Indole Alkaloids and Phenolic Amides from the Rhizomes of Cimicifuga heracleifolia and Their In Vitro Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase (sEH) Inhibitory Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
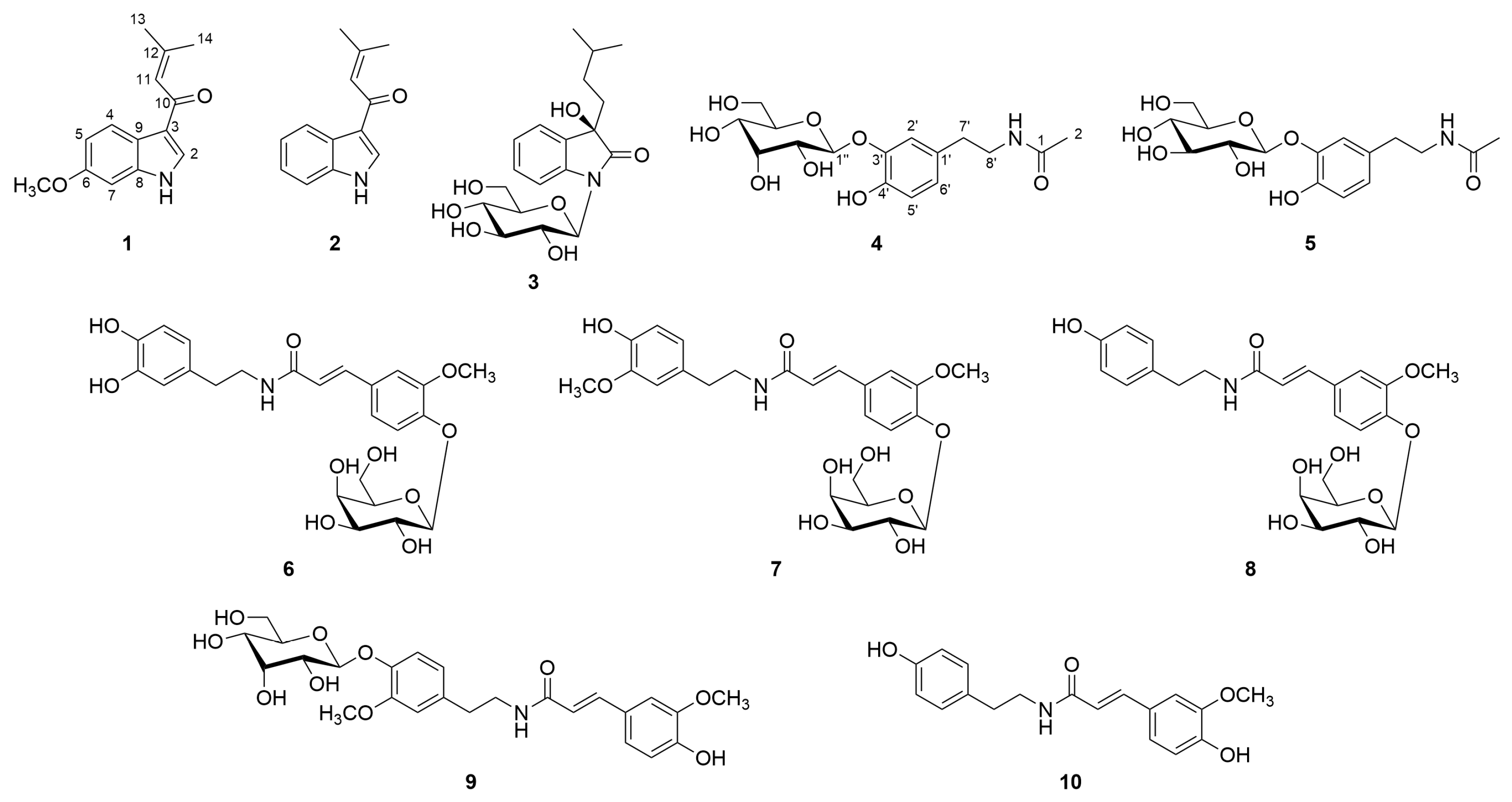
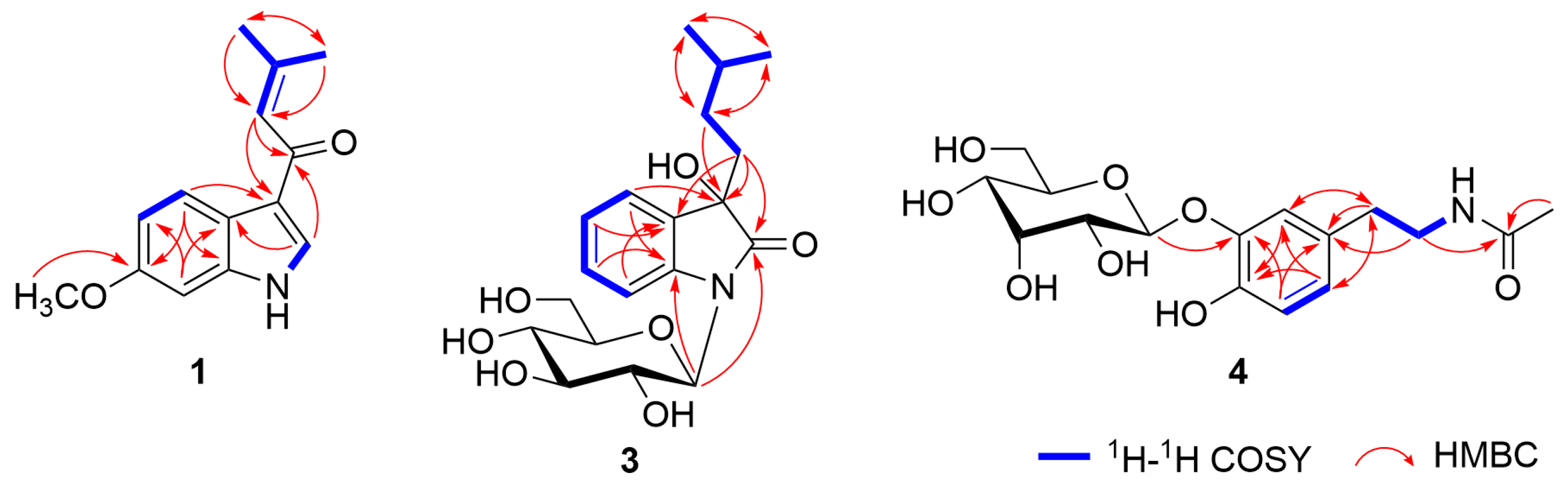
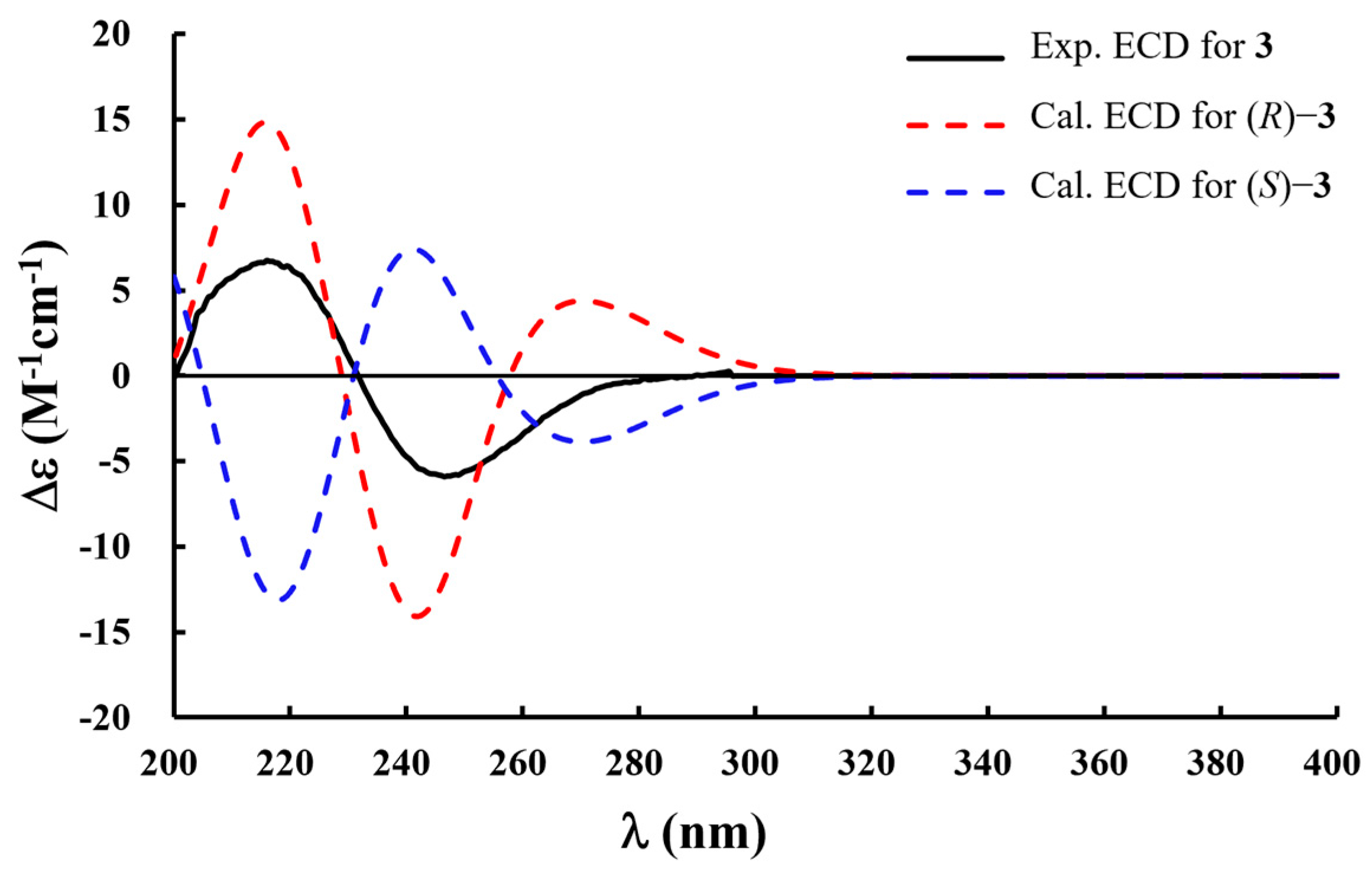
2.1. Isolation and Structural Determination of Compounds 1−10
2.2. Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase (sEH) Inhibitory Activity of Compounds 1−10
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experiment Procedures
3.2. Plant Material and sEH Information
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Acid Hydrolysis of Compounds 3 and 4
3.5. ECD Calculations
3.6. sEH Inhibitory Activity
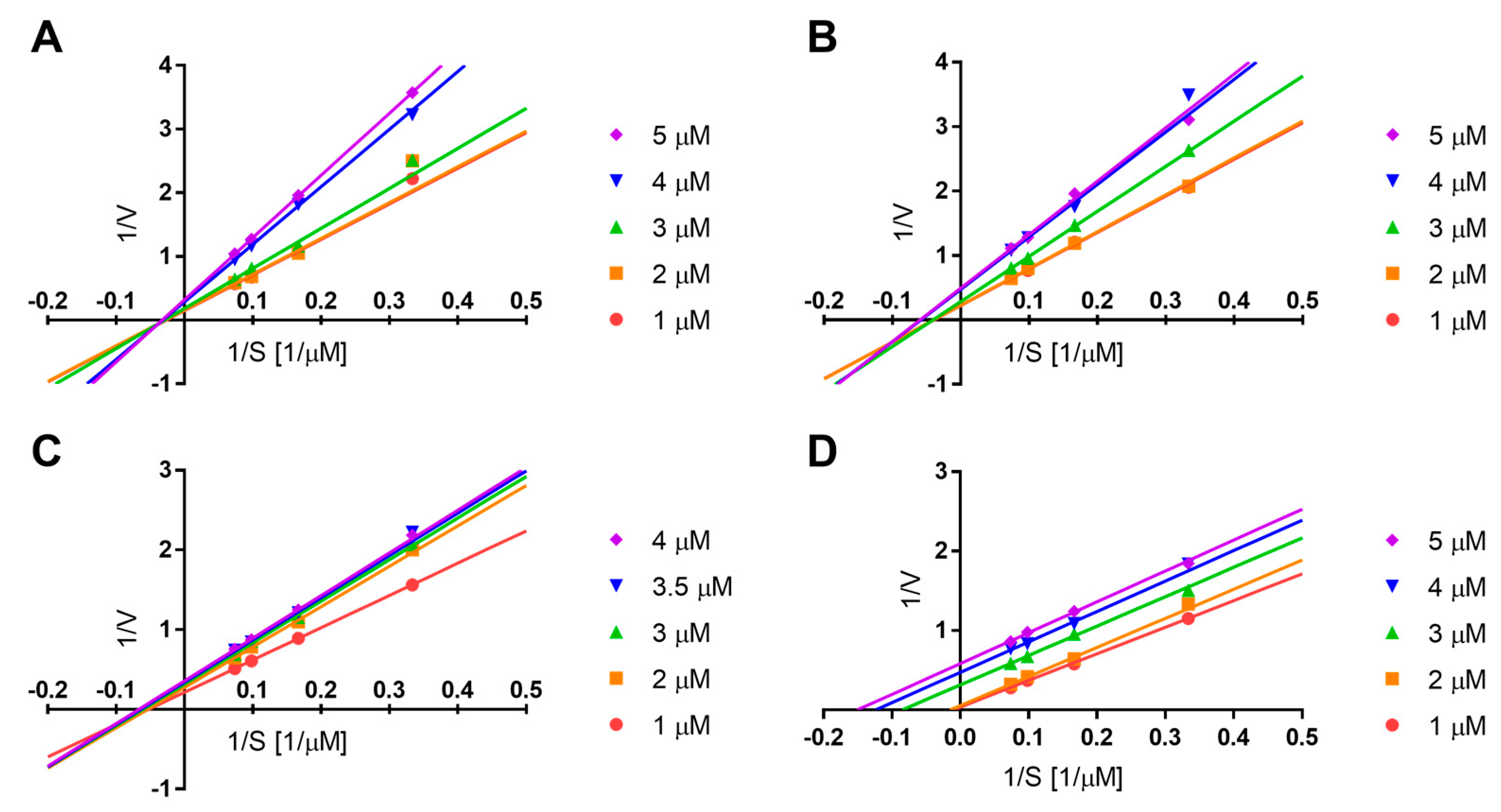
3.7. sEH Kinetic Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- eFloras. Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, MO & Harvard University Herbaria, Cambridge, MA. 2008. Available online: http://www.efloras.org (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- POWO. Plants of the World Online. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. 2025. Available online: https://powo.science.kew.org (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- Li, J.X.; Yu, Z.Y. Cimicifugae rhizoma: From origins, bioactive constituents to clinical outcomes. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 2927–2951. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.E.; Kim, B.B.; Ko, Y.; Jeong, S.H.; Park, J.B. Effects of Cimicifugae Rhizoma on the osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of stem cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.Y.; Chu, T.T.H.; Li, P.; Jiang, Y.; Li, H.J. Cimicifuga heracleifolia is therapeutically similar to black cohosh in relieving menopausal symptoms: Evidence from pharmacological and metabolomics studies. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 17, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Song, X.; Nagai, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Dai, Y.; He, L.; Kiyohara, H.; Yao, X.; Yao, Z. Chemical profile of Cimicifuga heracleifolia Kom. and immunomodulatory effect of its representative bioavailable component, cimigenoside on Poly(I:C)-induced airway inflammation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 267, 113615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wei, W.; Jin, X.; Lu, J.; Chen, S.; Ogaji, O.D.; Wang, S.; Du, K.; Chang, Y.; Li, J. Traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, quality control and clinical studies of Cimicifugae Rhizoma: A comprehensive review. Chin. Med. 2024, 19, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.J.; Li, C.T.; Xi, F.M.; Sun, L.N.; Chen, W.S. Heracleifolinosides A-F, new triterpene glycosides from Cimicifuga heracleifolia, and their inhibitory activities against hypoxia and reoxygenation. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yin, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Pan, G.; Lv, H.; Wang, X.; Owoicho Orgah, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, H. Traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of the genus Cimicifuga: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 209, 264–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautheron, J.; Jéru, I. The multifaceted role of epoxide hydrolases in human health and disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, K.; Hammock, B.D. Cytosolic and microsomal epoxide hydrolases: Differential properties in mammalian liver. Science 1980, 207, 1479–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurén, D.J.; Halarnkar, P.P.; Hammcock, B.D.; Hinton, D.E. Microsomal and cytosolic epoxide hydrolase and glutathione S-transferase activities in the gill, liver, and kidney of the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Baseline levels and optimization of assay conditions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1989, 38, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.W.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D. Epoxide hydrolases: Their roles and interactions with lipid metabolism. Prog. Lipid. Res. 2005, 44, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Huo, X.; Ning, J.; Yu, Z.; Morisseau, C.; Sun, C.; Hammock, B.D.; Ma, X. Macrophage Inactivation by Small Molecule Wedelolactone via Targeting sEH for the Treatment of LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury. ACS Cent. Sci. 2023, 3, 440–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, X.; Morisseau, C.; Hwang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Hammock, B.D.; Ma, X. Discovery of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors from chemical synthesis and natural products. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 1, 184–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, N.M.; Morisseau, C.; Jones, P.D.; Hock, B.; Hammock, B.D. Development of a high-throughput screen for soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 355, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Han, F.; Rong, Y.; Ding, L.; Qiu, F. Guided isolation of enantiomeric lignans from Cimicifuga heracleifolia Kom. by antioxidant activity and molecular networking. Phytochemistry 2024, 221, 114050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thao, N.P.; Luyen, B.T.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.H. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors of indolinone alkaloids and phenolic derivatives from Cimicifuga dahurica (Turcz.) Maxim. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 1874–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phong, N.V.; Lim, S.D.; Lee, H.J.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, J.A. Inhibitory effects of compounds from ice plant (Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L.) against tyrosinase and soluble epoxide hydrolase: In vitro and in silico studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1321, 140234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Bulumulla, H.N.K.; Wimalasiri, W.R.; Reisch, J. Coumarins and an indole alkaloid from Pamburus missionis. Phytochemistry 1994, 36, 879–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, T.L.; Morgan, T.D.; Mueller, D.D.; Tomer, K.B.; Kramer, K.J. Identification of catecholamine β-glucosides in the hemolymph of the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta (L.), during development. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 25, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Han, L.F.; Pan, G.X.; Peng, S.; Andre, N. A new phenolic amide glycoside from Cimicifuga dahurica. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2013, 48, 1281–1285. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.J.; Chen, D.H.; Xiao, P.G. Cimicifugamide and isocimicifugamide, two new cinnamamide derivatives isolated from Cimicifuga dahurica. Chin. Chem. Lett. 1993, 4, 891–892. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, P.Y.; Zhu, X.X.; Cai, M.S.; Yu, D.Q. Studies on synthesis and pharmacological activities of cimicifugamide from Cimicifuga dahurica, and its analogues. Acta Pharm. Sin. 1977, 32, 755–760. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; Zhang, W.Y.; Pan, D.B.; Shi, D.F.; Pang, Q.Q.; Li, H.B.; Yao, X.J.; Yao, Z.H.; Yu, Y.; Yao, X.S. Phenolic acids and their glycosides from the rhizomes of Cimicifuga dahurica. Fitoterapia 2019, 134, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Hui, Y.; Rupprecht, J.K.; McLaughlin, J.L.; Wood, K.V. Additional bioactive compounds and trilobacin, a novel highly cytotoxic acetogenin, from the bark of Asimina triloba. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, L.H.; Joffé, E.B.; Puricelli, L.; Tatian, M.; Seldes, A.M.; Palermo, J.A. Indole alkaloids from the tunicate Aplidium meridianum. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1130–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Bai, J.; Fang, Z.F.; Yu, S.S.; Ma, S.G.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Qu, J.; Ren, J.H.; Li, L.; et al. Indole alkaloids and quassinoids from the stems of Brucea mollis. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2438–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, M.B.; Bisht, G.S.; Kumari, P.; Gnanaprakasam, B. Ruthenium-catalyzed direct α-alkylation of amides using alcohols. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 9215–9220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorin, A.J.P.; Mazurek, M. Further studies on the assignment of signals in 13C magnetic resonance spectra of aldoses and derived methyl glycosides. Can. J. Chem. 1975, 53, 1212–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.B.; Sun, C.P.; Xu, J.X.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D.; Qiu, F. Phytochemical constituents from Scutellaria baicalensis in soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition: Kinetics and interaction mechanism merged with simulations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Choi, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Yang, S.Y. Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase by phytochemical constituents of the root bark of Ulmus davidiana var. japonica. J. Enzyme. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Abis, G.; Mattingly-Peck, F.; Lynham, S.; Fraternali, F.; Conte, M.R. Allosteric regulation of the soluble epoxide hydrolase by nitro fatty acids: A combined experimental and computational approach. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pescitelli, G.; Bruhn, T. Good computational practice in the assignment of absolute configurations by TDDFT calculations of ECD spectra. Chirality 2016, 28, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmistrov, V.; Morisseau, C.; Harris, T.R.; Butov, G.; Hammock, B.D. Effects of adamantane alterations on soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition potency, physical properties and metabolic stability. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 76, 510–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| No. | 1 | 3 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | COSY | HMBC | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | COSY | HMBC | |||
| 1 | 11.77 br s | H-2 | ||||||||
| 2 | 132.1 | CH | 8.20 s | H-1 | C-9/10 | 177.2 | C | |||
| 3 | 118.4 | C | 75.3 | C | ||||||
| 4 | 122.4 | CH | 8.12 d (8.7) | H-5 | C-3/6/8 | 123.6 | CH | 7.32 d (8.6) | H-5 | C-3/8 |
| 5 | 111.4 | CH | 6.80 dd (8.7, 2.3) | H-4 | 122.4 | CH | 7.08 t (9.8) | H-4/6 | C-7/9 | |
| 6 | 156.4 | C | 128.7 | CH | 7.27 t (9.8) | H-5/7 | C-4/8 | |||
| 7 | 95.0 | CH | 6.92 d (2.3) | C-5/9 | 111.6 | CH | 7.14 d (8.6) | H-6 | C-5/9 | |
| 8 | 137.6 | C | 140.7 | C | – | |||||
| 9 | 119.9 | C | 131.3 | C | – | |||||
| 10 | 186.1 | C | 35.5 | CH2 | 1.81 m | H-11 | C-2/3/9 | |||
| 11 | 122.3 | CH | 6.80 br s | H-12 | C-3/10 | 31.5 | CH2 | 0.94 m | H-10/12 | C-13/14 |
| 12 | 151.0 | C | H-11/13/14 | 27.7 | CH | 1.40 m | H-11/13/14 | |||
| 13 | 27.3 | CH3 | 1.94 br s | H-14 | C-11/14 | 22.4 a | CH3 | 0.77 d (5.8) | H-12 | C-11/12/14 |
| 14 | 20.8 | CH3 | 2.17 br s | H-13 | C-11/13 | 22.3 a | CH3 | 0.77 d (5.8) | H-12 | C-11/12/13 |
| 6-OCH3 | 55.2 | CH3 | 3.77 s | C-6 | ||||||
| Glc-1′ | 81.9 | CH | 5.12 d (9.2) | H-2′ | C-2/8 | |||||
| 2′ | 68.3 | CH | 3.84 m | H-1′/3′ | C-4′ | |||||
| 3′ | 77.2 | CH | 3.30 m | H-2′/4′ | C-1′ | |||||
| 4′ | 69.7 | CH | 3.26 m | H-3′/5′ | C-2′/6′ | |||||
| 5′ | 79.8 | CH | 3.32 m | H-4′/6′ | C-1′/3′ | |||||
| 6′ | 60.9 | CH2 | 3.72 d (11.7) | H-5′/6′ | C-4′ | |||||
| 3.50 dd (11.7, 5.6) | ||||||||||
| No. | 4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | COSY | HMBC | ||
| 1 | 169.0 | C | |||
| 2 | 22.6 | CH3 | 1.77 s | C-1 | |
| 1′ | 129.8 | C | |||
| 2′ | 117.3 | CH | 6.91 d (1.5) | C-4′/7′ | |
| 3′ | 145.6 | C | |||
| 4′ | 146.0 | C | |||
| 5′ | 115.8 | CH | 6.68 d (8.1) | H-6′ | C-1′/3′ |
| 6′ | 122.8 | CH | 6.66 dd (8.1, 1.5) | H-5′ | C-2′/4′/7′ |
| 7′ | 34.7 | CH2 | 2.55 m | H-8′ | C-1′/2′/6′ |
| 8′ | 40.4 | CH2 | 3.19 m | H-7′/N-H | C-1/1′ |
| N-H | 7.85 t (5.5) | H-8′ | |||
| 1″ | 100.6 | CH | 4.94 d (7.9) | H-2″ | C-3′ |
| 2″ | 70.5 | CH | 3.45 dd (8.2, 2.7) | H-1″/3″ | |
| 3″ | 71.1 | CH | 3.96 m | H-2″/4″ | C-5″ |
| 4″ | 67.1 | CH | 3.40 dd (9.7, 2.7) | H-3″/5″ | C-6″ |
| 5″ | 74.9 | CH | 3.65 m | H-4″/6″ | C-1″ |
| 6″ | 61.0 | CH2 | 3.68 m | H-5″ | C-4″ |
| 3.48 m | |||||
| Compound | IC50 (μM) a |
| 1 | >100 |
| 2 | >100 |
| 3 | >100 |
| 4 | >100 |
| 5 | >100 |
| 6 | 8.74 ± 0.42 |
| 7 | 15.63 ± 0.10 |
| 8 | 20.58 ± 0.89 |
| 9 | >100 |
| 10 | 17.16 ± 0.31 |
| AUDA b | 0.004 ± 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Fan, C.; Chen, L.; Cui, X.; Otsuki, K.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, F.; Ding, L.; Li, W. Indole Alkaloids and Phenolic Amides from the Rhizomes of Cimicifuga heracleifolia and Their In Vitro Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase (sEH) Inhibitory Activity. Plants 2025, 14, 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121742
Sun Y, Fan C, Chen L, Cui X, Otsuki K, Zhang M, Qiu F, Ding L, Li W. Indole Alkaloids and Phenolic Amides from the Rhizomes of Cimicifuga heracleifolia and Their In Vitro Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase (sEH) Inhibitory Activity. Plants. 2025; 14(12):1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121742
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yanwen, Chunyu Fan, Liyi Chen, Xueting Cui, Kouharu Otsuki, Mi Zhang, Feng Qiu, Liqin Ding, and Wei Li. 2025. "Indole Alkaloids and Phenolic Amides from the Rhizomes of Cimicifuga heracleifolia and Their In Vitro Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase (sEH) Inhibitory Activity" Plants 14, no. 12: 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121742
APA StyleSun, Y., Fan, C., Chen, L., Cui, X., Otsuki, K., Zhang, M., Qiu, F., Ding, L., & Li, W. (2025). Indole Alkaloids and Phenolic Amides from the Rhizomes of Cimicifuga heracleifolia and Their In Vitro Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase (sEH) Inhibitory Activity. Plants, 14(12), 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121742








