Genomic Analyses of Wild and Cultivated Bacanora Agave (Agave angustifolia var. pacifica) Reveal Inbreeding, Few Signs of Cultivation History and Shallow Population Structure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
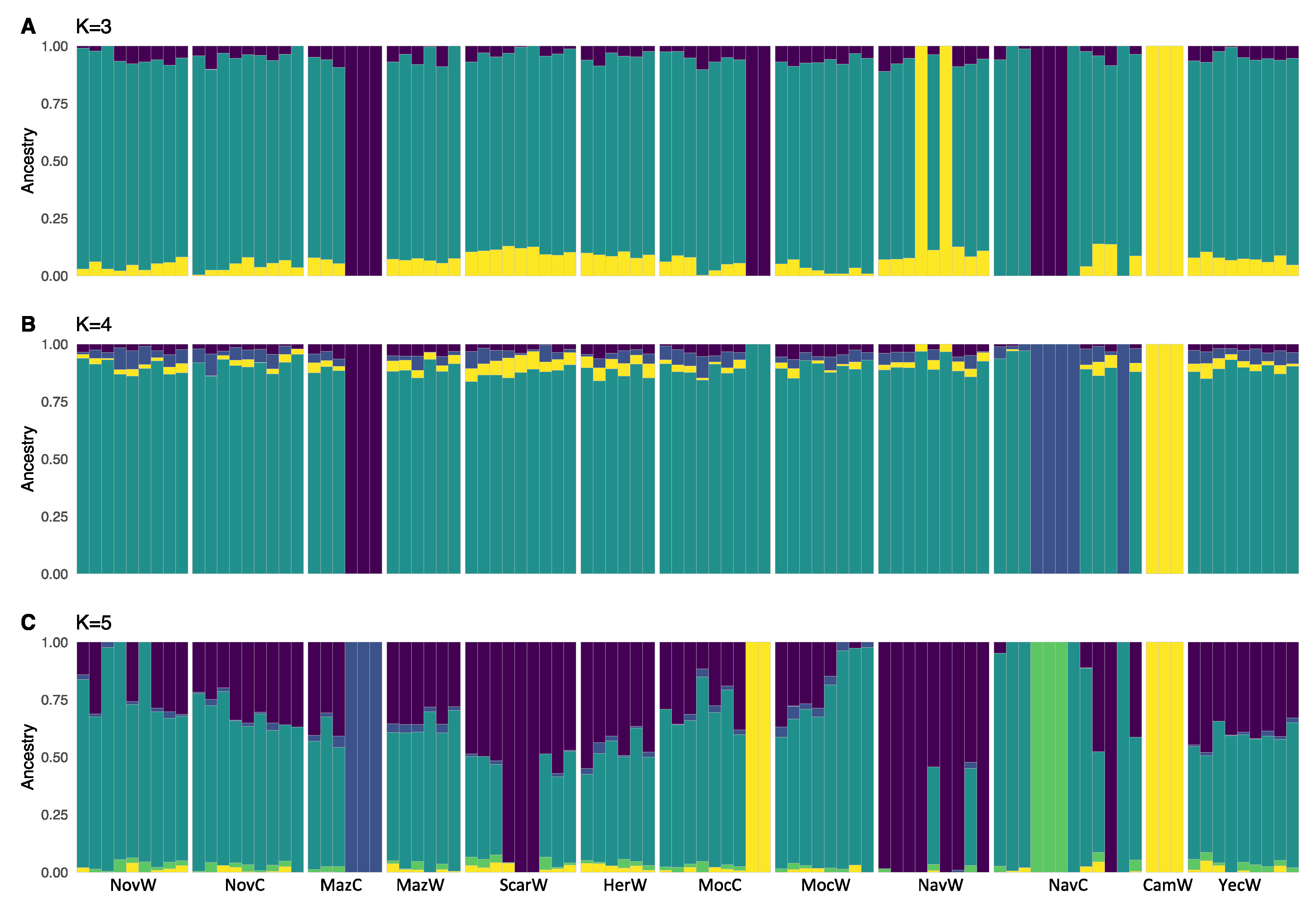
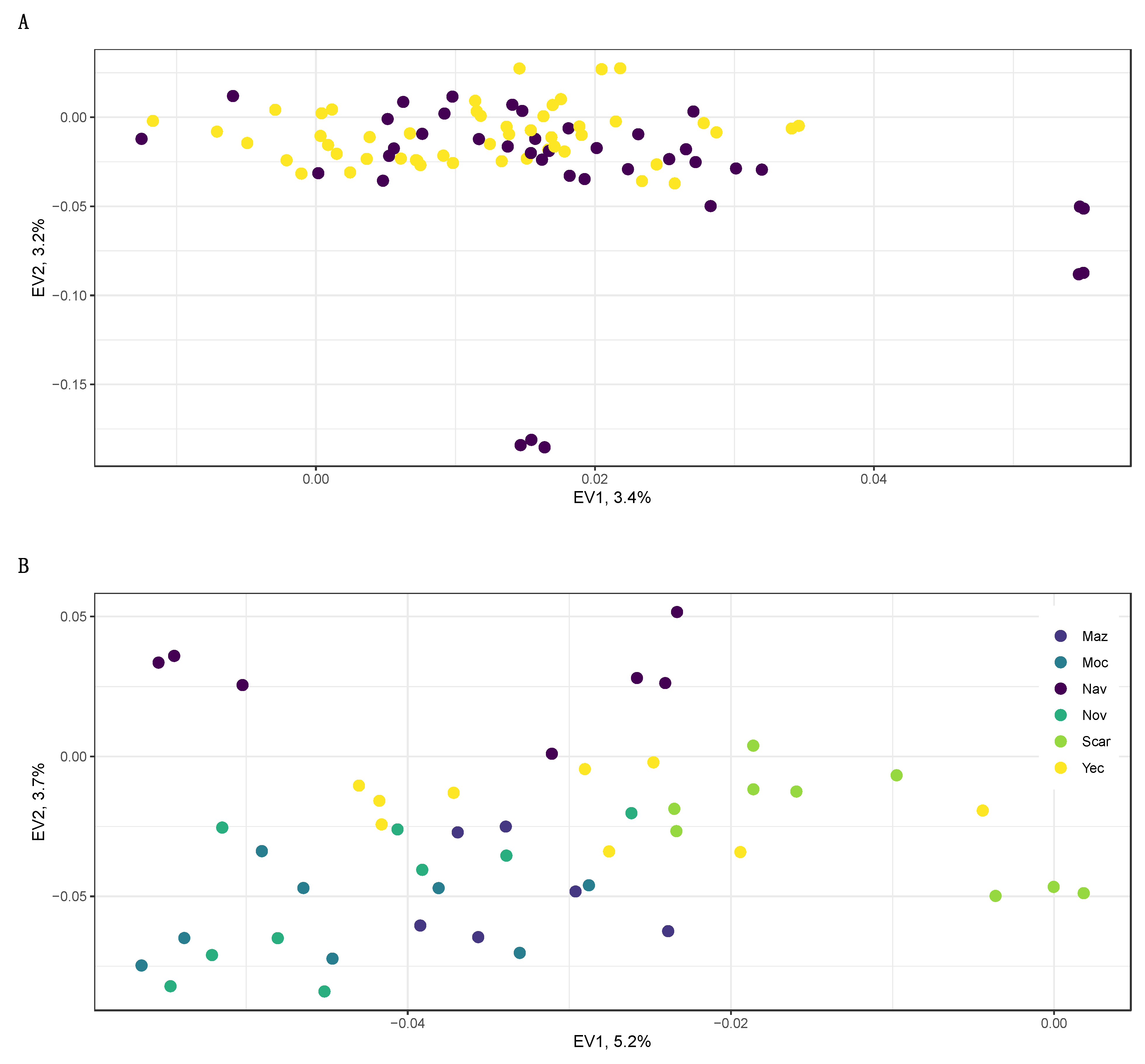
2.1. Population Structure
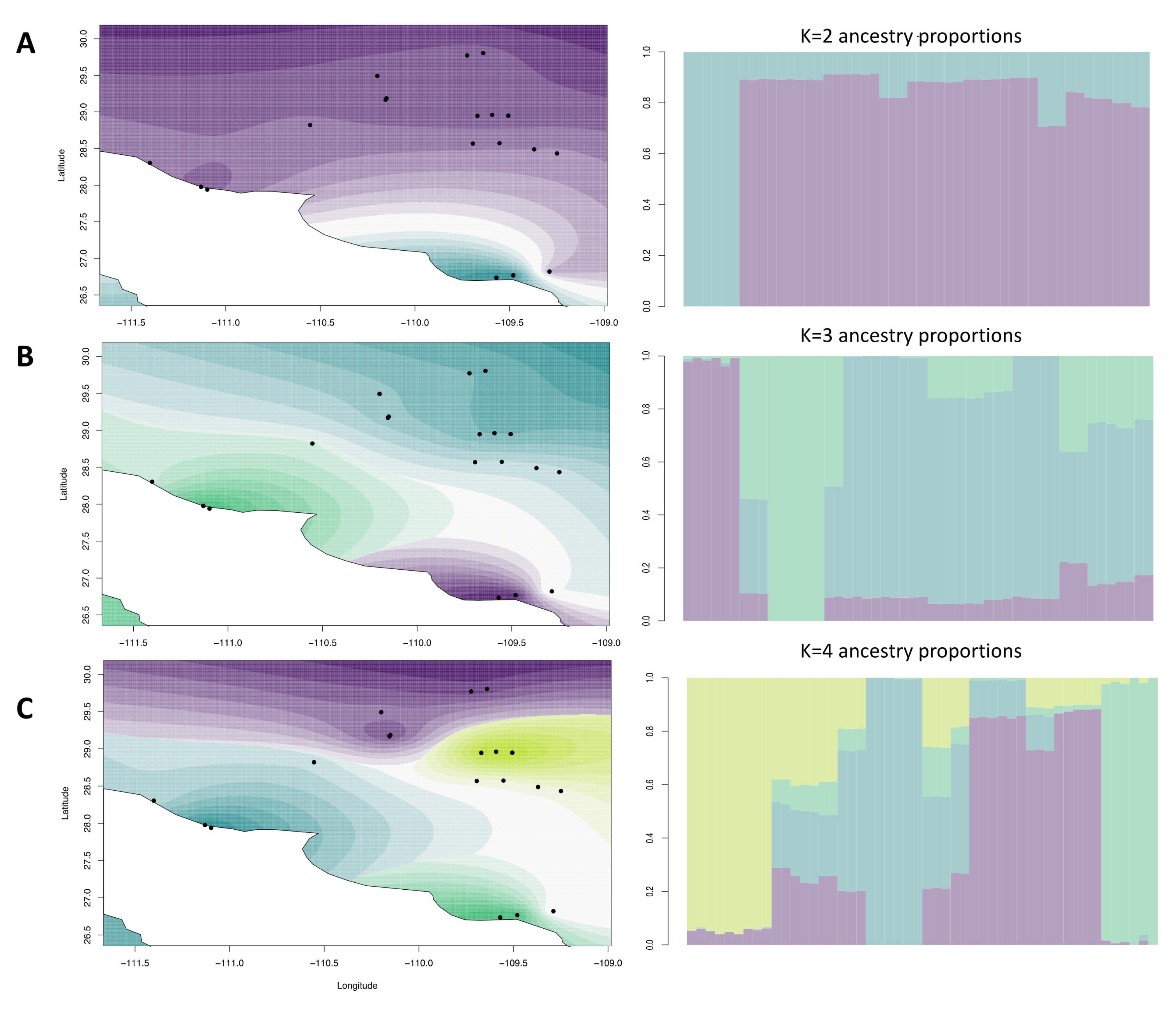
2.2. Spatial Genetics
2.3. Genetic Diversity
3. Discussion
3.1. Population Structure in Wild and Cultivated Agaves
3.2. Genetic Diversity
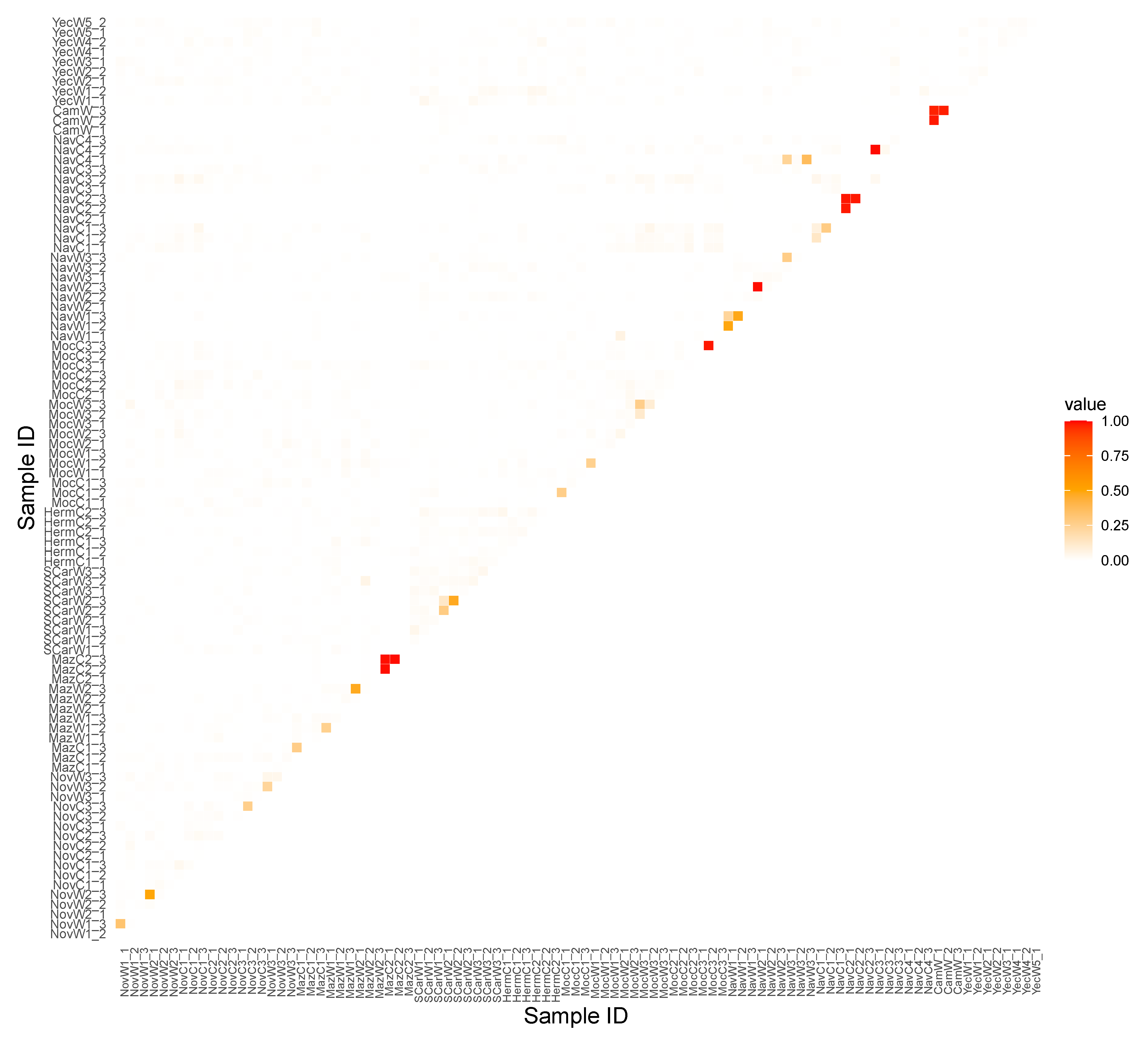
3.3. Inbreeding
3.4. Conservation and Management Implications
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. DNA Extraction, Library Preparation and Sequencing
4.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.4. Patterns of Genetic Structure in Wild and Cultivated Individuals
4.5. Spatial Genetics
4.6. Genetic Diversity
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loveless, M.D.; Hamrick, J.L. Ecological determinants of genetic structure in plant populations. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1984, 15, 65–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. The genetical structure of populations. Ann. Eugen. 1949, 15, 323–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, H.M.; Navarro, L.M.; Martins, I.S. Global biodiversity change: The bad, the good, and the unknown. Ann. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2012, 37, 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, R.J.; el Mousadik, A.; Pons, O. Identifying populations for conservation on the basis of genetic markers. Conserv. Biol. 1998, 12, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrick, J.L.; Godt, M.J.W. Effects of life history traits on genetic diversity in plant species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1996, 351, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, R.; Muller-Landau, H.C. Spatial patterns of seed dispersal, their determinants and consequences for recruitment. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2000, 15, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruzan, M.B.; Hendrickson, E.C. Landscape genetics of plants: Challenges and opportunities. Plant Commun. 2020, 1, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, M.L.; Milligan, B.G.; Strand, A.E. Long-distance seed dispersal in plant populations. Am. J. Bot. 2000, 87, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, R. Long-Distance dispersal of plants. Science 2006, 313, 786–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, E.; Búrquez, A.; Scheinvar, E.; Eguiarte, L.E. Population genetic structure of a widespread bat-pollinated columnar cactus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cresswell, J.E.; Bassom, A.P.; Bell, S.A.; Collins, S.J.; Kelly, T.B. Predicted pollen dispersal by honey-bees and three species of bumble-bees foraging on oil-seed rape: A comparison of three models. Funct. Ecol. 1995, 9, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrick, J.L.; Nason, J.D.; Fleming, T.H.; Nassar, J.M. Genetic diversity in columnar cacti. In Columnar Cacti and Their Mutualists; Fleming, T.H., Valiente-Banuet, A., Eds.; The University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2002; pp. 122–133. [Google Scholar]
- Robledo-Arnuncio, J.J.; Klein, E.K.; Muller-Landau, H.C.; Santamaría, L. Space, time and complexity in plant dispersal ecology. Mov. Ecol. 2014, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamrick, J.L.; Murawski, D.A.; Nason, J.D. The influence of seed dispersal mechanisms on the genetic structure of tropical tree populations. Vegetatio 1993, 107–108, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, J.E.; Pennington, L.K.; Montiel-Molina, J.A.; Toews, D.J.; Hendrickson, B.T.; Sexton, J.P. Rules of plant species ranges: Applications for conservation strategies. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 700962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arizaga, S.; Ezcurra, E.; Peters, E.; de Arellano, F.R.; Vega, E. Pollination ecology of Agave macroacantha (Agavaceae) in a Mexican tropical desert. II. The role of pollinators. Am. J. Bot. 2000, 87, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duminil, J.; Fineschi, S.; Hampe, A.; Jordano, P.; Salvini, D.; Vendramin, G.; Petit, R. Can population genetic structure be predicted from life-history traits? Am. Nat. 2007, 169, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, J.; Schmid, B.; Caldeira, M.C.; Dimitrakopoulos, P.G.; Good, J.; Harris, R.; Hector, A.; Huss-Danell, K.; Jumpponen, A.; Minns, A.; et al. Local adaptation enhances performance of common plant species. Ecol. Lett. 2001, 4, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosil, P.; Funk, D.J.; Ortiz-Barrientos, D. Divergent selection and heterogeneous genomic divergence. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 375–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, L.; Vanoverbeke, J.; Swillen, I.; Mergeay, J.; de Meester, L. Drivers of population genetic differentiation in the wild: Isolation by dispersal limitation, isolation by adaptation and isolation by colonization. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 5983–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.H.D. Human impact on plant gene pools and sampling for their conservation. Biol. Conserv. 1992, 62, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Lehman, C. Human-caused environmental change: Impacts on plant diversity and evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5433–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baucom, R.S.; Estill, J.C.; Cruzan, M.B. The effect of deforestation on the genetic diversity and structure in Acer saccharum (Marsh): Evidence for the loss and restructuring of genetic variation in a natural system. Conserv. Genet. 2005, 6, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, M.R.; Jain, M.S. Genetic Diversity and Erosion in Plants: Case Histories, 1st ed.; Softcover Reprint of the Original 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Khoury, C.K.; Brush, S.; Costich, D.E.; Curry, H.A.; Haan, S.; Engels, J.M.M.; Guarino, L.; Hoban, S.; Mercer, K.L.; Miller, A.J.; et al. Crop genetic erosion: Understanding and responding to loss of crop diversity. New Phytol. 2021, 233, 84–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reif, J.C.; Zhang, P.; Dreisigacker, S.; Warburton, M.L.; van Ginkel, M.; Hoisington, D.; Bohn, M.; Melchinger, A.E. Wheat genetic diversity trends during domestication and breeding. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 110, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Wouw, M.; van Hintum, T.; Kik, C.; van Treuren, R.; Visser, B. Genetic diversity trends in twentieth century crop cultivars: A meta analysis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2010, 120, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Mendoza, A. Los agaves de Mexico. Ciencias 2007, 087, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Eguiarte, L.E.; Jiménez Barrón, O.A.; Aguirre-Planter, E.; Scheinvar, E.; Gámez, N.; Gasca-Pineda, J.; Castellanos-Morales, G.; Moreno-Letelier, A.; Souza, V. Evolutionary ecology of Agave: Distribution patterns, phylogeny, and coevolution (an homage to Howard S. Gentry). Am. J. Bot. 2021, 108, 216–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slauson, L.A. Pollination biology of two chiropterophilous agaves in Arizona. Am. J. Bot. 2000, 87, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, H.S. Agaves of Continental North America, 3rd ed.; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Good-Avila, S.V.; Souza, V.; Gaut, B.S.; Eguiarte, L.E. Timing and rate of speciation in Agave (Agavaceae). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9124–9129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-García, I.; Rendón-Sandoval, F.J.; Blancas, J.; Casas, A.; Moreno-Calles, A.I. The genus Agave in agroforestry systems of Mexico. Bot. Sci. 2019, 97, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, S.; Zapata, A.V. Geographical indications, terroir, and socioeconomic and ecological sustainability: The case of tequila. J. Rural Stud. 2009, 25, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahre, C.J.; Bradbury, D.E. Manufacture of mescal in Sonora, Mexico. Econ. Bot. 1980, 34, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esqueda, M.; Coronado, M.L.; Gutiérrez, A.H.; Fragoso, T. Agave Angustifolia Haw. Técnicas Para el Trasplante de Vitroplantas a Condiciones de Agostadero; Secretaría de Agricultura Ganadería, Pesca y Alimentación (SAGARPA): Uruapan, Mexico, 2013.
- Council for Mescal Regulation. El Mezcal: La Cultura Líquida de México. 2020. Available online: https://comercam-dom.org.mx (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Tetreault, D.; McCulligh, C.; Lucio, C. Distilling agro-extractivism: Agave and tequila production in Mexico. J. Agrar. Chang. 2021, 21, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Freaner, F.; Eguiarte, L.E. The pollination biology of two paniculate agaves (Agavaceae) from northwestern Mexico: Contrasting roles of bats as pollinators. Am. J. Bot. 2003, 90, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno Salazar, S.F.; Esqueda, M.; Martínez, J.; Palomino, G. Tamaño del genoma y cariotipo en Agave angustifolia y A. rhodacantha de Sonora, México. Rev. Fitotec. Mex. 2007, 30, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Lugo, M.; García-Mendoza, A.; Simpson, J.; Solano, E.; Gil-Vega, K. Taxonomic implications of the morphological and genetic variation of cultivated and domesticated populations of the Agave angustifolia complex (Agavoideae, Asparagaceae) in Oaxaca, Mexico. Plant Syst. Evol. 2018, 304, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, H.S. The Agave Family in Sonora; Agriculture Handbook No. 399; Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1972.
- Delgado-Lemus, A.; Torres, I.; Blancas, J.; Casas, A. Vulnerability and risk management of Agave species in the Tehuacán Valley, México. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2014, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Solano, V. La industria del bacanora: Historia y tradición de resistencia en la sierra sonorense. Región Soc. 2007, 19, 105–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna Zamora, R. La Construcción Cultural y Económico del Tequila; Universidad de Guadalajara; Núcleo Universitario Los Belenes: Guadalajara, Mexico, 2015; ISBN 978-607-8336-84-5. [Google Scholar]
- Gil-Vega, K.; Díaz, C.; Nava-Cedillo, A.; Simpson, J. AFLP analysis of Agave tequilana varieties. Plant Sci. 2006, 170, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Ponce, O.; Zizumbo-Villarreal, D.; Martínez-Castillo, J.; Coello-Coello, J.; Colunga-GarcíaMarín, P. Diversity and structure of landraces of Agave grown for spirits under traditional agriculture: A comparison with wild populations of A. angustifolia (Agavaceae) and commercial plantations of A. tequilana. Am. J. Bot. 2009, 96, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, R. Saving the agave. Nature 2005, 438, 1070–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguiarte, L.E.; Aguirre-Planter, E.; Aguirre, X.; Colín, R.; González, A.; Rocha, M.; Scheinvar, E.; Trejo, L.; Souza, V. From Isozymes to Genomics: Population genetics and conservation of Agave in México. Bot. Rev. 2013, 79, 483–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, D.L.; Swift, J.F.; Lance, R.F.; Edwards, C.E. A comparison of patterns of genetic structure in two co-occurring Agave species (Asparagaceae) that differ in the patchiness of their geographical distributions and cultivation histories. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2018, 186, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Dugua, X.; Eguiarte, L.E. Genetic diversity, conservation and sustainable use of wild Agave cupreata and Agave potatorum extracted for mezcal production in Mexico. J. Arid. Environ. 2013, 90, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueredo, C.J.; Casas, A.; Colunga-GarcíaMarín, P.; Nassar, J.M.; González-Rodríguez, A. Morphological variation, management and domestication of ‘maguey alto’ (Agave inaequidens) and ‘maguey manso’ (A. hookeri) in Michoacán, México. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2014, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera-Toledo, D.; Vargas-Ponce, O.; Ascencio-Ramírez, S.; Valadez-Sandoval, L.M.; Pérez-Alquicira, J.; Morales-Saavedra, J.; Huerta-Galván, O.F. Morphological and genetic variation in monocultures, forestry systems and wild populations of Agave maximiliana of Western Mexico: Implications for its conservation. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo, L.; Limones, V.; Peña, G.; Scheinvar, E.; Vargas-Ponce, O.; Zizumbo-Villarreal, D.; Colunga-GarcíaMarín, P. Genetic variation and relationships among agaves related to the production of Tequila and Mezcal in Jalisco. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 125, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchaca, A.; Arteaga, M.C.; Medellin, R.A.; Jones, G. Conservation units and historical matrilineal structure in the tequila bat (Leptonycteris yerbabuenae). Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 23, e01164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, G.S.; Fleming, T.H. Migration and evolution of lesser long-nosed bats Leptonycteris curasoae, inferred from mitochondrial DNA. Mol. Ecol. 1996, 5, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Garza, M.; Arizmendi, M.D.C.; Campos, J.; Martínez-Garcia, M.; Valiente-Banuet, A. Evidences on the migratory movements of the nectar-feeding bat Leptonycteris curasoae in Mexico using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD). J. Arid Environ. 2007, 68, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westberg, E.; Kadereit, J.W. The influence of sea currents, past disruption of gene flow and species biology on the phylogeographical structure of coastal flowering plants. J. Biogeogr. 2009, 36, 1398–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Witte, L.C.; Stöcklin, J. Longevity of clonal plants: Why it matters and how to measure it. Ann. Bot. 2010, 106, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arafeh, R.; Kadereit, J.W. Long-distance seed dispersal, clone longevity and lack of phylogeographical structure in the European distributional range of the coastal Calystegia soldanella (L.) R. Br. (Convolvulaceae). J. Biogeogr. 2006, 33, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieringa, J.G.; Boot, M.R.; Dantas-Queiroz, M.V.; Duckett, D.; Fonseca, E.M.; Glon, H.; Hamilton, N.; Kong, S.; Lanna, F.M.; Mattingly, K.Z.; et al. Does habitat stability structure intraspecific genetic diversity? It’s complicated. Front. Biogeogr. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Arias, G.A.; Caballero-Villalobos, L.; Giudicelli, G.C.; Freitas, L.B. Landscape and climatic features drive genetic differentiation processes in a South American coastal plant. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2021, 21, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savolainen, O.; Lascoux, M.; Merilä, J. Ecological genomics of local adaptation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Garay, B.; Lomelí-Sención, J.; Tapia-Campos, E.; Gutiérrez-Mora, A.; García-Galindo, J.; Rodríguez-Domínguez, J.; Urbina-López, D.; Vicente-Ramírez, I. Morphological and molecular diversity of Agave tequilana Weber var. Azul and Agave angustifolia Haw. var. Lineño. Ind. Crops Prod. 2009, 29, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galinat, W.C. The domestication and genetic erosion of maize. Econ. Bot. 1974, 28, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaut, B.S.; Díez, C.M.; Morrell, P.L. Genomics and the contrasting dynamics of annual and perennial domestication. Trends Genet. 2015, 31, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doebley, J.F.; Gaut, B.S.; Smith, B.D. The molecular genetics of crop domestication. Cell 2006, 127, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantar, M.B.; Nashoba, A.R.; Anderson, J.E.; Blackman, B.K.; Rieseberg, L.H. The genetics and genomics of plant domestication. BioScience 2017, 67, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smýkal, P.; Nelson, M.; Berger, J.; von Wettberg, E. The impact of genetic changes during crop domestication on healthy food development. Agronomy 2018, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Hu, F.; Wang, Z.; Lyu, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Zhao, R.; Tian, Z.; et al. Decrease of gene expression diversity during domestication of animals and plants. BMC Evol. Biol. 2019, 19, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaro-Rojas, G.; Legaria, J.; Rodríguez-Pérez, J. Genetic diversity in populations of pulquero agaves (Agave spp.) in northeastern México state. Rev. Fitotec. Mex. 2007, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Figueredo-Urbina, C.J.; Álvarez-Ríos, G.D.; García-Montes, M.A.; Octavio-Aguilar, P. Morphological and genetic diversity of traditional varieties of agave in Hidalgo State, Mexico. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, B.L.; Olsen, K.M. Genetic perspectives on crop domestication. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peláez, P.; Orona-Tamayo, D.; Montes-Hernández, S.; Valverde, M.E.; Paredes-López, O.; Cibrián-Jaramillo, A. Comparative transcriptome analysis of cultivated and wild seeds of Salvia hispanica (chia). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, G.; Tieman, D.; Zhu, G. Genomics Approaches to Domestication Studies of Horticultural Crops. Hortic. Plant J. 2019, 5, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Du, H.; Li, P.; Shen, Y.; Peng, H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, G.A.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Shi, M.; et al. Pan-Genome of Wild and Cultivated Soybeans. Cell 2020, 182, 162–176.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohra, A.; Kilian, B.; Sivasankar, S.; Caccamo, M.; Mba, C.; McCouch, S.R.; Varshney, R.K. Reap the crop wild relatives for breeding future crops. Trends Biotechnol. 2021, 40, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix-Valdez, L.I.; Vargas-Ponce, O.; Cabrera-Toledo, D.; Casas, A.; Cibrian-Jaramillo, A.; de la Cruz-Larios, L. Effects of traditional management for mescal production on the diversity and genetic structure of Agave potatorum (Asparagaceae) in central Mexico. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2015, 63, 1255–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, R.; Epperson, B.K.; Oyama, K. High levels of genetic variability and inbreeding in two Neotropical dioecious palms with contrasting life histories. Heredity 2007, 99, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonesson, A.K.; Meuwissen, T.H.E. Minimization of rate of inbreeding for small populations with overlapping generations. Genet. Res. 2001, 77, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Trame, A.M.; Coddington, A.J.; Paige, K.N. Field and genetic studies testing optimal outcrossing in Agave schottii, a long-lived clonal plant. Oecologia 1995, 104, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, D.H.; Frankham, R. Correlation between fitness and genetic diversity. Biol. Conserv. 2003, 17, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ruiz, E.P.; Lacher Jr, T.E.; Moreno-Talamantes, A.; Flores Maldonado, J.J. Impacts of land cover change on the plant resources of an endangered pollinator. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKey, D.; Elias, M.; Pujol, B.; Duputié, A. The evolutionary ecology of clonally propagated domesticated plants. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.A. The Genetical Theory of Natural Selection; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1930. [Google Scholar]
- Kondrashov, A.S. Deleterious mutations and the evolution of sexual reproduction. Nature 1988, 336, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Managing Global Genetic Resources: Agricultural Crop Issues and Policies; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, E.L.; Díez-del-Molino, D.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Bertola, L.D.; Borges, F.; Cubric-Curik, V.; de Navascués, M.; Frandsen, P.; Heuertz, M.; Hvilsom, C.; et al. Ancient and historical DNA in conservation policy. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2022, 37, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochemistry 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Lobo, A. Filogenia de Hongos Endófitos del Género Pinus L.: Implementación de Técnicas Moleculares y Resultados Preliminares. Tesis de Licenciatura en Biología (Bachelor’s Thesis in Biology), Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Mexico City, Mexico, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, D.A.R.; Overcast, I. ipyrad: Interactive assembly and analysis of RADseq datasets. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2592–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, T.D.; Fu, W.; Mychaleckyj, J.C.; Logsdon, B.; Auer, P.; Carlson, C.S.; Leal, S.M.; Smith, J.D.; Rieder, M.J.; Bamshad, M.J.; et al. Rare variation facilitates inferences of fine-scale population structure in humans. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 32, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pembleton, L.W.; Cogan, N.O.I.; Forster, J.W. StAMPP: An R package for calculation of genetic differentiation and structure of mixed-ploidy level populations. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, D.H.; Novembre, J.; Lange, K. Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, D.H.; Lange, K. Enhancements to the ADMIXTURE algorithm for individual ancestry estimation. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Levine, D.; Shen, J.; Gogarten, S.M.; Laurie, C.; Weir, B.S. A high-performance computing toolset for relatedness and principal component analysis of SNP data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3326–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caye, K.; Deist, T.M.; Martins, H.; Michel, O.; François, O. TESS3: Fast inference of spatial population structure and genome scans for selection. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 16, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frichot, E.; Schoville, S.; Bouchard, G.; François, O. Correcting principal component maps for effects of spatial autocorrelation in population genetic data. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jombart, T. adegenet: A R package for the multivariate analysis of genetic markers. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1403–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougeard, S.; Dray, S. Supervised Multiblock Analysis in R with the ade4 Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2018, 86, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thioulouse, J.; Chessel, D.; Champely, S. Multivariate analysis of spatial patterns: A unified approach to local and global structures. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 1995, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersts, P. Geographic Distance Matrix Generatos (v. 1.2.3). American Museum of Natural History, Center for Biodiversity and Conservation. Available online: https://biodiversityinformatics.amnh.org/open_source/gdmg/ (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Goudet, J. hierfstat, a package for r to compute and test hierarchical F-statistics. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2005, 5, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alho, J.S.; Välimäki, K.; Merilä, J. Rhh: An R extension for estimating multilocus heterozygosity and heterozygosity–heterozygosity correlation. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 720–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffel, M.A.; Esser, M.; Kardos, M.; Humble, E.; Nichols, H.; David, P.; Hoffman, J.I. inbreedR: An R package for the analysis of inbreeding. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.C.; Visscher, P.M.; Goddard, M.E. Quantification of inbreeding due to distant ancestors and its detection using dense single nucleotide polymorphism data. Genetics 2011, 189, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lee, S.H.; Goddard, M.E.; Visscher, P.M. GCTA: A tool for genome-wide complex trait analysis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, T.C.; Coltman, D.; Pemberton, J.; Slate, J.; Spalton, J.A.; Guinness, F.E.; Smith, J.A.; Pilkington, J.G.; Clutton–Brock, T.H. Estimating the prevalence of inbreeding from incomplete pedigrees. Proc. R. Soc. B 2002, 269, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Wang, J. coancestry: A program for simulating, estimating and analysing relatedness and inbreeding coefficients. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 11, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. Estimating pairwise relatedness in a small sample of individuals. Heredity 2017, 119, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamvar, Z.N.; Tabima, J.F.; Grünwald, N.J. Poppr: An R package for genetic analysis of populations with clonal, partially clonal, and/or sexual reproduction. PeerJ 2014, 2, e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Diversity Index | Wild Populations | Full Dataset Wild | Cultivated | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| South Coastal | Central Coastal | Inland | |||
| N | 6 | 9 | 35 | 50 | 42 |
| sMLH | 1.00 (0.063) | 0.98 (0.011) | 1.00 (0.018) | 0.99 (0.014) | 1.00 (0.03) |
| MLH | 0.22 (0.013) | 0.22 (0.002) | 0.22 (0.004) | 0.22 (0.003) | 0.22 (0.002) |
| IR | 0.05 (0.048) | 0.06 (0.007) | 0.06 (0.014) | 0.05 (0.011) | 0.05 (0.02) |
| Fis | 0.13 (0.054) | 0.14 (0.009) | 0.13 (0.016) | 0.13 (0.012) | 0.13 (0.03) |
| Fhat3 | 0.11 (0.047) | 0.13 (0.001) | 0.13 (0.017) | 0.13 (0.012) | 0.13 (0.02) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klimova, A.; Ruiz Mondragón, K.Y.; Molina Freaner, F.; Aguirre-Planter, E.; Eguiarte, L.E. Genomic Analyses of Wild and Cultivated Bacanora Agave (Agave angustifolia var. pacifica) Reveal Inbreeding, Few Signs of Cultivation History and Shallow Population Structure. Plants 2022, 11, 1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11111426
Klimova A, Ruiz Mondragón KY, Molina Freaner F, Aguirre-Planter E, Eguiarte LE. Genomic Analyses of Wild and Cultivated Bacanora Agave (Agave angustifolia var. pacifica) Reveal Inbreeding, Few Signs of Cultivation History and Shallow Population Structure. Plants. 2022; 11(11):1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11111426
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlimova, Anastasia, Karen Y. Ruiz Mondragón, Francisco Molina Freaner, Erika Aguirre-Planter, and Luis E. Eguiarte. 2022. "Genomic Analyses of Wild and Cultivated Bacanora Agave (Agave angustifolia var. pacifica) Reveal Inbreeding, Few Signs of Cultivation History and Shallow Population Structure" Plants 11, no. 11: 1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11111426
APA StyleKlimova, A., Ruiz Mondragón, K. Y., Molina Freaner, F., Aguirre-Planter, E., & Eguiarte, L. E. (2022). Genomic Analyses of Wild and Cultivated Bacanora Agave (Agave angustifolia var. pacifica) Reveal Inbreeding, Few Signs of Cultivation History and Shallow Population Structure. Plants, 11(11), 1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11111426







