Physiological and Transcriptional Regulation of Salt Tolerance in Thinopyrum ponticum and Screening of Salt-Tolerant Candidate Genes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Salt Stress on Growth of Thinopyrum ponticum
2.2. Physiological Response of Thinopyrum ponticum to Salt Stress
2.2.1. Salt Stress Reduced Relative Water Content of Leaves
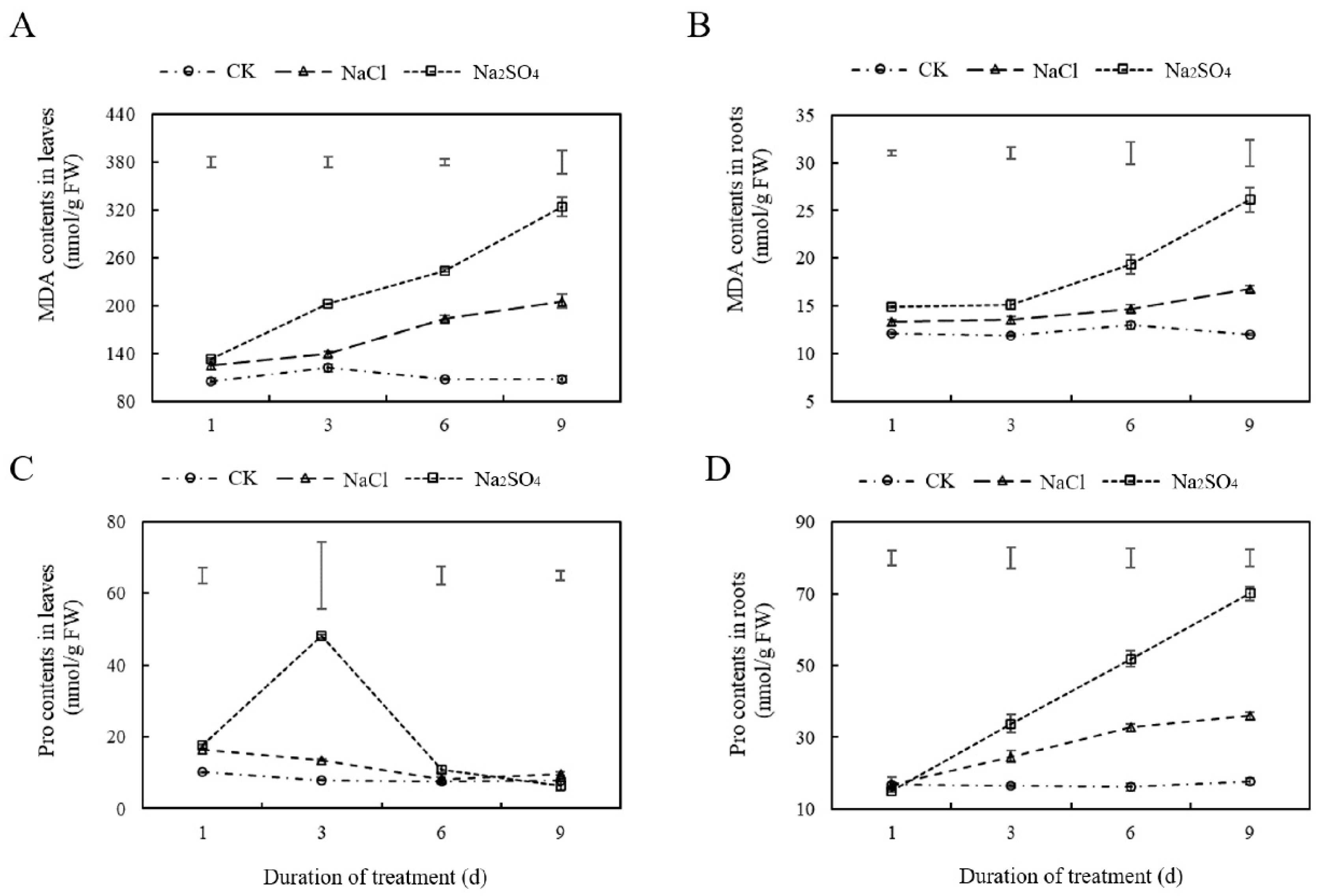
2.2.2. Salt Stress Induced Lipid Peroxidation and Proline Content
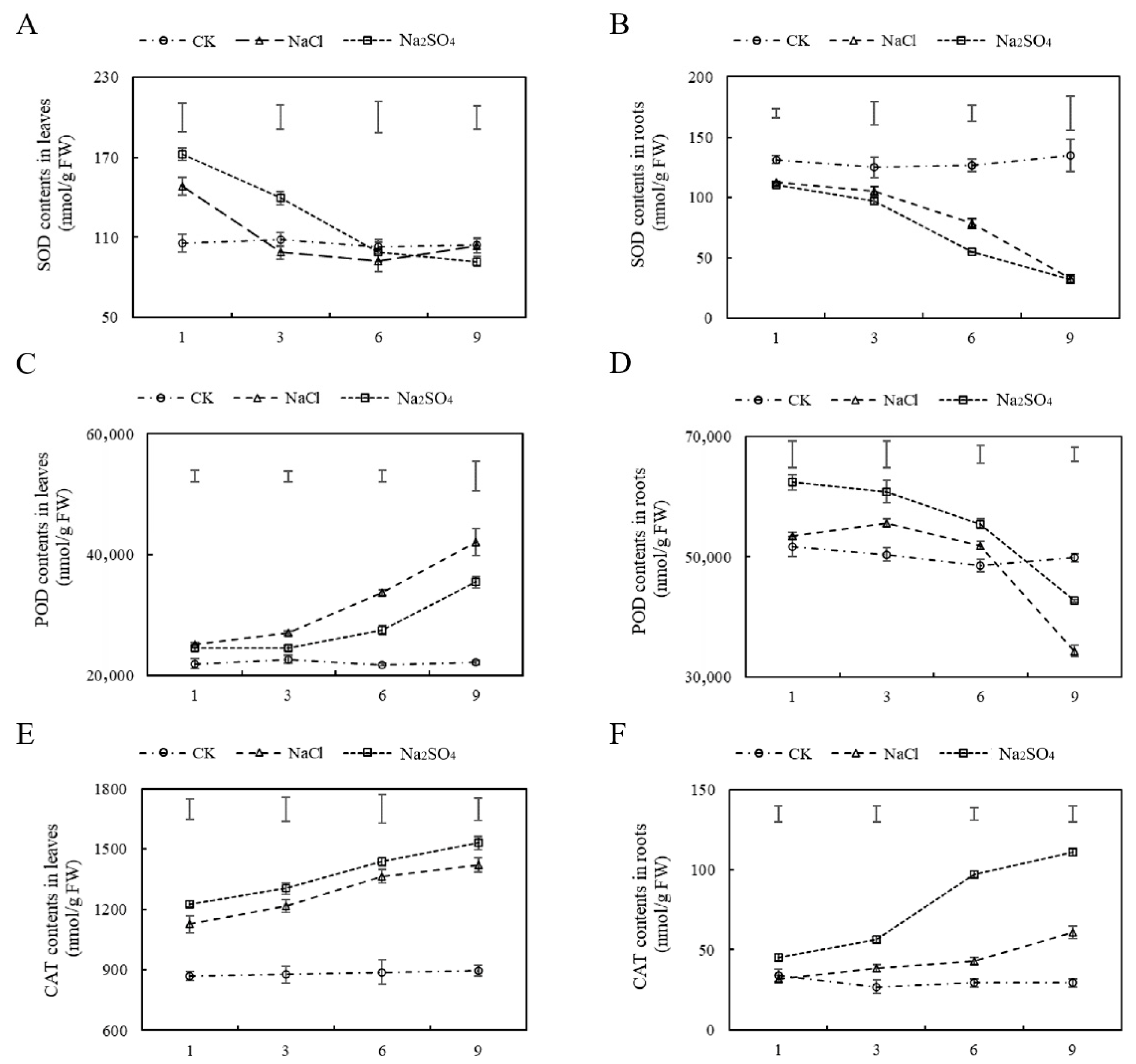
2.2.3. Salt Stress Affected POD, SOD, and CAT Activities
2.2.4. Salt Stress Affected Ion Content
2.3. RNA-Seq Analyses of Leaves and Roots of Thinopyrum ponticum Under Na2SO4 Stress
2.3.1. Identification of DEGs and Venn Diagram Analysis
2.3.2. GO Enrichment Analysis
2.3.3. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
2.3.4. KEGG Enrichment Pathway Analysis
2.4. Analysis of Transcriptional Regulation Mechanisms in DEGs Under Salt Stress
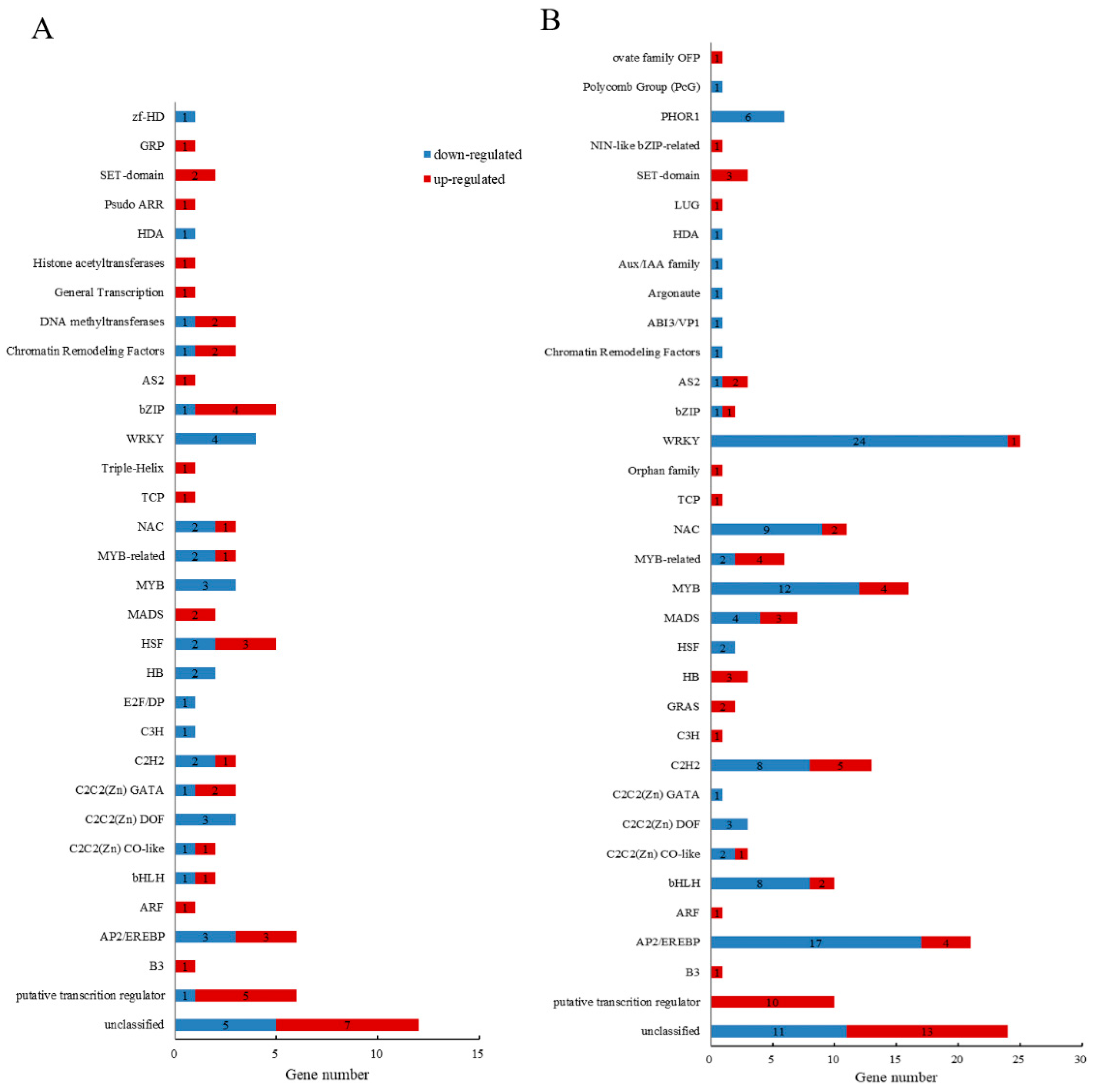
2.4.1. TF Analysis of DEGs Related to Transcriptional Regulation
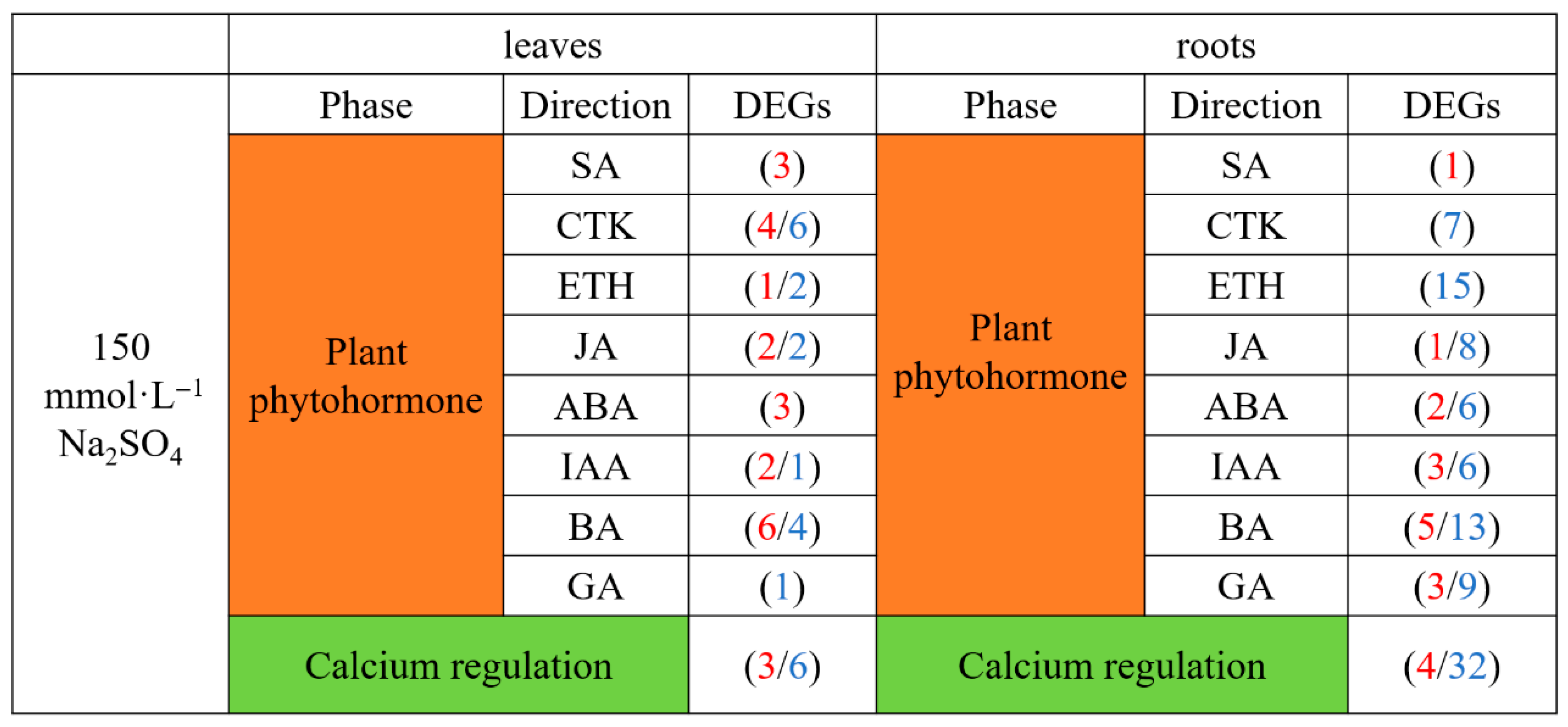
2.4.2. Analysis of Hormone-Related and Calcium Regulatory DEGs Related to Transcriptional Regulation
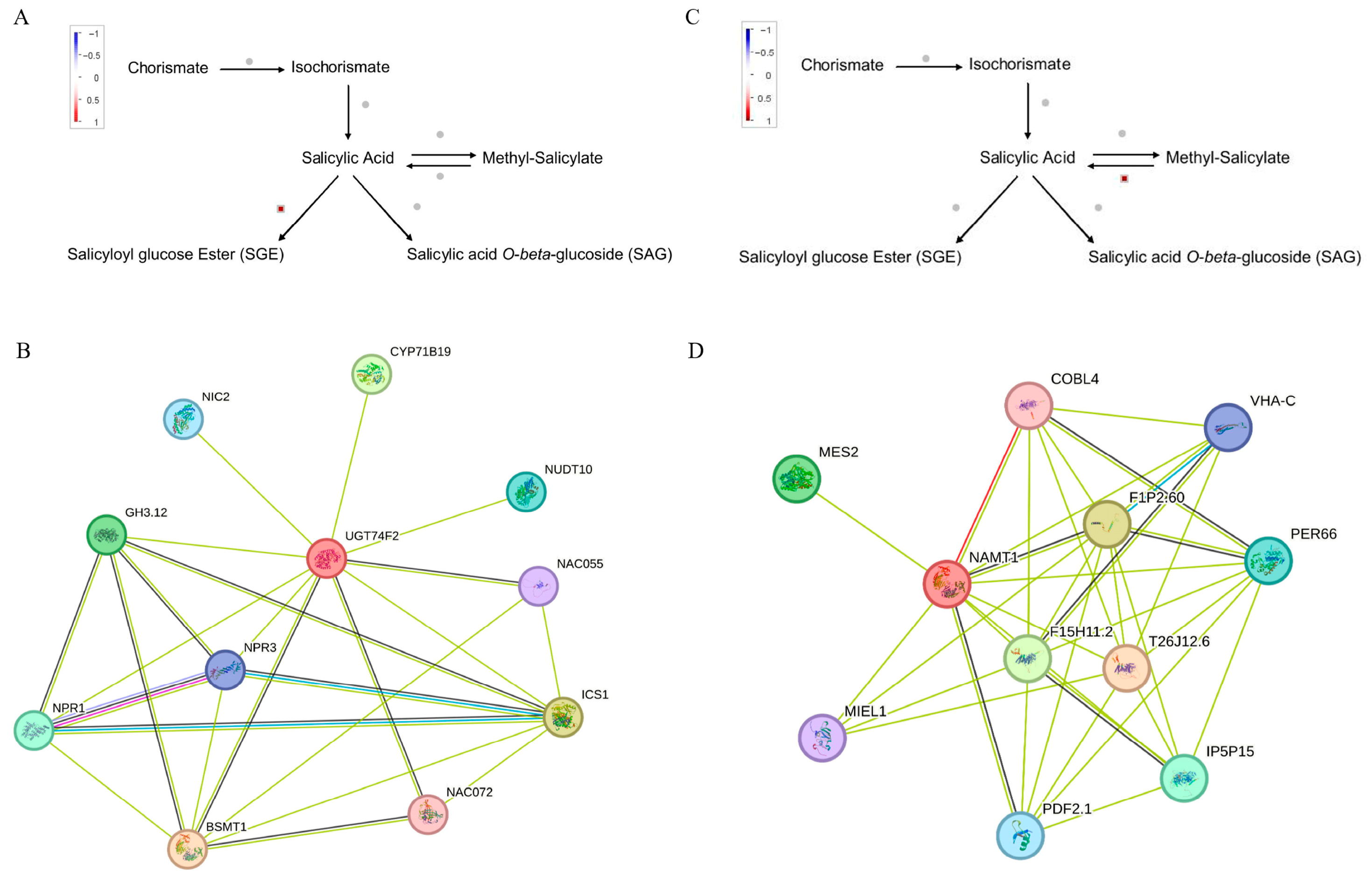
2.4.3. DEGs in SA, ETH Signaling Pathway Signaling, and Prediction of Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Networks
SA Signaling Pathway
ETH Signaling Pathway
Ca2+ Signaling Pathway
2.5. Salt-Tolerant Candidate Gene Screening and qRT-PCR Verification
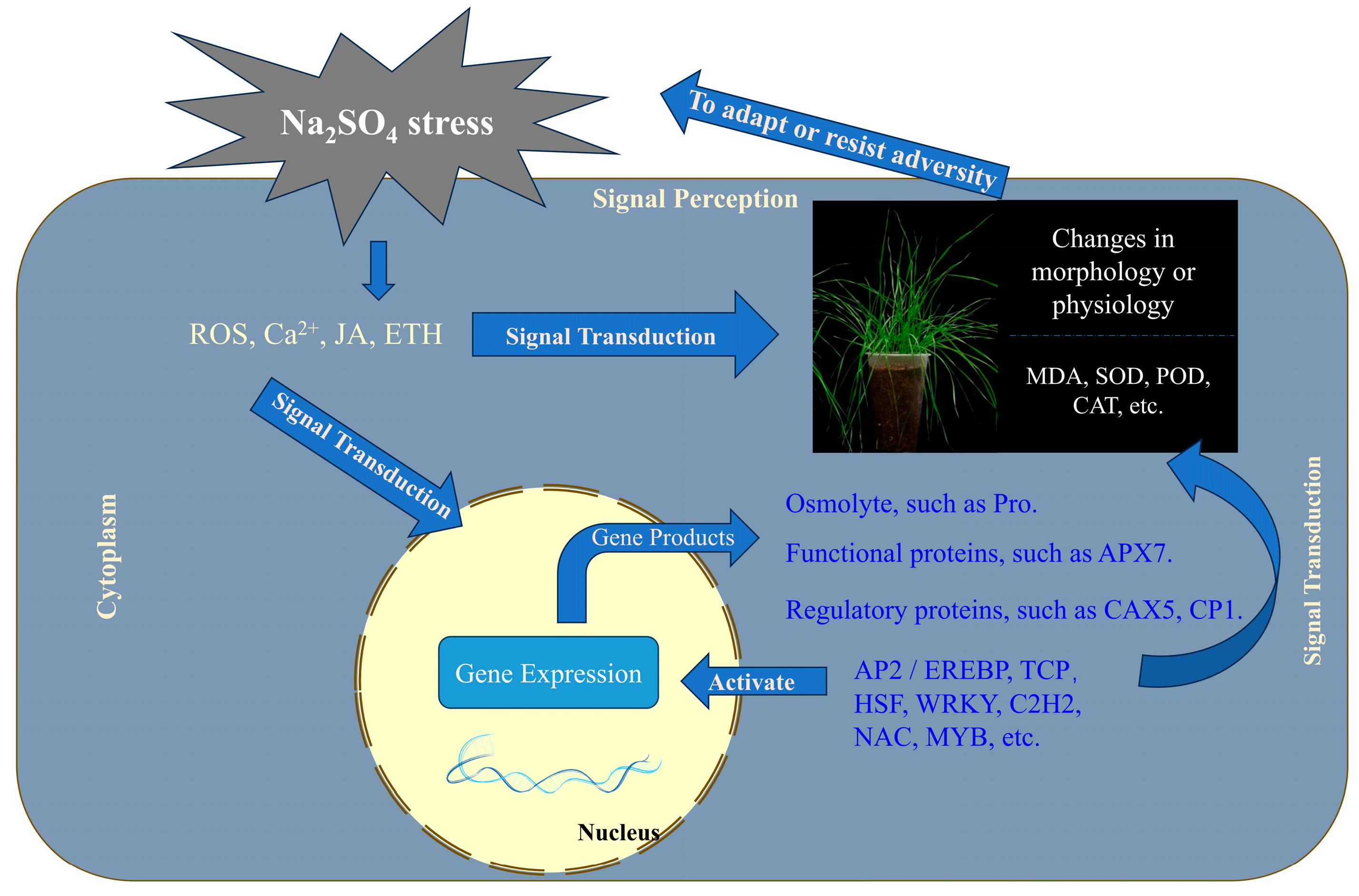
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Plant Growth Conditions and Treatments
5.2. Determination of Growth and Physiological Indexes
5.3. Determination of Ions
5.4. RNA Extraction and Transcriptome Sequencing
5.5. Pathway Enrichment Analysis
5.6. Prediction and Classification of Transcriptional Regulatory Factors
5.7. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Analysis
5.8. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) Confirmation
5.9. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Xie, W.J.; Wu, L.F.; Zhang, Y.P.; Wu, T.; Li, X.P.; Ouyang, Z. Effects of straw application on coastal saline topsoil salinity and wheat yield trend. Soil Till. Res. 2017, 169, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheswari, J.; Bose, J.; Babourina, O.; Rengel, Z.; Shabala, S. Salicylic acid in plant salinity stress signalling and tolerance. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 76, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.W.; Li, W.; Zheng, Q.; Zhao, M.L.; Wang, J.L.; Li, B.; Li, Z.S. Salinity Threshold of Tall Wheatgrass for Cultivation in Coastal Saline and Alkaline Land. Agriculture 2023, 13, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Yang, G.; Bolige, A.; Terigen; Li, H.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Zheng, Q. Screening of salt-tolerant Thinopyrum ponticum under two coastal region salinity stress levels. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 832013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, A.; Takeda, S.; Nick, P. Life and death under salt stress: Same players, different timing? J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2963–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakkoli, E.; Fatehi, F.; Coventry, S.; Rengasamy, P.; McDoald, G.K. Additive effects of Na+ and Cl− ions on barley growth under salinity stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 2189–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.K. Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell 2014, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Q.; Guo, Y. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.J.; Ma, X.L.; Wan, P.; Liu, L.Y. Plant salt-tolerance mechanism: A review. BBRC 2018, 495, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhou, X.P.; Wu, X.M.; Jiang, Z.H. Structure and function of the CBL-CIPK Ca2+-decoding system in plant calcium signaling. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 31, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.H.; Zhou, X.P.; Tao, M.; Yuan, F.; Liu, L.L.; Wu, F.H.; Wu, X.M.; Xiang, Y.; Niu, Y.; Liu, F.; et al. Plant cell-surface GIPC sphingolipids sense salt to trigger Ca2+ influx. Nature 2019, 572, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.Y.; Xiong, T.T.; Li, X.P.; Chen, W.X.; Zhu, X.Y. Calcium and calcium sensors in fruit development and ripening. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 253, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, L.; Whelan, S.; Hirschi, K.D.; Pittman, J.K. Protein phylogenetic analysis of Ca2+/cation antiporters and insights into their evolution in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, M.; Tyagi, S.; Sharma, S.; Upadhyay, S.K. Ca2+/Cation antiporters (CaCA): Identification, characterization and expression profiling in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, R.; Jones, J.D. Role of plant hormones in plant defense responses. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 69, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. ABA signaling in stress-response and seed development. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, K.T.; Fukuyo, T.; Keiki, O.; Ohwaki, Y. The ACC deaminase expressing endophyte Pseudomonas spp. enhances NaCl stress tolerance by reducing stress-related ethylene production, resulting in improved growth, photosynthetic performance, and ionic balance in tomato plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 127, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.N.; Shih, M.C.; Li, N. The GUS reporter-aided analysis of the promoter activities of Arabidopsis ACC synthase genes AtACS4, AtACS5, and AtACS7 induced by hormones and stresses. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.H.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Gao, Y.R.; Zheng, S.F.; Du, B.X.; Zhang, J.S.; Chen, S.Y. Expression of tobacco ethylene receptor NTHK1 alters plant responses to salt stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2006, 29, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.B.; Wang, F.F.; Peng, P.; Zhou, Y.; Miao, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Gao, Y.D.; Qi, Y.D.; et al. Rice OsDOF15 contributes to ethylene-inhibited primary root elongation under salt stress. New Phytol. 2019, 223, 798–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhen, Z.; Peng, J.; Chang, L.; Gong, Q.; Wang, N.N. Loss of ACS7 confers abiotic stress tolerance by modulating ABA sensitivity and accumulation in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 4875–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ma, B.; He, S.J.; Xiong, Q.; Duan, K.X.; Yin, C.C.; Chen, H.; Lu, X.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhang, J.S. MHZ6/OsEIL1 and OsEIL2 regulate ethylene response of roots and coleoptiles and negatively affect salt tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalaga, R.R.; Mohammad, W.A.; Ranjan, K.S.; Ratnum, K.W.; Narendra, T.; Vellanki, R.K. Salicylic acid modulates ACS, NHX1, SOS1 and HKT1;2 expression to regulate ethylene overproduction and Na+ ions toxicity that leads to improved physiological status and enhanced salinity stress tolerance in tomato plants cv. Pusa Ruby. Plant Signal. Behav. 2021, 16, 1950888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poór, P.; Borbely, P.; Bodi, N.; Bagyanszki, M.; Tari, I. Effects of salicylic acid on photosynthetic activity and chloroplast morphology under light and prolonged darkness. Photosynthetica 2019, 57, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Yan, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Wu, W. Humic acids enhance salt stress tolerance associated with pyrroline 5-carboxylate synthetase gene expression and hormonal alteration in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1272987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.Y.; Liu, Y.Q.; Duan, H.R.; Yin, X.X.; Cui, Y.N.; Chai, W.W.; Song, X.; Flowers, T.J.; Wang, S.M. SsHKT1;1 is coordinated with SsSOS1 and SsNHX1 to regulate Na+ homeostasis in Suaeda salsa under saline conditions. Plant Soil. 2020, 449, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Li, W.; Hu, P.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, Q.; Li, H.; Li, Z. An Integrated Method for Evaluation of Salt Tolerance in a Tall Wheatgrass Breeding Program. Plants 2025, 14, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reginato, M.A.; Turcios, A.E.; Luna, V.; Papenbrock, J. Differential effects of NaCl and Na2SO4 on the halophyte Prosopis strombulifera are explained by different responses of photosynthesis and metabolism. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 141, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajanzadeh, T.A.; Reich, M.; Kopriva, S.; Kok, L.J.D. Impact of chloride (NaCl, KCl) and sulfate (Na2SO4, K2SO4) salinity on glucosinolate metabolism in Brassica rapa. J. Agron. Crop. Sci. 2018, 204, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.Y.; Ali, Z.; Park, H.J.; Park, S.J.; Cha, J.Y.; Javier, P.H.; Quintero, F.J.; Sgin, G.; Kim, M.R.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Release of SOS2 kinase from sequestration with GIGANTEA determines salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.B.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, K.Y.; Deng, X.P.; Kwak, S.S. Analysis of antioxidant enzyme activity during germination of alfalfa under salt and drought stresses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 47, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julkowska, M.M.; Hoefsloot, H.C.J.; Mol, S.; Feron, R.; Boer, G.J.; Haring, M.A.; Testerink, C. Capturing Arabidopsis root architecture dynamics with ROOT-FIT reveals diversity in responses to salinity. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 1387–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Moe-Lange, J.; Hennet, L.; Feldman, L.J. Salt stress affects the redox status of Arabidopsis root meristems. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarchoune, I.; Degl’Innocenti, E.; Kaddour, R.; Guidi, L.; Lachaal, M.; Navari-Izzo, F.; Ouerghi, Z. Effects of NaCl or Na2SO4 salinity on plant growth, ion content, and photosynthetic activity in Ocimum basilicum L. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2012, 34, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, M.E.; Albacete, A.; Martínez-Andújar, C.; Acosta, M.; Romero-Aranda, R.; Dodd, L.C.; Lutts, S.; Pérez-Alfocea, F. Hormonal changes during salinity-induced leaf senescence in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 3039–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumwald, E. Engineering salt tolerance in plants. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 13, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.; Suzuki, N.; Ciftci-Yilmaz, S.; Mittler, R. Reactive oxygen species homeostasis and signaling during drought and salinity stresses. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reginato, M.; Sosa, L.; Llanes, A.; Hampp, E.; Vettorazzi, N.; Reinoso, H.; Luna, V. Growth responses and ion accumulation in the halophytic legume Prosopis strombulifera are determined by Na2SO4 and NaCl. Plant Biol. 2014, 16, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, S.H.; Wang, P.F.; Hou, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.J. Metabolic adaptations to ammonia-induced oxidative stress in leaves of the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 87, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.S.; Elsayed, A.I.; Moore, M.; Dietz, K.J. Redox and reactive oxygen species network in acclimation for salinity tolerance in sugar beet. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 1283–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Yin, S.; Huang, L. Towards plant salinity tolerance-implications from ion transporters and biochemical regulation. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 76, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Mo, J.; Zhou, H.; Shen, X.; Xie, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, S. Comparative transcriptome analysis of gene responses of salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive rice cultivars to salt stress. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazanin, A.; Ahmad, I.; Mohammad, R.G.; Firouzabadi, F.N.; Shobbar, Z.S. Transcriptome response of roots to salt stress in a salinity-tolerant bread wheat cultivar. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharoni, A.M.; Nuruzzaman, M.; Satoh, K.; Shimizu, T.; Kondoh, H.; Sasaya, T.; Choi, I.R.; Omura, T.; Kikuchi, S. Gene structures, classification, and expression models of the AP2/EREBP transcription factor family in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 344–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebrián, G.; Iglesias-Moya, J.; García, A.; Martínez, J.; Romero, J.; Regalado, J.J.; Martínez, C.; Valenzuela, J.L.; Jamilena, M. Involvement of ethylene receptors in the salt tolerance response of Cucurbita pepo. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divi, U.K.; Rahman, T.; Krishna, P. Brassinosteroid-mediated stress tolerance in Arabidopsis shows interactions with abscisic acid, ethylene, and salicylic acid pathways. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, L.; Kong, X.; Wang, X.; Si, A.; Zhao, F.; Huang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Z. Time-Course Transcriptomics Analysis Reveals Molecular Mechanisms of Salt-Tolerant and Salt-Sensitive Cotton Cultivars in Response to Salt Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashif, M.H.; Feng, J.; Dai, R.; Fan, Y.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Z. Salicylic acid-mediated alleviation of salt stress: Insights from physiological and transcriptomic analysis in Asarum sieboldii Miq. Chemosphere 2024, 362, 142604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.; Senaratna, T.; Sivasithamparam, K. Salicylic acid induces salinity tolerance in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum cv. Roma): Associated changes in gas exchange, water relations, and membrane stabilization. Plant Growth Regul. 2006, 49, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reginato, M.; Cenzano, A.M.; Arslan, I.; Furlán, A.; Varela, C.; Cavallin, V.; Papenbrock, J.; Luna, V. Na2SO4 and NaCl salts differentially modulate the antioxidant systems in the highly stress-tolerant halophyte Prosopis strombulifera. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 167, 748–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.C.; Ronzier, E.; Sanchez, F.; Corratgé-Faillie, C.; Mazars, C.; Thibaud, J.B. Imaging long-distance propagating calcium signals in intact plant leaves with the BRET-based GFP-aequorin reporter. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.G.; Toyota, M.; Kim, S.H.; Hilleary, R.; Gilroy, S. Salt stress-induced Ca2+ waves are associated with rapid, long-distance root-to-shoot signaling in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6497–6502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Liu, X.J.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.H.; Yu, J.Q.; Hu, D.G.; Hao, Y.J. Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression analysis of calmodulin-like proteins (CMLs) in apple. Hortic. Plant J. 2017, 3, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hou, C.C.; Tian, Y.D.; Tang, M.T.G.; Feng, C.X.; Ren, Z.J.; Song, J.L.; Wang, X.H.; Li, T.G.; Li, M.G.; et al. Interaction between AtCML9 and AtMLO10 regulates pollen tube development and seed setting. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, K.J.; Ma, X.; Liang, G.L.; Ma, H.L.; Jia, Z.F.; Liu, W.H.; Yu, Q.Q. 5-Aminolevulinic acid modulates antioxidant defense systems and mitigates drought-induced damage in Kentucky bluegrass seedlings. Protoplasma 2017, 254, 2083–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.F.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.R.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.W.; Sun, S.; Ge, W.Y.; Zhao, L.F.; Hou, B.Q.; Wang, K.; Lyu, Z.F.; Chen, L.Y.; Xu, S.S.; Guo, J.; et al. Horizontal gene transfer of Fhb7 from fungus underlies Fusarium head blight resistance in wheat. Science 2020, 368, eaba5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.Q.; Lu, X.K.; Chen, X.G.; Malik, W.A.; Wang, D.L.; Zhao, L.J.; Wang, J.J.; Wang, S.; Cui, R.F.; Han, M.G.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of upland cotton revealed novel pathways to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) responding to Na2SO4 tolerance. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelo, S.; Giorgio, T.; Danilo, F.S.; Salvatore, L.C.; Angela, R.L.P. RNA Seq analysis of giant cane reveals the leaf transcriptome dynamics under long term salt stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najib, A.; Min, J.K.; Tae, J.C. Transcriptome analysis of gene expression in Chlorella vulgaris under salt stress. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
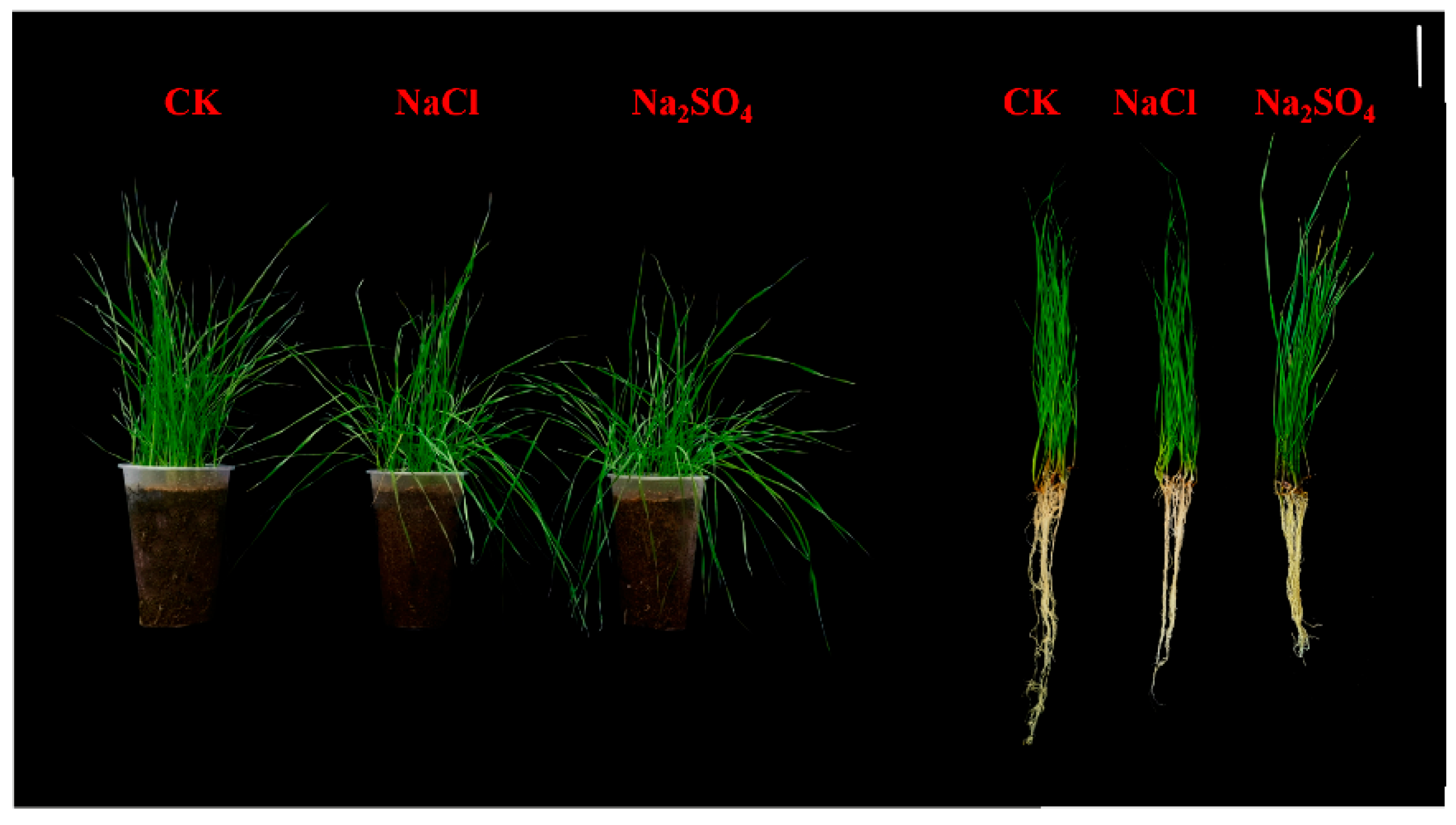





| Treatment | Mean Seedling Length (cm) | Mean Root Length (cm) | Mean Seedling Weight (g) | Mean Root Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 25.64 ± 0.62 a | 18.82 ± 0.70 a | 2.29 ± 0.10 a | 1.10 ± 0.01 a |
| NaCl | 23.94 ± 0.60 a | 16.16 ± 0.27 b | 2.09 ± 0.15 b | 1.07 ± 0.03 a |
| Na2SO4 | 26.08 ± 0.94 a | 14.50 ± 0.45 b | 1.64 ± 0.07 c | 0.96 ± 0.05 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Zhong, R.; Niu, K.; Jia, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Physiological and Transcriptional Regulation of Salt Tolerance in Thinopyrum ponticum and Screening of Salt-Tolerant Candidate Genes. Plants 2025, 14, 2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172771
Zhang R, Zhong R, Niu K, Jia F, Liu Y, Li X. Physiological and Transcriptional Regulation of Salt Tolerance in Thinopyrum ponticum and Screening of Salt-Tolerant Candidate Genes. Plants. 2025; 14(17):2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172771
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ran, Rui Zhong, Kuiju Niu, Fang Jia, Yuehan Liu, and Xiaoxia Li. 2025. "Physiological and Transcriptional Regulation of Salt Tolerance in Thinopyrum ponticum and Screening of Salt-Tolerant Candidate Genes" Plants 14, no. 17: 2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172771
APA StyleZhang, R., Zhong, R., Niu, K., Jia, F., Liu, Y., & Li, X. (2025). Physiological and Transcriptional Regulation of Salt Tolerance in Thinopyrum ponticum and Screening of Salt-Tolerant Candidate Genes. Plants, 14(17), 2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172771





