Dynamic Monitoring of Chilo suppressalis Resistance to Insecticides and the Potential Influencing Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
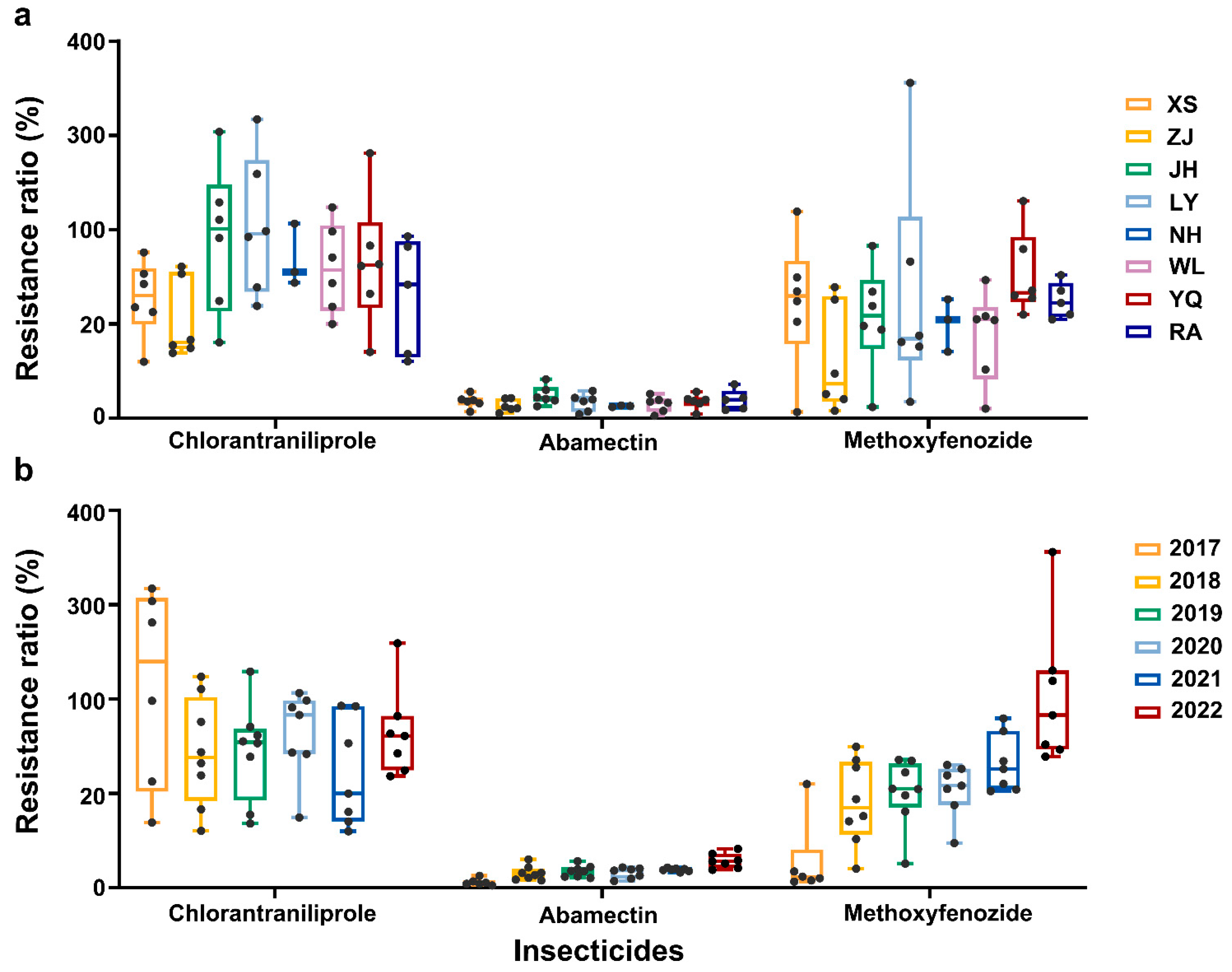
2.1. Toxicological Responses to Abamectin, Chlorantraniliprole, and Methoxyfenozide
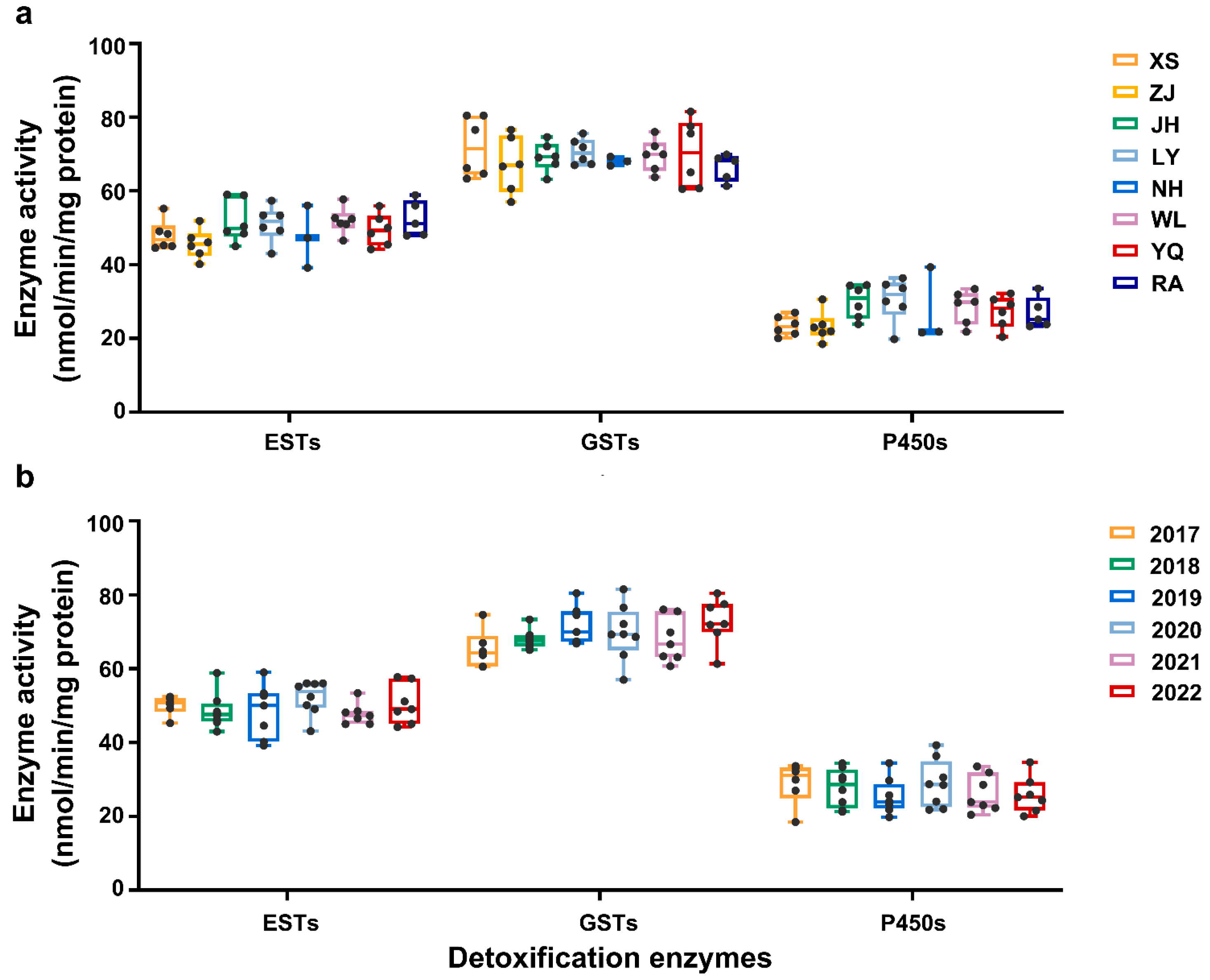
2.2. EST, GST, and Cytochrome P450 Activities
2.3. Correlations of Resistance to Three Insecticides
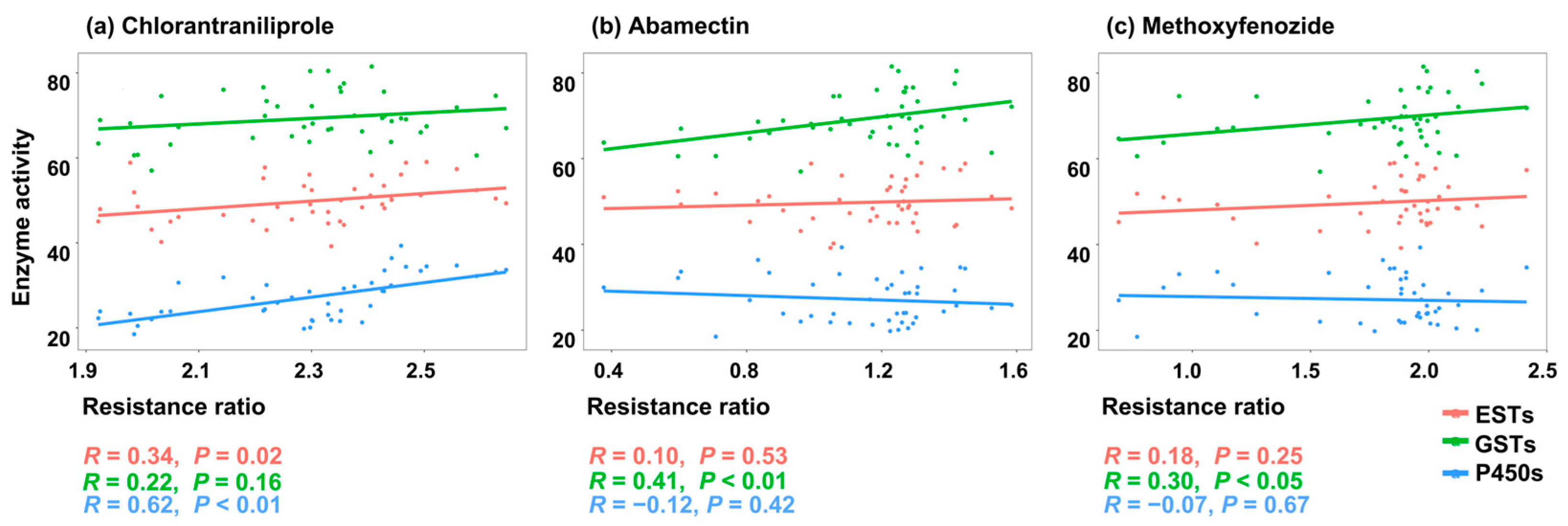
2.4. Correlations Between Detoxification Enzyme Activities and Insecticide Toxicities
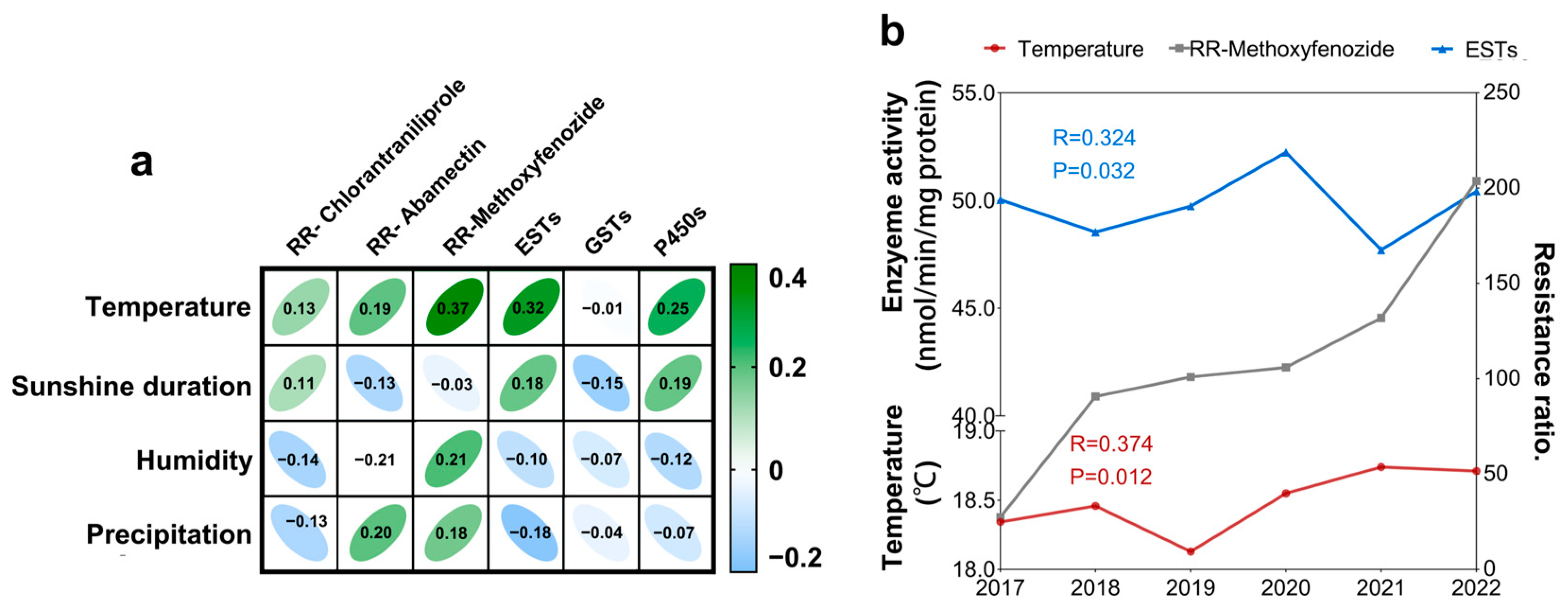
2.5. Correlations Between the Resistance Ratio and Climate Factors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. C. suppressalis Populations
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. Bioassays
4.4. Detoxification Enzyme Activity Assays
4.5. Climatic Data Sources
4.6. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Li, X.F.; Han, Z.G.; Chen, C.K.; Li, G.Q. Monitoring for resistance of rice stem borer (Chilo suppressalis Walker) to 4 conventional insecticides. J. Nanjing Agricul. Univ. 2001, 24, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.B.; Yan, R.; Zhou, Q.L.; Qiao, L.Y.; Zhu, G.N.; Chen, M.L. Monitoring and mechanisms of chlorantraniliprole resistance in Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) in China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 1348–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.X.; Zhu, P.Y.; Gurr, G.M.; Zheng, X.S.; Chen, G.H.; Heong, K.L. Rice pest management by ecological engineering: A pioneering attempt in China. In Rice Planthoppers; Heong, K.L., Cheng, J., Eds.; Zhejiang University Press: Hangzhou, China, 2015; pp. 161–178. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.H.; Wang, G.R.; Zhong, L.Q.; Zhang, F.C.; Bai, Q.; Zheng, X.S.; Lu, Z.X. Resistance monitoring of Chilo suppressalis (Walker) (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) to chlorantraniliprole in eight field populations from east and central China. Crop Prot. 2017, 100, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Han, Z.; Xu, X.; Yue, L.N. Triazophos resistance mechanisms in the rice stem borer (Chilo suppressalis Walker). Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2019, 77, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.P.; Zhang, J.F.; Gao, C.F.; Su, J.Y.; Chen, J.M.; Chen, J.L. Regression analysis of dynamics of insecticide resistance in field populations of Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) during 2002–2011 in China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 1832–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, K.K.; Li, W.H.; Liao, X.; Liu, C.Y.; Qin, Y.; Ren, Z.J.; Qin, X.Y.; Wan, H.; Sheng, F.; Li, J.H. Dynamics of insecticide resistance in different geographical populations of Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) in China 2016–2018. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 1866–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, C.F.; Wang, H.T.; Sheng, S.Y.; Xuan, W.J. Pest status and loss assessment of crop damage caused by the rice borers, Chilo suppressalis and Tryporyza incertulas in China. Chinese J. Appl. Entomol. 2003, 40, 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, P.P.; Yao, Y.J.; Zhu, X.J.; Zeng, X.J. Occurrence, damage and chemical control of Chilo suppressalis in Jiangxi during past sixty years. Acta Agricul. Jiangxi 2011, 23, 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.B. Dilemma and way-out of hybrid rice during the transition period in China. Acta Agron. Sin. 2016, 42, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wang, Q.Q.; Qi, H.L.; Wang, Q.Y.; Yuan, H.Z.; Rui, C.H. Resistance selection of indoxacarb in Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae), cross-resistance, biochemical mechanisms and associated fitness costs. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, A.; Sgrò, C. Climate change and evolutionary adaptation. Nature 2011, 70, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Caren, J.; Reddy, G.V.P.; Li, W.H.; Yao, J.X. Effect of age on insecticide susceptibility and enzymatic activities of three detoxification enzymes and one invertase in honey bee workers (Apis mellifera). Comp. Biochemi. Phys. C 2020, 238, 108844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhamalawy, O.; Bakr, A.; Eissa, F. Impact of pesticides on non-target invertebrates in agricultural ecosystems. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2024, 202, 10594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaepfer, D.R.; Bradford, J.B.; Lauenroth, W.K.; Munson, A.M.; Tietjen, B.; Hall, S.A. Climate change reduces extent of temperate drylands and intensifies drought in deep soils. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzrafi, M. Climate change exacerbates pest damage through reduced pesticide efficacy. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Wang, Z.; Chung, H. Climate change and the genetics of insecticide resistance. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.A.A. Characterization of permethrin resistance in a Musca domestica strain: Resistance development, cross-resistance potential and realized heritability. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2969–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Cao, G.C.; Song, J.X.; Yin, Q.; Han, Z.J. Biochemical mechanisms conferring cross-resistance between tebufenozide and abamectin in Plutella xylostella. Pestic Biochem. Phys. 2008, 91, 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Shabana, W.; Sarfraz, A.S. Development of fipronil resistance, fitness cost, cross-resistance to other insecticides, stability, and risk assessment in Oxycarenus hyalinipennis (Costa). Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 803, 150026. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.P.; Chang, J.; Feng, T.; Gao, X.W. Differential effects of insecticides on mitochondrial membrane fluidity and ATPase activity between the wolf spider and the rice stem borer. J. Integr. Agricul. 2015, 14, 2574–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhu, B.; Liang, P.; Gao, X.W. Identification of carboxylesterase genes contributing to multi-insecticide resistance in Plutella xylostella (L.). Entomol. Gen. 2022, 42, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.Z.; Downes, S.; Bird, L.; Zalucki, M.P.; Fan, Y.; Xie, Z.M.; Ahmad, M.; Lu, Z. Long-term changes in pest resistance dynamics in China and Australia in response to the introduction of Bt cotton and patterns of insecticide use. Entomol. Gen. 2023, 43, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.Z.; Shen, J.L.; Zhang, J.Z.; Lu, M.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhou, W.J. Monitoring of insecticide resistance and genetic analysis of triazophos resistance in Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera, Pyralidae). Rice Sci. 2004, 11, 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.P.; Gao, C.F.; Cao, M.Z.; Chen, W.M.; Li, Q.H.; Zhou, W.J.; Liu, X.G.; Shen, L.J.; Yu, Y.C. Survey of susceptibilities to monosultap, triazophos, fipronil, and abamectin in Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera: Cramidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2007, 100, 1854–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.P.; Zhang, J.F.; Chen, J.M.; Shen, J.L. Using synergists to detect multiple insecticide resistance in field populations of rice stem borer. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2012, 103, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.J.; Chen, Q.; Qin, W.J.; Sun, Y.; Qin, H.G. Resistance monitoring of four insecticides and a description of an artificial diet incorporation method for Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 2554–2561. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.Y.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Wu, M.; Gao, C.F. Geographic susceptibility of Chilo suppressalis walker (Lepidoptera: Crambidae), to chlorantraniliprole in China. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Zhao, D.D.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, L.Q.; Wang, X.; Gao, C.F.; Wu, S.F. Monitoring and mechanisms of insecticide resistance in Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae), with special reference to diamides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Chang, C.; Dai, S.M. Responses of striped stem borer, Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera, Pyralidae), from Taiwan to a range of insecticides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chen, W.M.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Zheng, X.S.; Jin, J.C.; Su, J.Y.; Gao, C.-F.; Shen, J.-L. Insecticide resistance monitoring of Chilo suppressalis in the drainage area of the Yangtze River, China. Chinese J. Rice Sci. 2010, 24, 509–515. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Lin, Q.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Yin, F.; Feng, X. Identification of a novel cytochrome P450 gene, CYP321E1 from the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.) and RNA interference to evaluate its role in chlorantraniliprole resistance. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2014, 104, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbinghaus-Kintscher, U.; Luemmen, P.; Lobitz, N.; Schulte, T.; Funke, C.; Fischer, R.; Masaki, T.; Yasokawa, N.; Tohnishi, M. Phthalic acid diamides activate ryanodine-sensitive Ca2+ release channels in insects. Cell Calcium 2006, 39, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.K.; Guan, D.J.; Zhang, N.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, C.Y.; Ge, H.C.; Wei, J.P.; Wang, J.J.; Qian, K. Comparative phosphoproteomics analysis provides insights into the responses of Chilo suppressalis to sublethal chlorantraniliprole exposure. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 2338–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauen, R. Insecticide mode of action: Return of the ryanodine receptor. Pest Manag. Sci. 2006, 62, 690–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.M.; Scott, J.G.; Campos, F.; Bloomquist, J.R. Resistance to avermectins: Extent, mechanisms, and management implications. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1995, 40, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaclocha, P.; Jones, M.M.; Tansey, J.A.; Monzó, C.; Chen, X.L.; Stansly, P.A. Residual toxicity of insecticides used against the Asian citrus psyllid and resistance management strategies with thiamethoxam and abamectin. J. Pest. Sci. 2019, 92, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.Y.; Yao, W.; Han, L.J.; Qiao, C.K.; Song, S.Y.; Qin, F.Y.; Dong, Q.; Hao, X.H.; Xu, Y.J. Method validation and residue analysis of methoxyfenozide and metaflumizone in Chinese broccoli under field conditions by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 3860–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhadialla, T.S.; Carlson, G.R.; Le, D.P. New insecticides with ecdysteroidal and juvenile hormone activity. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1998, 43, 545–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denholm, I.; Rowland, M.W. Tactics for managing pesticide resistance in ar-thropods: Theory and practice. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1992, 37, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.G.; Yin, Y.; Li, M.Y.; Wu, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Cheng, Q.H.; Gong, C.W.; Shen, L.T. Mechanisms for multiple resistances in field populations of rice stem borer, Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) from Sichuan Province, China. Pestic Biochem. Phys. 2021, 171, 104720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparks, T.C.; Nauen, R. IRAC: Mode of action classification and insecticide resistance management. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 121, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paula, D.P.; Lozano, R.E.; Menger, J.P.; Andow, D.A.; Koch, R.L. Identification of point mutations related to pyrethroid resistance in voltage-gated sodium channel genes in Aphis glycines. Entomol. Gen. 2021, 41, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocchetti, A.; Dermauw, W.; Van Leeuwen, T. Incidence and molecular mechanisms of insecticide resistance in Frankliniella occidentalis, Thrips tabaci and other economically important thrips species. Entomol. Gen. 2023, 43, 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, V.; Buer, B.; Lueke, B.; Mazzoni, E.; Pym, A.; Bass, C.; Nauen, R. Molecular characterization of pyrethroid resistance in field-collected populations of the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Entomol. Gen. 2023, 43, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidi, N.; Tseliou, V.; Riga, M.; Nauen, R.; Van Leeuwen, T.; Labrou, N.E.; Vontas, J. Functional characterization of glutathione S-transferases associated with insecticide resistance in Tetranychus urticae. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2015, 121, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.M.; Chang, C.; Huang, X.Y. Distinct contributions of A314S and novel R667Q substitutions of acetylcholinesterase 1 to carbofuran resistance of Chilo suppressalis Walker. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, Q.; Qin, W.J.; Huang, S.J.; Jiang, Y.; Qin, H.G. Chlorantraniliprole resistance and its biochemical and new molecular target mechanisms in laboratory and field strains of Chilo suppressalis (Walker). Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1416–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.C.; Sheng, C.W.; John, E.C.; Zhao, C.Q.; Han, Z.J. Ryanodine receptor genes of the rice stem borer, Chilo suppressalis: Molecular cloning, alternative splicing and expression profiling. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2017, 135, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.R.; Huang, R.; Wan, H.; Li, J.H.; Li, J.K.; Zhang, X.L. Insecticide resistance monitoring in field populations of Chilo suppressalis Walker (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) from central China. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1029319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Rui, C.; Wang, L.; Nahiyoon, S.A.; Huang, W.L.; Zhu, J.S.; Ji, X.J.; Yang, Q.G.; Yuan, H.Z.; Gui, L. Field-evolved resistance to 11 insecticides and the mechanisms involved in Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 5086–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maino, J.L.; Umina, P.A.; Hoffmann, A.A. Climate contributes to the evolution of pesticide resistance. Global Ecol. Biogeogr. 2018, 27, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, K.; Yadav, J.S. P450 monooxygenases (P450ome) of the model white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 38, 339–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Délye, C. Unravelling the genetic bases of non-target-site-based resistance (NTSR) to herbicides: A major challenge for weed science in the forthcoming decade. Pest Manag. Sci. 2013, 69, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.N.; Zhou, T.L.; Li, Y.; Dai, W.; Du, S.K. Activation of the CncC pathway is involved in the regulation of P450 genes responsible for clothianidin resistance in Bradysia odoriphaga. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 3071–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, H.Y.; Ning, Y.B.; Qiao, K.; Wang, K.Y. Resistance selection and characterization of chlorantaniliprole resistance in Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereniki, P.; Fotini, P.; Nikolaos, E.L. Recent advances in protein engineering and biotechnological applications of glutathione transferases. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 38, 511–528. [Google Scholar]
- Ketterman, A.J.; Saisawang, C.; Wongsantichon, J. Insect glutathione transferases. Drug Metab. Rev. 2011, 43, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Han, Z. Tebufenozide resistance selected in Plutella xylostella and its cross-resistance and fitness cost. Pest Manag. Sci. 2006, 62, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeOra Software. Polo-Plus, a User’s Guide to Probit or Logit Analysis; LeOra Software: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]

| Chlorantraniliprole | Abamectin | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Abamectin | R value | −0.017 | |
| p value | 0.914 | ||
| Methoxyfenozide | R value | 0.055 | 0.698 ** |
| p value | 0.724 | <0.001 |
| Chlorantraniliprole | Abamectin | Methoxyfenozide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETSs | R value | 0.340 * | 0.097 | 0.177 |
| p value | 0.024 | 0.531 | 0.249 | |
| GSTs | R value | 0.216 | 0.410 ** | 0.302 * |
| p value | 0.160 | 0.006 | 0.046 | |
| P450s | R value | 0.621 ** | −0.125 | −0.066 |
| p value | <0.001 | 0.420 | 0.669 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mo, W.; Li, Q.; Lu, Z.; Ullah, F.; Guo, J.; Xu, H.; Lu, Y. Dynamic Monitoring of Chilo suppressalis Resistance to Insecticides and the Potential Influencing Factors. Plants 2025, 14, 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050724
Mo W, Li Q, Lu Z, Ullah F, Guo J, Xu H, Lu Y. Dynamic Monitoring of Chilo suppressalis Resistance to Insecticides and the Potential Influencing Factors. Plants. 2025; 14(5):724. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050724
Chicago/Turabian StyleMo, Wujia, Qiang Li, Zhongxian Lu, Farman Ullah, Jiawen Guo, Hongxing Xu, and Yanhui Lu. 2025. "Dynamic Monitoring of Chilo suppressalis Resistance to Insecticides and the Potential Influencing Factors" Plants 14, no. 5: 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050724
APA StyleMo, W., Li, Q., Lu, Z., Ullah, F., Guo, J., Xu, H., & Lu, Y. (2025). Dynamic Monitoring of Chilo suppressalis Resistance to Insecticides and the Potential Influencing Factors. Plants, 14(5), 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14050724







