Profiling Hydrophilic Cucurbita pepo Seed Extracts: A Study of European Cultivar Variability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Water Content and Elemental Analysis
2.1.1. Water Content
2.1.2. Metal Analysis
2.1.3. Total Carbon and Total Nitrogen Content
2.2. LC-PDA-HRMS Analysis
2.3. Analysis of Carbohydrates
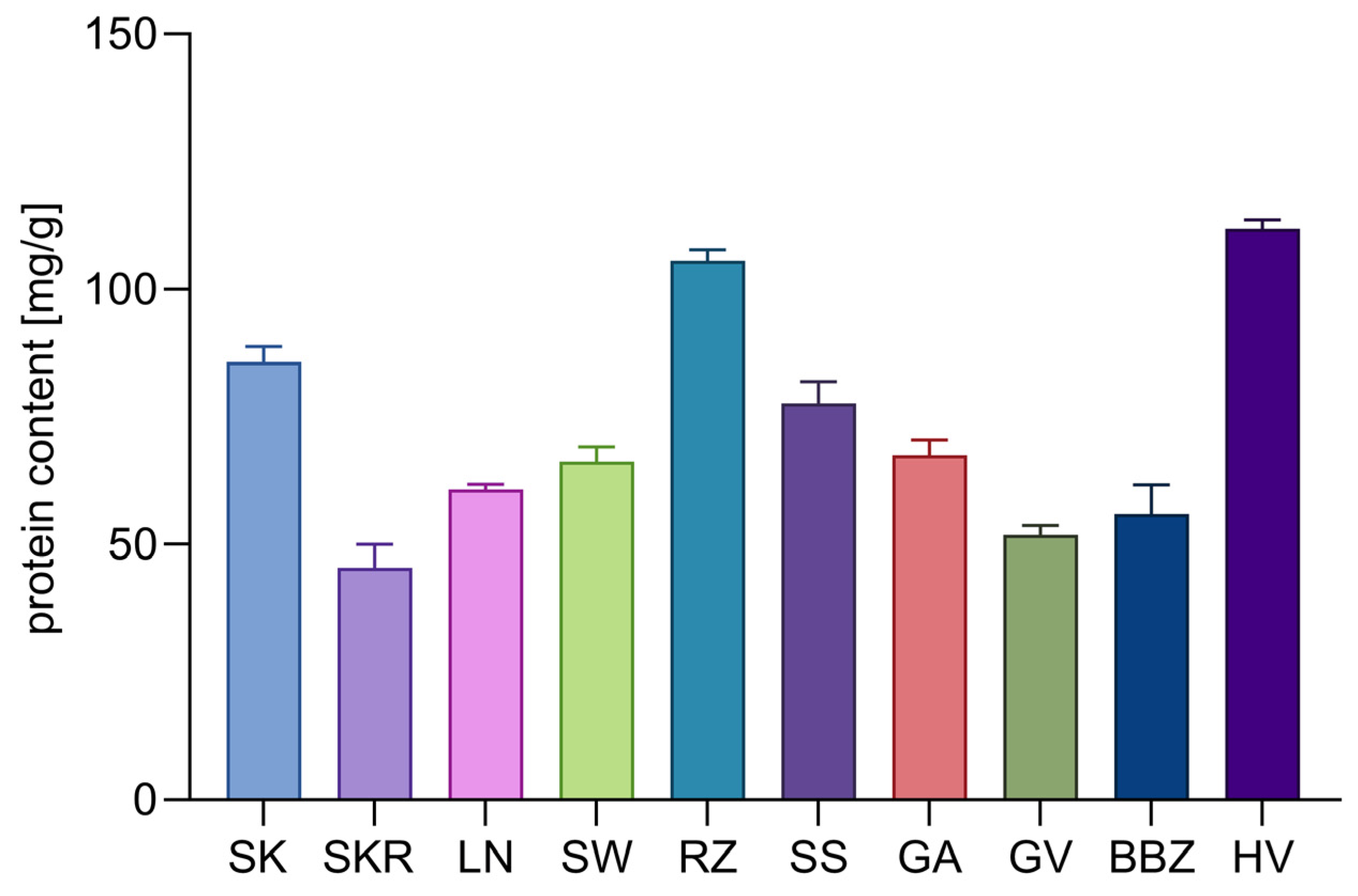
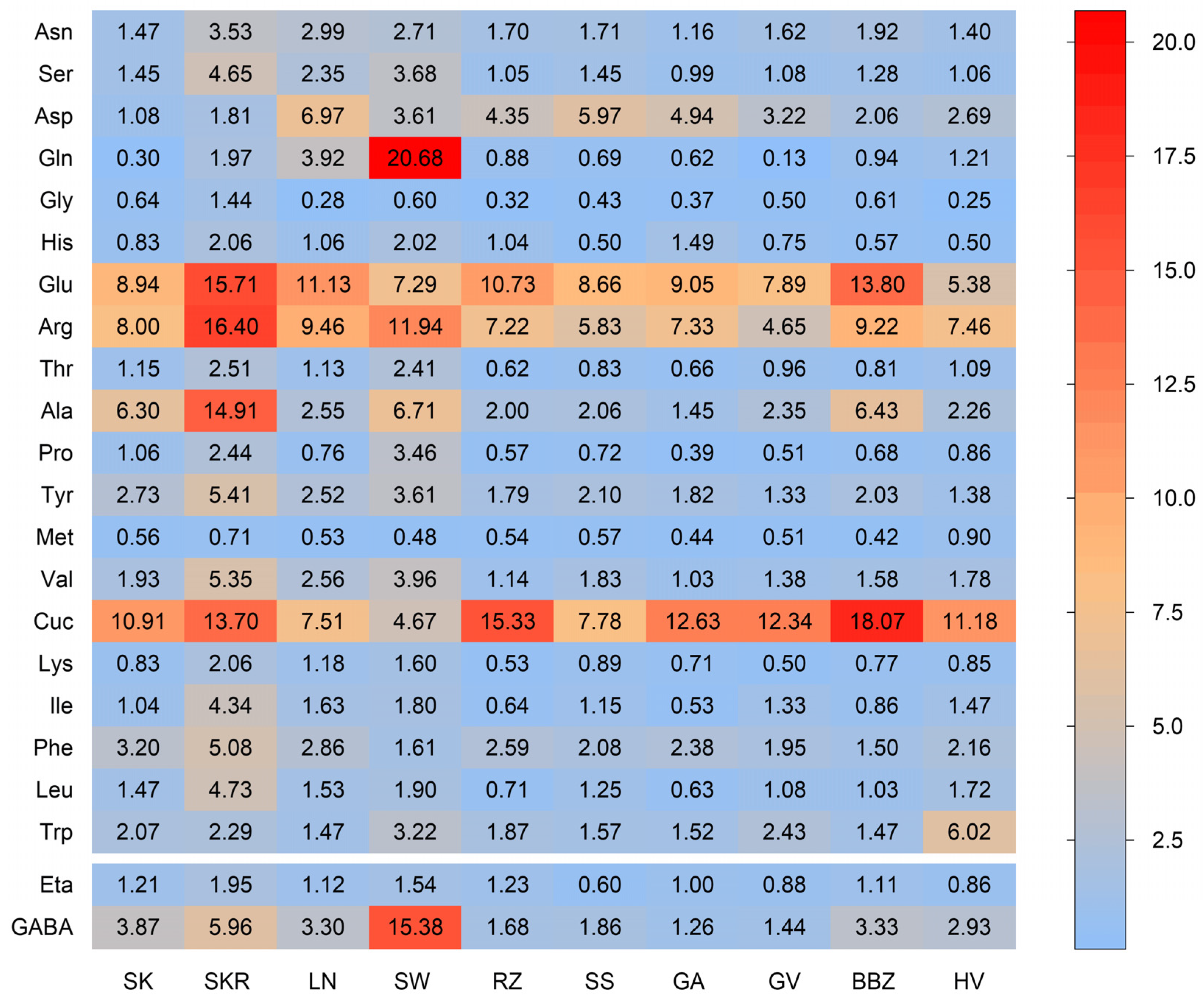
2.4. Analysis of Proteins and Free Amino Acids
2.5. Analysis of Lignans
2.6. Analysis of Trigonelline
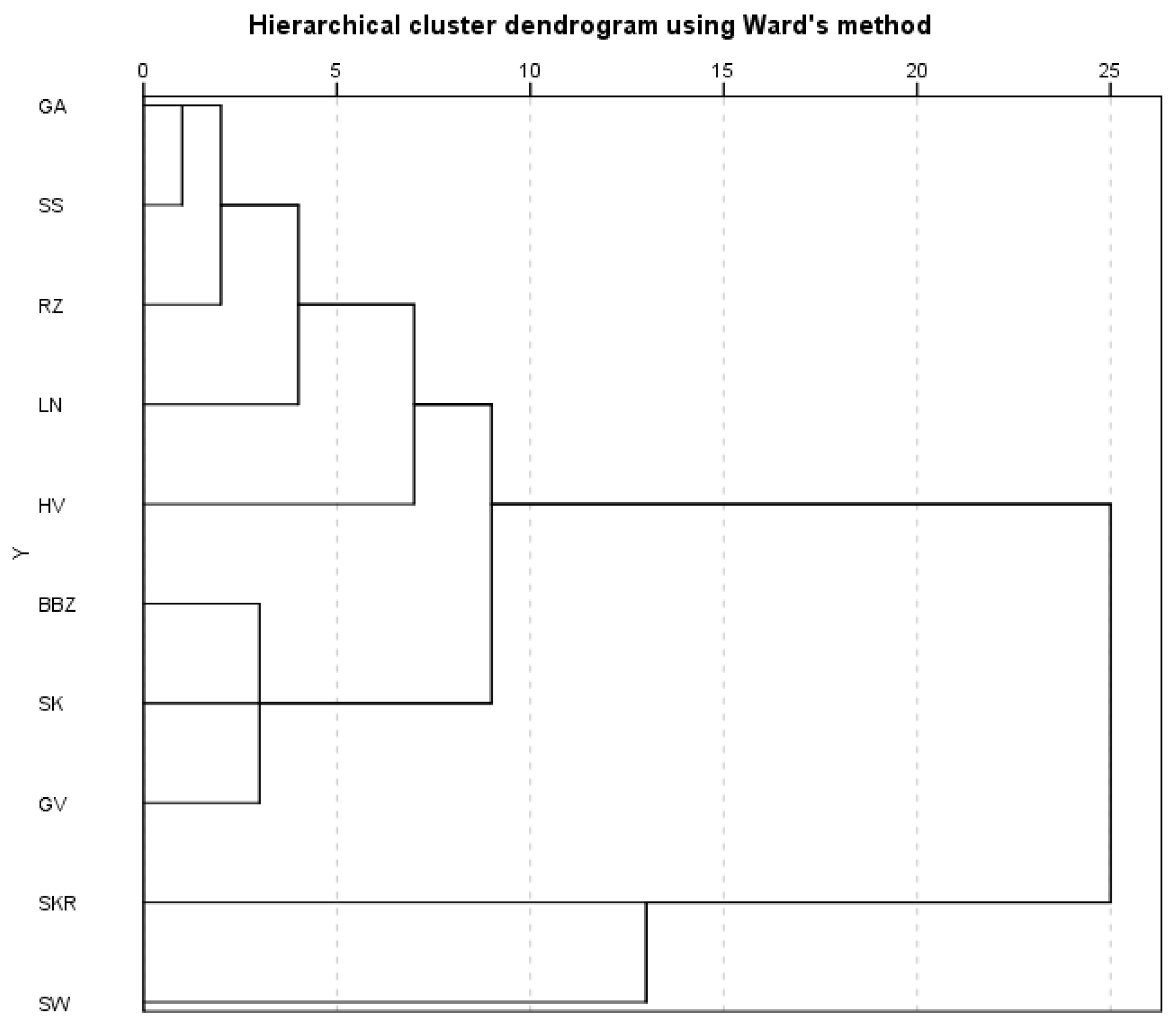
2.7. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Plant Material
4.3. Extract Preparation
4.4. Water Content and Elemental Analysis
4.4.1. Water Content
4.4.2. Metal Elements
4.4.3. TC and TN Content
4.5. HPTLC Analysis
4.6. LC-PDA-HRMS Analysis
4.7. Total Carbohydrate Content
4.8. UPLC Analysis of Saccharides
4.9. Total Protein Content
4.10. HPLC Analysis of Free Amino Acids
4.11. UPLC Analysis of Lignans
4.12. UPLC Analysis of Trigonelline
4.13. Multivariate Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| No. | RT (min) | Compound Name | Chemical Formula | Chemical Class | Calculated Mass | Main Fragment | Ion Type | Other Fragments | Identified | Not Identified | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.47 | Cucurbitin | C5H10N2O2 | amino acid | 130.0742 | 131.0819 | [M+H]+ | 85.0766 | 1–10 | [37] | |
| 2 | 4.17 | Trigonelline | C7H7NO2 | alkaloid | 137.0477 | 138.0557 | [M+H]+ | 94.0601 | 1–10 | [54] | |
| 3 | 8.594 | Nicotinic acid | C6H5NO2 | pyridine-3-carboxylic acid | 123.0320 | 124.0399 | [M+H]+ | 106.0271 | 1–10 | [54] | |
| 4 | 14.93 | Adenosine | C10H13N5O4 | nucleoside | 267.0968 | 268.1045 | [M+H]+ | 136.0624 | 1–10 | [38] | |
| 5 | 15.37 | Guanosine | C10H13N5O5 | nucleoside | 283.0917 | 282.0841 | [M-H]− | 152.0531 135.0305 | 1–10 | [38] | |
| 6 | 16.32 | Gallic acid | C7H6O5 | phenolic acids | 170.0200 | 169.0133 | [M-H]− | 125.0236 | 1–10 | [39,64] | |
| 7 | 24.39 | Protocatechuic acid | C7H6O4 | phenolic acids | 154.0266 | 153.0188 | [M-H]− | 109.0292 | 1–10 | [39,40] | |
| 8 | 25.16 | Cucurbitoside L | C24H29NO12 | phenolic glycoside | 523.1689 | 522.1614 | [M-H]− | 457.1924 411.1865 122.0247 | 1–10 | [42] | |
| 9 | 34.07 | Epigallocatechin | C15H14O7 | flavonoid | 306.0739 | 307.0818 | [M+H]+ | 289.0715 165.0218 | 1–10 | ||
| 10 | 35.61 | Chlorogenic acid | C16H18O9 | phenolic acid | 354.0951 | 353.0811 | [M-H]− | 191.0560, 375.0696, 443.0560, 511.0439, | 1–3, 5–7, 9 | 4, 8, 10 | [39] |
| 11 | 35.87 | Catechin | C15H14O6 | flavonoid | 290.0790 | 289.0715 | [M-H]− | 357.0585, 245.0805 | 1–10 | [39,64] | |
| 12 | 39.41 | Cucurbitoside H | C25H31NO12 | phenolic glycoside | 537.1846 | 536.1776 | [M-H]− | 383.2079 122.0247 | 1–10 | [41] | |
| 13 | 39.42 | Caffeic acid | C9H8O4 | phenolic acids | 180.0423 | 179.0349 | [M-H]− | 153.0190, 135.0448, 109.0290 | 2, 3, 5, 6, 10 | 1, 2, 4, 7–9 | [39,40] |
| 14 | 40.69 | Cucurbitoside M | C25H31NO12 | phenolic glycoside | 537.1846 | 536.1776 | [M-H]− | 399.1300 136.0402 | 1–10 | [42] | |
| 15 | 40.98 | Gibberelin A 39 | C20H26O8 | terpenoid | 394.1627 | 393.1555 | [M-H]− | 319.1184, 290.1255, 231.1384 | 1–10 | [43] | |
| 16 | 42.81 | Epicatechin | C15H14O6 | flavonoid | 290.0790 | 289.0715 | [M-H]− | 245.0808 | 1–10 | [39] | |
| 17 | 44.37 | Gibberelin A 8 | C19H24O7 | terpenoid | 364.152 | 363.1449 | [M-H]− | 275.1650, 257.1543 | 1–10 | [43] | |
| 18 | 44.98 | Cucurbitoside D | C25H30O13 | phenolic glycoside | 538.1686 | 537.1608 | [M-H]− | 186.1130 137.0236 | 1–10 | [41] | |
| 19 | 46.21 | Cucurbitoside I | C26H33NO12 | phenolic glycoside | 551.2003 | 550.1920 | [M-H]− | 413.1453 | 1–10 | [42] | |
| 20 | 46.92 | Gibberelin A 1 | C19H24O6 | terpenoid | 348.1572 | 347.1491 | [M-H]− | 241.0126 | 1–10 | [43] | |
| 21 | 48.97 | Homoorientin | C21H20O11 | flavonoid | 448.1006 | 449.1081 | [M+H]+ | 471.0893; 431.0974; 329.0657 | 4, 5, 7, 9 | 1–3, 6, 8, 10 | |
| 22 | 49.38 | p-coumaric acid | C9H8O3 | phenolic acid | 164.0473 | 163.0395 | [M-H]− | 119.0499 | 1–6, 8–10 | 7 | [39] |
| 23 | 49.77 | Secoisolariciresinol-diglucoside | C20H22O6 | lignan | 686.2786 | 327.159 | [M+H]+ | 704.3115 295.1328 163.0755 137.0594 | 3–7, 9, 10 | 1, 2, 8 | |
| 24 | 50.42 | Orientin | C21H20O11 | flavonoid | 448.1006 | 449.1075 | [M+H]+ | 431.0966 329.0656 | 4, 5, 7, 9 | 1–3, 6, 8, 10 | |
| 25 | 48.70 | Hydroxypinoresinol glucopyranoside | C26H32O12 | lignan | 536.1894 | 559.1791 (Na adduct) | [M+H]+ | 163.0754 | 3, 10 | 1, 2, 4–9 | |
| 26 | 51.09 | Cucurbitoside B | C26H32O13 | phenolic glycoside | 552.1843 | 551.1759 | [M-H]− | 137.0234 | 1–10 | [41] | |
| 27 | 51.76 | Vitexin-2-glucoside | C27H30O15 | flavonoid glycoside | 594.1585 | 595.1657 | [M+H]+ | 617.1475, 475.3251 453.3431 | 1–10 | ||
| 28 | 53.84 | Rutin | C27H30O16 | flavonoid | 610.1534 | 609.1453 | [M-H]− | 677.1335 | 1, 5–8 | 2–4, 9, 10 | [39,64] |
| 29 | 54.71 | Olivil | C20H24O7 | lignan | 376.1522 | 399.1412 (Na adduct) | [M+H]+ | 341.1387 323.1279 187.0756 | 3–5, 7–9 | 1, 2, 6, 10 | |
| 30 | 55.33 | Vitexin-2-rhamnoside | C27H30O14 | flavonoid glycoside | 578.1636 | 579.171 | [M+H]+ | 601.1523 | 1–10 | ||
| 31 | 55.36 | Vitexin | C21H20O10 | flavonoid | 432.1056 | 433.1129 | [M+H]+ | 415.1014 | 1–10 | [39] | |
| 32 | 54.41 | Myrcitrin | C21H20O12 | flavonoid | 464.0955 | 463.087 | [M-H]− | 509.0938 | 1, 6 | 2–5, 7–10 | |
| 33 | 54.84 | Cucurbitoside K | C23H34O12 | phenolic glycoside | 502.205 | 501.1969 | [M-H]− | 399.1287 123.0447 | 1–10 | [42] | |
| 34 | 54.91 | Hyperoside | C21H20O12 | flavonoid | 464.0955 | 463.0876 | [M-H]− | 301.0354, 151.0014 | 1–10 | ||
| 35 | 55.12 | Epicatechin gallate | C22H18O10 | flavonoid | 442.09 | 441.0819 | [M-H]− | 473.0710 | 1–10 | ||
| 36 | 55.67 | Isoquercitrin | C21H20O12 | flavonoid | 464.0955 | 463.0871 | [M-H]− | 301.0324, 151.0018 | 1–10 | ||
| 37 | 56.38 | Cucurbitoside C | C25H30O12 | phenolic glycoside | 522.1737 | 521.1652 | [M-H]− | 121.0291 | 1–10 | [41] | |
| 38 | 54.47 | Cucurbitoside E | C24H28O12 | phenolic glycoside | 508.1581 | 507.1497 | [M-H]− | 121.0291 | 1–10 | [41] | |
| 39 | 57.50 | Naringin | C27H32O14 | flavanone 7-O glycoside | 580.1792 | 579.1414 | [M-H]− | 647.1518 | 1–10 | [39,64] | |
| 40 | 57.58 | Cucurbitoside J | C25H38O13 | phenolic glycoside | 546.2312 | 545.2236 | [M-H]− | 353.1692 | 1–10 | [42] | |
| 41 | 57.70 | Cucurbitoside A | C26H32O12 | phenolic glycoside | 536.1894 | 535.1805 | [M-H]− | 413.1449 347.1494 121.0295 | 1–10 | [41] | |
| 42 | 57.72 | Quercitrin | C21H20O11 | flavonoid | 448.1006 | 447.0929 | [M-H]− | 303.0469 | 1–10 | ||
| 43 | 58.18 | Cucurbitoside F | C23H36O12 | phenolic glycoside | 516.2207 | 515.2123 | [M-H]− | 413.1451 137.0606 | 1–10 | [42] | |
| 44 | 59.78 | Myricetin | C15H10O8 | flavonoid | 318.0297 | 317.0298 | [M-H]− | 287.0165 | 1–10 | [64] | |
| 45 | 59.87 | Secoisolariciresinol | C20H26O6 | lignan | 362.1729 | 327.1593 | [M+H]+ | 385.1620 295.1328 163.0758 137.0598 | 3–10 | 1, 2 | [65] |
| 46 | 60.15 | Salicylic acid | C7H6O3 | carboxylic acid | 138.0317 | 137.0239 | [M-H]− | 297.0372 | 1–10 | [66] | |
| 47 | 60.80 | Lariciresinol | C20H24O6 | lignan | 360.1573 | 219.1019 | [M+H]+ | 189.0912 721.1034 | 3–10 | 1,2 | [57] |
| 48 | 63.37 | Daidzein | C15H10O4 | isoflavone | 254.0579 | 253.0504 | [M-H]− | 223.0413 | 1–10 | [65] | |
| 49 | 59.29 | Quercetin | C15H10O7 | flavonoid | 302.0427 | 301.0349 | [M-H]− | 179.0108 125.0114 | 1–10 | [64] | |
| 50 | 63.94 | Isolariciresinol | C32H46O16 | lignan | 360.1573 | 361.1646 | [M+H]+ | 209.0814 | 1–10 | ||
| 51 | 64.96 | Pinoresinol | C20H22O6 | lignan | 358.1416 | 341.1385 | [M+H]+ | 323.1273 175,0756 | 3–10 | 1, 2 | [67] |
| 52 | 65.16 | Cucurbitacin E-2-O glucoside | C38H54O13 | cucurbitacin type triterpene | 718.3564 | 741.3465 | [M+H]+ | 479.2796 461.2689 | 3 | 1, 2, 4–10 | [67] |
| 53 | 65.86 | Cucurbitacin A | C32H46O9 | cucurbitacin type triterpene | 574.3142 | 597.3035 | [M+H]+ | 515.3007 467.2791 | 1–10 | [67] | |
| 54 | 65.60 | Apigenin | C15H10O5 | flavonoid | 270.0528 | 271.0609 | [M+H]+ | 158.0123 | 1–10 | [39] | |
| 55 | 66.49 | Cucurbitacin D | C30H44O7 | cucurbitacin type triterpene | 516.3087 | 539.2978 | [M+H]+ | 481.2951 499.3055 | 1–10 | [44] | |
| 56 | 66.50 | Kaempferol | C15H10O6 | flavonoid | 286.0477 | 285.0402 | [M-H]− | 164.9982 119.0323 | 1–10 | [64] | |
| 57 | 68.14 | Cucurbitacin I | C30H42O7 | cucurbitacin type triterpene | 514.2931 | 537.2821 | [M+H]+ | 97.2896 479.2794 461.2686 | 1–10 | [44] | |
| 58 | 71.11 | Cucurbitacin B | C32H46O8 | cucurbitacin type triterpene | 558.3193 | 581.3089 | [M+H]+ | 481.295 463.2846 | 3 | 1, 2, 4–10 | [44] |
| 59 | 75.51 | Matairesinol | C20H22O6 | lignan | 358.1416 | 359.2412 | [M+H]+ | 375.2146 175.1334 103.0756 | 1–10 |
Appendix B. List of Routine Solvents and General Laboratory Reagents
References
- Castellanos-Morales, G.; Ruiz-Mondragon, K.Y.; Hernandez-Rosales, H.S.; Sanchez-de la Vega, G.; Gamez, N.; Aguirre-Planter, E.; Montes-Hernandez, S.; Lira-Saade, R.; Eguiarte, L.E. Tracing back the origin of pumpkins (Cucurbita pepo ssp. pepo L.) in Mexico. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2019, 286, 20191440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.; Munger, H.; Whitaker, T.; Bohn, G. Genes of the Curcurbitaceae. Hort. Sci. 1976, 11, 554–568. [Google Scholar]
- Batool, M.; Ranjha, M.; Roobab, U.; Manzoor, M.F.; Farooq, U.; Nadeem, H.R.; Nadeem, M.; Kanwal, R.; AbdElgawad, H.; Al Jaouni, S.K.; et al. Nutritional Value, Phytochemical Potential, and Therapeutic Benefits of Pumpkin (Cucurbita sp.). Plants 2022, 11, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnam, N.; Naijibullah, M.; Ibrahim, M. A review on Cucurbita pepo. Int. J. Pharm. Phytochem. Res. 2017, 9, 1190–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, T.T.T.; Quach, T.T.M.; Yuguchi, Y.; Nguyen, N.T.; Van Ngo, Q.; Van Bui, N.; Kawashima, S.; Ho, C.D. Molecular structure and anti-diabetic activity of a polysaccharide extracted from pumpkin Cucurbita pepo. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1239, 130507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedigheh, A.; Jamal, M.S.; Mahbubeh, S.; Somayeh, K.; Mahmoud, R.; Azadeh, A.; Fatemeh, S. Hypoglycaemic and hypolipidemic effects of pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo L.) on alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 5, 2620–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahlensieck, W.; Theurer, C.; Pfitzer, E.; Patz, B.; Banik, N.; Engelmann, U. Effects of pumpkin seed in men with lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia in the one-year, randomized, placebo-controlled GRANU study. Urol. Int. 2015, 94, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossell-Williams, M.; Davis, A.; O’Connor, N. Inhibition of testosterone-induced hyperplasia of the prostate of sprague-dawley rats by pumpkin seed oil. J. Med. Food 2006, 9, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerafatjou, N.; Amirzargar, M.; Biglarkhani, M.; Shobeirian, F.; Zoghi, G. Pumpkin seed oil (Cucurbita pepo) versus tamsulosin for benign prostatic hyperplasia symptom relief: A single-blind randomized clinical trial. BMC Urol. 2021, 21, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, M.; Ohkawara, T.; Sato, H.; Takeda, H.; Nishihira, J. Pumpkin Seed Oil Extracted From Cucurbita maxima Improves Urinary Disorder in Human Overactive Bladder. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2014, 4, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogabe, H.; Terado, T. Open clinical study of effects of pumpkin seed extract/soybean germ extract vixture-containing processed food on nocturia. Jpn. J. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 46, 727–737. [Google Scholar]
- Terado, T.; Sogabe, H.; Saito, K. Clinical Study of mixed processed foods containing of pumpkin seed extract and soybean germ extract on pollakiuria in night infielder men. Jpn. J. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 52, 551–561. [Google Scholar]
- Abrams, P.; Kelleher, C.; Kerr, L.A.; Rogers, R.G. Overactive bladder significantly affects quality of life. Am. J. Manag. Care. 2000, 6, S580–S590. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, B.; Jeong, H.; Lee, S.; Hwang, S.; Moon, B.; Storni, C. A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial of a product containing pumpkin seed extract and soy germ extract to improve overactive bladder-related voiding dysfunction and quality of life. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 8, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, E.; Satoh, I. Clinical study of mixed processed foods containing of pumpkin seed extract and soybean germ extract on stress urinary incontinence (SUI) in women. Jpn. J. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 50, 313–322. [Google Scholar]
- Leibbrand, M.; Siefer, S.; Schon, C.; Perrinjaquet-Moccetti, T.; Kompek, A.; Csernich, A.; Bucar, F.; Kreuter, M.H. Effects of an oil-free hydroethanolic pumpkin seed extract on symptom frequency and severity in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia: A pilot study in humans. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, S.; Seibt, S.; Stier, H.; Moré, M.I. Uromedic® pumpkin seed derived Δ7-sterols, extract and oil inhibit 5α-reductases and bind to androgen receptor in vitro. Pharmacol. Pharm. 2018, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramak, P.; Mahboubi, M. The beneficial effects of pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo L.) seed oil for health condition of men. Food Rev. Int. 2019, 35, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA; HMPC (Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products). Final Community Herbal Monograph on Cucurbita pepo L., semen; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Widy-Tyszkiewicz, E.; Matlawska, I.; Bylka, W. Assessment Report on Cucurbita pepo L., Semen; EMA/HMPC/136022/2010; Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products (HMPC): Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chahal, G.K.; Kaur, A.; Dhatt, A.S. A single-gene mutation changed the architecture of pumpkin seed: A review. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 41, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedláčková, V.H.; Avagyan, A. Morphological characteristics of selected fruit parts and naked seeds of Cucurbita pepo var. styriaca. Agrobiodivers. Improv. Nutr. Health Life Qual. 2022, 6, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelley, T.; Loy, B.; Murkovic, M. Hull-Less Oil Seed Pumpkin. In Oil Crops; Vollmann, J., Rajcan, I., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 469–492. [Google Scholar]
- EDQM. Pumpkin seed (2941). In European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.), 11th ed.; Council of Europe, Ed.; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2023; pp. 4858–4859. [Google Scholar]
- Paris, H.S.; Burger, Y.; Schaffer, A.A. Genetic variability and introgression of horticulturally valuable traits in squash and pumpkins of Cucurbita pepo. Isr. J. Plant Sci. 2006, 54, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebeda, A.; Křístková, E.; Paris, H. Variation for morphological traits within and among Cucurbita pepo genotypes. Acta. Hortic. 2010, 871, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomić, D.; Radovanović, M.; Marjanović, M.; Đurović, V.; Stevović, V.; Pavlović, N.; Lazarević, Đ.; Zornić, V.; Madić, M. Divergence analysis of Cucurbita pepo L. population for seed oil production. Not. Bot. Horti. Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2024, 52, 13907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meru, G.; Fu, Y.; Leyva, D.; Sarnoski, P.; Yagiz, Y. Phenotypic relationships among oil, protein, fatty acid composition and seed size traits in Cucurbita pepo. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 233, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, Y.M.; Ghirmay, S.; al-Shihry, S.S. African Cucurbita pepo L.: Properties of seed and variability in fatty acid composition of seed oil. Phytochem. Anal. 2000, 54, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymen, M.; Uslu, N.; Türkmen, Ö.; Al Juhaimi, F.; Özcan, M.M. Chemical compositions and mineral contents of some hull-less pumpkin seed and oils. J. Am. Oil. Chem. Soc. 2016, 93, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkovic, L.; Kolmanic, A. Elemental composition and nutritional characteristics of Cucurbita pepo subsp. pepo seeds, oil cake and pumpkin oil. J. Elem. 2021, 26, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glew, R.H.; Glew, R.S.; Chuang, L.T.; Huang, Y.S.; Millson, M.; Constans, D.; Vanderjagt, D.J. Amino acid, mineral and fatty acid content of pumpkin seeds (Cucurbita spp) and Cyperus esculentus nuts in the Republic of Niger. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2006, 61, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intrenational Council for Harmonisation (ICH). Guideline for Elemental Impurities Q3D (R2); European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, J. Codex Nutrient Reference Values; FAO-WHO: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Elinge, C.; Muhammad, A.; Atiku, F.; Itodo, A.; Peni, I.; Sanni, O.; Mbongo, A. Proximate, mineral and anti-nutrient composition of pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo L) seeds extract. Int. J. Plant. Res. 2012, 2, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cindric, I.J.; Zeiner, M.; Steffan, I. Trace elemental characterization of edible oils by ICP–AES and GFAAS. Microchem. J. 2007, 85, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzybek, M.; Kukula-Koch, W.; Strachecka, A.; Jaworska, A.; Phiri, A.M.; Paleolog, J.; Tomczuk, K. Evaluation of Anthelmintic Activity and Composition of Pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo L.) Seed Extracts-In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.C.; Xiang, H.; Li, D.; Gao, H.Y.; Cai, H.; Wu, L.J.; Deng, X.M. Purine-containing cucurbitane triterpenoids from Cucurbita pepo cv dayangua. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1434–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, C.; Silva, A.M.; Ferreira, A.S.; Moreira, M.M.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Rodrigues, F. Microwave- and ultrasound-assisted extraction of Cucurbita pepo seeds: A Comparison study of antioxidant activity, phenolic profile, and in vitro cells effects. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peričin, D.; Krimer, V.; Trivić, S.; Radulović, L. The distribution of phenolic acids in pumpkin’s hull-less seed, skin, oil cake meal, dehulled kernel and hull. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, K.; Li, W.; Liu, L.; Hata, E.; Nikaido, T. New phenolic glycosides from the seeds of Cucurbita moschata. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 53, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Koike, K.; Tatsuzaki, M.; Koide, A.; Nikaido, T. Cucurbitosides F−M, Acylated Phenolic Glycosides from the Seeds of Cucurbita pepo. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1754–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, T.; Kappler, J.; Fischer, A.; Frisse, A.; Padeffke, T.; Schmidtke, S.; Lange, M.J. Gibberellin biosynthesis in developing pumpkin seedlings. Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía-Morales, C.; Rodríguez-Macías, R.; Salcedo-Pérez, E.; Zamora-Natera, J.; Rodríguez-Zaragoza, F.; Molina-Torres, J.; Délano-Frier, J.; Zañudo-Hernández, J. Contrasting metabolic fingerprints and seed protein profiles of Cucurbita foetidissima and C. radicans fruits from feral plants sampled in central Mexico. Plants 2021, 10, 2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, P.; Varshney, V.; Majee, M. Raffinose family oligosaccharides (RFOs): Role in seed vigor and longevity. Biosci. Rep. 2022, 42, BSR20212896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, E.H.; Dworschák, E.; Lugasi, A.; Barna, É.; Gergely, A. Nutritive value of pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo Kakai 35) seed products. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 1993, 61, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, N.; Fernandes, Â.; Calhelha, R.C.; Petrović, J.; Soković, M.; Ferreira, I.C.; Barros, L.; Petropoulos, S.A. Biochemical composition of pumpkin seeds and seed by-products. Plants 2024, 13, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, J.; Gerhardt, H.; Theiner, J.; Lindner, W. Correlation between amino acid racemization and processing conditions for various wheat products, oil seed press cakes and lignin samples. Food Bioprod. Process. 2014, 92, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krimer-Malešević, V. Pumpkin seeds: Phenolic acids in pumpkin seed (Cucurbita pepo L.). In Nuts and Seeds in Health and Disease Prevention; Preedy, V.R., Watson, R.R., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2020; pp. 533–542. [Google Scholar]
- Abuelgassim, A.O.; Al-Showayman, S.I. The effect of pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo L.) seeds and L-arginine supplementation on serum lipid concentrations in atherogenic rats. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 9, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustățea, G.; Ungureanu, E.L.; Iorga, E. Protein acidic hydrolysis for amino acids analysis in food-progress over time: A short review. J. Hyg. Eng. Des. 2019, 26, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, A.; Nunes, M.T.; Maldaner, V.; Coradi, P.C.; de Moraes, R.S.; Martens, S.; Leal, A.F.; Pereira, V.F.; Marin, C.K. Rice drying, storage and processing: Effects of post-harvest operations on grain quality. Rice Sci. 2022, 29, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Taine, E.G.; Meng, D.; Cui, T.; Tan, W. Pharmacological activities, therapeutic effects, and mechanistic actions of trigonelline. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ramaswamy, S.H.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Irshad, A.; Ren, Y. Nutrient evaluation of the seed, pulp, flesh, and peel of spaghetti squash. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appendino, G.; Jakupovic, J.; Belloro, E.; Marchesini, A. Triterpenoid p-aminobenzoates from the seeds of zucchini. Fitoterapia 2000, 71, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appendino, G.; Jakupovic, J.; Belloro, E.; Marchesini, A. Multiflorane triterpenoid esters from pumpkin. An unexpected extrafolic source of PABA. Phytochemistry 1999, 51, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicilia, T.; Niemeyer, H.B.; Honig, D.M.; Metzler, M. Identification and stereochemical characterization of lignans in flaxseed and pumpkin seeds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milder, I.E.; Arts, I.C.; van de Putte, B.; Venema, D.P.; Hollman, P.C. Lignan contents of Dutch plant foods: A database including lariciresinol, pinoresinol, secoisolariciresinol and matairesinol. Br. J. Nutr. 2005, 93, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria-e-Silva, A.; Heckel, L.; Belli, R.; Lohbauer, U. Determination of water content in direct resin composites using coulometric Karl Fischer Titration. Materials 2022, 15, 8524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuko, T.; Minami, A.; Iwasaki, N.; Majima, T.; Nishimura, S.; Lee, Y.C. Carbohydrate analysis by a phenol-sulfuric acid method in microplate format. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 339, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phenomenex Inc. Luna Omega Sugar Application Guide; Phenomenex Inc.: Torrance, CA, USA, 2018; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P.K.; Krohn, R.I.; Hermanson, G.; Mallia, A.; Gartner, F.; Provenzano, M.; Fujimoto, E.; Goeke, N.; Olson, B.; Klenk, D. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 150, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guba, A.; Bába, O.; Tőzsér, J.; Csősz, É.; Kalló, G. Fast and sensitive quantification of AccQ-Tag derivatized amino acids and biogenic amines by UHPLC-UV analysis from complex biological samples. Metabolites 2022, 12, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švarc-Gajić, J.; Rodrigues, F.; Moreira, M.M.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Morais, S.; Dorosh, O.; Silva, A.M.; Bassani, A.; Dzedik, V.; Spigno, G. Chemical composition and bioactivity of oilseed cake extracts obtained by subcritical and modified subcritical water. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2022, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murkovic, M.; Piironen, V.; Lampi, A.M.; Kraushofer, T.; Sontag, G. Changes in chemical composition of pumpkin seeds during the roasting process for production of pumpkin seed oil (Part 1: Non-volatile compounds). Food Chem. 2004, 84, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmonsef, M.; Shawky, E.; Ghareeb, D.A.; El Naggar, E.M.B.; El Newehy, N.M. Comprehensive metabolomics and chemometrics unravel potential anti-diabetic metabolites of pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo L.) fruits through UPLC-QqQ-MS and GC–MS analyses. Food Res. Int. 2024, 192, 114771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghallab, D.S.; Ghareeb, D.A. UPLC-MS/MS-based metabolomics and chemometrics unveil metabolic patterns and their regulatory pathways over the course of pumpkin seeds (Cucurbita maxima) germination. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 337, 113563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Nr. | Sample | TOC [mg/g] | IC [mg/g] | TC [mg/g] | TN [mg/g] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SK | 449.37 ± 1.05 | 2.95 ± 0.17 | 452.32 ± 1.04 | 14.32 ± 0.02 |
| 2 | SKR | 340.61 ± 3.34 | 3.68 ± 0.07 | 344.29 ± 3.34 | 19.25 ± 0.16 |
| 3 | LN | 394.42 ± 0.68 | 2.35 ± 0.03 | 396.77 ± 0.67 | 16.22 ± 0.07 |
| 4 | SW | 337.48 ± 1.68 | 2.46 ± 0.01 | 339.94 ± 1.68 | 26.57 ± 0.03 |
| 5 | RZ | 397.61 ± 3.08 | 2.08 ± 0.01 | 399.69 ± 3.08 | 14.39 ± 0.18 |
| 6 | SS | 341.83 ± 1.91 | 4.55 ± 0.03 | 346.37 ± 1.91 | 13.32 ± 0.07 |
| 7 | GA | 306.43 ± 0.43 | 2.31 ± 0.15 | 308.74 ± 0.40 | 12.59 ± 0.09 |
| 8 | GV | 528.16 ± 0.75 | 3.11 ± 0.13 | 531.27 ± 0.74 | 13.59 ± 0.02 |
| 9 | BBZ | 297.33 ± 1.95 | 7.05 ± 0.13 | 304.38 ± 1.95 | 14.81 ± 0.14 |
| 10 | HV | 444.47 ± 1.10 | 3.29 ± 0.24 | 447.76 ± 1.07 | 27.09 ± 0.24 |
| Number | Extract | Trigonelline Content [mg/g] | ±SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SK | 1.764 | 0.004 |
| 2 | SKR | 1.685 | 0.002 |
| 3 | LN | 1.765 | 0.023 |
| 4 | SW | 3.447 | 0.027 |
| 5 | RZ | 0.459 | 0.008 |
| 6 | SS | 1.975 | 0.001 |
| 7 | GA | 0.985 | 0.002 |
| 8 | GV | 0.413 | 0.016 |
| 9 | BBZ | 0.407 | 0.006 |
| 10 | HV | 1.333 | 0.002 |
| Nr. | Name | Code | Extraction Yield [g] | Country of Origin | Distributor | Batch | Macroscopy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C. pepo convar. citrullina, var styriaca | SK | 10.25 | Austria | Estyria Naturprodukte GmbH | 21-039676 0001 | Medium, dark green seeds, with a very thin shell and a pointed tip. Length 1.3–1.7 cm, width 0.4–0.6 cm. |
| 2 | C. pepo var. styriaca cultivar Gleisdorfer Rustikal | SKR | 10.01 | Switzerland | Vitaplant AG | CUP 22_2202 | Medium, dark green seeds, with a very thin shell and a pointed tip. Length 1.2–2.1 cm, width 0.5–0.7 cm. |
| 3 | C. pepo—Lady Nail | LN | 11.21 | Switzerland | Vitaplant AG | CUP 22_2021 | Medium, sharp light-yellow seeds. Length 1.5–2.0 cm, width 0.4–0.5 cm. |
| 4 | C. pepo—Snow White | SW | 15.63 | Switzerland | Vitaplant AG | CUP 22_2103 | Large, with a thick shell, and light-yellow seeds. Length 2.0–2.5 cm, width 1.0–1.4 cm. |
| 5 | C. pepo var. giromontia -Radu | RZ | 10.35 | Romania | Agrosem Impex | 2MS1196 | Small, round, light yellow seeds. Length 0.8–1.5 cm, width 0.5–0.6 cm. |
| 6 | C. pepo—Shine Skin | SS | 13.37 | Ukraine | M.A.R. Pumpkin Seeds | CUS18006/20 | Medium, with a thick shell, pointed tip, and light-yellow seeds. Length 1.5–2.5 cm, width 0.8–1.0 cm. |
| 7 | C. pepo -Greek Cultivar | GA | 10.21 | Greece | Antonio Foods | CUS19001(S/K/H) | Medium, narrow and sharp, light-yellow seeds. Length 1.4–2.1 cm, width 0.4–0.5 cm. |
| 8 | C. pepo—Grey Volga | GV | 12.44 | Ukraine | M.A.R. Pumpkin Seeds | CUS18005/20 | Medium, with a soft smooth shell, and light-yellow seeds. Length 1.5–2.2 cm, width 0.9–1.0 cm. |
| 9 | C. pepo var. cylindrica—Black Beauty | BBZ | 10.33 | Romania | Agrosem Impex | 2MS1197 | Small, round, light yellow seeds. Length 0.9–1.2 cm, width 0.5–0.6 cm. |
| 10 | C. pepo—Hungarian Cultivar | HV | 14.67 | Hungary | H.F.I. Hungarian Food Ingredients | CUS18008/20 | Medium, round, with a thick orange shell. Length 1.5–2.2 cm, width 0.7–1.0 cm. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grasu, A.-E.; Senn, R.; Halbsguth, C.; Schenk, A.; Butterweck, V.; Miron, A. Profiling Hydrophilic Cucurbita pepo Seed Extracts: A Study of European Cultivar Variability. Plants 2025, 14, 2308. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152308
Grasu A-E, Senn R, Halbsguth C, Schenk A, Butterweck V, Miron A. Profiling Hydrophilic Cucurbita pepo Seed Extracts: A Study of European Cultivar Variability. Plants. 2025; 14(15):2308. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152308
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrasu, Adina-Elena, Roman Senn, Christiane Halbsguth, Alexander Schenk, Veronika Butterweck, and Anca Miron. 2025. "Profiling Hydrophilic Cucurbita pepo Seed Extracts: A Study of European Cultivar Variability" Plants 14, no. 15: 2308. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152308
APA StyleGrasu, A.-E., Senn, R., Halbsguth, C., Schenk, A., Butterweck, V., & Miron, A. (2025). Profiling Hydrophilic Cucurbita pepo Seed Extracts: A Study of European Cultivar Variability. Plants, 14(15), 2308. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152308





