Selenium Compounds and Their Bioactivities: Molecular Mechanisms and Prospects for Functional Food and Therapeutic Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Properties of Selenium and Functions
3. Global Research Progress on Selenium in Plants (2000–2025)
4. Plant Absorption, Conversion, and Metabolism of Selenium
4.1. Mechanisms of Selenium Uptake, Transformation, and Accumulation in Plants
4.2. Types and Metabolism of Selenium-Containing Functional Factors in Plants
4.3. Absorption, Transport, Metabolism, and Utilization of Plant-Derived Selenium Compounds in the Human Body
5. Selenium Compounds and Their Biological Activity
5.1. Selenoproteins
5.2. Selenopeptides
5.3. Selenopolysaccharides
5.3.1. Biological Activities of Selenopolysaccharides
5.3.2. Sources and Structure of Selenopolysaccharides
5.4. Selenium-Enriched Polyphenols
5.5. Nano-Selenium
6. Applications and Prospects of Selenium Compounds
6.1. Selenium-Based Strategies in Drug Development and Therapeutic Applications
6.2. Applications of Selenium in Food and Nutrition: Biofortification and Health Implications
6.3. Applications of Selenium in the Cosmetics and Skincare Industry
6.4. Medical Consumables and Biomaterials
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, P.S.; Huang, R.; Zhong, X.; Chen, X.; Lei, Y.H. A comprehensive review on selenium and blood pressure: Recent advances and research perspectives. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2025, 88, 127607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binsuwaidan, R.; Masry, T.A.E.; Nagar, M.M.F.E.; Zahaby, E.I.E.; Gaballa, M.M.S.; Bouseary, M.M.E. Investigating the Antibacterial, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of a Lycopene Selenium Nano-Formulation: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.X.; Liang, L.; Miao, F.; Ji, T.; Ye, Z.Q.; Chu, M.; Ren, J.Y.; Xu, X. Synthesis, stability and anti-fatigue activity of selenium nanoparticles stabilized by Lycium barbarum polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 179, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.C.; Zheng, C.Q.; Luo, R.; Cao, X.; Liu, M.J.; Gu, Q.Q.; Li, F.; Li, J.S.; Wu, X.S.; Yang, Z.L.; et al. Integrative analysis of multiomics data identifies selenium-related gene ALAD associating with keshan disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 193, 702–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.W.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Y.L.; He, Z.J. Selenium in cancer management: Exploring the therapeutic potential. Front. Oncol. 2025, 14, 1490740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gac, P.; Czerwinska, K.; Macek, P.; Jaremków, A.; Mazur, G.; Pawlas, K.; Poreba, R. The importance of selenium and zinc deficiency in cardiovascular disorders. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 82, 103553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, Z.H.; Shen, L.M.; Song, G.L.; Tian, J.; Liu, Q.; Ni, J.Z. Selenium metabolism and selenoproteins function in brain and encephalopathy. Sci. China-Life Sci. 2025, 68, 628–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.L.U.; Sena-Evangelista, K.C.M.; de Azevedo, E.P.; Pinheiro, F.I.; Cobucci, R.N.; Pedrosa, L.F.C. Selenium in Human Health and Gut Microflora: Bioavailability of Selenocompounds and Relationship With Diseases. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 685317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, T.-Z.; Fu, Y.; Wang, X.-S.; Jiang, N.; Zhai, D.-D.; Shang, X.-D.; Dong, H.-R.; Luan, T.-Y.; Tang, G.-R.; Yu, H.-L. Research Progress of Selenium-Enriched Edible Fungi. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Zhang, M.; Tang, S.; Li, M.; Wu, R.; Wan, S.; Chen, L.; Wei, X.; Feng, S. Effects and Impact of Selenium on Human Health, A Review. Molecules 2025, 30, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Wei, Y. Selenium and Selenoproteins in Health. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Liu, G.J.; Yousaf, B.; Ali, M.U.; Irshad, S.; Abbas, Q.; Ahmad, R. A comprehensive review on environmental transformation of selenium: Recent advances and research perspectives. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 1003–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, A.; Köppe, R. Synthesis of selenium doted pyrite single crystals prepared by chemical vapor transport. J. Cryst. Growth 2012, 349, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oropeza-Moe, M.; Wisløff, H.; Bernhoft, A. Selenium deficiency associated porcine and human cardiomyopathies. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 31, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidin; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, T.; Wu, X.; Yuan, W.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zi, C. Selenium and Selenoproteins: Mechanisms, Health Functions, and Emerging Applications. Molecules 2025, 30, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasim, M.J.; Zuraik, M.M.; Abdin, A.Y.; Ney, Y.; Jacob, C. Selenomethionine: A Pink Trojan Redox Horse with Implications in Aging and Various Age-Related Diseases. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burk, R.F.; Hill, K.E. Regulation of Selenium Metabolism and Transport. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2015, 35, 109–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Skalicky, M.; Brestic, M.; Maitra, S.; Sarkar, S.; Ahmad, Z.; Vemuri, H.; Garai, S.; Mondal, M.; Bhatt, R.; et al. Selenium Biofortification: Roles, Mechanisms, Responses and Prospects. Molecules 2021, 26, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryukov, G.V.; Castellano, S.; Novoselov, S.V.; Lobanov, A.V.; Zehtab, O.; Guigó, R.; Gladyshev, V.N. Characterization of mammalian selenoproteomes. Science 2003, 300, 1439–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Y.; Zhang, L. Study Advances on Toxicity of Selenium. J. Prev. Med. Inf. 2012, 28, 216–218. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.T.; Liu, M.C.; Zhou, Y.B.; Wu, H.Y. Synthesis of Organoselenium Compounds with Elemental Selenium. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2021, 363, 5386–5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçükbay, F.Z.; Yazlak, H.; Karaca, I.; Sahin, N.; Tuzcu, M.; Cakmak, M.N.; Sahin, K. The effects of dietary organic or inorganic selenium in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) under crowding conditions. Aquac. Nutr. 2009, 15, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Yang, L.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Z. Associations between serum selenium and serum lipids in adolescents aged 12–19: A cross-sectional study. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. Organ Soc. Miner. Trace Elem. (GMS) 2024, 87, 127572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, P.Y.; Yan, Y.M.C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B.Q.; Chen, M.M.; Zhang, S.E.; Zhang, X.F. A comprehensive review on potential role of selenium, selenoproteins and selenium nanoparticles in male fertility. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raisbeck, M.F. Selenosis in ruminants. Vet. Clin. Food Anim. Pract. 2020, 36, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, L.S.A.L.d.; Campos, R.d.O.; Braga Filho, J.d.S.; Jesus, J.d.S.d.; Ramos, H.E.; Anunciação, S.M.; Cassemiro, J.F.; Rende, P.R.F.; Hecht, F. Selenium nutritional status and thyroid dysfunction. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 69, e230348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, J.O. Chapter 32-Selenium. In Veterinary Toxicology, 4th ed.; Gupta, R.C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonego, J.M.; de Diego, S.I.; Szajnman, S.H.; Gallo-Rodriguez, C.; Rodriguez, J.B. Organoselenium Compounds: Chemistry and Applications in Organic Synthesis. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202300030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.Q.; Duan, A.L.; Ng, K. Selenosugar, selenopolysaccharide, and putative selenoflavonoid in plants. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Gupta, S. An Overview of Selenium Uptake, Metabolism, and Toxicity in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavon, M.; Pilon-Smits, E.A.H. Selenium Biofortification and Phytoremediation Phytotechnologies: A Review. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Xing, Y.; Li, A.M.; Liang, P.X.; Jiang, Z.P.; Liu, Y.X.; Huang, D.L. Enhancing selenium biofortification: Strategies for improving soil-to-plant transfer. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2024, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Han, C.; Liu, W.J.; Fan, G.C.; Zhang, H.; Lei, Z.; Hu, C.X.; Zhao, X.H. Selenium: The Toxicant for Pathogen and Pest but the Guardian of Soil and Crop. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 11495–11514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.J. Selenium accumulation by plants. Ann. Bot. 2015, 117, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danso, O.P.; Asante-Badu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Song, J.; Wang, Z.; Yin, X.; Zhu, R. Selenium Biofortification: Strategies, Progress and Challenges. Agriculture 2023, 13, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbert, Z.; Molnár, Á.; Feigl, G.; Van Hoewyk, D. Plant selenium toxicity: Proteome in the crosshairs. J. Plant Physiol. 2019, 232, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.K.; Dinh, Q.T.; Qi, M.X.; Wang, M.; Yang, W.X.; Zhou, F.; Liang, D.L. Radicular and foliar uptake, and xylem- and phloem-mediated transport of selenium in maize (Zea mays L.): A comparison of five Se exogenous species. Plant Soil 2020, 446, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garousi, F. The essentiality of selenium for humans, animals, and plants, and the role of selenium in plant metabolism and physiology. Acta Univ. Sapientiae Aliment. 2017, 10, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, E.; Vanhaecke, F.; Cornelis, R. Selenium speciation from food source to metabolites: A critical review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 1304–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari, S.; Salinitro, M.; Simoni, A.; Ciavatta, C.; Tassoni, A. Foraging for selenium: A comparison between hyperaccumulator and non-accumulator plant species. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Liang, X.; Nong, K.; Gong, Z.; Qin, T.; Qin, X.; Wang, D.; Zhu, Y. Advances in Research on the Toxicological Effects of Selenium. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Moscoso, M.; González-García, Y.; Pérez-Hernández, H.; Juárez-Maldonado, A. Scope of Nanomaterials in Phytoremediation Actions of Agricultural Crops. In Nanomaterials in Agroforestry Systems; Jabborova, D., Sarkar, D.S.R., Datta, R., Singh, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2025; pp. 345–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Y.Q.; Li, K.; Wan, Y.N.; Wang, Q.; Zhuang, Z.; Guo, Y.B.; Li, H.F. Uptake, translocation and biotransformation of selenium nanoparticles in rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.). J. Nanobiotechnology 2020, 18, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, N.; Zhong, L.; Hao, L.H.; Luan, C.Z.; Li, X.R. Speciation of Selenium in Enriched Garlic Sprouts by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Lett. 2015, 48, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, S.J.; Yuan, Y.X.; Faquin, V.; Guilherme, L.R.G.; Li, L. Evaluation of Genotypic Variation of Broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. italic) in Response to Selenium Treatment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3657–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Fang, Q.; He, P.; Tu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, B. Unveiling the potential of selenium-enriched tea: Compositional profiles, physiological activities, and health benefits. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 145, 104356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Byrne, P.F.; Pilon-Smits, E.A.H. Mapping quantitative trait loci associated with selenate tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 2006, 170, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sors, T.G.; Ellis, D.R.; Na, G.N.; Lahner, B.; Lee, S.; Leustek, T.; Pickering, I.J.; Salt, D.E. Analysis of sulfur and selenium assimilation in Astragalus plants with varying capacities to accumulate selenium. Plant J. 2005, 42, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallenberg, M.; Olm, E.; Hebert, C.; Björnstedt, M.; Fernandes, A.P. Selenium compounds are substrates for glutaredoxins: A novel pathway for selenium metabolism and a potential mechanism for selenium-mediated cytotoxicity. Biochem. J. 2010, 429, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barillas, J.R.V.; Quinn, C.F.; Pilon-Smits, E.A.H. Selenium accumulation in plants-phytotechnological applications and ecological implications. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2011, 13, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, L.J.; Sun, X.D.; Zhang, M.Y.; Duan, J.L.; Xiao, F.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, F.P.; Kong, X.P.; Ding, Z.J.; et al. Incorporation of Selenium Derived from Nanoparticles into Plant Proteins in Vivo. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 15847–15856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Dato, C.; Gianfrilli, D.; Greco, E.; Astolfi, M.; Canepari, S.; Lenzi, A.; Isidori, A.M.; Giannetta, E. Profiling of selenium absorption and accumulation in healthy subjects after prolonged L-selenomethionine supplementation. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2017, 40, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minich, W.B. Selenium Metabolism and Biosynthesis of Selenoproteins in the Human Body. Biochemistry 2022, 87, S168–S177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, R.F.; Hill, K.E. Selenoprotein P: An extracellular protein with unique physical characteristics and a role in selenium homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2005, 25, 215–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.Y.; Alfulaij, N.; Berry, M.J.; Seale, L.A. From Selenium Absorption to Selenoprotein Degradation. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 192, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairweather-Tait, S.J.; Bao, Y.; Broadley, M.R.; Collings, R.; Ford, D.; Hesketh, J.E.; Hurst, R. Selenium in Human Health and Disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 1337–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genchi, G.; Lauria, G.; Catalano, A.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Carocci, A. Biological activity of selenium and its impact on human health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, B.; Akanksha, A.; Kaur, P.S.; Gupta, S. Understanding selenoproteins: Structural insights, biological functions and transformative applications in therapeutics. Process Biochem. 2025, 150, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Maria, M.B.; Lamarche, J.; Ronga, L.; Messori, L.; Szpunar, J.; Lobinski, R. Selenol (-SeH) as a target for mercury and gold in biological systems: Contributions of mass spectrometry and atomic spectroscopy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 474, 214836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, Y.; Yamazaki, H.; Nishimura, K.; Nomura, M.; Shigehiro, T.; Suzuki, T.; Zang, W.; Tatara, Y.; Ito, H.; Hayashi, Y.; et al. Selenoprotein-mediated redox regulation shapes the cell fate of HSCs and mature lineages. Blood 2025, 145, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah; Wani, K.I.; Hayat, K.; Naeem, M.; Aftab, T. Multifaceted role of selenium in plant physiology and stress resilience: A review. Plant Sci. 2025, 355, 112456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.J. Selenium metabolism in plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 2333–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, H.; Xiang, J.; Yin, H.; Hou, T. Selenium-Containing Proteins/Peptides from Plants: A Review on the Structures and Functions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 15061–15073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladyshev, V.N.; Arnér, E.S.; Berry, M.J.; Brigelius-Flohé, R.; Bruford, E.A.; Burk, R.F.; Carlson, B.A.; Castellano, S.; Chavatte, L.; Conrad, M.; et al. Selenoprotein Gene Nomenclature. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 24036–24040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Roh, Y.J.; Han, S.-J.; Park, I.; Lee, H.M.; Ok, Y.S.; Lee, B.C.; Lee, S.-R. Role of Selenoproteins in Redox Regulation of Signaling and the Antioxidant System: A Review. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mita, Y.; Nakayama, K.; Inari, S.; Nishito, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Sakai, N.; Sotani, K.; Nagamura, T.; Kuzuhara, Y.; Inagaki, K.; et al. Selenoprotein P-neutralizing antibodies improve insulin secretion and glucose sensitivity in type 2 diabetes mouse models. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schomburg, L.; Orho-Melander, M.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; Melander, O. Selenoprotein-P Deficiency Predicts Cardiovascular Disease and Death. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solovyev, N.; Drobyshev, E.; Bjorklund, G.; Dubrovskii, Y.; Lysiuk, R.; Rayman, M.P. Selenium, selenoprotein P, and Alzheimer’s disease: Is there a link? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 127, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Fan, B.; Lei, N.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tong, L.; Wang, F.; Maesen, P.; Blecker, C. Selenium Biofortification of Soybean Sprouts: Effects of Selenium Enrichment on Proteins, Protein Structure, and Functional Properties. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 849928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Gao, J.; Hogenkamp, A.; Knippels, L.M.J.; Garssen, J.; Bai, J.; Yang, A.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H. Selenium-Enriched Soy Protein Has Antioxidant Potential via Modulation of the NRF2-HO1 Signaling Pathway. Foods 2021, 10, 2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Farooq, M.U.; Zhang, G.; Tang, Z.C.; Zheng, T.D.; Su, Y.; Hussain, S.; Liang, Y.K.; Ye, X.Y.; Jia, X.M.; et al. Dissecting the Potential of Selenoproteins Extracted from Selenium-Enriched Rice on Physiological, Biochemical and Anti-Ageing Effects In Vivo. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 196, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Cao, H.; Wu, Q.; Mao, K.; Yang, X.; Su, J.; Zhang, H. Agronomic and Genetic Strategies to Enhance Selenium Accumulation in Crops and Their Influence on Quality. Foods 2023, 12, 4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Rao, S.; Chen, Q.W.; Zhang, W.W.; Cheng, S.Y.; Cong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Xu, F. Research Progress on the Effects of Selenium on the Growth and Quality of Tea Plants. Plants 2022, 11, 2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somagattu, P.; Chinnannan, K.; Yammanuru, H.; Reddy, U.K.; Nimmakayala, P. Selenium dynamics in plants: Uptake, transport, toxicity, and sustainable management strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 175033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Sandoval, S.N.; Jiménez-Rodríguez, A.; Hernández-Pérez, J.; Chavez-Santoscoy, R.A.; Guardado-Félix, D.; Antunes-Ricardo, M. Selenized Chickpea Sprouts Hydrolysates as a Potential Anti-Aging Ingredient. Molecules 2023, 28, 3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.P.; He, Z.K.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, L.; Yin, C.Y.; Zhang, N.; Lin, J.; Zhao, H. Selenization of ovalbumin by dry-heating in the presence of selenite: Effect on protein structure and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2014, 148, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.P.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X.Y.; Huang, R.; Enomoto, H.; He, Z.K.; Li, C.P. Characteristics and Enhanced Antioxidant Activity of Egg White Protein Selenized by Dry-Heating in the Presence of Selenite. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 3131–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; He, H.; Hou, T. Molecular mechanisms of selenium-biofortified soybean protein and polyphenol conjugates in protecting mouse skin damaged by UV-B. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 3563–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanza, M.; dos Reis, A.R. Roles of selenium in mineral plant nutrition: ROS scavenging responses against abiotic stresses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 164, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, H.C.; Li, H.; Ying, Z.W.; Liu, X.Q. Research progress on separation of selenoproteins/Se-enriched peptides and their physiological activities. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 1390–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeler, J.C.; Weerapana, E. Chemical-Biology Approaches to Interrogate the Selenoproteome. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2832–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlivan, Ö.; Waliczek, M.; Kijewska, M.; Stefanowicz, P. Selenium in Peptide Chemistry. Molecules 2023, 28, 3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Chotana, G.A.; Faisal, A.; Saleem, R.S.Z. Chemical Synthesis of Selenium-containing Peptides. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2023, 23, 1090–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.Y.; Huang, Y.T.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.F.; Liu, L.Y.; Wang, L.L.; Tong, L.T.; Wang, F.Z.; Fan, B. A Review of Plant Selenium-Enriched Proteins/Peptides: Extraction, Detection, Bioavailability, and Effects of Processing. Molecules 2023, 28, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.T.; He, X.D.; Zhang, J.X.; Liu, G.Y.; Xu, X. A review on selenium-enriched proteins: Preparation, purification, identification, bioavailability, bioactivities and application. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 5498–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.D.; Zhang, Y.; Cong, X.; Huang, D.J.; Yu, R.P.; Chen, S.W.; Zhu, S. Protective effect of selenium-enriched protein from Cardamine violifolia digestion products on PC12 cells injury induced by Aβ1-42. Food Biosci. 2025, 68, 106492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.Y.; Fan, B.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.F.; Wang, X.R.; Fei, C.X.; Tong, L.T.; Wang, F.Z.; Huang, Y.T. Effects of different drying methods on the structure, bioaccessibility, and bioavailability of selenium-enriched peptides from soybean sprouts. Food Chem. 2025, 468, 142442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.Q.; Ji, Y.; Ma, G.X.; Xu, J.; Hu, Q.H. Identification and preparation of selenium-containing peptides from selenium-enriched Pleurotus eryngii and their protective effect on lead-induced oxidative damage in NCTC1469 hepatocytes. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 4522–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Du, C.D.; Yu, T.; Cong, X.; Liu, Y.F.; Chen, S.W.; Li, Y. Antioxidant Activity of Selenium-Enriched Peptides from the Protein Hydrolysate of Cardamine violifolia. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 3504–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yang, W.; Lin, Y.; Du, C.; Huang, D.; Chen, S.; Yu, T.; Cong, X. Antioxidant and anti-fatigue activities of selenium-enriched peptides isolated from Cardamine violifolia protein hydrolysate. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 79, 104412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Guo, J.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z.Z.; Cheng, S.Y.; Cong, X. Protective effects of selenium-enriched peptides from Cardamine violifolia on D-galactose-induced brain aging by alleviating oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and neuron apoptosis. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ding, J.; Shi, Y.; Fang, Y.; Li, P.; Fan, F.; Zhao, E.; Sun, X.; Shen, X.; Hu, Q. Inhibition of immunotoxicity of Pb2+-induced RAW264.7 macrophages by selenium species in selenium-enriched rice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 148, 111943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhao, E.M.; Shi, Y.; Shen, X.C.; Wu, J.; Pei, F.; Hu, Q.H.; Qiu, W.F. Isolation and identification of immunomodulatory selenium-containing peptides from selenium-enriched rice protein hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, P.; Shi, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Fan, F.J.; Pei, F.; Xia, J.; Xie, M.H.; Hu, Q.H. Neuroprotective effects of two selenium-containing peptides, TSeMMM and SeMDPGQQ, derived from selenium-enriched rice protein hydrolysates on Pb2+-induced oxidative stress in HT22 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 135, 110932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Li, H.; Chen, X.W.; Liu, W.L.; Liu, X.Q. Antioxidant activity of SSeCAHK in HepG2 cells: A selenopeptide identified from selenium-enriched soybean protein hydrolysates. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 33872–33882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H. Preparation and Anti-Fatigue Function of Selenium-Rich Soybean Oligopeptide. J. Chin. Cereals Oils 2021, 36, 46–50+58. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.W.; Hou, T.; Shi, W.; Guo, D.J.; He, H. Hepatoprotective effects of selenium-biofortified soybean peptides on liver fibrosis induced by tetrachloromethane. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 50, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Hou, T.; Zhang, Y.; He, H. Structural Identification of Seleno-peptides and Seleno-amino Acids in Se-enriched Corn Protein Hydrolysates. Food Sci. 2013, 34, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.J.; He, H.; Hou, T. Selenium-biofortified corn peptides: Attenuating concanavalin A-Induced liver injury and structure characterization. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2019, 51, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.Y.; Zhang, J.T.; Li, G.M.; Cai, M.Y.; Lu, J.; Gu, R.Z.; Liu, W.Y. Selenium-chelating corn oligopeptide as a potential antioxidant supplement: Investigation of the protein conformational changes and identification of the antioxidant fragment composition. Int. J. Food Eng. 2020, 16, 20190166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.-Y.; Zhang, J.-T.; Li, G.-M.; Zhou, M.; Gu, R.-Z.; Lu, J.; Liu, W.-Y. Structure and composition of a potential antioxidant obtained from the chelation of pea oligopeptide and sodium selenite. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Miao, J.; Ye, H.; Xia, Z.; Huang, W.; Guo, J.; Liang, X.; Yin, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Cao, Y. Purification, Identification, and Mechanistic Investigation of Novel Selenium-Enriched Antioxidant Peptides from Moringa oleifera Seeds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 4625–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.X.; Du, M.K.; Wu, M.R.; Yue, P.X.; Yang, X.F.; Wei, X.L.; Wang, Y.F. Preparation, physicochemical characterization and identification of two novel mixed ACE-inhibiting peptides from two distinct tea alkali-soluble protein. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 1483–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, B.W.; Ming, J.J.; Wang, L.L.; Xu, C.F.; Xiao, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.; Shang, L.C. Selenium Modification of Natural Products and Its Research Progress. Foods 2023, 12, 3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Wei, W.; He, S.; Chen, L. Progress of the Source and Biological Activities of Plant-derivedSelenium-containing Peptides. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2024, 45, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, N.; Liu, Y.H.; Xiong, X.; Kim, K.; Wu, Z.H.; Bravo, D.M.; Blanchard, A.; Ji, P. Organic selenium supplement partially alleviated diquat-induced oxidative insults and hepatic metabolic stress in nursery pigs. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 124, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Lin, W.; Yang, X.Q.; Su, D.X.; He, S.; Nag, A.; Zeng, Q.Z.; Yuan, Y. Development, characterization and in vitro bile salts binding capacity of selenium nanoparticles stabilized by soybean polypeptides. Food Chem. 2022, 391, 133286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.R.; Zhao, L.Y.; Shen, Q.S.; Qi, L.W.; Jiang, S.; Guo, Y.J.; Zhang, C.H.; Richel, A. Preparation of cattle bone collagen peptides-calcium chelate and its structural characterization and stability. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 144, 111264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.W.; Wu, X.P.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, S.Y. Organic selenium derived from chelation of soybean peptide-selenium and its functional properties in vitro and in vivo. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 4761–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, J.; Greiner, A.; Drexler, H.; Göen, T. Determination of eleven small selenium species in human urine by chromatographic-coupled ICP-MS methods. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 61, 126519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajin, B.; Kuehnelt, D.; Jensen, K.B.; Francesconi, K.A. Investigating the intra-individual variability in the human metabolic profile of urinary selenium. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2016, 37, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busto, M.E.D.; Ward-Deitrich, C.; Evans, S.O.; Rayman, M.P.; Jameson, M.B.; Goenaga-Infante, H. Selenium speciation studies in cancer patients to evaluate the responses of biomarkers of selenium status to different selenium compounds. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 2835–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.W.; Liu, K.L. Selenium-Polysaccharide: Structural and Physical Characterization, Bioactivities and Application. Food Rev. Int. 2024, 40, 3291–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wei, X. Extraction, characterization and antioxidant activities of Se-enriched tea polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 77, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Chen, L.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X. Antitumor activity of Se-containing tea polysaccharides against sarcoma 180 and comparison with regular tea polysaccharides and Se-yeast. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, N.W.; Shi, X.L.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, L.M.; Wang, D.Y.; Yang, X.B. Inhibitory Effects and Molecular Mechanisms of Selenium-Containing Tea Polysaccharides on Human Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.Z.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wen, Y.H.; Li, L.H.; Zheng, L.H. Tumoricidal effects of a selenium (Se)-polysaccharide from Ziyang green tea on human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.N.; Zhao, P.G.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.P.; Qi, C.; Liu, Y.L. Preparation of Two Organoselenium Compounds and Their Induction of Apoptosis to SMMC-7221 Cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 154, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.N.; Chen, H.; Li, W.T.; He, Q.; Liang, J.Y.M.; Yan, X.H.; Yuan, Y.H.; Yue, T.L. Selenium-containing tea polysaccharides ameliorate DSS-induced ulcerative colitis via enhancing the intestinal barrier and regulating the gut microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wei, X.; Li, Z.; Hu, Z.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yue, T.; Yuan, Y. Characterization of selenium-containing polysaccharides isolated from selenium-enriched tea and its bioactivities. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.G.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.F.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.W.; Xu, J.N.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhou, K.; Gao, P.Y.; Li, D.Q. Selenium-containing polysaccharides isolated from Rosa laevigata Michx fruits exhibit excellent anti-oxidant and neuroprotective activity in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, A.N.; Li, W.T.; Zhao, Y.N.; Ju, H.M.; Xu, S.; Zhao, S.Y.; Yue, T.L.; Yuan, Y.H. Purification, characterization and antioxidant activity of selenium-containing polysaccharides from pennycress (Thlaspi arvense L.). Carbohydr. Res. 2022, 512, 108498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.-Y.; Lin, Y.-R.; Li, L.-Y.; Tang, Z.-M.; Zhao, X.-H.; Shi, J. In Vitro Immunomodulation of the Polysaccharides from Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) in Response to a Selenylation of Lower Extent. Foods 2021, 10, 2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.-M.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, T.-T.; Li, J.; Zhu, M.-M.; Liu, C.-Y.; Yang, Y.-J.; Jia, X.-B.; Feng, L. Synthesis, characterization, and immunological activity of Rehmannia glutinosa seleno-polysaccharides. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi = Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi = China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2022, 47, 2938–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-K.; Choi, Y.-R.; Park, J.; Jung, S.K.; Chang, Y.H. The characterization, selenylation and anti-inflammatory activity of pectic polysaccharides extracted from Ulmus pumila L. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.H.; Li, S.H.; Zhou, G.Q.; Wang, S.X.; Zhang, J.C. Extraction, selenylation modification and antitumor activity of the glucan from Castanea mollissima Blume. Glycoconj. J. 2017, 34, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, K.X.; Zhu, X.Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, G.; Gu, X.L. Selenylation modification: Enhancement of the antioxidant activity of a Glycyrrhiza uralensis polysaccharide. Glycoconj. J. 2018, 35, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Hu, J.; Liu, S.; Guo, S.; Jia, Y.; Li, M.; Kong, W.; Liang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Synthesis of Se-polysaccharide mediated by selenium oxychloride: Structure features and antiproliferative activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 246, 116545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.Z.; Chen, J.; Qiu, S.L.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, D.Y.; Liu, C.; Li, X.P.; Hou, R.R.; Yue, C.J.; Liu, J.; et al. Optimization of selenylation modification for garlic polysaccharide based on immune-enhancing activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, R.; Ji, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, M.; Li, J. The characterization of optimal selenized garlic polysaccharides and its immune and antioxidant activity in chickens. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Yang, X.Q.; Kou, M.; Lu, C.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Peng, J.; Chen, P.; Jiang, J.H. Selenylation of Polysaccharide from the Sweet Potato and Evaluation of Antioxidant, Antitumor, and Antidiabetic Activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.Y.; Bian, J.; Xu, S.S.; Liu, C.F.; Sun, Y.Q.; Zhang, G.L.; Li, D.Q.; Liu, X.G. Structural features, selenization modification, antioxidant and anti-tumor effects of polysaccharides from alfalfa roots. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Wang, X.; Xiu, W.Y.; Ma, Y.Q. Characteristics of selenium polysaccharide from sweet corncob and its effects on non-enzymatic glycosylation in vivo. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2022, 65, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yu, C.; Han, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y. Comparative analysis of existence form for selenium and structural characteristics in artificial selenium-enriched and synthetic selenized green tea polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raics, M.; Balogh, A.K.; Kishor, C.; Timari, I.; Medrano, F.J.; Romero, A.; Go, R.M.; Blanchard, H.; Szilagyi, L.; Kover, K.E.; et al. Investigation of the Molecular Details of the Interactions of Selenoglycosides and Human Galectin-3. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.M.; Bai, J.W.; Bu, X.Y.; Yin, Y.T.; Wang, L.B.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.Q. Characterization of selenized polysaccharides from Ribes nigrum L. and its inhibitory effects on α-amylase and α-glucosidase. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 259, 117729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Yu, C.; Wang, H.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y. Comparison and structural characterization of polysaccharides from natural and artificial Se-enriched green tea. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Liang, P.X.; Xing, Y.; Yao, Z.F.; Chen, J.P.; Pan, L.P.; Deng, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.X.; Huang, D.L. Optimizing Selenium Application for Enhanced Quality and Nutritional Value of Spring Tea (Camellia sinensis). Horticulturae 2025, 11, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yan, D.N.; Chen, Q.Y.; Peng, H.Y.; Jin, L.; Feng, C.; Zhang, L.X.; Zhao, G.M.; Yang, D.P.; Zhao, Z.M. Modification of a O-acetyl-glucomannan from Dendrobium officinale by selenylation modification and its anti-gastric cancer enhancing activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 295, 138852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhang, T. Preparation on the Seleno-polysaccharides from Infructescence of Platycarya Strobilacea via Microwave Assisted Method. Guangdong Chem. Ind. 2019, 46, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Cheng, H.; Chen, L.; Zhan, X.; Xia, W. Synthesis, characterization, and biological evaluation of novel selenium-containing chitosan derivatives. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 284, 119185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, C.M.C.; Pérez de la Lastra, J.M.; Juan, C.A.; Plou, F.J.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. Antioxidant Metabolism Pathways in Vitamins, Polyphenols, and Selenium: Parallels and Divergences. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentkowska, A.; Pyrzynska, K. Investigation of antioxidant activity of selenium compounds and their mixtures with tea polyphenols. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 3019–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.F.; Chang, T.C.; Chiang, C.C.; Tsai, C.J.; Hsu, L.Y. Synthesis of selenium-containing polyphenolic acid esters and evaluation of their effects on antioxidation and 5-lipoxygenase inhibition. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 53, 1402–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Jia, W.; Du, A.; Xia, Z.; Kang, J.; Xue, L.; Sun, Y.; Shi, L. Discovery of Se-containing flavone in Se-enriched green tea and the potential application value in the immune regulation. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, N.; Wensheng, Z.; Jinchao, W.; Youhua, X. Phytochemistry, biological function and metabolism of Seleno-flavonoids. J. Food Bioact. 2025, 29, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Guan, M.; Ma, H.; Dong, X.; Feng, J.; Zhang, T.; Wei, Y. Gallic acid-selenium nanoparticles with dual anti-inflammatory and antioxidant functions for synergistic treatment of acute kidney injury. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2024, 62, 102775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Xu, W.; Chen, L.; He, J.; Cheng, S.; Cai, J. Selenium Nanoparticles Synergistically Stabilized by Starch Microgel and EGCG: Synthesis, Characterization, and Bioactivity. Foods 2023, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, I.L.; Charneira, C.; Gandin, V.; da Silva, J.L.F.; Justino, G.C.; Telo, J.P.; Vieira, A.; Marzano, C.; Antunes, A.M.M. Selenium-Containing Chrysin and Quercetin Derivatives: Attractive Scaffolds for Cancer Therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4250–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.X.; Hou, G.Q.; Mei, S.Q.; Gao, X.X.; Zhang, C.; Shang, L.C.; Chen, S. Structural Characterization and Bioactivity Evaluation of Selenium-Modified Dihydromyricetin from Vine Tea. Foods 2025, 14, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-x.; Zhang, P. Synthesis of vitamin–selenium complex and its effects on proteins and tumor cells. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 83, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.X.; Chen, K.S. Biophysical Studies on the Site-Selective Binding of a Synthesized Selenium-Quercetin Complex on a Protein. J. Solut. Chem. 2012, 41, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorito, S.; Epifano, F.; Marchetti, L.; Genovese, S. Semisynthesis of Selenoauraptene. Molecules 2021, 26, 2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Wang, Z.; Lai, J.; Liang, Y.; Qian, K. The Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles and Their Applications in Enhancing Plant Stress Resistance: A Review. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, R.; Jin, H. Synthesis, characterizations, properties, modifications and applications of zero-dimensional monoelemental selenium nanomaterials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2025, 535, 216626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, S.; Sultan, R.M.S.; Saxena, K.; Bano, F.; Goyal, R.; Chopra, S.; Chopra, H.; Verma, S.K. Nano Selenium: A Promising Solution for Infectious Diseases—Current Status and Future Prospects. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2025, 31, 2795–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.; Javed, B.; Raja, N.I.; Mashwani, Z.U.R. Biomedical Potential of Plant-Based Selenium Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review on Therapeutic and Mechanistic Aspects. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, S.; Sunderam, V.; Manjusha, M.; Dlamini, Z.; Lawrance, A.V. Selenium Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Examination of Synthesis Techniques and Their Diverse Applications in Medical Research and Toxicology Studies. Molecules 2024, 29, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, N.; Phalswal, P.; Khanna, P.K. Selenium nanoparticles: A review on synthesis and biomedical applications. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 1415–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghazaly, M.A.; Fadel, N.; Rashed, E.; El-Batal, A.; Kenawy, S.A. Anti-inflammatory effect of selenium nanoparticles on the inflammation induced in irradiated rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 95, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.A.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.; Reynolds, E.C.; Pantarat, N.; Biswas, D.P.; O’Connor, A.J. Low cytotoxic trace element selenium nanoparticles and their differential antimicrobial properties against S-aureus and E-coli. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 045101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, F.G.; Moreno-Martin, G.; Pescuma, M.; Madrid-Albarrán, Y.; Mozzi, F. Biotransformation of Selenium by Lactic Acid Bacteria: Formation of Seleno-Nanoparticles and Seleno-Amino Acids. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Wang, Q.Q.; Dai, F.J.; Li, H.F. Reduction of selenite to selenium nanospheres by Se(IV)-resistant Lactobacillus paralimentarius JZ07. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lashani, E.; Moghimi, H.; Turner, R.J.; Amoozegar, M.A. Characterization and biological activity of selenium nanoparticles biosynthesized by Yarrowia lipolytica. Microb. Biotechnol. 2024, 17, e70013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulla, N.A.; Otari, S.V.; Bohara, R.A.; Yadav, H.M.; Pawar, S.H. Rapid and size-controlled biosynthesis of cytocompatible selenium nanoparticles by Azadirachta indica leaves extract for antibacterial activity. Mater. Lett. 2020, 264, 127353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrzynska, K. Plant Extracts for Production of Functionalized Selenium Nanoparticles. Materials 2024, 17, 3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagime, P.V.; Pandey, V.K.; Rajpal, C.; Jayeoye, T.J.; Kumar, A.; Chidrawar, V.R.; Singh, S. Biogenic selenium nanoparticles: A comprehensive update on the multifaceted application, stability, biocompatibility, risk, and opportunity. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsafran, M.; Razavi, M.M.; Rizwan, M.; Usman, K. A review on synthesis and characterization of selenium nanoparticles from plant extracts for applications in agriculture, biomedicine, and environment. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2025, 18, 2488237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Zalam, H.B.; El Denshary, E.E.D.; Abdalsalam, R.A.; Khalil, I.A.; Khattab, M.M.; Hamzawy, M.A. Revolutionizing Hyperlipidemia Treatment: Nanoencapsulated CoQ10 and Selenium Combat Simvastatin-Induced Myopathy and Insulin Resistance in Rats. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2024, 14, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alafari, H.A.; Albaqami, N.M.; Abd El-Aziz, Y.M.; Reyad, Y.A.; Eissa, E.-S.H.; Abdul Kari, Z.; Eissa, M.E.H.; Ibrahim, S.; Khan, S.; Munir, M.B.; et al. The effects of nano-selenium and/or vitamin C on the growth performance, blood health, organ histology, molecular alterations, and disease resistance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) against Saprolegnia ferax. Aquac. Int. 2024, 33, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, S.; Hashim, M.; Imran, M.; Babur, S.; Adnan, S.; Hano, C.; Ibrahim, W.N. Selenium Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy: Unveiling Cytotoxic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Cancer Rep. 2025, 8, e70210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.-W.; Patel, K.D.; Kwak, J.-H.; Jun, S.-K.; Jang, T.-S.; Lee, S.-H.; Knowles, J.C.; Kim, H.-W.; Lee, H.-H.; Lee, J.-H. Selenium Nanoparticles as Candidates for Antibacterial Substitutes and Supplements against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardsadegh, B.; Vaghari, H.; Mohammad-Jafari, R.; Najian, Y.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H. Biosynthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activities assessment of fabricated selenium nanoparticles using Pelargonium zonale leaf extract. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Changzhe, C.; Junjie, Z.; Yue, Z.; Jingpeng, Z.; Anqi, J.; Yingjie, K.; Xijian, L.; Kefei, D.; and Wang, Q. Se@SiO2 nanocomposites attenuate doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through combatting oxidative damage. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anu, K.; Singaravelu, G.; Murugan, K.; Benelli, G. Green-Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles Using Garlic Cloves (Allium sativum): Biophysical Characterization and Cytotoxicity on Vero Cells. J. Clust. Sci. 2017, 28, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, V.; Loganathan, C.; Thayumanavan, P. Green synthesized selenium nanoparticle as carrier and potent delivering agent of s-allyl glutathione: Anticancer effect against hepatocarcinoma cell line (HepG2) through induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafavi, E.; Medina-Cruz, D.; Truong, L.B.; Kaushik, A.; Iravani, S. Selenium-based nanomaterials for biosensing applications. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 7742–7756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Zhai, Y.H.; Lu, W.H.; Jiang, X.H.; Zhou, J.S.; Wu, L.L.; Du, L.H.; Ou, C.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; He, H.L.; et al. ROS-sensitive PD-L1 siRNA cationic selenide nanogels for self-inhibition of autophagy and prevention of immune escape. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 41, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turck, D.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Kearney, J.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; Pelaez, C.; et al. Scientific opinion on the safety of selenite triglycerides as a source of selenium added for nutritional purposes to food supplements. Efsa J. 2020, 18, e06134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radomska, D.; Czarnomysy, R.; Radomski, D.; Bielawski, K. Selenium Compounds as Novel Potential Anticancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Han, Y.; Zhang, S.; Luo, Y.; Luo, K. Bioavailability of selenium and the influence of trace elements in crops grown in selenium-rich areas. Food Chem. 2025, 476, 143463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Zhang, M.; Adhikari, B. Advances in selenium-enriched foods: From the farm to the fork. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 76, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, T. Selenium transformation and selenium-rich foods. Food Biosci. 2021, 40, 100875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Liu, K. Selenium and selenoproteins: Their function and development of selenium-rich foods. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 7026–7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, J.; Jiang, J.; Cai, H.; Yang, F.; Jin, H.; Yang, P.; Cai, J.; Chen, Z.W. GE11 peptide conjugated selenium nanoparticles for EGFR targeted oridonin delivery to achieve enhanced anticancer efficacy by inhibiting EGFR-mediated PI3K/AKT and Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathways. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørklund, G.; Shanaida, M.; Lysiuk, R.; Antonyak, H.; Klishch, I.; Shanaida, V.; Peana, M. Selenium: An Antioxidant with a Critical Role in Anti-Aging. Molecules 2022, 27, 6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; Xu, G.; Lu, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Pan, X. Ultra-Fast Selenol-Yne Click (SYC) Reaction Enables Poly(selenoacetal) Covalent Adaptable Network Formation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202410245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, P.; Abidi, N.; Bergfeld, N.; Shashtri, M.; Reid, T.W. Selenium Bandages and Cotton Cloth That Kill Microorganisms in Wounds. Mil. Med. 2024, 189, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akor, F.O.; Edo, G.D.; Nelson, F.A.; Johnson, A.U.; Iyam, S.O.; Abubakar, M.N.; Gulack, A.O.; Ubah, C.B.; Ekpong, B.O.; Benjamin, I. Surface modification of graphene and fullerene with Sulfur (S), Selenium (Se), and Oxygen (O): DFT Simulation for enhanced zidovudine delivery in HIV treatment. BMC Chem. 2024, 18, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, M.S.; Pervez, M.M. Selenium as a Nutritional Shield in Viral Defense: A Narrative Review. Preprints 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huwiler, V.V.; Maissen-Abgottspon, S.; Stanga, Z.; Mühlebach, S.; Trepp, R.; Bally, L.; Bano, A. Selenium Supplementation in Patients with Hashimoto Thyroiditis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Thyroid 2024, 34, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, P.; Wei, J.; Lv, H.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Peng, X.; Rijntjes, E.; et al. Increased Incidence of Hashimoto Thyroiditis in Selenium Deficiency: A Prospective 6-Year Cohort Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e3603–e3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Cui, L.; Zhao, J.; Liao, L. Selenium and thyroid diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1133000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, C.B.; Winther, K.H.; Cramon, P.K.; Rasmussen, A.K.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U.; Knudsen, N.J.; Bjorner, J.B.; Schomburg, L.; Demircan, K.; Chillon, T.S.; et al. Selenium supplementation and placebo are equally effective in improving quality of life in patients with hypothyroidism. Eur. Thyroid J. 2024, 13, e230175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Qin, L.; Cao, J.H.; Zhang, L.P.; Liu, M.; Qu, C.F.; Miao, J.L. κ-Selenocarrageenan Oligosaccharides Prepared by Deep-Sea Enzyme Alleviate Inflammatory Responses and Modulate Gut Microbiota in Ulcerative Colitis Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alehagen, U.; Opstad, T.B.; Alexander, J.; Larsson, A.; Aaseth, J. Impact of Selenium on Biomarkers and Clinical Aspects Related to Ageing. A Review. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, K.; Guo, C.Y.; Zhu, J.X.; Wei, Y.; Wu, M.R.; Huang, X.D.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.D.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; et al. The Whitening, Moisturizing, Anti-aging Activities, and Skincare Evaluation of Selenium-Enriched Mung Bean Fermentation Broth. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 837168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Y.; Peng, C.; Weihong, L.; Cuiping, F.; Xiaowen, W.; Qiling, W. Synthesis of Nano-Selenium from Bombyx batryticatus Polypeptide and Exploring Its Antioxidant and Skin Whitening Ability. Molecules 2025, 30, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, S.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, B.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, H.; Siwakoti, P.; Qu, X.Y.; Ye, P.; He, Y.; Kumeria, T.; et al. Microneedle-mediated hypoxic extracellular vesicle-encapsulated selenium nanoparticles delivery to treat androgenetic alopecia. J. Control. Release 2025, 381, 113597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, T.; Emadi, N.; Barimani, S.; Kazeminejad, A. Serum Selenium Level in Patients with Genital Warts Compared to Healthy Individuals. J. Maz. Univ. Med. Sci. 2023, 33, 134–139. [Google Scholar]
- Abou Elmaaty, T.; Sayed-Ahmed, K.; Elsisi, H.; Ramadan, S.M.; Sorour, H.; Magdi, M.; Abdeldayem, S.A. Novel Antiviral and Antibacterial Durable Polyester Fabrics Printed with Selenium Nanoparticles (SeNPs). Polymers 2022, 14, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.A.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.; Palmer, J.A.; Bock, N.; Reynolds, E.C.; Webster, T.J.; Deva, A.; Morrison, W.A.; O’Connor, A.J. Selenium nanoparticles as anti-infective implant coatings for trauma orthopedics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and epidermidis: In vitro and in vivo assessment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4613–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
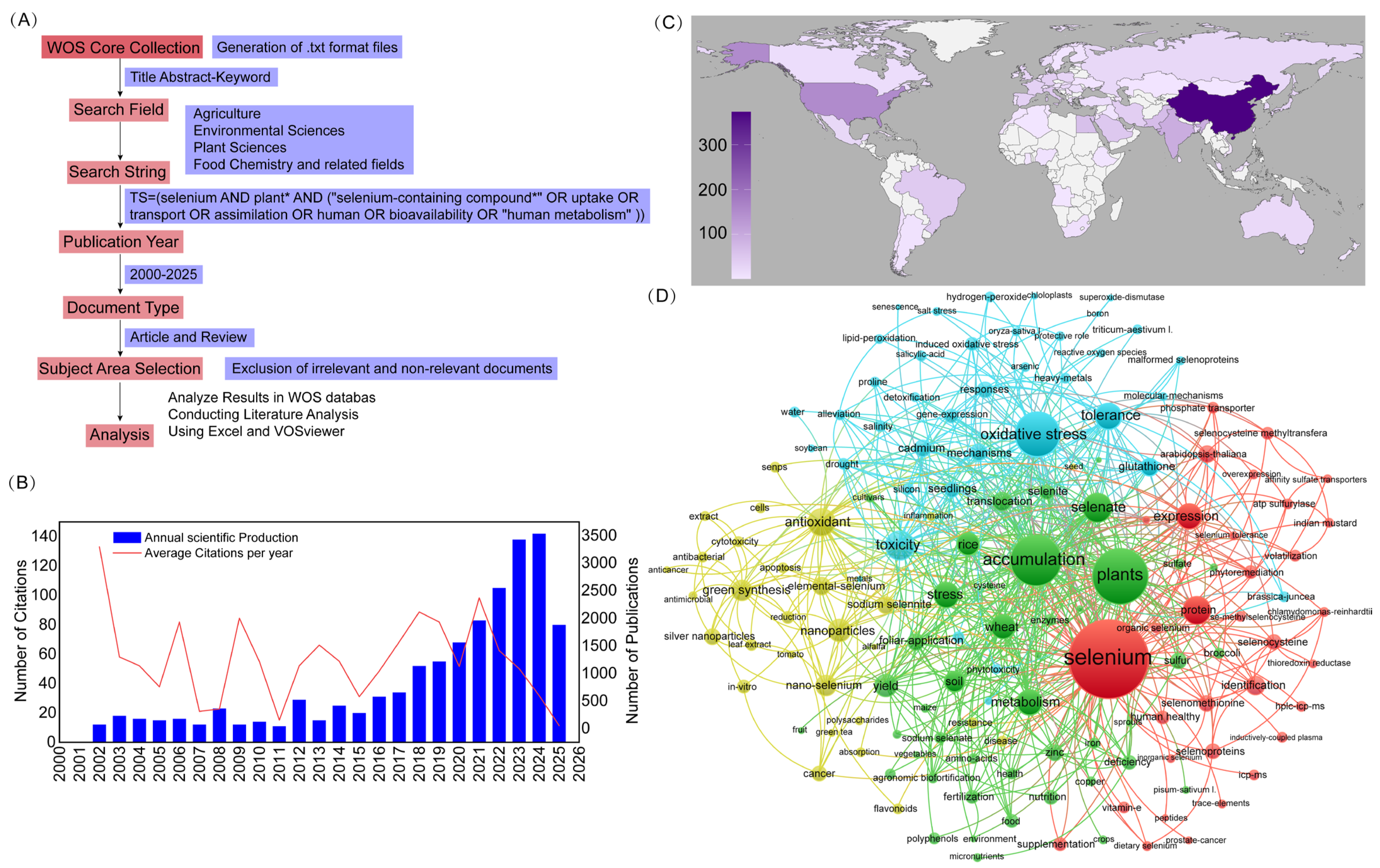
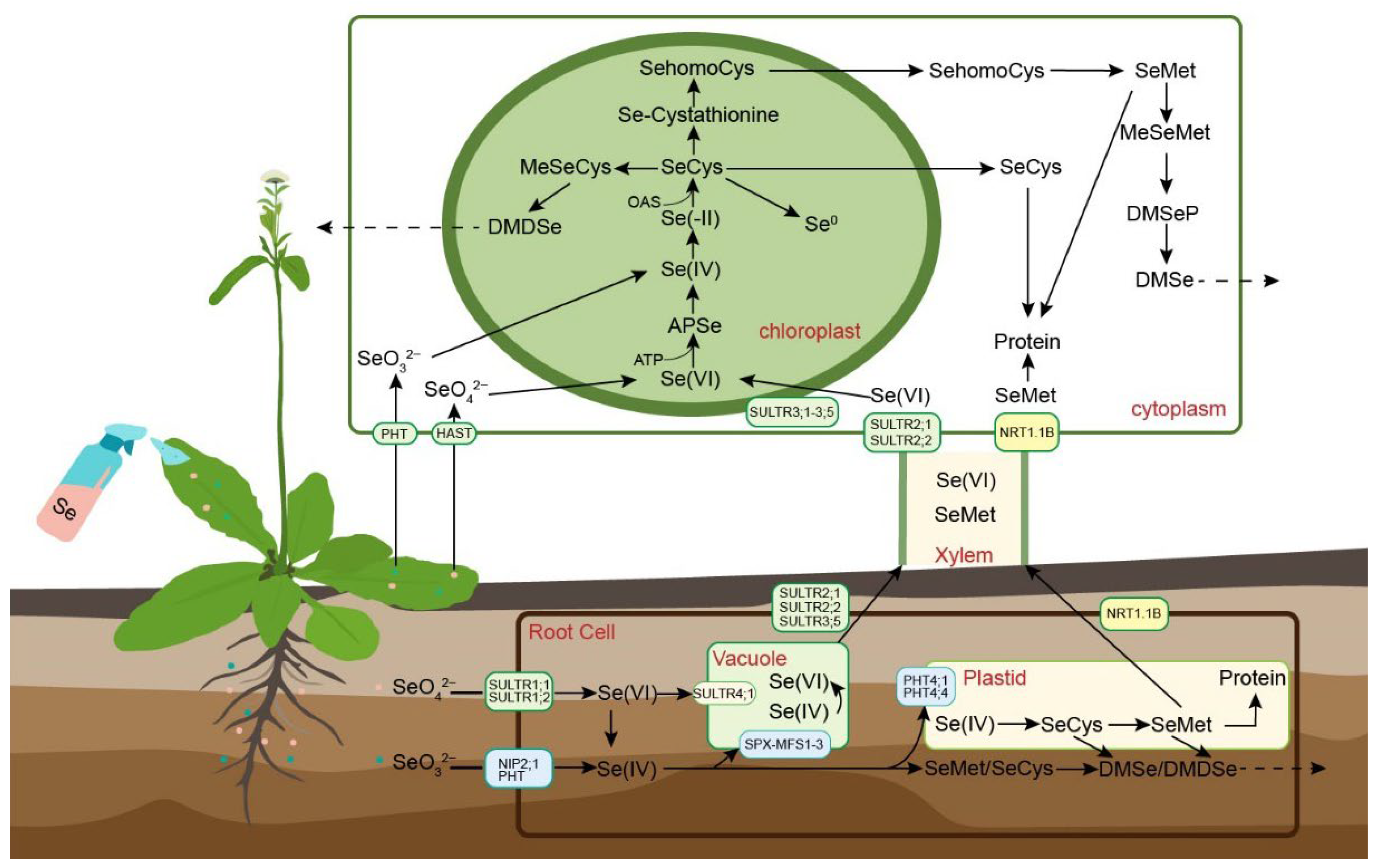
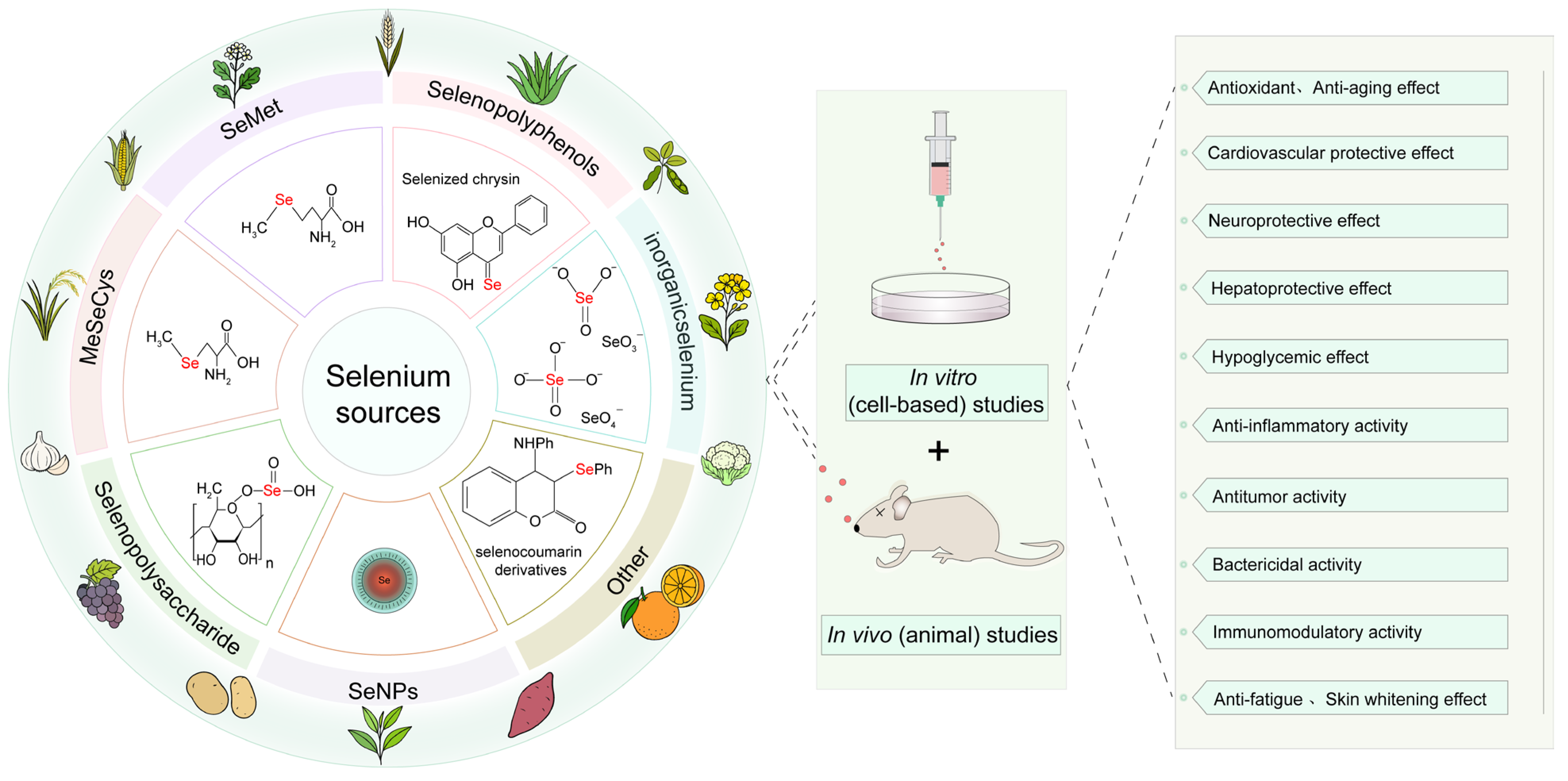
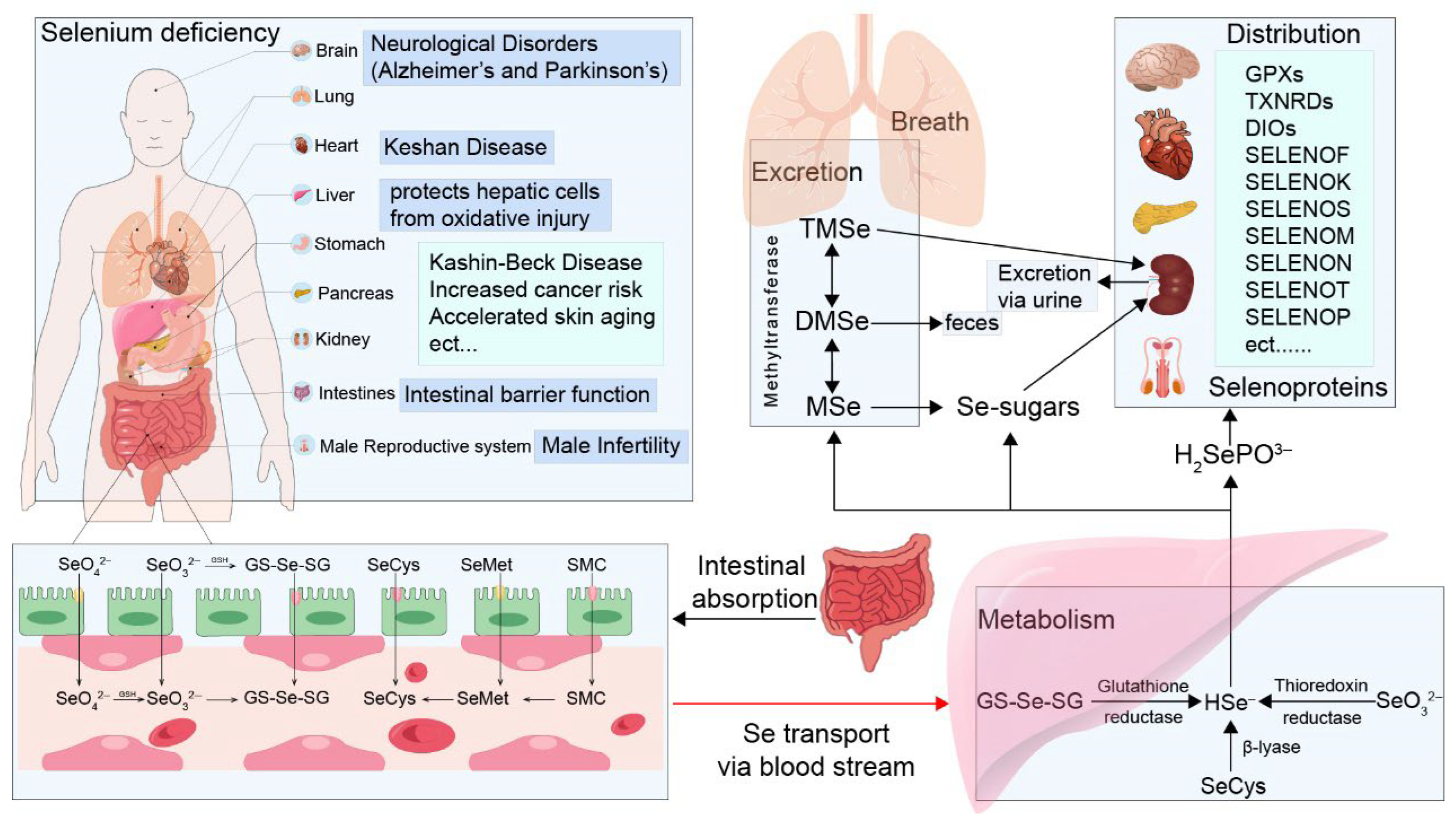
| Plant Source | Se Source | Selenium Speciation | Se Content (μg/kg) | Biological Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean | Artificial se-enriched | SeMet; MeSeCys; SeCys | 2882; 2035; 4301 | Antioxidant activity | [69] |
| Soy | Natural | / | 339.25 | Antioxidant activity | [70] |
| Rice | Natural | / | 22,010 ± 340 (Water-soluble protein); 8260 ± 400 (Alkali-soluble protein); 1670 ± 70 (Salt-soluble protein); 73 ± 130 (Alcohol-soluble protein) | Liver protection; Immunomodulatory effects; Anti-aging activity; Antioxidant activity | [71] |
| Plant Source | Se Source | Peptide Sequences | Selenium Speciation | Se Content in Se-Peptides(µg/g) | Biological Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardamine violifolia | Natural | GRVGSSSeC; GRAGGSYSeM; GHPNFKLNSeCGG; GTKSSeCKA; ASSNARDSeMI; TAGGSeCYIPI; MeSeCALQ | SeCys; SeMet; MeSeCys | 505 ± 22~2970 ± 16 (CPR1-15); | Antioxidant activity | [89] |
| Natural | YLPGSeMV; FSeCLVEST; VHTSeCPISeCTS; LLTMeSeCPA; SVIATISeMVP; SSeCSeCSPTP; KKSeCSL; CPQSMeSeK; NSeCVASPL; NLIVNSeMKN | SeMet; SeCys; MeSeCys | 2450 ± 80 (SPE); 914 ± 18 (SPE1); 1841 ± 24 (SPE2); 1987 ± 37 (SPE3); 3104 ± 55 (SPE4) | Antioxidant activity; anti-fatigue activity | [90] | |
| Artificial se-enriched | / | / | / | Protective effects against brain aging; alleviation of neuroinflammation; antioxidant activity | [91] | |
| Rice | Natural | SeMet-Pro-Ser; Met-MeSeCys-Glu; SeMet-MeSeCys-Glu | SeMet; MeSeCys; MeSeCys-Glu | 3.62 (SPHs); 0.875 ± 0.044~4.154 ± 0.049 (SPHs 1-4) | Immunomodulatory effects; anti-inflammatory activity; reduction of Pb2+-induced cytotoxicity | [92] |
| Rice | Natural | TSeMMM; SeMDPGQQ | SeMet | 8.95 ± 0.02~13.61 ± 0.01 (SPHA/N/T/P/F7) | Immunomodulatory effects; anti-inflammatory activity; antioxidant activity; neuroprotective effect | [93,94] |
| Soybean | Natural | SSeCAHK | SeCys | 110.4 (SSP) | Anti-fatigue activity; inhibition of lipid peroxidation | [95] |
| Soybean | Natural | / | SeCys; SeMet | 90.03 ± 3.23 | Anti-fatigue activity | [96] |
| Soybean | Artificial se-enriched | SeMVVSeC; SSeCRDCV; FI/LFSeCF; SeCI/LSSeC | SeCys | 21.78 ± 0.17 (SSPs) | Antioxidant activity; liver protection | [97] |
| Corn | Natural | SeMet-MeSe Cys-Glu; Met-MeSeCysGlu; MeSeCys-Glu-Asp; Ile-MeSeCys-Glu | SeMet; SeEt; γ-GluMeSeCys; MeSeCys; SeCys2 | 6.05 | Alcohol detoxification effect | [98] |
| Corn | Artificial se-enriched | FSeC; WSeMQE; WSeMKE; SeCYE; FMSeCM; SeCCAMSeC; FMSeCVQ; FMSeCVK | SeCys; SeMet; MeSeCys | 32.37 (SeCPs) | Antioxidant activity; inhibition of lipid peroxidation; liver protection | [99] |
| Corn | Artificial se-enriched | FLPPVTS; IGPRLPWPE; IIGGA; LLPPY | / | 428.95 (LLPPY) | Antioxidant activity | [100] |
| Pea | Artificial se-enriched | PPKIYP | Se4+ forms covalent bonds through coordination with-NH2 or -COOH groups. | 29.47 (PPKIYP) | Antioxidant activity | [101] |
| Moringa oleifera Seeds | Natural | FLSeML; mLSe- MAAL; mmLASeMMVL; mSeMLLAA; mLSeMAL | SeMet; SeCys | 13.772 (F1-3); 2.253 (protein hydrolysate) | Antioxidant activity | [102] |
| Tea | Natural | LQPSLGFP; mAETGEIKGHY | / | 2.82 (Se-TAP); 2.25 (Se-TAPep 1) | Antihypertensive activity (ACE inhibitory activity) | [103] |
| chickpea | Artificial se-enriched | / | / | 8.84 ± 1.65 (Protein extract) | Anti-aging effect | [75] |
| Plant Source | SePS | Se Source | Se Content in SePS(µg/g) | Se Bond | Biological Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tea | ASeTP | Natural | 7.93 ± 0.14 (SeTPS-1); 5.59 ± 2.28 (SeTPS-2); 6.00 ± 2.93 (SeTPS-3) | Se-O-c; O-Se-O; Se-O | Enhancement of intestinal barrier function; modulation of gut microbiota composition | [119] |
| Ziyang tea | Se-ZYTP | Natural | 2.14 | / | Antitumor activity | [117] |
| Tea | Se-TPS | Natural | 1.987 (Se-TPS); 0.97 (Se-TPS1); 0.44 (Se-TPS2); 0.34 (Se-TPS3) | / | Antioxidant activity | [114] |
| Tea | Se-TPS | Natural | 2.76 ± 0.10 | / | Antitumor activity; Immunomodulatory activity | [115] |
| Tea | SeTPS-1; SeTPS-2 | Natural | 23.50 (SeTPS-1); 13.47 (SeTPS-2) | O-Se-O; Se=O | Reduction of H2O2-induced DNA damage | [120] |
| Rosa laevigata | Se-RLFPs | Natural | 16.49 (Se-RLFP-I); 21.61 (Se-RLFP-II) | Se-O-C; Se=O | Neuroprotective effects | [121] |
| pennycress (Thlaspi arvense L.) | Se-PPSs | Natural | 13.56 ± 1.87 (Se-PPS1; 15.36 ± 2.30 (Se-PPS3) | Se=O; O-Se-O; | Antioxidant activity | [122] |
| Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) | SeYPS-1, SeYPS-2 | Artificial se-enriched | 715 (SeYPS-1); 1545 (SeYPS-2) | / | Immunomodulatory activity | [123] |
| Rehmannia glutinosa | / | Artificial se-enriched | 2239 | Se=O; Se-C | Immunomodulatory activity | [124] |
| Ulmus pumila L. | Se-PPU | Artificial se-enriched | / | / | Anti-inflammatory activity | [125] |
| Castanea mollissima Blume | sCPA | Artificial se-enriched | 573.9 | Se-O-C | Antitumor activity | [126] |
| Glycyrrhiza uralensis | SeGUP | Artificial se-enriched | 1339 | O-Se-O; | Antioxidant activity | [127] |
| Artemisia sphaerocephala | SeASP | Artificial se-enriched | 22,400 | Se=O; C-O-Se | Antitumor activity | [128] |
| Garlic | sGPSs | Artificial se-enriched | NA-SS: 29,400 (sGPS8); GA-SA: 26,300 (sGPS9); GA-SS: 10,500 (sGPS2); SOC: 9200 (sGPS9) | OSeC; SeO | Immunostimulatory activity | [129] |
| Garlic | sGPSs | Artificial se-enriched | 10.53~38.27 (sGPS1–9) | Se = O; Se-O- c | Antioxidant activity; immunomodulatory activity | [130] |
| Sweet Potato | Se-SWP | Artificial se-enriched | 12,740 | C−O−Se; Se=O | Antioxidant activity; anticancer activity; antidiabetic activity | [131] |
| Alfalfa roots | Se-RAPS-2 | Artificial se-enriched | 320 | C-O-Se; Se=O | Antioxidant activity; anticancer activity | [132] |
| Sweet corncob | Se-SCP | Artificial se-enriched | / | C-O-Se; Se=O | Antidiabetic activity | [133] |
| Plant Source | Types of polyphenols | Se Source | Se Bond | Se Content (µg/L−1) | Biological Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green tea | Flavonoids | Natural | Se=O; Se-O-C; An esterification reaction between the 3-–OH group and hydrogen selenite (HSeO3−). | 15,690.4 | Immunomodulatory activity; anti-inflammatory activity | [145] |
| Ampelopsis grossedentata | Dihydromyricetin | Artificial se-enriched | O-Se-O | / | Blood glucose-lowering effect; antitumor activity | [150] |
| / | Chrysin, Quercetin | Artificial se-enriched | Se=C | / | Anticancer activity | [149] |
| / | Quercetin | Artificial se-enriched | Se- o | / | / | [152] |
| / | Vitamin P | Artificial se-enriched | O-Se-O | / | Antitumor activity | [151] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, X.; Wang, Z.; Peng, M. Selenium Compounds and Their Bioactivities: Molecular Mechanisms and Prospects for Functional Food and Therapeutic Applications. Plants 2025, 14, 2622. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172622
Hou X, Wang Z, Peng M. Selenium Compounds and Their Bioactivities: Molecular Mechanisms and Prospects for Functional Food and Therapeutic Applications. Plants. 2025; 14(17):2622. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172622
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Xue, Zhiyong Wang, and Mu Peng. 2025. "Selenium Compounds and Their Bioactivities: Molecular Mechanisms and Prospects for Functional Food and Therapeutic Applications" Plants 14, no. 17: 2622. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172622
APA StyleHou, X., Wang, Z., & Peng, M. (2025). Selenium Compounds and Their Bioactivities: Molecular Mechanisms and Prospects for Functional Food and Therapeutic Applications. Plants, 14(17), 2622. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14172622






