Insights into Variations in Chemical Profiles and Antioxidant Properties Among Different Parts of Dalbergia odorifera
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
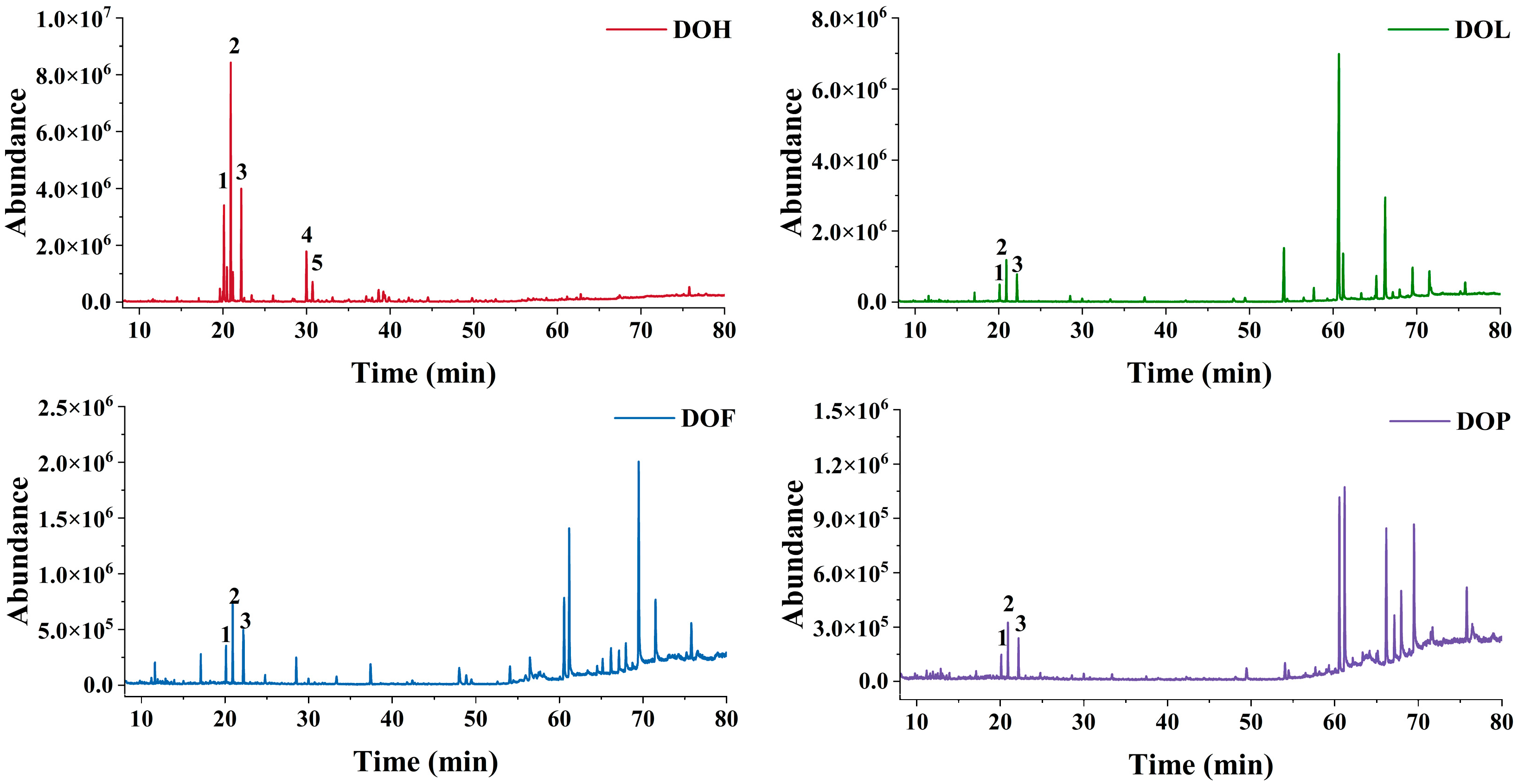
2.1. VOCs Analysis of Four Parts of D. odorifera Based on GC-MS
2.2. Discrepancies in VOCs of Different D. odorifera Parts
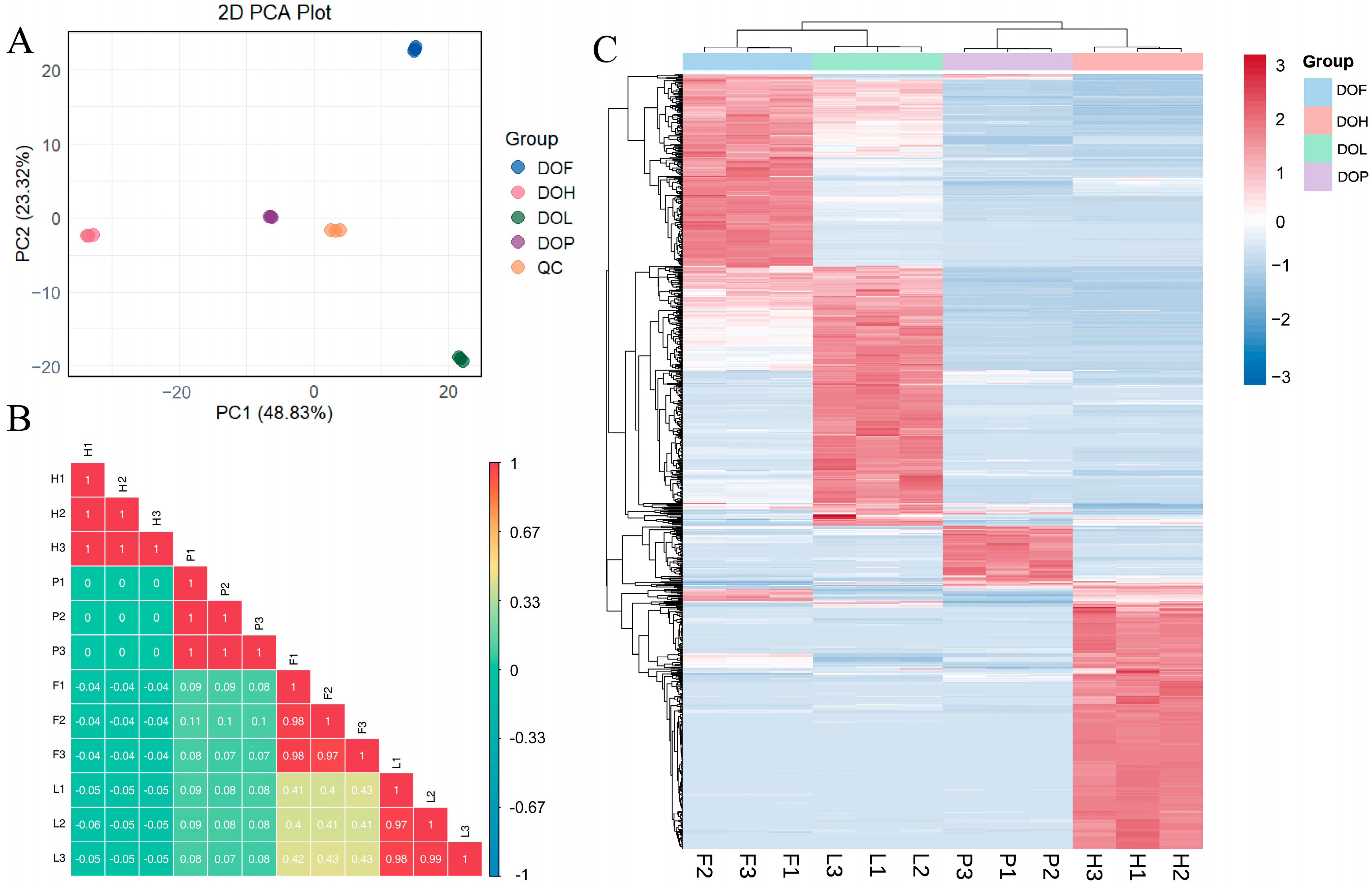
2.3. NVOCs Analysis of Four Parts of D. odorifera Based on UPLC-MS/MS
2.4. Discrepancies in NVOCs of Different D. odorifera Parts
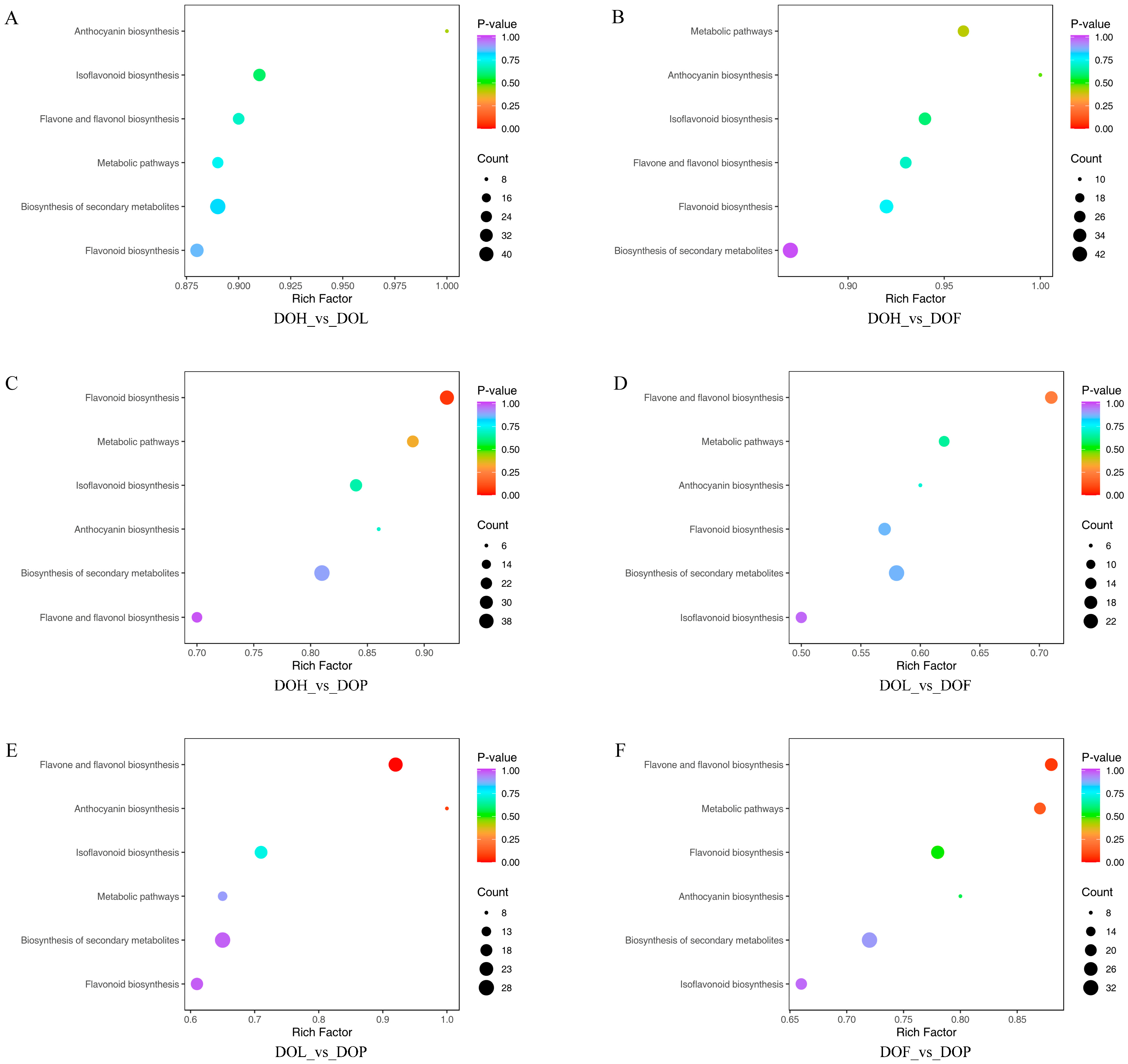
2.5. KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis of DMs
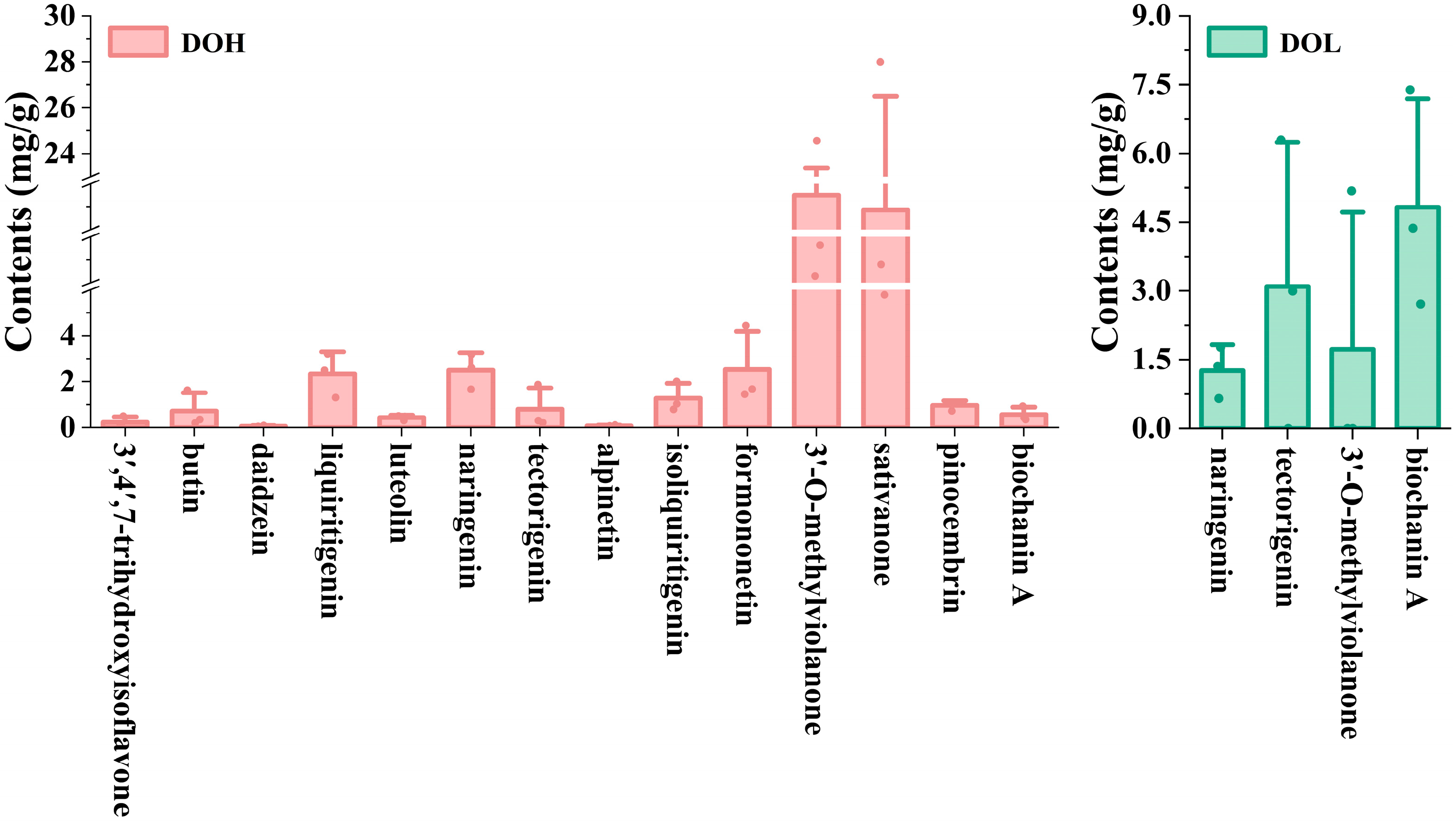
2.6. Quantitative Analysis of Main Compounds in Different D. odorifera Parts
2.6.1. Contents of Trans-Nerolidol Evaluated by GC-MS
2.6.2. Contents of Fourteen Flavonoids Evaluated by UPLC-DAD
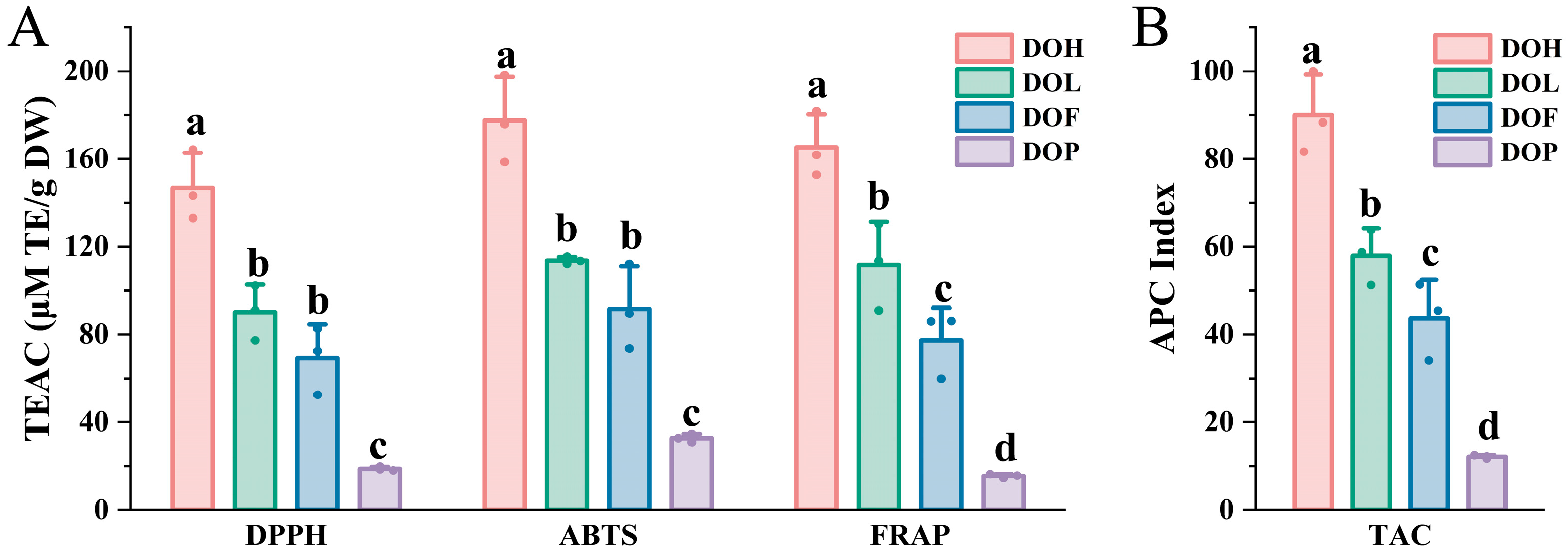
2.7. Antioxidant Activity Evaluation of Four Plant Parts of D. odorifera
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemical Reagents
3.2. Determination of Fourteen Flavonoid Compounds by UPLC-DAD
3.3. Determination of Trans-Nerolidol and Metabolomics Analysis of VOCs by GC–MS
3.4. Metabolomics Analysis of NVOCs by UPLC-ESI-Q TRAP-MS/MS
3.5. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
3.6. Determination of Antioxidant Activity
3.7. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DOH | Dalbergia odorifera heartwood. |
| DOL | Dalbergia odorifera leaves. |
| DOF | Dalbergia odorifera flowers. |
| DOP | Dalbergia odorifera pods. |
| VOCs | Volatile organic compounds. |
| NVOCs | Non-volatile organic compounds. |
References
- Zhao, X.; Wang, C.; Meng, H.; Yu, Z.; Yang, M.; Wei, J. Dalbergia odorifera: A review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and quality control. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 248, 112328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wei, J. Selection and validation of reference genes for gene expression studies by RT-PCR in Dalbergia odorifera. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Gu, C.; Li, C.; Luo, M.; Wang, W.; Zu, Y.; Li, J.; Fu, Y. Microwave-assisted aqueous two-phase extraction of isoflavonoids from Dalbergia odorifera T. Chen leaves. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 115, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, N.; Lu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Liang, N.; Huo, H.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Y.; Tu, P.; Zheng, J.; et al. Anti-inflammatory flavonoid derivatives from the heartwood of Dalbergia odorifera T. Chen. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 37, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Kang, K.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Jin, J.; Gan, L. Phenolic compounds from Dalbergia odorifera and their hepatoprotective activity. Phytochem. Lett. 2025, 65, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lai, X.; Lai, X.; Zhang, D.; Huang, H. Identification of Dalbergia odorifera and study on its volatile oil content and composition. J. Guangzhou Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 1992, 2, 102–106+112. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Gong, B.; Meng, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wei, J. Dalbergia odorifera essential oil protects against myocardial ischemia through upregulating Nrf2 and inhibiting caspase signaling pathways in isoproterenol-induced rats. World J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2023, 9, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, Y.; Gong, B.; Zhao, X.; Meng, H.; Mou, J.; Cheng, X.; Tan, Y.; Wei, J. Dalbergia odorifera Trans-Nerolidol protects against myocardial ischemia via downregulating cytochrome- and caspase-signaling pathways in isoproterenol-induced rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, D.; Yang, M.; Wei, J. Analysis of flavonoids in Dalbergia odorifera by ultra-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. Molecules 2020, 25, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S. AMPK-mediated GSK3β inhibition by isoliquiritigenin contributes to protecting mitochondria against iron-catalyzed oxidative stress. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 1352–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, P.; Ouyang, X.; Yang, M.; Lin, L.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, R.; Hu, D. Luteolin protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis through the p53 pathway. J. Integr. Med. 2024, 22, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, L.; Hu, D. Liquiritigenin alleviates doxorubicin-induced chronic heart failure via promoting ARHGAP18 and suppressing RhoA/ROCK1 pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 411, 113008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X. Liquiritigenin attenuates cardiac injury induced by high fructose-feeding through fibrosis and inflammation suppression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 86, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.; Chaudhary, R.; Rajput, S.; Agarwal, V.; Kaushik, A.S.; Srivastava, S.; Srivastava, S.; Singh, R.; Aziz, I.; Singh, S.; et al. Butein ameliorates chronic stress induced atherosclerosis via targeting anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic and BDNF pathways. Physiol. Behav. 2023, 267, 114207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Pan, Q. Butein inhibits oxidative stress injury in rats with chronic heart failure via ERK/Nrf2 signaling. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2022, 2022, 8684014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Deng, W.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, S.; Luo, Y.; Xiang, W.; He, Q. Mechanisms of ferroptosis regulating oxidative stress and energy metabolism in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and a novel perspective of natural plant active ingredients for its treatment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 114706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Zhong, Y. Measurement of antioxidant activity. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 757–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, B.; Chi, Y.; Yan, W.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, C. Determination of trans-nerolidol concentration in rat plasma by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Zhongguo Yaoye (China Pharm.) 2022, 31, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, A.; Sussmann, R.; Kimura, E.; Cassera, M.; Katzin, A. Quantification of nerolidol in mouse plasma using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 111, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhang, B.; Xu, L.; Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Qi, L.; Li, P.; Wen, X. Application of a sensitive liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry method to a pharmacokinetic study of nerolidol in rat plasma. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Zhang, W.; Ma, L.; Zhao, W. Determination of trans-nerolidol and four oxidized isomers in Dalbergia odorifera by GC. Yaowu Fenxi Zazhi (Chin. J. Pharm. Anal.) 2014, 34, 2083–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Huang, A.; Yin, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, J. Multilevel profiling and identification of Dalbergia odorifera and Dalbergia stevensonii by FTIR, NMR and GC/MS. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 1395–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hassan, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Rehman, A.; Yan, S.; Jin, H. Discovery of potent anti-MRSA components from Dalbergia odorifera through UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and targeting PBP2a protein through in-depth transcriptomic, in vitro, and in-silico studies. J. Pharm. Anal. 2024, 14, 100938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Song, X.; Han, C.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H. Study on volatile oil components from the leaves of Dalbergia odorifera. Zhongyaocai (Chin. Med. Mater.) 2004, 10, 733–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.; Tan, L.; Chan, K.; Lee, L.; Goh, B. Nerolidol: A sesquiterpene alcohol with multi-faceted pharmacological and biological activities. Molecules 2016, 21, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Pan, Z.; Xi, B.; Asiago, V.; Musselman, B.; Raftery, D. Principal component directed partial least squares analysis for combining nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry data in metabolomics: Application to the detection of breast cancer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 686, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, N.; Wang, T.; Gan, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Jin, B. Plant flavonoids: Classification, distribution, biosynthesis, and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.; Lv, Y.; Yao, X.; Ye, H.; Li, C.; Peng, X.; Gao, Z.; Mao, K. Revealing quality chemicals of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum roots in different geographical origins using untargeted metabolomics and random-forest based spectrum-effect analysis. Food Chem. 2024, 449, 139207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ma, C.; Liu, L.; Dong, G.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Lei, S.; Liu, Y. Comprehensive investigation on non-volatile and volatile flavor compounds in different varieties of rose tea by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS-based metabolomics and GC-IMS, GC-MS. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 136, 106708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Badrealam, K.; Kuo, C.; Daddam, J.; Shibu, M.A.; Lin, K.; Ho, T.; Viswanadha, V.P.; Kuo, W.; Huang, C. Small molecule compound nerolidol attenuates hypertension induced hypertrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats through modulation of Mel-18-IGF-IIR signalling. Phytomedicine 2021, 84, 153450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Xu, H.; Xiao, S.; Wang, Y. Study on the quality of different varieties of Dalbergia odorifera. Zhongyaocai (Chin. Med. Mater.) 1997, 7, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, Q.; Guo, H.; Li, L.; Bi, K.; Guo, D. Simultaneous determination of 10 major flavonoids in Dalbergia odorifera by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 39, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, J.; Luo, M.; Wang, W.; Huang, Y.; Efferth, T.; Wang, H.; Fu, Y. Efficient extraction and preparative separation of four main isoflavonoids from Dalbergia odorifera T. Chen leaves by deep eutectic solvents-based negative pressure cavitation extraction followed by macroporous resin column chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1033–1034, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhu, M.; Fan, S.; Gong, X.; Yang, S.; Tang, F.; Shao, F. Establishment of HPLC fingerprint and determination of two isoflavones in Dalbergia odorifera leaves from different producing areas. Jiangxi Zhongyiyao (Jiangxi J. Tradit. Chin. Med.) 2024, 55, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Weng, X.; Cheng, D. Antioxidant activities of natural phenolic components from Dalbergia odorifera T. Chen. Food Chem. 2000, 71, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolovich, M.; Prenzler, P.; Patsalides, E.; McDonald, S.; Robards, K. Methods for testing antioxidant activity. Analyst 2002, 127, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeram, N.; Aviram, M.; Zhang, Y.; Henning, S.M.; Feng, L.; Dreher, M.; Heber, D. Comparison of antioxidant potency of commonly consumed polyphenol-rich beverages in the United States. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Hu, H.; Lv, Y.; Ma, G.; Tang, F.; Hong, Z.; Shao, F. The hypolipidemic effect of Dalbergia odorifera T. C. Chen leaf extract on hyperlipidemic rats and its mechanism investigation based on network pharmacology. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 3155266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ao, J.; Fu, L.; Wu, Y.; Shao, F.; Xu, T.; Jiang, M.; Xiong, S.; Lv, Y. Exploring the attenuation mechanisms of Dalbergia odorifera leaves extract on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Biocell 2023, 47, 1611–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaipong, K.; Boonprakob, U.; Crosby, K.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Byrne, D. Comparison of ABTS, DPPH, FRAP, and ORAC assays for estimating antioxidant activity from guava fruit extracts. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhao, X. Insights into Variations in Chemical Profiles and Antioxidant Properties Among Different Parts of Dalbergia odorifera. Plants 2025, 14, 3279. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14213279
Xiao Y, Zhou Y, Wei J, Zhao X. Insights into Variations in Chemical Profiles and Antioxidant Properties Among Different Parts of Dalbergia odorifera. Plants. 2025; 14(21):3279. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14213279
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Yujie, Yakui Zhou, Jianhe Wei, and Xiangsheng Zhao. 2025. "Insights into Variations in Chemical Profiles and Antioxidant Properties Among Different Parts of Dalbergia odorifera" Plants 14, no. 21: 3279. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14213279
APA StyleXiao, Y., Zhou, Y., Wei, J., & Zhao, X. (2025). Insights into Variations in Chemical Profiles and Antioxidant Properties Among Different Parts of Dalbergia odorifera. Plants, 14(21), 3279. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14213279





