Chemical Composition and Selective Bioactivities of Piper platylobum Sodiro Essential Oil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Yield and Chemical Composition
2.2. Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oil
2.3. Antioxidant Capacity
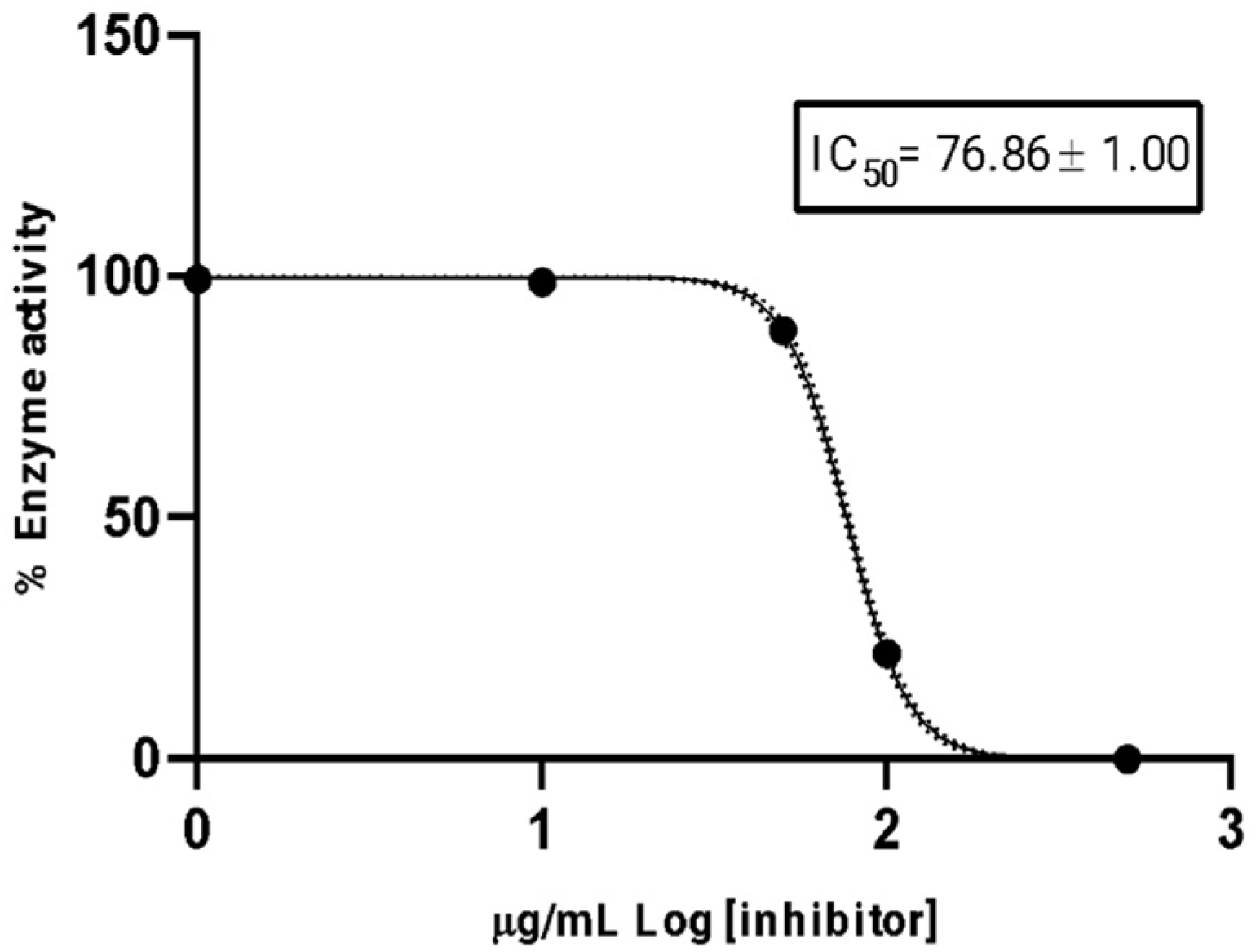
2.4. Anticholinesterase Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
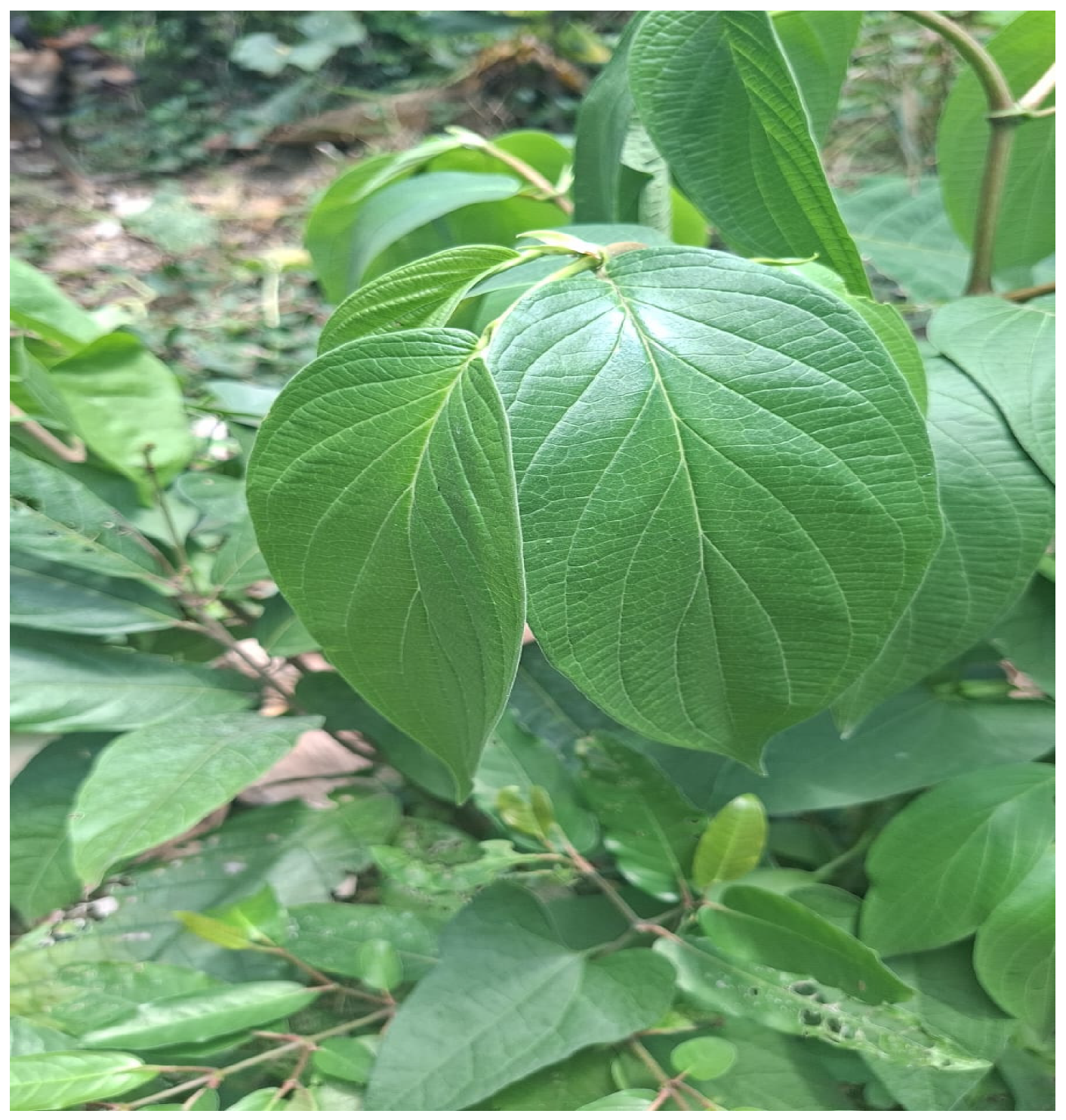
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Essential Oil Isolation
4.3. Identification and Quantification of Essential Oil
4.3.1. Qualitative Analysis
4.3.2. Quantitative Analysis
4.4. Antimicrobial Activity
4.5. Antioxidant Capacity
4.6. Cholinesterase Assay
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Last 40 Years and Future Perspectives. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabricant, D.S.; Farnsworth, N.R. The Value of Plants Used in Traditional Medicine for Drug Discovery. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109 (Suppl. S1), 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Gurib-Fakim, A. Medicinal Plants: Traditions of Yesterday and Drugs of Tomorrow. Mol. Asp. Med. 2006, 27, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Natural Products: A Continuing Source of Novel Drug Leads. Pure Appl. Chem. 2013, 85, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baser, K.H.C.; Buchbauer, A. Handbook of Essential Oils: Science, Technology, and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bakkali, F.; Averbeck, S.; Averbeck, D.; Idaomar, M. Biological effects of essential oils—A Review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 446–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichersky, E.; Gershenzon, J. The Formation and Function of Plant Volatiles: Perfumes for Pollination and Defense. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2002, 5, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burt, S. Essential oils: Their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods—A Review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 223–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hzounda Fokou, J.B.; Jazet Dongmo, P.M.; Boyom, F.F. Essential Oil’s Chemical Composition and Pharmacological Properties; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, J.; Klugman, D.; Theuretzbacher, U. Discovery, Research, and Development of New Antibiotics: The WHO Priority Pathogens List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regnault-Roger, C.; Vincent, C.; Arnason, J.T. Essential Oils in Insect Control: Low-Risk Products in a High-Stakes World. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2019, 64, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, W.D. Piperaceae. In Flora de Nicaragua; Missouri Botanical Garden Press: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2001; pp. 1957–1988. [Google Scholar]
- Parmar, V.S.; Jain, S.C.; Bisht, K.S.; Jain, R.; Taneja, P.; Jha, A.; Errington, W. Phytochemistry of the Genus Piper. Phytochemistry 1997, 46, 597–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.S.; Sultan, M.T.; Butt, M.S.; Iqbal, J. Piperine: A Valuable Alkaloid from Piper nigrum L. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 1251–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, T.M.; Silveira, J.C.G.; Ferreira, T.C.; Leite, L.I.L.; Martins, I.S.; Carvalho, J.C. Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity of the Essential Oil from Piper marginatum Jacq. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2017, 27, 724–731. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, V.L.F.; Blank, A.F.; de Jesus, B.M.; de Medeiros, K.A.F.; da Costa, J.P.; Lima, M.S. Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of the Essential Oil from Piper aduncum L. Leaves. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2014, 24, 555–560. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, S.M.O.; Andrade, R.A.; Morais, S.M.; Oliveira, E.F.; Medeiros, I.M.; Almeida, R.N. Chemical Composition and Central Nervous System Depressant Activity of Essential Oil from Piper marginatum Jacq. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2012, 22, 863–868. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, C.-P.; Shi, Y.-N.; Liu, F.-F.; Li, H.-Z.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Yang, C.-R.; Xu, M. A Survey of the Chemical Compounds of Piper spp. (Piperaceae) and Their Biological Activities. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondello, L.; Tranchida, P.Q.; Dugo, P.; Dugo, G. Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry in the Analysis of Essential Oils. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1067, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.P. Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry, 4th ed.; Allured Publishing Corporation: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 2007; ISBN 10-1932633219. [Google Scholar]
- Dognini, J.; Meneghetti, E.K.; Teske, M.N.; Begnini, I.M.; Rebelo, R.A.; Dalmarco, E.M.; Verdi, M.; de Gasper, A.L. Antibacterial Activity of High Safrole Contain Essential Oils from Piper xylosteoides (Kunth) Steudel. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2012, 24, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.; Salgueiro, L.; Vila, R.; Tomi, F.; Cañigueral, S.; Casanova, J.; da Cunha, A.P.; Adzet, T. Essential Oils from Four Piper Species. Phytochemistry 1998, 49, 2019–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.K.; da Trindade, R.; Alves, N.S.; Figueiredo, P.L.; Maia, J.G.S.; Setzer, W.N. Essential Oils from Neotropical Piper Species and Their Biological Activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes da Camara, C.A.; do Nascimento, A.F.; Monteiro, V.B.; de Moraes, M.M. Larvicidal, ovicidal, and antifeedant activities of essential oils and constituents against Spodoptera frugiperda. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2022, 55, 851–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, P.; Alves, A.; do Vale, V.F.; de Oliveira Monteiro, C.M.; Barrozo, M.M.; Stanton, M.A.; Yamaguchi, L.F.; Kato, M.J.; Araújo, R.N. Effects of Piper aduncum (Piperales: Piperaceae) Essential Oil and Its Main Component Dillapiole on Detoxifying Enzymes and Acetylcholinesterase Activity of Amblyomma sculptum (Acari: Ixodidae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontoura, B.H.; Perin, E.C.; Buratto, A.P.; Schreiner, J.F.; Cavalcante, K.M.; Teixeira, S.D.; Manica, D.; Narzetti, R.A.; da Silva, G.B.; Bagatini, M.D.; et al. Chemical Profile and Biological Properties of the Piper corcovadense C.DC. Essential Oil. Saudi Pharm. J. 2024, 32, 101993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramin, N.M.; Salleh, W.M.N.H.W.; Salihu, A.S.; Ab Ghani, N.; Agosto, N.J.; Sungthong, B.; Abed, S.A. Exploring the Chemical Composition and Bioactivities of the Essential Oil of Piper rostratum Roxb. Nat. Prod. Res. 2025, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Manap, M.Y.B.A.; Solati, Z. Antioxidant activity of Piper nigrum L. essential oil extracted by supercritical CO2 extraction and hydro-distillation. Talanta 2014, 121, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Martínez, R.; Arrieta, J.; Cruz-Antonio, L.; Arrieta-Baez, D.; Velázquez-Méndez, A.M.; Sánchez-Mendoza, M.E. Dillapiole, Isolated from Peperomia pellucida, Shows Gastroprotector Activity against Ethanol-Induced Gastric Lesions in Wistar Rats. Molecules 2013, 18, 11327–11337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Özek, G.; Özek, T.; Kirpotina, L.N.; Klein, R.A.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Quinn, M.T. Composition and Biological Activity of the Essential Oils from Wild Horsemint, Yarrow, and Yampah from Subalpine Meadows in Southwestern. Montana: Immunomodulatory Activity of Dillapiole. Plants 2023, 12, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriega, P.; Ballesteros, J.; De la Cruz, A.; Veloz, T. Chemical Composition and Preliminary Antimicrobial Activity of the Hydroxylated Sesquiterpenes in the Essential Oil from Piper barbatum Kunth Leaves. Plants 2020, 9, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, L.T.; Dai, D.N.; Van Chinh, H.; Le, T.V.A.; Hung, N.H.; Son, N.T.; Tai, T.A. Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils of Piper minutistigmum. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2024, 60, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, F.S.; Cruz, J.N.; de Farias Ramos, I.N.; do Nascimento Brandão, D.L.; Queiroz, R.N.; da Silva, G.V.; da Silva, G.V.; Dolabela, M.F.; da Costa, M.L.; Khayat, A.S.; et al. Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity and Cytotoxicity Effects of Extracts of Piper nigrum L. and Piperine. Separations 2023, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, P.; Pruss, A.; Wojciuk, B.; Dołęgowska, B.; Wajs-Bonikowska, A.; Sienkiewicz, M.; Mężyńska, M.; Łopusiewicz, Ł. The Influence of Essential Oil Compounds on Antibacterial Activity of Mupirocin-Susceptible and Induced Low-Level Mupirocin-Resistant MRSA Strains. Molecules 2019, 24, 3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratini, F.; Pecorini, C.; Resci, I.; Copelotti, E.; Nocera, F.P.; Najar, B.; Mancini, S. Evaluation of the Synergistic Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils and Cecropin A Natural Peptide on Gram-Negative Bacteria. Animals 2025, 15, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezod, U.J.; Salleh, W.M.N.H.W.; Salihu, A.S.; Ghani, N.A. Chemical Composition, Anticholinesterase Activity, and Molecular Docking Studies of Piper crassipes Korth. ex Miq. Essential Oil. Nat. Prod. Res. 2025, 39, 4513–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, W.M.N.H.W.; Hashim, N.A.; Ahmad, F.; Yen, K.H. Anticholinesterase and Antityrosinase Activities of Ten Piper Species from Malaysia. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 4 (Suppl. S2), 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Han, J.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Qu, Y.; Hao, C.; Li, H.; Yang, C.; et al. Chemical Composition and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activity of Essential Oils from Piper Species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3702–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prior, R.L.; Wu, X.; Schaich, K. Standardized Methods for the Determination of Antioxidant Capacity and Phenolics in Foods and Dietary Supplements. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4290–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apak, R.; Özyürek, M.; Güçlü, K.; Çapanoğlu, E. Antioxidant Activity/Capacity Measurement. 1. Classification, Physicochemical Principles, Mechanisms, and Electron Transfer (ET)-Based Assays. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 997–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, A.; Proença, C.; Ferreira, A.; Serralheiro, M.; Nogueira, J.; Araújo, M. Antioxidant and antiacetylcholinesterase activities of five plants used as Portuguese food spices. Food Chem. 2006, 103, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valarezo, E.; Flores-Maza, P.; Cartuche, L.; Ojeda-Riascos, S.; Ramírez, J. Phytochemical profile, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of essential oil extracted from Ecuadorian species Piper ecuadorense Sodiro. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 6014–6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriana, Y.; Xuan, T.D.; Quy, T.N.; Tran, H.-D.; Le, Q.-T. Biological Activities and Chemical Constituents of Essential Oils from Piper cubeba Bojer and Piper nigrum L. Molecules 2019, 24, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramarao, K.D.R.; Razali, Z.; Somasundram, C.; Kunasekaran, W.; Jin, T.L. Effects of Drying Methods on the Antioxidant Properties of Piper betle Leaves. Molecules 2024, 29, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadros-Siguas, C.F.; Herrera-Calderon, O.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; Almohmadi, N.H.; Aljarba, N.H.; Apesteguia-Infantes, J.A.; Loyola-Gonzales, E.; Tataje-Napuri, F.E.; Kong-Chirinos, J.F.; Almeida-Galindo, J.S.; et al. Volatile Components, Antioxidant and Phytotoxic Activity of the Essential Oil of Piper acutifolium Ruiz & Pav. from Peru. Molecules 2023, 28, 3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.J.; Saucedo-Hernández, Y.; Vander Heyden, Y.; Simó-Alfonso, E.F.; Ramis-Ramos, G.; Lerma-García, M.J.; Monteagudo, U.; Bravo, L.; Medinilla, M.; de Armas, Y.; et al. Chemical analysis and antioxidant activity of the essential oils of three Piperaceae species growing in the central region of Cuba. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 1325–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, J.G.; Vargas, L.F. Evaluation of Sde, Sfe and Spme/Cg-Ms for Extraction and Determination of Aroma Compounds from Vilcabamba-Ecuadorian Roasted Coffee. Quim. Nova 2016, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Cartuche, L.; Vallejo, C.; Castillo, E.; Cumbicus, N.; Morocho, V. Chemical Profiling of Drimys granadensis (Winteraceae) Essential Oil, and Their Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and Anticholinesterase Properties. Plants 2024, 13, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.; Courtney, D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

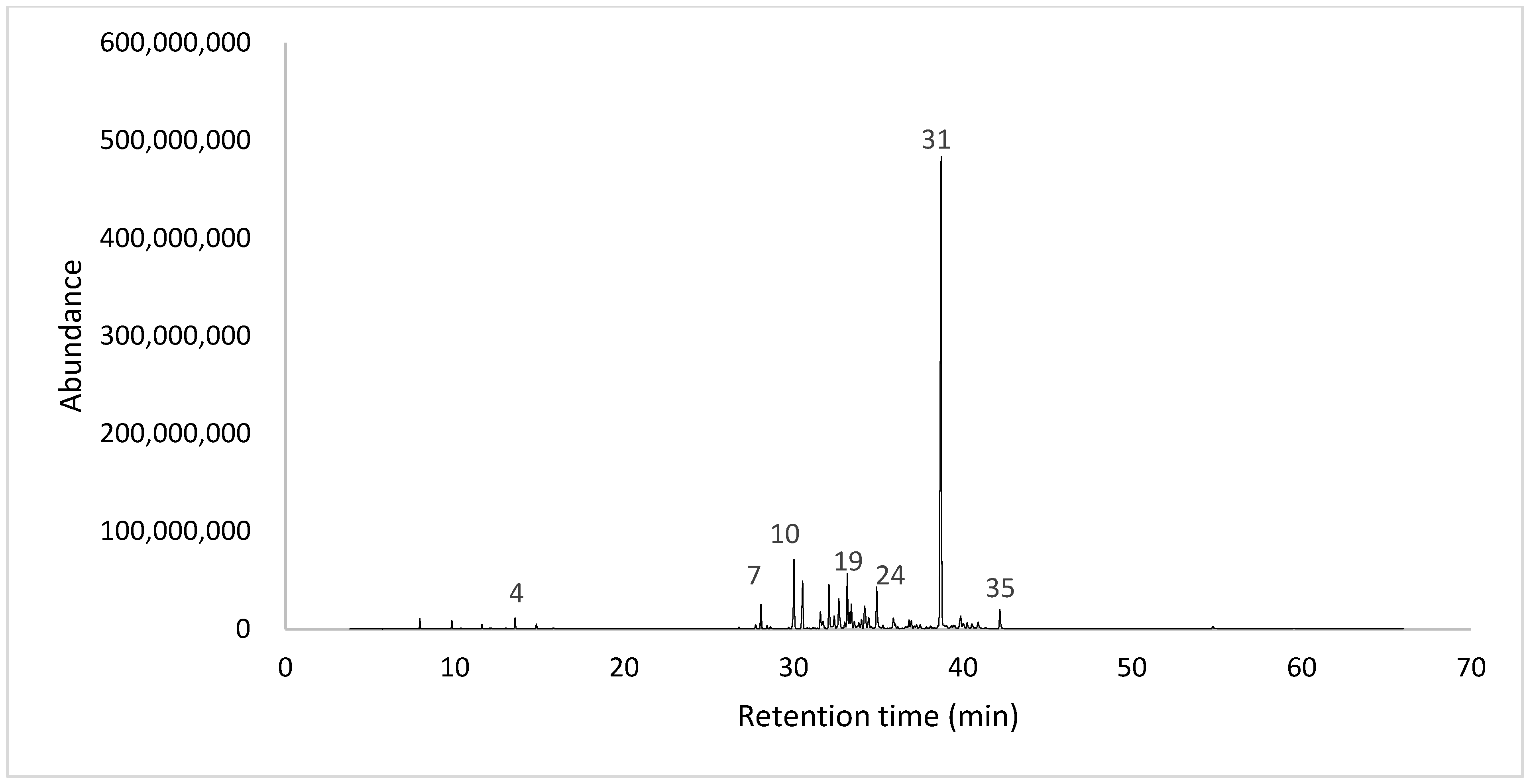
| No. | RT | Compound | LRI Calculate | LRI Literature | Media ± SD | MF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7.94 | α-Pinene | 932 | 932 | 0.95 ± 0.05 | C10H16 |
| 2 | 9.83 | β-Pinene | 979 | 974 | 0.93 ± 0.05 | C10H16 |
| 3 | 11.60 | α-Terpinene | 1019 | 1014 | 0.41 ± 0.02 | C10H16 |
| 4 | 13.55 | γ-Terpinene | 1062 | 1054 | 1.14 ± 0.07 | C10H16 |
| 5 | 14.82 | Terpinolene | 1089 | 1086 | 0.57 ± 0.04 | C10H16 |
| 6 | 27.77 | α-Ylangene | 1370 | 1374 | 0.45 ± 0.00 | C15H24 |
| 7 | 28.08 | α-Copaene | 1377 | 1374 | 2.33 ± 0.09 | C15H24 |
| 8 | 28.43 | β-Bourbonene | 1385 | 1387 | 0.36 ± 0.09 | C15H24 |
| 9 | 30.02 | (E)-Caryophyllene | 1422 | 1417 | 5.01 ± 3.86 | C15H24 |
| 10 | 30.53 | α-(E)-Bergamotene | 1434 | 1432 | 5.69 ± 1.18 | C15H24 |
| 11 | 31.59 | α-Humulene | 1460 | 1452 | 1.52 ± 1.22 | C15H24 |
| 12 | 31.75 | allo-Aromadendrene | 1464 | 1458 | 1.09 ± 0.91 | C15H24 |
| 13 | 32.09 | Croweacin | 1472 | 1457 | 3.01 ± 1.92 | C11H12O3 |
| 14 | 32.40 | γ-Muurolene | 1479 | 1478 | 1.97 ± 1.51 | C15H24 |
| 15 | 32.67 | Germacrene D | 1486 | 1480 | 2.50 ± 1.15 | C15H24 |
| 16 | 33.02 | α-Amorphene | 1494 | 1483 | 2.66 ± 0.86 | C15H24 |
| 17 | 33.17 | n-Pentadecane | 1498 | 1500 | C15H32 | |
| 18 | 33.29 | Bicyclogermacrene | 1501 | 1500 | 0.93 ± 0.10 | C15H24 |
| 19 | 33.41 | α-Muurolene | 1504 | 1500 | 3.74 ± 0.10 | C15H24 |
| 20 | 33.59 | (E,E)-α-Farnesene | 1508 | 1505 | 0.19 ± 0.13 | C15H24 |
| 21 | 33.85 | Asaricin | 1515 | 1495 | 0.41 ± 0.18 | C11H12O3 |
| 22 | 34.01 | γ-Cadinene | 1519 | 1513 | 0.71 ± 0.10 | C15H24 |
| 23 | 34.19 | δ-Amorphene | 1524 | 1511 | 1.41 ± 0.12 | C15H24 |
| 24 | 34.90 | (E)-Isocroweacin | 1541 | 1553 | 3.75 ± 0.09 | C11H12O3 |
| 25 | 35.27 | α-Calacorene | 1551 | 1544 | 0.34 ± 0.05 | C15H20 |
| 26 | 35.89 | Elemicin | 1566 | 1555 | 0.72 ± 0.02 | C12H16O3 |
| 27 | 36.01 | (E)-Nerolidol | 1569 | 1561 | 0.57 ± 0.02 | C15H26O |
| 28 | 36.82 | Spathulenol | 1590 | 1577 | 0.77 ± 0.10 | C15H24O |
| 29 | 36.95 | Caryophyllene oxide | 1593 | 1582 | 1.30 ± 0.23 | C15H24O |
| 30 | 37.47 | Guaiol | 1607 | 1600 | 0.41 ± 0.07 | C15H26O |
| 31 | 38.71 | Dillapiole | 1640 | 1620 | 42.00 ± 1.53 | C12H14O4 |
| 32 | 39.86 | α-Cadinol | 1670 | 1652 | 0.55 ± 0.35 | C15H26O |
| 33 | 40.25 | Elemol acetate | 1681 | 1680 | 0.47 ± 0.11 | C17H28O2 |
| 34 | 40.53 | Cadalene | 1688 | 1675 | 0.64 ± 0.29 | C15H18 |
| 35 | 40.89 | (E)-Asarone | 1698 | 1675 | 1.62 ± 0.10 | C12H16O3 |
| Hydrocarbon monoterpenes (HM) | 4.00 | |||||
| Hydrocarbon sesquiterpenes (HS) | 31.54 | |||||
| Oxygenated sesquiterpenes (OS) | 3.61 | |||||
| Other compounds | 51.97 | |||||
| Total identified | 91.11 | |||||
| Microorganisms | P. platylobum essential Oil † | Antimicrobial Agent (Positive Control) † |
|---|---|---|
| Cocci Bacteria | Ampicillin (1 mg/mL) | |
| Enterococcus faecium ATCC® 27270 | 1000 | <0.3906 |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC® 25923 | Non active | <0.3906 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC® 12228 | Non active | <0.3906 |
| Rod-shaped Bacteria | Ciprofloxacin (1 mg/mL) | |
| Escherichia coli (O157:H7) ATCC® 43888 | Non active | 1.5625 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC® 10145 | Non active | <0.3906 |
| Yeasts and sporulated fungi | Amphotericin B (250 µg/mL) | |
| Aspergillus niger ATCC® 6275 | Non active | <0.098 |
| Candida albicans ATTC® 10231 | Non active | <0.098 |
| Essential oil | ABTS | DPPH | TEAC |
|---|---|---|---|
| SC50 ± SD (µg/mL—µM *) | µM Trolox/g EO | ||
| P. platylobum | 335.71 ± 1.43 | - | 45.85 ± 1.68 |
| Trolox * | 29.09 ± 1.05 | 35.54 ± 1.04 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaime-Carvajal, J.; Pesántez, N.; Ballesteros, J.; Morocho, V.; Malagón, O. Chemical Composition and Selective Bioactivities of Piper platylobum Sodiro Essential Oil. Plants 2025, 14, 3287. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14213287
Jaime-Carvajal J, Pesántez N, Ballesteros J, Morocho V, Malagón O. Chemical Composition and Selective Bioactivities of Piper platylobum Sodiro Essential Oil. Plants. 2025; 14(21):3287. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14213287
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaime-Carvajal, Jairo, Nicole Pesántez, José Ballesteros, Vladimir Morocho, and Omar Malagón. 2025. "Chemical Composition and Selective Bioactivities of Piper platylobum Sodiro Essential Oil" Plants 14, no. 21: 3287. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14213287
APA StyleJaime-Carvajal, J., Pesántez, N., Ballesteros, J., Morocho, V., & Malagón, O. (2025). Chemical Composition and Selective Bioactivities of Piper platylobum Sodiro Essential Oil. Plants, 14(21), 3287. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14213287







