Genome-Wide Identification of Wheat Gene Resources Conferring Resistance to Stripe Rust
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
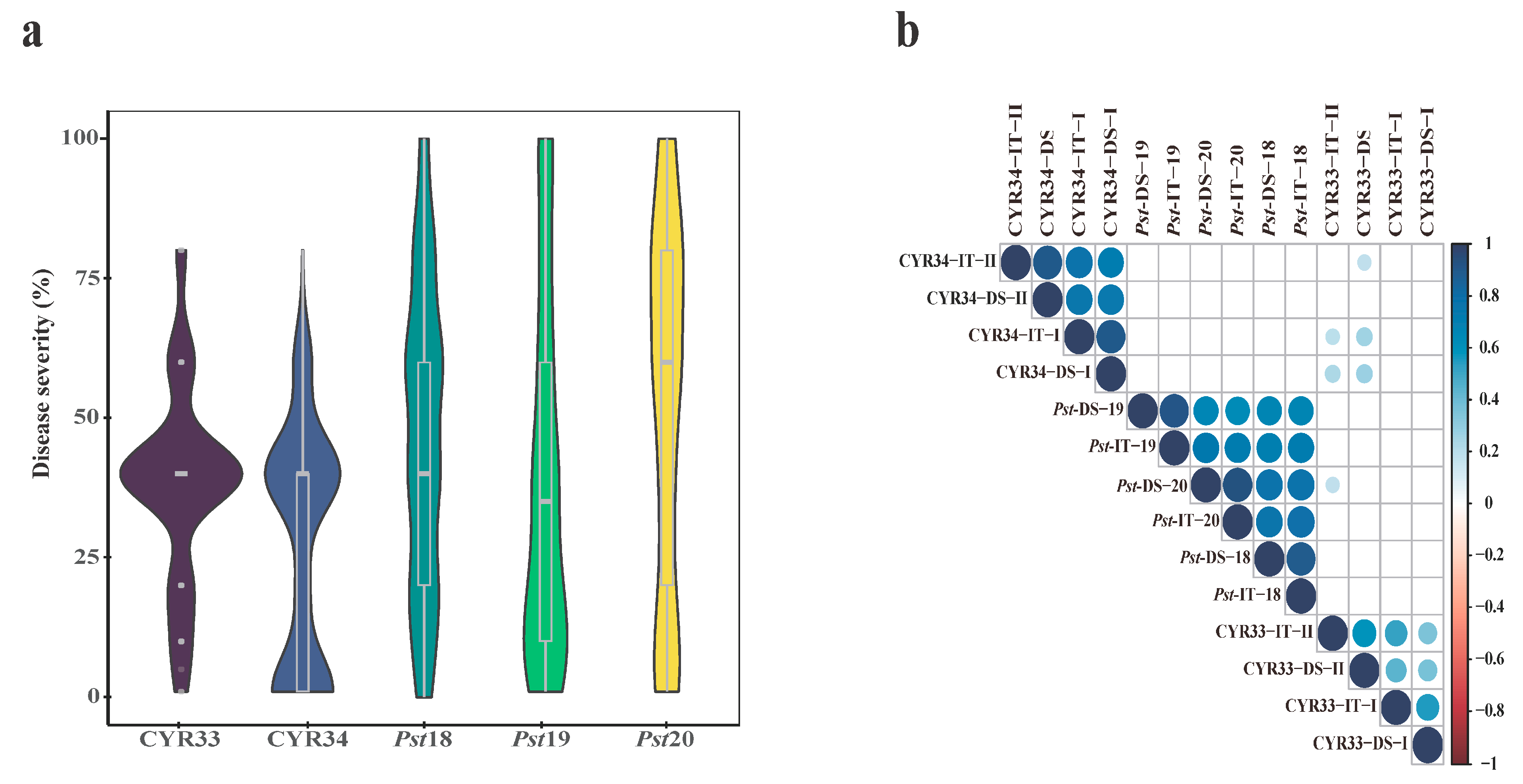
2.1. Stripe Rust Response at the Seedling Stage
2.2. Stripe Rust Response at the Adult-Plant Stage
2.3. Population Structure, Genetic Diversity, and LD
2.4. GWAS and Haplotype Analysis for Stripe Rust Resistance
2.4.1. QTL Resistant to CYR33 at the Seedling Stage
2.4.2. QTL for Resistance to CYR34 at the Seedling Stage
QTL on Chromosome 1B
QTL on Chromosome 1D
QTL on Chromosome 6DL
QTL on Chromosome 7DS
2.4.3. QTL Resistant to Stripe Rust at the Adult-Plant Stage
2.4.4. Distributions and Frequency of Favorable Haplotypes for Stripe Rust Resistance
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Evaluation for Stripe Rust Resistance at the Seedling Stage
4.3. Evaluation of Stripe Rust Resistance at the Adult-Plant Stage
4.4. Genotyping and Genetic Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.M. Pathogens which threaten food security: Puccinia striiformis, the wheat stripe rust pathogen. Food Secur. 2020, 12, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Q.; Wu, L.R.; Liu, T.G.; Xu, S.C.; Jin, S.L.; Peng, Y.L.; Wang, B.T. Race dynamics, diversity, and virulence evolution in Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici, the causal agent of wheat stripe rust in China from 2003 to 2007. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, D.; Zuo, S.X.; Chen, X.M.; Zhuang, H.; Huang, L.L.; Kang, Z.S.; Zhao, J. Inheritance and linkage of virulence genes in Chinese predominant race CYR32 of the wheat stripe rust pathogen Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, J.G.; Lagudah, E.S.; Spielmeyer, W.; Dodds, P.N. The past, present and future of breeding rust resistant wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwessinger, B. Fundamental wheat stripe rust research in the 21(st) century. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambuthenne, D.T.; Riaz, A.; Athiyannan, N.; Alahmad, S.; Ng, W.L.; Ziems, L.; Afanasenko, O.; Periyannan, S.K.; Aitken, E.; Platz, G.; et al. Mining the Vavilov wheat diversity panel for new sources of adult plant resistance to stripe rust. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 1355–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, S.A.; McIntosh, R.A.; Uauy, C.; Krattinger, S.G.; Dubcovsky, J.; Rogers, W.J.; Xia, X.C.; Badaeva, E.D.; Bentley, A.R.; Brown-Guedira, G.; et al. Updated guidelines for gene nomenclature in wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2023, 136, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Yu, C.; Cheng, Y.K.; Yao, F.J.; Long, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Wang, J.R.; Jiang, Q.T.; et al. Genome-wide association mapping reveals potential novel loci controlling stripe rust resistance in a Chinese wheat landrace diversity panel from the southern autumn-sown spring wheat zone. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klymiuk, V.; Chawla, H.S.; Wiebe, K.; Ens, J.; Fatiukha, A.; Govta, L.; Fahima, T.; Pozniak, C.J. Discovery of stripe rust resistance with incomplete dominance in wild emmer wheat using bulked segregant analysis sequencing. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliana, P.; Singh, R.P.; Huerta-Espino, J.; Bhavani, S.; Randhawa, M.S.; Kumar, U.; Joshi, A.K.; Bhati, P.K.; Mir, H.E.V.; Mishra, C.N.; et al. Genome-wide mapping and allelic fingerprinting provide insights into the genetics of resistance to wheat stripe rust in India, Kenya and Mexico. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Zeid, M.A.; Mourad, A.M.I. Genomic regions associated with stripe rust resistance against the Egyptian race revealed by genome-wide association study. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvet, L.; Holdgate, S.; James, L.; Thomas, J.; Mackay, I.J.; Cockram, J. The evolving battle between yellow rust and wheat: Implications for global food security. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.Q.; Kang, Z.S.; Man, Z.H.; Xu, S.C.; Jin, S.L. Integrated management of wheat stripe rust caused by Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici in China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2013, 20, 4254–4262. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, B.B.; Liu, T.G.; Liu, B.; Gao, L.; Chen, W.Q. High relative parasitic fitness of G22 derivatives is associated with the epidemic potential of wheat stripe rust in China. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, T.G.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Jia, Q.Z.; Wang, B.T.; Gao, L.; Peng, Y.L.; Jin, S.L.; Chen, W.Q. Discovery and pathogenicity of CYR34, a new race of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici in China. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2017, 47, 681–687. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.J.; Wang, Q.L.; Chen, X.M.; Zeng, Q.D.; Wu, J.H.; Xue, W.B.; Zhan, G.M.; Huang, L.L.; Kang, Z.S. Emerging Yr26-virulent races of Puccinia striiformis f. tritici are threatening wheat production in the Sichuan basin, China. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.D.; Shen, C.; Yuan, F.P.; Wang, Q.L.; Wu, J.H.; Xue, W.B.; Zhan, G.M.; Yao, S.; Chen, W. The resistance evaluation of the Yr genes to the main prevalent pathotypes of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici in China. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2015, 45, 641–650. [Google Scholar]
- Zegeye, H.; Rasheed, A.; Makdis, F.; Badebo, A.; Ogbonnaya, F.C. Genome-wide association mapping for seedling and adult plant resistance to stripe rust in synthetic hexaploid wheat. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccaferri, M.; Zhang, J.; Bulli, P.; Abate, Z.; Chao, S.; Cantu, D.; Bossolini, E.; Chen, X.M.; Pumphrey, M.; Dubcovsky, J. A genome-wide association study of resistance to stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici) in a worldwide collection of hexaploid spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). G3 (Bethesda) 2015, 5, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Yao, F.J.; Yu, C.; Ye, X.L.; Cheng, Y.K.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J.R.; Jiang, Q.T.; et al. Genome-wide association study for adult-plant resistance to stripe rust in Chinese wheat landraces (Triticum aestivum L.) from the Yellow and Huai river valleys. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Gao, X.; Cao, N.; Ding, Y.Q.; Gao, Y.; Chen, T.Q.; Xin, Z.H.; Zhang, L.Y. Genome-wide association analysis of stripe rust resistance loci in wheat accessions from southwestern China. J. Appl. Genet. 2020, 61, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikram, P.; Sehgal, D.; Sharma, A.; Bhavani, S.; Gupta, P.; Randhawa, M.; Pardo, N.; Basandra, D.; Srivastava, P.; Singh, S.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis of Mexican bread wheat landraces for resistance to yellow and stem rust. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, Z.; Ali, M.; Mirza, J.I.; Fayyaz, M.; Majeed, K.; Naeem, M.K.; Aziz, A.; Trethowan, R.; Ogbonnaya, F.C.; Poland, J.; et al. Genome-wide association and genomic prediction for stripe rust resistance in synthetic-derived wheats. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 788593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marone, D.; Laidò, G.; Saccomanno, A.; Petruzzino, G.; Giaretta Azevedo, C.V.; de Vita, P.; Mastrangelo, A.M.; Gadaleta, A.; Ammar, K.; Bassi, F.M.; et al. Genome-wide association study of common resistance to rust species in tetraploid wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1290643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 1443.1-2007; Rules for Resistance Evaluation of Wheat to Diseases and Insect Pests Part 1: Rule for Resistance Evaluation of Wheat to Yellow Rust (Puccinia striiformis West. f. sp. tritici Eriks. et Henn.). Ministry of Agriculture: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Zhou, C.E.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Q.M.; Liu, S.J.; Zeng, Q.D.; Wang, Q.L.; Wang, C.F.; Li, C.L.; Singh, R.P.; et al. Combined linkage and association mapping reveals two major QTL for stripe rust adult plant resistance in Shaanmai 155 and their haplotype variance in common wheat germplasm. Crop J. 2022, 10, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Hu, Y.L.; Gong, F.Y.; Jin, Y.R.; Xia, Y.J.; He, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; He, J.S.; Feng, L.H.; et al. Identification and mapping of QTL for stripe rust resistance in the Chinese wheat cultivar Shumai126. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.J.; Tian, B.; Cao, J.H.; Liu, S.J.; Zhou, C.E.; Wang, X.T.; Zhang, Y.B.; Li, J.L.; Yuan, X.Y.; Wan, J.F.; et al. Yr29 combined with QYr.nwafu-4BL.3 confers durable resistance to stripe rust in wheat cultivar Jing 411. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2024, 137, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.J.; Guan, F.N.; Duan, L.Y.; Long, L.; Tang, H.; Jiang, Y.F.; Li, H.; Jiang, Q.T.; Wang, J.R.; Qi, P.F.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis of stable stripe rust resistance loci in a Chinese wheat landrace panel using the 660K SNP array. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 783830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehseen, M.M.; Tonk, F.A.; Tosun, M.; Randhawa, H.S.; Kurtulus, E.; Ozseven, I.; Akin, B.; Nur Zulfuagaoglu, O.; Nazari, K. QTL mapping of adult plant resistance to stripe rust in a doubled haploid wheat population. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 900558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.F.; Zheng, T.C.; He, Z.H.; Li, G.Q.; Xu, S.C.; Li, X.P.; Yang, G.Y.; Singh, R.P.; Xia, X.C. Molecular tagging of stripe rust resistance gene YrZH84 in Chinese wheat line Zhou 8425B. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 112, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.Y.; Gan, A.H.; Feng, J.; Wang, F.T.; Lin, R.M.; Chen, W.Q.; Xu, S.C. Genetic analysis of resistance to Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici of Chinese differential hosts Lovrin 10 and Lovrin 13. Acta Phytopathol. 2015, 45, 401–409. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.W.; Wang, M.; Wu, J.H.; Guo, W.L.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, G.W.; Wang, Y.P.; Shi, W.M.; Xia, G.M.; Fu, D.L.; et al. WheatOmics: A platform combining multiple omics data to accelerate functional genomics studies in wheat. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 1965–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.F.; Chao, K.X.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.H.; Cheng, P.; Li, Q.; Wang, B.T. Functional verification of two genes related to stripe rust resistance in the wheat-Leymus mollis introgression line M8664-3. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 754823. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.Z.; Wang, C.Y.; Liu, M.; Li, H.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Nie, Y.B.; Liu, X.L.; Ji, W.Q. Large-scale transcriptome comparison reveals distinct gene activations in wheat responding to stripe rust and powdery mildew. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKown, A.D.; Guy, R.D.; Quamme, L.; Klápště, J.; La Mantia, J.; Constabel, C.P.; El-Kassaby, Y.A.; Hamelin, R.C.; Zifkin, M.; Azam, M.S. Association genetics, geography and ecophysiology link stomatal patterning in Populus trichocarpa with carbon gain and disease resistance trade-offs. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 5771–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Lin, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Feng, J.; Chen, W.; Xu, S. TabZIP74 acts as a positive regulator in wheat stripe rust resistance and involves root development by mRNA splicing. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.B.; Li, S.F.; Deng, Z.Y.; Wang, X.P.; Chen, T.; Zhang, J.S.; Chen, S.Y.; Ling, H.Q.; Zhang, A.M.; Wang, D.W.; et al. Molecular analysis of three new receptor-like kinase genes from hexaploid wheat and evidence for their participation in the wheat hypersensitive response to stripe rust fungus infection. Plant J. 2007, 52, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Sun, J.W.; Liu, N.; Sun, X.Z.; Liu, C.J.; Wu, L.Z.; Liu, G.; Zeng, F.L.; Hou, C.Y.; Han, S.F.; et al. A novel cysteine-rich receptor-like kinase gene, TaCRK2, contributes to leaf rust resistance in wheat. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 21, 732–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reveguk, T.; Fatiukha, A.; Potapenko, E.; Reveguk, I.; Sela, H.; Klymiuk, V.; Li, Y.; Pozniak, C.; Wicker, T.; Coaker, G.; et al. Tandem kinase proteins across the plant kingdom. Nat. Genet. 2025, 57, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.; Zhang, J.; Dubcovsky, J. High-resolution mapping of Yr78, an adult plant resistance gene to wheat stripe rust. Plant Genome 2022, 15, e20212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ren, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Sun, X.; Lv, C.; et al. Genomic analysis of Zhou8425B, a key founder parent, reveals its genetic contributions to elite agronomic traits in wheat breeding. Plant Commun. 2025, 6, 101222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tao, F.; Hao, Y.; Tong, J.; Xiao, Y.; He, Z.; Reynolds, M. Variations in phenological, physiological, plant architectural and yield-related traits, their associations with grain yield and genetic basis. Ann. Bot. 2023, 19, mcad003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Ye, M.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, D.; Li, C.; Zeng, Q.; Wu, J.; Han, D.; Jiang, L. Genome-wide association study for grain zinc concentration in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1169858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahinnia, F.; Mohler, V.; Hartl, L. Genetic basis of resistance to Warrior (-) yellow rust race at the seedling stage in current Central and Northern European winter wheat germplasm. Plants 2023, 12, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahinnia, F.; Geyer, M.; Schürmann, F.; Rudolphi, S.; Holzapfel, J.; Kempf, H.; Stadlmeier, M.; Löschenberger, F.; Morales, L.; Buerstmayr, H.; et al. Genome-wide association study and genomic prediction of resistance to stripe rust in current Central and Northern European winter wheat germplasm. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 3583–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 15795–2011; Rules for Monitoring and Forecast of the Wheat Stripe Rust (Puccinia striiformis West). Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Rosenberg, N.A.; Donnelly, P. Association mapping in structured populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2000, 67, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradbury, P.J.; Zhang, Z.; Kroon, D.E.; Casstevens, T.M.; Ramdoss, Y.; Buckler, E.S. TASSEL: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.X. Quality Characteristics and Molecular Marker Analysis of 58 Wheat Cultivars (Lines). Master’s Thesis, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang, China, 2016. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.J. Molecular Characterization of 1B/1R Translocation Lines and Stem Rust Resistance Genes in Common Wheat. Master’s Thesis, XinJiang Agricultural Unviersity, Ürümqi, China, 2010. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.W.; Yin, G.H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.N.; Han, Y.L.; Huang, F.; Yu, H.F.; Yang, G.Y.; Li, X.P.; Xiao, Y.G.; et al. Comprehensive analysis on agronomic traits and processing quality of core parent Zhou8425B and its derivatives. J. Triticeae Crops 2016, 35, 777–784. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, E.N. A study on Allelic Variation for High Molecular Weight Glutenin Subunit (HMW-GS) and 1B/1R Translocation from Resent Released Wheat Varieties in Sichuan Province. Master’s Thesis, SiChuan Agricultural University, Ya’an, China, 2008. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]


| QTL | Trait | Stage | Chr. | Position | Peak Marker | −log(P) | Marker R2 | Region | FH | FH Frequency | QTL/Gene | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Mb) | (%) | (Mb) | ||||||||||
| Yr.baafs-1B.1 | CYR34DS-I/II, CYR34IT-I/II | Seedling | 1BS | 56.89 | AX-111170724 | 3.52–6.42 | 8.23–16.67 | 46.03–57.38 | Hap2 | 0.202 | ||
| Yr.baafs-1B.2 | CYR34DS-I/II, CYR34IT-I/II | Seedling | 1BS | 95.67 | AX-94432535 | 3.23–6.93 | 8.84–18.32 | 90.55–96.88 | Hap2 | 0.209 | ||
| Yr.baafs-1B.3 | CYR34DS-I/II, CYR34IT-I/II | Seedling | 1BS | 229.31 | AX-110084126 | 3.68–6.08 | 10.41–15.80 | 224.21–230.95 | Hap1 | 0.213 | ||
| Yr.baafs-1B.4 | 20DS,19/20IT | Adult-plant | 1BL | 488.6 | AX-108791049 | 3.00–3.72 | 7.44–9.25 | 487.94–491.08 | ||||
| Yr.baafs-1D.1 | CYR34DS-I/II, CYR34IT-I/II | Seedling | 1DS | 73.73 | AX-94802245 | 3.04–6.24 | 7.68–17.54 | 59.53–84.62 | Hap3 | 0.358 | ||
| Yr.baafs-1D.2 | CYR34DS-I/II, CYR34IT-I/II | Seedling | 1DS | 109.82 | AX-94747357 | 3.46–6.54 | 8.56–17.08 | 102.78–109.82 | Hap2 | 0.189 | ||
| Yr.baafs-2B.1 | CYR33IT-I/II, CYR33DS-I | Seedling | 2BL | 646.9 | AX-108773165 | 3.05–6.60 | 7.61–17.16 | 643.69–655.52 | Hap6 | 0.032 | QYrSM155.1 | [26] |
| Yr.baafs-2B.2 | CYR33IT-I/II | Seedling | 2BL | 675.36 | AX-111026674 | 3.01~4.05 | 7.54–10.33 | 673.05–675.79 | Hap7 | 0.016 | ||
| Yr.baafs-2B.3 | CYR33IT-I/II | Seedling | 2BL | 706.85 | AX-111077615 | 3.26–5.70 | 8.65–14.82 | 706.72–707.18 | Hap4 | 0.063 | ||
| Yr.baafs-2B.4 | 18DS,18IT | Adult-plant | 2BL | 785.83 | AX-108900982 | 3.06–3.15 | 6.04–7.79 | 780.02–787.23 | qNV.Yr-2B.3 | [6] | ||
| Yr.baafs-6B | 18/20DS,20IT | Adult-plant | 6BS | 90.4 | AX-109912248 | 3.08–3.61 | 6.50–9.27 | 73.54–91.01 | Hap5 | 0.042 | QYr.sicau-6BS | [27] |
| QYr.nwafu-6BS.3 | [28] | |||||||||||
| Yr.baafs-6D | CYR34DS-I/II, CYR34IT-I/II | Seedling | 6DL | 467.52 | AX-109362174 | 4.69–5.88 | 12.55–15.15 | 465.05–472.82 | Hap3 | 0.202 | QYrCL.sicau-6DL | [29] |
| Yr.baafs-7B | CYR33IT-I, CYR33DS-I | Seedling | 7BS | 64.33 | AX-111143711 | 3.00–3.50 | 6.06–8.70 | 64.32–66.51 | ||||
| Yr.baafs-7D | CYR34DS-II, CYR34IT-I/II | Seedling | 7DS | 104.49 | AX-111855949 | 3.01–3.60 | 7.49–9.03 | 100.65–104.74 | QYr.rcrrc-7D | [30] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Q.; Yan, D.; Pang, B.; Bai, J.; Yang, W.; Gao, J.; Chen, X.; Hou, Q.; Zhang, H.; Tian, L.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification of Wheat Gene Resources Conferring Resistance to Stripe Rust. Plants 2025, 14, 1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121883
Ma Q, Yan D, Pang B, Bai J, Yang W, Gao J, Chen X, Hou Q, Zhang H, Tian L, et al. Genome-Wide Identification of Wheat Gene Resources Conferring Resistance to Stripe Rust. Plants. 2025; 14(12):1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121883
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Qiaoyun, Dong Yan, Binshuang Pang, Jianfang Bai, Weibing Yang, Jiangang Gao, Xianchao Chen, Qiling Hou, Honghong Zhang, Li Tian, and et al. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification of Wheat Gene Resources Conferring Resistance to Stripe Rust" Plants 14, no. 12: 1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121883
APA StyleMa, Q., Yan, D., Pang, B., Bai, J., Yang, W., Gao, J., Chen, X., Hou, Q., Zhang, H., Tian, L., Li, Y., Jia, J., Zhang, L., Chen, Z., Gao, L., & Liao, X. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification of Wheat Gene Resources Conferring Resistance to Stripe Rust. Plants, 14(12), 1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121883







