Biostimulant Response of Foliar Application of Rare Earth Elements on Physiology, Growth, and Yield of Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Experiment 1
2.1.1. REE Concentrations in Shoots
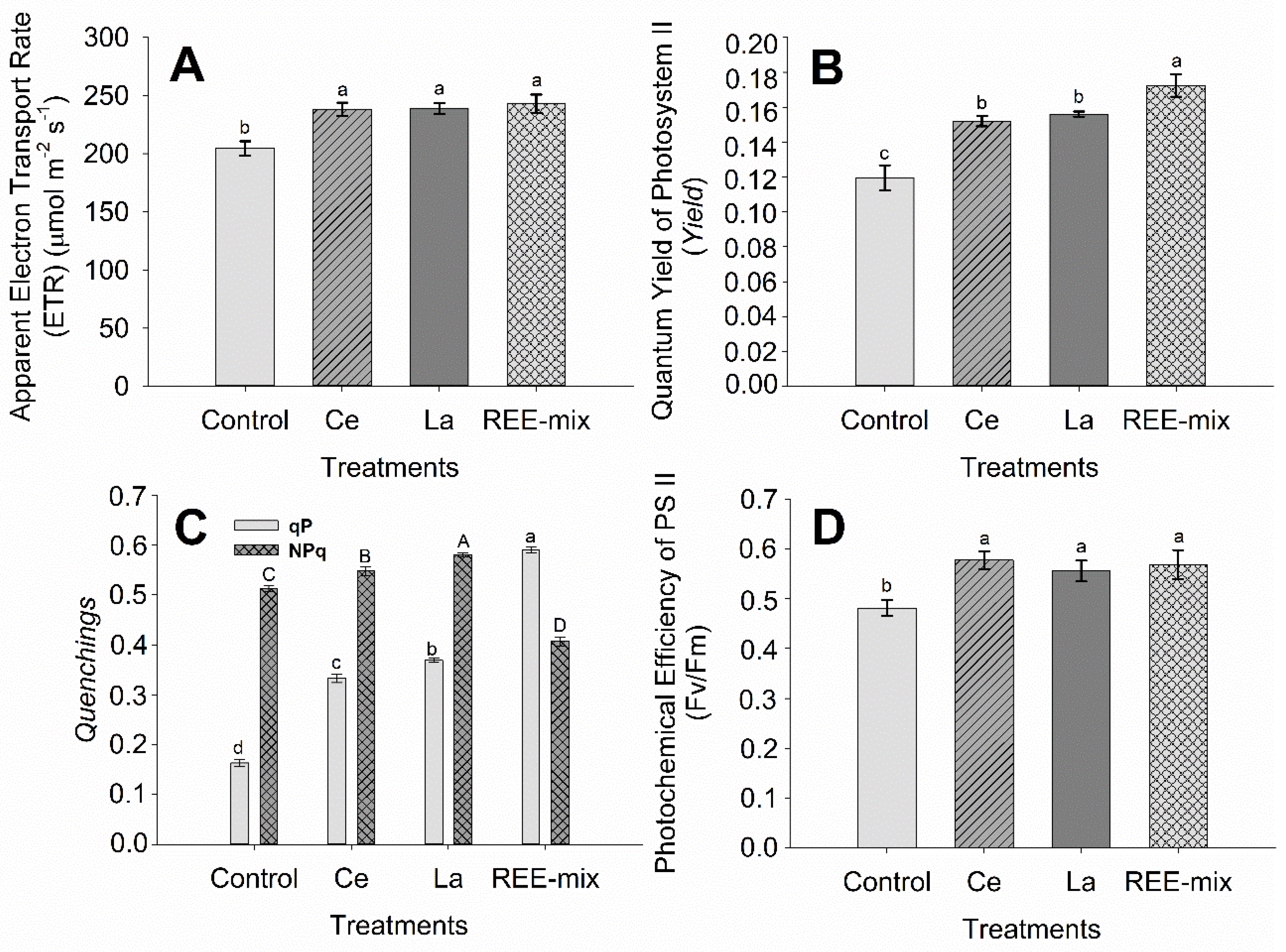
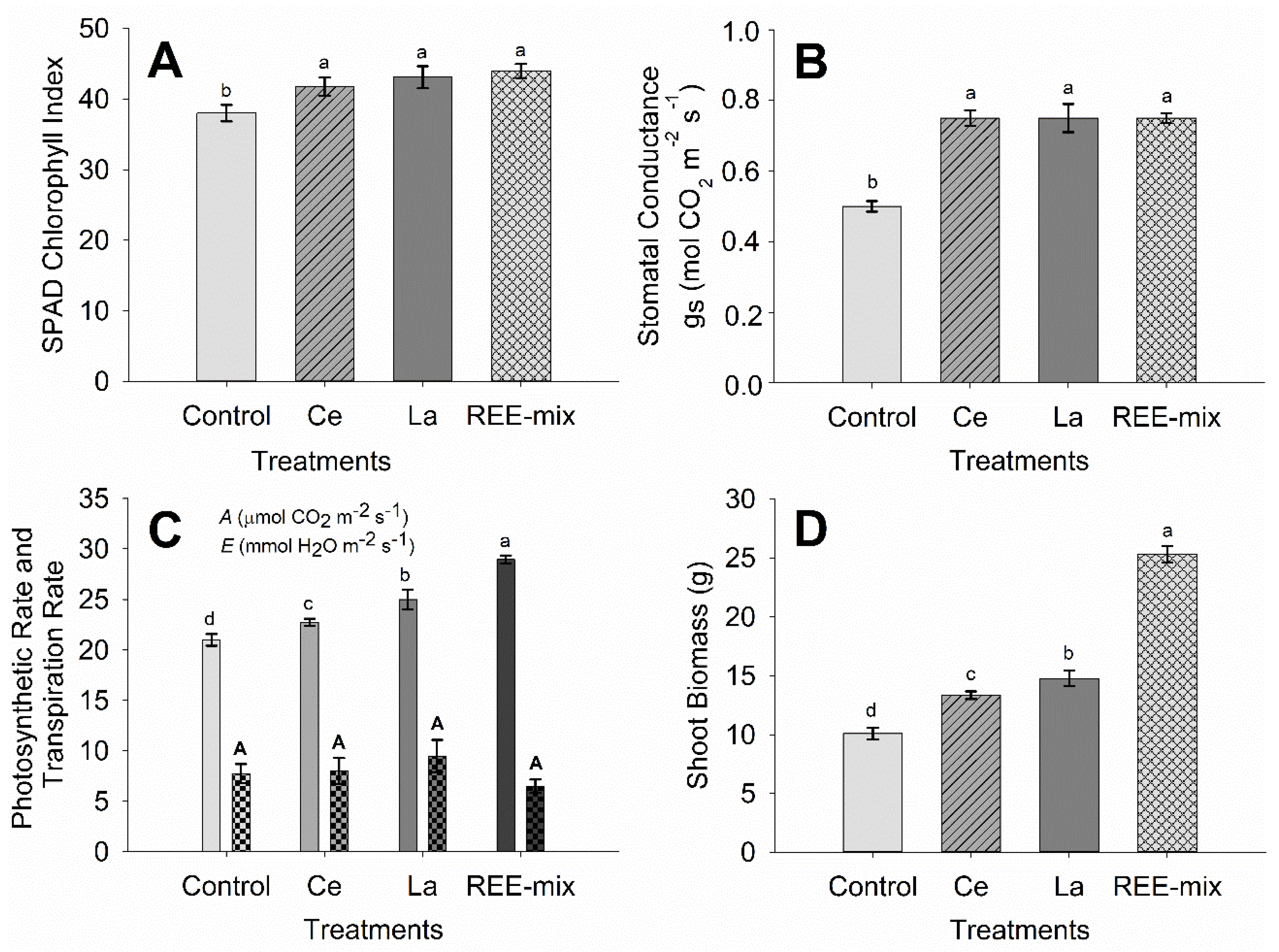
2.1.2. Effect of REE on Characteristics of Fluorescence of Chlorophyll a, SPAD Index, Gas Exchanges, and Growth of Rice Plants
2.2. Experiment 2
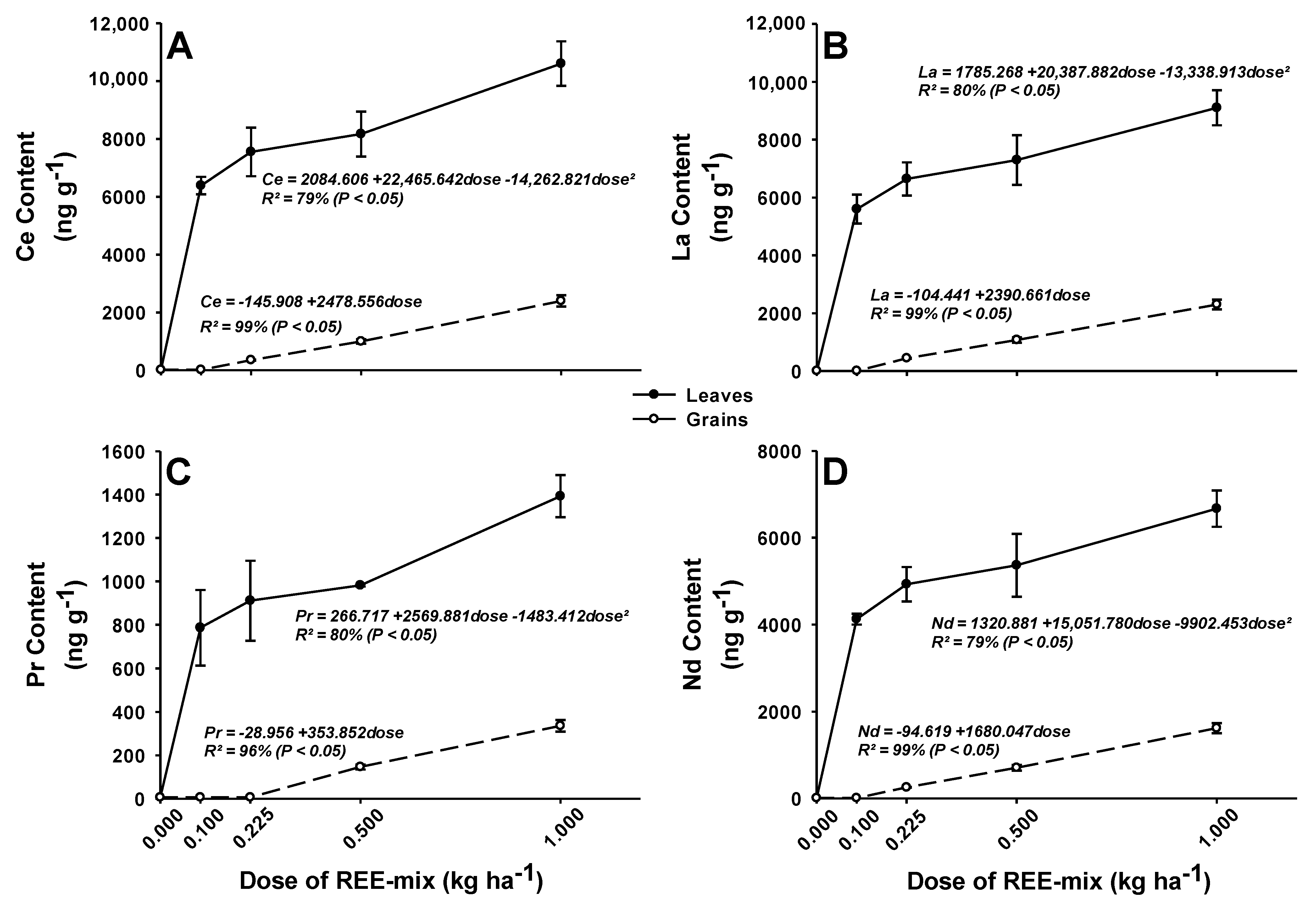
2.2.1. REE Concentrations in Leaves and Grains of Rice Plants
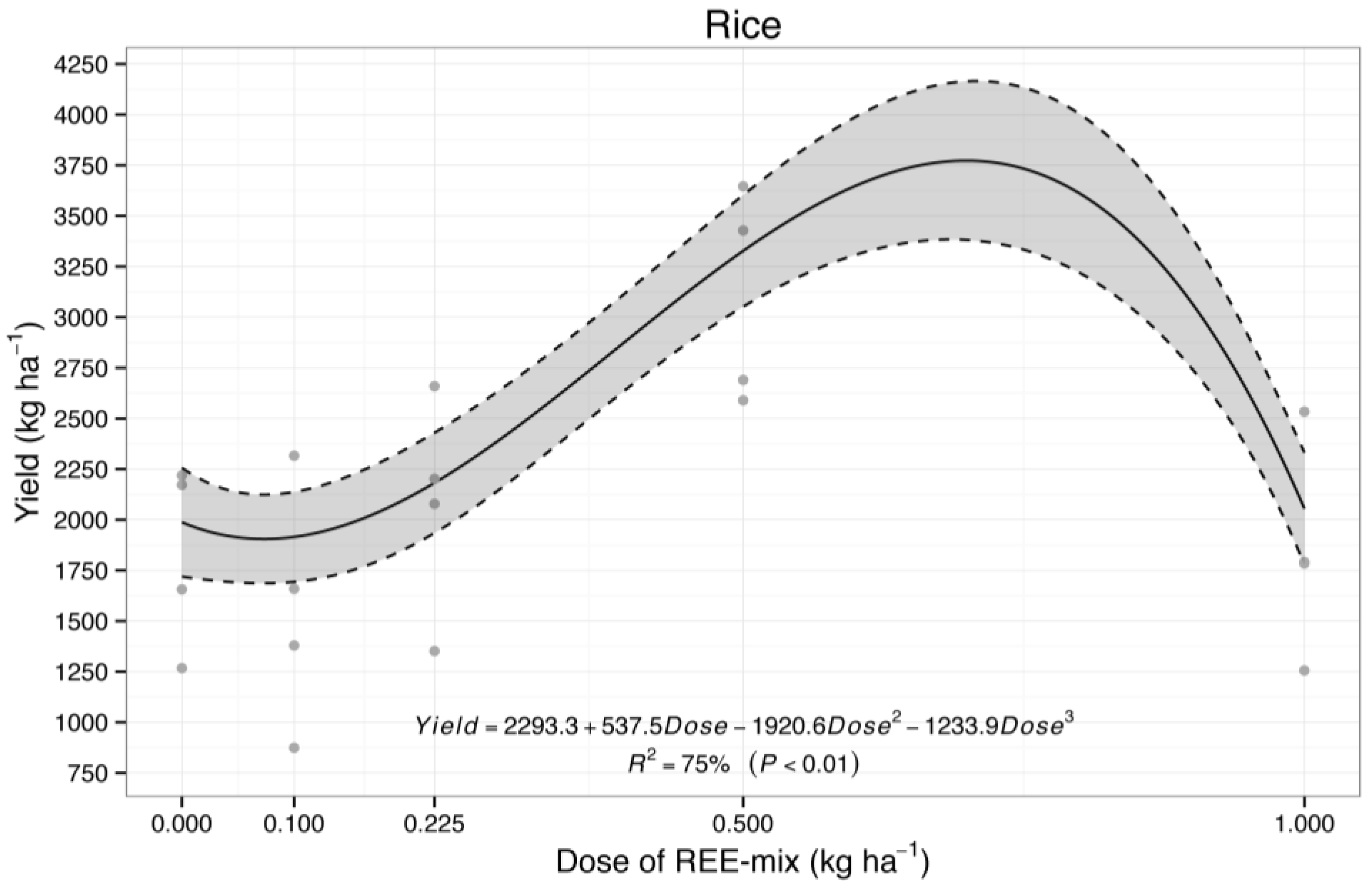
2.2.2. Effect of REE Mix on Rice Grain Yield
2.2.3. Effect of REE Mix on Mineral Rice Nutrition
3. Discussion
3.1. Experiment 1
3.1.1. REE Concentrations in Shoots
3.1.2. Effect of REE on Characteristics of Fluorescence of Chlorophyll a, SPAD Index, Gas Exchanges, and Growth of Rice Plants
3.2. Experiment 2
3.2.1. REE Concentrations in Leaves and Grains of Rice Plants
3.2.2. Effect of REE Mix on Rice Grain Yield
3.2.3. Effect of REE Mix on Mineral Rice Nutrition
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experiment 1—Pot Conditions
4.1.1. Plant Material, Treatments, and Experimental Design
4.1.2. Shoot Biomass and REE Concentrations
4.1.3. Photochemical Characteristics of Photosynthesis
4.1.4. SPAD Index
4.1.5. Gas Exchange Analysis
4.1.6. Statistical Analysis
4.2. Experiment 2—Field Conditions
4.2.1. Plant Material, Treatments, and Experimental Design
4.2.2. REE Concentrations in Shoots and Grains
4.2.3. Grain Yield
4.2.4. Nutrient Concentrations
4.2.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry, IUPAC Recommendations 2005 (The “RedBook”); Connelly, N., Damhus, T., Harshorn, R.M., Eds.; RSC Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Richter, H.; Sparovek, G.; Schnug, E. Physiological and biochemical effects of rare earth elements on plants and their agricultural significance: A review. J. Plant Nutr. 2004, 27, 183–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, G. Rare earth elements in soil and plant systems—A review. Plant Soil. 2004, 267, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, S.J.; Dinali, G.S.; Oliveira, C.; Martins, G.C.; Moreira, C.G.; Siqueira, J.O.; Guilherme, L.R.G. Rare earth elements in the soil environment. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2016, 2, 28–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.S. The application of rare earth elements on agriculture and breeding. Chin. Rare Earths 1993, 15, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Redling, K. Rare Earth Elements in Agriculture with Emphasis on Animal Husbandry. Ph.D. Thesis, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, München, Germany, 2006; p. 360. [Google Scholar]
- Turra, C. Sustainability of rare earth elements chain: From production to food—A review. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2018, 28, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tommasi, F.; Thomas, P.J.; Lyons, D.M.; Pagano, G.; Oral, R.; Siciliano, A.; Toscanesi, M.; Guida, M.; Trifuoggi, M. Evaluation of rare earth element-associated hormetic effects in candidate fertilizers and livestock feed additives. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 2573–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.K. Application of rare earths in Chinese agriculture and their perspectives of development. In Proceedings of the Rare Earths in Agriculture Seminar 20, Canberra, ACT, Australia, 15–17 September 1995; pp. 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Q.; Tian, J.; Peng, H.; Zhang, X.; Lee, D.; Woo, C.; Ryu, J.; Park, C. The effects of rare earth on increasing yield, improving quality and reducing agricultural chemical remained in crop production. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on Trace Elements and Food Chain, Wuhan, China, 12–15 November 1998; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- El-Ramady, H.R.H. Ecotoxicology of Rare Earth Elements: Ecotoxicology of Rare Earth Elements within Soil and Plant Environments; Institut für Pflanzenbau und Bodenkunde, Julius Kühn-Institut, Bundesforschungsinstitut für Kulturpflanzen: Quedlinburg, Germany, 2010; p. 278. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez-Olvera, S.M.; Trejo-Téllez, L.I.; García-Morales, S.; Pérez-Sato, A.; Gómez-Merino, F.C. Cerium enhances germination and shoot growth, and alters mineral nutrient concentration in rice. PLoS ONE 2018, 26, e0194691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X. A novel evaluation of the effect of lanthanum exposure on plant populations. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 377–386; [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhang, C.; Shi, C.; Wang, J.; Sun, G.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, F.Z.; Wang, X. Bioaccumulation, subcellular distribution and chemical forms of yttrium in rice seedling. J. Rare Earths 2018, 36, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Shen, L.; Feng, C.; Yang, R.; Qu, J.; Ju, H.; Zhang, Y. Distribution of rare earth elements (REEs) and their roles in plant growth: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 298, 118540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathokleous, E.; Kitao, M.; Calabrese, E.J. Hormetic dose responses induced by lanthanum in plants. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Z. Effects of lanthanum on growth and accumulation in roots of rice seedlings. Plant Soil Environ. 2013, 59, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukagawa, N.K.; Ziska, L.H. Rice: Importance for global nutrition. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2019, 65, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skovran, E.; Martinez-Gomez, N.C. Just add lanthanides. Science 2015, 348, 862–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, C.G.; de Carvalho, T.S.; de Oliveira, C.; de Abreu, L.B.; de Castro, A.C.S.; Ribeiro, P.G.; Bispo, F.H.A.; Boutin, C.; Guilherme, L.R.G. Ecological risk assessment of cerium for tropical agroecosystems. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, D.N.; Silva, S.R.; Marinho, J.D.; Bazzo, J.H.B.; Fonseca, I.C.D.; Zucareli, C. Wheat yield and seed physiological quality as influenced by seed vigor, nitrogen fertilization and edaphoclimatic conditions. Semin.—Ciências Agrárias 2021, 42, 3581–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Shan, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, S. Evaluation of plant availability of rare earth elements in soils by chemical fractionation and multiple regression analysis. Environ. Pollut. 1998, 102, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y. Study on the contents of trace rare earth elements and their distribution in wheat and rice samples by RNA. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1994, 179, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.M.; Zhang, J.H. Modifications in photosystem II photochemistry in senescent leaves of maize plants. J. Exp. Bot. 1998, 49, 1671–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; He, E.; Qiu, H.; Li, J.; Ji, J.; Zhao, L.; Cao, X. Phytotoxicity of individual and binary mixtures of rare earth elements (Y, La, and Ce) in relation to bioavailability. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp, F.N.; Arikan, B.; Ozfidan-Konakci, C.; Ekim, R.; Yildiztugay, E.; Turan, M. Rare earth element scandium mitigates the chromium toxicity in Lemna minor by regulating photosynthetic performance, hormonal balance and antioxidant machinery. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikanai, T.; Munekage, Y.; Kimura, K. Regulation of proton-to-electron stoichiometry in photosynthetic electron transport: Physiological function in photoprotection. J. Plant Res. 2002, 115, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Wan, P.Y.; Sun, L.G.; Zhang, J.J.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.W.; Chen, G.X. Alleviation of cadmium toxicity by cerium in rice seedlings is related to improved photosynthesis, elevated antioxidant enzymes and decreased oxidative stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2014, 74, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zou, H.; Gu, H.; Shi, D.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Y. Stimulatory effect of lanthanum nitrate on the root tuber yield of Pseudostellaria heterophylla via improved photosynthetic characteristics. J. Rare Earths 2017, 35, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-F.; Ji, H.-B.; Tian, W.-M. Photosystem 2 photochemistry and pigment composition of Dicranopteris dichotoma Bernh under different irradiances. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 13453–13460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Hu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X. Effects of rare earth and acid rain pollution on plant chloroplast ATP synthase and element contents at different growth stages. Chemosphere 2018, 194, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafpour, M.M.; Remger, G.; Holýnska, M.; Moghaddam, A.N.; Aro, E.; Carpentier, R.; Nishhara, H.; Eaton-Rye, J.J.; Shen, J.; Allakhverdiev, S.I. Manganese compounds as water-oxidizing catalysts: From the natural water-oxidizing complex to nanosized manganese oxide structures. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2886−2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fa-Shui, H.; Ling, W.; Ye, T. Mechanism of LaCl3 on increasing photosystem II activity of spinach. Chin. J. Chem. 2005, 23, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Gong, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Hong, M.; Wang, L.; Hong, F. Improvement of cerium of photosynthesis functions of maize under magnesium deficiency. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 142, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Luo, X.; Tian, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Tian, L.; Wang, X. Biphasic effects of lanthanum on Vicia faba L. seedlings under cadmium stress, implicating finite antioxidation and potential ecological risk. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.G. Ecotoxicological Risk of Cerium for Tropical Soils. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal de Lavras, Lavras, Brazil, 2019; p. 114. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X. Combined effects of lanthanum (III) chloride and acid rain on photosynthetic parameters in rice. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maksimović, I.; Kastori, R.; Putnik-Delić, M.; Borišev, M. Effect of yttrium on photosynthesis and water relations in young maize plants. J. Rare Earths 2014, 32, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, O.G.G.; Teodoro, J.C.; Alvarenga, J.P.; de Oliveira, C.; de Carvalho, T.S.; Domiciano, D.; Marchiori, P.E.R.; Guilherme, L.R.G. Cerium alleviates drought-induced stress in Phaseolus vulgaris. J. Rare Earths 2020, 38, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.; Ramos, S.J.; Siqueira, J.O.; Faquin, V.; Castro, E.M.; Amaral, D.C.; Techio, V.H.; Coelho, L.C.; Silva, P.H.P.; Schnug, E.; et al. Bioaccumulation and effects of lanthanum on growth and mitotic index in soybean plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ding, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Dai, L. Bioaccumulation of lanthanum and cerium and their effects on the growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedlings. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Zhao, R.; Zhao, W.; Fu, R.; Guo, J.; Bi, N.; Zhang, J. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on maize (Zea mays L.) and sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) grown in rare earth elements of mine tailings. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2013, 72, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtangeeva, I.; Ayrault, S. Effects of Eu and Ca on yield and mineral nutrition of wheat (Triticum aestivum) seedlings. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 59, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtangeeva, I. Europium and cerium accumulation in wheat and rye seedlings. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 1964–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; He, J.Y. The inhibitory effect of Ca2+ on the flavonoid production of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum suspension cells induced by metal elicitors. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2013, 49, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q. Technologies and effect of REEs enriched La on rice. Chin. Rare Earths 2014, 16, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.B.; Zhu, J.G.; Chu, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zeng, Q.; Ma, H.L.; Cao, Z.H. Effect of lanthanum on rice production, nutrient uptake, and distribution. J. Plant Nutr. 2022, 25, 2315–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Cai, X.; Liu, W.; Tao, G.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Q. Effects of lanthanum nitrate on growth and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of Alternanthera philoxeroides under perchlorate stress. J. Rare Earths 2013, 31, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, H.; Wang, L. The effects of cerium on the growth and some antioxidant metabolisms in rice seedlings. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 3282–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, P.G.; Dinali, G.S.; Boldrin, P.; Carvalho, T.S.; de Oliveira, C.; Ramos, S.J.; Siqueira, J.O.; Moreira, C.G.; Guilherme, L.R.G. Rare Earth Elements (REEs) rich-phosphate fertilizers used in Brazil are more effective in increasing legume crops yield than their rees-poor counterparts. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2021, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathokleous, E.; Zhou, B.; Geng, C.; Xu, J.; Saitanis, C.; Feng, Z.; Tack, F.M.G.; Rinklebe, J. Mechanisms of cerium-induced stress in plants: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, A. Photosynthesis, grain yield, and nitrogen utilization in rice and wheat. Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miziorko, H.M.; Lorimer, G.H. Ribulose-l,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1983, 52, 507–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamoi, M.; Nagaoka, M.; Miyagawa, Y.; Shigeoka, S. Contribution of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and sedoheptulose-1,7- bisphosphatase to the photosynthetic rate and carbon flow in the Calvin cycle in transgenic plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006, 47, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komeili, A.; Wedaman, K.; O’Shea, E.K.; Powers, T. Mechanism of metabolic control: Target of rapamycin signaling links nitrogen quality to the activity of the Rtg1 and Rtg3 transcription factors. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 151, 863–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diatloff, E.; Asher, C.J.; Smith, F.W. The effects of rare earth elements on the growth and nutrition of plants. Mater. Sci. Forum 1999, 315–317, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diatloff, E.; Smith, F.W.; Asher, C.J. Effects of lanthanum and cerium on the growth and mineral nutrition of corn and mungbean. Ann. Bot. 2008, 101, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.Z.; Zhou, X.B.; Mohamed, O.M. Mechanism of application of Nd to increase yield of rapeseed. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 1999, 5, 186–188. [Google Scholar]
- Jie, H.G.; Yu, Z.H. Effects of REEs on increasing yield and physiology of wheat. J. Heilongjiang Agric. Sci. 1985, 1, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, D.A.C. Mineral sources of potassium for plant nutrition: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saa, S.; Olivos-Del Rio, A.; Castro, S.; Brown, P.H. Foliar application of microbial and plant based biostimulants increases growth and potassium uptake in almond (Prunus dulcis [Mill.] D. A. Webb). Front Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Verweij, R.A.; van Gestel, C.A.M. Lanthanum toxicity to five different species of soil invertebrates in relation to availability in soil. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BRASIL—EMBRAPA: Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária. Cultivar BRSMG Caçula; EMBRABA: Brasília, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária (EMBRAPA). Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos, 3rd ed.; Embrapa Solos: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Survey Staff. Soil Taxonomy: A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making and Interpreting Soil Surveys, 2nd ed.; Natural Resources Conservation Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture Handbook: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; p. 436.
- Malavolta, E.; Vitti, G.C.; Oliveira, A.S. Avaliação do Estado Nutricional das Plantas: Princípios e Aplicações, 2nd ed.; Associação Brasileira para Pesquisa da Potassa e do Fosfato: Piracicaba, Brazil, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, B.; Yuan, D.; Shan, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, S. The influence of rare earth element fertilizer application on the distribution and bioaccumulation of rare earth elements in plants under field conditions. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2001, 13, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Method 3051 A: Microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludges, soils and oils. In SW__84: Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, Physical and Chemical Methods; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, D.F. Sisvar: A computer statistical analysis system. Ciênc. Agrotecnol. 2001, 35, 1039–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.M.; Keeney, D.R. Steam distillation methods for determination of ammonium, nitrate and nitrite. Anal. Cmim. Acta 1965, 32, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
| Treatments | Rare Earth Element | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ce | La | Pr | Nd | |
| ng g−1 | ||||
| Control | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Ce | 588.75 ± 48.83 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| La | n.d. | 593.30 ± 30.57 | n.d. | n.d. |
| REE mix | 579.25 ± 15.92 | 616.65 ± 64.58 | 137.38 ± 10.37 | 378.44 ± 95.90 |
| Nutrients | Nutrient Concentration in Leaves for Each REE Mix Treatment (kg ha−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.1 | 0.225 | 0.5 | 1.0 | |
| N (g kg−1 DW) | 8.70 ± 0.3606 b | 9.50 ± 0.2784 b | 9.10 ± 0.3122 b | 11.03 ± 0.4537 a | 8.93 ± 0.2466 b |
| P (g kg−1 DW) | 0.60 ± 0.0132 a | 0.56 ± 0.0076 a | 0.57 ± 0.0076 a | 0.62 ± 0.0161 a | 0.58 ± 0.0132 a |
| K (g kg−1 DW) | 14.15 ± 0.4479 b | 16.02 ± 0.3184 b | 17.09 ± 0.6769 b | 19.48 ± 0.2952 a | 15.75 ± 0.7970 b |
| Ca (g kg−1 DW) | 3.63 ± 0.1351 a | 3.35 ± 0.0828 a | 3.94 ± 0.0835 a | 3.93 ± 0.2105 a | 3.32 ± 0.1583 a |
| Mg (g kg−1 DW) | 1.92 ± 0.0633 b | 1.82 ± 0.1037 b | 2.41 ± 0.1678 a | 2.61 ± 0.1477 a | 1.85 ± 0.1675 b |
| S (g kg−1 DW) | 1.50 ± 0.0050 a | 1.48 ± 0.0126 a | 1.60 ± 0.0562 a | 1.56 ± 0.0058 a | 1.49 ± 0.0229 a |
| B (mg kg−1 DW) | 6. 63 ± 0.4381 b | 7.59 ± 0. 0000 a | 7.59 ± 0.0000 a | 5.87 ± 0.2850 b | 6.82 ± 0.3320 b |
| Cu (mg kg−1 DW) | 5.51 ± 0.8101 a | 5.33 ± 0.0650 a | 4.91 ± 0.3219 a | 7.50 ± 0.6283 a | 5.94 ± 0.2291 a |
| Fe (mg kg−1 DW) | 607.95 ± 128.1468 a | 394.81 ± 58.3299 a | 298.48 ± 46.5421 a | 250.89 ± 33.7862 a | 486.72 ± 102.9976 a |
| Mn (mg kg−1 DW) | 314.81 ± 7.7011 b | 432.04 ± 18.5765 a | 362.08 ± 17.7165 b | 578.99 ± 39.7377 a | 375.66 ± 33.0049 a |
| Zn (mg kg−1 DW) | 41.87 ± 6.3462 a | 53.56 ± 3.1036 a | 54.59 ± 3.0711 a | 61.33 ± 2.4874 a | 42.97 ± 7.0213 a |
| Nutrients | Nutrient Concentration in Grains for Each REE Mix Treatment (kg ha−1) | ||||
| 0 | 0.1 | 0.225 | 0.5 | 1.0 | |
| N (g kg−1 DW) | 16.73 ± 0.3547 a | 16.23 ± 0.2754 a | 15.17 ± 0.3253 a | 16.30 ± 0.3122 a | 16.17 ± 0.3055 a |
| P (g kg−1 DW) | 2.94 ± 0.1207 a | 2.67 ± 0.1156 a | 2.50 ± 0.0501 a | 2.45 ± 0.0076 a | 2. 68 ± 0.0690 a |
| K (g kg−1 DW) | 3.37 ± 0.2599 a | 2.54 ± 0.0247 b | 3.25 ± 0.0861 a | 2.68 ± 0.1147 b | 2.47 ± 0.1476 b |
| Ca (g kg−1 DW) | 0.62 ± 0.0568 a | 0.51 ± 0.0328 a | 0.61 ± 0.0132 a | 0.52 ± 0.0577 a | 0.56 ± 0.1660 a |
| Mg (g kg−1 DW) | 1.35 ± 0.0551 a | 1.20 ± 0.0563 a | 1.15 ± 0.016 a | 1.12 ± 0.369 a | 1.13 ± 0.0723 a |
| S (g kg−1 DW) | 1.22 ± 0.0029 a | 1.20 ± 0.0275 a | 1.19 ± 0.0132 a | 1.21 ± 0.0275 a | 1.25 ± 0.0050 a |
| B (mg kg−1 DW) | 2.71 ± 0.0000 b | 1.25 ± 0.1559 d | 3.64 ± 0.1617 a | 3.08 ± 0.1617 b | 2.16 ± 0.0000 c |
| Cu (mg kg−1 DW) | 5.71 ± 0.0247 a | 5.79 ± 0.2499 a | 5.82 ± 0.1291 a | 5.38 ± 0.1239 a | 5.51 ± 0.0321 a |
| Fe (mg kg−1 DW) | 763.95 ± 147.1187 b | 173.68 ± 29.4010 b | 1594.70 ± 385.5715 a | 158.23 ± 8.4310 b | 111.53 ± 24.8830 b |
| Mn (mg kg−1 DW) | 139.20 ± 7.0452 a | 115.19 ± 4.6474 b | 113.78 ± 5.3530 b | 99.32 ± 4.4464 c | 78.22 ± 9.5380 c |
| Zn (mg kg−1 DW) | 36.36 ± 0.2397 a | 33.71 ± 0.2757 a | 34.68 ± 0.7671 a | 36.04 ± 1.5273 a | 33.95 ± 0.2875 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Oliveira, C.; Ramos, S.J.; Dinali, G.S.; de Carvalho, T.S.; Martins, F.A.D.; Faquin, V.; Castro, E.M.d.; Sarkis, J.E.S.; Siqueira, J.O.; Guilherme, L.R.G. Biostimulant Response of Foliar Application of Rare Earth Elements on Physiology, Growth, and Yield of Rice. Plants 2024, 13, 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13111435
de Oliveira C, Ramos SJ, Dinali GS, de Carvalho TS, Martins FAD, Faquin V, Castro EMd, Sarkis JES, Siqueira JO, Guilherme LRG. Biostimulant Response of Foliar Application of Rare Earth Elements on Physiology, Growth, and Yield of Rice. Plants. 2024; 13(11):1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13111435
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Oliveira, Cynthia, Silvio Junio Ramos, Guilherme Soares Dinali, Teotonio Soares de Carvalho, Fábio Aurélio Dias Martins, Valdemar Faquin, Evaristo Mauro de Castro, Jorge Eduardo Souza Sarkis, José Oswaldo Siqueira, and Luiz Roberto Guimarães Guilherme. 2024. "Biostimulant Response of Foliar Application of Rare Earth Elements on Physiology, Growth, and Yield of Rice" Plants 13, no. 11: 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13111435
APA Stylede Oliveira, C., Ramos, S. J., Dinali, G. S., de Carvalho, T. S., Martins, F. A. D., Faquin, V., Castro, E. M. d., Sarkis, J. E. S., Siqueira, J. O., & Guilherme, L. R. G. (2024). Biostimulant Response of Foliar Application of Rare Earth Elements on Physiology, Growth, and Yield of Rice. Plants, 13(11), 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13111435









