Effects of Different Slope Aspects on Leaf Non-Structural Carbohydrate Characteristics and Leaf–Soil Stoichiometry of Sapindus mukorossi
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
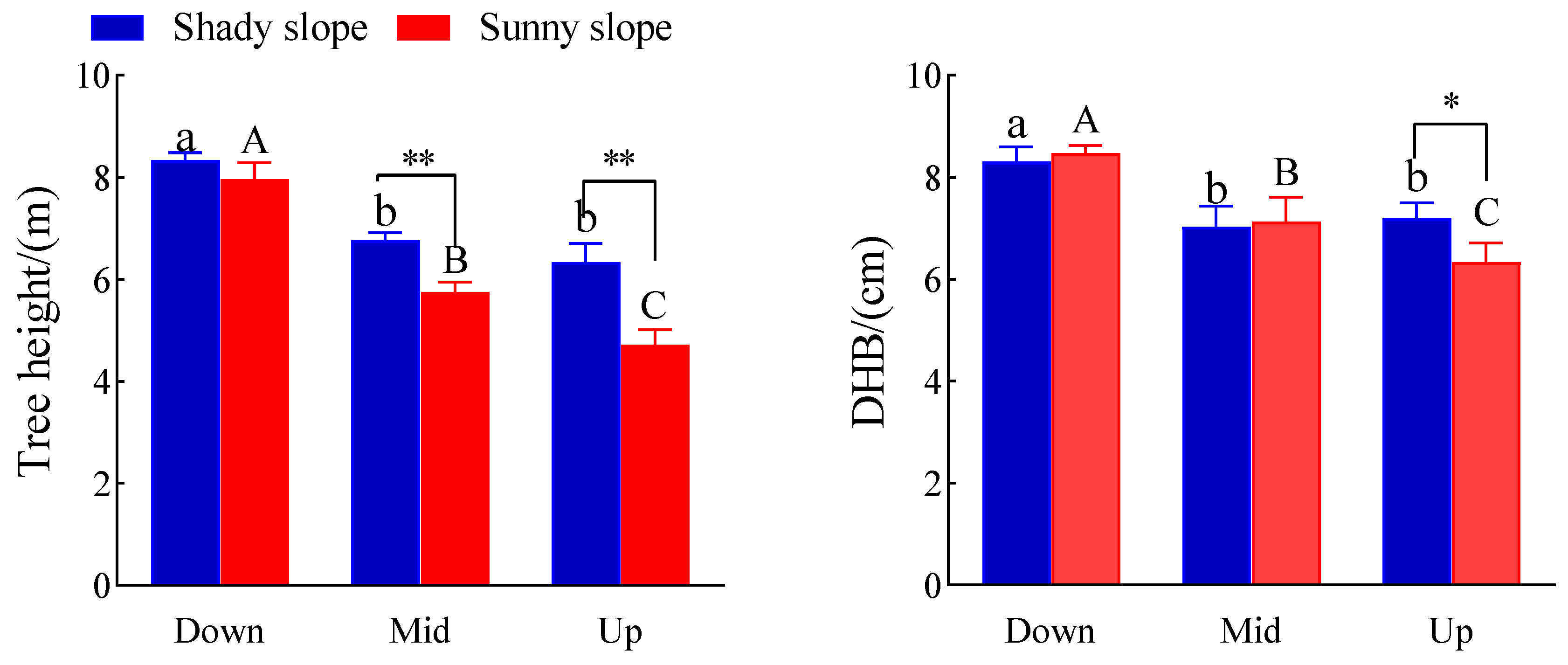
2.1. Effects of Slope Aspect and Position on Tree Height and DBH of S. mukorossi
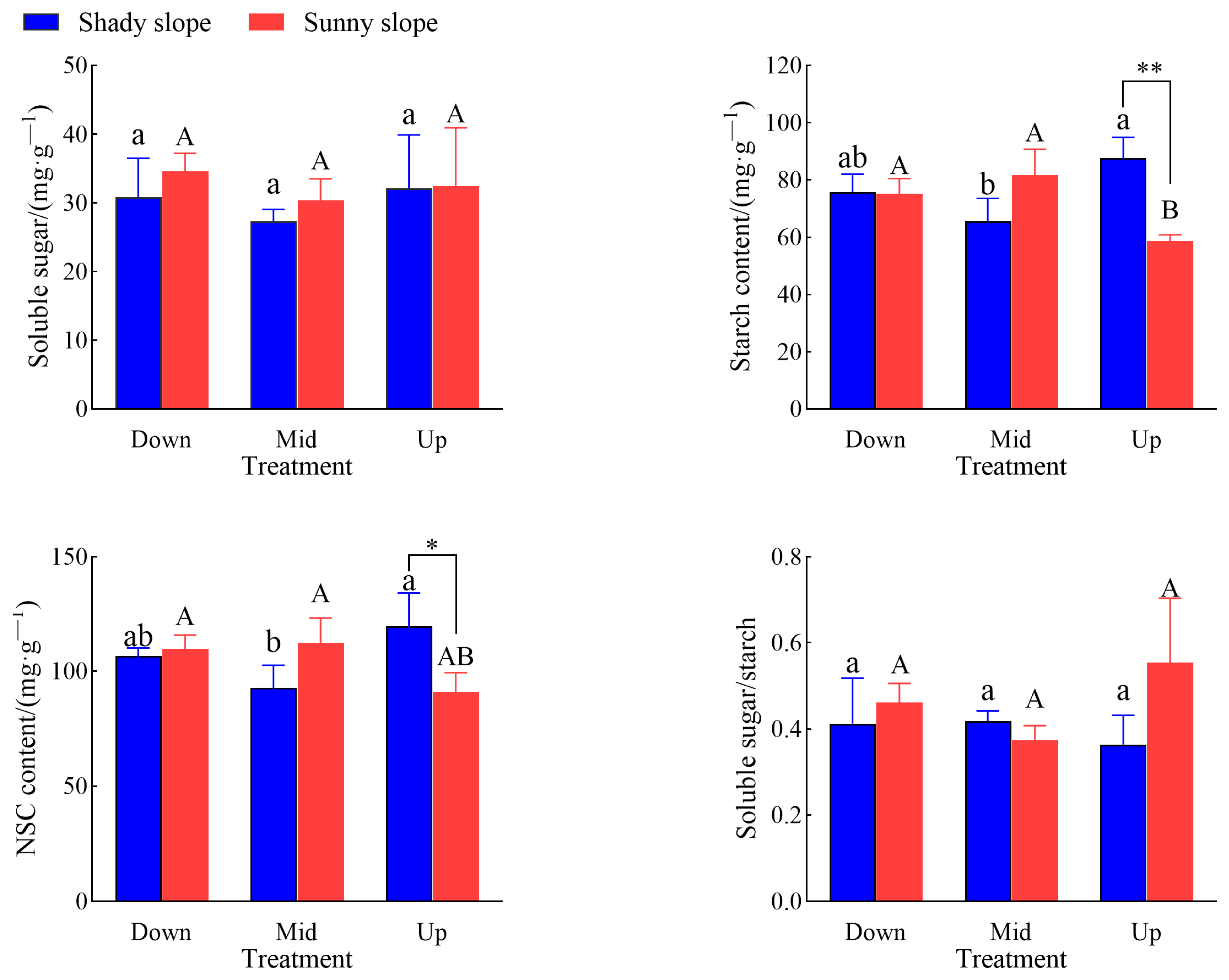
2.2. Effects of Slope Aspect and Position on Leaf NSC Characteristics of S. mukorossi
2.3. Effects of Slope Aspect and Position on Leaf Stoichiometry of S. mukorossi
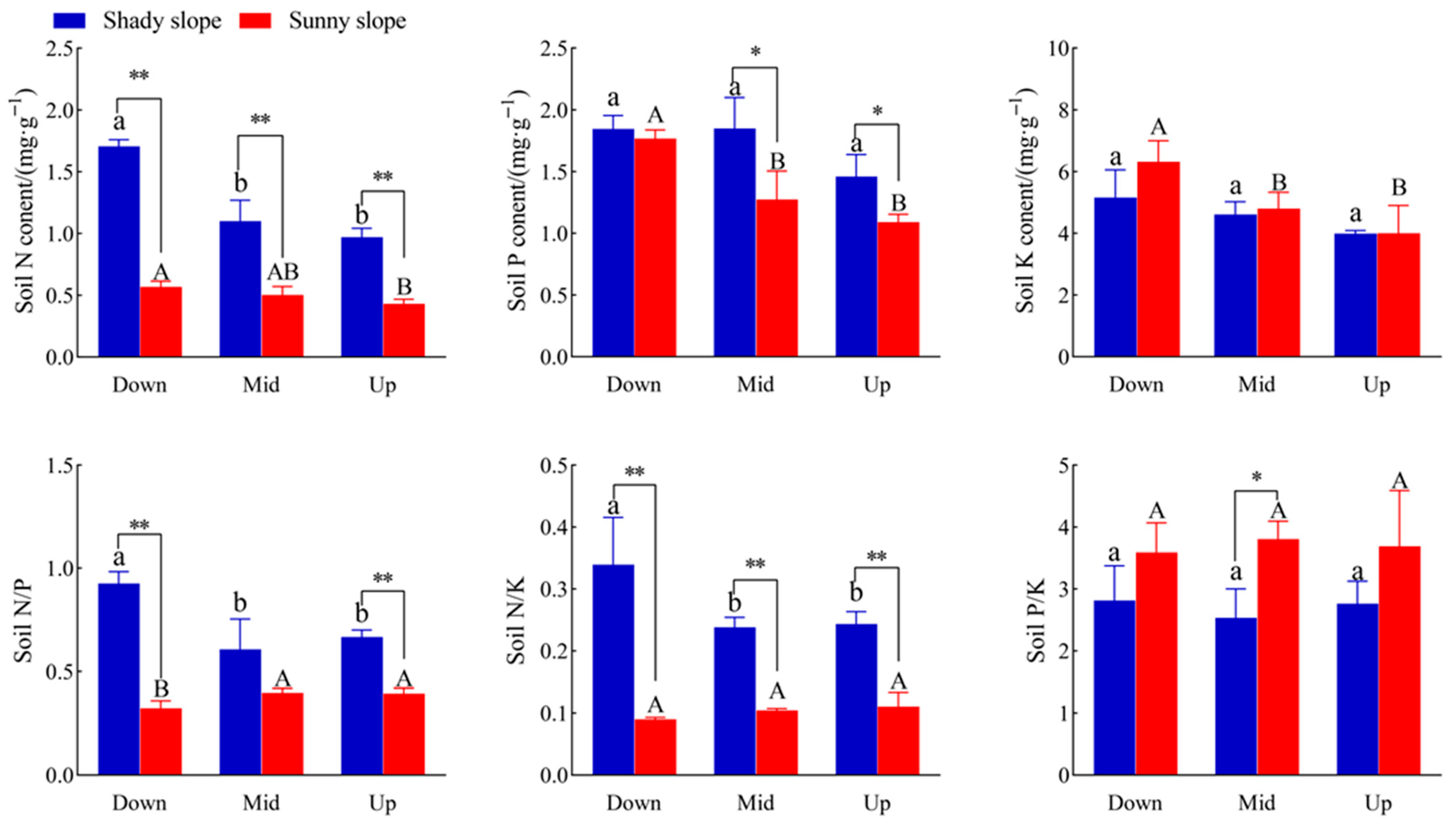
2.4. Effects of Slope Aspect and Position on Soil Stoichiometry of S. mukorossi
2.5. Variation Characteristics of Various Indicators of S. mukorossi with Different Slope Aspects
2.6. Phenotypic Plasticity Indices for Different Slope Aspects
2.7. Correlation of Various Indicators of S. mukorossi with Different Slope Aspects
3. Discussion
3.1. Effects of Slope Aspect and Position on Tree Height and DBH of S. mukorossi
3.2. Effects of Different Slope Aspect and Position on Leaf NSC Characteristics of S. mukorossi
3.3. Effects of Different Slope Directions and Slope Positions on Leaf–Soil Stoichiometric Characteristics of S. mukorossi
3.4. Variation Characteristics, Plasticity, and Correlation Analysis of S. mukorossi Plantations with Different Slope Aspects
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Situation of the Test Site
4.2. Design of Experiment
4.3. Indicator Determination
| 2.5 mL digested liquid to be tested |
| ↓ |
| 1 mL sodium tartrate |
| ↓ |
| 2.7 mL KOH |
| ↓ |
| Add water to 20 mL |
| ↓ |
| Nessler’s reagent 1.25 mL |
| ↓ |
| Add water to 25 mL |
| ↓ |
| 30 min of color development, spectrophotometer for 420 nm determination |
4.4. Data Processing and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, R.; Liu, L.; Zheng, J.; Li, J.; Han, W.; Liu, Y. Combined Effects of Meteorological Factors, Terrain, and Greenhouse Gases on Vegetation Phenology in Arid Areas of Central Asia from 1982 to 2021. Land 2024, 13, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.X.; Hai, L.; Huang, L.M.; Mao, Z.R.; Chai, Y.J. Effects of slope direction on soil nutrient and its ecological stoichiometry in bamboo forest. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 2915–2922. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G.; Han, J.; Zhang, W.; Wu, J. Effects of Fertilizer Application on Growth and Stoichiometric Characteristics of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium in Balsa Tree (Ochroma lagopus) Plantations at Different Slope Positions. Plants 2025, 14, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P. The role of soil properties in the relationship between slope aspect and tree species growth potential. China For. Ind. 2025, 1, 120–121. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Li, J.; Song, Y.; Jing, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Ma, R. Characteristics of Soil Nutrients and Relations with Stand Growth of Pinus tabulaeformis and Pinus sylvestnis var. mongolica Plantations under Different Slopes in Low Mountains and Hill District of Eastern Liaoning Province. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. 2017, 48, 522–529. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Wen, A.; Lv, Y. Comparison on Armeniaca sibirica Natural Forest Growth and Soil Physicochemical Properties in Different Slope Position. J. For. Eng. 2019, 35, 36–41+54. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Z.; Duan, G.; Wen, C.; Du, G.; Wu, J. Response of Non-Structural Carbohydrates and Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Stoichiometric Characteristics of Ochroma lagopus Leaves to Nitrogen Addition. Forests 2025, 16, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, P.; Xing, S.; Wang, C. Soil C, N and P contents and their stoichiometry as affected by typical plant communities on steep gully slopes of the Loess Plateau, China. Catena. 2022, 208, 105740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jia, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, Y. Combined effects of tillage direction and slope gradient on soil translocation by hoeing. Catena 2019, 175, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhao, L.; Wu, X.; Fang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, G.; Yue, G.; Sheng, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; et al. Soil moisture and texture primarily control the soil nutrient stoichiometry across the Tibetan grassland. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannenberg, S.A.; Phillips, R.P. Non-structural carbohydrate pools not linked to hydraulic strategies or carbon supply in tree saplings during severe drought and subsequent recovery. Tree Physiol. 2019, 40, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, D.; Reich, B.P.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Xiang, Y.Z.; Luo, Y.Q.; Shen, Y.; Meng, C.; Han, W.X.; Niu, S.L. Global changes alter plant multi-element stoichiometric coupling. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Y. Optimized Application of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Enhances Yield and Quality by Improving Nutrient Uptake Dynamics in Winter Wheat with Straw Return. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2025, 44, 5028–5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Li, F.; Jin, G. Non-destructively predicting leaf area, leaf mass and specific leaf area based on a linear mixed-effect model for broadleaf species. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 78, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Shangguan, Z.; Xi, W. Seasonal variations of leaf traits and drought adaptation strategies of four common woody species in South Texas, USA. J. For. Res. 2019, 30, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, D.; Yan, X.; Jia, L.; Chen, N.; Liu, J.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, L.; Cao, Q. Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilization management on soil properties and leaf traits and yield of Sapindus mukorossi. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1300683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ai, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Leng, P.; Qiao, Y.; Li, Z.; Tian, C.; Cheng, H.; Chen, G.; Li, F. Impacts of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) fertilizers on maize yields, nutrient use efficiency, and soil nutrient balance: Insights from a long-term diverse NPK omission experiment in the North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2024, 318, 109616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Jia, L.; Ye, H.; Gao, Y.; Xiong, C.; Weng, X. Evaluation on geographical variation of economic traits and correlation with fatty acid composition of Sapindus mukorossi fruit. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2016, 38, 73–83. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Q.; Le, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, W.; Gao, L.; Qian, C.; Liu, Y. Effects of southwest hilly areas’ s purple soil acidity on the growth and photosynthetic characteristics of Sapindus mukorossi Gaertn saplings. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 3756–3763. [Google Scholar]
- Muntaha, S.; Khan, N. Natural surfactant extracted from Sapindus mukurossi as an eco-friendly alternate to synthetic surfactant—A dye surfactant interaction study. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 93, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, K.N.; Ćirić, A.; Glamočlija, J.; Calhelha, R.C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Soković, M. Antimicrobial activity, growth inhibition of human tumour cell lines, and phytochemical characterization of the hydromethanolic extract obtained from Sapindus saponaria L. aerial parts. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 659183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Wang, L.; Zhong, J.; Jia, L.; Chen, Z. Genome-Wide Analysis of bZIP Transcription Factor Family and Its Expression in Graft Healing of Soapberry (Sapindus mukorossi Gaertn.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahito, Z.A.; Zehra, A.; Yu, S.; Chen, S.; He, Z.; Yang, X. Chinese sapindaceous tree species (Sapindus mukorosii) exhibits lead tolerance and long-term phytoremediation potential for moderately contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamyae, E.; Zakaria, E.; Laila, S. Genome-wide association and genomic prediction study of elite spring bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes under drought conditions across different locations. Plant Gene 2024, 39, 100466. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Man, X.; Chen, L.; Li, W. Effects of Site Condition on Growth and Spatial Differences of Soil Nutrient in Populus simonii Carr. Plantations. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2007, 5, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Peng, J.; Wei, X.; Peng, M.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Stability assessment of tree ring growth of Pinus armandii Franch in response to climate change based on slope directions at the Lubanling in the Funiu Mountains, China. J. For. Res. 2024, 35, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auslander, M.; Nevo, E.; Inbar, M. The effects of slope orientation on plant growth, developmental instability and susceptibility to herbivores. J. Arid. Environ. 2003, 55, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, H.; Ziegler, W.; Trumbore, S. Lethal drought leads to reduction in nonstructural carbohydrates in Norway spruce tree roots but not in the canopy. Funct. Ecol. 2013, 27, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, B. Osmotic adjustment is a prime drought stress adaptive engine in support of plant production. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 4–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hoch, G.; Richter, A.; Korner, C. Non-structural carbon compounds in temperate forest trees. Plant Cell Environ. 2003, 26, 1067–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, J.; Huang, L.; Zhao, P.; Su, Y.; Li, H.; Cao, L.; Zhang, T. Effect of different slope characteristics on root nonstructural carbon of Quercus mongolica in the southern Daxing’anling Mountains. Arid. Zone Res. 2024, 41, 1572–1582. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Wu, J.; Gu, J.; Duan, H. Responses of non-structural carbohydrate and carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus chemometrics in needles of early shaded Pinus yunnanensis seedlings to drought. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wu, J.; Gu, J.; Duan, H. Response of Non-Structural Carbohydrates and Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Stoichiometry in Pinus yunnanensis Seedlings to Drought Re-Watering. Forests 2024, 15, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, B.; Mota, M.; Coelho, P.; Lima, T.; Durán, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Neto, J. Different physiognomies of the Brazilian savanna determine changes in soil C, N and P pools. Plant Ecol. 2025, 226, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Gao, R.; Yu, C.; Han, R.; Tian, X.; Sun, F.; Lin, Y.; Wang, D. Responses of plant C:N:P stoichiometry to soil properties on unstable slopes of dry-hot valley. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 33, 2743–2752. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; Yu, G.; Tao, B.; Wang, S. Leaf Nitrogen and Phosphorus Stoichiometry Across 654 Terrestrial Plant Species in NSTEC. Environ. Sci. 2007, 28, 2665–2673. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Cai, K.; Huo, G.; Tian, X.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zahng, J.; Kuang, X.; Hu, J.; Zheng, Y.; et al. The promoting effect of the rhizosphere potassium-solubilizing bacterium TK35 on growth, potassium uptake and yield and quality of tobacco leaves. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2025, 64, 90–94+107. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Sheng, M.; Ai, S.; Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Chen, T.; Kou, J.; Ai, Y.; Ai, X. Soil Aggregate Stability and Characteristics of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Contents in Cut Slope Soils with Different Aspects in Plateau Areas. Land Degrad. Dev. 2025, 36, 2095–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Chen, H.; Reich, P. Global-scale latitudinal patterns of plant fine-root nitrogen and phosphorus. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güsewell, S. N:P Ratios in Terrestrial Plants: Variation and Functional Significance. New Phytol. 2004, 164, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Tang, J.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Cai, N. Effect of fertilization on stoichiometric ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in Pinus yunnanensis seedling and soil. J. Northwest A&F Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 52, 40–50. [Google Scholar]
- Riyaz, A.R. Shaping Plant Growth Beneath the Soil: A Theoretical Exploration of Fungal Endophyte’s Role as Plant Growth-Promoting Agents. MicrobiologyOpen 2025, 14, e70026. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yang, S.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, P.; Awais, M.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Fu, H.; Li, T. The allocation patterns of plant phosphorus and soil phosphorus availability enhance tomato plant growth under long-term balanced nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization. Sci. Hortic. 2025, 344, 114121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Hong, X.Q.; Lin, H.; Chen, C.; Xie, A.Q.; Zhang, B. Ecological stoichiometric characteristics of leaves and soil in different broad-leaved plantations in northern Fujian Province. J. For. Env. 2025, 45, 246–253. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.K.; Huang, J.L. Principles and Techniques of Plant Physiological and Biochemical Experiments, 3rd ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agrochemical Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]



| Slope | Indicators | Mean | SD | Value Range | CV/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shady slope | Tree height | 7.14 | 0.94 | 5.9–8.5 | 13 |
| DHB | 7.51 | 0.66 | 6.6–8.6 | 9 | |
| Soluble sugar | 30.10 | 5.35 | 23.10–37.29 | 18 | |
| Starch | 76.32 | 11.44 | 60.14–94.90 | 15 | |
| NSCs | 106.41 | 14.68 | 86.10–131.43 | 14 | |
| Soluble sugar/starch | 0.40 | 0.07 | 0.29–0.53 | 17 | |
| Leaf N | 4.21 | 0.60 | 3.64–5.57 | 14 | |
| Leaf P | 0.97 | 0.18 | 0.72–1.28 | 18 | |
| Leaf K | 4.38 | 0.66 | 3.2–5.34 | 15 | |
| Leaf N/P | 4.43 | 0.77 | 3.31–5.46 | 17 | |
| Leaf N/K | 0.97 | 0.14 | 0.73–1.17 | 15 | |
| Leaf K/P | 4.56 | 0.40 | 3.92–5.37 | 9 | |
| Soil N | 1.26 | 0.35 | 0.89–1.77 | 28 | |
| Soil P | 1.72 | 0.25 | 1.26–2.10 | 15 | |
| Soil K | 4.59 | 0.71 | 3.9–5.75 | 15 | |
| Soil N/P | 0.73 | 0.17 | 0.44–0.98 | 23 | |
| Soil N/K | 0.27 | 0.06 | 0.22–0.43 | 23 | |
| Soil K/P | 2.70 | 0.43 | 2.00–3.25 | 16 | |
| Sunny slope | Tree height | 6.15 | 1.46 | 4.4–8.2 | 24 |
| DHB | 7.31 | 0.98 | 5.9–8.6 | 13 | |
| Soluble sugar | 32.48 | 5.06 | 22.81–38.90 | 16 | |
| Starch | 71.86 | 11.60 | 56.14–92.05 | 16 | |
| NSCs | 104.34 | 12.55 | 82.48–124.29 | 12 | |
| Soluble sugar/starch | 0.46 | 0.11 | 0.35–0.65 | 24 | |
| Leaf N | 5.05 | 1.30 | 3.06–6.59 | 26 | |
| Leaf P | 0.97 | 0.29 | 0.60–1.56 | 30 | |
| Leaf K | 3.09 | 0.85 | 1.96–4.29 | 28 | |
| Leaf N/P | 5.37 | 1.17 | 3.78–7.11 | 22 | |
| Leaf N/K | 1.64 | 0.15 | 1.50–1.87 | 9 | |
| Leaf K/P | 3.29 | 0.73 | 2.15–4.07 | 22 | |
| Soil N | 0.50 | 0.07 | 0.39–0.60 | 15 | |
| Soil P | 1.38 | 0.33 | 1.02–1.83 | 24 | |
| Soil K | 5.04 | 1.20 | 3.23–6.85 | 24 | |
| Soil N/P | 0.37 | 0.04 | 0.28–0.42 | 12 | |
| Soil N/K | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.09–0.14 | 14 | |
| Soil K/P | 3.69 | 0.54 | 2.79–4.60 | 15 |
| Slope Aspect | Slope Position | Soil Temperature (°C) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Illuminance (lx) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunny slope | Up | 35.6 | 0.417 | 1072 × 100 |
| Mid | 36.8 | 0.413 | 1012 × 100 | |
| Down | 37.3 | 0.433 | 1035 × 100 | |
| Shady slope | Up | 37.1 | 1.000 | 1128 × 100 |
| Mid | 36.4 | 1.375 | 1114 × 100 | |
| Down | 36.8 | 0.658 | 1142 × 100 |
| Tube Number | 100 ug/mL Sucrose Standard Solution (mL) | Distilled Water (mL) | Sugar Content (μg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.00 | 2.00 | 0 |
| 1–2 | 0.20 | 1.80 | 20 |
| 3–4 | 0.40 | 1.60 | 40 |
| 5–6 | 0.60 | 1.40 | 60 |
| 7–8 | 0.80 | 1.20 | 80 |
| 9–10 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 100 |
| Tube Number | 100 ug/mL Starch Standard Solution (mL) | Distilled Water (mL) | Starch Content (μg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.00 | 2.00 | 0 |
| 1–2 | 0.40 | 1.60 | 40 |
| 3–4 | 0.80 | 1.20 | 80 |
| 5–6 | 1.20 | 0.80 | 120 |
| 7–8 | 1.60 | 0.40 | 160 |
| 9–10 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Wei, D.; Zhou, Y.; He, T.; Zhao, T.; Peng, C.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Y. Effects of Different Slope Aspects on Leaf Non-Structural Carbohydrate Characteristics and Leaf–Soil Stoichiometry of Sapindus mukorossi. Plants 2025, 14, 3131. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14203131
Wang H, Liu C, Wei D, Zhou Y, He T, Zhao T, Peng C, Wang L, Zheng Y. Effects of Different Slope Aspects on Leaf Non-Structural Carbohydrate Characteristics and Leaf–Soil Stoichiometry of Sapindus mukorossi. Plants. 2025; 14(20):3131. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14203131
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Heng, Chengyao Liu, Dingming Wei, Yunbin Zhou, Tingwen He, Tangjie Zhao, Chengbo Peng, Lianchun Wang, and Yuan Zheng. 2025. "Effects of Different Slope Aspects on Leaf Non-Structural Carbohydrate Characteristics and Leaf–Soil Stoichiometry of Sapindus mukorossi" Plants 14, no. 20: 3131. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14203131
APA StyleWang, H., Liu, C., Wei, D., Zhou, Y., He, T., Zhao, T., Peng, C., Wang, L., & Zheng, Y. (2025). Effects of Different Slope Aspects on Leaf Non-Structural Carbohydrate Characteristics and Leaf–Soil Stoichiometry of Sapindus mukorossi. Plants, 14(20), 3131. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14203131




