Plants and Phytoplasmas: When Bacteria Modify Plants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Phytoplasma Discovery
3. Phytoplasma Classification
4. Relationship between Phytoplasma Symptomatology and Classification
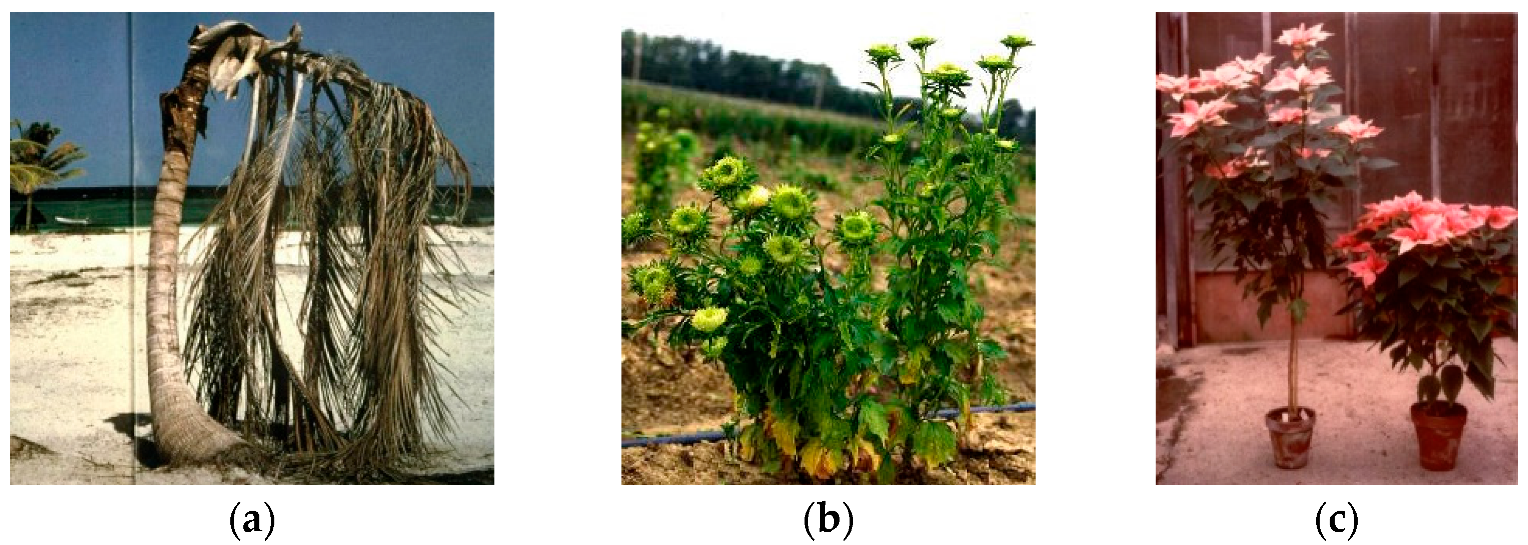
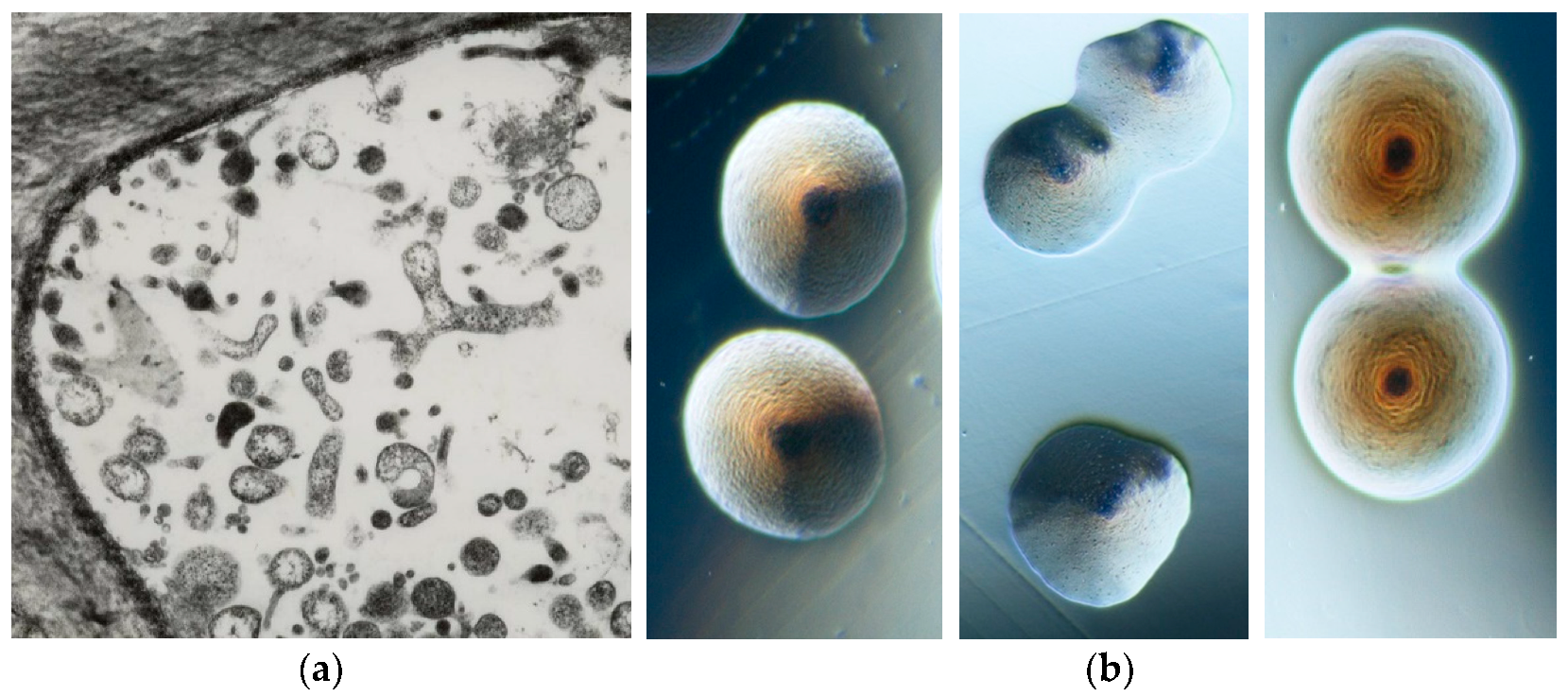
4.1. Shoot Proliferation and Witches’ Broom
4.2. Stunting and Little Leaf
4.3. Phyllody and Virescence
4.4. Yellowing and Decline
4.5. White Leaf
4.6. Purple Top and Other Malformations
5. Phytoplasma Genomics
6. Mechanisms to Infect Plants and Insects
7. Genetic Factors Determining Symptom Development
8. Management
9. Concluding Remarks
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCann, H.C.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Pan, H.; Zhong, C.; Rikkerink, E.; Templeton, M.D.; Straub, C.; Colombi, E.; et al. Origin and evolution of the kiwifruit canker pandemic. Gen. Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bové, J.-M. Huanglongbing: A destructive, newly-emerging, century-old disease of citrus. J. Plant Pathol. 2006, 88, 7–37. [Google Scholar]
- IRPCM. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma’, a taxon for the wall-less, non-helical prokaryotes that colonise plant phloem and insects. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bertaccini, A.; Arocha-Rosete, Y.; Contaldo, N.; Duduk, B.; Fiore, N.; Montano, H.G.; Kube, M.; Kuo, C.-H.; Martini, M.; Oshima, K.; et al. Revision of the ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma’ species description guidelines. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 74, 005353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namba, S. Molecular and biological properties of phytoplasmas. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2019, 95, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doi, Y.; Teranaka, M.; Yora, K.; Asuyama, H. Mycoplasma or PLT grouplike microrganisms found in the phloem elements of plants infected with mulberry dwarf, potato witches’ broom, aster yellows or pawlownia witches’ broom. Ann. Phytopath. Soc. Jpn. 1967, 33, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contaldo, N.; Bertaccini, A.; Paltrinieri, S.; Windsor, H.M.; Windsor, G.D. Axenic culture of plant pathogenic phytoplasmas. Phytopath. Medit. 2012, 51, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contaldo, N.; Satta, E.; Zambon, Y.; Paltrinieri, S.; Bertaccini, A. Development and evaluation of different complex media for phytoplasma isolation and growth. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2016, 127, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contaldo, N.; D’Amico, G.; Paltrinieri, S.; Diallo, H.A.; Bertaccini, A.; Arocha Rosete, Y. Molecular and biological characterization of phytoplasmas from coconut palms affected by the lethal yellowing disease in Africa. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 223-225, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis Pantoja, M.; Paredes-Tomás, C.; Uneau, Y.; Myrie, W.; Morillon, R.; Satta, E.; Contaldo, N.; Pacini, F.; Bertaccini, A. Identification of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma’ species in “huanglongbing” infected citrus orchards in the Caribbean. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2021, 160, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt, C.; Pardo, J.; Muñoz, J.; Alvarez, E. Isolation of phytoplasmas associated to frogskin disease in cassava. Rev. UDCA Actual. Divulg. Cient. 2019, 22, e1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, I.-M.; Gundersen-Rindal, D.E.; Davis, R.E.; Bartoszyk, I.M. Revised classification scheme of phytoplasmas based on RFLP analyses of 16S rRNA and ribosomal protein gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1998, 48, 1153–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, X.; Zhang, J.; Ewing, A.; Miller, S.A.; Radek, A.J.; Shevchenko, D.V.; Tsukerman, K.; Walunas, T.; Lapidus, A.; Campbell, J.W.; et al. Living with genome instability: The adaptation of phytoplasmas to diverse environments of their insect and plant hosts. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 3682–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, I.-M.; Gundersen-Rindal, D.E.; Davis, R.E.; Bottner, K.D.; Marcone, C.; Seeműller, E. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma asteris’, a novel taxon associated with aster yellows and related diseases. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jomantiene, R.; Davis, R.E.; Maas, J.; Dally, E.L. Classification of new phytoplasmas associated with diseases of strawberry in Florida, based on analysis of 16S rRNA and ribosomal protein gene operon sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1998, 48, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arocha-Rosete, Y.; Zunnoon-Khan, S.; Krukovets, I.; Crosby, W.; Scott, J.; Bertaccini, A.; Michelutti, R. Identification and molecular characterization of the phytoplasma associated with peach rosette-like disease at the Canadian clonal Genebank based on the 16S rRNA gene analysis. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2011, 33, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundersen, D.E.; Lee, I.-M.; Rehner, S.A.; Davis, R.E.; Kingsbury, D.T. Phylogeny of mycoplasmalike organisms (phytoplasmas): A basis for their classification. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 5244–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zreik, L.; Carle, P.; Bové, J.-M.; Garnier, M. Characterization of the mycoplasmalike organism associated with witches’ broom disease of lime and proposition of a ‘Candidatus’ taxon for the organism, ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma aurantifolia’. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1995, 45, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Wei, W.; Davis, R.E.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y. Genetic diversity among phytoplasmas infecting Opuntia species: Virtual RFLP analysis identifies new subgroups in the peanut witches’ broom phytoplasma group. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 1448–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mafia, R.G.; Barreto, R.W.; Vanetti, C.A.; Hodgetts, J.; Dickinson, M.; Alfenas, A.C. A phytoplasma is associated with witches’ broom disease of Tabebuia pentaphylla in Brazil. New Dis. Rep. 2007, 15, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-López, E.; Luna-Rodríguez, M.; Olivier, C.Y.; Dumonceaux, T.J. The underestimated diversity of phytoplasmas in Latin America. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 492–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.E.; Zhao, Y.; Dally, E.L.; Lee, I.-M.; Jomantiene, R.; Douglas, S. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma pruni’, a novel taxon associated with X-disease of stone fruits, Prunus spp.: Multilocus characterization based on 16S rRNA, secY, and ribosomal protein genes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montano, H.G.; Davis, R.E.; Dally, E.L.; Pimentel, J.P.; Brioso, P.S.T. Identification and phylogenetic analysis of a new phytoplasma from diseased chayote in Brazil. Plant Dis. 2000, 84, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, R.E.; Dally, E.L.; Converse, R.H. Molecular identification of a phytoplasma associated with witches’-broom disease of black raspberry in Oregon and its classification in group 16SrIII, new subgroup Q. Plant Dis. 2001, 85, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galdeano, E.; Guzmán, F.A.; Fernández, F.; Conci, R.G. Genetic diversity of 16SrIII group phytoplasmas in Argentina. Predominance of subgroups 16SrIII-J and B and two new subgroups 16SrIII-W and X. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2013, 137, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-Y.; Sawayanagi, T.; Kakizawa, S.; Nishigawa, H.; Wei, W.; Oshima, K.; Miyata, S.; Ugaki, M.; Hibi, T.; Namba, S. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma ziziphi’, a novel phytoplasma taxon associated with jujube witches’ broom disease. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Win, N.K.K.; Lee, S.-Y.; Bertaccini, A.; Namba, S.; Jung, H.-Y. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma balanitae’ associated with witches’ broom disease of Balanites triflora. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, F.; Song, C.S.; Ren, Z.G.; Lin, C.L.; Xu, Q.C.; Li, Y.; Piao, C.G.; Yu, S.S.; Guo, M.W.; Tian, G.Z. Molecular characterization of a new member of the 16SrV group of phytoplasma associated with Bischofia polycarpa (Levl.) Airy Shaw witches’ broom disease in China by a multiple gene-based analysis. Austral. Plant Pathol. 2014, 43, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fránová, J.; de Sousa, E.; Mimoso, C.; Cardoso, F.; Contaldo, N.; Paltrinieri, S.; Bertaccini, A. Multigene characterization of a new ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma rubi’-related strain associated with blackberry witches’ broom in Portugal. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1438–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hiruki, C.; Wang, K. Clover proliferation phytoplasma: ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma trifolii’. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1349–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barros, T.S.L.; Davis, R.E.; Resende, R.O.; Dally, E.L. Erigeron witches’ broom phytoplasma in Brazil represents new subgroup VII-B in 16S rRNA gene group VII, the ash yellows phytoplasma group. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conci, L.; Meneguzzi, N.; Galdeano, E.; Torres, L.; Nome, C.; Nome, S. Detection and molecular characterisation of an alfalfa phytoplasma in Argentina that represents a new subgroup in the 16S rDNA ash yellows group (‘Candidatus Phytoplasma fraxini’). Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2005, 113, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flôres, D.; Amaral Mello, A.O.; Pereira, T.B.C.; Rezende, J.A.M.; Bedendo, I.P. A novel subgroup 16SrVII-D phytoplasma identified in association with erigeron witches’ broom. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 2761–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.E.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, W.; Dally, E.L.; Lee, I.-M. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma luffae’, a novel taxon associated with witches’ broom disease of loofah, Luffa aegyptica Mill. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 3127–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundersen, D.E.; Lee, I.-M.; Schaff, D.A.; Harrison, N.A.; Chang, C.J.; Davis, R.E.; Kinsbury, D.T. Genomic diversity among phytoplasma strains in 16S rRNA group I (aster yellows and related phytoplasmas) and III (X-disease and related phytoplasmas). Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1996, 46, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdin, E.; Salar, P.; Danet, J.-L.; Choueiri, E.; Jreijiri, F.; El Zammar, S.; Gélie, B.; Bové, J.-M.; Garnier, M. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma phoenicium’ sp. nov., a novel phytoplasma associated with an emerging lethal disease of almond trees in Lebanon and Iran. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, R.E.; Dally, E.; Zhao, Y.; Lee, I.-M.; Jomantiene, R.; Detweiler, A.J.; Putnam, M.L. First report of a new subgroup 16SrIX-E (‘Candidatus Phytoplasma phoenicium’-related) phytoplasma associated with juniper witches’ broom disease in Oregon, USA. Plant Pathol. 2010, 59, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino Lova, M.; Quaglino, F.; Abou-Jawdah, Y.; Choueiri, E.; Sobh, H.; Casati, P.; Tedeschi, R.; Alma, A.; Bianco, P.A. Identification of new 16SrIX subgroups, -F and -G, among ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma phoenicium’ strains infecting almond, peach and nectarine in Lebanon. Phytopath. Medit. 2011, 50, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemüller, E.; Schneider, B. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma mali’, ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma pyri’ and ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma prunorum’, the causal agents of apple proliferation, pear decline and European stone fruit yellows, respectively. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcone, C.; Gibb, K.S.; Streten, C.; Schneider, B. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma spartii’, ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma rhamni’ and ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma allocasuarinae’, respectively associated with Spartium witches’ broom, buckthorn witches’ broom and Allocasuarina yellows diseases. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seemüller, E.; Schneider, B.; Maurer, R.; Ahrens, U.; Daire, X.; Kison, H.; Lorenz, K.; Firrao, G.; Avinent, L.; Sears, B.B.; et al. Phylogenetic classification of phytopathogenic mollicutes by sequence analysis of 16S ribosomal DNA. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1994, 44, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montano, H.G.; Davis, R.E.; Dally, E.L.; Hogenhout, S.; Pimentel, J.P.; Brioso, P.S. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma brasiliense’, a new phytoplasma taxon associated with hibiscus witches’ broom disease. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villalobos, W.; Martini, M.; Garita, L.; Muñoz, M.; Osler, R.; Moreira, L. Guazuma ulmifolia (Sterculiaceae), a new natural host of 16SrXV phytoplasma in Costa Rica. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2011, 36, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, H.-Y.; Sawayanagi, T.; Kakizawa, S.; Nishigawa, H.; Miyata, S.; Oshima, K.; Ugaki, M.; Lee, J.T.; Hibi, T.; Namba, S. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma castaneae’, a novel phytoplasma taxon associated with chestnut witches’ broom disease. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, W.; Davis, R.E.; Lee, I.-M.; Zhao, Y. Computer-simulated RFLP analysis of 16S rRNA genes: Identification of ten new phytoplasma groups. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 1855–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saady, N.A.; Khan, A.J.; Calari, A.; Al-Subhi, A.M.; Bertaccini, A. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma omanense’, associated with witches’ broom of Cassia italica (Mill.) Spreng in Oman. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esmailzadeh Hosseini, S.A.; Salehi, M.; Mirchenari, S.M.; Contaldo, N.; Paltrinieri, S.; Bertaccini, A. Occurrence of a ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma omanense’-related strain in bindweed showing a witches’ broom disease in Iran. Phytopath. Moll. 2016, 6, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wei, W.; Davis, R.E.; Wu, W.; Liu, Q. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma tamaricis’, a novel taxon discovered in witches’-broom-diseased salt cedar (Tamarix chinensis Lour.). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2496–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duduk, B.; Tian, J.B.; Contaldo, N.; Fan, X.P.; Paltrinieri, S.; Chen, Q.F.; Zhao, Q.F.; Bertaccini, A. Occurrence of phytoplasmas related to “stolbur” and to ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma japonicum’ in woody host plants in China. J. Phytopath. 2010, 158, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wei, W.; Davis, R.E.; Lee, I.-M.; Bottner-Parker, K.D. The agent associated with blue dwarf disease in wheat represents a new phytoplasma taxon, ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma tritici’. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 004604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiunas, D.; Jomantiene, R.; Davis, R.E. A ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma asteris’-related phytoplasma associated with cherry little leaf disease represents a new subgroup, 16SrI-Q. Phytopathology 2005, 95, S106. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Cervantes, M.E.; Chávez-Medina, J.A.; Acosta-Pardini, J.; Flores-Zamora, G.L.; Méndez-Lozano, J.; Leyva-López, N.E. Genetic diversity and geographical distribution of phytoplasmas associated with potato purple top disease in Mexico. Plant Dis. 2010, 94, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Che, H.; Cao, X.; Luo, D. Identification of a novel subgroup 16SrII-U phytoplasma associated with papaya little leaf disease. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 3485–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malembic-Maher, S.; Salar, P.; Filippin, L.; Carle, P.; Angelini, E.; Foissac, X. Genetic diversity of European phytoplasmas of the 16SrV taxonomic group and proposal of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma rubi’. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 2129–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, A.B.M.; Agrawal, G.K.; Alam, N.; Krishina Reddy, M. Electron microscopy and molecular characterization of phytoplasmas associated with little leaf disease of brinjal (Solanum melongena) and periwinkle (Catharanthus roseus) in Bangladesh. J. Phytopath. 2001, 149, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, A.; Ajayakumar, P.V.; Shasany, A.K.; Gupta, M.K.; Alam, M.; Rastogi, S. Occurrence of a clover proliferation (16SrVI) group phytoplasma associated with little leaf disease of Portulaca grandiflora in India. Plant Dis. 2008, 92, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, I.-M.; Bottner-Parker, K.D.; Zhao, Y.; Villalobos, W.; Moreira, L. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma costaricanum’ a novel phytoplasma associated with an emerging disease in soybean (Glycine max). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 2822–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seemüller, E.; Marcone, C.; Lauer, U.; Ragozzino, A.; Göschl, M. Current status of molecular classification of the phytoplasmas. J. Plant Pathol. 1998, 80, 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Martini, M.; Lee, I.-M.; Bottner, K.D.; Zhao, Y.; Botti, S.; Bertaccini, A.; Harrison, N.A.; Carraro, L.; Marcone, C.; Khan, J.; et al. Ribosomal protein gene-based phylogeny for finer differentiation and classification of phytoplasmas. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2037–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomantiene, R.; Maas, J.L.; Takeda, F.; Davis, R.E. Molecular identification and classification of strawberry phylloid fruit phytoplasma in group 16SrI, new subgroup. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggioli, F.; Pasquini, G.; Lumia, V.; Campobasso, G.; Widmer, T.L.; Quimby, P.C. Molecular identification of a new member of the clover proliferation phytoplasma group (16SrVI) associated with yellow starthistle virescence in Italy. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2004, 110, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duduk, B.; Mejia, J.F.; Calari, A.; Bertaccini, A. Identification of 16SrIX group phytoplasmas infecting Colombian periwinkles and molecular characterization on several genes. In Proceedings of the 17th IOM Congress, Tienjin, China, 6–11 July 2008; p. 83. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, J.N.; Ahmad, S.J.N.; Irfan, M.; Paltrinieri, S.; Contaldo, N.; Bertaccini, A. Molecular detection, identification, characterization and transmission study of sarsoon phyllody in Punjab–Pakistan associated with phytoplasmas affiliated to the new subgroup 16SrIX-H. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 149, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawayanagi, T.; Horikoshi, N.; Kanehira, T.; Shinohara, M.; Bertaccini, A.; Cousin, M.-T.; Hiruki, C.; Namba, S. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma japonicum’, a new phytoplasma taxon associated with Japanese hydrangea phyllody. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1999, 49, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, R.E.; Harrison, N.A.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, W.; Dally, E.L. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma hispanicum’, a novel taxon associated with Mexican periwinkle virescence disease of Catharanthus roseus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 3463–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejat, N.; Vadamalai, G.; Davis, R.E.; Harrison, N.A.; Sijam, K.; Dickinson, M.; Abdullah, S.N.A.; Zhao, Y. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma malaysianum’, a novel taxon associated with virescence and phyllody of Madagascar periwinkle (Catharanthus roseus). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.-M.; Martini, M.; Bottner, K.D.; Dane, R.A.; Black, M.C.; Troxclair, N. Ecological implications from a molecular analysis of phytoplasmas involved in an aster yellows epidemic in various crops in Texas. Phytopathology 2003, 93, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Šeruga, M.; Škorić, D.; Botti, S.; Paltrinieri, S.; Juretić, N.; Bertaccini, A. Molecular characterization of a phytoplasma from the aster yellows (16SrI) group naturally infecting Populus nigra L. ‘Italica’ trees in Croatia. For. Pathol. 2003, 33, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.T.; Blackall, L.L.; Scott, P.T.; Walsh, K.B. Phylogenetic positions of phytoplasmas associated with dieback, yellow crinkle and mosaic diseases of papaya, and their proposed inclusion in ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma australiense’ and a new taxon, ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma australasia’. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.E.; Jomantiene, R.; Dally, E.L.; Wolf, T.K. Phytoplasmas associated with grapevine yellows in Virginia belong to group 16SrI, subgroup A (tomato big bud phytoplasma subgroup), and group 16SrIII, new subgroup I. Vitis 1998, 37, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wei, W.; Lee, I.-M.; Shao, J.; Suo, X.; Davis, R.E. Construction of an interactive online phytoplasma classification tool, iPhyClassifier, and its application in analysis of the peach X-disease phytoplasma group (16SrIII). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2582–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, N.A.; Richardson, P.A.; Kramer, J.B.; Tsai, J.H. Detection of the mycoplasma-like organism associated with lethal yellowing disease of palms in Florida by polymerase chain reaction. Plant Pathol. 1994, 43, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, N.A.; Helmick, E.E.; Elliott, M.L. Lethal yellowing-type diseases of palms associated with phytoplasmas newly identified in Florida, USA. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2008, 153, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, R.T.; Narvaez, M.; Fabre, S.; Harrison, N.A.; Oropeza, C.; Dollet, M.; Hichez, E. Coconut lethal yellowing on the southern coast of the Dominican Republic is associated with a new 16SrIV group phytoplasma. New Dis. Rep. 2007, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.-M.; Martini, M.; Marcone, C.; Zhu, S.F. Classification of phytoplasma strains in the elm yellows group (16SrV) and proposal of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma ulmi’ for the phytoplasma associated with elm yellows. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martini, M.; Murari, E.; Mori, N.; Bertaccini, A. Identification and epidemic distribution of two “flavescence dorée”-related phytoplasmas in Veneto (Italy). Plant Dis. 1999, 83, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, K.A.; Lee, I.-M.; Griffiths, H.M.; Miller, F.D., Jr.; Bottner, K.D. A new member of the clover proliferation phytoplasma group (16SrVI) associated with elm yellows in Illinois. Plant Dis. 2003, 87, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffiths, H.M.; Sinclair, W.A.; Smart, C.D.; Davis, R.E. The phytoplasma associated with ash yellows and lilac witches’ broom: ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma fraxini’. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1999, 49, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-Y.; Sawayanagi, T.; Wongkaew, P.; Kakizawa, S.; Nishigawa, H.; Wei, W.; Oshima, K.; Miyata, S.; Ugaki, M.; Hibi, T.; et al. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma oryzae’, a novel phytoplasma taxon associated with rice yellow dwarf disease. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1925–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglino, F.; Zhao, Y.; Casati, P.; Bulgari, D.; Bianco, P.A.; Wei, W.; Davis, R.E. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma solani’, a novel taxon associated with “stolbur” and “bois noir”-related diseases of plants. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 2879–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, R.E.; Dally, E.L.; Gundersen, D.E.; Lee, I.-M.; Habili, N. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma australiense’ a new phytoplasma taxonb associated with Australian grapevine yellows. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997, 47, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padovan, A.; Gibb, K.; Persley, D. Association of ’Candidatus Phytoplasma australiense’ 38 with green petal and lethal yellows diseases in strawberry. Plant Pathol. 2000, 49, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiunas, D.; Staniulis, J.; Davis, R.E. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma fragariae’, a novel phytoplasma taxon discovered in yellows diseased strawberry, Fragaria × ananassa. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quaglino, F.; Zhao, Y.; Bianco, P.A.; Wei, W.; Casati, P.; Durante, G.; Davis, R.E. New 16Sr subgroups and distinct single nucleotide polymorphism lineages among grapevine “bois noir” phytoplasma populations. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2009, 154, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.; Marcone, C.; Mitrovic, J.; Maixner, M.; Delic, D.; Myrta, A.; Ermacora, P.; Bertaccini, A.; Duduk, B. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma convolvuli’, a new phytoplasma taxon associated with bindweed yellows in four European countries. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 2910–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández, F.D.; Galdeano, E.; Kornowski, M.V.; Arneodo, J.D.; Conci, L.R. Description of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma meliae’, a phytoplasma associated with Chinaberry (Melia azedarach L.) yellowing in South America. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 5244–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arocha, Y.; López, M.; Piñol, B.; Fernández, M.; Picornell, B.; Almeida, R.; Palenzuela, I.; Wilson, M.R.; Jones, P. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma graminis’ and ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma caricae’, two novel phytoplasmas associated with diseases of sugarcane, weeds and papaya in Cuba. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 2451–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, B.; Torres, E.; Martín, M.P.; Schröder, M.; Behnke, H.D.; Seemüller, E. ’Candidatus Phytoplasma pini’, a novel taxon from Pinus silvestris and Pinus halepensis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, N.A.; Davis, R.E.; Oropeza, C.; Helmick, E.E.; Narváez, M.; Eden-Green, S.; Dollet, M.; Dickinson, M. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma palmicola’, associated with a lethal yellowing-type disease of coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) in Mozambique. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 1890–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tymon, A.M.; Jones, P.; Harrison, N.A. Phylogenetic relationships of coconut phytoplasmas and the development of specific oligonucleotide PCR primers. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1998, 132, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, A.; Shigaki, T.; Koinuma, H.; Iwabuchi, N.; Rauka, G.B.; Kembu, A.; Saul, J.; Watanabe, K.; Nijo, T.; Maejima, K.; et al. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma noviguineense’, a novel taxon associated with Bogia coconut syndrome and banana wilt disease on the island of New Guinea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.M.; Pease, B.; Perkins, S.L.; Constable, F.E.; Kinoti, W.M.; Warmington, D.; Allgood, B.; Powell, S.; Taylor, P.; Pearce, C.; et al. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma dypsidis’, a novel taxon associated with a lethal wilt disease of palms in Australia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 004818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jardim, B.R.; Kinoti, W.M.; Tran-Nguyen, L.T.T.; Gambley, C.; Rodoni, B.; Constable, F.E. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma stylosanthis’, a novel taxon with a diverse host range in Australia, characterised using multilocus sequence analysis of 16S rRNA, secA, tuf, and rp genes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 004589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderali, N.; Nejat, N.; Vadamalai, G.; Davis, R.E.; Wei, W.; Harrison, N.A.; Kong, L.L.; Kadir, J.; Tan, H.-Y.; Zhao, Y. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma wodyetiae’, a new taxon associated with yellow decline disease of foxtail palm (Wodyetia bifurcata) in Malaysia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 3765–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedeschi, R.; Bertaccini, A. Transovarial transmission in insect vectors. In Phytoplasmas: Plant Pathogenic Bacteria-II Transmission and Management of Phytoplasma Associated Diseases; Bertaccini, A., Weintraub, P.G., Rao, G.P., Mori, N., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 115–130. [Google Scholar]
- Kirdat, K.; Tiwarekar, B.; Thorat, V.; Sathe, S.; Shouche, Y.; Yadav, A. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma sacchari’, a novel taxon-associated with sugarcane grassy shoot (SCGS) disease. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 71, 004591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Li, W.F.; Huang, Y.K.; Wang, X.Y.; Shan, H.L.; Luo, Z.-M.; Yin, J. Group 16SrXI phytoplasma strains, including subgroup 16SrXI-B and a new subgroup, 16SrXI-D, are associated with sugar cane white leaf. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcone, C.; Schneider, B.; Seemüller, E. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma cynodontis’, the phytoplasma associated with Bermuda grass white leaf disease. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salehi, M.; Izadpanah, K.; Siampour, M.; Taghizadeh, M. Molecular characterization and transmission of bermuda grass white leaf phytoplasma in Iran. J. Plant Pathol. 2009, 91, 655–661. [Google Scholar]
- Mitrovic, J.; Smiljković, M.; Seemüller, E.; Reinhardt, R.; Hüttel, B.; Büttner, C.; Bertaccini, A.; Kube, M.; Duduk, B. Differentiation of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma cynodontis’ based on 16S rRNA and groEL genes and identification of a new subgroup, 16SrXIV-C. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.E.; Grau, C.R.; Lukaesko, L.A.; Lee, I.-M. Identification of aster yellows phytoplasmas in soybean in Wisconsin based on RFLP analysis of PCR-amplified products (16S rDNAs). Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2002, 24, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, K.I.; Zamora, L.; Piñol, B.E.; Fernández, A.; Chávez, A.; Flores, G.; Méndez, J.; Santos, M.; Leyva, N.; Arocha, Y. Identification and molecular characterization of phytoplasmas and rickettsia pathogens associated with bunchy top symptom (BTS) and papaya bunchy top (PBT) of papaya in Cuba. Crop Prot. 2013, 45, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arocha, Y.; Antesana, O.; Montellano, E.; Franco, P.; Plata, G.; Jones, P. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma lycopersici’, a phytoplasma associated with “hoja de perejil” disease in Bolivia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 1704–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acosta-Pérez, K.I.; Piñol-Pérez, B.E.; Zamora-Gutierrez, L.; Quiñones-Pantoja, M.L.; Miranda-Cabrera, I.; Leyva-López, N.E.; Arocha-Rosete, Y. A phytoplasma representative of a new subgroup 16SrI-Z associated with bunchy top symptoms (BTS) on papaya in Cuba. Rev. Protec. Veg. 2017, 32, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, A.; Bhale, U.; Thorat, V.; Shouche, Y. First report of a new subgroup 16SrII-M ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma aurantifolia’ associated with witches’ broom disease of Tephrosia purpurea in India. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, E.; Mejía, J.F.; Llano, G.A.; Loke, J.B.; Calari, A.; Duduk, B.; Bertaccini, A. Detection and molecular characterization of a phytoplasma associated with frogskin disease in cassava. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valiunas, D.; Jomantiene, R.; Ivanauskas, A.; Abraitis, R.; Staniene, G.; Zhao, Y.; Davis, R.E. First report of a new phytoplasma subgroup, 16SrIII-T, associated with decline disease affecting sweet and sour cherry trees in Lithuania. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.E.; Zhao, Y.; Dally, E.L.; Jomantiene, R.; Lee, I.-M.; Wei, W.; Kitajima, E.W. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma sudamericanum’, a novel taxon, and strain PassWB-Br4, a new subgroup 16SrIII-V phytoplasma, from diseased passion fruit (Passiflora edulis f. flavicarpa Deg.). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.-M.; Polashock, J.; Bottner-Parker, K.D.; Bagadia, P.G.; Rodriguez-Saona, C.; Zhao, Y.; Davis, R.E. New subgroup 16SrIII-Y phytoplasmas associated with false-blossom diseased cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon) plants and with known and potential insect vectors in New Jersey. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 139, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šafárová, D.; Zemánek, T.; Válová, P.; Navrátil, M. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma cirsii’, a novel taxon from creeping thistle [Cirsium arvense (L.) Scop]. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1745–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Thorat, V.; Deokule, S.; Shouche, Y.; Prasad, D.T. New subgroup 16SrXI-F phytoplasma strain associated with sugarcane grassy shoot (SCGS) disease in India. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Dong, J.; Lee, I.-M.; Bottner-Parker, K.D.; Zhao, Y.; Davis, R.E.; Laski, P.J.; Zhang, Z.; McBeath, J.H. Group 16SrXII phytoplasma strains, including subgroup 16SrXII-E (‘Candidatus Phytoplasma fragariae’) and a new subgroup, 16SrXII-I, are associated with diseased potatoes (Solanum tuberosum) in the Yunnan and Inner Mongolia regions of China. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 142, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, L.; Silva, E.; Flôres, D.; Ventura, J.; Costa, H.; Bedendo, I. A phytoplasma representative of a new subgroup, 16SrXIII-E, associated with papaya apical curl necrosis. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2013, 137, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, F.D.; Meneguzzi, N.G.; Guzmán, F.A.; Kirschbaum, D.S.; Conci, V.C.; Nome, C.F.; Conci, L.R. Detection and identification of a novel 16SrXIII subgroup phytoplasma associated with strawberry red leaf disease in Argentina. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 2741–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, I.-M.; Bottner, K.D.; Secor, G.; Rivera-Varas, V. ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma americanum’, a phytoplasma associated with a potato purple top wilt disease complex. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1593–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kakizawa, S.; Oshima, K.; Kuboyama, T.; Nishigawa, H.; Jung, H.-Y.; Sawayanagi, T.; Tsuchizaki, T.; Miyata, S.; Ugaki, M.; Namba, S. Cloning and expression analysis of phytoplasma protein translocation genes. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2001, 14, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oshima, K.; Kakizawa, S.; Nishigawa, H.; Jung, H.-Y.; Wei, W.; Suzuki, S.; Arashida, R.; Nakata, D.; Miyata, S.; Ugaki, M.; et al. Reductive evolution suggested from the complete genome sequence of a plant-pathogenic phytoplasma. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arashida, R.; Kakizawa, S.; Hoshi, A.; Ishii, Y.; Jung, H.-Y.; Kagiwada, S.; Yamaji, Y.; Oshima, K.; Namba, S. Heterogeneic dynamics of the structures of multiple gene clusters in two pathogenetically different lines originating from the same phytoplasma. DNA Cell Biol. 2008, 27, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomantiene, R.; Davis, R.E. Clusters of diverse genes existing as multiple, sequence-variable mosaics in a phytoplasma genome. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 255, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toruño, T.Y.; Musić, M.S.; Simi, S.; Nicolaisen, M.; Hogenhout, S.A. Phytoplasma PMU1 exists as linear chromosomal and circular extrachromosomal elements and has enhanced expression in insect vectors compared with plant hosts. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 77, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, P.G.; Beanland, L. Insect vectors of phytoplasmas. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 51, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Kakizawa, S.; Suzuki, S.; Jung, H.-Y.; Nishigawa, H.; Miyata, S.; Oshima, K.; Ugaki, M.; Hibi, T.; Namba, S. In planta dynamic analysis of onion yellows phytoplasma using localized inoculation by insect transmission. Phytopathology 2004, 94, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertaccini, A.; Oshima, K.; Kakizawa, S.; Duduk, B.; Namba, S. Dissecting the multifaceted mechanisms that drive leafhopper host–phytoplasma specificity. In Vector-Mediated Transmission of Plant Pathogens; Brown, J.K., Ed.; APS Press: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakizawa, S.; Oshima, K.; Ishii, Y.; Hoshi, A.; Maejima, K.; Jung, H.-Y.; Yamaji, Y.; Namba, S. Cloning of immunodominant membrane protein genes of phytoplasmas and their in planta expression. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 293, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, S.; Oshima, K.; Kakizawa, S.; Arashida, R.; Jung, H.-Y.; Yamaji, Y.; Nishigawa, H.; Ugaki, M.; Namba, S. Interaction between the membrane protein of a pathogen and insect microfilament complex determines insect-vector specificity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 4252–4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galetto, L.; Bosco, D.; Balestrini, R.; Genre, A.; Fletcher, J.; Marzachì, C. The major antigenic membrane protein of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma asteris’ selectively interacts with ATP synthase and actin of leafhopper vectors. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boonrod, K.; Munteanu, B.; Jarausch, B.; Jarausch, W.; Krczal, G. An immunodominant membrane protein (Imp) of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma mali’ binds to plant actin. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2012, 25, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oshima, K.; Ishii, Y.; Kakizawa, S.; Sugawara, K.; Neriya, Y.; Himeno, M.; Minato, N.; Miura, C.; Shiraishi, T.; Yamaji, Y.; et al. Dramatic transcriptional changes in an intracellular parasite enable host switching between plant and insect. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, K.; Kakizawa, S.; Arashida, R.; Ishii, Y.; Hoshi, A.; Hayashi, Y.; Kagiwada, S.; Namba, S. Presence of two glycolytic gene clusters in a severe pathogenic line of ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma asteris’. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2007, 8, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himeno, M.; Kitazawa, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Maejima, K.; Yamaji, Y.; Oshima, K.; Namba, S. Purple top symptoms are associated with reduction of leaf cell death in phytoplasma-infected plants. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoshi, A.; Oshima, K.; Kakizawa, S.; Ishii, Y.; Ozeki, J.; Hashimoto, M.; Komatsu, K.; Kagiwada, S.; Yamaji, Y.; Namba, S. A unique virulence factor for proliferation and dwarfism inplants identified from a phytopathogenic bacterium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6416–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugawara, K.; Honma, Y.; Komatsu, K.; Himeno, M.; Oshima, K.; Namba, S. The alteration of plant morphology by small peptides released from the proteolytic processing of the bacterial peptide TENGU. Plant Physiol. 2013, 162, 2005–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minato, N.; Himeno, M.; Hoshi, A.; Maejima, K.; Komatsu, K.; Takebayashi, Y.; Kasahara, H.; Yusa, A.; Yamaji, Y.; Oshima, K.; et al. The phytoplasmal virulence factor TENGU causes plant sterility by downregulating of the jasmonic acid and auxin pathways. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arashida, R.; Kakizawa, S.; Ishii, Y.; Hoshi, A.; Jung, H.-Y.; Kagiwada, S.; Yamaji, Y.; Oshima, K.; Namba, S. Cloning and characterization of the antigenic membrane protein (Amp) gene and in situ detection of Amp from malformed flowers infected with Japanese hydrangea phyllody phytoplasma. Phytopathology 2008, 98, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Himeno, M.; Neriya, Y.; Minato, N.; Miura, C.; Sugawara, K.; Ishii, Y.; Yamaji, Y.; Kakizawa, S.; Oshima, K.; Namba, S. Unique morphological changes in plant pathogenic phytoplasma-infected petunia flowers are related to transcriptional regulation of floral homeotic genes in an organ-specific manner. Plant J. 2011, 67, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLean, A.M.; Sugio, A.; Makarova, O.V.; Findlay, K.C.; Grieve, V.M.; Toth, R.; Nicolaisen, M.; Hogenhout, S.A. Phytoplasma effector SAP54 induces indeterminate leaf-like flower development in Arabidopsis plants. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maejima, K.; Iwai, R.; Himeno, M.; Komatsu, K.; Kitazawa, Y.; Fujita, N.; Ishikawa, K.; Fukuoka, M.; Minato, N.; Yamaji, Y.; et al. Recognition of floral homeotic MADS domain transcription factors by a phytoplasmal effector, phyllogen, induces phyllody. Plant J. 2014, 78, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLean, A.M.; Orlovskis, Z.; Kowitwanich, K.; Zdziarska, A.M.; Angenent, G.C.; Immink, R.G.; Hogenhout, S.A. Phytoplasma effector SAP54 hijacks plant reproduction by degrading MADS-box proteins and promotes insect colonization in a RAD23-dependent manner. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitazawa, Y.; Iwabuchi, N.; Himeno, M.; Sasano, M.; Koinuma, H.; Nijo, T.; Tomomitsu, T.; Yoshida, T.; Okano, Y.; Yoshikawa, N.; et al. Phytoplasma-conserved phyllogen proteins induce phyllody across the Plantae by degrading floral MADS domain proteins. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 2799–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertaccini, A.; Paltrinieri, S.; Contaldo, N. Standard detection protocol: PCR and RFLP analyses based on 16S rRNA gene. In Phytoplasmas; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, P.A.; Romanazzi, G.; Mori, N.; Myrie, W.; Bertaccini, A. Integrated management of phytoplasma diseases. In Phytoplasmas: Plant Pathogenic Bacteria-II Transmission and Management of Phytoplasma Associated Diseases; Bertaccini, A., Weintraub, P.G., Rao, G.P., Mori, N., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; Volume 2, pp. 237–258. [Google Scholar]
- Tanno, K.; Maejima, K.; Miyazaki, A.; Koinuma, H.; Iwabuchi, N.; Kitazawa, Y.; Nijo, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Yamaji, Y.; Namba, S. Comprehensive screening of antimicrobials to control phytoplasma diseases using an in vitro plant-phytoplasma co-culture system. Microbiology 2018, 164, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.L.; Clark, M.F. Maintenance of mycoplasma-like organisms occurring in Pyrus species by micropropagation and their elimination by tetracycline therapy. Plant Pathol. 1994, 43, 819–823. [Google Scholar]
- Aldaghi, M.; Massart, S.; Druart, P.; Bertaccini, A.; Jijakli, M.H.; Lepoivre, P. Preliminary in vitro evaluation of antimicrobial activity of some chemicals and essential oils on apple proliferation disease. Commun. Appl. Biol. Sci. Ghent Univ. 2008, 73, 335–341. [Google Scholar]
- Bertaccini, A. Containment of phytoplasma-associated plant diseases by antibiotics and other antimicrobial molecules. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Disease (Acronym) | Continent | 16Sr Subgroups | ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma’ Species | GenBank Accession Number | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aster yellows w. b. (AY-WB) | America | 16SrI-A | ‘Ca. P. asteris’ | NC_007716 | [13] |
| Paulownia w. b. (PaWB) | Asia | 16SrI-D | AY265206 | [14] | |
| Strawberry witches’ broom (STRAWB1), (STRAWB2) | America | 16SrI-I / -K | U96614, U96616 | [15] | |
| Peach rosette-like (PRU0382) | America | 16SrI-W | HQ450211 | [16] | |
| Peanut witches’ broom (PnWB) | America | 16SrII-A | L33765 | [17] | |
| Lime witches’ broom (WBDL) | Asia | 16SrII-B | ‘Ca. P. aurantifolia’ | U15442 | [18] |
| Cactus witches’ broom (CWB) | Asia | 16SrII-G to -L | EU099568, EU099552, EU099569, EU099572, EU099551, EU099546, EF647744 | [19] | |
| Tabebuia witches’ broom | America | 16SrII-O | [20] | ||
| Tomatillo witches’ broom | America | 16SrII-T | U125185 | [21] | |
| Walnut witches’ broom (WWB) | America | 16SrIII-G | AF190226, AF190227 | [22] | |
| Poinsettia branch-inducing (PoiBI) | Europe, America | 16SrIII-H | AF190223 | [22] | |
| Chayote w. b. (ChWBIII) | America | 16SrIII-J | AF147706 | [23] | |
| Black raspberry w. b. (BRWB7) | America | 16SrIII-Q | AF302841 | [24] | |
| Conyza witches’ broom | America | 16SrIII-X | KC412026 | [25] | |
| Jujube witches’ broom (JWB-G1) | Asia | 16SrV-B | ‘Ca. P. ziziphi’ | AB052876 | [26] |
| Balanites triflora w. b. (BltWB) | Asia | 16SrV-F | Ca. P. balanitae’ | AB689678 | [27] |
| Korean jujube witches’ broom | Asia | 16SrV-G | AB052879 | [26] | |
| Bischofia polycarpa witches’ broom | Asia | 16SrV-H | KJ452547 | [28] | |
| Blackberry witches’ broom | Europe | 16SrV-I | KR233473 | [29] | |
| Clover proliferation (CP) | America | 16SrVI-A | ‘Ca. P. trifolii’ | AY390261 | [30] |
| Erigeron witches’ broom (ErWB) | America | 16SrVII-B | AY034608 | [31] | |
| Argentinian alfalfa w.b. (ArAWB) | America | 16SrVII-C | AY147038 | [32] | |
| Erigeron w. b. (EboWB-Br0) | America | 16SrVII-D | KJ831066 | [33] | |
| Loofah witches’ broom (LufWB) | Asia | 16Sr VIII-A | ‘Ca. P. luffae’ | AF086621 | [34] |
| Pigeon pea w. b. (PPWB) | America | 16SrIX-A | AF248957 | [35] | |
| Almond witches’ broom (AlWB) | Asia | 16SrIX-B/-D | ‘Ca. P. phoenicium’ | AF515636, AF515637 | [36] |
| Juniperus witches’ broom | America | 16SrIX-E | GQ925918 | [37] | |
| Almond and stone fruit witches’ broom (N27-2), (A1-1) | Asia | 16SrIX-F/-G | ‘Ca. P. phoenicium’ | HQ407532, HQ407514 | [38] |
| Apple proliferation (AP) | Europe, Asia | 16SrX-A | ‘Ca. P. mali’ | AJ542541 | [39] |
| Spartium witches’ broom (SpaWB) | Europe | 16SrX-D | ‘Ca. P. spartii’ | X92869 | [40] |
| Black alder w. b. (BAWB, BWB) | Europe | 16SrX-E | X76431 | [41] | |
| Hibiscus witches’ broom (HibWB) | America, Asia | 16SrXV-A | ‘Ca. P. brasiliense’ | AF147708 | [42] |
| Guazuma w. b. (GWB) | America | 16SrXV-B | HQ258882 | [43] | |
| Chestnut witches’ broom | Asia | 16SrXIX-A | ‘Ca. P. castaneae’ | AB054986 | [44] |
| Rhamnus witches’ broom | Europe | 16SrXX-A | ‘Ca. P. rhamni’ | AJ583009 | [40] |
| Weeping tea witches’ broom | Oceania | 16SrXXV-A * | AF521672 | [45] | |
| Cassia w. b. (CaWB) | Asia | 16SrXXIX-A | ‘Ca. P. omanense’ | EF666051 | [46] |
| Bindweed witches’ broom (RBiWB) | Asia | 16SrXXIX-B | KY047493 | [47] | |
| Salt cedar witches’ broom | Asia | 16SrXXX-A | ‘Ca. P. tamaricis’ | FJ432664 | [48] |
| Disease (Acronym) | Continent | 16Sr Subgroups | ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma’ Species | GenBank Accession Number | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blue dwarf wheat (BDW) | Asia | 16SrI-C | ‘Ca. P. tritici’ | DQ078304 | [50] |
| Blueberry stunt (BBS3) | America | 16SrI-E | AY265213 | [14] | |
| Cherry little leaf (ChLL) | Europe | 16SrI-Q | AY034089 | [51] | |
| Pepper little leaf (PeLL) | America | 16SrI-S | DQ092321 | [52] | |
| Tomato little leaf (ToLL) | America | 16SrI-T | DQ375238 | [52] | |
| Vasconcellea cundinamarcensis little leaf | China | 16SrII-U | KP057205 | [53] | |
| Spiraea stunt (SP1) | America | 16SrIII-E | AF190228 | [23] | |
| Heterothalamus little leaf (HetLL) | America | 16SrIII-W | KC412029 | [26] | |
| Broccoli stunt (BSP-21) | America | 16SrIII-Z | JX626327 | [22] | |
| Rubus stunt (RuS) | Europe | 16SrV-E | ‘Ca. P. rubi’ | AY197648 | [54] |
| Fragaria multicipita, multiplier disease | America | 16SrVI-B | AF190224 | [15] | |
| Periwinkle little leaf (PLL-Bd) | Asia | 16SrVI-D | AF228053 | [55] | |
| Portulaca little leaf (PLL-Ind) | Asia | 16SrVI-H | EF651786 | [56] | |
| Soybean stunt (SoyST1c1) | America | 16SrXXXI-A | ‘Ca. P. costaricanum’ | HQ225630 | [57] |
| Disease (Acronym) | Continent | 16Sr Subgroups | ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma’ Species | GenBank Accession Number | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clover phyllody (CPh) | America | 16SrI-C | AF222065 | [15] | |
| Faba bean phyllody (FBP) | Asia, Africa | 16SrII-C | X83432 | [58] | |
| Pichris echioides phyllody (PEY) | Europe | 16SrII-E | Y16393 | [58] | |
| Cotton phyllody (CoP) | Africa | 16SrII-F | EF186827 | [59] | |
| Strawberry leafy fruit (SLF) | America | 16SrIII-K | AF274876 | [15] | |
| Dandelion virescence (DanVir) | Europe | 16SrIII-O/-P | AF370120, AF370119 | [60] | |
| Heterothalamus little leaf (HetLL) | America | 16SrIII-W | KC412029 | [26] | |
| Centarurea solstitialis virescence (CSVI) | Europe | 16SrVI-E | AY270156 | [61] | |
| Catharanthus phyllody (CPS) | Africa | 16SrVI-F | EF186819 | [59] | |
| Naxos periwinkle virescence (NAXOS) | Europe, Asia, America | 16SrIX-C | HQ589191 | [62] | |
| Sarsoon phyllody | Asia | 16SrIX-H | KU892213 | [63] | |
| Japanese hydrangea phyllody | Asia | 16SrXII-D | ‘Ca. P. japonicum’ | AB010425 | [64] |
| Mexican periwinkle virescence (MPV) | America | 16SrXIII-A | ‘Ca. P. hispanicum’ | AF248960 | [65] |
| Strawberry green petal (STRAWB2) | America | 16SrXIII-B | U96616 | [15] | |
| Malaysian periwinkle virescence (MaPV) | Asia | 16SrXXXII-A | ‘Ca. P. malaysianum’ | EU371934 | [66] |
| Disease (Acronym) | Continent | 16Sr Subgroups | ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma’ Species | GenBank Accession Number | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aster yellows (MAY) | America | 16SrI-B | ‘Ca. P. asteris’ | M30790 | [14] |
| Aster yellows apricot Spain (A-AY) | Europe, America | 16SrI-F | AY265211 | [14] | |
| Aster yellows (AV2192 | Europe | 16SrI-L | AY180957 | [67] | |
| Aster yellows (AVUT) | Europe | 16SrI-M | AY265209 | [17] | |
| Aster yellows (IoWB) | America | 16SrI-N | AY265205 | [17] | |
| Aster yellows from Populus (PopAY) | Europe | 16SrI-P | AF503568 | [68] | |
| Papaya mosaic (PpM) | Oceania | 16SrII-D | ‘Ca. P. australasia’ | Y10096 | [69] |
| Echinopsis yellow patch | America | 16SrII-R | DQ535900 | [21] | |
| Peach X-disease (PX11CT1) | America | 16SrIII-A | ‘Ca. P. pruni’ | JQ044393 | [22] |
| Clover yellow edge (CYE) | America, Europe | 16SrIII-B | AF173558 | [22] | |
| Goldenrod yellows (GR1) | America | 16SrIII-D | GU004372 | [22] | |
| Milkweed yellows (MW1) | America | 16SrIII-F | AF510724 | [22] | |
| Virginia grapevine yellows (VGYIII) | America | 16SrIII-I | AF060875 | [70] | |
| Western peach X-disease (WX) | America | 16SrIII-S | L04682 | [71] | |
| Coconut lethal yellowing (LYJ-C8) | America | 16SrIV-A | ‘Ca. P. palmae’ | AF498307 | [4] |
| Yucatan coconut lethal decline (LDY) | America | 16SrIV-B | U18753 | [72] | |
| Tanzanian coconut lethal decline (LDT) | Africa | 16SrIV-C | ‘Ca. P. cocostanzaniae’ | X80117 | [72] |
| Texas phoenix decline (TPD | America | 16SrIV-D | AF434969 | [73] | |
| Coconut lethal yellowing (LYDR-B5) | America | 16SrIV-E | DQ631639 | [74] | |
| Washingtonia robusta decline | America | 16SrIV-F | EU241512 | [73] | |
| Elm yellows (EY) | Europe, America | 16SrV-A | ‘Ca. P. ulmi’ | AY197655 | [75] |
| ‘Flavescence dorée’ (FD-C) | Europe | 16SrV-C | X76560 | [76] | |
| ‘Flavescence dorée’ (FD-D) | Europe | 16SrV-D | AJ548787 | [76] | |
| Illinois elm yellows (EY-IL1) | America | 16SrVI-C | AF409069 | [77] | |
| Ash yellows (AshY) | America, Europe, Asia | 16SrVII-A | ‘Ca. P. fraxini’ | AF092209 | [78] |
| European stone fruit yellows (ESFY) | Europe, Asia | 16SrX-B | ‘Ca. P. prunorum’ | AJ542544 | [39] |
| Pear decline (PD) | Europe, America | 16SrX-C | ‘Ca. P. pyri’ | AJ542543 | [39] |
| Rice yellow dwarf (RYD) | Asia | 16SrXI-A | ‘Ca. P. oryzae’ | AB052873 | [79] |
| ”Stolbur” (STOL11) | Europe, America, Asia, Africa | 16SrXII-A | ’Ca. P. solani’ | AF248959 | [80] |
| Australian grapevine yellows (AUSGY) | Oceania | 16SrXII-B | ‘Ca. P. australiense’ | L76865 | [81] |
| Strawberry lethal yellows (StrawLY) | Oceania | 16SrXII-C | AJ243045 | [82] | |
| Yellows diseased strawberry (StrawY) | Europe | 16SrXII-E | ‘Ca. P. fragariae’ | DQ086423 | [83] |
| “Bois noir” (BN-Op30), (BN-Fc3) | Europe | 16SrXII-F /-G | EU836652, EU836647 | [84] | |
| Bindweed yellows (BY-S57/11) | Europe | 16SrXII-H | ‘Ca. P. convolvuli’ | JN833705 | [85] |
| Chinaberry yellows (CBY1) | America | 16SrXIII-C | AF495882 | [86] | |
| Chinaberry yellowing (ChTY) | America | 16SrXIII-G | ‘Ca. P. meliae’ | KU850940 | [86] |
| Sugarcane yellow leaf syndrome | America | 16SrXVI-A | ‘Ca. P. graminis’ | AY725228 | [87] |
| Pinus phytoplasma (PinP) | Europe, America, Africa | 16SrXXI-A | ‘Ca. P. pini’ | AJ310849 | [88] |
| Lethal yellowing Mozambique (LYDM 178) | Africa | 16SrXXII-A | ‘Ca. P. palmicola’ | KF751387 | [89] |
| Cape Saint Paul Wilt Ghana (LDG) | Africa | 16SrXXII-B | Y13912 | [90] | |
| Buckland valley grapevine yellows | Oceania | 16SrXXIII-A * | AY083605 | [45] | |
| Malayan yellow dwarf (MYD) | Asia | 16SrXXXII-B | EU498727 | [66] | |
| Malayan oil palm (MOP) | Asia | 16SrXXXII-C | EU498728 | [66] | |
| Allocasuarina phytoplasma | Oceania | 16SrXXXIII-A | ‘Ca. P. allocasuarinae’ | AY135523 | [40] |
| Bogia coconut syndrome (BCS) | Oceania | Not determ. | ‘Ca. P. noviguineense’ | LC228755 | [91] |
| Palm decline (RID7692) | Oceania | Not determ. | ‘Ca. P. dypsidis’ | MT233886 | [92] |
| Not described | Oceania | Not determ. | ‘Ca. P. stylosanthis’ | MT431550 | [93] |
| Palm decline | Oceania | 16SrXXXVI | ‘Ca. P. wodyetiae’ | KY069029 | [94] |
| Disease (Acronym) | Continent | 16Sr Subgroups | ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma’ Species | GenBank Accession Number | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cirsium white leaf (CirWL) | Europe | 16SrIII-R | AF373105 | [72] | |
| Cirsium white leaf (CWL) | Europe | 16SrIII-U | AF373105, AF373106 | [81] | |
| Sugarcane white leaf (SCWL) | Asia | 16SrXI-B | ‘Ca. P. sacchari’ | X76432 | [96] |
| Sugarcane white leaf (SCWL) | Asia | 16SrXI-D | KR020685 | [97] | |
| Bermudagrass white leaf (BGWL) | Europe | 16SrXIV-A | ‘Ca. P. cynodontis’ | AJ550984 | [98] |
| Bermudagrass white leaf Iran | Asia | 16SrXIV-B | EF444485 | [99] | |
| Bermudagrass white leaf (RS304/13) | Europe | 16SrXIV-C | KP019339 | [100] |
| Disease (Acronym) | Continent | 16Sr Subgroups | ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma’ Species | GenBank Accession Number | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean purple stem (SPS) | America | 16SrI-O | AF268405 | [101] | |
| Mexican potato purple top (JAL8), (SON18) | America | 16SrI-U/-V | FJ914650, FJ914642 | [53] | |
| Papaya bunchy top (BTS) | America | 16SrI-X | JF781308 | [102] | |
| Tomato “brote grande” | America | 16SrI-Y | ‘Ca. P. lycopersici’ | EF199549 | [103] |
| Papaya bunchy top (BTS) | America | 16SrI-Z | JF781311 | [104] | |
| Potato purple top | Asia | 16SrII-M | FJ914643 | [105] | |
| Papaya BTSp | America | 16SrII-N | JF781309 | [102] | |
| Cuban papaya | America | 16SrII-P | DQ286948 | [22] | |
| Papaya bunchy top (TSpHav02-IIA) | America | 16SrII-Q | JF78131 | [22] | |
| Echinopsis yellow patch | America | 16SrII-R | DQ535900 | [22] | |
| Amaranthus hypochondriacus 52A | America | 16SrII-S | FJ357164 | [22] | |
| Pecan bunch (PB) | America | 16SrIII-C | GU004371 | [23] | |
| Cassava frog skin (CFSD) | America | 16SrIII-L | EU346761 | [106] | |
| Potato purple top (MT117) | America | 16SrIII-M | FJ226074 | [23] | |
| Potato purple top (AKpot6) | America | 16SrIII-N | GU004365 | [23] | |
| Sweet and sour cherry (ChD) | Europe | 16SrIII-T | FJ231728 | [107] | |
| Passion fruit phytoplasma (PassWB-Br4) | America | 16SrIII-V | GU292082 | [108] | |
| Cranberry false-blossom | America | 16SrIII-Y | KF62652 | [109] | |
| Passionfruit (WB-Br4) | America | 16SrVI-I | ‘Ca. P. sudamericanum’ | GU292081 | [110] |
| Leafhopper-borne (BVK) | Europe | 16SrXI-C | X76429 | [13] | |
| Cirsium phytoplasma | Europe | 16SrXI-E | ‘Ca. P. cirsii’ | KR869146 | [111] |
| Sugarcane grassy shoot (SCGS) | Asia | 16SrXI-F | HF586636 | [112] | |
| Potato (169/Hezuo 88) | Asia | 16SrXII-I | EU338445 | [112] | |
| Mexican potato purple top (SINPV) | America | 16SrXIII-D | FJ914647 | [53] | |
| Papaya apical curl necrosis (PACN) | America | 16SrXIII-E | EU719111 | [113] | |
| Strawberry red leaf | America | 16SrXIII-F | KJ921641 | [114] | |
| Papaya bunchy top | America | 16SrXVII-A | ‘Ca. P. caricae’ | AY725234 | [88] |
| American potato purple top wilt | America | 16SrXVIII-A | ‘Ca. P. americanum’ | DQ174122 | [115] |
| Sorghum bunchy shoot | Oceania | 16SrXXIV-A * | AF509322 | [45] | |
| Sugarcane phytoplasma D3T1 | Africa | 16SrXXVI-A * | AJ539179 | [45] | |
| Sugarcane phytoplasma D3T2 | Africa | 16SrXXVII-A * | AY539180 | [45] | |
| Derbid phytoplasma | Africa | 16SrXXVIII-A * | AY744945 | [45] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertaccini, A. Plants and Phytoplasmas: When Bacteria Modify Plants. Plants 2022, 11, 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11111425
Bertaccini A. Plants and Phytoplasmas: When Bacteria Modify Plants. Plants. 2022; 11(11):1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11111425
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertaccini, Assunta. 2022. "Plants and Phytoplasmas: When Bacteria Modify Plants" Plants 11, no. 11: 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11111425
APA StyleBertaccini, A. (2022). Plants and Phytoplasmas: When Bacteria Modify Plants. Plants, 11(11), 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11111425






