Screening of Highly Virulent Beauveria bassiana Strains Against Tuta absoluta Larvae and Evaluation of Their Endophytic Colonization-Mediated Suppression in Tomato Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Entomopathogenic Fungi, Insects, and Plants
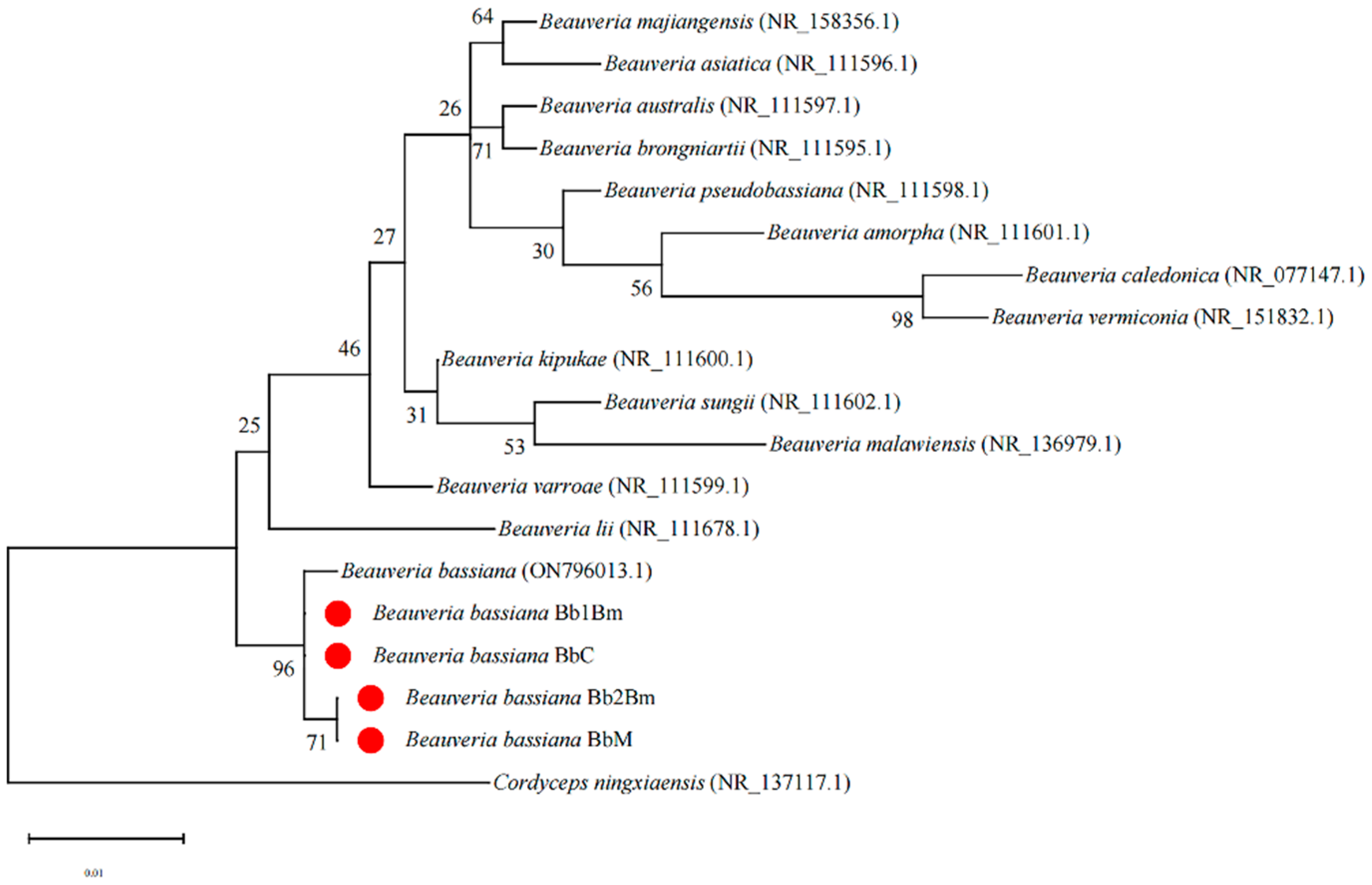
2.2. Identification of B. bassiana
2.3. Pathogenicity Bioassay of B. bassiana Strains Against T. absoluta
2.4. Lethal Concentration and Time of B. bassiana Bb1Bm Against T. absoluta
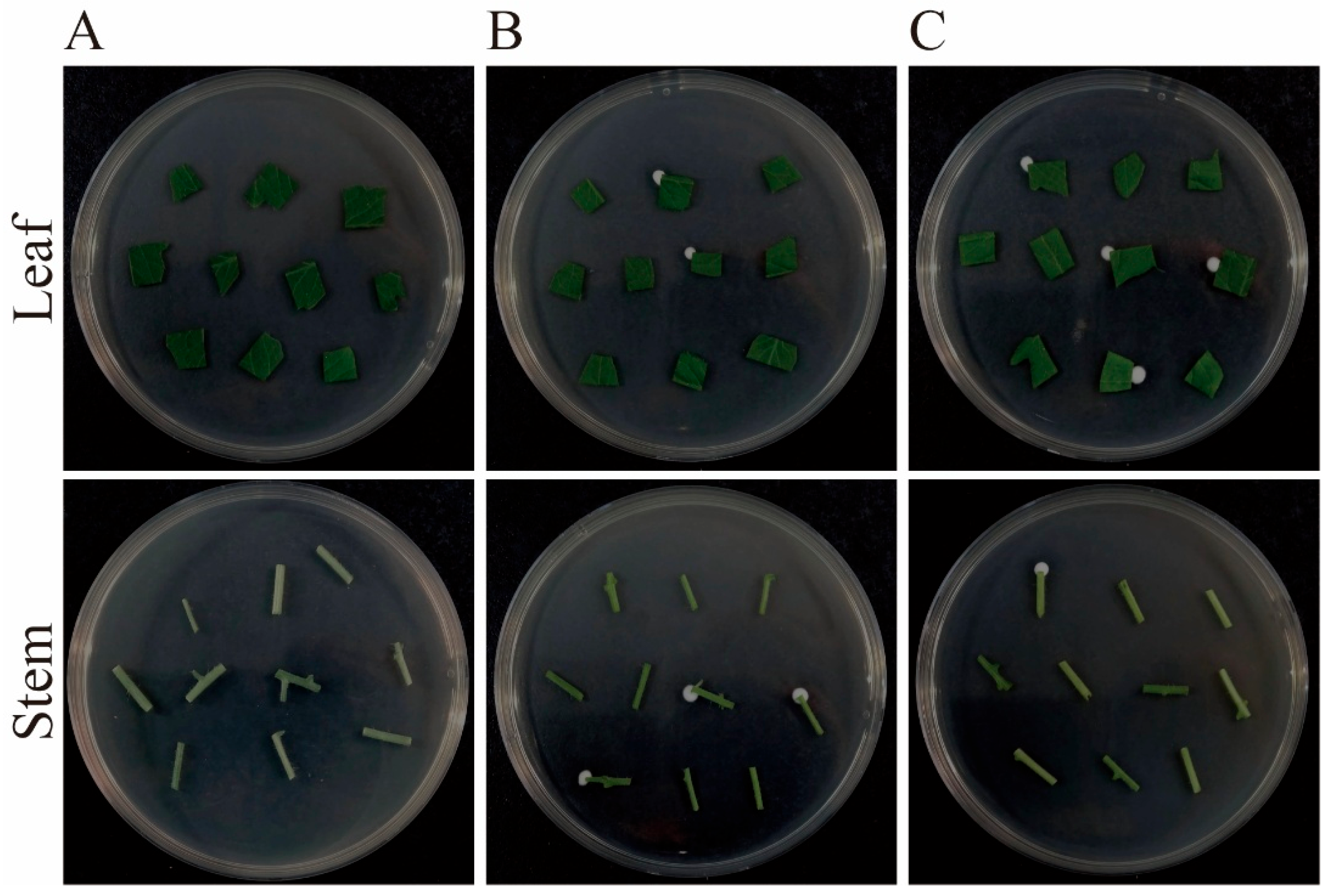
2.5. Inoculation and Detection of B. bassiana Colonization
2.6. Age-Stage, Two-Sex Life Table Analysis of T. absoluta Populations Grown on B. bassiana Colonized Tomato Plants
2.7. Life Table Analysis
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Strains
3.2. Evaluation of the Insecticidal Activity of B. bassiana Against Larvae of T. absoluta
3.3. Virulence of B. bassiana Bb1Bm Against Larvae of T. absoluta
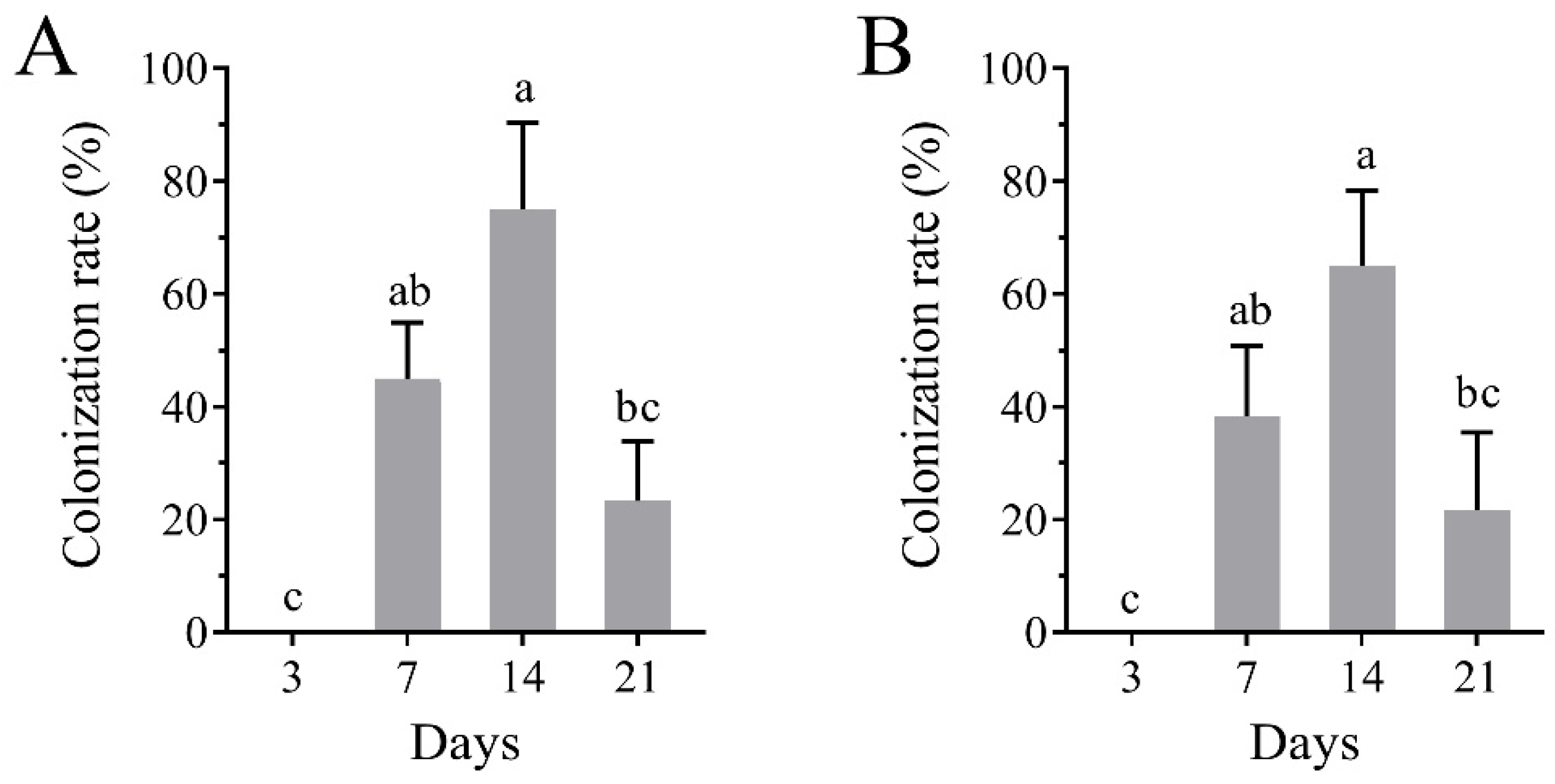
3.4. Colonization of B. bassiana in Tomato Plants
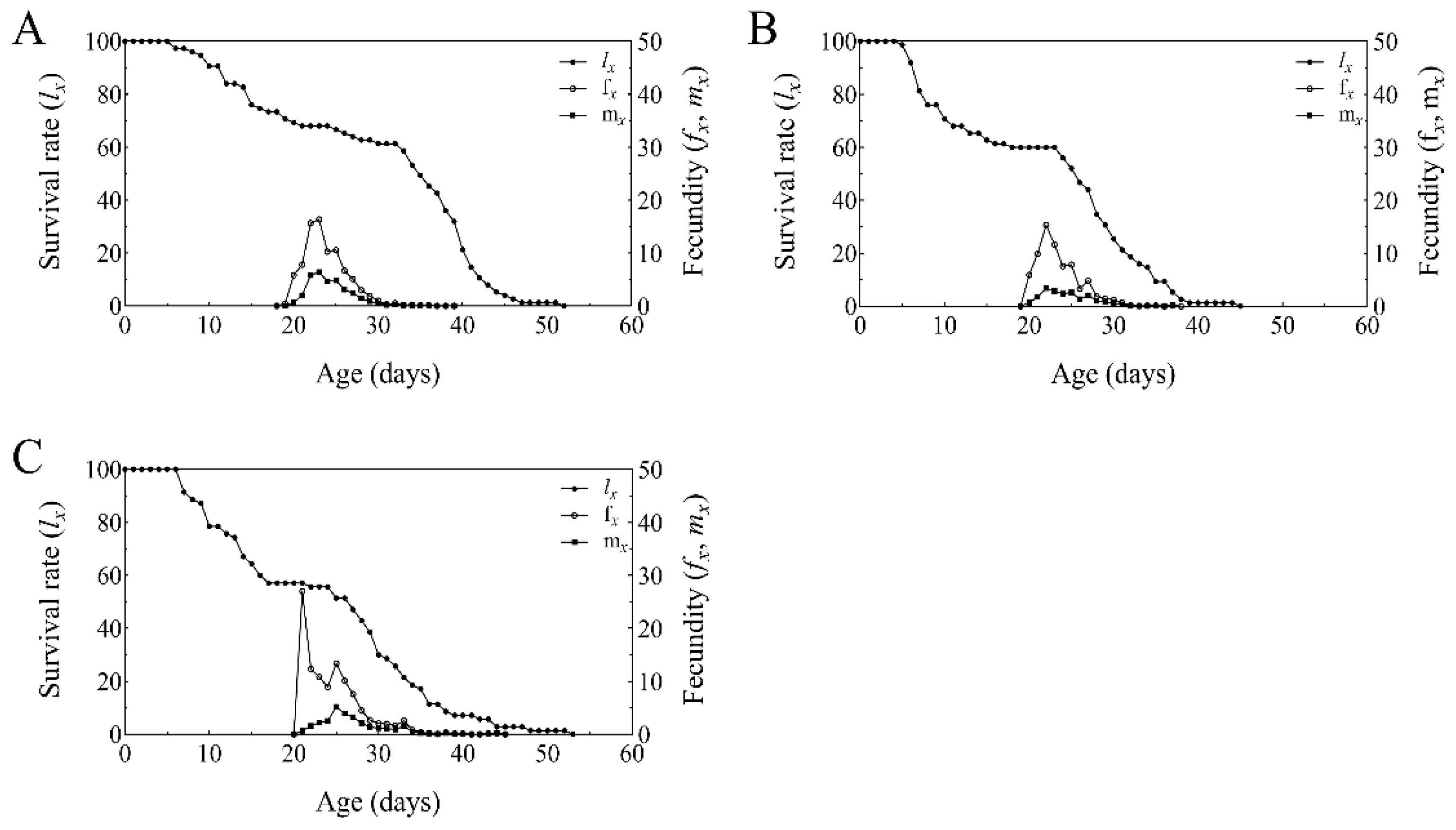
3.5. Developmental Duration, Fecundity, and Offspring Sex Ratio of T. absoluta on Endophytic B. bassiana in Tomato
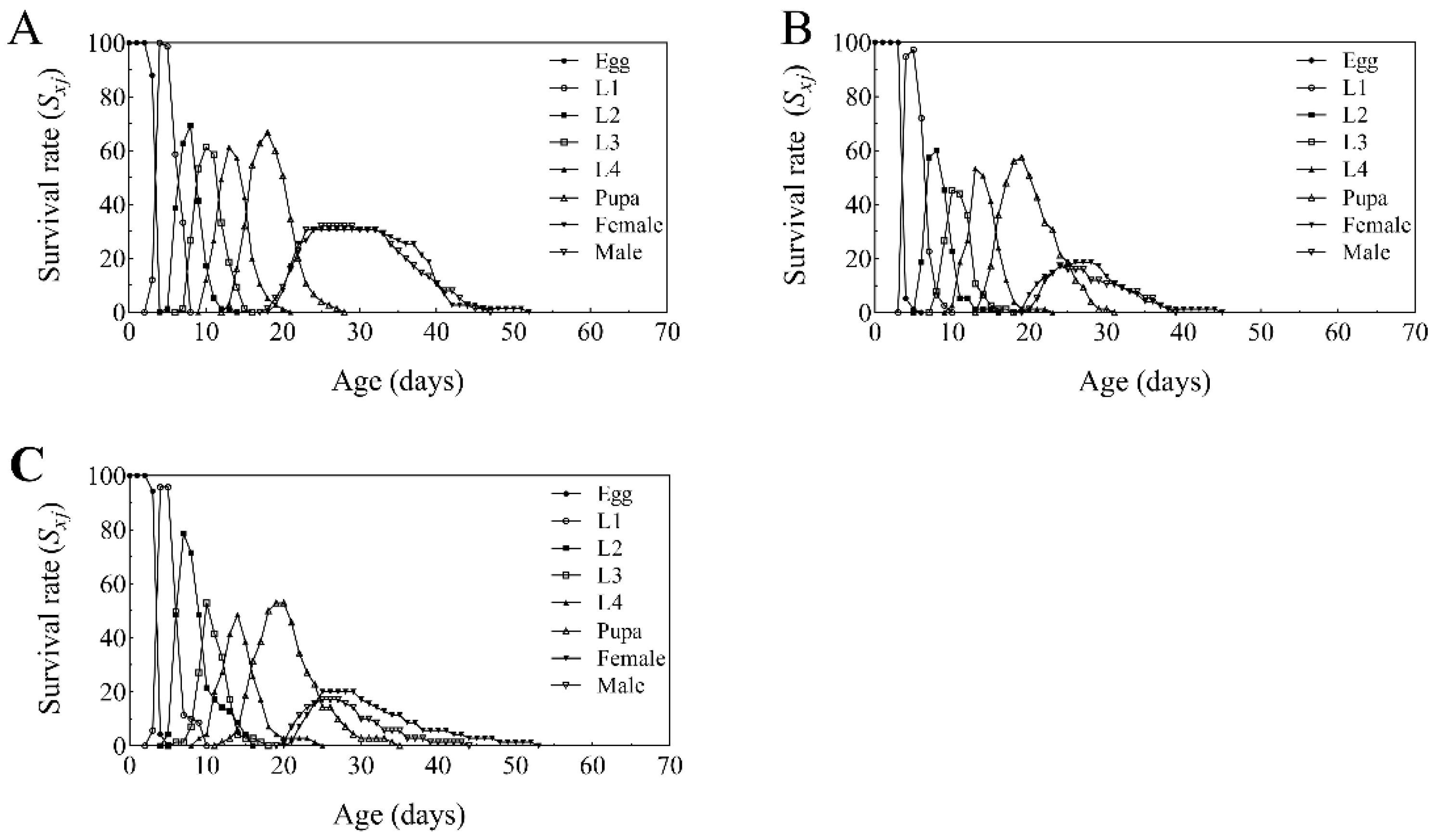
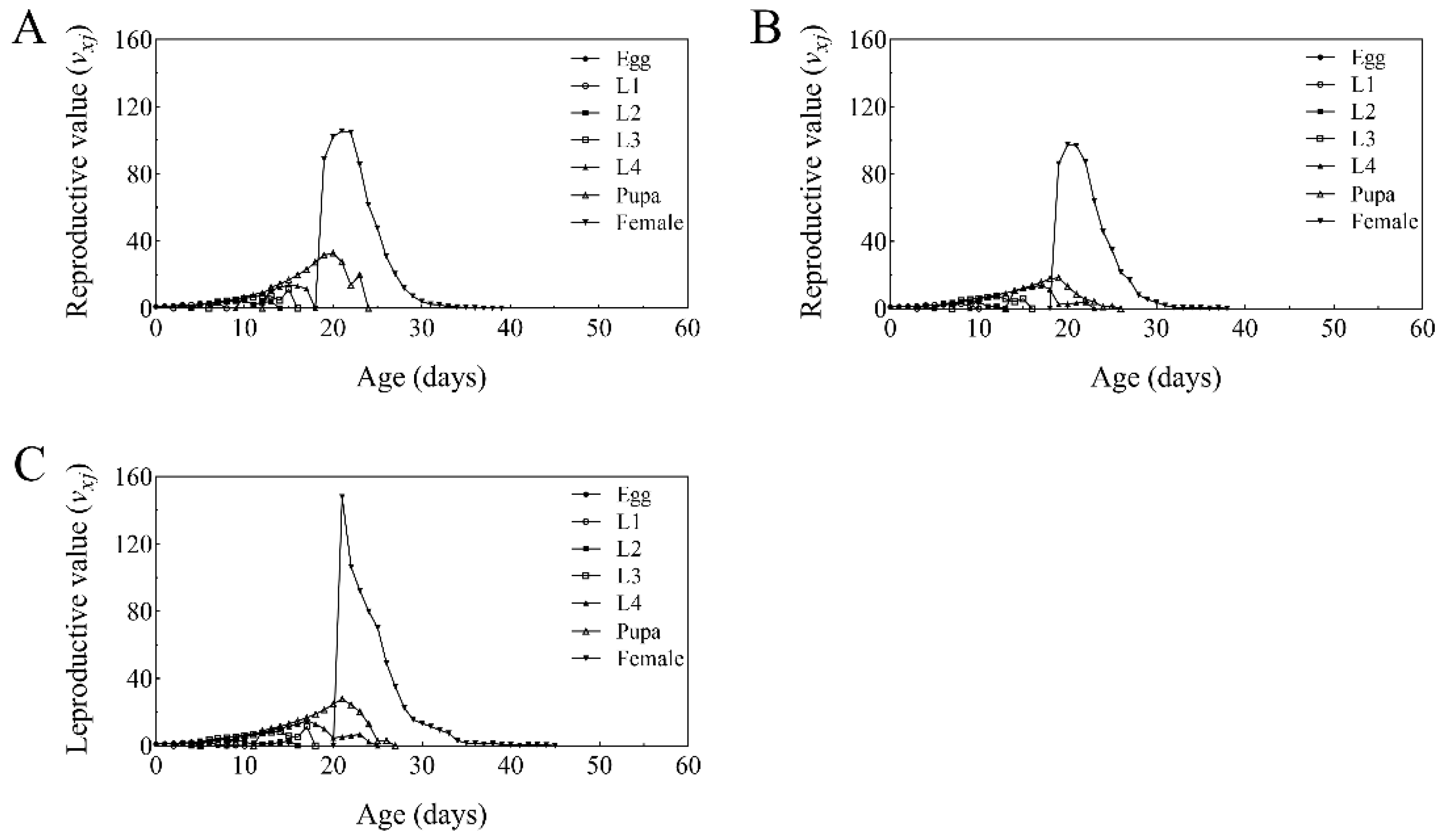
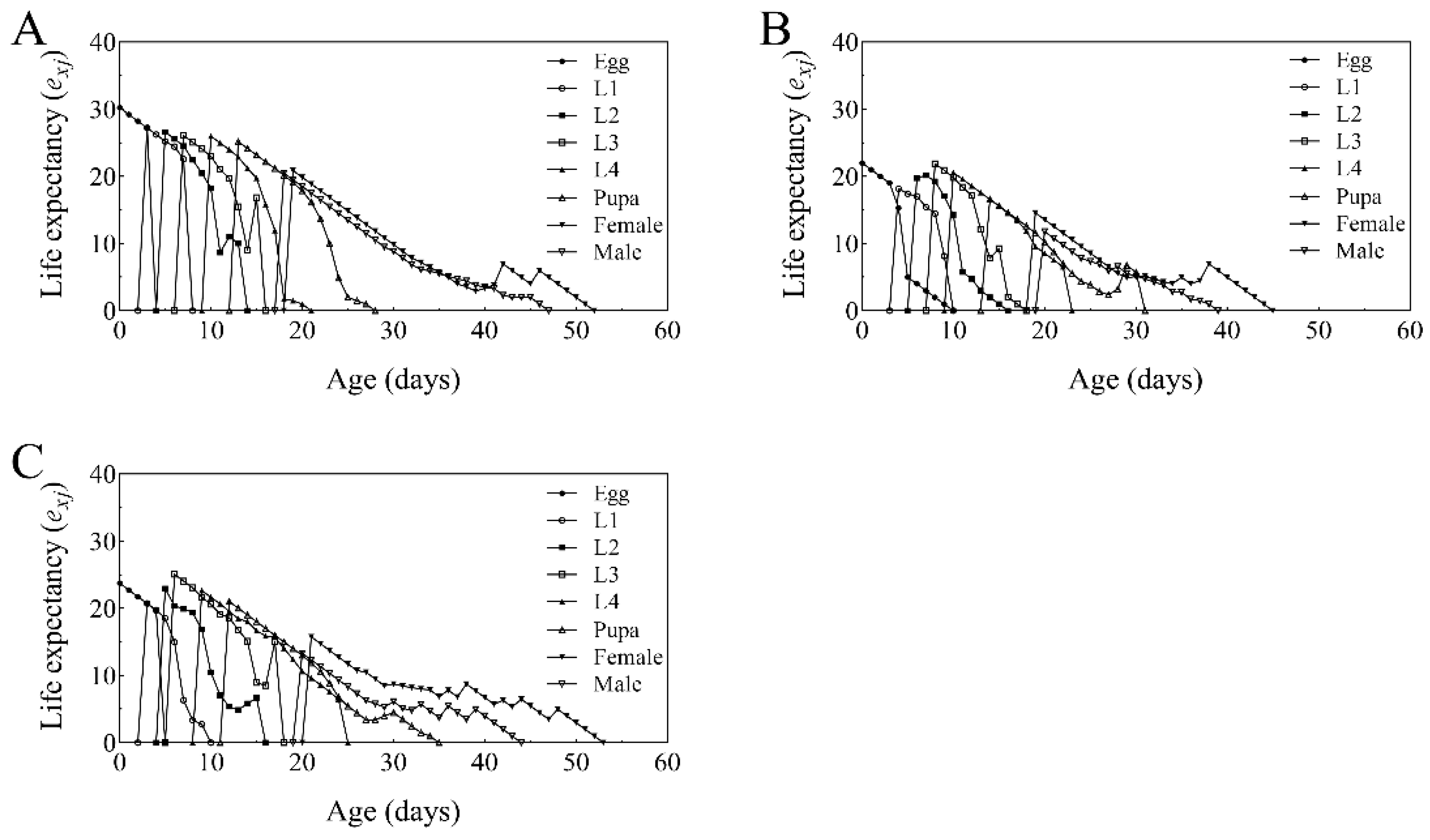
3.6. Life Table Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Costa, J.M.; Heuvelink, E.P. The Global Tomato Industry. In Tomatoes; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2018; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Biondi, A.; Guedes, R.N.C.; Wan, F.-H.; Desneux, N. Ecology, Worldwide Spread, and Management of the Invasive South American Tomato Pinworm, Tuta absoluta: Past, Present, and Future. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, R.N.C.; Picanço, M.C. The Tomato Borer Tuta absoluta in South America: Pest Status, Management and Insecticide Resistance. EPPO Bull. 2012, 42, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desneux, N.; Wajnberg, E.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Burgio, G.; Arpaia, S.; Narváez-Vasquez, C.A.; González-Cabrera, J.; Catalán Ruescas, D.; Tabone, E.; Frandon, J.; et al. Biological Invasion of European Tomato Crops by Tuta absoluta: Ecology, Geographic Expansion and Prospects for Biological Control. J. Pest Sci. 2010, 83, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, R.N.C.; Roditakis, E.; Campos, M.R.; Haddi, K.; Bielza, P.; Siqueira, H.A.A.; Tsagkarakou, A.; Vontas, J.; Nauen, R. Insecticide Resistance in the Tomato Pinworm Tuta absoluta: Patterns, Spread, Mechanisms, Management and Outlook. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 1329–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roditakis, E.; Vasakis, E.; García-Vidal, L.; del Rosario Martínez-Aguirre, M.; Rison, J.L.; Haxaire-Lutun, M.O.; Nauen, R.; Tsagkarakou, A.; Bielza, P. A Four-Year Survey on Insecticide Resistance and Likelihood of Chemical Control Failure for Tomato Leaf Miner Tuta absoluta in the European/Asian Region. J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Pérez, E.; Ortega-Amaro, M.A.; Bautista, E.; Delgado-Sánchez, P.; Jiménez-Bremont, J.F. The Entomopathogenic Fungus Metarhizium anisopliae Enhances Arabidopsis, Tomato, and Maize Plant Growth. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 176, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkara, A.; Akyıl, D.; Konuk, M.; Özkara, A.; Akyıl, D.; Konuk, M. Pesticides, Environmental Pollution, and Health. In Environmental Health Risk—Hazardous Factors to Living Species; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-953-51-2402-3. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, J.L.; Antunes, S.C.; Castro, B.B.; Marques, C.R.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; Gonçalves, F.; Pereira, R. Toxicity Evaluation of Three Pesticides on Non-Target Aquatic and Soil Organisms: Commercial Formulation versus Active Ingredient. Ecotoxicology 2009, 18, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, D.; Bailey, A.S.; Tatchell, G.M.; Davidson, G.; Greaves, J.; Grant, W.P. The Development, Regulation and Use of Biopesticides for Integrated Pest Management. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 366, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhajj, A.K.; Rizk, H.; Gharib, M.; Houssein, M.; Talj, V.; Taha, N.; Aleik, S.; Moussa, Z. Management of Tuta absoluta Meyrick (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) Using Biopesticides on Tomato Crop under Greenhouse Conditions. J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.T.; Kammar, V.; Keerthi, M.C.; Rani, V.; Majumder, S.; Pandey, K.K.; Singh, J. Biopesticides: An Alternative to Synthetic Insecticides. In Microbial Technology for Sustainable Environment; Bhatt, P., Gangola, S., Udayanga, D., Kumar, G., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 439–466. ISBN 978-981-16-3840-4. [Google Scholar]
- Rajula, J.; Rahman, A.; Krutmuang, P. Entomopathogenic Fungi in Southeast Asia and Africa and Their Possible Adoption in Biological Control. Biol. Control 2020, 151, 104399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.C.L.; Silva, G.A.; Abib, P.H.N.; Carolino, A.T.; Samuels, R.I. Endophytic Colonization of Tomato Plants by the Entomopathogenic Fungus Beauveria bassiana for Controlling the South American Tomato Pinworm, Tuta absoluta. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2020, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.L.; Pelizza, S.A.; Cabello, M.N.; Stenglein, S.A.; Scorsetti, A.C. Endophytic Colonisation of Tobacco, Corn, Wheat and Soybeans by the Fungal Entomopathogen Beauveria bassiana (Ascomycota, Hypocreales). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2015, 25, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondot, Y.; Reineke, A. Endophytic Beauveria bassiana in Grapevine Vitis vinifera (L.) Reduces Infestation with Piercing-Sucking Insects. Biol. Control 2018, 116, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachoute, J.; Nascimento, V.L.; de Souza, D.J. Beauveria bassiana Enhances the Growth of Cowpea Plants and Increases the Mortality of Cerotoma arcuata. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 3762–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, F.E. The Use of Fungal Entomopathogens as Endophytes in Biological Control: A Review. Mycologia 2018, 110, 4–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resquín-Romero, G.; Garrido-Jurado, I.; Delso, C.; Ríos-Moreno, A.; Quesada-Moraga, E. Transient Endophytic Colonizations of Plants Improve the Outcome of Foliar Applications of Mycoinsecticides against Chewing Insects. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 136, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wraight, S.P.; Ramos, M.E.; Avery, P.B.; Jaronski, S.T.; Vandenberg, J.D. Comparative Virulence of Beauveria bassiana Isolates against Lepidopteran Pests of Vegetable Crops. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010, 103, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarusikirwa, V.L.; Machekano, H.; Mutamiswa, R.; Chidawanyika, F.; Nyamukondiwa, C. Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) on the “Offensive” in Africa: Prospects for Integrated Management Initiatives. Insects 2020, 11, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivekanandhan, P.; Swathy, K.; Sarayut, P.; Patcharin, K. Biology, Classification, and Entomopathogen-Based Management and Their Mode of Action on Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) in Asia. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1429690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiberu, T.; Degaga, E. Entomopathogenic Effect of Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) and Metarrhizium anisopliae (Metschn.) on Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) Larvae Under Laboratory and Glasshouse Conditions in Ethiopia. J. Plant Pathol. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgi, I.; Dupuy, J.-W.; Blibech, I.; Lapaillerie, D.; Lomenech, A.-M.; Rebai, A.; Ksantini, M.; Bonneu, M.; Gargouri, A. Hyper-Proteolytic Mutant of Beauveria bassiana, a New Biological Control Agent against the Tomato Borer. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aynalem, B.; Muleta, D.; Jida, M.; Shemekite, F.; Aseffa, F. Biocontrol Competence of Beauveria bassiana, Metarhizium anisopliae and Bacillus thuringiensis against Tomato Leaf Miner, Tuta absoluta Meyrick 1917 under Greenhouse and Field Conditions. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghany, N.M.A.; Abdel-Razek, A.S.; Ebadah, I.M.A.; Mahmoud, Y.A. Evaluation of Some Microbial Agents, Natural and Chemical Compounds for Controlling Tomato Leaf Miner, Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). J. Plant Prot. Res. 2016, 56, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndereyimana, A.; Nyalala, S.; Murerwa, P.; Gaidashova, S. Pathogenicity of Some Commercial Formulations of Entomopathogenic Fungi on the Tomato Leaf Miner, Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2019, 29, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Mahmoud, F.; Bendebbah, R.; Benssaci, B.; Toudji, F.; Tafifet, L.; Krimi, Z. Entomopathogenic Efficacy of the Endophytic Fungi: Clonostachys Sp. and Beauveria bassiana on Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) Larvae under Laboratory and Greenhouse Conditions. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2021, 31, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, W.S. A Method of Computing the Effectiveness of an Insecticide. J. Econ. Entomol. 1925, 18, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; You, M.; Atlıhan, R.; Smith, C.L.; Kavousi, A.; Özgökçe, M.S.; Güncan, A.; Tuan, S.-J.; Fu, J.-W.; Xu, Y.-Y.; et al. Age-Stage, Two-Sex Life Table: An Introduction to Theory, Data Analysis, and Application. Entomol. Gen. 2020, 40, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Liu, H. Two New Methods for Study of Insect Population Ecology. Bull. Inst. Zool. Acad. Sin. 1984, 24, 225–240. [Google Scholar]
- Akca, I.; Ayvaz, T.; Yazici, E.; Smith, C.L.; Chi, H. Demography and Population Projection of Aphis fabae (Hemiptera: Aphididae): With Additional Comments on Life Table Research Criteria. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 1466–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Leger, R.; Screen, S. Prospects for Strain Improvement of Fungal Pathogens of Insects and Weeds. In Fungi as Biocontrol Agents: Progress, Problems and Potential; CABI Books: Wallingford, UK, 2001; pp. 219–237. ISBN 978-0-85199-356-0. [Google Scholar]
- Mascarin, G.M.; Jaronski, S.T. The Production and Uses of Beauveria bassiana as a Microbial Insecticide. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idrees, A.; Afzal, A.; Qadir, Z.A.; Li, J. Bioassays of Beauveria bassiana Isolates against the Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Wakil, W.; Ali, A.; Sahi, S. Pathogenicity of Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae Isolates against Larvae of the Polyphagous Pest Helicoverpa armigera. Entomol. Gen. 2018, 38, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agboyi, L.K.; Ketoh, G.K.; Douro Kpindou, O.K.; Martin, T.; Glitho, I.A.; Tamò, M. Improving the Efficiency of Beauveria bassiana Applications for Sustainable Management of Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) in West Africa. Biol. Control 2020, 144, 104233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.M.N.; Chowdhury, M.Z.H.; Mim, M.F.; Momtaz, M.B.; Islam, T. Biocontrol Potential of Native Isolates of Beauveria bassiana against Cotton Leafworm Spodoptera litura (Fabricius). Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aynalem, B.; Muleta, D.; Venegas, J.; Assefa, F. Molecular Phylogeny and Pathogenicity of Indigenous Beauveria bassiana against the Tomato Leafminer, Tuta absoluta Meyrick 1917 (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae), in Ethiopia. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, S.; Karimi, J.; Cheniany, M.; Seifi, A.; Loverodge, J.; Butt, T.M. Endophytic Entomopathogenic Fungi Enhance Plant Immune Responses against Tomato Leafminer. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2025, 209, 108270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, D.C.; Sword, G.A. The Endophytic Fungal Entomopathogens Beauveria bassiana and Purpureocillium lilacinum Enhance the Growth of Cultivated Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) and Negatively Affect Survival of the Cotton Bollworm (Helicoverpa zea). Biol. Control 2015, 89, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.-Y.; Li, Y.-Y.; Xu, C.; Wu, Y.-X.; Zhang, Y.-R.; Liu, H. Endophytic Colonization by Beauveria bassiana Increases the Resistance of Tomatoes against Bemisia tabaci. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2020, 14, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasambala Donga, T.; Vega, F.E.; Klingen, I. Establishment of the Fungal Entomopathogen Beauveria bassiana as an Endophyte in Sugarcane, Saccharum officinarum. Fungal Ecol. 2018, 35, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, O.; Sushida, H.; Higashi, Y.; Iida, Y. Epiphytic and Endophytic Colonisation of Tomato Plants by the Entomopathogenic Fungus Beauveria bassiana Strain GHA. Mycology 2021, 12, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegrucci, N.; Velázquez, M.S.; Russo, M.L.; Pérez, M.E.; Scorsetti, A.C. Endophytic Colonisation of Tomato by the Entomopathogenic Fungus Beauveria bassiana: The Use of Different Inoculation Techniques and Their Effects on the Tomato Leafminer Tuta absoluta (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). J. Plant Prot. Res. 2017, 57, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra-Bucarei, L.; González, M.G.; Iglesias, A.F.; Aguayo, G.S.; Peñalosa, M.G.; Vera, P.V. Beauveria bassiana Multifunction as an Endophyte: Growth Promotion and Biologic Control of Trialeurodes vaporariorum, (Westwood) (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) in Tomato. Insects 2020, 11, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, C.K.; Bamisile, B.S.; Keppanan, R.; Qasim, M.; Lin, Y.; Islam, S.U.; Hussain, M.; Wang, L. Endophytic Entomopathogenic Fungi Enhance the Growth of Phaseolus vulgaris L. (Fabaceae) and Negatively Affect the Development and Reproduction of Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae). Microb. Pathog. 2018, 125, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, G.; Ownley, B.H.; Augé, R.M.; Toler, H.; Dee, M.; Vu, A.; Köllner, T.G.; Chen, F. Colonization by Arbuscular Mycorrhizal and Endophytic Fungi Enhanced Terpene Production in Tomato Plants and Their Defense against a Herbivorous Insect. Symbiosis 2015, 65, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, R.; Xuelian, G.; Hui, D.; Xiuzhen, L.; Umer, M.J.; Rwomushana, I.; Ali, A.; Attia, K.A.; Jingfei, G.; Zhenying, W. Endophytic Fungi-Mediated Defense Signaling in Maize: Unraveling the Role of WRKY36 in Regulating Immunity against Spodoptera frugiperda. Physiol. Plant. 2024, 176, e14243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yan, G.; Liu, W.; Chen, H.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H. Endophytic Beauveria bassiana of Tomato Resisted the Damage from Whitefly Bemisia tabaci by Mediating the Accumulation of Plant-Specialized Metabolites. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 13244–13254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamisile, B.S.; Dash, C.K.; Akutse, K.S.; Keppanan, R.; Wang, L. Fungal Endophytes: Beyond Herbivore Management. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kaushik, N. Metabolites of Endophytic Fungi as Novel Source of Biofungicide: A Review. Phytochem. Rev. 2012, 11, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segaran, G.; Sathiavelu, M. Fungal Endophytes: A Potent Biocontrol Agent and a Bioactive Metabolites Reservoir. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 21, 101284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Strain | Corrected Mortality Rate (%) | Regression Equation | R2 | LT50 (Days) | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bb1Bm | 57.00 ± 10.91 a | Y = 58.781/(1 + Exp(3.142 − 0.560X)) | 0.956 | 8.71 | 8.74−10.70 |
| Bb2Bm | 50.00 ± 4.47 a | Y = 49.349/(1 + Exp(3.677 − 0.719X)) | 0.995 | — | — |
| BbM | 55.00 ± 9.22 a | Y = 56.994/(1 + Exp(3.749 − 0.708X)) | 0.977 | 0.977 | 7.21−8.94 |
| BbC | 33.00 ± 4.36 a | Y = 36.042/(1 + Exp(3.731 − 0.508X)) | 0.938 | — | — |
| Spore Concentration (Spores/mL) | Corrected Mortality of Larvae at Different Time Points After Infection (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 Days | 7 Days | 14 Days | |
| 1 × 108 | 10.00 ± 3.78 a | 61.25 ± 5.32 a | 85.00 ± 4.43 a |
| 1 × 107 | 7.50 ± 3.66 a | 34.38 ± 6.37 b | 57.50 ± 9.11 b |
| 1 × 106 | 5.00 ± 3.27 a | 29.38 ± 4.36 b | 38.75 ± 5.32 b,c |
| 1 × 105 | 5.00 ± 3.27 a | 21.25 ± 3.10 b,c | 33.75 ± 5.88 b,c |
| 1 × 104 | 2.50 ± 2.50 a | 5.63 ± 3.71 c | 18.13 ± 6.19 c |
| Parameters | Treatment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | BbFS | BbRI | |
| Duration of egg (d) | 3.89 ± 0.05 a | 3.96 ± 0.04 a | 3.96 ± 0.04 a |
| Duration of 1st instar larval (d) | 2.68 ± 0.10 a,b | 2.93 ± 0.13 a | 2.22 ± 0.08 b |
| Duration of 2nd instar larval (d) | 2.51 ± 0.10 b | 2.68 ± 0.12 b | 3.30 ± 0.13 a |
| Duration of 3rd instar larval (d) | 3.09 ± 0.15 a | 2.79 ± 0.13 a | 3.07 ± 0.16 a |
| Duration of 4th instar larval (d) | 3.32 ± 0.10 a | 3.68 ± 0.19 a | 3.52 ± 0.15 a |
| Duration of Larva stage (d) | 11.60 ± 0.18 a | 12.07 ± 0.21 a | 12.11 ± 0.26 a |
| Duration of Pupa stage (d) | 5.94 ± 0.16 b | 6.11 ± 0.25 a,b | 6.78 ± 0.19 a |
| Adult female longevity (d) | 18.48 ± 0.72 a | 12.20 ± 1.36 b | 13.27 ± 1.63 b |
| Adult male longevity (d) | 17.13 ± 0.86 a | 9.08 ± 1.20 b | 11.25 ± 1.19 b |
| Number of eggs laid per female | 147.82 ± 4.99 a | 112.07 ± 8.92 b | 124.79 ± 9.60 b |
| Parameters | Treatment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | BbFS | BbRI | |
| Net reproductive rate (R0) | 44.84 ± 7.93 a | 20.53 ± 5.22 b | 25.95 ± 6.22 b |
| Finite rate of increase (λ) | 1.16 ± 0.00 a | 1.13 ± 0.00 b | 1.13 ± 0.01 b |
| Intrinsic rate of increase (r) | 0.15 ± 0.00 a | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | 0.12 ± 0.00 b |
| Mean generation time (T) | 24.85 ± 0.26 b | 24.59 ± 0.46 b | 26.45 ± 0.51 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, B.; Huang, C.; Cheng, S.; Romeis, J.; Collatz, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wan, F. Screening of Highly Virulent Beauveria bassiana Strains Against Tuta absoluta Larvae and Evaluation of Their Endophytic Colonization-Mediated Suppression in Tomato Plants. Plants 2025, 14, 2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182932
Xu B, Huang C, Cheng S, Romeis J, Collatz J, Zhang G, Zhang Y, Zhang G, Wan F. Screening of Highly Virulent Beauveria bassiana Strains Against Tuta absoluta Larvae and Evaluation of Their Endophytic Colonization-Mediated Suppression in Tomato Plants. Plants. 2025; 14(18):2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182932
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Bo, Cong Huang, Sheng Cheng, Jörg Romeis, Jana Collatz, Guifen Zhang, Yibo Zhang, Guohui Zhang, and Fanghao Wan. 2025. "Screening of Highly Virulent Beauveria bassiana Strains Against Tuta absoluta Larvae and Evaluation of Their Endophytic Colonization-Mediated Suppression in Tomato Plants" Plants 14, no. 18: 2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182932
APA StyleXu, B., Huang, C., Cheng, S., Romeis, J., Collatz, J., Zhang, G., Zhang, Y., Zhang, G., & Wan, F. (2025). Screening of Highly Virulent Beauveria bassiana Strains Against Tuta absoluta Larvae and Evaluation of Their Endophytic Colonization-Mediated Suppression in Tomato Plants. Plants, 14(18), 2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14182932







