signaling Genes Showing Differential Expression Patterns in Arabidopsis max Mutants. Plants, 8(9), 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8090352