GhNRPB3 Negatively Regulates Drought and Salt Tolerance in Cotton
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
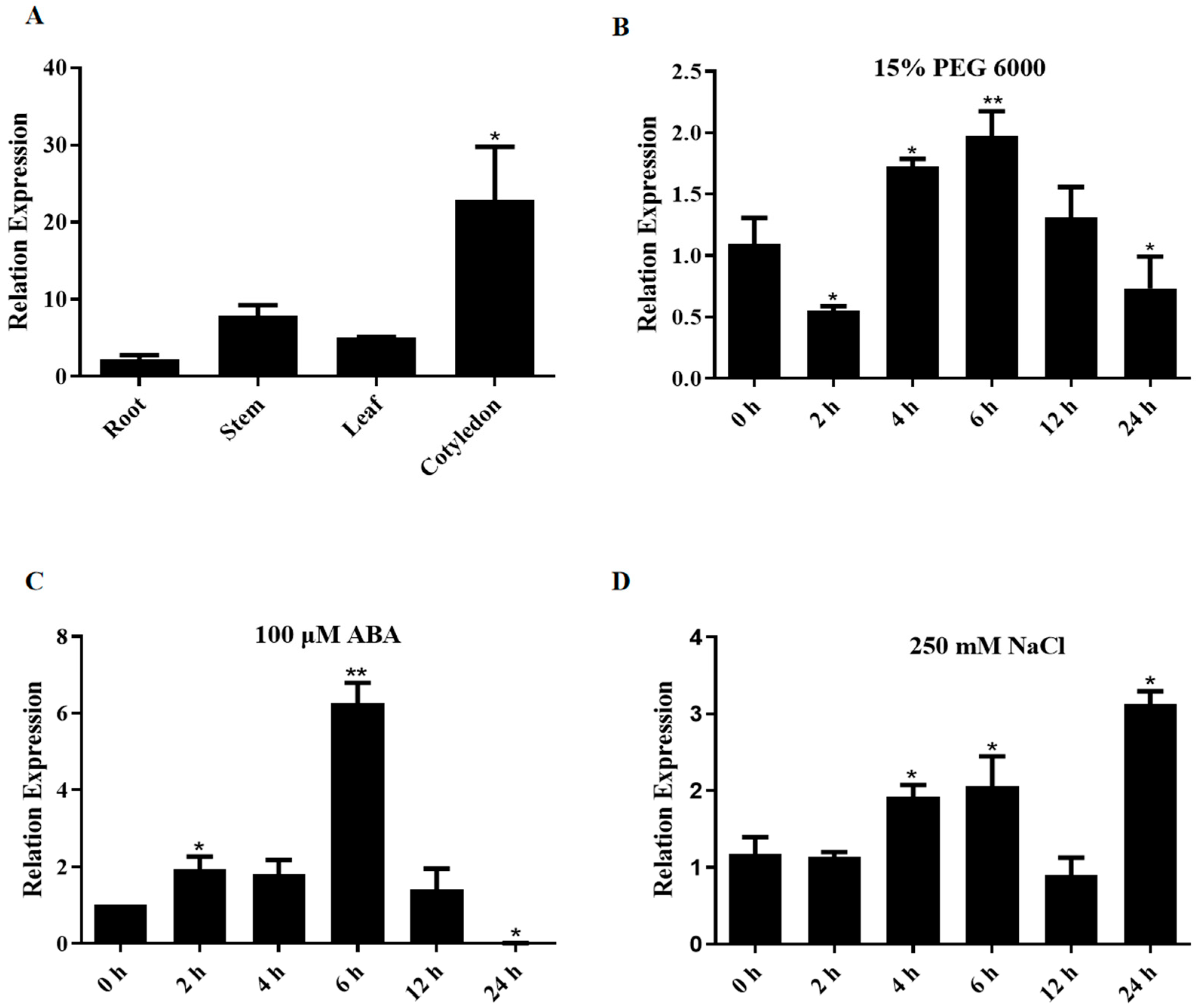
2.1. GhNRPB3 Is Expressed in Various Tissues, and Its Expression Changes in Response to Stress
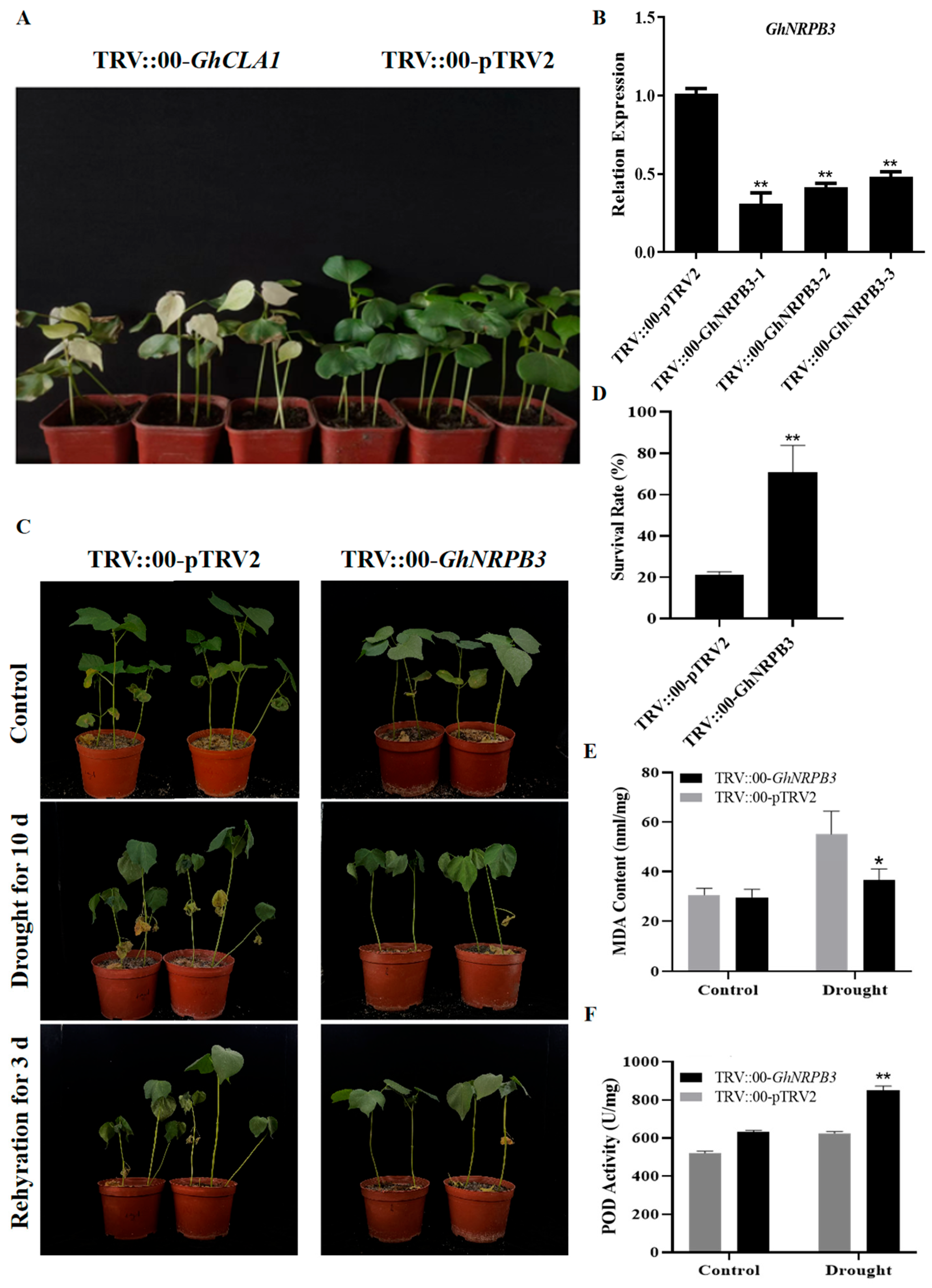
2.2. Silencing of GhNRPB3 Enhances Cotton Drought Resistance
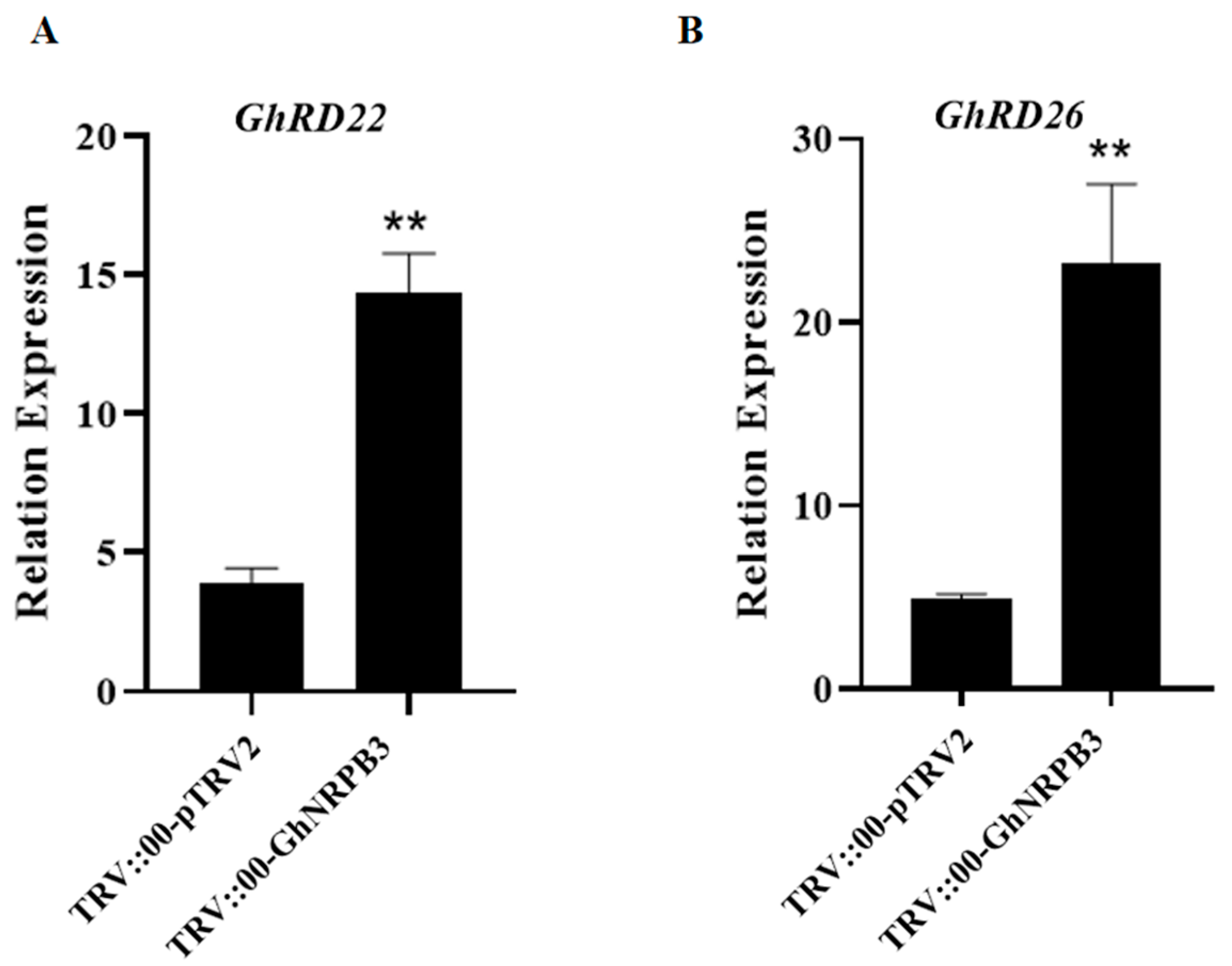
2.3. Analysis of Drought Stress-Related Gene Expression
2.4. Silencing of GhNRPB3 Expression Enhances the Salt Tolerance of Cotton
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Extraction of Total RNA from Cotton and Synthesis of First-Strand cDNA
4.3. qPCR
4.4. VIGS and Gene Expression Assessment
4.5. Stress Treatment
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, D.L.; Huang, K.; Deng, D.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. DNA-dependent RNA polymerases in plants. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 3641–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Ishiguro, A.; Ishihama, A. RNA polymerase II subunits 2, 3, and 11 form a core subassembly with DNA binding activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 25851–25855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios-Abella, A.; López-Perrote, A.; Boskovic, J.; Fonseca, S.; Úrbez, C.; Rubio, V.; Llorca, O.; Alabadí, D. The structure of the R2T complex reveals a different architecture from the related HSP90 cochaperone R2TP. Structure 2025, 33, 740–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choder, M. Rpb4 and Rpb7: Subunits of RNA polymerase II and beyond. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004, 29, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, T.; Cramer, P. Biogenesis of multisubunit RNA polymerases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012, 37, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acker, J.; De Graaff, M.; Cheynel, I.; Khazak, V.; Kedinger, C.; Vigneron, M. Interactions between the human RNA polymerase II subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 16815–16821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, R.; Iezzi, S.; Bruno, T.; Corbi, N.; Di Padova, M.; Floridi, A.; Fanciulli, M.; Passananti, C. Functional interaction of the subunit 3 of RNA polymerase II (RPB3) with transcription factor-4 (ATF4). FEBS Lett. 2003, 547, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbi, N.; Di Padova, M.; De Angelis, R.; Bruno, T.; Libri, V.; Iezzi, S.; Floridi, A.; Fanciulli, M.; Passananti, C. The alpha-like RNA polymerase II core subunit 3 (RPB3) is involved in tissue-specific transcription and muscle differentiation via interaction with the myogenic factor myogenin. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 1639–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.P.; Jiang, B.G.; Zhang, F.B.; Wang, A.D.; Ji, Y.M.; Xu, Y.F.; Li, J.C.; Zhou, W.P.; Zhou, W.J.; Han, H.X. Rpb3 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma through its N-terminus. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 9256–9268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Bao, L.; Zhu, J.; Duan, W.; Zheng, H.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, M.; et al. RNA Pol II preferentially regulates ribosomal protein expression by trapping disassociated subunits. Mol. Cell 2023, 83, 1280–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolotti, A.; Melot, T.; Acker, J.; Vigneron, M.; Delattre, O.; Tora, L. EWS, but not EWS-FLI-1, is associated with both TFIID and RNA polymerase II: Interactions between two members of the TET family, EWS and hTAFII68, and subunits of TFIID and RNA polymerase II complexes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Guan, L.; Qian, P.; Xu, F.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Y.; He, K.; Gou, X.; Li, J.; Hou, S. NRPB3, the third largest subunit of RNA polymerase II, is essential for stomatal patterning and differentiation in Arabidopsis. Development 2016, 143, 1600–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, M.; Wu, Z.; Chen, S.; Rojo, E.; Luo, J.; Li, P.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; Deng, J.; et al. RNA polymerase II associated proteins regulate stomatal development through direct interaction with stomatal transcription factors in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 2021, 230, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. GhMYB4, and GbTCP5 for GbTCP4 Functional Identification of Drought and Salt Stress Response in Cotton. Ph.D. Thesis, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Urumqi, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.C. Screening of GhMYB4 Interacting Proteins and Functional Identification of Interacting Proteins in Response to Drought and Salt Stress. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Urumqi, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Onodera, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Haag, J.R.; Pikaard, D.; Mikami, T.; Ream, T.; Ito, Y.; Pikaard, C.S. Sex-biased lethality or transmission of defective transcription machinery in Arabidopsis. Genetics 2008, 180, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Miao, R.; Zhao, X.; Ni, Y.; Li, W.; Feng, R.; Yang, D. Reference gene selection for quantitative real-time PCR analysis of Hymenopellis radicata under abiotic stress. Fungal Biol. 2024, 128, 1567–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Dias, F.O.; Gentile, A.; Menossi, M.; Begcy, K. ScRpb4, encoding an RNA polymerase subunit from sugarcane, is ubiquitously expressed and resilient to changes in response to stress conditions. Agriculture 2022, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffer, A.; Varon, M.; Choder, M. Rpb7 can interact with RNA polymerase II and support transcription during some stresses independently of Rpb4. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, J.; Deng, F.; Wang, W.; Cheng, Y.; Song, L.; Hu, M.; Shen, J.; Xu, Q.; Shen, F. The long non-coding RNA lncRNA973 is involved in cotton response to saltstress. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Z.; Li, W.J.; Hu, X.H.; Guo, J.R.; Liu, A.M.; Zhang, B.L. A cotton MYB transcription factor, GbMYB5, is positively involved in plant adaptive response to drought stress. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Ni, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Q.; Gao, W.W.; Cai, Y.S.; Li, M.Y.; Sun, G.Q.; Qu, Y.Y. The gene encoding subunit a of the vacuolar H+-ATPase from cotton plays an important role in conferring tolerance to water deficit. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.Q.; Britt, R.C.J.; Shan, L.B.; He, P. Agrobacterium-mediated virus-induced gene silencing assay in cotton. Vis. Exp. 2011, 20, e2938. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Yu, Y.; Ni, Z. GhNRPB3 Negatively Regulates Drought and Salt Tolerance in Cotton. Plants 2025, 14, 2575. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162575
Wang Y, Zeng J, Yu Y, Ni Z. GhNRPB3 Negatively Regulates Drought and Salt Tolerance in Cotton. Plants. 2025; 14(16):2575. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162575
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yi, Jiacong Zeng, Yuehua Yu, and Zhiyong Ni. 2025. "GhNRPB3 Negatively Regulates Drought and Salt Tolerance in Cotton" Plants 14, no. 16: 2575. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162575
APA StyleWang, Y., Zeng, J., Yu, Y., & Ni, Z. (2025). GhNRPB3 Negatively Regulates Drought and Salt Tolerance in Cotton. Plants, 14(16), 2575. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162575





