Agronomic and Quality Traits of 30 Eggplant Germplasm Resources from China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Appearance and Morphology of Chinese Eggplant Fruits
2.2. Saccharides Content in Chinese Eggplant Fruits
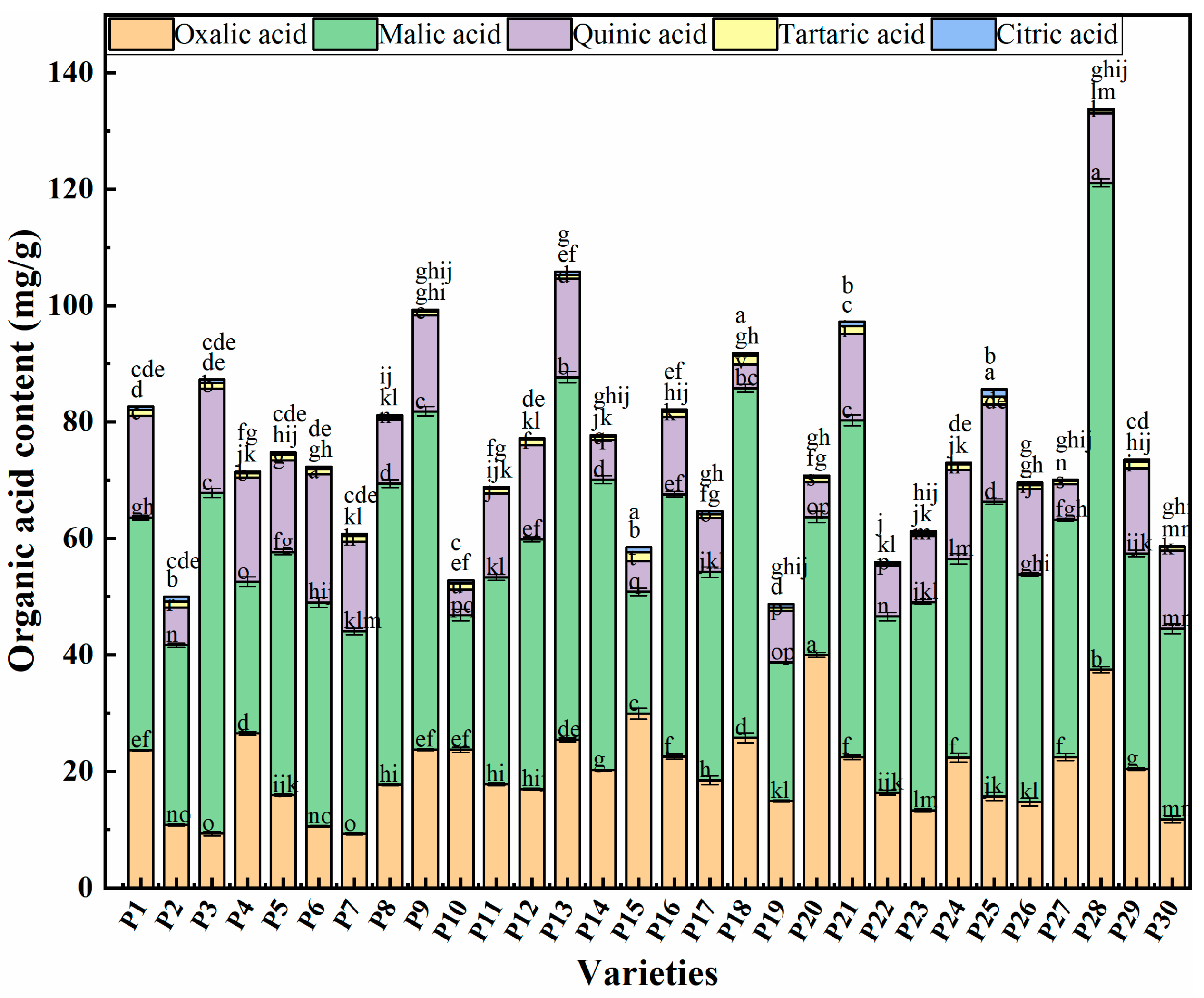
2.3. Organic Acid Components Content in Chinese Eggplant Fruits
2.4. Other Quality Indicators in Chinese Eggplant Fruits
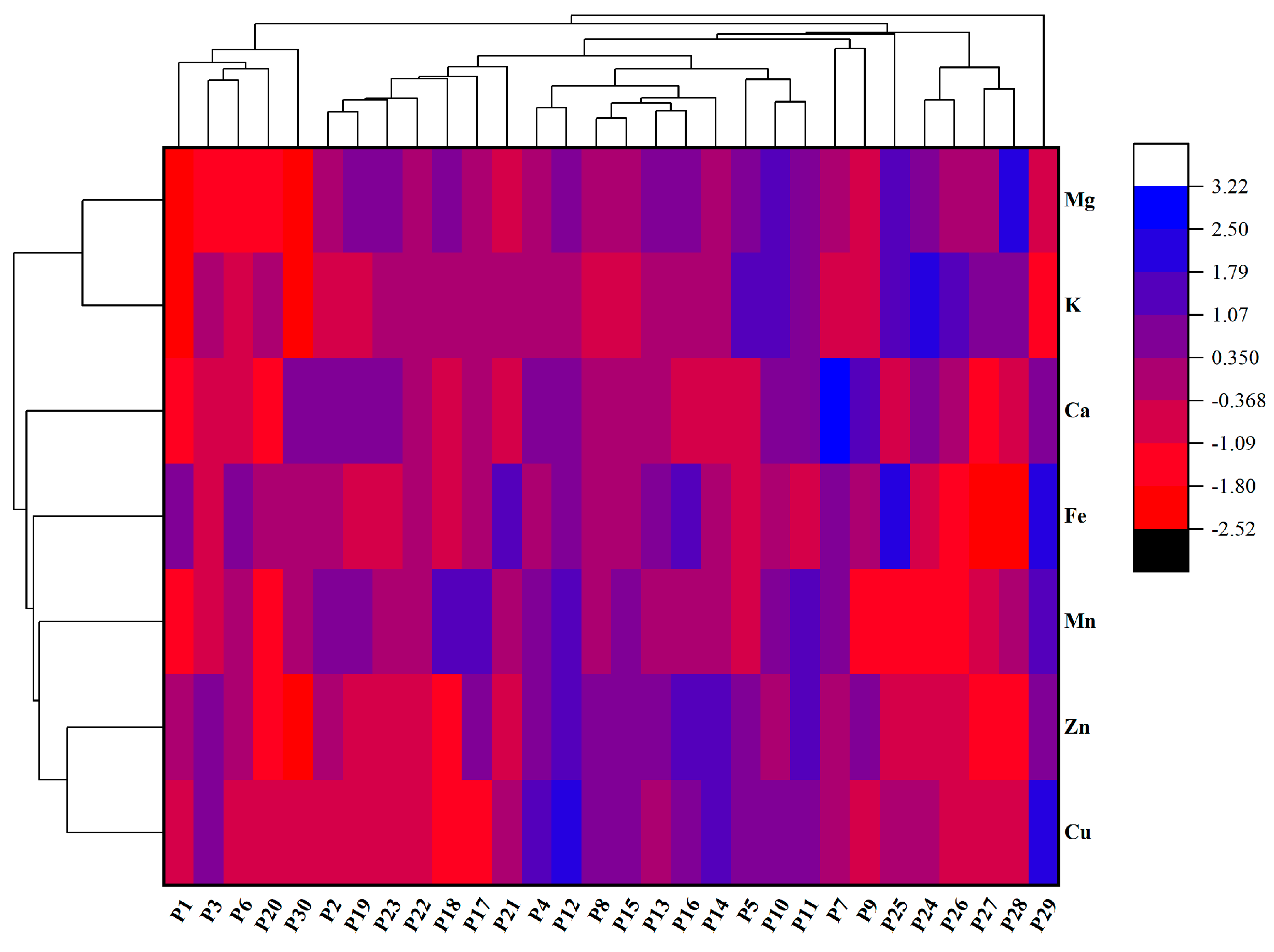
2.5. Mineral Element Content in Chinese Eggplant Fruits
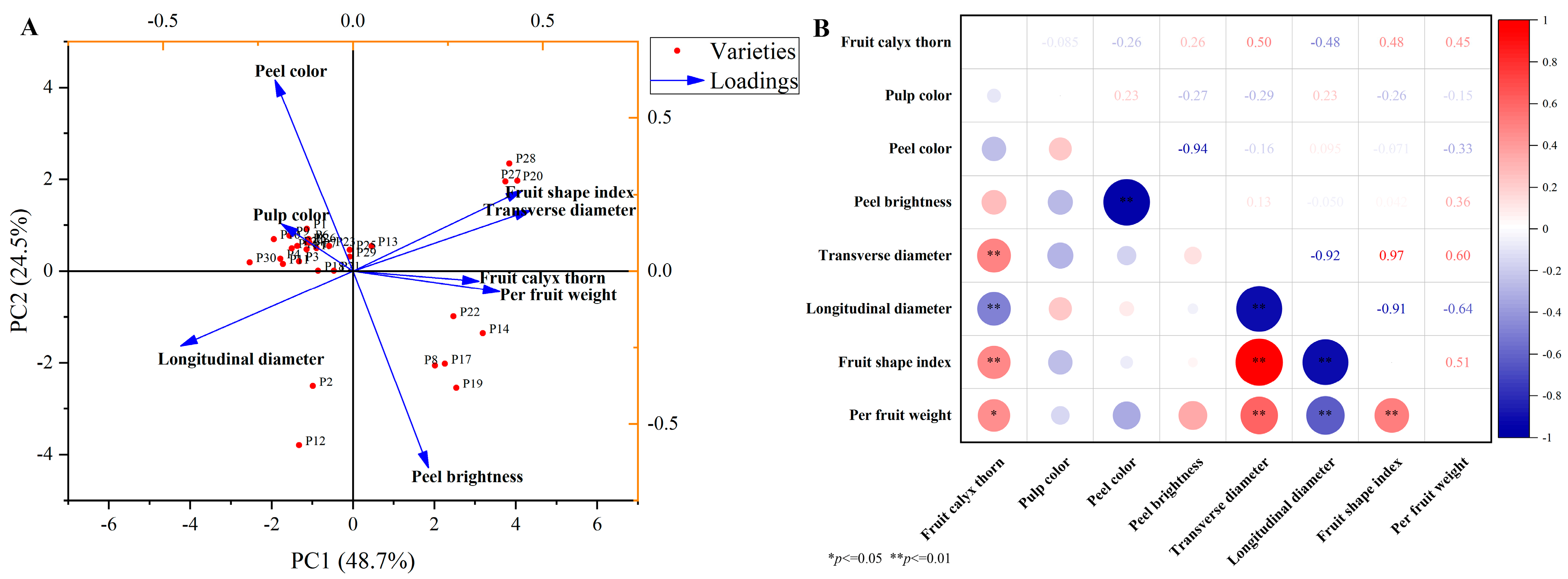
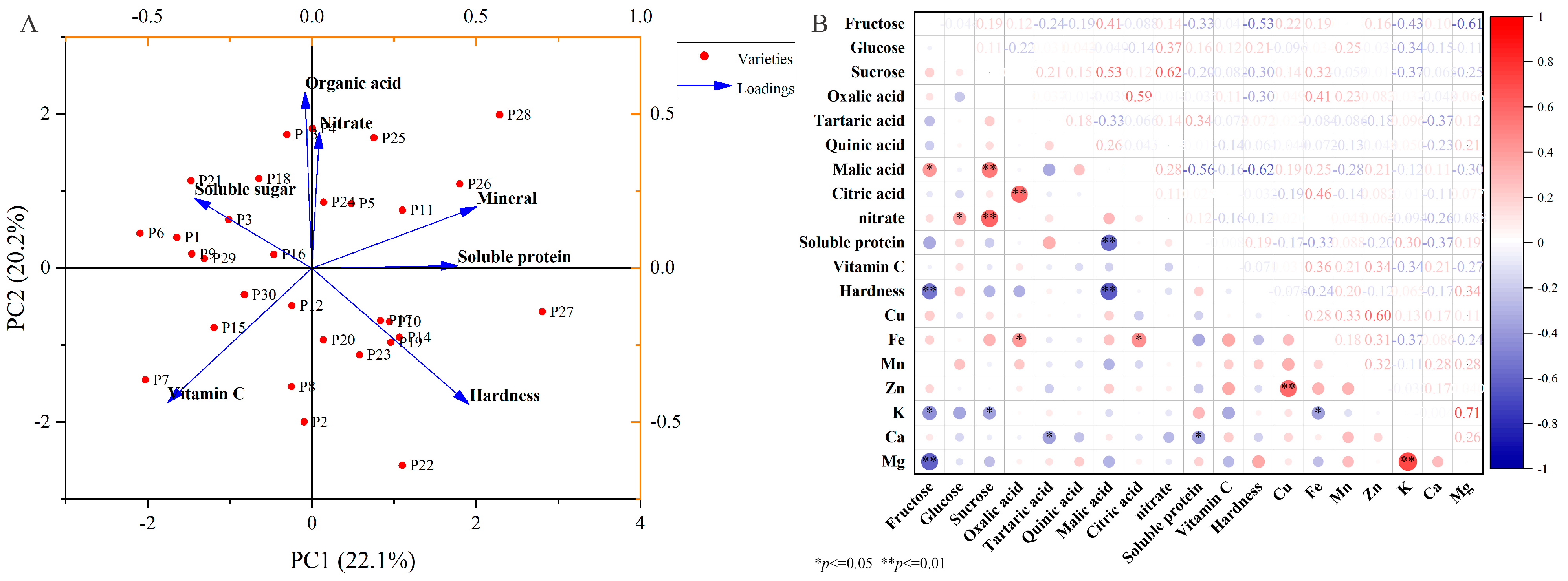
2.6. Comparative Assessment of the Appearance and Nutritional Traits of Chinese Eggplant Fruits
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Determination of Eggplant Fruit Appearance Characteristics
4.2.1. Color and Fruit Calyx Thorns
4.2.2. Fruit Hardness
4.2.3. Peel Brightness
4.2.4. Longitudinal and Transverse Diameters, and Fruit Shape Index
4.3. Determination of Eggplant Fruit Quality
4.3.1. Soluble Proteins, Vitamin C, and Nitrates Contents
4.3.2. Organic Acids Contents
4.3.3. Soluble Sugar Contents
4.3.4. Mineral Contents
4.4. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gürbüz, N.; Uluişik, S.; Frary, A.; Frary, A.; Doğanlar, S. Health benefits and bioactive compounds of eggplant. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, A.; Kazemi, M.; Samani, S.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Bioactive compounds from by-products of eggplant: Functional properties, potential applications and advances in valorization methods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 518–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. Chemistry and anticarcinogenic mechanisms of glycoalkaloids produced by eggplants, potatoes, and tomatoes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3323–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siasos, G.; Tousoulis, D.; Tsigkou, V.; Kokkou, E.; Oikonomou, E.; Vavuranakis, M.; Basdra, E.; Papavassiliou, A.; Stefanadis, C. Flavonoids in atherosclerosis: An overview of their mechanisms of action. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 2641–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.Y.; Ugur, S. Nutritional content and health benefits of eggplant. Turk. J. Agric. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 7, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekweogu, C.N.; Ude, V.C.; Nwankpa, P.; Emmanuel, O.; Ugbogu, E.A. Ameliorative effect of aqueous leaf extract of Solanum aethiopicum on phenylhydrazine-induced anaemia and toxicity in rats. Toxicol. Res. 2020, 36, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koley, T.K.; Tiwari, S.K.; Sarkar, A.; Nishad, J.; Goswami, A.; Singh, B. Antioxidant potential of Indian eggplant: Comparison among white, purple and green genotypes using chemometrics. Agric. Res. 2019, 8, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casati, L.; Pagani, F.; Braga, P.C.; Scalzo, R.L.; Sibilia, V. Nasunin, a new player in the field of osteoblast protection against oxidative stress. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 23, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, B.; Ramesh Kumar, P. Genetically modified (GM) crops face an uncertain future in India: Bt brinjal appraisal—A perspective. Ann. Plant Sci. 2015, 4, 960–975. [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy, A.; Mukamal, K.J.; Liu, L.; Franz, M.; Eliassen, A.H.; Rimm, E.B. High anthocyanin intake is associated with a reduced risk of myocardial infarction in young and middle-aged women. Circulation 2013, 127, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quamruzzaman, A.; Khatun, A.; Islam, F. Nutritional content and health benefits of bangladeshi eggplant ccultivars. Eur. J. Agric. Food Sci. 2020, 2, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, P.; Gramazio, P.; Vilanova, S.; Raigón, M.D.; Prohens, J.; Plazas, M. Phenolics content, fruit flesh colour and browning in cultivated eggplant, wild relatives and interspecific hybrids and implications for fruit quality breeding. Food Res. Int. 2017, 102, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afful, N.; Nyadanu, D.; Akromah, R.; Amoatey, H.; Annor, C.; Diawouh, R. Nutritional and antioxidant composition of eggplant accessions in Ghana. Afr. Crop Sci. J. 2019, 27, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, M.; Vilanova, S.; Plazas, M.; Gramazio, P.; Fonseka, H.H.; Fonseka, R.; Prohens, J. Diversity and relationships of eggplants from three geographically distant secondary centers of diversity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weese, T.L.; Bohs, L. Eggplant origins: Out of Africa, into the Orient. Taxon 2010, 59, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husnudin, U.B.; Suharyanto, S.; Daryono, B.S.; Purnomo, P. Variation and Non-formal Classification of Indonesian Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) Accessions Based on Macro and Micro-morphological Characters. AGRIVITA J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 41, 544–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, R.S.; Karol, K.G.; Little, D.P.; Nee, M.H.; Litt, A. Phylogeographic relationships among Asian eggplants and new perspectives on eggplant domestication. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2012, 63, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Akhtar, S.; Kumar, R.; Verma, R.; Kumari, R. Influence of seasonal variation on phenolic composition and antioxidant capacity of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) hybrids. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 295, 110865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, M.G. Plant Systematics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Plazas, M.; Andújar, I.; Vilanova, S.; Gramazio, P.; Herraiz, F.J.; Prohens, J. Conventional and phenomics characterization provides insight into the diversity and relationships of hypervariable scarlet (Solanum aethiopicum L.) and gboma (S. macrocarpon L.) eggplant complexes. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, P.; Prohens, J.; Vilanova, S.; Gramazio, P.; Plazas, M. Phenotyping of eggplant wild relatives and interspecific hybrids with conventional and phenomics descriptors provides insight for their potential utilization in breeding. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 198883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Ijaz, U.; Shah, T.I.; Najeebullah, M.; Niaz, S. Association and genetic assessment in brinjal. Eur. J. Biotechnol. Biosci. 2014, 2, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid Khan, R.K.; Singh, Y. Germplasm Characterization in Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.); Maharana Pratap University of Agriculture and Technology Location: Udaipur, India, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, S.K.; Bisht, I.; Kumar, G.; Karihaloo, J. Diversity in brinjal (Solanum melongena L.) landraces for morphological traits of evolutionary significance. Veg. Sci. 2016, 43, 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, R.A.; Watson, K.; Bohs, L. A four-gene study of evolutionary relationships in Solanum section Acanthophora. Am. J. Bot. 2005, 92, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruccelli, R.; Ganino, T.; Ciaccheri, L.; Maselli, F.; Mariotti, P. Phenotypic diversity of traditional cherry accessions present in the Tuscan region. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 150, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, P.; Lee, J.M.; Tsukamoto, C.; Takahashi, Y.; Singh, R.J.; Lee, J.D.; Chung, G. Evaluation of genetic structure of Korean wild soybean (Glycine soja) based on saponin allele polymorphism. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2014, 61, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prohens, J.; Whitaker, B.; Plazas, M.; Vilanova, S.; Hurtado, M.; Blasco, M.; Gramazio, P.; Stommel, J. Genetic diversity in morphological characters and phenolic acids content resulting from an interspecific cross between eggplant, Solanum melongena, and its wild ancestor (S. incanum). Ann. Appl. Biol. 2013, 162, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Chu, G.; Huang, C.; Tian, S.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, G. Anthocyanin accumulation and molecular analysis of anthocyanin biosynthesis-associated genes in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2906–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docimo, T.; Francese, G.; Ruggiero, A.; Batelli, G.; De Palma, M.; Bassolino, L.; Toppino, L.; Rotino, G.L.; Mennella, G.; Tucci, M. Phenylpropanoids accumulation in eggplant fruit: Characterization of biosynthetic genes and regulation by a MYB transcription factor. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6, 172292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, A.; Di Matteo, A.; Lombardi, N.; Trotta, N.; Punzo, B.; Mari, A.; Barone, A. Quantitative trait loci pyramiding for fruit quality traits in tomato. Mol. Breed. 2013, 31, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcarcel, J.; Reilly, K.; Gaffney, M.; O’Brien, N. Effect of genotype and environment on the glycoalkaloid content of rare, heritage, and commercial potato varieties. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, T1039–T1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennella, G.; Rotino, G.L.; Fibiani, M.; D’Alessandro, A.; Francese, G.; Toppino, L.; Cavallanti, F.; Acciarri, N.; Lo Scalzo, R. Characterization of health-related compounds in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) lines derived from introgression of allied species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7597–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Mata, M.-C.; Yokoyama, W.E.; Hong, Y.-J.; Prohens, J. α-Solasonine and α-solamargine contents of gboma (Solanum macrocarpon L.) and scarlet (Solanum aethiopicum L.) eggplants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5502–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, M.; Wei, P.; Yang, S.-T. Polymalic acid fermentation by Aureobasidium pullulans for malic acid production from soybean hull and soy molasses: Fermentation kinetics and economic analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 223, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.F.P.; Pereira, E.; Melgar, B.; Stojković, D.; Sokovic, M.; Calhelha, R.C.; Pereira, C.; Abreu, R.M.; Ferreira, I.C.; Barros, L. Eggplant fruit (Solanum melongena L.) and bio-residues as a source of nutrients, bioactive compounds, and food colorants, using innovative food technologies. Appl. Sci. 2020, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ispizua, E.; Calatayud, Á.; Marsal, J.I.; Mateos-Fernández, R.; Díez, M.J.; Soler, S.; Valcárcel, J.V.; Martínez-Cuenca, M.-R. Phenotyping local eggplant varieties: Commitment to biodiversity and nutritional quality preservation. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 696272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, P.M.; Yang, R.-Y.; Tsou, S.C.; Ledesma, D.; Engle, L.; Lee, T.-C. Diversity in eggplant (Solanum melongena) for superoxide scavenging activity, total phenolics, and ascorbic acid. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, A.; Stoltze, S. Nitrate and nitrite in vegetables on the Danish market: Content and intake. Food Addit. Contam. 1999, 16, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, V.R. Trace element biology: The knowledge base and its application for the nutrition of individuals and populations. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 1581S–1587S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, M.; Nordberg, G.F. Trace element research-historical and future aspects. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2016, 38, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.; Rahman, M.; Quamruzzaman, A. Genetic divergence in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) genotypes. Bangladesh J. Agric. Res. 2016, 41, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tembe, K.O.; Chemining’wa, G.; Ambuko, J.; Owino, W. Evaluation of African tomato landraces (Solanum lycopersicum) based on morphological and horticultural traits. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2018, 52, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, R.S.; Purugganan, M.D. Evolution of crop species: Genetics of domestication and diversification. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandro, M.; Riccardi, P.; Fiore, M.; Ricciardi, L. Genetic diversity and characterization of African eggplant germplasm collection. Afr. J. Plant Sci. 2010, 4, 231–241. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, R.; Akhtar, S.; Solankey, S.S.; Aakanksha. Variation in the eggplant (Solanum melongena) genotypes for health-promoting bioactive compounds and agro-morphological traits. Agric. Res. 2023, 12, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, K. Studies in Relation to Commercial Hybrid Development in Brinjal (Solanum melongena L.). Ph.D. Thesis, Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology, Kashmir, India, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Datta, D.R.; Rafii, M.Y.; Misran, A.; Jusoh, M.; Yusuff, O.; Haque, M.A.; Jatto, M.I. Evaluation of eggplant accessions based on their quantitative and qualitative traits performance under tropical climate. Plant Arch. 2023, 23, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBPGR (1991) Annual Report 1990. International Board for Plant Genetic Resources, Rome. Available online: https://alliancebioversityciat.org/ (accessed on 22 June 2024).
- Sedmak, J.J.; Grossberg, S.E. A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal. Biochem. 1977, 79, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, D.; Maroon, M.; Schrader, L.E.; Youngs, V.L. Rapid colorimetric determination of nitrate in plant tissue by nitration of salicylic acid. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1975, 6, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jin, N.; Jin, L.; Xiao, X.; Hu, L.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, W.; Lyu, J. Response of tomato fruit quality depends on period of LED supplementary light. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 833723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.; Zhang, D.; Jin, L.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Lei, Y.; Meng, X.; Xu, Z.; Sun, J.; Lyu, J. Controlling water deficiency as an abiotic stress factor to improve tomato nutritional and flavour quality. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Index | Mean | SD | SE | Min. | Max. | CV (%) | H′ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fruit calyx thorn | 1.60 | 1.07 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 3.00 | 66.87 | 1.30 |
| Pulp color | 2.33 | 0.76 | 0.14 | 1.00 | 4.00 | 32.49 | 1.45 |
| Peel color | 4.77 | 1.48 | 0.27 | 2.00 | 6.00 | 31.01 | 1.33 |
| Peel brightness | 25.04 | 15.36 | 2.81 | 14.18 | 62.01 | 61.36 | 1.41 |
| Transverse diameter (cm) | 4.46 | 1.64 | 0.30 | 2.37 | 8.57 | 36.68 | 1.34 |
| Longitudinal diameter (cm) | 14.72 | 3.44 | 0.63 | 6.88 | 22.23 | 23.37 | 1.25 |
| Fruit shape index (%) | 0.37 | 0.29 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 1.19 | 79.35 | 1.33 |
| Per fruit weight (g) | 309.40 | 90.16 | 16.46 | 173.30 | 476.50 | 29.14 | 1.16 |
| ID | Species | Form | Peel Color | Per Fruit Weight | Breeder Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 1871 | Round | Purple | 210–230 g | Zhumadian Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| P2 | Zhengqie 924 | Round | Purple | 430–480 g | Zhengzhou Vegetable Research Institute |
| P3 | 420 | Round | Purple | 390–440 g | Institute of Vegetable and Flower Research, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| P4 | cw213 | Round | Purple | 370–400 g | Institute of Vegetable and Flower Research, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| P5 | 1777 | Round | Purple | 375–405 g | Zhumadian Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| P6 | Zhengqie 907 | Round | Green | 450–490 g | Zhengzhou Vegetable Research Institute |
| P7 | 1942 | Round | Green | 410–460 g | Zhumadian Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| P8 | 1908 | Round | Green | 420–465 g | Zhumadian Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| P9 | Zhengqie 908 | Round | Green | 410–450 g | Zhengzhou Vegetable Research Institute |
| P10 | 1919 | Round | Green | 400–435 g | Zhumadian Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| P11 | 216 | Long | Purple | 320–370 g | Institute of Vegetable and Flower Research, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| P12 | Yuzaoqie No. 9 | Long | Purple | 330–390 g | Chongqing Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| P13 | E160516 | Long | Purple | 150–205 g | Jilin Scientific Research Institute of Vegetables and Flowers |
| P14 | 19-824 | Long | Purple | 260–310 g | Chongqing Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| P15 | Weichangqie 101 | Long | Purple | 250–310 g | Weifang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Shandong Province |
| P16 | Yuqie No. 6 | Long | Purple | 155–200 g | Chongqing Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| P17 | Ron 19-14 | Long | Purple | 150–200 g | Chengdu Academy of Agriculture and Forestry |
| P18 | Huhei 6 | Long | Purple | 200–260 g | Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| P19 | Changqie 719 | Long | Purple | 230–280 g | Shandong Vegetable Institute |
| P20 | Weichangqie 71 | Long | Purple | 320–380 g | Weifang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Shandong Province |
| P21 | Ron17-66 | Long | Purple | 150–200 g | Chengdu Academy of Agriculture and Forestry |
| P22 | Weichangqie 78 | Long | Purple | 270–320 g | Weifang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Shandong Province |
| P23 | Huqie 316 | Long | Purple | 150–200 g | Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| P24 | Changqie1016 | Long | Purple | 300–340 g | Shandong Vegetable Institute |
| P25 | Zhengqie 809 | Long | Purple | 245–305 g | Zhengzhou Vegetable Research Institute |
| P26 | E150725 | Long | Purple | 310–360 g | Jilin Scientific Research Institute of Vegetables and Flowers |
| P27 | Zhengqie 903 | Long | Purple | 280–330 g | Zhengzhou Vegetable Research Institute |
| P28 | 1952 | Long | Purple | 280–320 g | Zhumadian Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| P29 | Lvtianshi | Long | Green | 200–250 g | Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Sciences |
| P30 | Wanqie 048 | Long | Green | 150–190 g | Anhui Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Institute of Horticulture |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, J.; Jin, L.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, M.; Jin, N.; Wang, S.; Hu, L.; Yu, J. Agronomic and Quality Traits of 30 Eggplant Germplasm Resources from China. Plants 2025, 14, 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121838
Lyu J, Jin L, Ma X, Li Y, Sun M, Jin N, Wang S, Hu L, Yu J. Agronomic and Quality Traits of 30 Eggplant Germplasm Resources from China. Plants. 2025; 14(12):1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121838
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Jian, Li Jin, Xianglan Ma, Yansu Li, Mintao Sun, Ning Jin, Shuya Wang, Linli Hu, and Jihua Yu. 2025. "Agronomic and Quality Traits of 30 Eggplant Germplasm Resources from China" Plants 14, no. 12: 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121838
APA StyleLyu, J., Jin, L., Ma, X., Li, Y., Sun, M., Jin, N., Wang, S., Hu, L., & Yu, J. (2025). Agronomic and Quality Traits of 30 Eggplant Germplasm Resources from China. Plants, 14(12), 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121838








