Integrative Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Insights Into Saline-Alkali Stress Tolerance in Foxtail Millet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurements of Physio-Biochemical Characteristics of Foxtail Millet Response to Saline-Alkali Stress
2.4. Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analysis of Foxtail Millet Response to Saline-Alkali Stress
2.4.1. Total RNA Quality Control of Sequencing Samples
2.4.2. Sample Preparation and Metabolic Analysis
2.4.3. Screening and Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes and Metabolites
2.4.4. GO and KEGG Enrichment Analysis
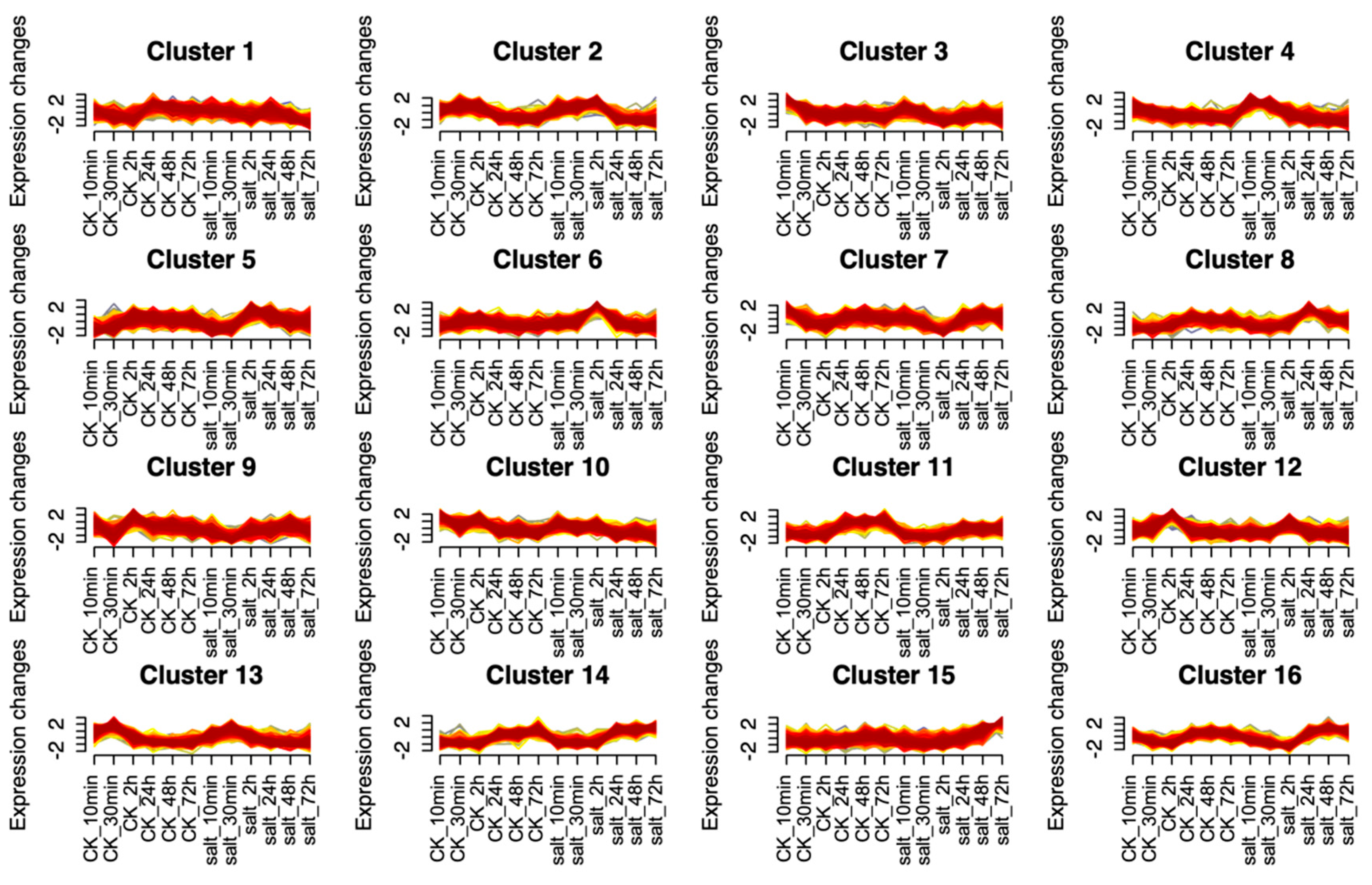
2.4.5. Profiling the Gene Expression Patterns of Xiaomi Under Saline-Alkali Stress
2.4.6. Correlation Network Diagram
2.4.7. Metabolic Pathway Analysis
3. Results
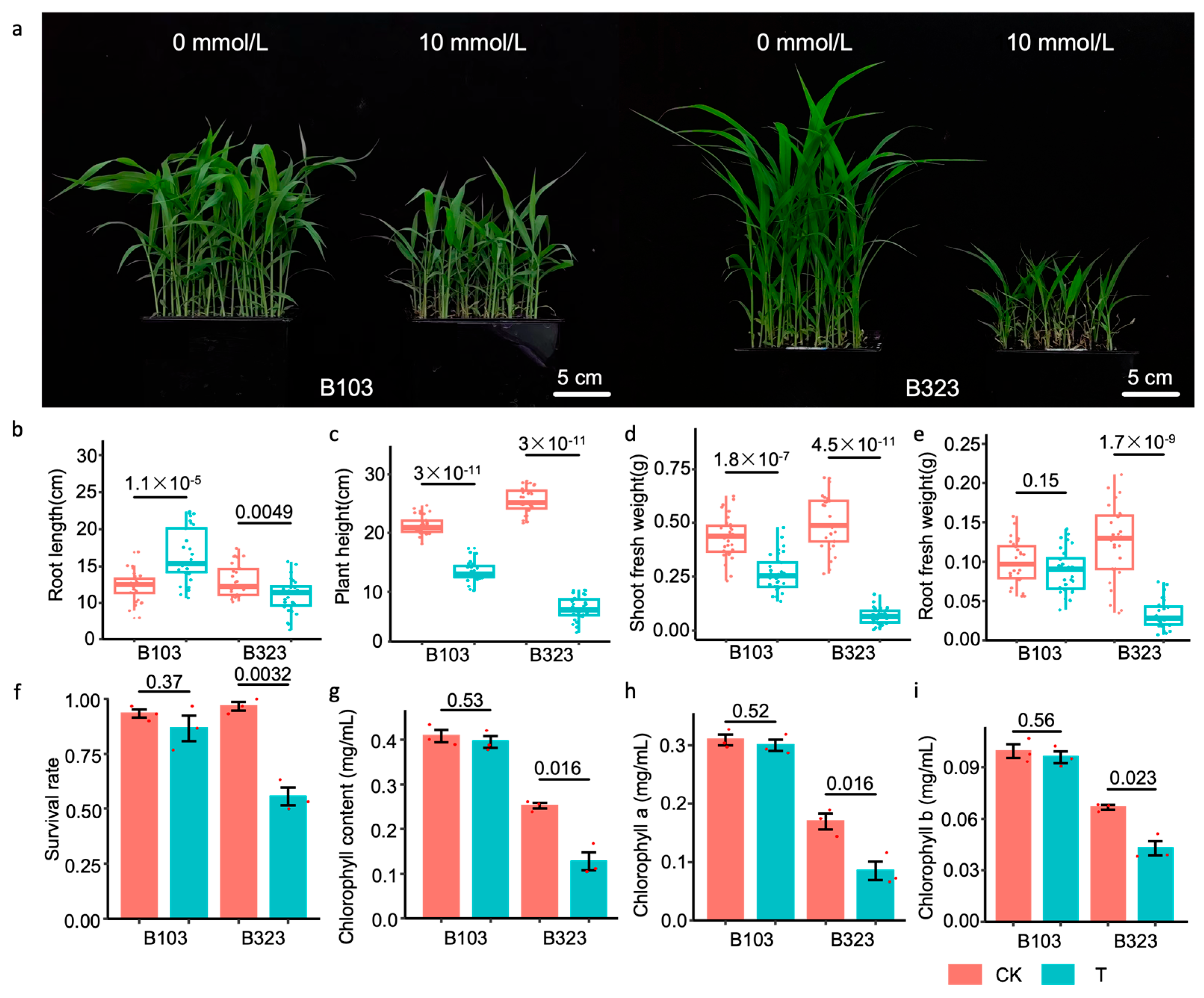
3.1. Phenotypic and Physiological Analysis
3.2. Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analysis
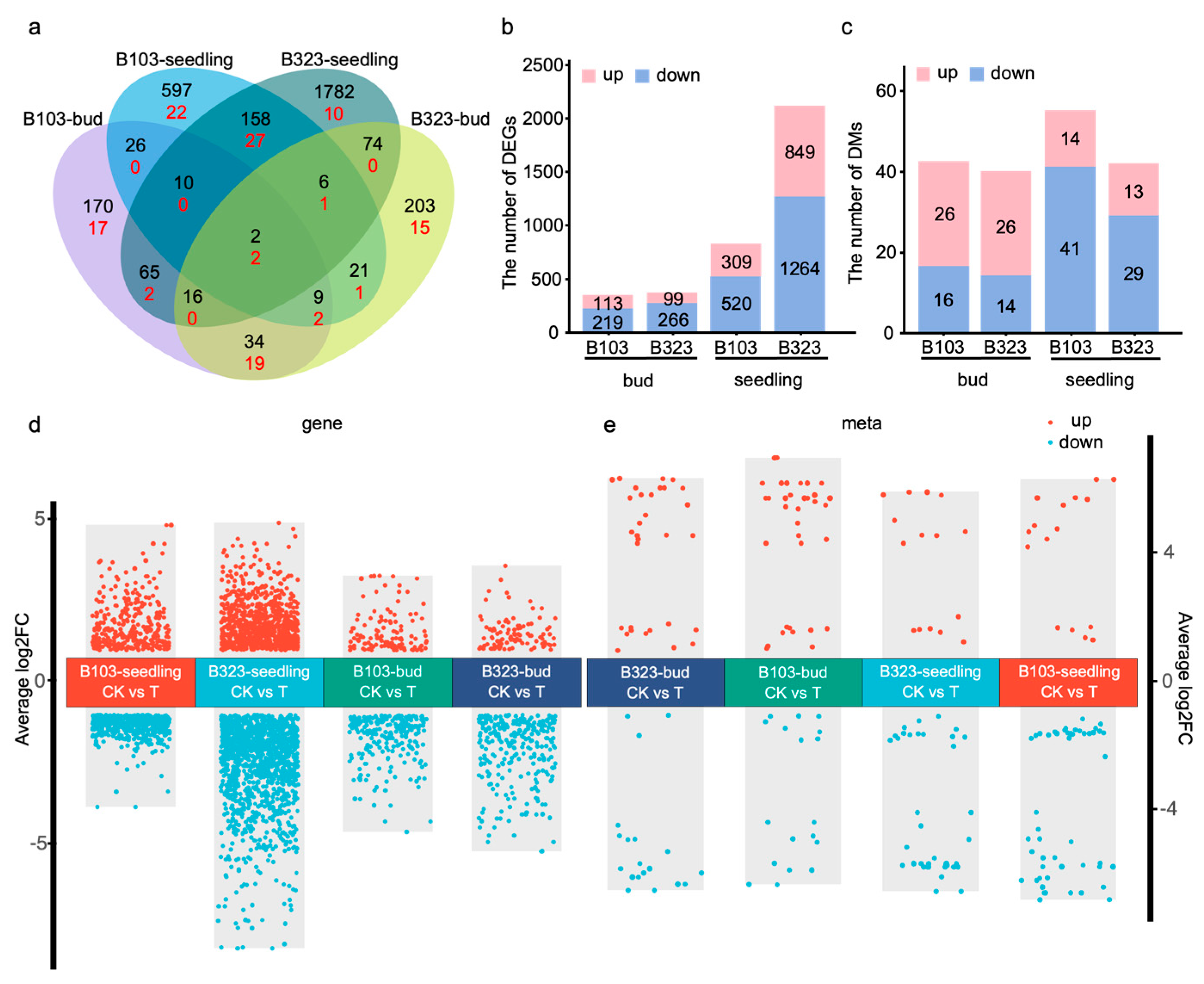
3.2.1. Screening and Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes and Metabolites
3.2.2. Transcription Factor Analysis Under Saline-Alkali Stress
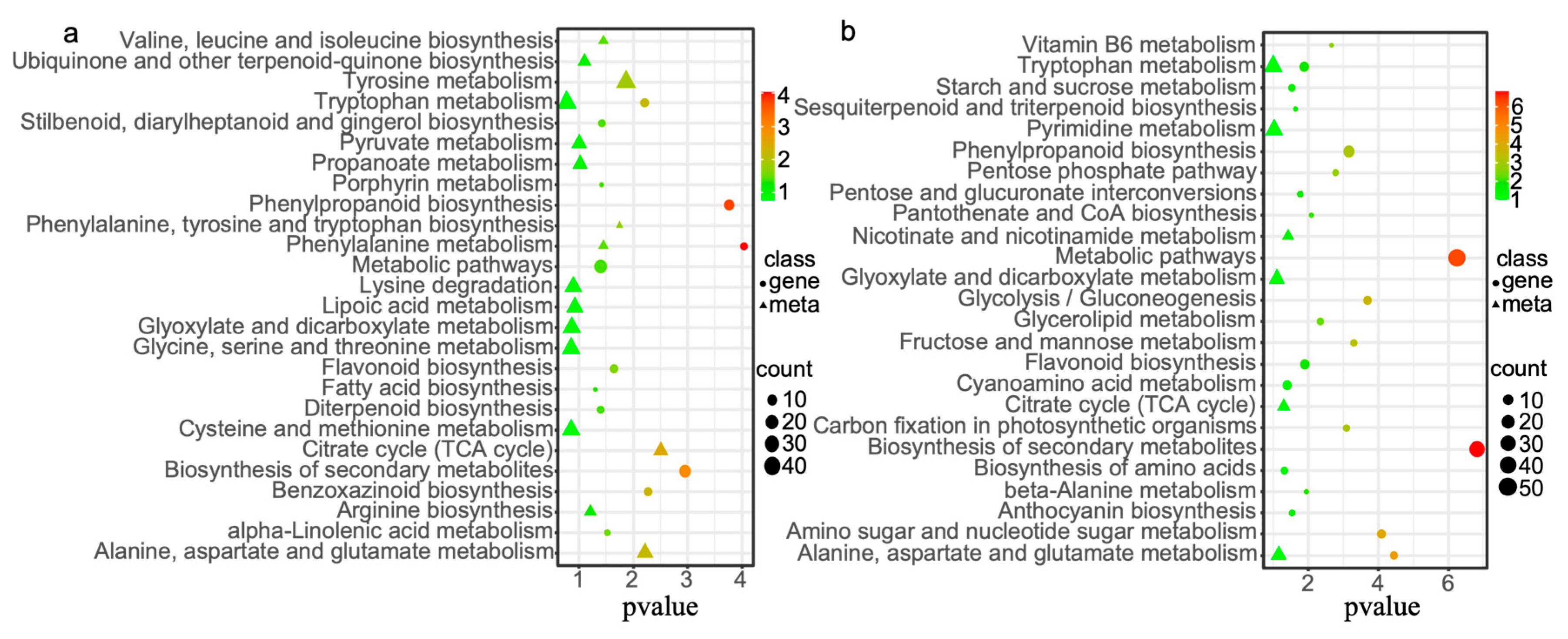
3.2.3. GO and KEGG Enrichment Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes and Differential Metabolites
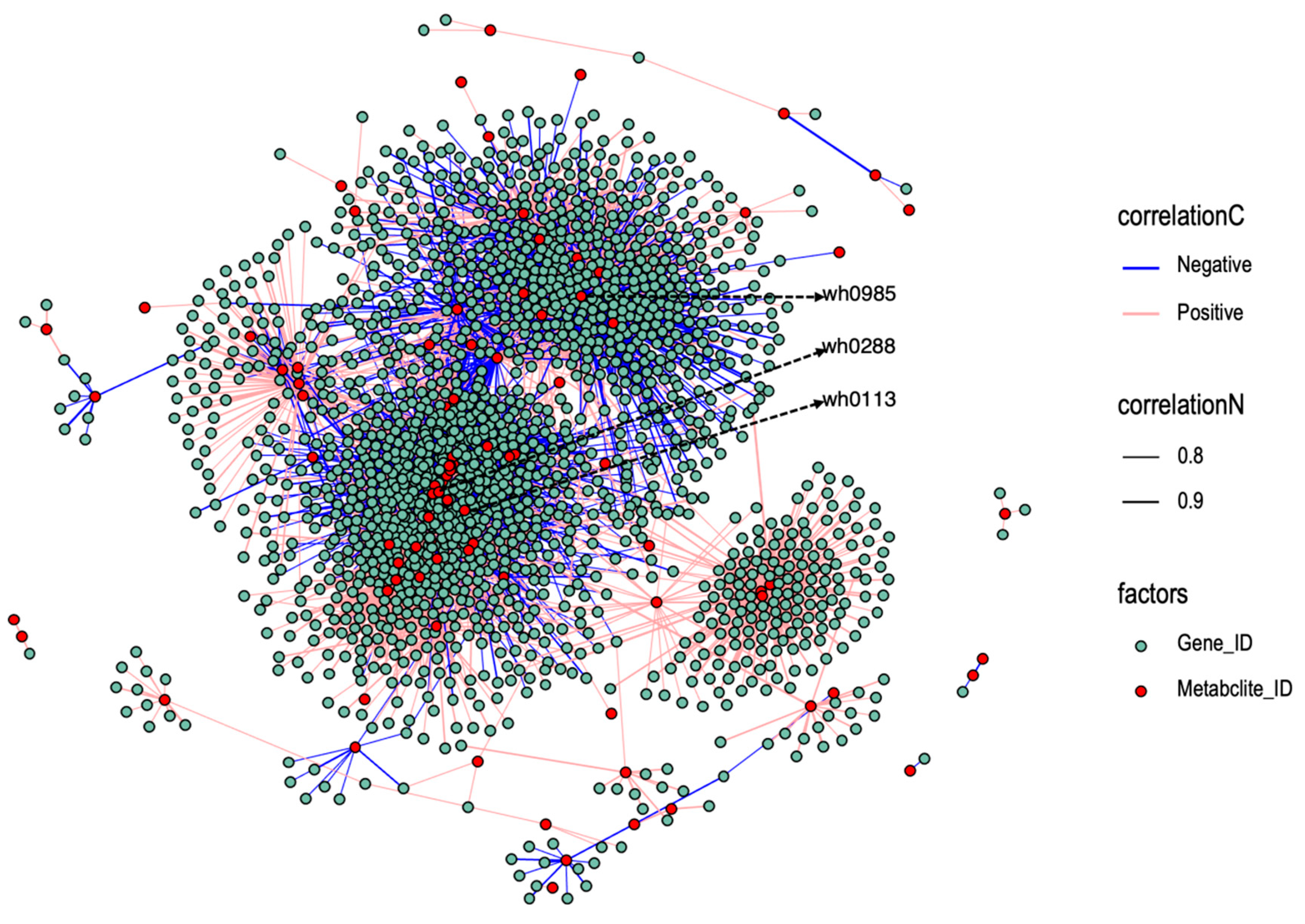
3.2.4. Correlation Network of Differentially Expressed Genes and Differential Metabolites
3.2.5. The Gene Expression Patterns of Xiaomi
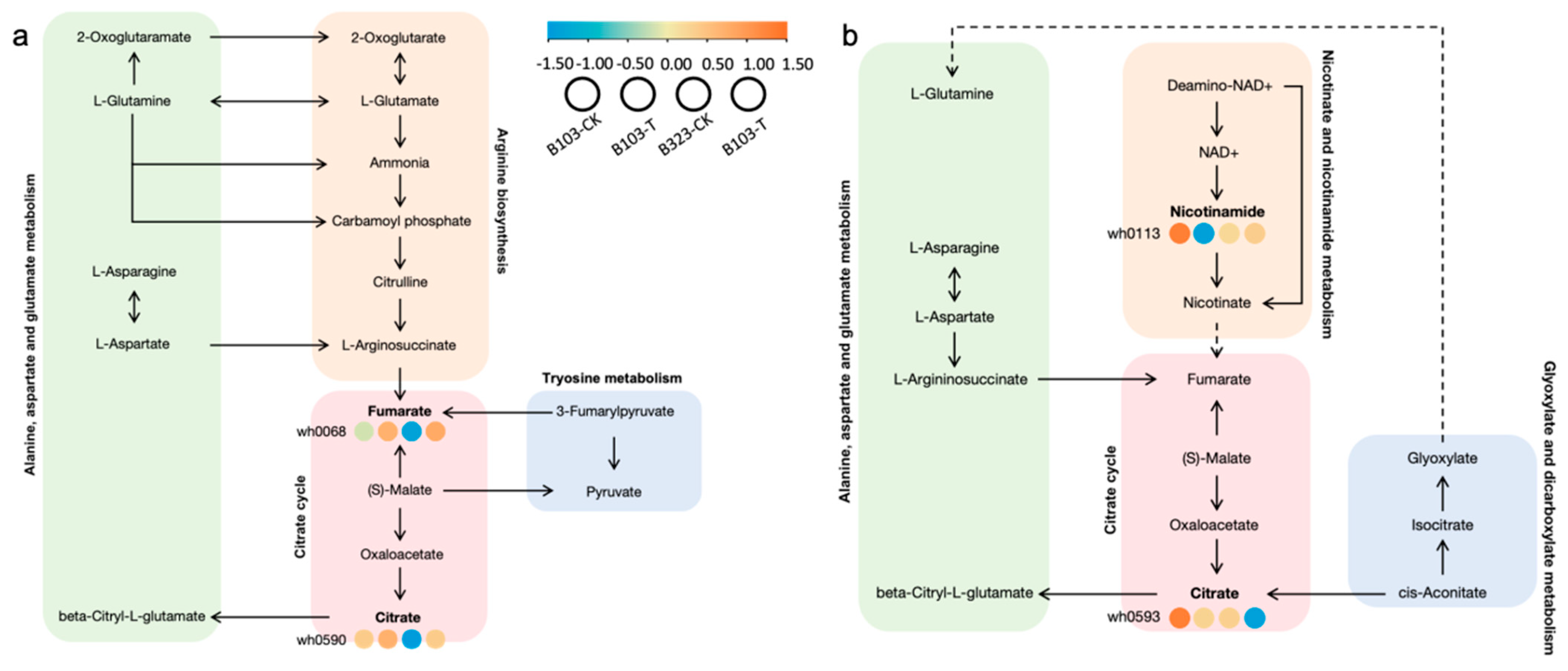
3.2.6. Analysis of Significant Biological Pathway Changes
4. Discussion
4.1. Integrated Multi-Omics Reveals Foxtail Millet’s Saline-Alkali Stress Response
4.2. Regulatory Mechanisms of TF Families in Abiotic Stress Responses
4.3. Nicotinamide Plays a Crucial Role in Saline-Alkali Stress Responses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, P.; Brutnell, T.P. Setaria viridis and Setaria italica, model genetic systems for the Panicoid grasses. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 3031–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthamilarasan, M.; Prasad, M. Advances in Setaria genomics for genetic improvement of cereals and bioenergy grasses. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzigianni, M.; Savvas, D.; Papadopoulou, E.A.; Aliferis, K.A.; Ntatsi, G. Combined Effect of Salt Stress and Nitrogen Level on the Primary Metabolism of Two Contrasting Hydroponically Grown Cichorium spinosum L. Ecotypes. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Li, X.W.; Chen, J.Y.; Yang, Y.L.; Lao, C.C.; Xu, Y.Y. Effects of Different salt contents of undisturbed saline soil on soil moisture characteristic curves. Water Sav. Irrig. 2021, 1, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Li, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Sun, W.; Cao, H.; Xu, R.; Kong, F.; Zhang, D. A novel miR160a-GmARF16-GmMYC2 module determines soybean salt tolerance and adaptation. New Phytol. 2024, 241, 2176–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Yuan, S.; Xie, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, Q.; Shao, M. IAA Plays an Important Role in Alkaline Stress Tolerance by Modulating Root Development and ROS Detoxifying Systems in Rice Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wei, C.; Huang, H.; Kang, J.; Long, R.; Chen, L.; Li, M.; Yang, Q. The GARP family transcription factor MtHHO3 negatively regulates salt tolerance in Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 209, 108542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Jia, Y.; Xu, X.; Fu, P.; Zhou, J.; Yang, G. Structural insights into the Oryza sativa cation transporters HKTs in salt tolerance. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2024, 66, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon, D.I. Copper Enzymes in Isolated Chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1949, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Ultrafast one-pass FASTQ data preprocessing, quality control, and deduplication using fastp. iMeta 2023, 2, e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksander, S.A.; Balhoff, J.; Carbon, S.; Cherry, J.M.; Drabkin, H.J.; Ebert, D.; Feuermann, M.; Gaudet, P.; Harris, N.L.; Hill, D.P.; et al. The Gene Ontology knowledgebase in 2023. Genetics 2023, 224, iyad031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, H.; Goto, S.; Sato, K.; Fujibuchi, W.; Bono, H.; Kanehisa, M. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; EFutschik, M. Mfuzz: A software package for soft clustering of microarray data. Bioinformation 2007, 2, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futschik, M.E.; Carlisle, B. Noise-robust Soft Clustering of Gene Expression Time-course Data. J. Bioinform. Comput. Biol. 2005, 3, 965–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, N.F.C.; Zhou, A.; Li, B.; Markel, K.; Ornelas, I.J.; Shih, P.M. The trans-regulatory landscape of gene networks in plants. Cell Syst. 2023, 14, 501–511.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoi, J.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. AP2/ERF family transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gene Regul. Mech. 2012, 1819, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Pang, S.; Lu, Z.; Jin, B. Function and Mechanism of WRKY Transcription Factors in Abiotic Stress Responses of Plants. Plants 2020, 9, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Niu, Y.; Zheng, Y. Multiple Functions of MYB Transcription Factors in Abiotic Stress Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tang, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, S.; Si, H. Role of bZIP Transcription Factors in Plant Salt Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Takasaki, H.; Mizoi, J.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. NAC transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1819, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Tang, K.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Wu, H.; Mao, Z.; An, S.; Chang, S.; Kuang, T.; Shen, J.; et al. Architecture of the chloroplast PSI-NDH supercomplex in Hordeum vulgare. Nature 2022, 601, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Si, L.; Zhang, L.; Guo, R.; Wang, R.; Dong, H.; Guo, C. Metabolomics and transcriptomics analysis revealed the response mechanism of alfalfa to combined cold and saline-alkali stress. Plant J. 2024, 19, 1900–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zong, Y.; Li, L.; Wu, S.; Duan, M.; Lu, R.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z. Integrated analysis of transcriptome and metabolome reveals molecular mechanisms of salt tolerance in seedlings of upland rice landrace 17SM-19. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 961445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.-Q.; Lin, H.-X. Contribution of phenylpropanoid metabolism to plant development and plant–environment interactions. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 180–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.Q.; Song, M.R.; Guo, Y.N.; Liu, L.F.; Xue, H.; Dai, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.H. MdMYB46 could enhance salt and osmotic stress tolerance in apple by directly activating stress-responsive signals. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 2341–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaiuolo, M.; Cocetta, G.; Ferrante, A. The Antioxidants Changes in Ornamental Flowers during Development and Senescence. Antioxidants 2013, 2, 132–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Ji, J.; Zhao, W.; Guo, W.; Li, J.; Bai, Y.; Wang, D.; Yan, Z.; Guo, C. Flavonol synthase gene MsFLS13 regulates saline-alkali stress tolerance in alfalfa. Crop J. 2023, 11, 1218–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Zhou, J.; Yang, F.; Li, F. Metabolic responses of wheat roots to alkaline stress. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2017, 41, 683–692. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Yang, L.; Li, A.; Guo, J.; Wang, H.; Qi, H.; Li, M.; Yang, P.; Song, S. An AP2/ERF transcription factor confers chilling tolerance in rice. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eado4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Li, C.; Sun, L.; Ma, X.; Qiao, H.; Zhao, W.; Yang, R.; Song, S.; Wang, S.; Huang, H. The SlWRKY57-SlVQ21/SlVQ16 module regulates salt stress in tomato. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2023, 65, 2437–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakabayashi, R.; Yonekura-Sakakibara, K.; Urano, K.; Suzuki, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nishizawa, T.; Matsuda, F.; Kojima, M.; Sakakibara, H.; Shinozaki, K.; et al. Enhancement of oxidative and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis by overaccumulation of antioxidant flavonoids. Plant J. 2014, 77, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Jia, Y.; Ma, Q.; Wang, T.; Xu, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, M.; Song, H.; Cao, S. The transcription factor bZIP44 cooperates with MYB10 and MYB72 to regulate the response of Arabidopsis thaliana to iron deficiency stress. New Phytol. 2024, 242, 2586–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiren, N.V.; Klair, S.; Bansal, S.; Briat, J.F.; Khodr, H.; Shioiri, T.; Leigh, R.A.; Hider, R.C. Nicotianamine chelates both FeIII and FeII. Implications for metal transport in plants. Plant Physiol. 1999, 119, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Pichersky, E. Nicotinamidase participates in the salvage pathway of NAD biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2007, 49, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Mao, S.; Du, K.; Wu, M.; Zhou, X.; Chu, C.; Wang, Y. Comparative proteomiccs analysis of OsNAS1 Transgenic Brassica napus under salt stress. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 2343–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agledal, L.; Niere, M.; Ziegler, M. The phosphate makes a difference: Cellular functions of NADP. Redox Rep. 2010, 15, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Qi, F.; Liang, Y. Fuels for ROS signaling in plant immunity. Trends Plant Sci. 2023, 28, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, T.; Shikanai, T.; Takabayashi, A.; Asada, K.; Sato, F. The role of chloroplastic NAD(P)H dehydrogenase in photoprotection. FEBS Lett. 1999, 457, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, M.; Tan, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Integrative Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Insights Into Saline-Alkali Stress Tolerance in Foxtail Millet. Plants 2025, 14, 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111602
Han M, Tan Q, Yang Y, Zhang H, Wang X, Li X. Integrative Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Insights Into Saline-Alkali Stress Tolerance in Foxtail Millet. Plants. 2025; 14(11):1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111602
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Mengxia, Qing Tan, Yulu Yang, Hui Zhang, Xingchun Wang, and Xukai Li. 2025. "Integrative Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Insights Into Saline-Alkali Stress Tolerance in Foxtail Millet" Plants 14, no. 11: 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111602
APA StyleHan, M., Tan, Q., Yang, Y., Zhang, H., Wang, X., & Li, X. (2025). Integrative Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Insights Into Saline-Alkali Stress Tolerance in Foxtail Millet. Plants, 14(11), 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111602





