Evolutionary Analysis of the Land Plant-Specific TCP Interactor Containing EAR Motif Protein (TIE) Family of Transcriptional Corepressors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
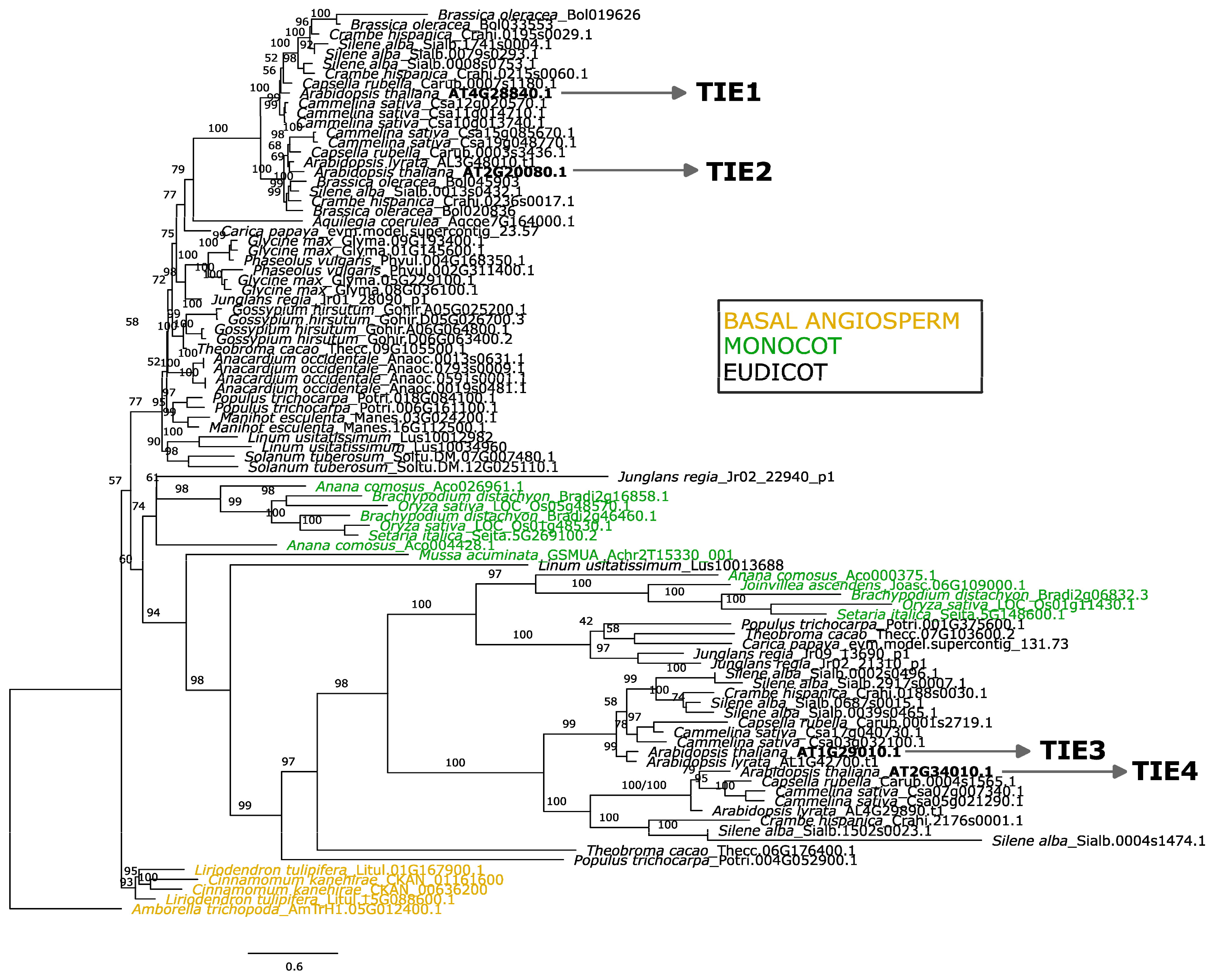
2.1. Two Alternative Scenarios Might Explain the Origin of TIE Proteins
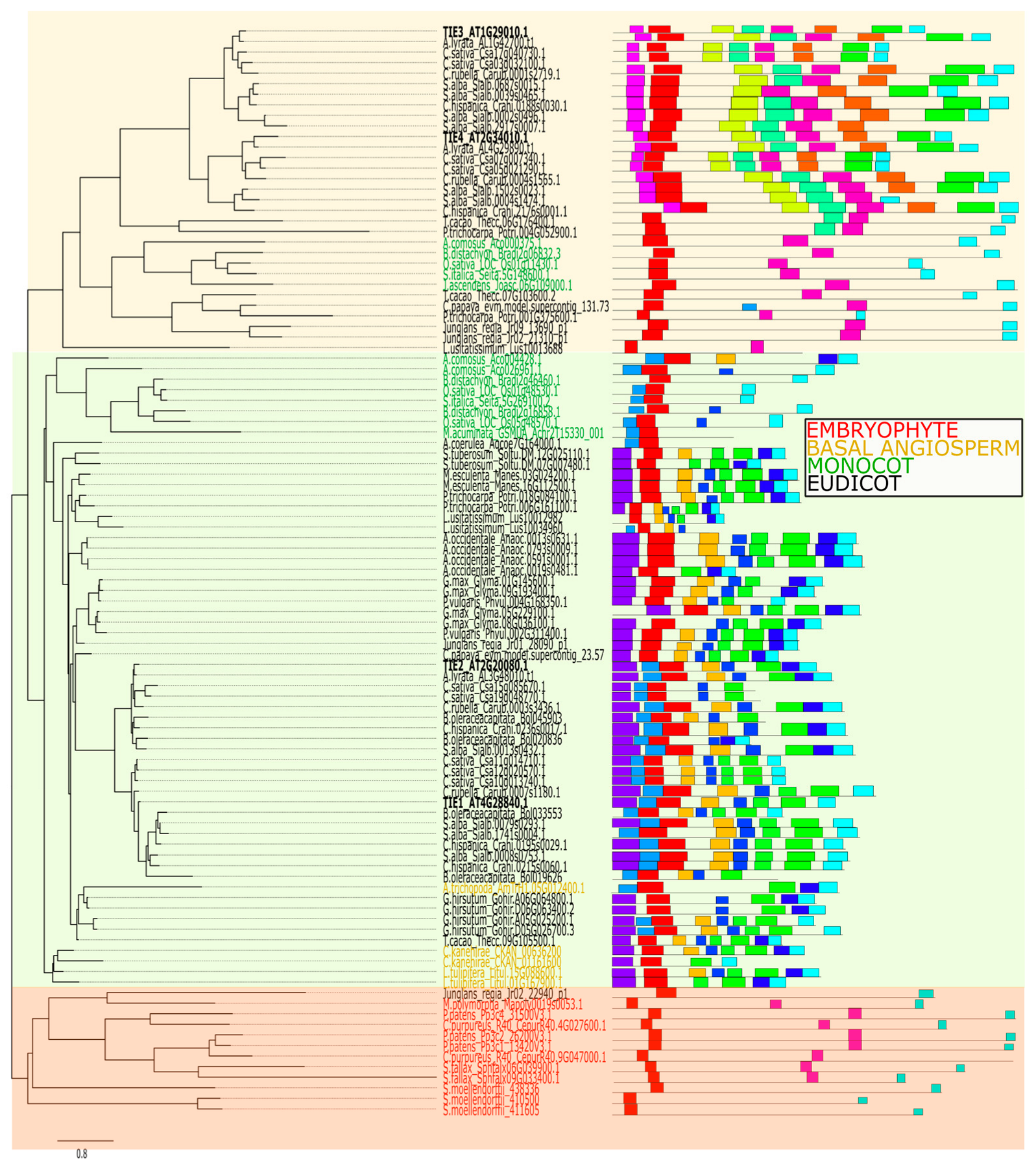
2.2. Diversification Trends of TIE Proteins Contrast with TCP Expansion in Angiosperms
2.3. Diversification of Protein Motifs Supports TIE Family Classification and Reveals Potential Neo-Functionalization
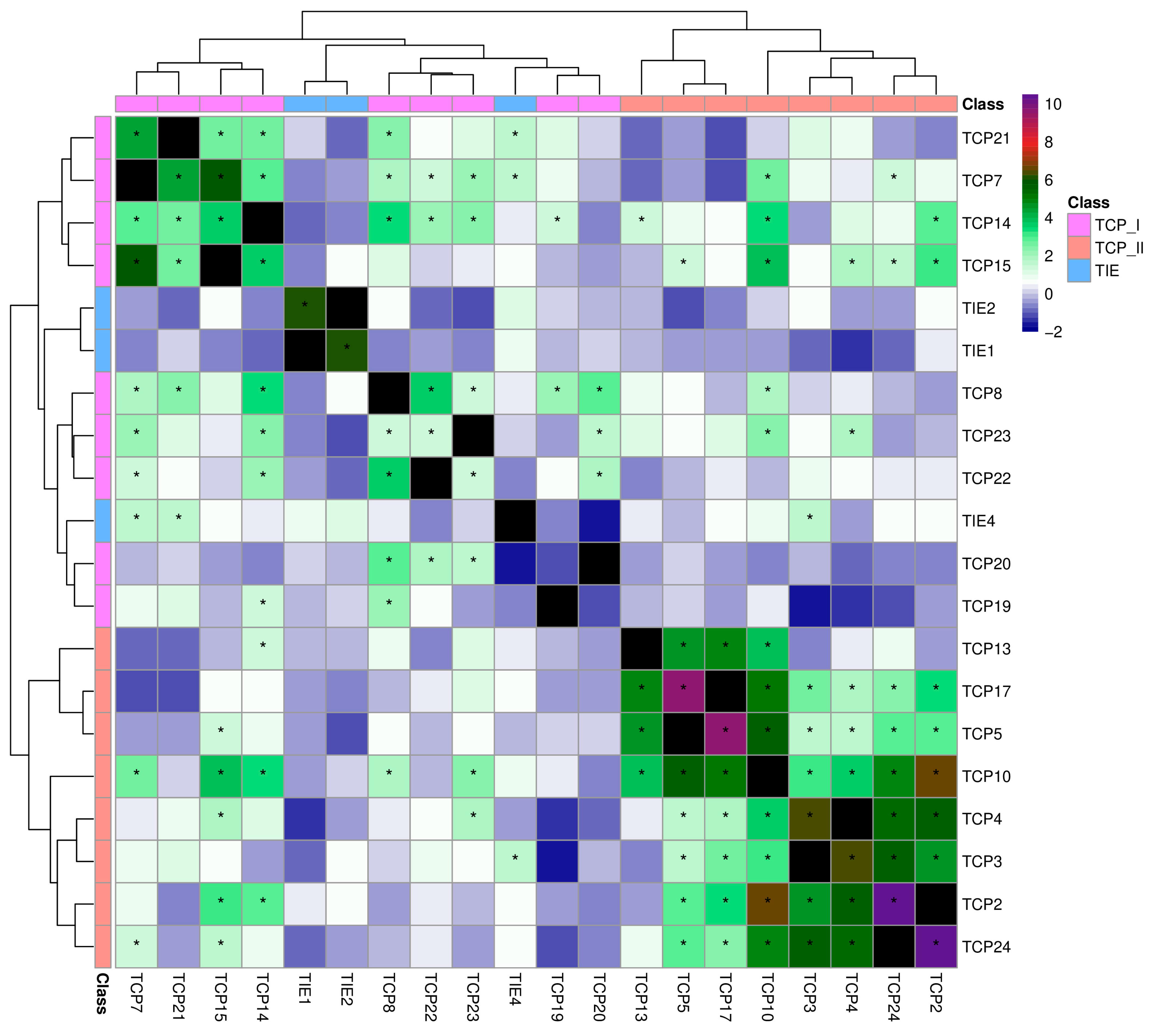
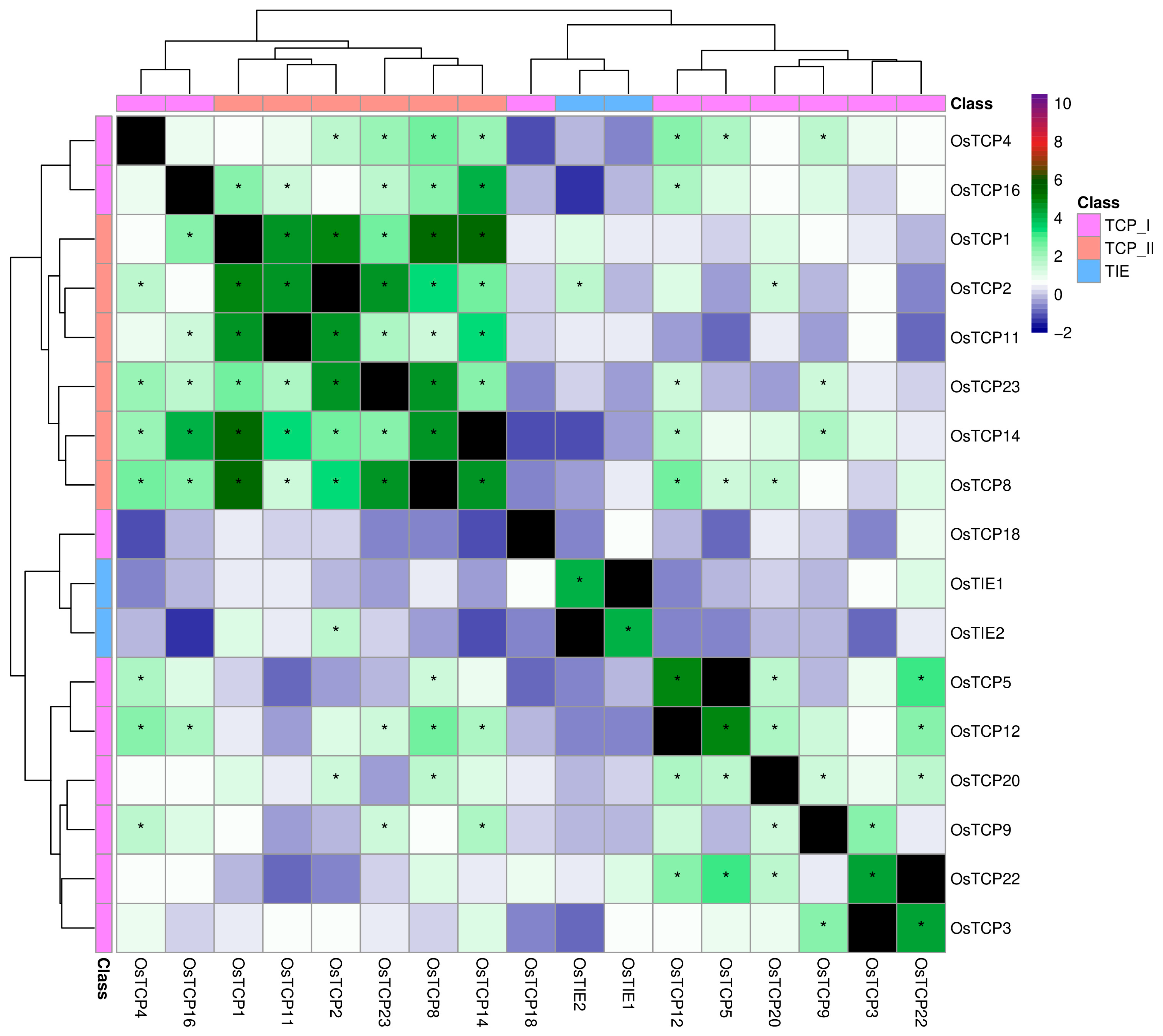
2.4. Co-Expression Analyses Revealed Conserved Patterns of TIE and TCP Genes Across Flowering Plants
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sequence Retrieval, Phylogenetic Analyses, and Protein Domains Identification
3.2. Gene Co-Expression Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doebley, J.; Stec, A.; Gustus, C. Teosinte branched1 and the Origin of Maize: Evidence for Epistasis and the Evolution of Dominance. Genetics 1995, 141, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Carpenter, R.; Vincent, C.; Copsey, L.; Coen, E. Origin of Floral Asymmetry in Antirrhinum. Nature 1996, 383, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosugi, S.; Ohashi, Y. PCF1 and PCF2 Specifically Bind to cis Elements in the Rice Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen Gene. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 1607–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cubas, P.; Lauter, N.; Doebley, J.; Coen, E. The TCP Domain: A Motif Found in Proteins Regulating Plant Growth and Development. Plant J. 1999, 18, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manassero, N.G.U.; Viola, I.L.; Welchen, E.; Gonzalez, D.H. TCP Transcription Factors: Architects of Plant Form. Biomol. Concepts 2013, 4, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, M.; Cubas, P. TCP Factors: New Kids on the Signaling Block. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2016, 33, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, T.; Sakayama, H.; de Vries, J.; Buschmann, H.; Saint-Marcoux, D.; Ullrich, K.K.; Haas, F.B.; Vanderstraeten, L.; Becker, D.; Lang, D.; et al. The Chara Genome: Secondary Complexity and Implications for Plant Terrestrialization. Cell 2018, 174, 448–464.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-L.; Wang, H.-W.; Cao, Y.-N.; Kan, S.-L.; Liu, Y.-Y. Comprehensive Evolutionary Analysis of the TCP Gene Family: Further Insights for Its Origin, Expansion, and Diversification. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 994567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero, L.E.; Uberti-Manassero, N.G.; Arce, A.L.; Colombatti, F.; Alemano, S.G.; Gonzalez, D.H. TCP15 Modulates Cytokinin and Auxin Responses During Gynoecium Development in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2015, 84, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Grandío, E.; Pajoro, A.; Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; Tarancón, C.; Immink, R.G.H.; Cubas, P. Abscisic Acid Signaling Is Controlled by a BRANCHED1/HD-ZIP I Cascade in Arabidopsis Axillary Buds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 114, E245–E254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Govindarajulu, R.; Feil, R.; Siddoway, M.L.; Nielsen, T.; Lunn, J.E.; Hawkins, J.; Whipple, C.; Chuck, G. The Regulatory Landscape of a Core Maize Domestication Module Controlling Bud Dormancy and Growth Repression. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi, S.; Ohashi, Y. DNA Binding and Dimerization Specificity and Potential Targets for the TCP Protein Family. Plant J. 2002, 30, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, I.L.; Manassero, N.G.U.; Ripoll, R.; Gonzalez, D.H. The Arabidopsis Class I TCP Transcription Factor AtTCP11 is a Developmental Regulator with Distinct DNA-Binding Properties Due to the Presence of a Threonine Residue at Position 15 of the TCP Domain. Biochem. J. 2011, 435, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, I.L.; Reinheimer, R.; Ripoll, R.; Manassero, N.G.U.; Gonzalez, D.H. Determinants of the DNA Binding Specificity of Class I and Class II TCP Transcription Factors. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zou, X.; Jiang, M.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Chen, L.; Wu, Y. The Crystal Structure of the TCP Domain of PCF6 in Oryza sativa L. Reveals an RHH-like Fold. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Q.; Guo, D.; Wei, B.; Zhang, F.; Pang, C.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wei, T.; Gu, H.; Qu, L.-J.; et al. The TIE1 Transcriptional Repressor Links TCP Transcription Factors with TOPLESS/TOPLESS-RELATED Corepressors and Modulates Leaf Development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Nicolas, M.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H.; Guo, D.; Yuan, R.; Zhang, T.; Yang, J.; Cubas, P.; Qin, G.; et al. The TIE1 Transcriptional Repressor Controls Shoot Branching by Directly Repressing BRANCHED1 in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Y.; Zhan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, P.; Wei, X.; Ding, Y.; Sajjad, M.; Hu, W.; Wang, P.; et al. GhTIE1 Regulates Branching Through Modulating the Transcriptional Activity of TCPs in Cotton and Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Yuan, R.; Zhang, T.; An, F.; Wang, N.; Lan, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Arabidopsis TIE1 and TIE2 Transcriptional Repressors Dampen Cytokinin Response During Root Development. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Guo, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, N.; Fang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Yu, D.; Zhang, B.; et al. Rice Transcriptional Repressor OsTIE1 Controls Anther Dehiscence and Male Sterility by Regulating JA Biosynthesis. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 1697–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, L.; Liu, Y.; He, Q.; Yu, N.; Gaowa, N.; Yi, Z.; Wang, J.; Han, W.; Peng, T.; et al. The Bryophyte Phylogeny Group: A Revised Familial Classification System Based on Plastid Phylogenomic Data. J. Syst. Evol. 2024, 62, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-H.; Sun, J.-Y.; Liu, M.; Liu, J.; Yang, W.-C. SPOROCYTELESS Is a Novel Embryophyte-Specific Transcription Repressor that Interacts with TPL and TCP Proteins in Arabidopsis. J. Genet. Genom. 2014, 41, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amborella Genome Project. The Amborella Genome and the Evolution of Flowering Plants. Science 2013, 342, 1241089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, J.L.; Kohchi, T.; Yamato, K.T.; Jenkins, J.; Shu, S.; Ishizaki, K.; Yamaoka, S.; Nishihama, R.; Nakamura, Y.; Berger, F.; et al. Insights into Land Plant Evolution Garnered from the Marchantia Polymorpha Genome. Cell 2017, 171, 287–304.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, D.-D.; Han, L.-H.; Tao, M.; Hu, Q.-Q.; Wu, W.-Y.; Zhang, J.-B.; Li, X.-B.; Huang, G.-Q. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of TCP Transcription Factor Genes in Upland Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obayashi, T.; Hibara, H.; Kagaya, Y.; Aoki, Y.; Kinoshita, K. ATTED-II v11: A Plant Gene Coexpression Database Using a Sample Balancing Technique by Subagging of Principal Components. Plant Cell Physiol. 2022, 63, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viola, I.L.; Alem, A.L.; Jure, R.M.; Gonzalez, D.H. Physiological Roles and Mechanisms of Action of Class I TCP Transcription Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, I.L.; Gonzalez, D.H. TCP Transcription Factors in Plant Reproductive Development: Juggling Multiple Roles. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast Model Selection for Accurate Phylogenetic Estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; Von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast Approximation for Phylogenetic Bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.A.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arce, A.; Schild, C.; Maslein, D.; Lucero, L. Evolutionary Analysis of the Land Plant-Specific TCP Interactor Containing EAR Motif Protein (TIE) Family of Transcriptional Corepressors. Plants 2025, 14, 2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152423
Arce A, Schild C, Maslein D, Lucero L. Evolutionary Analysis of the Land Plant-Specific TCP Interactor Containing EAR Motif Protein (TIE) Family of Transcriptional Corepressors. Plants. 2025; 14(15):2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152423
Chicago/Turabian StyleArce, Agustín, Camila Schild, Delfina Maslein, and Leandro Lucero. 2025. "Evolutionary Analysis of the Land Plant-Specific TCP Interactor Containing EAR Motif Protein (TIE) Family of Transcriptional Corepressors" Plants 14, no. 15: 2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152423
APA StyleArce, A., Schild, C., Maslein, D., & Lucero, L. (2025). Evolutionary Analysis of the Land Plant-Specific TCP Interactor Containing EAR Motif Protein (TIE) Family of Transcriptional Corepressors. Plants, 14(15), 2423. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152423





