Subchronic Toxicity and Effect of the Methanolic Extract of Micromeria frivaldszkyana (Degen) Velen on Cognition in Male Wistar Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
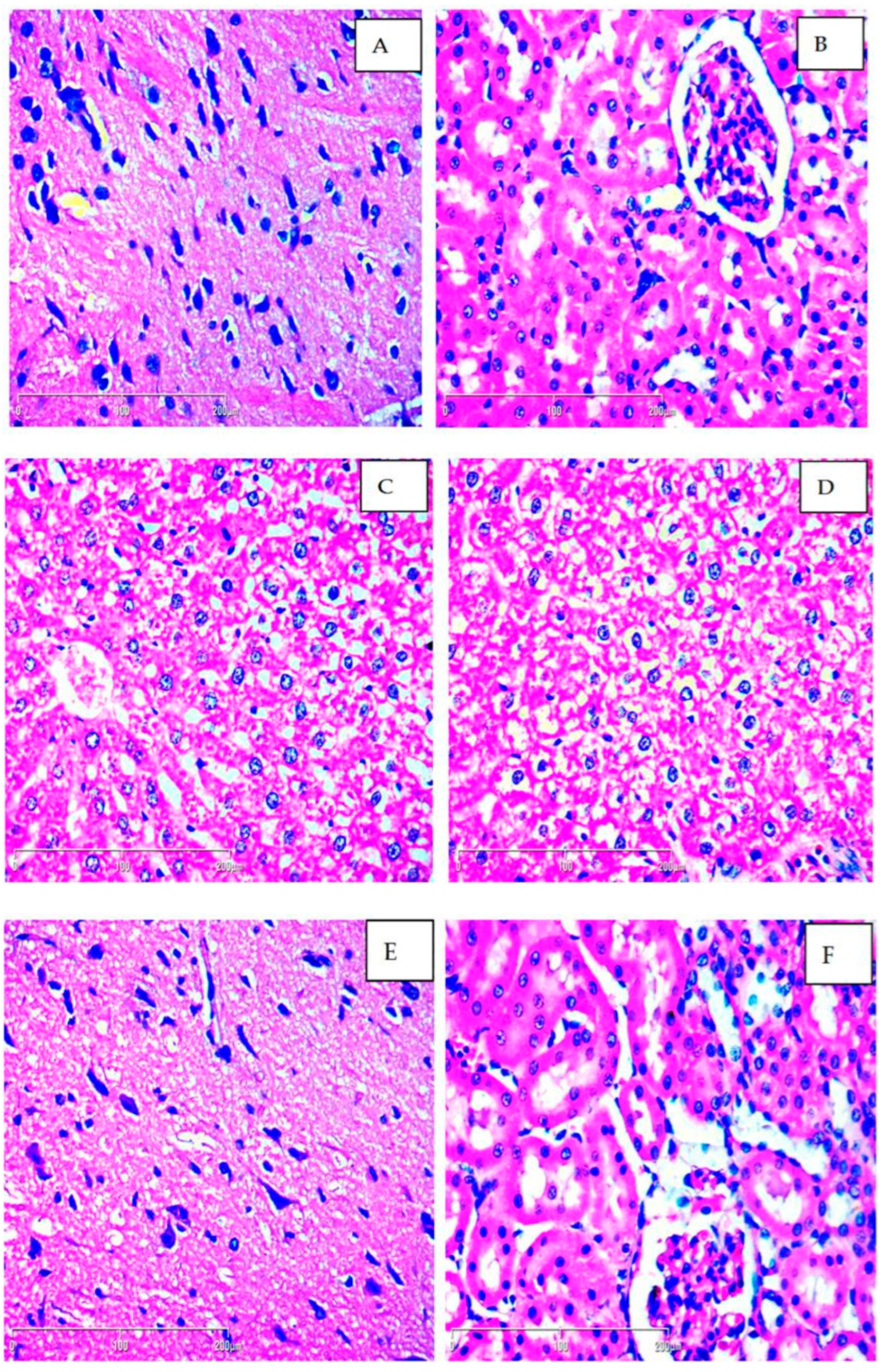
2.1. Subchronic Toxicity—Histopathological Evaluation
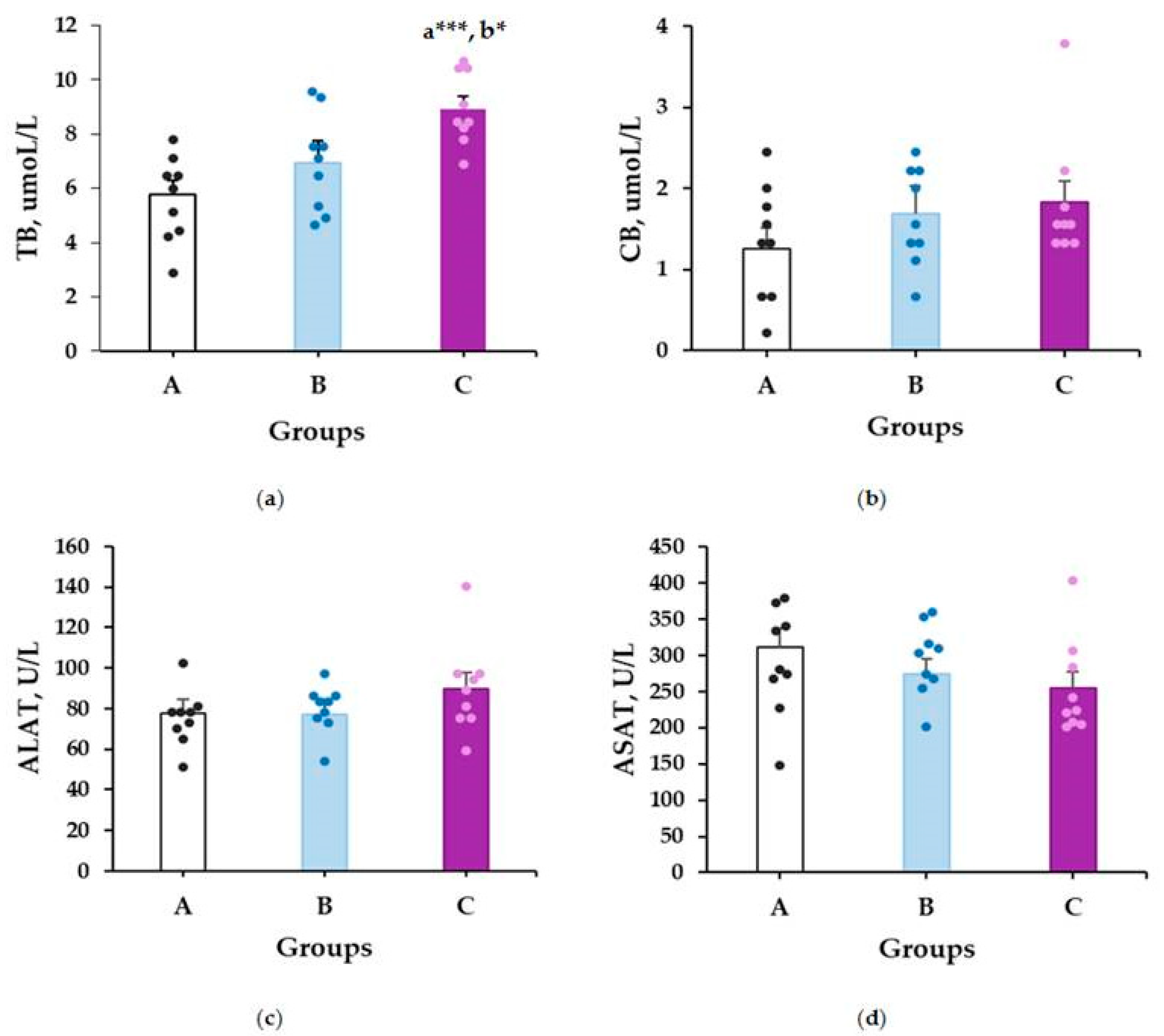
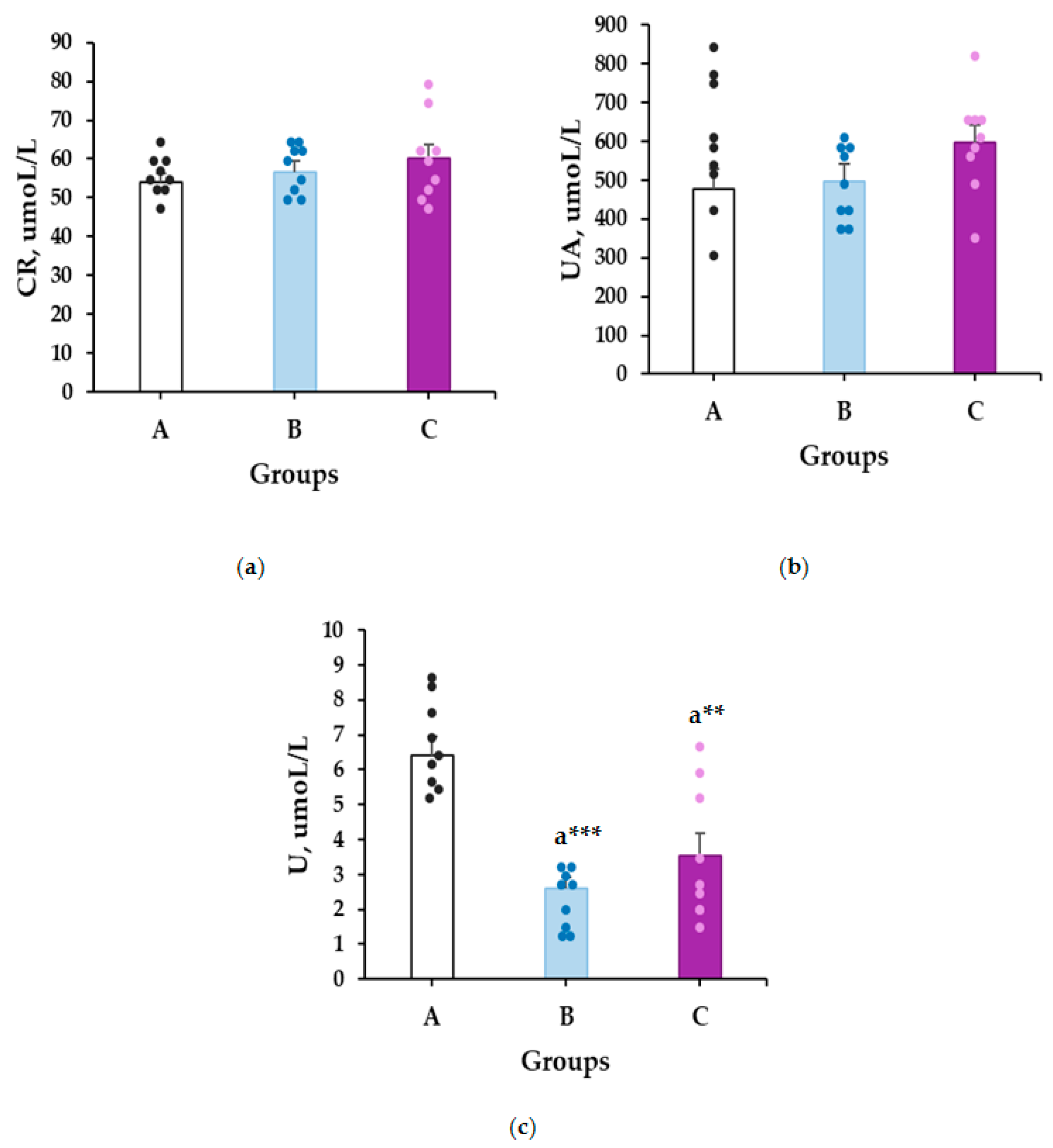
2.2. Subchronic Toxicity—Biochemical Markers
2.2.1. Liver Toxicity Markers
2.2.2. Kidney Toxicity Markers
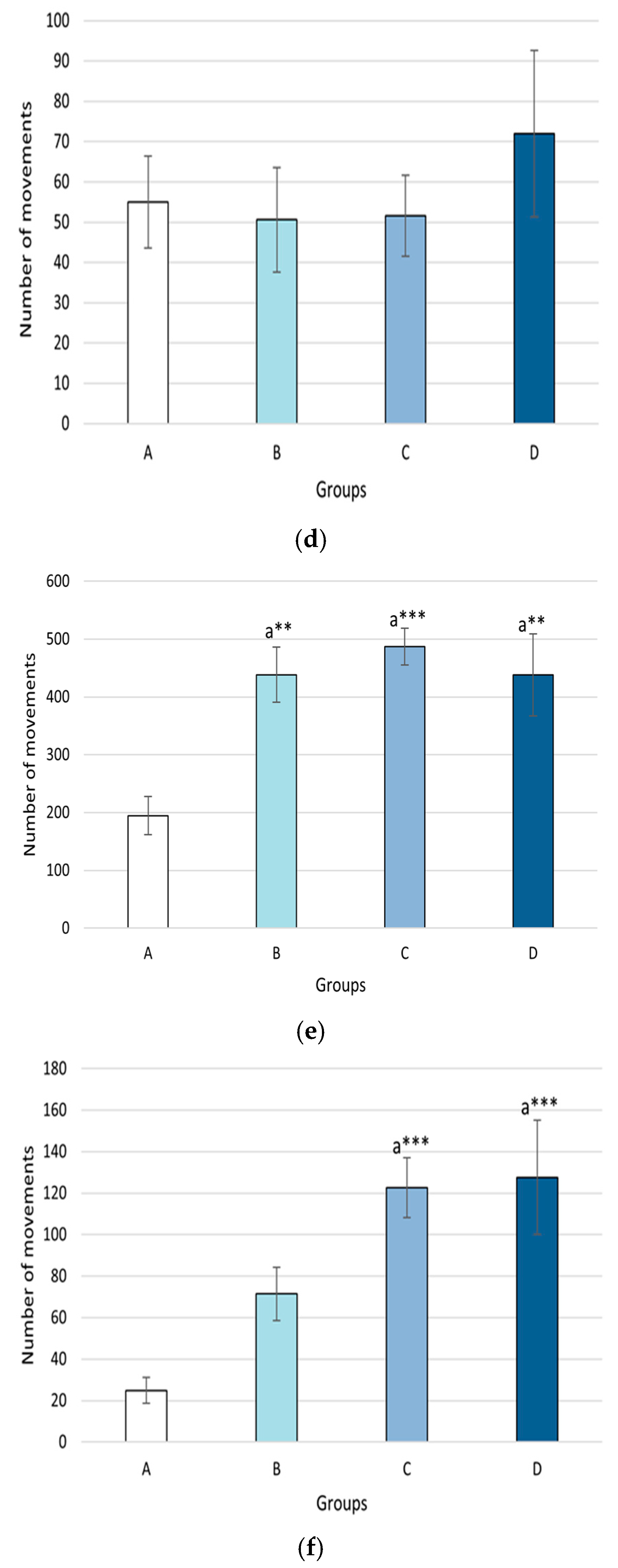
2.3. Effects on Cognitive Function
2.3.1. Activity Cage
2.3.2. Two-Way Active Avoidance Test
2.3.3. Step-Through Passive Avoidance Test
2.3.4. Step-Down Passive Avoidance Test
2.3.5. New Object Recognition Test
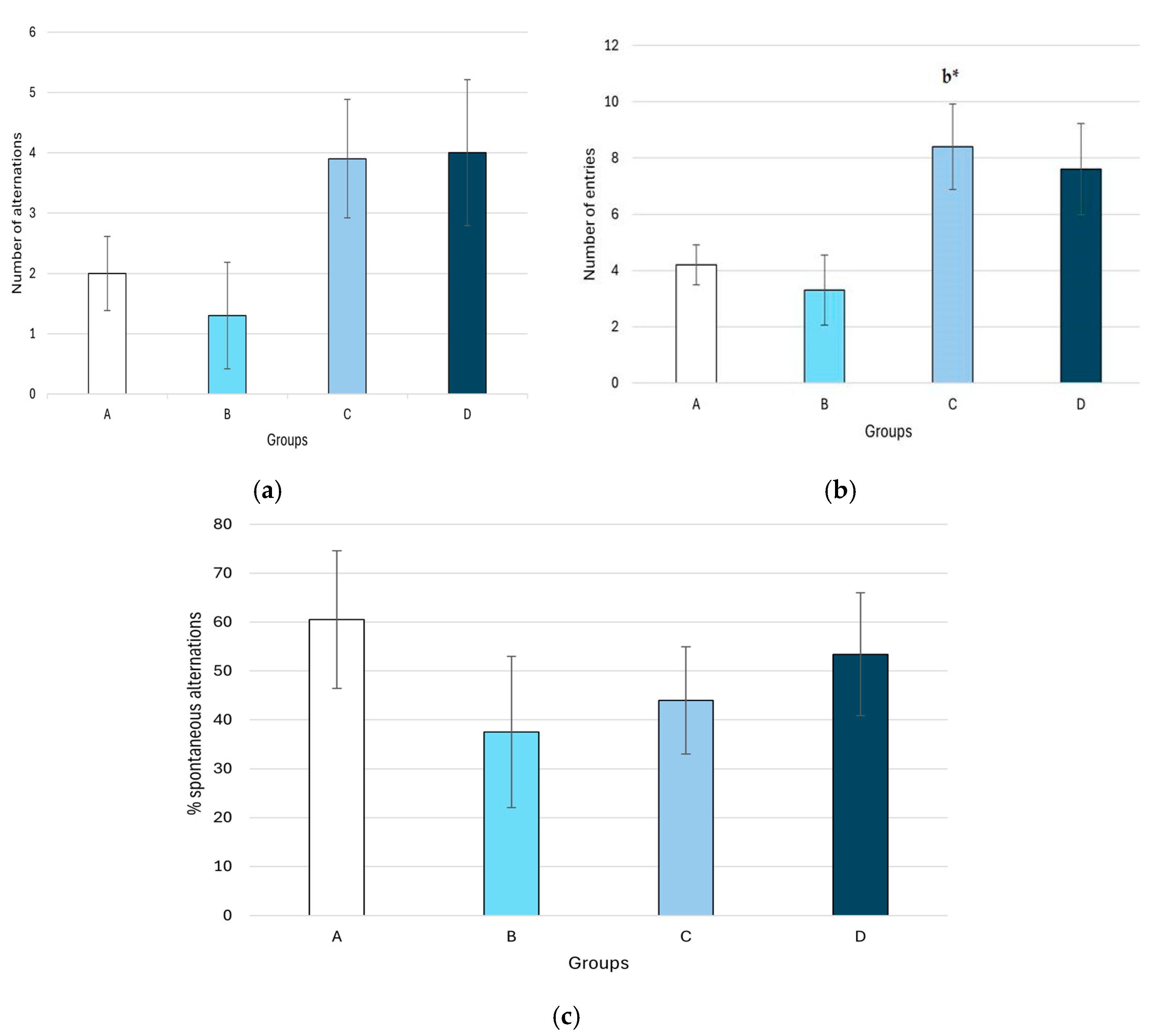
2.3.6. Y-Maze
2.3.7. Elevated Plus Maze
3. Discussion
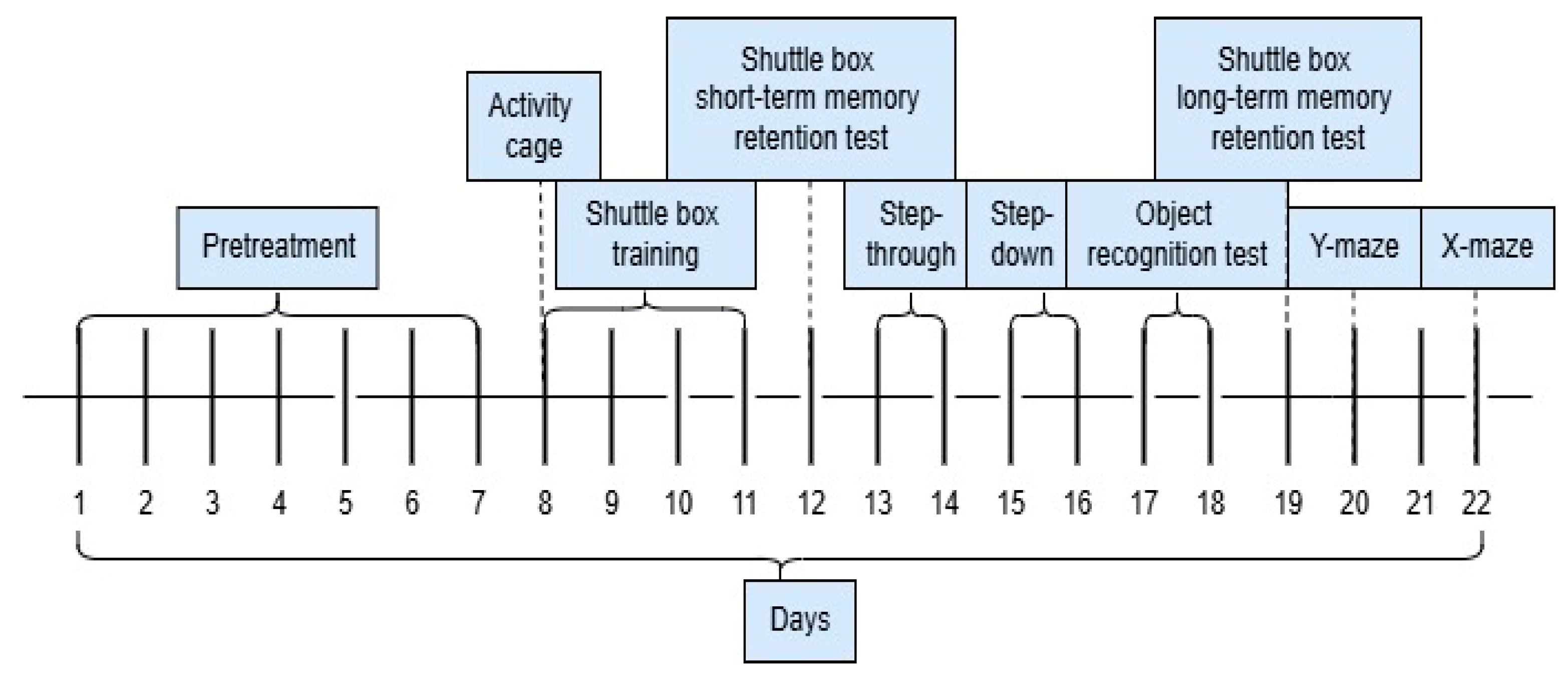
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Plant Material and Preparation of the Methanolic Extract
4.3. Animals
4.4. Subchronic Toxicity—Treatment
4.4.1. Histopathological Evaluation
4.4.2. Biochemical Markers
4.5. Evaluation of Cognitive Function
4.5.1. Locomotor Activity Test
4.5.2. Shuttle-Box Active Avoidance Test
4.5.3. Step-Through Passive Avoidance Test
4.5.4. Step-Down Passive Avoidance Test
4.5.5. New Object Recognition Test
4.5.6. Y-Maze Test
4.5.7. Elevated Plus Maze Test
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TB | total bilirubin |
| CB | conjugated bilirubin |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| CR | creatinine |
| UA | uric acid |
| U | urea |
References
- Ekor, M. The growing use of herbal medicines: Issues relating to adverse reactions and challenges in monitoring safety. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 4, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gvozdeva, Y.; Staynova, R. pH-dependent drug delivery systems for ulcerative colitis treatment. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, S.; Gvozdeva, Y.; Staynova, R.; Grekova-Kafalova, D.; Nalbantova, V.; Benbassat, N.; Koleva, N.; Ivanov, K. Essential oils—a review of the natural evolution of applications and some future perspectives. Pharmacia 2025, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peev, D. Plants and Fungi. In Red Data Book of the Republic of Bulgaria; BAS & MoEW: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2015; Volume 1, p. 550. [Google Scholar]
- Petrova, A. Atlas of Bulgarian Endemic Plants; Gea Libris: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2006; p. 399. [Google Scholar]
- Vukelić, D. Phytochemical Characterization of Polyphenols from Micromeria frivaldszkyana (Deg.) Vel. (Lamiaceae). Master’s Thesis, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolova, M.; Aneva, I.; Zhelev, P.; Dimitrova, M. Flavonoid compounds and antioxidant activity of Bulgarian species of Micromeria. Annu. De L’université De Sofia “St. Kliment Ohridski” Fac. De Biol. 2017, 102, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Mladenova, T.; Stoyanov, P.; Denev, P.; Dimitrova, S.; Katsarova, M.; Teneva, D.; Todorov, K.; Bivolarska, A. Phytochemical composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of the Balkan endemic Micromeria frivaldszkyana (Degen) Velen. (Lamiaceae). Plants 2021, 10, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, S.; Pashova, S.; Dyankov, S.; Georgieva, Y.; Ivanov, K.; Benbassat, N.; Koleva, N.; Bozhkova, M.; Karcheva-Bahchevanska, D. Chemical composition and future perspectives of essential oil obtained from a wild population of Stachys germanica L. distributed in the Balkan Mountains in Bulgaria. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2023, 2023, 4275213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabanca, N.; Kirimer, N.; Demirci, B.; Demirci, F.; Başer, K.H. Composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oils of Micromeria cristata subsp. phrygia and the enantiomeric distribution of borneol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4300–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duru, M.E.; Oztürk, M.; Uğur, A.; Ceylan, O. The constituents of essential oil and in vitro antimicrobial activity of Micromeria cilicica from Turkey. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 94, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanović, G.; Palić, I. Antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of Micromeria Bentham species. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 3196–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azab, A. Micromeria: Chemistry and medicinal activities. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2016, 5, 300–307. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Gharbieh, E.; Ahmed, N.G. Bioactive content, hepatoprotective and antioxidant activities of whole plant extract of Micromeria fruticosa (L) Druce ssp Serpyllifolia F Lamiaceae against Carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2016, 15, 2099–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, M.; Prakash, O.; Bachheti, R.K.; Kumar, M.; Pant, A.K. Essential oil composition and pharmacological activities of Micromeria biflora (Buch. Ham. Ex, D. Don) Benth. collected from Uttarakhand region of India. J. Med. Plants Res. 2013, 7, 2538–2544. [Google Scholar]
- Sarikurkcu, C.; Hanine, H.; Sarikurkcu, R.B.; Sarikurkcu, R.T.; Amarowicz, R. Micromeria myrtifolia: The influence of the extracting solvents on phenolic composition and biological activity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 145, 111923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladimir-Knežević, S.; Blažeković, B.; Štefan, M.B.; Alegro, A.; Kőszegi, T.; Petrik, J. Antioxidant activities and polyphenolic contents of three selected Micromeria species from Croatia. Molecules 2011, 16, 1454–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavrakeva, K.; Metodieva, K.; Benina, M.; Bivolarska, A.; Dimov, I.; Choneva, M.; Kokova, V.; Alseekh, S.; Ivanova, V.; Vatov, E.; et al. Metabolic composition of methanolic extract of the Balkan endemic species Micromeria frivaldszkyana (Degen) Velen and its anti-inflammatory effect on male Wistar rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottaghipisheh, J.; Taghrir, H.; Boveiri Dehsheikh, A.; Zomorodian, K.; Irajie, C.; Mahmoodi Sourestani, M.; Iraji, A. Linarin, a glycosylated flavonoid, with potential therapeutic attributes: A comprehensive review. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Di, X. Linarin inhibits the acetylcholinesterase activity in-vitro and ex-vivo. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 14, 949–954. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Lan, Y.; Wang, F.; Gao, T. Linarin protects against CCl4-induced acute liver injury via activating autophagy and inhibiting the inflammatory response: Involving the TLR4/MAPK/Nrf2 pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2023, 17, 3589–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Hejazi, V.; Abbas, M.; Kamboh, A.A.; Khan, G.J.; Shumzaid, M.; Ahmad, F.; Babazadeh, D.; FangFang, X.; Modarresi-Ghazani, F.; et al. Chlorogenic acid (CGA): A pharmacological review and call for further research. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Xie, M.; He, L.; Song, X.; Cao, T. Chlorogenic acid: A review on its mechanisms of anti-inflammation, disease treatment, and related delivery systems. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1218015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik, N.; Tajik, M.; Mack, I.; Enck, P. The potential effects of chlorogenic acid, the main phenolic components in coffee, on health: A comprehensive review of the literature. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 2215–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Zheng, Z.; Shi, L.; Jin, Y.; Ji, L. Natural polyphenol chlorogenic acid protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by activating ERK/Nrf2 antioxidative pathway. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2018, 162, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani, A. Mechanisms of antidiabetic effects of flavonoid rutin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.S.; Park, H.R.; Lee, K.A. A comparative study of rutin and rutin glycoside: Antioxidant activity, anti-inflammatory effect, effect on platelet aggregation and blood coagulation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeshpurkar, A.; Saluja, A.K. The pharmacological potential of rutin. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Hyun Lee, D.; Jung, Y.J.; Shin, S.Y.; Lee, Y.H. The natural flavone eupatorin induces cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase and apoptosis in HeLa cells. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2016, 59, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chriscensia, E.; Arham, A.A.; Wibowo, E.C.; Gracius, L.; Nathanael, J.; Hartrianti, P. Eupatorin from Orthosiphon aristatus: A review of the botanical origin, pharmacological effects and isolation methods. Curr. Bioact. Compd. 2023, 19, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.; Imran, M.; Aslam Gondal, T.; Imran, A.; Shahbaz, M.; Muhammad Amir, R.; Wasim Sajid, M.; Batool Qaisrani, T.; Atif, M.; Hussain, G.; et al. Therapeutic potential of rosmarinic acid: A comprehensive review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyarikpunchai, W.; Sukrong, S.; Towiwat, P. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of rosmarinic acid isolated from Thunbergia laurifolia Lindl. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 124, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanein, P.; Mahtaj, A.K. Ameliorative effect of rosmarinic acid on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 585, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, D.R.; Lott, J.A.; Nolte, F.S.; Gretch, D.R.; Koff, R.S.; Seeff, L.B. Diagnosis and monitoring of hepatic injury. II. Recommendations for use of laboratory tests in screening, diagnosis, and monitoring. Clin. Chem. 2000, 46, 2050–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaiah, S.K. A toxicologist guide to the diagnostic interpretation of hepatic biochemical parameters. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, D.G.; Levitt, M.D. Quantitative assessment of the multiple processes responsible for bilirubin homeostasis in health and disease. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2014, 7, 307–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küpeli Akkol, E.; Gürağaç Dereli, F.T.; Ilhan, M. Assessment of antidepressant effect of the aerial parts of Micromeria myrtifolia Boiss. & Hohen on mice. Molecules 2019, 24, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamwi, M.; Aboul, E.; Maha, P.; El-Lakany, A. Genus Micromeria: A review article. BAU J. Health Wellbeing 2021, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbardar, M.G.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Effects of rosmarinic acid on nervous system disorders: An updated review. Naunyn Schmiedeberg Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 1779–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, S.; Dzhakova, Z.; Staynova, R.; Ivanov, K. Salvia verticillata (L.)—biological activity, chemical profile, and future perspectives. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Therapeutic effects of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) and its active constituents on nervous system disorders. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 1100–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thingore, C.; Kshirsagar, V.; Juvekar, A. Amelioration of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in lipopolysaccharide-induced memory impairment using Rosmarinic acid in mice. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanein, P.; Seifi, R.; Hajinezhad, M.R.; Emamjomeh, A. Rosmarinic acid protects against chronic ethanol-induced learning and memory deficits in rats. Nutrutional Neurosci. 2017, 20, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimojo, Y.; Kosaka, K.; Noda, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Shirasawa, T. Effect of rosmarinic acid inmotor dysfunction and life span in a mouse model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurosci Res. 2010, 88, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, H.; Jiang, H.; Du, X.; Sun, P.; Xie, J. Neurorescue effect of rosmarinic acid on 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned nigral dopamine neurons in rat model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 47, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, F.J.; Amber, S.; Hassan, D.; Ahmed, T.; Zahid, S. Rosmarinic acid and ursolic acid alleviate deficits in cognition, synaptic regulation and adult hippocampal neurogenesis in an Aβ1-42-induced mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Phytomedicine: Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2021, 83, 153490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, H.; Tsuji, M.; Inazu, M.; Egashira, T.; Matsumiya, T. Rosmarinic acid and caffeic acid produce antidepressive-like effect in forced swimming test in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 449, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, K.; El Omri, A.; Kondo, S.; Han, J.; Isoda, H. Rosmarinus officinalis polyphenols produce anti-depressant like effect through monoaminergic and cholinergic functions modulation. Behav Brain Res. 2013, 1, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Alaoui, C.; Chemin, J.; Fechtali, T.; Lory, P. Modulation of T-type Ca2+ channels by Lavender and Rosemary extracts. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Peng, Z.; Lao, N.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Fang, Z.; Hou, W.; Gao, F.; Li, X.; Xiong, L.; et al. Rosmarinic acid ameliorates PTSD-like symptoms in a rat model and promotes cell proliferation in the hippocampus. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 51, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoletto, J.; Oliveira, C.V.; Grauncke, A.C.; Souza, T.L.; Souto, N.S.; Freitas, M.L.; Furian, A.F.; Santos, A.R.; Oliveira, M.S. Rosmarinic acid is anticonvulsant against seizures induced by pentylenetetrazol and pilocarpine in mice. Epilepsy Behav. EB 2016, 62, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Dai, S.; Yin, Z.; Lu, H.; Jia, R.; Xu, J.; Song, X.; Li, L.; Shu, Y.; Zhao, X. Toxicological assessment of combined lead and cadmium: Acute and sub-chronic toxicity study in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 65, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.; Dadhaniya, P.; Hingorani, L.; Soni, M.G. Safety assessment of pomegranate fruit extract: Acute and subchronic toxicity studies. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2728–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuet Ping, K.; Darah, I.; Chen, Y.; Sreeramanan, S.; Sasidharan, S. Acute and subchronic toxicity study of Euphorbia hirta L. methanol extract in rats. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 182064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Al Tamimi, D.; Isab, A.; Alkhawajah, A.; Shawarby, M. Histological changes in kidney and liver of rats due to gold (III) compound [Au(en)Cl(2)]Cl. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berends, M.; van Oijen, M.; Snoek, J.; van de Kerkhof, P.; Drenth, J.; Han van Krieken, J.; de Jong, E. Reliability of the Roenigk classification of liver damage after methotrexate treatment for psoriasis: A clinicopathologic study of 160 liver biopsy specimens. Arch. Dermatol. 2007, 143, 1515–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, R.; Lecumberri, E.; Ramos, S.; Goya, L.; Bravo, L. Determination of malondialdehyde (MDA) by high-performance liquid chromatography in serum and liver as a biomarker for oxidative stress. Application to a rat model for hypercholesterolemia and evaluation of the effect of diets rich in phenolic antioxidants from fruits. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2005, 827, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafy, A.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Badr, J.M.; Ibrahim, A.K.; Abdel-Hady, S.E.-S. Evaluation of hepatoprotective activity of Adansonia digitata extract on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Evid. Based Complement Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 4579149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokova, V.; Apostolova, E. Effect of etifoxine on locomotor activity and passive learning in rats with diazepam-induced cognitive deficit. Sci. Pharm. 2023, 91, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, A.; Kostadinov, I.; Doncheva, N.; Zlatanova, H.; Delev, D. Effects of pramipexole on learning and memory processes in naïve and haloperidol-challenged rats in active avoidance test. Folia Med. 2019, 61, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, M.; Nasehi, M.; Vaseghi, S.; Alimohammadzadeh, K.; Islami Vaghar, M.; Mohammadi-Mahdiabadi-Hasani, M.H.; Zarrindast, M.R. The interaction effect of sleep deprivation and cannabinoid type 1 receptor in the CA1 hippocampal region on passive avoidance memory, depressive-like behavior and locomotor activity in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 396, 112901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalho, J.B.; Izaguirry, A.P.; Soares, M.B.; Spiazzi, C.C.; Pavin, N.F.; Affeldt, R.F.; Lüdtke, D.S.; Pinton, S.; Santos, F.W.; Prigol, M. Selenofuranoside improves long-term memory deficits in rats after exposure to monosodium glutamate: Involvement of Na+, K+-ATPase activity. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 184, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissner, L.J.; Wartchow, K.M.; Toniazzo, A.P.; Gonçalves, C.A.; Rodrigues, L. Object recognition and Morris water maze to detect cognitive impairment from mild hippocampal damage in rats: A reflection based on the literature and experience. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2021, 210, 173273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafarimoghadam, M.; Mashayekh, R.; Gholami, M.; Fereydani, P.; Shelley-Tremblay, J.; Kandezi, N.; Sabouri, E.; Motaghinejad, M. A review of behavioral methods for the evaluation of cognitive performance in animal models: Current techniques and links to human cognition. Physiol. Behav. 2022, 244, 113652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraeuter, A.-K.; Guest, P.; Sarnyai, Z. The Y-maze for assessment of spatial working and reference memory in mice. In Methods of Molecular Biology. Pre-Clinical Models, Techniques and Protocols, 1st ed.; Guest, P., Ed.; Springer Science+Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Knight, P.; Chellian, R.; Wilson, R.; Behnood-Rod, A.; Panunzio, S.; Bruijnzeel, A.W. Sex differences in the elevated plus-maze test and large open field test in adult Wistar rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2021, 204, 173168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Day Groups | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1.30 ± 0.34 | 1.80 ± 0.89 | 4.10 ± 1.48 | 4.10 ± 1.63 | 5.90 ± 1.68 | 5.30 ± 1.82 |
| B | 0.50 ± 0.23 | 0.50 ± 0.23 | 1.70 ± 0.77 | 2.00 ± 0.99 | 3.50 ± 1.51 | 3.30 ± 1.34 |
| C | 1.10 ± 0.41 | 0.50 ± 0.31 | 1.90 ± 1.15 | 3.10 ± 1.39 | 3.30 ± 1.72 | 4.80 ± 2.14 |
| D | 0.50 ± 0.17 | 0.50 ± 0.41 | 0.70 ± 0.39 | 3.00 ± 1.43 | 4.50 ± 1.67 | 5.20 ± 1.76 |
| Day Groups | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 12.5 ± 2.82 | 10.30 ± 2.72 | 13.2 ± 2.97 | 14.7 ± 3.12 | 15.1 ± 3.04 | 16.7 ± 3.11 |
| B | 11.3 ± 2.83 | 8.9 ± 2.41 | 9.1 ± 2.63 | 8.5 ± 2.83 | 9.2 ± 2.46 | 10.6 ± 2.38 |
| C | 17.2 ± 2.86 | 11.7 ± 3.33 | 11.9 ± 2.88 | 8.8 ± 2.98 | 12.5 ± 2.47 | 11.2 ± 3.02 |
| D | 16.8 ± 3.03 | 8.9 ± 2.87 | 10.1 ± 2.43 | 10.1 ± 2.17 | 10.9 ± 2.31 | 12.0 ± 2.08 |
| Day Groups | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|
| A | 17.96 ± 3.31 | 25.77 ± 5.76 |
| B | 23.12 ± 3.81 | 36.73 ± 6.71 |
| C | 23.42 ± 3.99 | 38.71 ± 5.26 |
| D | 24.61 ± 5.41 | 41.63 ± 4.74 |
| Groups | Seconds Spent Studying the New Object | Recognition Index |
|---|---|---|
| A | 3.40 ± 0.62 | 0.55 ± 0.08 |
| B | 11.30 ± 4.29 | 0.58 ± 0.08 |
| C | 18.30 ± 7.78 | 0.56 ± 0.07 |
| D | 16.70 ± 4.06 | 0.73 ± 0.06 |
| Groups | Seconds Spent in the Open Arms | Seconds Spent in the Closed Arms | Number of Entries into the Open Arms | Total Number of Entries | Ratio of the Number of Entries into the Open Arms to the Total Number of Entries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 142.00 ± 30.16 | 158.00 ± 30.16 | 1.70 ± 0.52 | 3.90 ± 0.98 | 0.32 ± 0.06 |
| B | 106.70 ± 23.07 | 193.30 ± 23.07 | 2.00 ± 0.54 | 4.70 ± 1.17 | 0.41 ± 0.07 |
| C | 104.70 ± 25.89 | 195.30 ± 25.89 | 2.70 ± 0.47 | 5.90 ± 1.06 | 0.45 ± 0.07 |
| D | 67.30 ± 22.67 | 232.70 ± 22.67 | 3.30 ± 0.86 | 6.40 ± 1.72 | 0.63 ± 0.08 * |
| Grade | Accumulation of Fats | Nuclear Pleomorphism | Fibrosis | Necrosis/Inflammation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mild or none | Mild or none | None | With or without mild portal inflammation |
| 2 | Moderate or severe | Moderate or severe | None | Moderate or severe portal inflammation |
| 3a | With or without | With or without | Mild (fibrosis extending into acini) | With or without |
| 3b | With or without | With or without | Moderate or severe | With or without |
| 4 | With or without | With or without | Cirrhosis | With or without |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Apostolova, E.; Stavrakeva, K.; Kokova, V.; Dimov, I.; Choneva, M.; Delev, D.; Kostadinov, I.; Bivolarski, I.; Koleva, M.; Mladenova, T.; et al. Subchronic Toxicity and Effect of the Methanolic Extract of Micromeria frivaldszkyana (Degen) Velen on Cognition in Male Wistar Rats. Plants 2025, 14, 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121837
Apostolova E, Stavrakeva K, Kokova V, Dimov I, Choneva M, Delev D, Kostadinov I, Bivolarski I, Koleva M, Mladenova T, et al. Subchronic Toxicity and Effect of the Methanolic Extract of Micromeria frivaldszkyana (Degen) Velen on Cognition in Male Wistar Rats. Plants. 2025; 14(12):1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121837
Chicago/Turabian StyleApostolova, Elisaveta, Kristina Stavrakeva, Vesela Kokova, Ivica Dimov, Mariya Choneva, Delyan Delev, Ilia Kostadinov, Iliya Bivolarski, Maria Koleva, Tsvetelina Mladenova, and et al. 2025. "Subchronic Toxicity and Effect of the Methanolic Extract of Micromeria frivaldszkyana (Degen) Velen on Cognition in Male Wistar Rats" Plants 14, no. 12: 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121837
APA StyleApostolova, E., Stavrakeva, K., Kokova, V., Dimov, I., Choneva, M., Delev, D., Kostadinov, I., Bivolarski, I., Koleva, M., Mladenova, T., Todorov, K., & Bivolarska, A. (2025). Subchronic Toxicity and Effect of the Methanolic Extract of Micromeria frivaldszkyana (Degen) Velen on Cognition in Male Wistar Rats. Plants, 14(12), 1837. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121837








