Comparative Effect of Inoculation of Phosphorus-Solubilizing Bacteria and Phosphorus as Sustainable Fertilizer on Yield and Quality of Mung Bean (Vigna radiata L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Agronomic Parameters Analysis
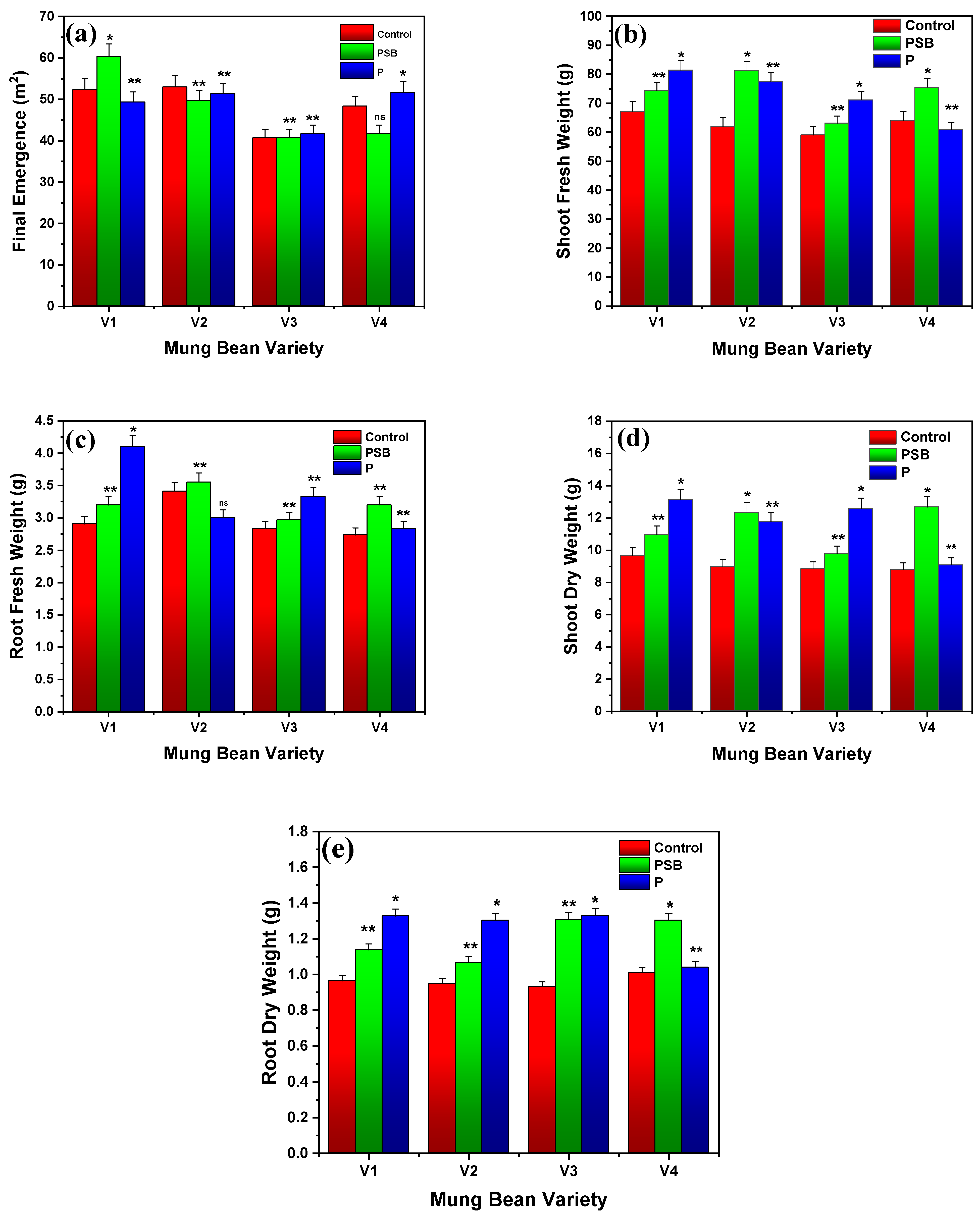
2.1.1. Final Emergence
2.1.2. Root/Shoot Fresh and Dry Weight
2.1.3. Numbers of Leaves, Leaf Area, and Leaf Index
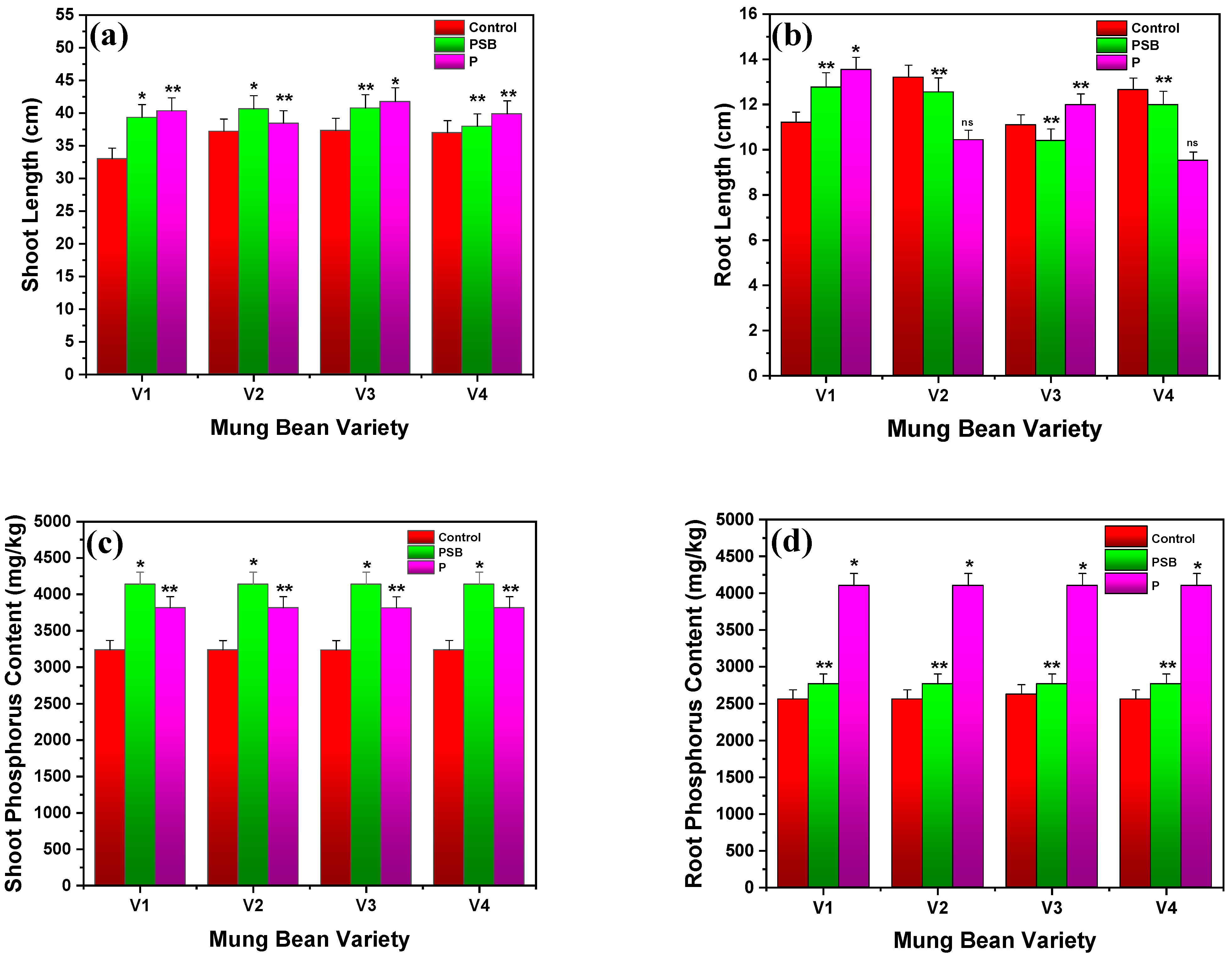
2.1.4. Shoot and Root Length
2.1.5. Root and Shoot Phosphorus Contents
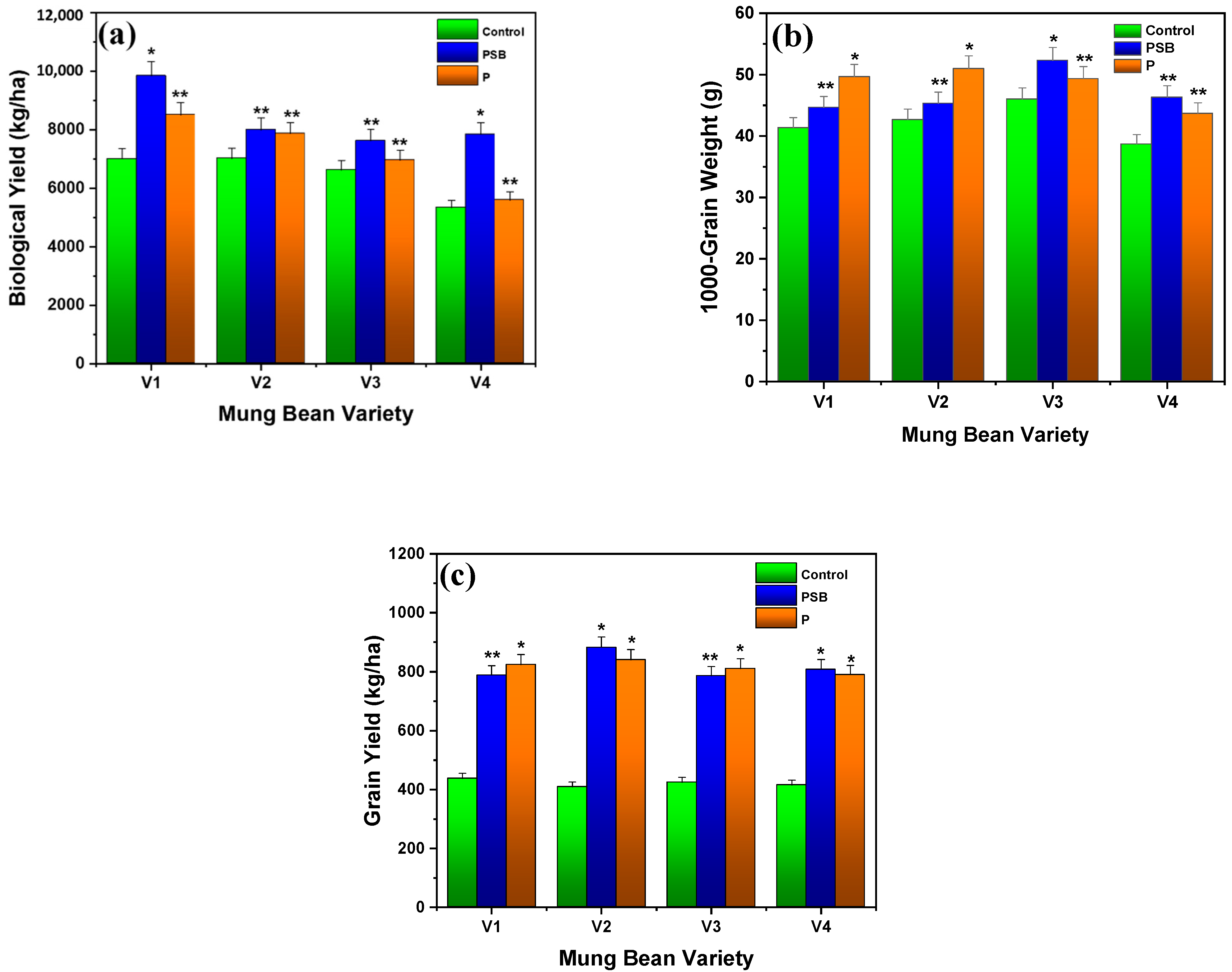
2.1.6. Biological Yield
2.2. Yield Parameters Assessment
2.2.1. Grain Yield
2.2.2. Number of Pods, Pod-Bearing Branches, and Grains
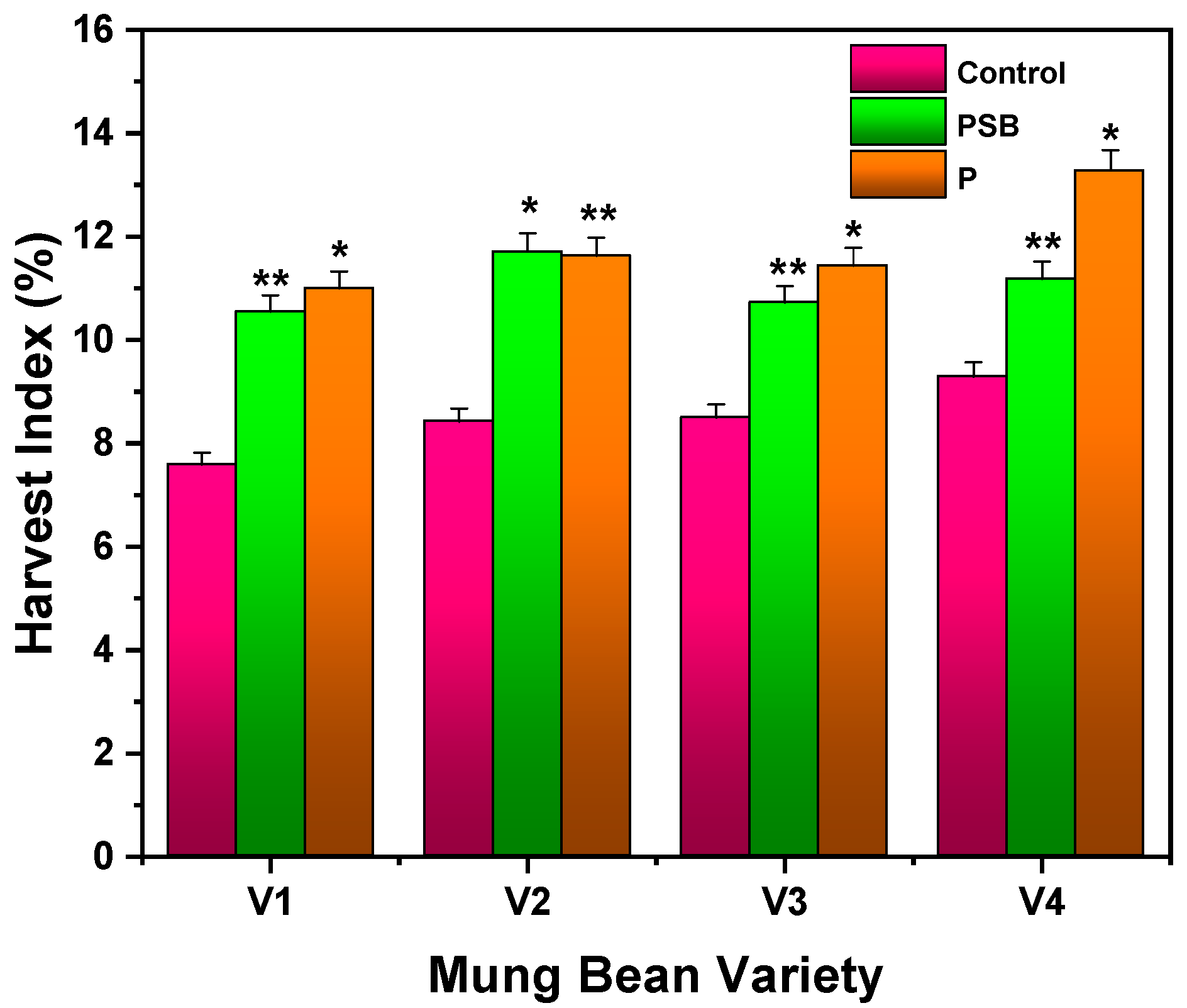
2.2.3. Harvest Index
2.3. Physiological Parameters
2.4. Soil Parameters Analysis
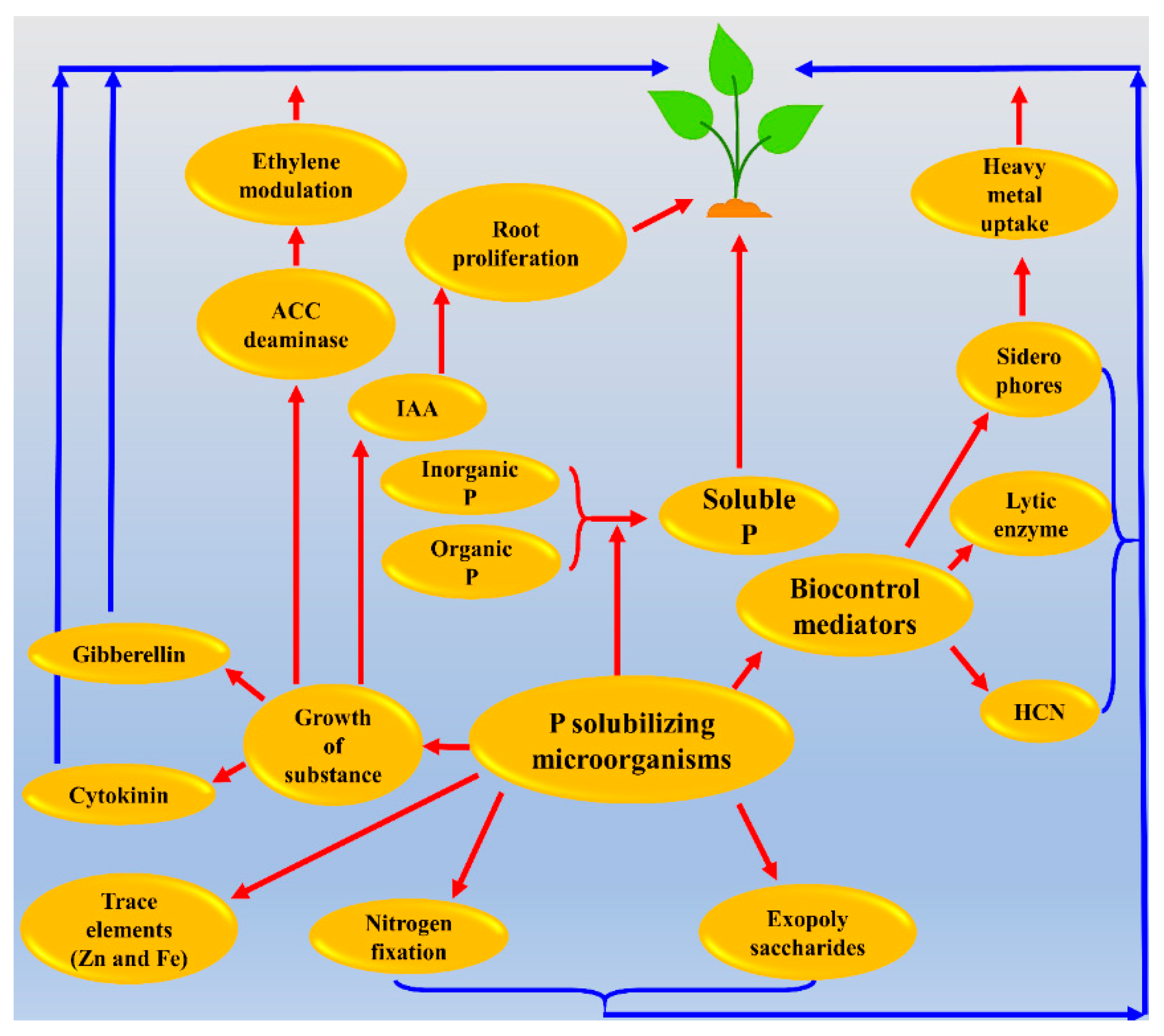
2.5. Mechanism of P Solubilization by PSB
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Soil Sampling, Characteristics, and Field Layout Plan
3.2. Experimental Design
3.3. Preparation and Application of Inoculum
3.4. Soil Management and Crop Husbandry
3.5. Measurements
3.5.1. Agronomic Parameters
3.5.2. Physiological and Yield-Related Parameters
3.5.3. Soil Parameters
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fahad, S.; Wang, J. Climate change, vulnerability, and its impacts in rural Pakistan: A review. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2020, 27, 1334–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandio, A.A.; Jiang, Y.; Rauf, A.; Mirani, A.A.; Shar, R.U.; Ahmad, F.; Shehzad, K. Does energy-growth and environment quality matter for agriculture sector in Pakistan or not? An application of cointegration approach. Energies 2019, 12, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ullah, A.; Shah, T.M.; Farooq, M. Pulses Production in Pakistan: Status, constraints and opportunities. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2020, 14, 549–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abro, A.A.; Awan, N.W. Comparative analysis of profitability of major and minor crops in Pakistan. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2020, 19, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi-Shen, Z.; Shuai, S.; FitzGerald, R. Mung bean proteins and peptides: Nutritional, functional and bioactive properties. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 62, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meena, S.K.; Gayacharan, M.P.S.; Pandey, R. Photosynthetic and yield traits identified through multivariate analysis in mungbean exhibiting tolerance to the combined stresses of low phosphorus and drought. Indian J. Genet. 2020, 80, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasution, F.M.; Hasanah, Y.; Mariati, M. Production Response of Mung Bean (Vigna radiata L.) on the Application of Phosphorus Fertilizer and Oil Palm Bunch Ash. Indones. J. Agric. Res. 2020, 3, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.R.P.; Aski, M.S.; Mishra, G.P.; Dikshit, H.K.; Singh, A.; Pandey, R.; Singh, M.P.; Ramtekey, V.; Rai, N.; Nair, R.M. Genetic variation for root architectural traits in response to phosphorus deficiency in mungbean at the seedling stage. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0221008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namlı, A.; Mahmood, A.; Sevilir, B.; Özkır, E. Effect of phosphorus solubilizing bacteria on some soil properties, wheat yield and nutrient contents. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2017, 6, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tahir, M.; Khalid, U.; Ijaz, M.; Shah, G.M.; Naeem, M.A.; Shahid, M.; Mahmood, K.; Ahmad, N.; Kareem, F. Combined application of bio-organic phosphate and phosphorus solubilizing bacteria (Bacillus strain MWT 14) improve the performance of bread wheat with low fertilizer input under an arid climate. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, N.M. Isolation and screening of phosphate solubilizing bacteria from paddy Rhizosphere Soil. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2020, 9, 477–485. [Google Scholar]
- Pastore, G.; Kernchen, S.; Spohn, M. Biochemistry Microbial solubilization of silicon and phosphorus from bedrock in relation to abundance of phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria in temperate forest soils. Soil Biol. 2020, 151, 108050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Bonilla, G.A.; Durrer, A.; Cardoso, E.J. Use of compost and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria affect sugarcane mineral nutrition, phosphorus availability, and the soil bacterial community. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 157, 103760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, S.; Xiao, J.; Song, C.; Zhou, Y. Community composition specificity and potential role of phosphorus solubilizing bacteria attached on the different bloom-forming cyanobacteria. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 205, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walpola, B.; Hettiarachchi, R. Plant Growth Promoting Traits of Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria Isolated from Agricultural Lands in Sothern Sri Lanka. J. Food Agric. 2020, 13, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.N.; Barua, S.; Ali, H.; Ali, M.N.; Chowdhury, M.S.H.; Hasan, M.M.; Ferdous, T.; Eti, F.S.; Khayer, A.; Hossen, K. Effects of Phosphorus Fertilization on Hybrid Varieties of mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] in a Salinity Prone Area of the Subtropics. Acta Agrobot. 2020, 73, 7338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, W.; Bashir, S.; Hanif, S.; Sher, A.; Sattar, A.; Wasaya, A.; Atif, H.; Hussain, M. Phosphorus solubilizing bacteria and growth and productivity of mung bean (Vigna radiata). Pak. J. Bot. 2017, 49, 331–336. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Y.; Xiao, L.; Liu, R. Response of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphorus solubilizing bacteria to remediation abandoned solid waste of coal mine. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2019, 6, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demeke, M.; Tesema, M.; Tana, T.; Abdulahi, J. Response of Mung Bean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] to Levels of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Fertilizer under Irrigation in Central Ethiopia. Asian Plant Res. J. 2020, 6, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widdig, M.; Schleuss, P.M.; Weig, A.R.; Guhr, A.; Biederman, L.A.; Borer, E.T.; Crawley, M.J.; Kirkman, K.P.; Seabloom, E.; Wragg, P. Nitrogen and phosphorus additions alter the abundance of phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria and phosphatase activity in grassland soils. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mpanga, I.K.; Nkebiwe, P.M.; Kuhlmann, M.; Cozzolino, V.; Piccolo, A.; Geistlinger, J.; Berger, N.; Ludewig, U.; Neumann, G. The form of N supply determines plant growth promotion by P-solubilizing microorganisms in maize. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parastesh, F.; Alikhani, H.A.; Etesami, H. Vermicompost enriched with phosphate–solubilizing bacteria provides plant with enough phosphorus in a sequential cropping under calcareous soil conditions. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 221, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandare, R.N.; Chandra, R.; Pareek, N.; Raverkar, K.P. Carrier-based and liquid bioinoculants of Azotobacter and PSB saved chemical fertilizers in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and enhanced soil biological properties in Mollisols. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viruel, E.; Erazzú, L.E.; Martínez Calsina, L.; Ferrero, M.A.; Lucca, M.E.; Siñeriz, F. Inoculation of maize with phosphate solubilizing bacteria: Effect on plant growth and yield. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2014, 14, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rafique, M.; Sultan, T.; Ortas, I.; Chaudhary, H.J. Enhancement of maize plant growth with inoculation of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and biochar amendment in soil. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 63, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sial, N.A.; Abro, S.A.; Abbas, M.; Irfan, M.; Memon, M.Y. Studies on different levels of phosphorus fertilizer and phosphorus solubilizing bacteria in mungbean (Vigna radiata L.). Pak. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 14, 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Chattha, M.U.; Hassan, M.U.; Khan, I.; Chattha, M.B.; Ashraf, I.; Ishque, W.; Farooq, M.U.; Usman, M.; Kharal, M. Effect of Different Nitrogen and Phosphorus Fertilizer Levels in Combination with Nitrogen and Phosphorus Solubilizing Inoculants on the Growth and Yield of Mung bean. Pak. J. Life Soc. Sci. 2017, 15, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ram, H.; Malik, S.; Dhaliwal, S.; Kumar, B.; Singh, Y. Growth and productivity of wheat affected by phosphorus-solubilizing fungi and phosphorus levels. Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 61, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zafar, N.; Munir, M.K.; Ahmed, S.; Zafar, M. Phosphorus Solubilizing Bacteria (PSB) in combination with different Fertilizer sources to enhance yield performance of chickpea. Life Sci. J. 2020, 17, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbisa, A.; Amdemariam, T. Effects of NPS and Bio-organic Fertilizers on Yield and Yield Components of Faba bean (Vicia faba L.) in Gozamin District, East Gojjam, Ethiopia. Preprint 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.K.; Joshi, P.; Suyal, P.; Bisht, J.K.; Bhatt, J.C. Potential of phosphate solubilising microorganisms in crop production. Bior. Sus. Plant Nut. Man 2014, 8, 201–212. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Shastri, B. Role of Phosphate-Solubilising Microorganisms in Sustainable Agricultural Development. In Agro-Environmental Sustainability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 271–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, A.; Khan, M.S.; Rizvi, A.; Saif, S.; Ahmad, B.; Shahid, M. Role of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria in legume improvement. In Microbes for Legume Improvement; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 175–197. [Google Scholar]
- Halder, A.; Mishra, A.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Chakrabartty, P. Solubilization of rock phosphate by Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 1990, 36, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.B.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Trivedi, M.H.; Gobi, T.A. Phosphate solubilizing microbes: Sustainable approach for managing phosphorus deficiency in agricultural soils. SpringerPlus 2013, 2, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gamalero, E.; Glick, B.R. Mechanisms used by plant growth-promoting bacteria. In Bacteria in Agrobiology: Plant Nutrient Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 17–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Patel, J.S.; Bahadur, I.; Meena, V.S. The molecular mechanisms of KSMs for enhancement of crop production under organic farming. In Potassium Solubilizing Microorganisms for Sustainable Agriculture; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaz, S.; Batool, S.; Anjum, M.A.; Naz, S.; Qayyum, M.F.; Naqqash, T.; Shah, K.H.; Ali, S. Effects of inoculation of root-associative Azospirillum and Agrobacterium strains on growth, yield and quality of pea (Pisum sativum L.) grown under different nitrogen and phosphorus regimes. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 270, 109401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribaudo, C.; Zaballa, J.I.; Golluscio, R. Effect of the phosphorus-solubilizing bacterium Enterobacter Ludwigii on barley growth promotion. Am. Sci. Res. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2020, 63, 144–157. [Google Scholar]
- Di Mola, I.; Ottaiano, L.; Cozzolino, E.; Senatore, M.; Giordano, M.; El-Nakhel, C.; Sacco, A.; Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G.; Mori, M. Plant-based biostimulants influence the agronomical, physiological, and qualitative responses of baby rocket leaves under diverse nitrogen conditions. Plants 2019, 8, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marín-Ortiz, J.C.; Gutierrez-Toro, N.; Botero-Fernández, V.; Hoyos-Carvajal, L.M. Linking physiological parameters with visible/near-infrared leaf reflectance in the incubation period of vascular wilt disease. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estefan, G.; Sommer, R.; Ryan, J. Methods of Soil, Plant, and Water Analysis: A Manual for the West Asia and North Africa Region: Third Edition; International Center for Agriculture Research in the Dry Area (ICARDA): Beirut, Lebanon, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F.; Ou, Y.; Ou, Q.; Zeng, L.; Yu, H.; Zheng, J.; Gao, L.; Li, W.; Li, N.; Peng, C. The invasive potential of a hybrid species: Insights from soil chemical properties and soil microbial communities. J. Plant Ecol. 2020, 13, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasaya, A.; Abbas, T.; Yasir, T.A.; Sarwar, N.; Aziz, A.; Javaid, M.M.; Akram, S. Mitigating Drought Stress in Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) Through Exogenous Application of β-Aminobutyric Acid. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mung Bean Variety | Number of Leaves (per Plant) | Leaf Area (cm−2) | Leaf Area Index (cm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | PSB | P | Control | PSB | P | Control | PSB | P | |
| V1 | 18 ± 0.36 | 21 ± 0.42 | 18 ± 0.36 | 582.22 ± 11.64 | 743.55 ± 14.87 | 628.88 ± 12.57 | 1.86 ± 0.037 | 2.14 ± 0.042 | 1.96 ± 0.039 |
| V2 | 16 ± 0.32 | 17 ± 0.34 | 18 ± 0.36 | 474.77 ± 9.49 | 508.11 ± 10.16 | 622.77 ± 12.45 | 1.51 ± 0.030 | 1.60 ± 0.033 | 1.78 ± 0.035 |
| V3 | 16 ± 0.32 | 17 ± 0.34 | 16 ± 0.32 | 486.31 ± 9.72 | 546.44 ± 10.92 | 628.55 ± 12.57 | 1.59 ± 0.031 | 1.69 ± 0.033 | 1.81 ± 0.036 |
| V4 | 17 ± 0.34 | 22 ± 0.44 | 19 ± 0.38 | 461.66 ± 9.23 | 563.88 ± 11.27 | 522.33 ± 10.44 | 1.58 ± 0.031 | 1.66 ± 0.033 | 1.59 ± 0.032 |
| Parameter | Mung Bean Variety (μmol/m2 s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | |
| Momentary fluorescent rate (MF) | ||||
| Control | 353.21 ± 7.06 | 296.13 ± 5.92 | 298.35 ± 5.96 | 348.66 ± 6.97 |
| PSB | 360.33 ± 7.20 | 365.33 ± 7.31 | 337.22 ± 6.74 | 355.33 ± 7.10 |
| P | 378.19 ± 7.56 | 400.53 ± 8.01 | 301.33 ± 6.03 | 320.27 ± 6.40 |
| Photosynthetic active radiation (PSAR) | ||||
| Control | 293.33 ± 5.86 | 326.66 ± 6.53 | 325.33 ± 6.50 | 290.66 ± 5.81 |
| PSB | 297.65 ± 5.93 | 364.32 ± 7.28 | 293.42 ± 5.86 | 302.14 ± 6.04 |
| P | 337.54 ± 6.75 | 305.32 ± 6.10 | 336.67 ± 6.73 | 291.33 ± 5.83 |
| Photosynthetic yield (PSY) | ||||
| Control | 0.69 ± 0.014 | 0.68 ± 0.014 | 0.67 ± 0.013 | 0.67 ± 0.013 |
| PSB | 0.69 ± 0.014 | 0.70 ± 0.014 | 0.68 ± 0.013 | 0.75 ± 0.015 |
| P | 0.63 ± 0.012 | 0.68 ± 0.013 | 0.69 ± 0.014 | 0.68 ± 0.013 |
| Electron transport rate (ETR) | ||||
| Control | 84.32 ± 1.68 | 90.21 ± 1.80 | 89.36 ± 1.78 | 84.93 ± 1.69 |
| PSB | 79.73 ± 1.59 | 87.72 ± 1.75 | 83.21 ± 1.66 | 96.12 ± 1.92 |
| P | 90.16 ± 1.80 | 90.86 ± 1.81 | 99.24 ± 1.98 | 95.36 ± 1.90 |
| Parameter | Concentration |
|---|---|
| Texture | Sandy loam |
| Sand (%) | 58.20 ± 0.62 |
| Silt (%) | 30.10 ± 0.81 |
| Clay (%) | 12.05 ± 0.31 |
| pH | 7.89 ± 0.05 |
| Electrical conductivity (dS/m) | 1.27 ± 0.05 |
| Phosphorus (mg/kg) | 8.65 ± 0.22 |
| Potassium (mg/L) | 128.32 ± 1.96 |
| Total nitrogen (%) | 0.050 ± 0.001 |
| Organic matter (%) | 0.62 ± 0.025 |
| Month | Week | Average Temperature (°C) | Mean Relative Humidity (%) | Total Rainfall (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| July | 22 Jul–28 Jul | 30.28 ± 1.51 | 71.42 ± 3.57 | 17.61 ± 0.88 |
| 29 Jul–4 Aug | 32.71 ± 1.63 | 71.28 ± 3.56 | 0.60 ± 0.03 | |
| August | 5 Aug–11 Aug | 32.70 ± 1.64 | 78.85 ± 3.94 | 65.62 ± 3.28 |
| 12 Aug–18 Aug | 33.22 ± 1.66 | 73.85 ± 3.69 | 11.00 ± 0.55 | |
| 19 Aug–25 Aug | 33.44 ± 1.67 | 67.00 ± 3.35 | 3.41 ± 0.17 | |
| 26 Aug–01 Sep | 34.34 ± 1.72 | 69.28 ± 3.46 | 0.90 ± 0.04 | |
| September | 02 Sep–08 Sep | 33.65 ± 1.68 | 65.71 ± 3.28 | --- |
| 09 Sep–15 Sep | 34.80 ± 1.74 | 67.00 ± 3.35 | --- | |
| 16 Sep–22 Sep | 32.28 ± 1.61 | 72.71 ± 3.63 | 6.63 ± 0.33 | |
| 23 Sep–29 Sep | 31.05 ± 1.55 | 73.42 ± 3.67 | 15.20 ± 0.76 | |
| October | 30 Sep–06 Oct | 27.18 ± 1.35 | 76.92 ± 3.84 | 1.91 ± 0.09 |
| 07 Oct–13 Oct | 26.72 ± 1.33 | 62.07 ± 3.10 | 6.41 ± 0.32 | |
| 14 Oct–20 Oct | 25.61 ± 1.28 | 69.21 ± 3.46 | 30.30 ± 1.51 | |
| 21 Oct–27 Oct | 24.47 ± 1.22 | 73.85 ± 3.69 | --- | |
| November | 28 Oct–03 Nov | 24.05 ± 1.20 | 77.00 ± 3.85 | 1.34 ± 0.067 |
| 04 Nov–10 Nov | 20.74 ± 1.04 | 72.01 ± 3.60 | --- |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bilal, S.; Hazafa, A.; Ashraf, I.; Alamri, S.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Ramzan, A.; Qamar, N.; Sher, F.; Naeem, M. Comparative Effect of Inoculation of Phosphorus-Solubilizing Bacteria and Phosphorus as Sustainable Fertilizer on Yield and Quality of Mung Bean (Vigna radiata L.). Plants 2021, 10, 2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102079
Bilal S, Hazafa A, Ashraf I, Alamri S, Siddiqui MH, Ramzan A, Qamar N, Sher F, Naeem M. Comparative Effect of Inoculation of Phosphorus-Solubilizing Bacteria and Phosphorus as Sustainable Fertilizer on Yield and Quality of Mung Bean (Vigna radiata L.). Plants. 2021; 10(10):2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102079
Chicago/Turabian StyleBilal, Shahid, Abu Hazafa, Imran Ashraf, Saud Alamri, Manzer H. Siddiqui, Amina Ramzan, Nimra Qamar, Farooq Sher, and Muhammad Naeem. 2021. "Comparative Effect of Inoculation of Phosphorus-Solubilizing Bacteria and Phosphorus as Sustainable Fertilizer on Yield and Quality of Mung Bean (Vigna radiata L.)" Plants 10, no. 10: 2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102079
APA StyleBilal, S., Hazafa, A., Ashraf, I., Alamri, S., Siddiqui, M. H., Ramzan, A., Qamar, N., Sher, F., & Naeem, M. (2021). Comparative Effect of Inoculation of Phosphorus-Solubilizing Bacteria and Phosphorus as Sustainable Fertilizer on Yield and Quality of Mung Bean (Vigna radiata L.). Plants, 10(10), 2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102079








