Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization, and Comparison of C3HC4 Family Genes in Salt Tolerance Between Barley and Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
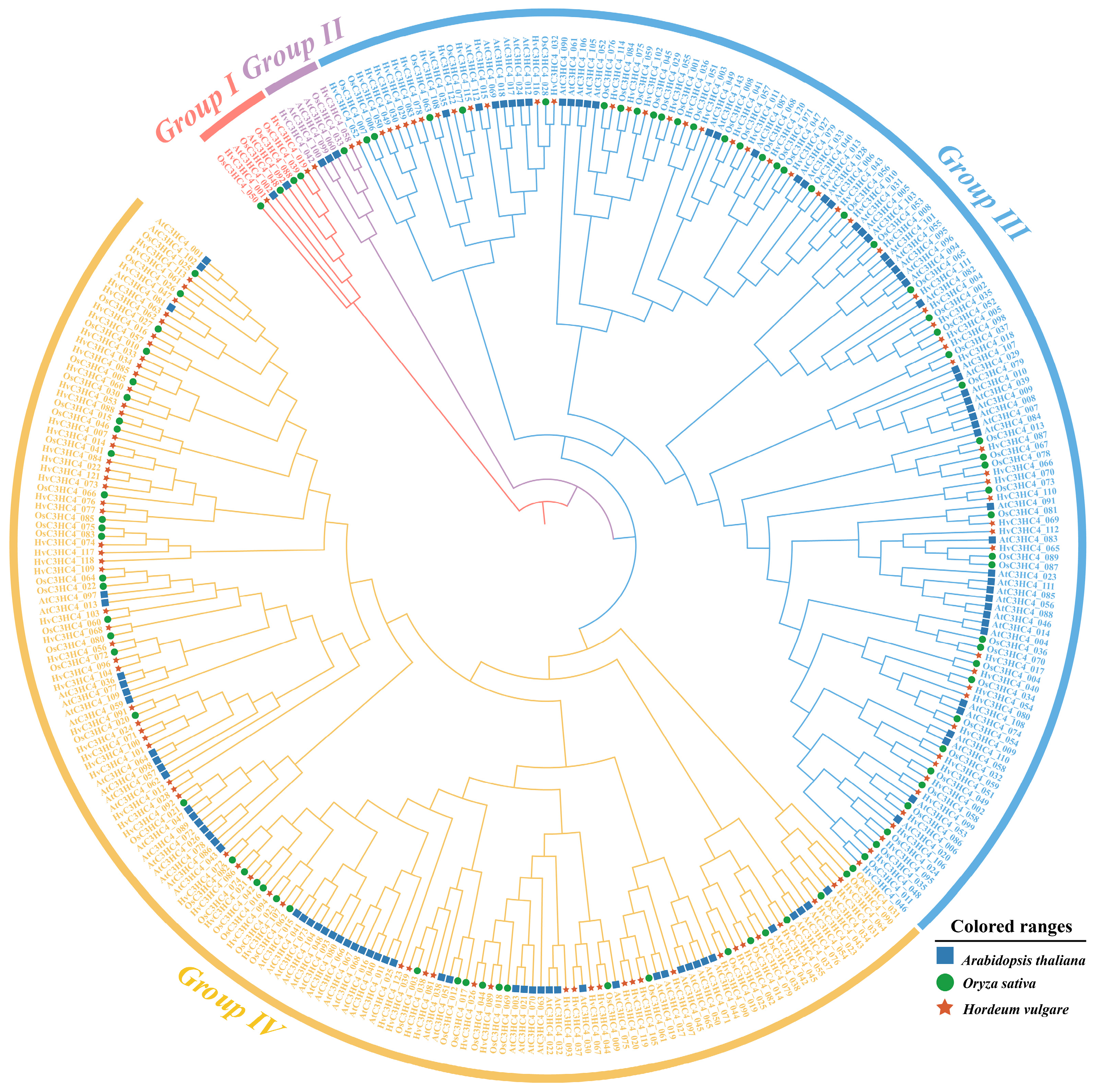
2.1. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of C3HC4 Genes in Barley and Rice
2.2. Gene Structure and Conserved Motifs of C3HC4 Family Members
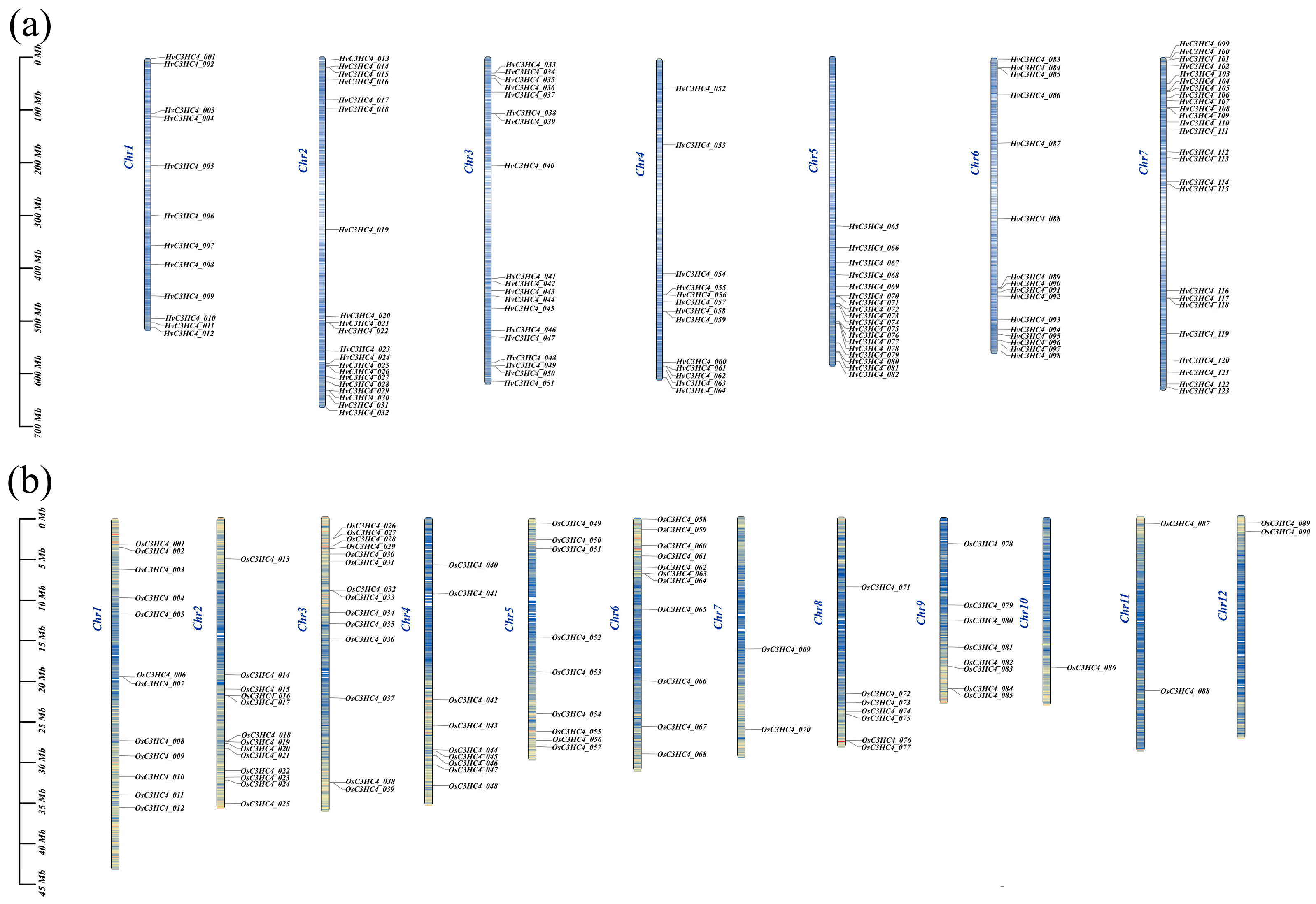
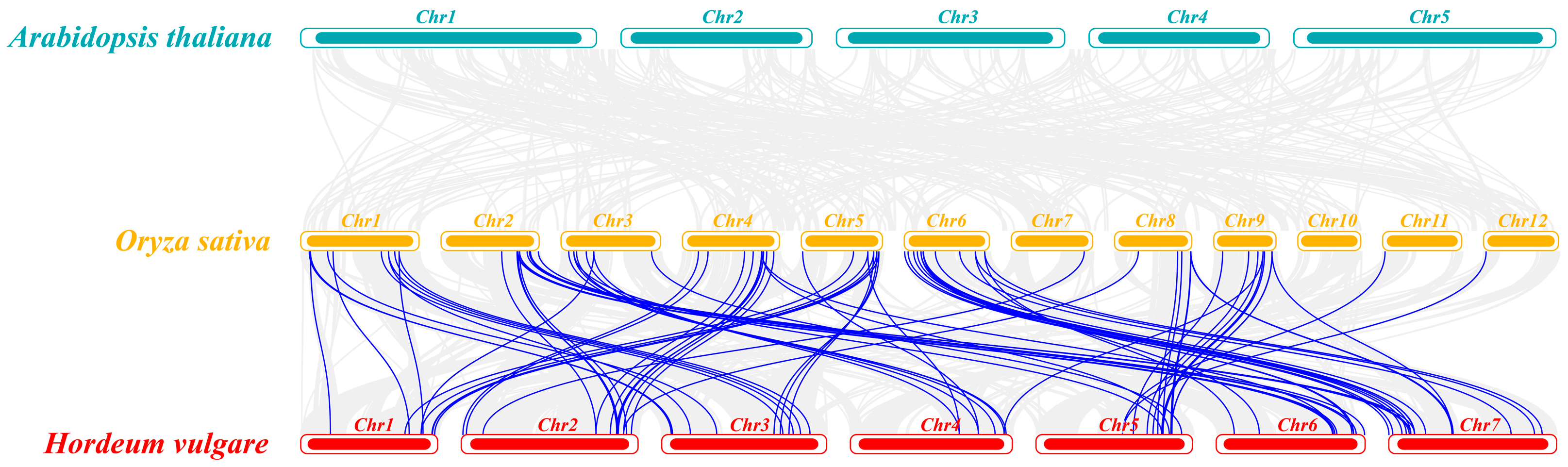
2.3. Chromosomal Distribution, Genome Synteny, and Gene Duplication of C3HC4 Genes in Barley and Rice
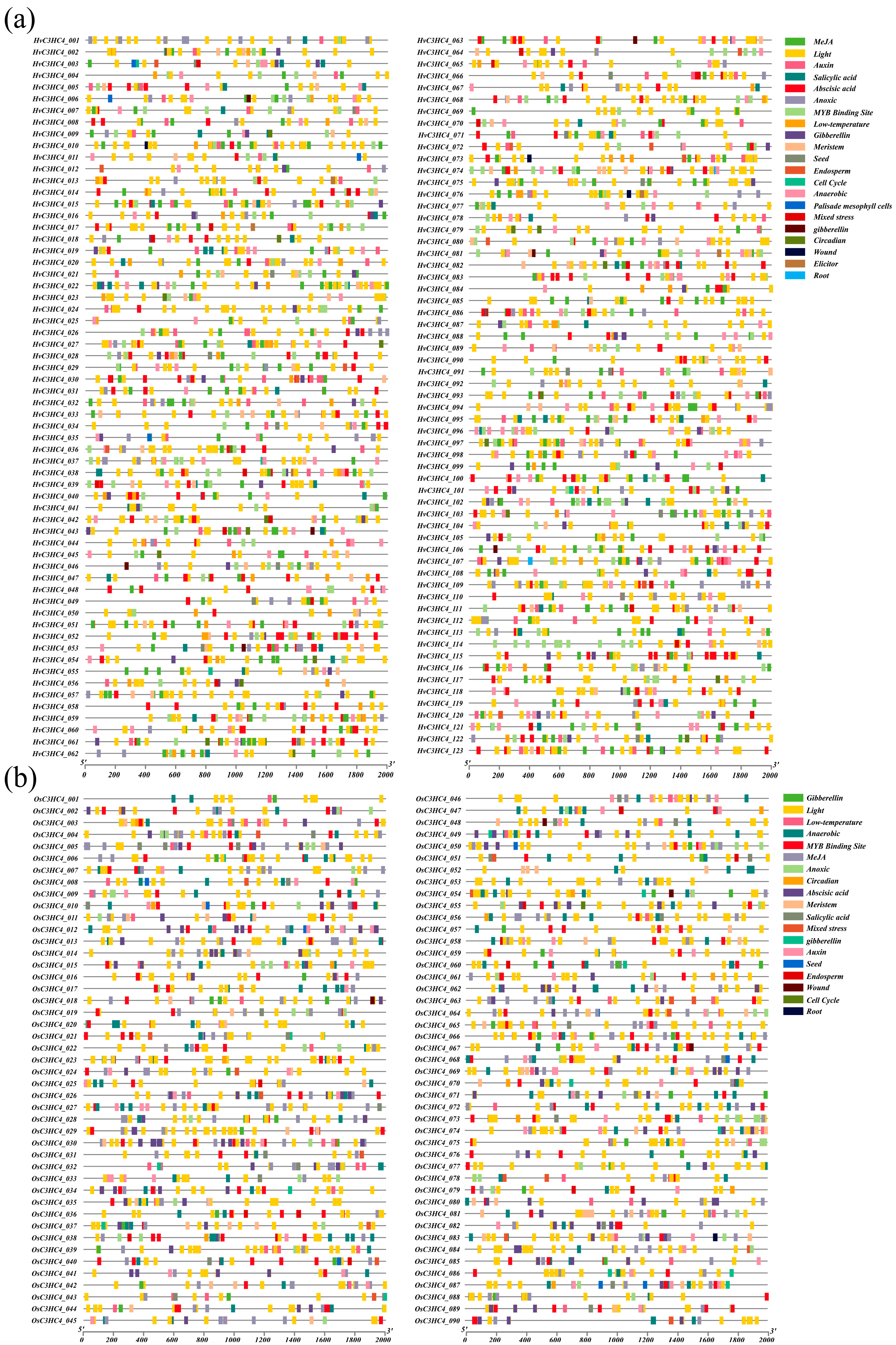
2.4. Analysis of Stress-Related Cis-Elements of the HvC3HC4 and OsC3HC4 Genes
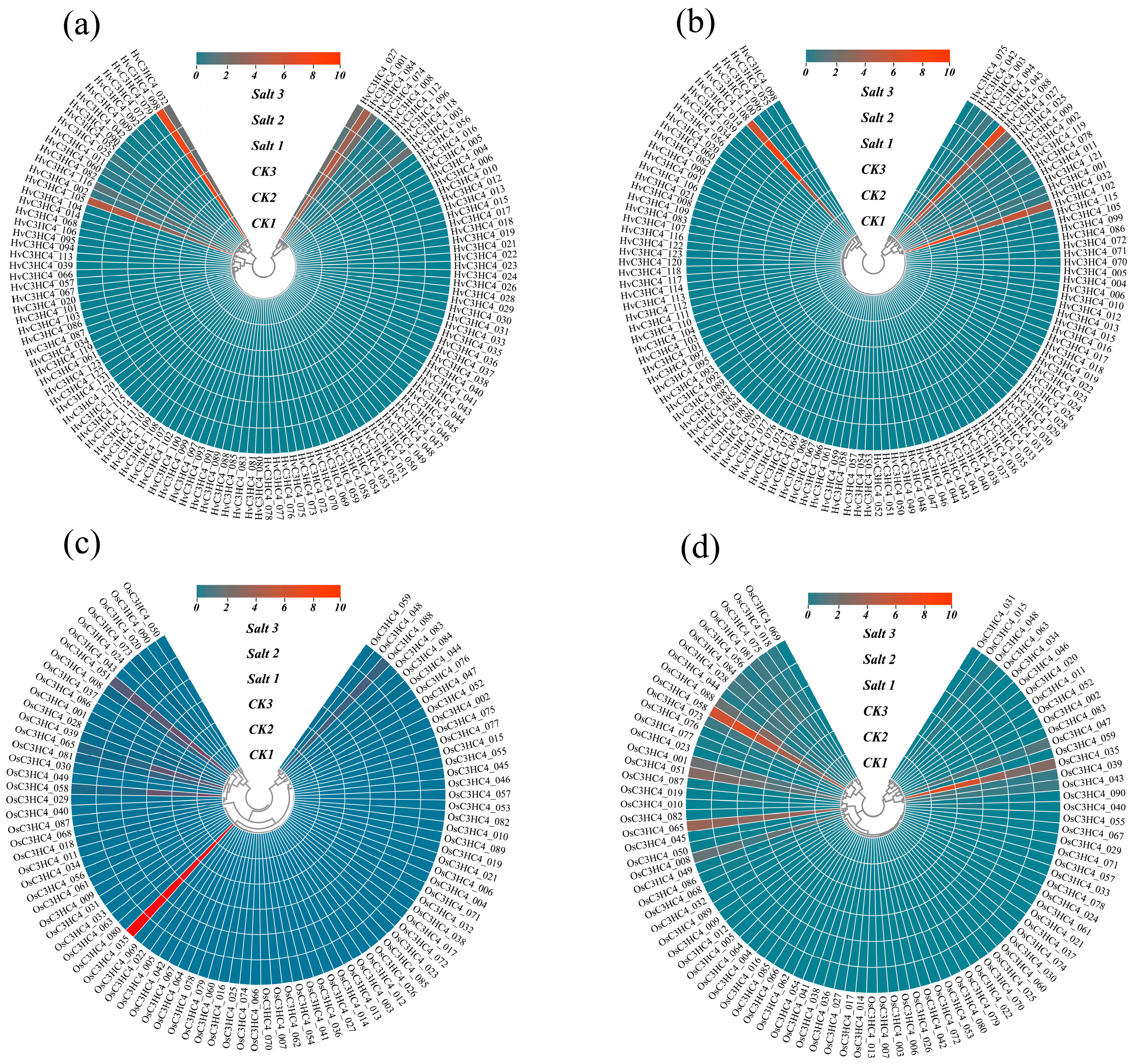
2.5. Expression Profiles of HvC3HC4s and OsC3HC4s in Different Tissues Under Salt Stress
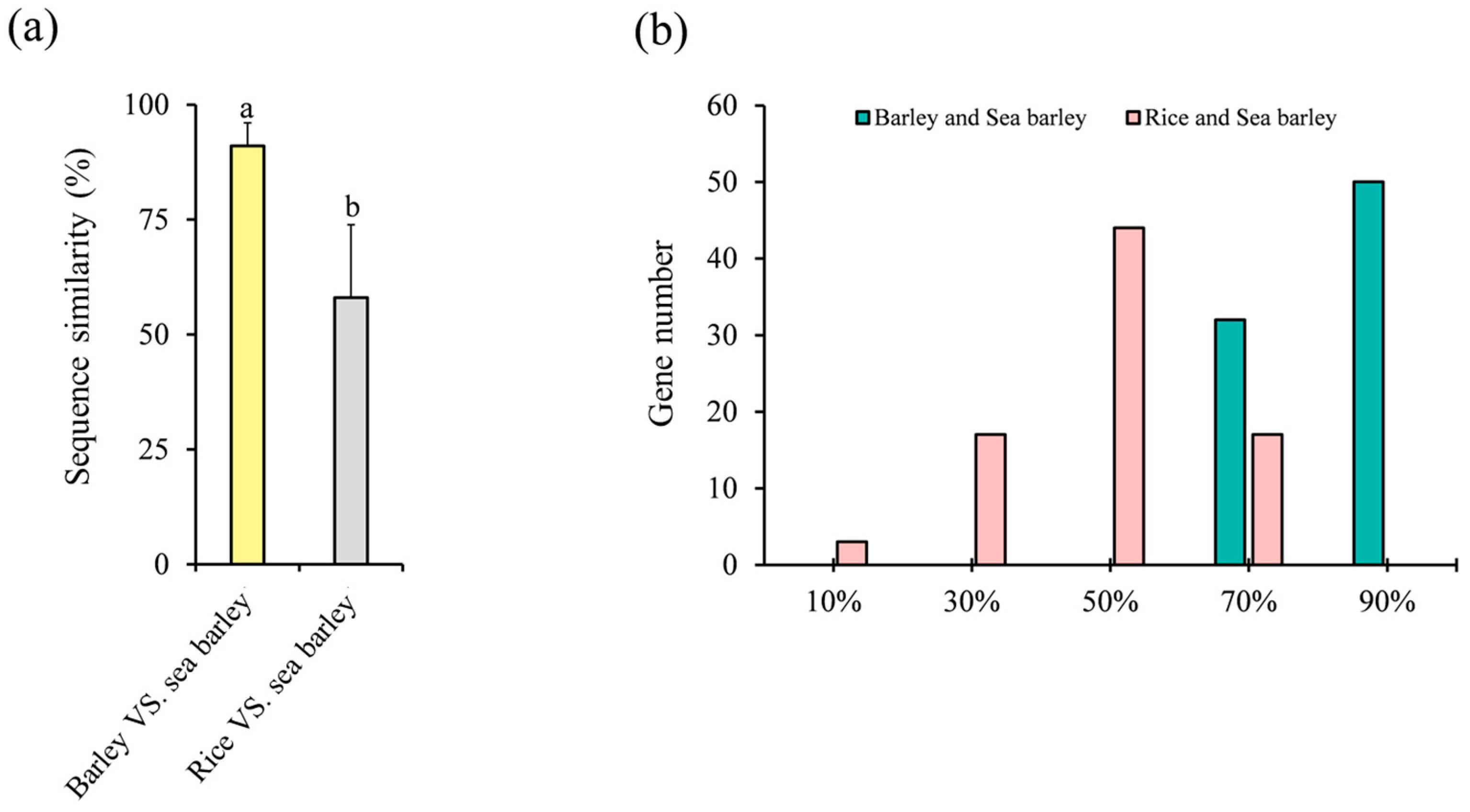
2.6. Homologous Gene Similarity of HvC3HC4 and OsC3HC4 in Evolution Compared with Salt-Tolerant Plants
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of C3HC4 Family Genes in the Barley, Rice, and Arabidopsis Genomes
4.2. Phylogenetic Analysis and Classification of the C3HC4 Gene Family in Barley and Rice
4.3. Analysis of Gene Structure and Conserved Motifs
4.4. Chromosomal Location and Gene Duplication Analyses
4.5. Analysis of Cis-Elements in Promoter Regions of HvC3HC4s and OsC3HC4s
4.6. Expression Patterns of HvC3HC4s and OsC3HC4s
4.7. Homologous Gene Similarity Analyses of C3HC4 in Evolution
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rengasamy, P. World Salinization with Emphasis on Australia. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadir, M.; Quillérou, E.; Nangia, V.; Murtaza, G.; Singh, M.; Thomas, R.J.; Drechsel, P.; Noble, A.D. Economics of Salt-induced Land Degradation and Restoration. Nat. Resour. Forum 2014, 38, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Xi, M.W.; Liu, T.; Wu, X.Y.; Ju, L.Y.; Wang, D.J. The Central Role of Transcription Factors in Bridging Biotic and Abiotic Stress Responses for Plants’ Resilience. New Crops 2024, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengasamy, P. Soil Processes Affecting Crop Production in Salt-Affected Soils. Funct. Plant Biol. 2010, 37, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.B.; Shen, Q.F.; Kuang, L.H.; Yu, J.H.; Wu, D.Z.; Zhang, G.P. Metabolite Profiling and Gene Expression of Na/K Transporter Analyses Reveal Mechanisms of the Difference in Salt Tolerance between Barley and Rice. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2018, 130, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligaba, A.; Katsuhara, M. Insights into the Salt Tolerance Mechanism in Barley (Hordeum vulgare) from Comparisons of Cultivars that Differ in Salt Sensitivity. J. Plant Res. 2010, 123, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.B.; Wu, D.Z.; Zhang, X.C.; Xu, Y.F.; Kuang, L.H.; Cai, S.G.; Zhang, G.P.; Shen, Q.F. Vacuolar H+-Pyrophosphatase HVP10 Enhances Salt Tolerance via Promoting Na+ Translocation into Root Vacuoles. Plant Physiol. 2022, 188, 1248–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhu, C.S.; Xuan, W.; An, H.Z.; Tian, Y.L.; Wang, B.X.; Chi, W.C.; Chen, G.M.; Ge, Y.W.; Li, J.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Studies Identify OsWRKY53 as a Key Regulator of Salt Tolerance in Rice. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevo, E.; Chen, G.X. Drought and Salt Tolerances in Wild Relatives for Wheat and Barley Improvement. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 670–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.Y.; Shi, Y.Y.; Wang, R.; Feng, Y.; Wang, L.S.; Zhang, H.S.; Shi, X.Y.; Jing, G.Q.; Deng, P.; Song, T.Z.; et al. The Transcription Factor OsMYBc and an E3 Ligase Regulate Expression of a K+ Transporter during Salt Stress. Plant Physiol. 2022, 190, 843–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Fokar, M.; Abdelmageed, H.; Allen, R.D. Arabidopsis SAP5 Functions as a Positive Regulator of Stress Responses and Exhibits E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Activity. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 75, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso-Gomila, O.; Merino-Cacho, L.; Muratore, V.; Perez, C.; Taibi, V.; Maspero, E.; Azkargorta, M.; Iloro, I.; Trulsson, F.; Vertegaal, A.C.O.; et al. BioE3 Identifies Specific Substrates of Ubiquitin E3 Ligases. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Y.; Ngea, G.L.N.; Wang, K.L.; Lu, Y.C.; Godana, E.A.; Ackah, M.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, H.Y. Deciphering the Mechanism of E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Plant Responses to Abiotic and Biotic Stresses and Perspectives on PROTACs for Crop Resistance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2024, 22, 2811–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.C.; Lim, S.D.; Moon, J.C.; Jang, C.S. A Rice Really Interesting New Gene H2-Type E3 Ligase, OsSIRH2-14, Enhances Salinity Tolerance via Ubiquitin/26S Proteasome-Mediated Degradation of Salt-Related Proteins. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 3061–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Shen, L.; Shen, Z.X.; Jing, W.; Ge, H.L.; Zhao, J.Z.; Zhang, W.H. The Potassium Transporter OsHAK21 Functions in the Maintenance of Ion Homeostasis and Tolerance to Salt Stress in Rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 2766–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.H.; Ren, G.Z.; Bai, Y.Z.; Gao, Y.K.; Yang, P.Y.; Chang, J.H. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the U-Box E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Gene Family Related to Salt Tolerance in Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1141617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hand, K.A.; Shabek, N. The Role of E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Chloroplast Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Xu, K.; Kong, D.Y.; Wu, L.Y.; Chen, Q.; Ma, X.S.; Ma, S.Q.; Li, T.F.; Xie, Q.; Liu, H.Y. Ubiquitin Ligase OsRINGzf1 Regulates Drought Resistance by Controlling the Turnover of OsPIP2;1. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1743–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.J.; Lee, I.H.; Nou, I.S.; Lee, K.D.; Rashotte, A.M.; Kang, K.K. BrRZFP1 a Brassica rapa C3HC4-type RING Zinc Finger Protein Involved in Cold, Salt and Dehydration Stress. Plant Biol. 2013, 15, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lim, S.D.; Jung, K.H.; Jang, C.S. Overexpression of a C3HC4-Type RING E3 Ligase Gene, OsRFPHC-13, Improves Salinity Resistance in Rice, Oryza sativa, by Altering the Expression of Na+/K+ Transporter Genes. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2023, 207, 105224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Q.H.; Liu, Z.B.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.M.; Li, X.F.; Yang, Y. Arabidopsis C3HC4-RING Finger E3 Ubiquitin Ligase AtAIRP4 Positively Regulates Stress-Responsive Abscisic Acid Signaling. J. Integr. Plant. Biol. 2016, 58, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, P.; Khurana, P. TaZnF, a C3HC4-Type RING Zinc Finger Protein from Triticum aestivum Is Involved in Dehydration and Salinity Stress. J. Plant Biochem. Biot. 2020, 29, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.Q.; Chen, M.J.; Wang, F.Y.; Tu, Y.S.; Xu, Y.F.; Fu, L.B.; Zeng, F.R.; Zhang, G.P.; Wu, D.Z.; Shen, Q.F. OsCaM1-1 Is Responsible for Salt Tolerance by Regulating Na+/K+ Homeostasis in Rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2025, 48, 1393–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeling, M. Bias in Plant Gene Content Following Different Sorts of Duplication: Tandem, Whole-Genome, Segmental, or by Transposition. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009, 60, 433–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.D.; Jung, C.G.; Park, Y.C.; Lee, S.C.; Lee, C.; Lim, C.W.; Kim, D.S.; Jang, C.S. Molecular Dissection of a Rice Microtubule-Associated RING Finger Protein and Its Potential Role in Salt Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2015, 89, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.F.; Fu, L.B.; Su, T.T.; Ye, L.Z.; Huang, L.; Kuang, L.H.; Wu, L.Y.; Wu, D.Z.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhang, G.P. Calmodulin HvCaM1 Negatively Regulates Salt Tolerance via Modulation of HvHKT1s and HvCAMTA4. Plant Physiol. 2020, 183, 1650–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, S.H.; Chen, J.Q.; Tian, D.C. Patterns of Exon-Intron Architecture Variation of Genes in Eukaryotic Genomes. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lyu, H.M.; Zhu, K.K.; Van de Peer, Y.; Cheng, Z.M. The Emergence and Evolution of Intron-Poor and Intronless Genes in Intron-Rich Plant Gene Families. Plant J. 2021, 105, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, S.B.; Mitra, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Young, N.D.; May, G. The Roles of Segmental and Tandem Gene Duplication in the Evolution of Large Gene Families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Xie, D.F.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Cheng, R.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhou, S.D.; He, X.J. Phylogeny and Adaptive Evolution of Subgenus Rhizirideum (Amaryllidaceae, Allium) Based on Plastid Genomes. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.Z.; Bai, Y.H.; Zhao, L.H.; Dou, X.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, L.L.; Li, Y.; Li, W.M.; Hui, Y.N.; Huang, X.Y. H2A. Z Represses Gene Expression by Modulating Promoter Nucleosome Structure and Enhancer Histone Modifications in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 1274–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The Neighbor-Joining Method: A New Method for Reconstructing Phylogenetic Trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.P.; Guo, A.Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.C.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An Upgraded Gene Feature Visualization Server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. Tbtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.P.; Li, J.P.; Paterson, A.H. Mcscanx-Transposed: Detecting Transposed Gene Duplications Based on Multiple Colinearity Scans. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1458–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Kaks_Calculator 3.0: Calculating Selective Pressure on Coding and Non-Coding Sequences. Genom. Proteom. Bioinf. 2022, 20, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | Segmental Duplication | Tandem Duplication | Dispersed Duplication |
|---|---|---|---|
| HvC3HC4s | 22 | 0 | 0 |
| OsC3HC4s | 36 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, K.; Wang, S.; Xu, X.; Zheng, X.; Wu, H.; Huang, L.; Dai, L.; Zhan, C.; Zeng, D.; Fu, L. Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization, and Comparison of C3HC4 Family Genes in Salt Tolerance Between Barley and Rice. Plants 2025, 14, 2404. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152404
Chen K, Wang S, Xu X, Zheng X, Wu H, Huang L, Dai L, Zhan C, Zeng D, Fu L. Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization, and Comparison of C3HC4 Family Genes in Salt Tolerance Between Barley and Rice. Plants. 2025; 14(15):2404. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152404
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Kerun, Shuai Wang, Xiaohan Xu, Xintong Zheng, Hongkai Wu, Linzhou Huang, Liping Dai, Chenfang Zhan, Dali Zeng, and Liangbo Fu. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization, and Comparison of C3HC4 Family Genes in Salt Tolerance Between Barley and Rice" Plants 14, no. 15: 2404. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152404
APA StyleChen, K., Wang, S., Xu, X., Zheng, X., Wu, H., Huang, L., Dai, L., Zhan, C., Zeng, D., & Fu, L. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization, and Comparison of C3HC4 Family Genes in Salt Tolerance Between Barley and Rice. Plants, 14(15), 2404. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152404







