Abstract
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1; SERPINE1) is a prominent member of the serine protease inhibitor superfamily (SERPIN) and a causative factor of multi-organ fibrosis as well as a key regulator of the tissue repair program. PAI-1 attenuates pericellular proteolysis by inhibiting the catalytic activity of both urokinase and tissue-type protease activators (uPA and tPA) effectively modulating, thereby, plasmin-mediated fibrinolysis and the overall pericellular proteolytic cascade. PAI-1 also impacts cellular responses to tissue injury and stress situations (growth, survival, migration) by titering the locale and temporal activation of multimeric cell-surface signaling complexes. This review will describe PAI-1 structure and function and detail the role of PAI-1 in the tissue repair program with an emphasis on cutaneous wound healing.
Keywords:
SERPINE1; PAI-1; migration; proliferation; pericellular proteolysis; tiplaxtinin; fibrosis; TGF-β; wound healing; apoptosis 1. Background
Since its discovery in 1984, PAI-1 (plasminogen activator inhibitor-1) [1] has been implicated in the pathophysiology of several clinically-significant human disorders, including cardiovascular disease, anomalies of wound healing, cancer and tissue fibrosis. PAI-1 is an early response-to-injury, acute phase gene, the expression of which is elevated by numerous growth factors and cytokines. PAI-1 is in fact, the most highly-upregulated member of the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β1)-responsive gene set and is a critical component of the TGF-β-mediated tissue remodeling program. PAI-1 is expressed in an assortment of cultured cells (e.g., vascular smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, fibroblasts) and participates in the temporal and spatial control of normal and abnormal wound repair.
2. Structure and Chemical Antagonists
PAI-1 is a single chain glycoprotein and a clade E member of the serine protease inhibitor (SERPIN) superfamily that consists of over 40 proteins with approximately 35% homology. Similar in tertiary structure to other SERPINs, PAI-1 is comprised of three beta-sheets (A, B, C), nine alpha helices (A-I), an N-terminal signal peptide and a C-terminal reactive center loop (RCL). Unlike other SERPINs, PAI-1 exists in three distinct conformations (active, latent, substrate/cleaved; Figure 1). PAI-1 is initially synthesized in the active conformation but spontaneously converts to a latent form with a rather short active half-life of 1–2 h that can be extended 2- to 10-fold upon binding of PAI-1 to vitronectin [2,3,4,5]. Furthermore, the latent conformation can be reversed by denaturants [6] and negatively-charged phospholipids [7]. In the active conformation, reactive center residues (Arg346/Met347) reside in a “strained loop” region acting as “bait” for the urokinase and tissue-type serine protease activators (uPA and tPA, respectively). During the interaction of PAI-1 with its target proteases, the scissile bond in the reactive center loop (RCL) is cleaved by the target protease in order to form a covalent ester bond between the hydroxyl group on the serine of the enzyme and the carboxyl group of PAI-1. Upon cleavage, the N-terminus of the RCL of PAI-1 inserts into β-sheet A, while the RCL C-terminus forms strand s1C in β-sheet C producing a 70Å separation of the P1 and P1’ residues, thereby deforming the protease and rendering it inactive. This cleavage also renders PAI-1 anti-proteolytically inactive, giving rise to its designation as a “suicide inhibitor”. A substrate form of PAI-1 exists as well. In this case, PAI-1 is cleaved by its target proteases without formation of PAI-1: Protease complex. Cleaved PAI-1 cannot interact with proteinases due to spatial distortion, allowing for increased plasmin activation [8,9,10,11].
Due to the complexity of PAI-1 structure and functions, several low-molecular weight PAI-1 antagonists were developed to evaluate specific contributions of this SERPIN to disease pathology (reviewed in [12]). Tiplaxtinin (PAI-039), the most well studied small-molecule inhibitor, attenuates asthmatic episodes, reduces both hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia, suppresses angiogenesis and has recently been identified as a potent inhibitor of carotid stenosis by stimulating vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. Similarly, other compounds that share a similar binding site on PAI-1 as tiplaxtinin have been synthesized [21,22]. One of these, TM5275 effectively reduces macrophage migration and inhibits lung fibrosis [23,24]. The mechanism by which these inhibitors (tiplaxtinin, TM5275) antagonize the anti-fibrinolytic activity of PAI-1 appears to be through promotion of a substrate-like conformation resulting in PAI-1 cleavage and impaired complexing with, and inhibition of, uPA and tPA [25,26]. While the exact binding site for tiplaxtinin on PAI-1 is not entirely clear, it is suggested to approximate that for vitronectin. Since it is known that tiplaxtinin and TM5275 promote PAI-1 substrate behavior, however, these inhibitors may prevent the conformational change in β-sheet A of PAI-1 necessary to accommodate insertion of the PAI-1 RCL during the protease inhibition reaction [25]. If tiplaxtinin or TM5275 were to complex with PAI-1 at the vitronectin-binding site, it has been suggested that these inhibitors would not be effective since the majority of circulating PAI-1 is bound to vitronectin; nevertheless, the available data confirm significant in vivo efficacy for these drugs [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,27].
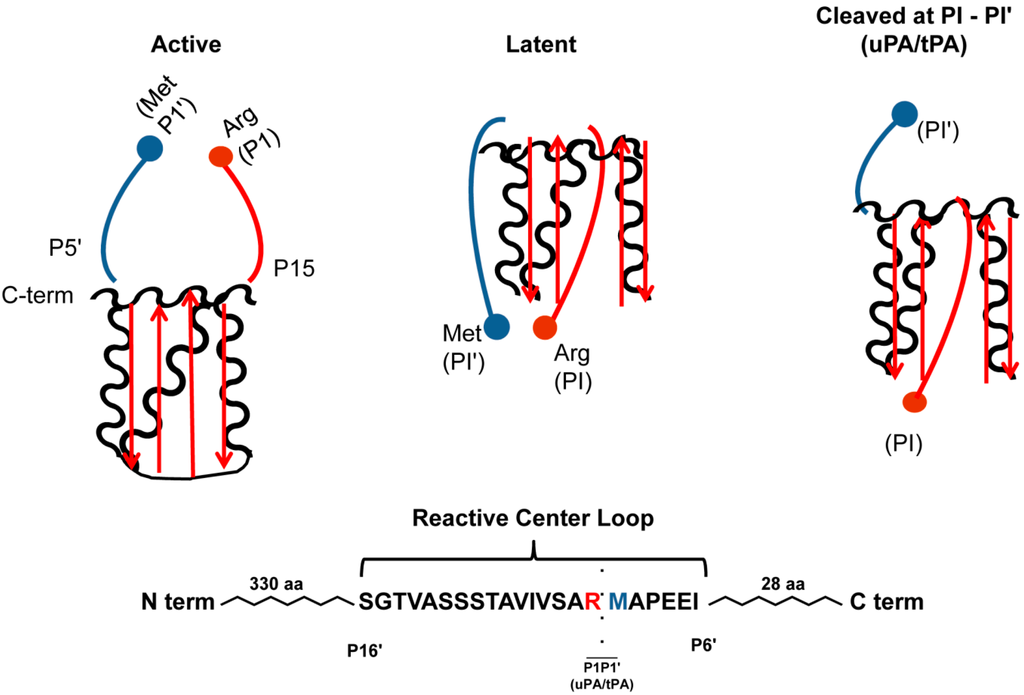
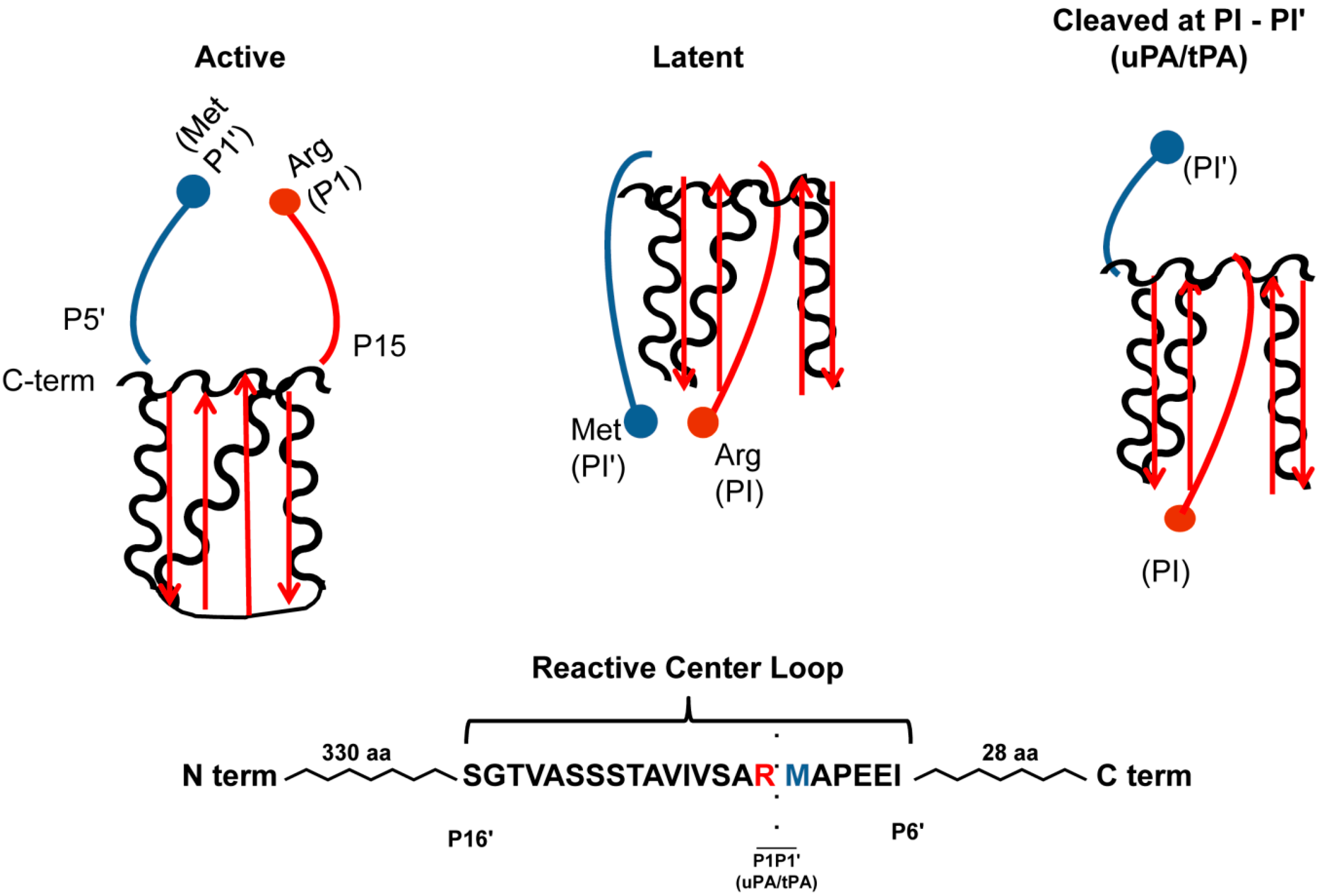
Figure 1.
PAI-1 Conformations. In the active conformation, the C-terminal PAI-1 reactive center-loop is in the strained position. Conversion into the latent conformation, implies the N-terminal side of the reactive center loop is inserted into β-sheet A (depicted in red) and forms the new β-strand 4A, and the formation of an extended loop by the C-terminal end of the reactive center loop and disruption of the P1-P1' peptide and does not inhibit proteases. Physiologically, this conformation is reversible, suggesting that PAI-1 can be “stored away” in the latent conformation, but reactivated under circumstances requiring antiproteolysis. When PAI-1 is in the substrate form, proteases are able to cleave PAI-1 at the scissile bond between the P1 (Arg346; red ball) and P1' (Met347; blue ball) residues. The cleaved N-terminal end of the reactive center loops inserts inserted into β-sheet A (depicted in red) and forms the new β-strand 4A, and again distorts the P1-P1' peptide. This conformation, unlike the latent, is not reversible and is permanently unable to inhibit proteases.
Figure 1.
PAI-1 Conformations. In the active conformation, the C-terminal PAI-1 reactive center-loop is in the strained position. Conversion into the latent conformation, implies the N-terminal side of the reactive center loop is inserted into β-sheet A (depicted in red) and forms the new β-strand 4A, and the formation of an extended loop by the C-terminal end of the reactive center loop and disruption of the P1-P1' peptide and does not inhibit proteases. Physiologically, this conformation is reversible, suggesting that PAI-1 can be “stored away” in the latent conformation, but reactivated under circumstances requiring antiproteolysis. When PAI-1 is in the substrate form, proteases are able to cleave PAI-1 at the scissile bond between the P1 (Arg346; red ball) and P1' (Met347; blue ball) residues. The cleaved N-terminal end of the reactive center loops inserts inserted into β-sheet A (depicted in red) and forms the new β-strand 4A, and again distorts the P1-P1' peptide. This conformation, unlike the latent, is not reversible and is permanently unable to inhibit proteases.
3. PAI-1 in Cellular Mechanisms of Disease Progression
Due to its rapid transcriptional induction and ubiquitous expression, PAI-1 likely functions as a central regulator of various injury-initiated cellular processes including migration, cell growth, senescence and survival in several organ sites (Figure 2). The available evidence suggests that the expression and antiproteolytic activity of PAI-1 dictates the physiological and pathophysiological cellular responses to injury. Indeed, several factors (including PAI-1) that are involved in cell motility participate in the regulation of growth arrest in the “go or grow” proliferation/migration dichotomy [28,29,30]. PAI-1 is deposited into cellular migration “trails” while knockdown approaches, PAI-1 add-back rescue as well as use of neutralizing antibodies and PAI-1−/− keratinocytes confirmed the requirement for PAI-1 in optimal monolayer wound repair [31,32]. Recent findings confirmed that PAI-1 is necessary for TGF-β-mediated keratinocyte migration both over planar substrates and through 3-D barriers [33]. PAI-1 and its target protease uPA are each up-regulated in healing wounds, particularly in the migrating epithelial cohort, and highly-expressed in cells adjacent to the denuded zone in cell culture models of epidermal injury suggesting involvement in the keratinocyte motility program [34,35]. PAI-1-expressing keratinocytes at the wound margin, moreover, are less mitotically active compared to cells more distal from the trauma site [31]; this SERPIN also mediates p53-induced fibroblast replicative senescence [36] and epithelial cytostasis downstream of TGF-β [37]. Elevated levels of PAI-1, moreover, protect against programmed cell death (apoptosis) while PAI-1 deficiency promotes pulmonary fibroblast apoptosis by attenuating Akt- and ERK-mediated survival [38] and stimulates FasL-dependent apoptosis in endothelial, colon, breast, lung and fibrosarcoma cancer cells [39,40]. PAI-1 expression driven by the SM22α promoter potently inhibits apoptosis by binding to, and preventing, caspase-3 activation in VSMC [41]. Expression alone, however, may not dictate functionality, since the small-molecule PAI-1 functional inhibitors, tiplaxtinin and TM5275, stimulate apoptosis in several cell types [24,27,42,43].
4. PAI-1 as a Multifunctional Signaling “Ligand”
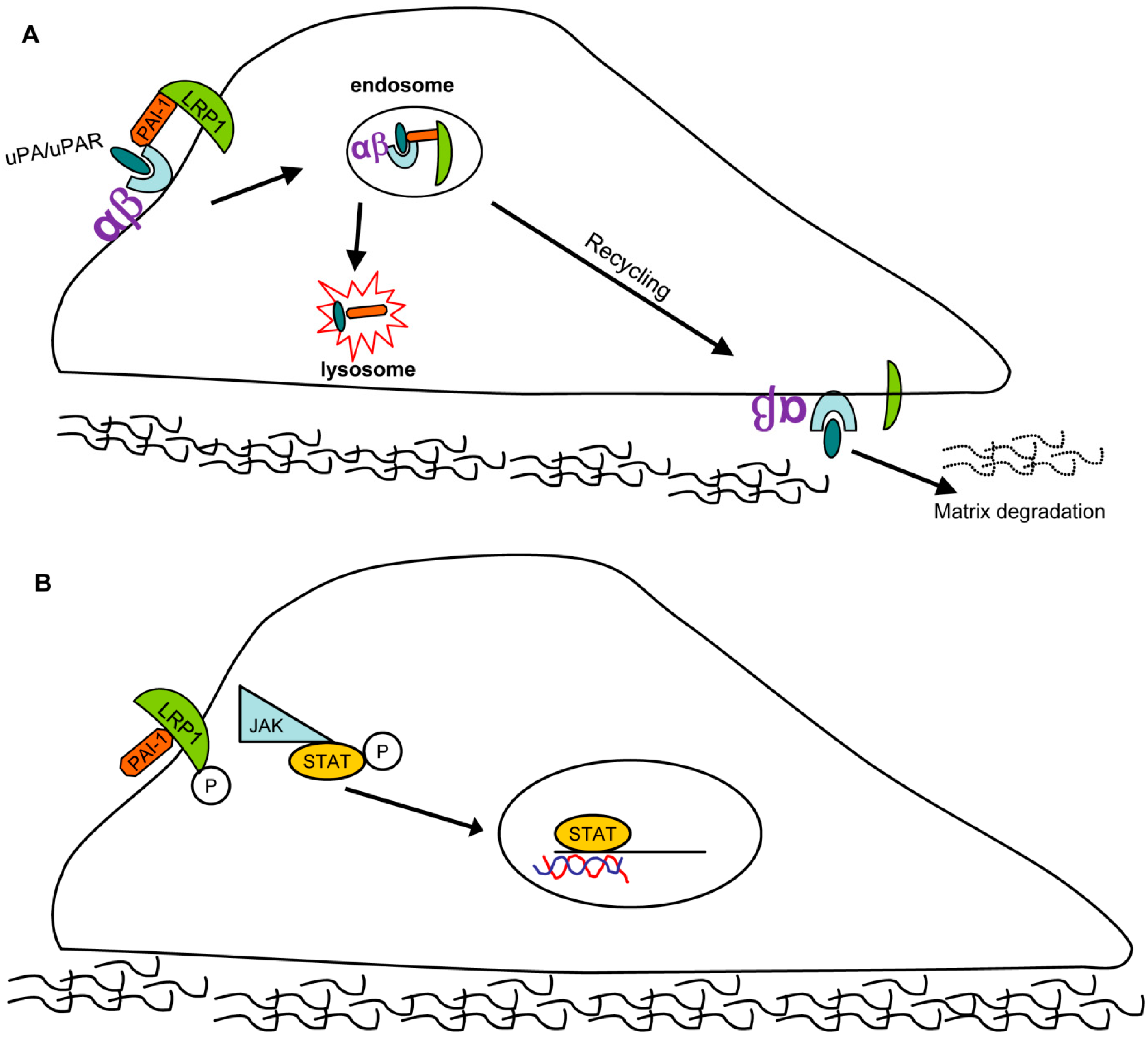
PAI-1 activates several signaling pathways. Independent of its function as a protease inhibitor, PAI-1 binds to the endocytic low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP1) where it triggers JAK/STAT1-mediated signaling and migration [30]. All three conformations of PAI-1 (active, latent, substrate/cleaved) bind LRP1 and activate the downstream JAK/STAT1 pathway to drive cell migration [44,45,46]. Furthermore, PAI-1also binds to, and endocytosis, several cell-surface integrins, (e.g., α3β1, αvβ3, and αvβ5) in an LRP1-dependent manner by forming a PAI-1/uPA/uPAR(uPA receptor)/LRPI/integrin complex. PAI-1 and uPA are subsequently degraded while uPAR, LRP1 and integrins are recycled back to the cell surface where they mediate cycles of detachment/re-attachment and extracellular pericellular proteolysis (Figure 3) [45,46,47].
Recently, another signaling network involving PAI-1 has been identified that involves the TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) and its cognate receptor FN14 (fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14). TWEAK stimulates proliferation, migration and survival mechanisms through engagement of FN14 in numerous cell types [48]. TWEAK-FN14 interaction in ApoE−/− pro-atherosclerotic mice, furthermore, stimulates PAI-1 expression in aortic lesions with co-localization of both PAI-1 and FN14 expression [49]. Coincidentally, full-length PAI-1 but not the cleaved SERPIN down-regulates surface FN14 expression via LRP1-mediated endocytosis [27]. It appears, therefore, that PAI-1 modulates not only cellular migration but also survival by cell surface receptor titration.
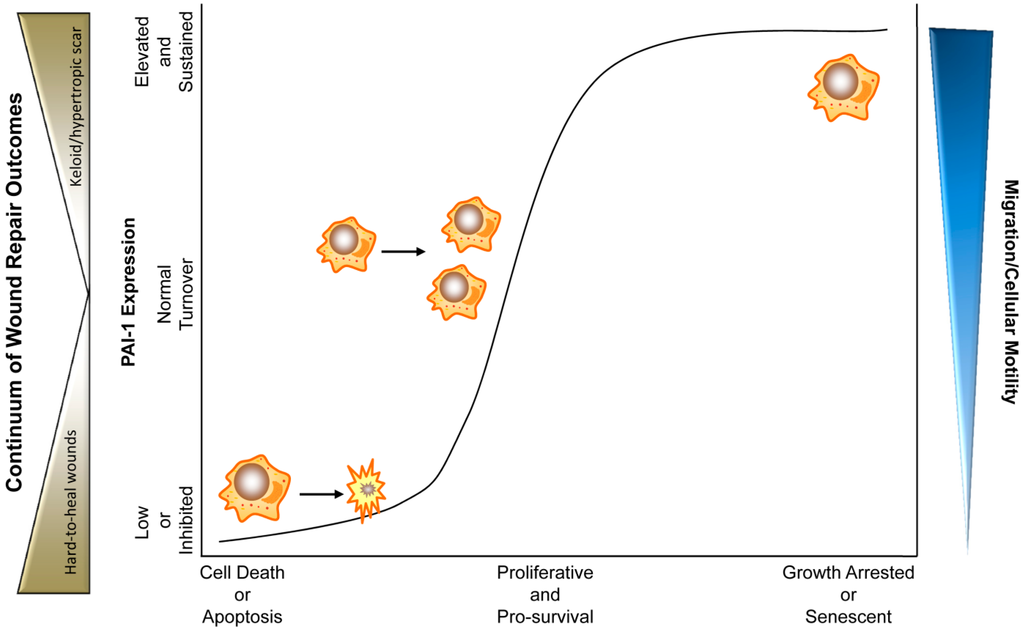
Figure 2.
PAI-1 levels and activity dictate cellular rheostasis and during physiological and pathophysiological wound healing. In this triaxial model, moderate expression of PAI-1 where PAI-1 is under constant homeostatic turnover, promotes a physiological pro-proliferative, pro-survival and pro-migratory phenotype. Upon tissue injury, cytokines (e.g., TGF-β and EGF) stimulate PAI-1 expression promoting wound closure. During final stages of wound repair, PAI-1 levels drop, halting the pro-repair processes (e.g., by increased myofibroblast apoptosis and reduced keratinocyte motility) finalizing proper injury resolution. Chronically low expression or inhibition of PAI-1 activity abrogates cellular migration and motility while stimulating cellular death (predominantly apoptosis). Ulcerations and hard-to-heal diabetic wounds might represent such wounds where reduced re-epithelialization and myofibroblast contractility, as a result of inhibited migration and premature apoptosis, contribute to insufficient wound closure. Pathologically elevated and/or sustained PAI-1 levels, in contrast, may promote a growth-arrested, pro-migratory pathophysiological phenotype (e.g., keloids, fibrosis) where dermatological hypercontractility is a result of persistence of wound bed myofibroblasts with continued extracellular matrix deposition and remodeling. In some instances, sustained PAI-1 expression, particularly in the context of p53 modulation, may activate a cellular senescence program [36]. In either pathological scenario, elevated (hypertrophic scar, keloid) or low (hard-to-heal chronic wounds) PAI-1 expression by genetic ablation/small-molecule antagonism or recombinant amplification, respectively, may constitute attractive therapeutic options.
Figure 2.
PAI-1 levels and activity dictate cellular rheostasis and during physiological and pathophysiological wound healing. In this triaxial model, moderate expression of PAI-1 where PAI-1 is under constant homeostatic turnover, promotes a physiological pro-proliferative, pro-survival and pro-migratory phenotype. Upon tissue injury, cytokines (e.g., TGF-β and EGF) stimulate PAI-1 expression promoting wound closure. During final stages of wound repair, PAI-1 levels drop, halting the pro-repair processes (e.g., by increased myofibroblast apoptosis and reduced keratinocyte motility) finalizing proper injury resolution. Chronically low expression or inhibition of PAI-1 activity abrogates cellular migration and motility while stimulating cellular death (predominantly apoptosis). Ulcerations and hard-to-heal diabetic wounds might represent such wounds where reduced re-epithelialization and myofibroblast contractility, as a result of inhibited migration and premature apoptosis, contribute to insufficient wound closure. Pathologically elevated and/or sustained PAI-1 levels, in contrast, may promote a growth-arrested, pro-migratory pathophysiological phenotype (e.g., keloids, fibrosis) where dermatological hypercontractility is a result of persistence of wound bed myofibroblasts with continued extracellular matrix deposition and remodeling. In some instances, sustained PAI-1 expression, particularly in the context of p53 modulation, may activate a cellular senescence program [36]. In either pathological scenario, elevated (hypertrophic scar, keloid) or low (hard-to-heal chronic wounds) PAI-1 expression by genetic ablation/small-molecule antagonism or recombinant amplification, respectively, may constitute attractive therapeutic options.
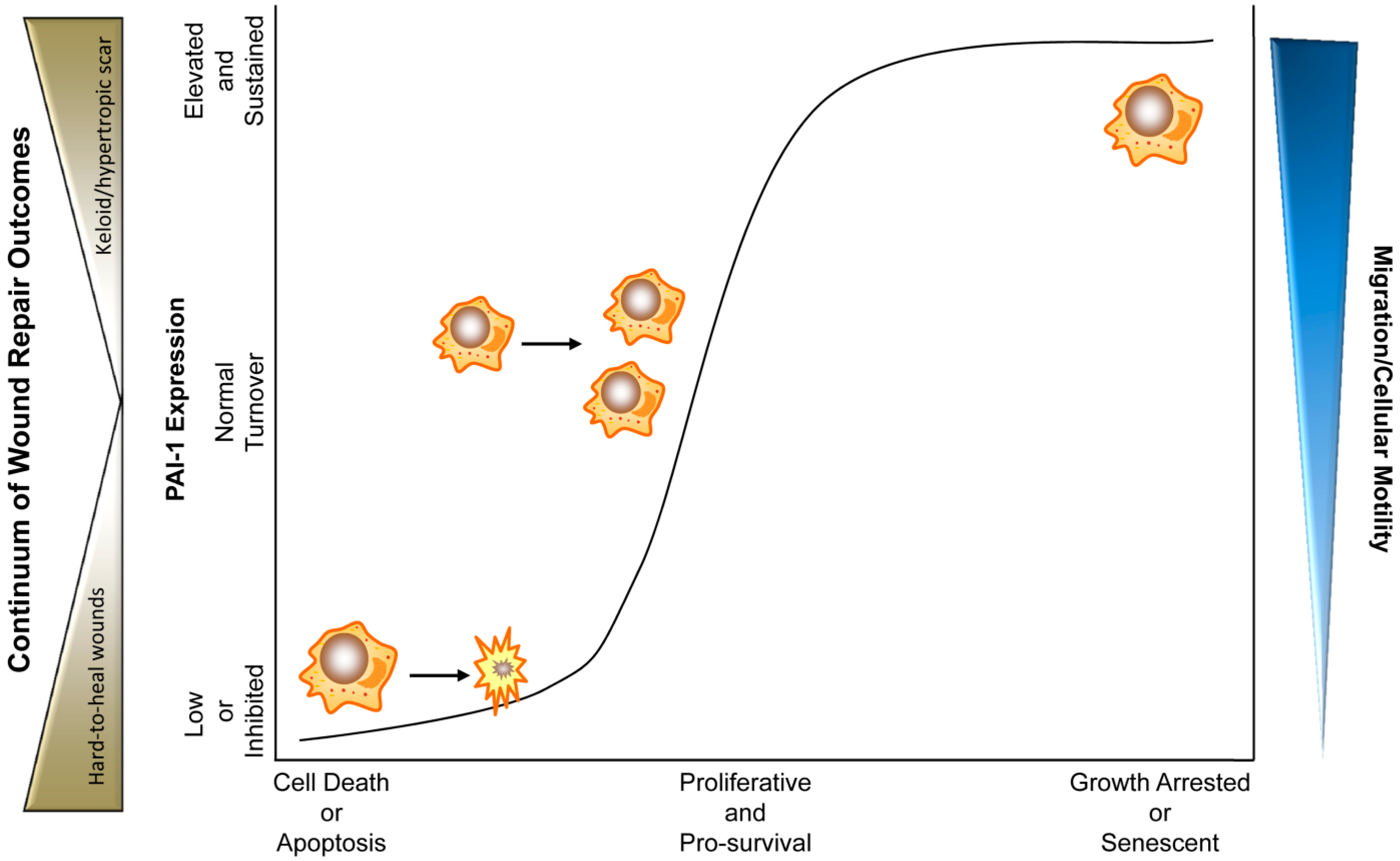
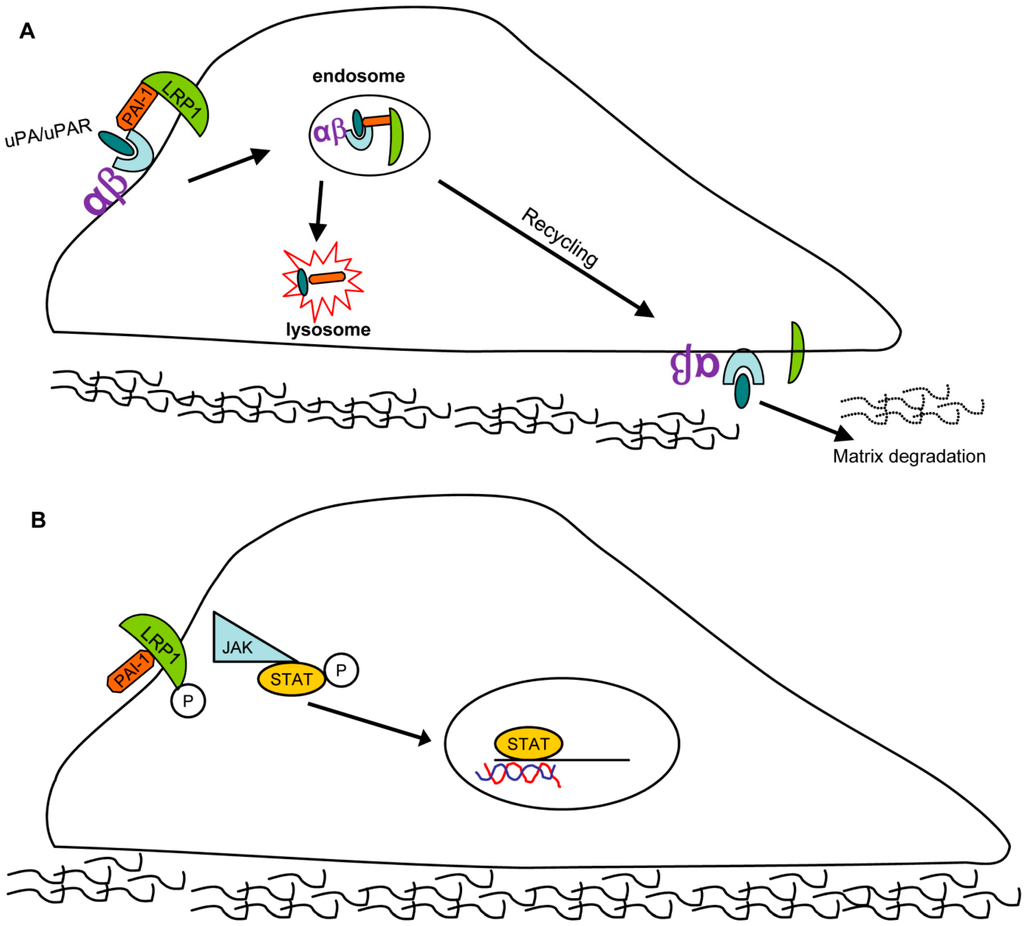
Figure 3.
PAI-1 contributes to wound repair by affecting cell migration: Two possible pathways. (A) Pathway 1: PAI-1/uPA/uPAR (uPA receptor)/LRP1/integrin complexes are endocytosed with subsequent uPAR/LRP1/integrin redistribution to the leading edge, causing an “adhesion-detachment-readhesion” cycle that promotes cell migration. (B) Pathway 2: PAI-1 binds to LRP1 in a uPA/uPAR-independent manner triggering JAK/STAT1 pathway activation resulting in stimulation of cell motility.
Figure 3.
PAI-1 contributes to wound repair by affecting cell migration: Two possible pathways. (A) Pathway 1: PAI-1/uPA/uPAR (uPA receptor)/LRP1/integrin complexes are endocytosed with subsequent uPAR/LRP1/integrin redistribution to the leading edge, causing an “adhesion-detachment-readhesion” cycle that promotes cell migration. (B) Pathway 2: PAI-1 binds to LRP1 in a uPA/uPAR-independent manner triggering JAK/STAT1 pathway activation resulting in stimulation of cell motility.
5. PAI-1 in Physiological and Pathophysiological Cutaneous Wound Healing
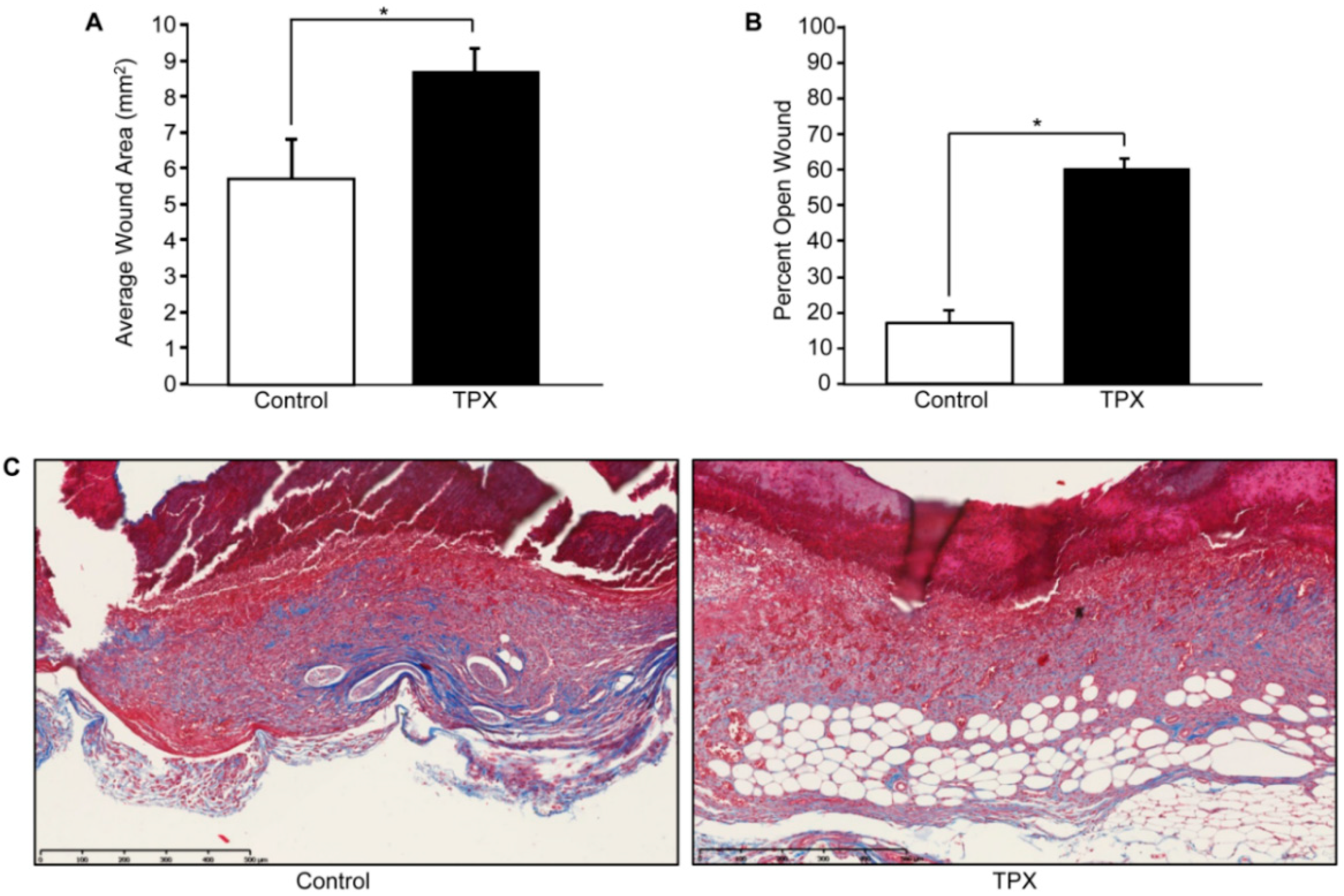
Wound resolution following cutaneous injury is a complex process that involves interactions, both spatially and temporally, between various cells and the repair site microenvironment. Dysregulated PAI-1 expression is a causative factor in aberrant wound healing and fibrosis. Following injury in vitro, PAI-1 is induced and its expression is restricted to the wound margin where it is required for efficient keratinocyte migration [31,34,50]. Coincidentally, uPA expression is also elevated at the migratory cohort [35]. Highlighting the antiproteolytic role of PAI-1 in wound repair, PAI-1−/− animals display accelerated injury closure [51], which, in part, likely reflects increased plasmin activation as plasminogen−/− mice exhibit defective wound healing [52]. Conversely, in a wild-type murine model, cutaneous wounds topically treated with tiplaxtinin remained largely unhealed, compared to vehicle controls (Figure 4A), with significant reductions in several repair criteria, including injury site closure, re-epithelialization and wound contraction [53]. One probable explanation for this paradox is that, while tiplaxtinin inhibits PAI-1/uPA complex formation and uPA/tPA antiproteolytic function, PAI-1-deficient mice are likely to have compensating mechanisms due to a significant and tissue-specific impact on gene expression [54].
While most wounds heal rapidly and efficiently, many remain either chronic (e.g., diabetic lesions) or are pathologically remodeled (e.g., keloids, hypertrophic scars). During the secondary phase of wound healing, quiescent fibroblasts distal from the wound side populate the dermis concomitant with keratinocyte re-epithelialization. Once established at the injury site, fibroblasts differentiate into activated myofibroblasts, which stimulate wound contracture [55,56]. Once tissue healing nears completion, myofibroblast populations are depleted via apoptosis [57]. Under certain circumstances, however, myofibroblasts persist resulting in excessive contracture and extracellular stiffening, a major feature of hypertrophic scarring and fibrosis. Myofibroblast differentiation and persistence are governed by a feedback loop whereupon actin filament restructuring and myosin-II light chain locomotion drives cellular contraction paralleling increases in tissue TGF-β1 activation and collagen deposition; such remodeling stimulates myofibroblast differentiation and persistence [58] Elevated PAI-1, likely due to autocrine TGF-β1 production in the wound bed microenvironment, is coincident with cutaneous and non-cutaneous pathologically-remodeled tissues (e.g., fibrosis, keloids and hypertrophic scars) [59]. Indeed, PAI-1−/− mice display reduced fibrosis and PAI-1 siRNA attenuates collagen levels in keloids [60,61]. In addition to reduced wound re-epithelialization and wound closure (Figure 4B), tiplaxtinin-treated wounds have a significant decrease in smooth-muscle α-actin-positive myofibroblasts and appear less contracted with reduced collagen organization compared to control wounds [53] (Figure 4C).
Myofibroblast differentiation is highly-dependent on cellular adhesion. PAI-1 binding to uPA differentiates corneal myofibroblasts on vitronectin matrices promoting vitronectin/integrin engagement and enhanced adhesion [62]. While it is not clear if LRP1 directly mediates myofibroblast differentiation, LRP1-1-stimulated JAK/STAT signaling stimulates actin polarization. There are, however, controversial findings. PAI-1-depleted cells exhibit a chronic myofibroblastic phenotype [63] and it is plausible that in the absence of PAI-1, uPA and integrins are free to engage vitronectin promoting adhesion. Alternatively, amplified plasmin activation may stimulate the conversion of latent to active TGF-β, resulting in the expression of profibrotic genes (i.e., PAI-1, collagen, fibronectin) and a phenotypic transition in wild-type cells. This process may be up-regulated in the context of genetic PAI-1 deficiency resulting in a subtype of myofibroblast. While there may be both PAI-1-dependent and -independent pathways to myofibroblastoid differentiation, it is also likely that not all myofibroblastic phenotypes are equivalent and that different myofibroblast subprograms may be influenced by genetic background. Regardless, PAI-1 function is clearly required for fibroblast, and more importantly, myofibroblast survival. The utility of small-molecule PAI-1 functional inhibitors to dissect PAI-1 sub-paradigms is evidenced in the finding that TM5275 induces pulmonary fibroblast and myofibroblast apoptosis, suggesting that tiplaxtinin may stimulate dermal myofibroblast apoptosis, thereby reducing wound contraction as part of the tiplaxtinin-induced defect in cutaneous wound repair. Interestingly, contradictions in PAI-1 mediated cellular outcomes are not exclusive to cutaneous biology; several reviews have highlighted the PAI-1 paradox in cardiovascular disease [64,65]. Given the ubiquitous expression of PAI-1 and diversity of functions and targets in a multitude of cell types, it is becoming increasingly obvious that global knockout PAI-1 approaches might inadequately represent discrete PAI-1 functionality in larger biological contexts.
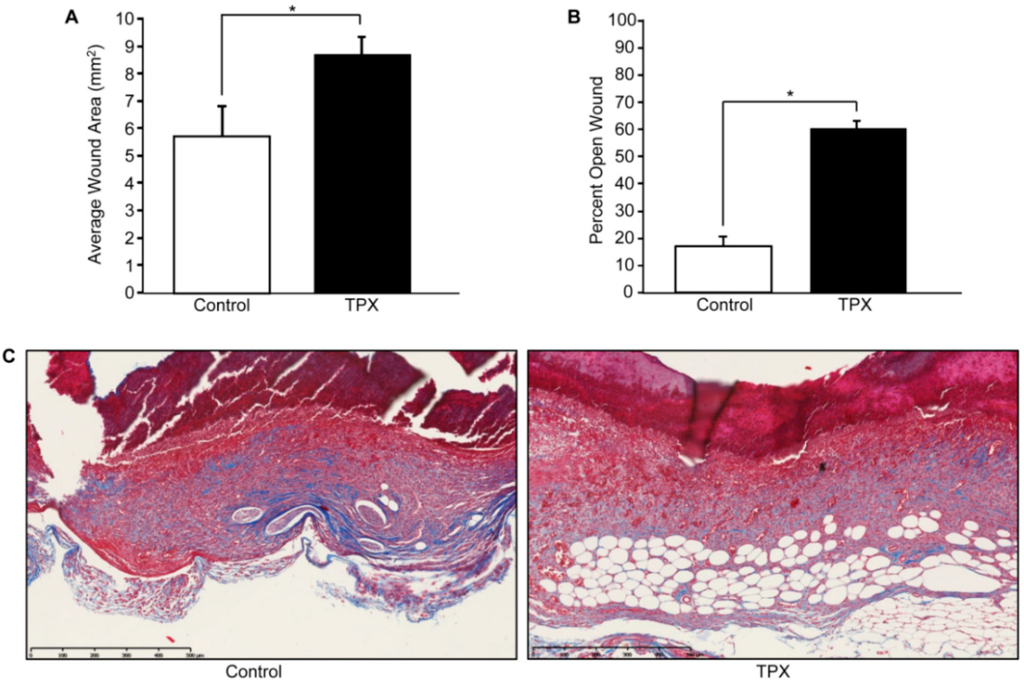
Figure 4.
Tiplaxtinin reduces cutaneous wound closure and collagen deposition. Adult FVB/NJ mice (6–10 weeks of age; Jackson Laboratories, Bar Harbor, ME, USA) were anesthetized and shaved; four full-thickness wounds were made on the dorsal skin using a sterile 4 mm biopsy punch as described [66]. Animals were separated into two groups, control (vehicle only) and tiplaxtinin-treated. Immediately following wounding, each site received 10 µL of either tiplaxtinin (6 mg/kg; 1.25 µL of a stock 48 mg/mL TPX solution solubilized in DMSO and diluted in PBS) or vehicle (1.25 µL DMSO diluted in PBS). Each wound was then additionally treated for four consecutive days. On the fifth day, wound area was measured using calipers (area = length × width) (A). Mice were then euthanized, wounds surgically-excised and bisected, fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, embedded in paraffin and sectioned (5 µm). Tissue was stained using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) (not shown) and percent wound closure was quantified using the freehand line-drawing tool in ImageJ. Wound closure was calculated using the formula = (# pixels closed wound − # pixels open wound)/(# pixels closed wound) × 100. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; * p < 0.05, n = 5. (B). Sectioned tissue was stained with trichrome reagent; red = cytoplasm, black = nuclei, blue = connective tissue (C).
Figure 4.
Tiplaxtinin reduces cutaneous wound closure and collagen deposition. Adult FVB/NJ mice (6–10 weeks of age; Jackson Laboratories, Bar Harbor, ME, USA) were anesthetized and shaved; four full-thickness wounds were made on the dorsal skin using a sterile 4 mm biopsy punch as described [66]. Animals were separated into two groups, control (vehicle only) and tiplaxtinin-treated. Immediately following wounding, each site received 10 µL of either tiplaxtinin (6 mg/kg; 1.25 µL of a stock 48 mg/mL TPX solution solubilized in DMSO and diluted in PBS) or vehicle (1.25 µL DMSO diluted in PBS). Each wound was then additionally treated for four consecutive days. On the fifth day, wound area was measured using calipers (area = length × width) (A). Mice were then euthanized, wounds surgically-excised and bisected, fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, embedded in paraffin and sectioned (5 µm). Tissue was stained using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) (not shown) and percent wound closure was quantified using the freehand line-drawing tool in ImageJ. Wound closure was calculated using the formula = (# pixels closed wound − # pixels open wound)/(# pixels closed wound) × 100. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; * p < 0.05, n = 5. (B). Sectioned tissue was stained with trichrome reagent; red = cytoplasm, black = nuclei, blue = connective tissue (C).
6. Conclusions and Therapeutic Considerations
Chronic wounds and excessive scarring, with their associated functional and cosmetic repercussions, affect the quality of life of millions of patients in the United States alone and is a major burden on the healthcare system. Dysregulated tissue levels of PAI-1 are common events in many repair anomalies and PAI-1 can promote or attenuate wound responses depending on levels of plasminogen activators, proteases/protease inhibitors and the growth factor repertoire at the injury site microenvironment. While fluctuations in PAI-1 expression in various cell types (e.g., keratinocytes, fibroblasts, inflammatory cells) drive the different phases of wound repair, it is apparent that PAI-1 is a major component of each stage (Figure 5).
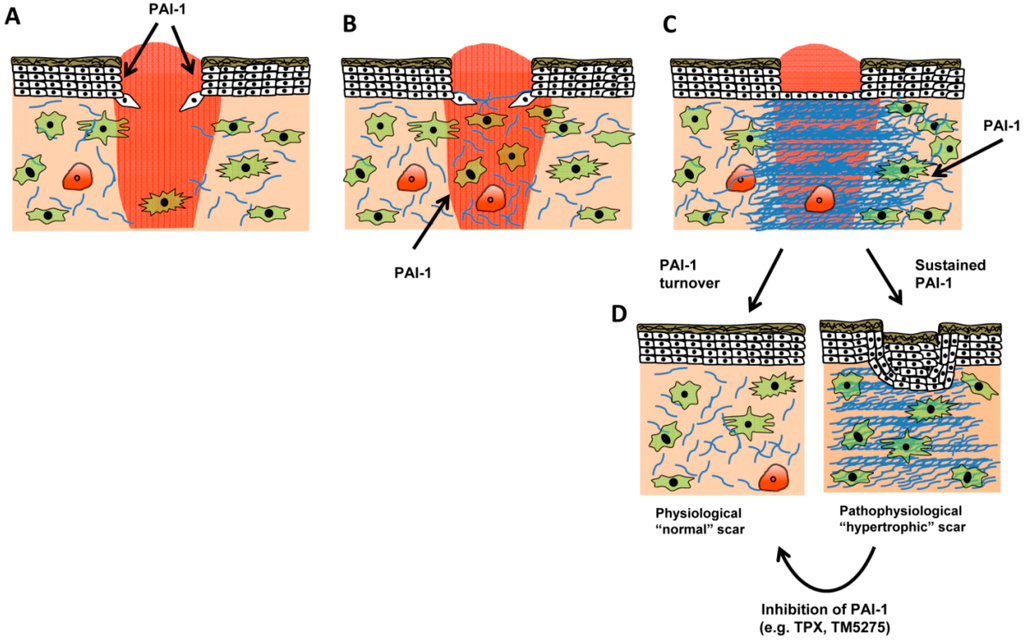
Figure 5.
Role of PAI-1 in normal and pathologic wound repair. (A) Following injury, a proliferative phase, characterized by keratinocyte proliferation and migration, serves to preliminarily re-epithelialize the injury site. PAI-1 expression is detectable in both wounded keratinocyte monolayers in vitro [34,51] and in vivo where PAI-1 activity is required for efficient wound closure. Injury-induced cytokine production (e.g., TGF-β and EGF) provides a stimulus for PAI-1 transcription. Concomitant with re-epithelialization, granulation tissue formation begins as fibroblasts emerge from quiescence, migrate into the wound bed, and initiate their differentiation into myofibroblasts (B). In the latter stage of granulation tissue formation (C), myofibroblasts continue to remodel the wound bed, both contributing to and responding to the increased tissue stiffening by depositing collagen matrix (blue), factors that contribute to wound closure. As tiplaxtinin-treated wounds display decreased extracellular matrix organization [53] and appear less-contracted, it is possible that during granulation tissue formation PAI-1 regulates myofibroblast functionality both by titering integrin/receptor cell adhesion (and spatial locale) and antiproteolytically modulating extracellular matrix organization. Under normal circumstances, myofibroblasts decrease by apoptosis; pathological scars, in contrast, display persistent contracture due to myofibroblast persistence with continued matrix contractility (D). Since inhibition of PAI-1 function attenuates vascular pathological remodeling via induction of smooth muscle cell apoptosis [27], reduced PAI-1 expression in the latter stages of wound healing may contribute to decreased myofibroblast numbers. Since elevated levels of PAI-1 are evident in keloids, targeted PAI-1 inhibition may be a novel therapeutic approach to resolve pathophysiological scars.
Figure 5.
Role of PAI-1 in normal and pathologic wound repair. (A) Following injury, a proliferative phase, characterized by keratinocyte proliferation and migration, serves to preliminarily re-epithelialize the injury site. PAI-1 expression is detectable in both wounded keratinocyte monolayers in vitro [34,51] and in vivo where PAI-1 activity is required for efficient wound closure. Injury-induced cytokine production (e.g., TGF-β and EGF) provides a stimulus for PAI-1 transcription. Concomitant with re-epithelialization, granulation tissue formation begins as fibroblasts emerge from quiescence, migrate into the wound bed, and initiate their differentiation into myofibroblasts (B). In the latter stage of granulation tissue formation (C), myofibroblasts continue to remodel the wound bed, both contributing to and responding to the increased tissue stiffening by depositing collagen matrix (blue), factors that contribute to wound closure. As tiplaxtinin-treated wounds display decreased extracellular matrix organization [53] and appear less-contracted, it is possible that during granulation tissue formation PAI-1 regulates myofibroblast functionality both by titering integrin/receptor cell adhesion (and spatial locale) and antiproteolytically modulating extracellular matrix organization. Under normal circumstances, myofibroblasts decrease by apoptosis; pathological scars, in contrast, display persistent contracture due to myofibroblast persistence with continued matrix contractility (D). Since inhibition of PAI-1 function attenuates vascular pathological remodeling via induction of smooth muscle cell apoptosis [27], reduced PAI-1 expression in the latter stages of wound healing may contribute to decreased myofibroblast numbers. Since elevated levels of PAI-1 are evident in keloids, targeted PAI-1 inhibition may be a novel therapeutic approach to resolve pathophysiological scars.
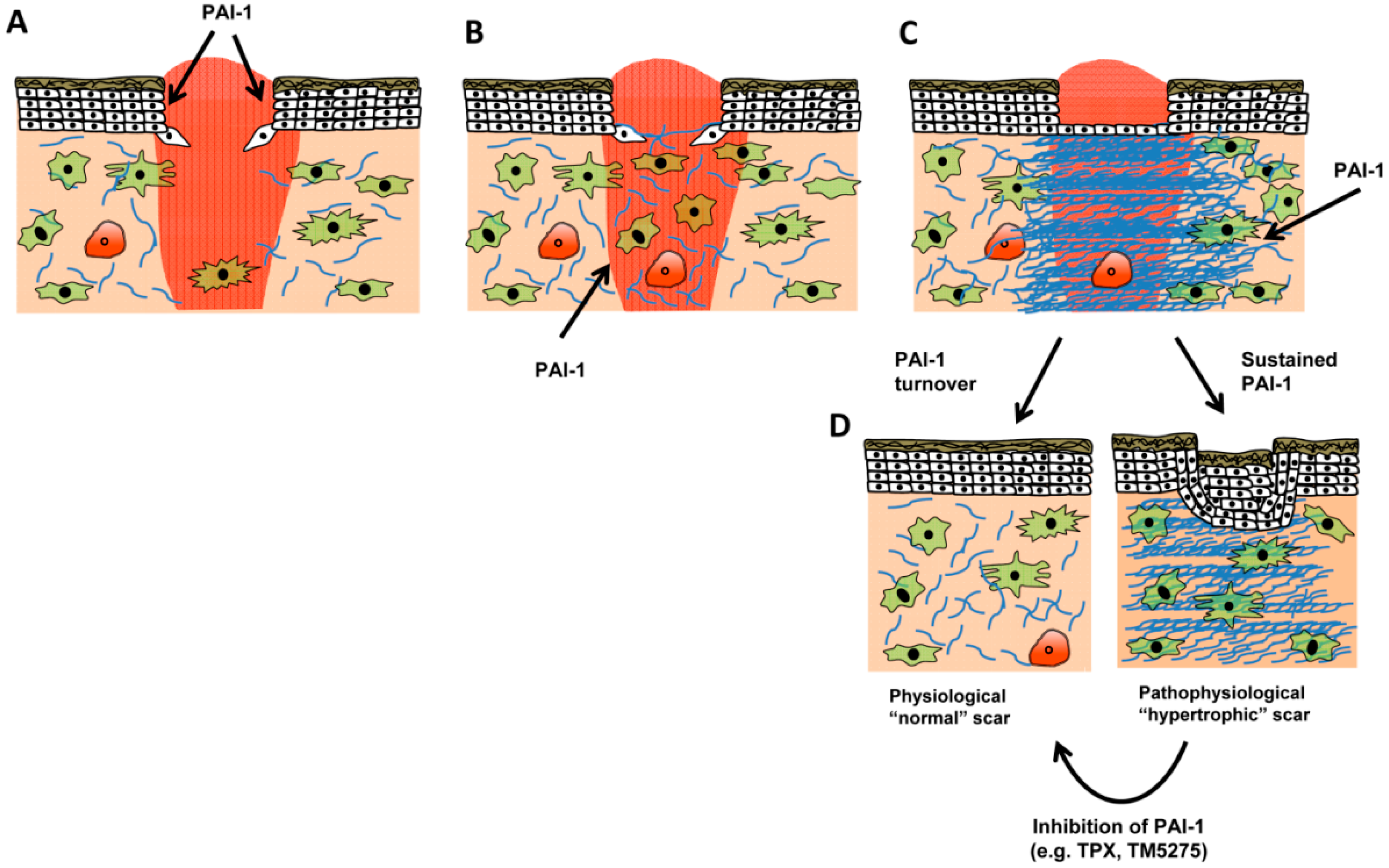
Immediately following injury, wound-released cytokines (TGF-β and EGF) induce PAI-1 expression at leading edge keratinocytes, which stimulate migration and re-epithelialization [54]. Continued PAI-1 expression likely contributes to fibroblast migration, and ultimately fibroblast-to-myofibroblast differentiation, since tiplaxtinin treated wounds appear less contracted [54] and have reduced extracellular matrix organization (Figure 4). In the context of normal wound healing where PAI-1 effectively regulates the activity of its target proteases and is subject to uptake and internalization (e.g., LRP1-mediated endocytosis and degradation), it plausible that PAI-1 reductions or compromised function would stimulate a decrease in granulation tissue cellularity. It is known that plasmin mediates fibroblast apoptosis [67]; it remains to be determined, however, if this mediated by decreased PAI-1 activity. It is possible, that in a scenario where PAI-1 remains elevated that the wound is subject to continuous repair cycles, where PAI-1 stimulates a feedforward loop that drives myofibroblast differentation, tissue stiffening, and matrix deposition. This concept derives support from the finding that PAI-1 remains elevated in keloids [62], suggesting that chronic PAI-1 expression mediates the pathological, hypertrophic scarring phenotype.
It would be of interest to evaluate PAI-1 expression in hard-to-heal wounds. Based on the model depicted in Figure 2, one would suppose that PAI-1 is either depleted, or lacks activity thereby reducing keratinocyte migration and wound closure. Given the diversity of PAI-1 targets and the complexities associated with deficient or overexpression strategies, including likely compensatory mechanisms in both genetic contexts, it would appear that functional inhibitor studies could shed new light on the impact of PAI-1 in cutaneous wound repair.
Acknowledgments
Supported by NIH grant GM057242 to PJH.
Author Contributions
Tessa M. Simone and Paul J. Higgins wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Eri ckson, L.A.; Ginsberg, M.H.; Loskutoff, D.J. Detection and partial characterization of an inhibitor of plasminogen activator in human platelets. J. Clin. Investig. 1984, 74, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellas, C.; Loskutoff, D.J. Historical analysis of PAI-1 from its discovery to its potential role in cell motility and disease. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 93, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mottonen, J.; Strand, A.; Symersky, J.; Sweet, R.M.; Danley, D.E.; Geoghegan, K.F.; Gerard, R.D.; Goldsmith, E.J. Structural basis of latency in plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Nature 1992, 355, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, E.G.; Santell, L. Conversion of the active to latent plasminogen activator inhibitor from human endothelial cells. Blood 1987, 70, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, T.L.; Sigurdardottir, O.; Wiman, B. Stability of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1). Thromb. Haemost. 1989, 62, 748–751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hekman, C.M.; Loskutoff, D.J. Endothelial cells produce a latent inhibitor of plasminogen activators that can be activated by denaturants. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 11581–11587. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lambers, J.W.; Cammenga, M.; Konig, B.W.; Mertens, K.; Pannekoek, H.; van Mourik, J.A. Activation of human endothelial cell-type plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) by negatively charged phospholipids. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 17492–17496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Declerck, P.J.; de Mol, M.; Vaughan, D.E.; Collen, D. Identification of a conformationally distinct form of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, acting as a noninhibitory substrate for tissue-type plasminogen activator. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 11693–11696. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patston, P.A.; Gettins, P.; Beechem, J.; Schapira, M. Mechanism of serpin action: Evidence that C1 inhibitor functions as a suicide substrate. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 8876–8882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gils, A.; Declerck, P.J. Proteinase specificity and functional diversity in point mutants of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 12662–12666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aertgeerts, K.; de Bondt, H.L.; de Ranter, C.J.; Declerck, P.J. Mechanisms contributing to the conformational and functional flexibility of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1995, 2, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simone, T.M.; Higgins, P.J. Low molecular weight antagonists of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1: Therapeutic potential in cardiovascular disease. Mol. Med. Ther. 2012, 1, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Eren, M.; Vaughan, D.E.; Schleimer, R.P.; Cho, S.H. A plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 inhibitor reduces airway remodeling in a murine model of chronic asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, M.P.; Moradi, J.; Nissar, A.A.; Riddell, M.C.; Hawke, T.J. Inhibition of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 restores skeletal muscle regeneration in untreated type 1 diabetic mice. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1964–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lijnen, H.R.; Alessi, M.C.; Frederix, L.; Collen, D.; Juhan-Vague, I. Tiplaxtinin impairs nutritionally induced obesity in mice. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 96, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schalkwijk, C.G.; Stehouwer, C.D. PAI-1 inhibition in obesity and the metabolic syndrome: A promising therapeutic strategy. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 96, 698–699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leik, C.E.; Su, E.J.; Nambi, P.; Crandall, D.L.; Lawrence, D.A. Effect of pharmacologic plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 inhibition on cell motility and tumor angiogenesis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 2710–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crandall, D.L.; Quinet, E.M.; el Ayachi, S.; Hreha, A.L.; Leik, C.E.; Savio, D.A.; Juhan-Vague, I.; Alessi, M.C. Modulation of adipose tissue development by pharmacological inhibition of PAI-1. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 2209–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lijnen, H.R.; Alessi, M.C.; van Hoef, B.; Collen, D.; Juhan-Vague, I. On the role of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in adipose tissue development and insulin resistance in mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisberg, A.D.; Albornoz, F.; Griffin, J.P.; Crandall, D.L.; Elokdah, H.; Fogo, A.B.; Vaughan, D.E.; Brown, N.J. Pharmacological inhibition and genetic deficiency of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 attenuates angiotensin II/salt-induced aortic remodeling. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izuhara, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Nangaku, M.; Takizawa, S.; Ishida, H.; Kurokawa, K.; van Ypersele de Strihou, C.; Hirayama, N.; Miyata, T. Inhibition of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1: Its mechanism and effectiveness on coagulation and fibrosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izuhara, Y.; Yamaoka, N.; Kodama, H.; Dan, T.; Takizawa, S.; Hirayama, N.; Meguro, K.; van Ypersele de Strihou, C.; Miyata, T. A novel inhibitor of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 provides antithrombotic benefits devoid of bleeding effect in nonhuman primates. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichimura, A.; Matsumoto, S.; Suzuki, S.; Dan, T.; Yamaki, S.; Sato, Y.; Kiyomoto, H.; Ishii, N.; Okada, K.; Matsuo, O.; et al. A small molecule inhibitor to plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 inhibits macrophage migration. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.T.; Vayalil, P.K.; Miyata, T.; Hagood, J.; Liu, R.M. Therapeutic value of small molecule inhibitor to plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 for lung fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorlatova, N.V.; Cale, J.M.; Elokdah, H.; Li, D.; Fan, K.; Warnock, M.; Crandall, D.L.; Lawrence, D.A. Mechanism of inactivation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 by a small molecule inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 9288–9296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elokdah, H.; Abou-Gharbia, M.; Hennan, J.K.; McFarlane, G.; Mugford, C.P.; Krishnamurthy, G.; Crandall, D.L. Tiplaxtinin, a novel, orally efficacious inhibitor of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1: Design, synthesis, and preclinical characterization. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 3491–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simone, T.M.; Higgins, S.P.; Archambeault, J.; Higgins, C.E.; Ginnan, R.G.; Singer, H.; Higgins, P.J. A small molecule PAI-1 functional inhibitor attenuates neointimal hyperplasia and vascular smooth muscle cell survival by promoting PAI-1 cleavage. Cell. Signal. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedotov, S.; Iomin, A. Migration and proliferation dichotomy in tumor-cell invasion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 118101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploplis, V.A.; Balsara, R.; Sandoval-Cooper, M.J.; Yin, Z.J.; Batten, J.; Modi, N.; Gadoua, D.; Donahue, D.; Martin, J.A.; Castellino, F.J. Enhanced in vitro proliferation of aortic endothelial cells from plasminogen activator inhibitor-1-deficient mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 6143–6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simone, T.M.; Higgins, C.E.; Czekay, R.P.; Law, B.K.; Archambeault, J.; Kutz, S.M.; Higgins, P.J. SERPINE1: A molecular switch in the proliferation/migration dichotomy in wound-“activated” keratinocytes. Adv. Wound Care 2014, 3, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Providence, K.M.; Higgins, P.J. PAI-1 expression is required for epithelial cell migration in two distinct phases of in vitro wound repair. J. Cell. Physiol. 2004, 200, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Providence, K.M.; White, L.A.; Tang, J.; Gonclaves, J.; Staiano-Coico, L.; Higgins, P.J. Epithelial monolayer wounding stimulates binding of USF-1 to an E-box motif in the plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 gene. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 3767–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freytag, J.; Wilkins-Port, C.E.; Higgins, C.E.; Higgins, S.P.; Samarakoon, R.; Higgins, P.J. PAI-1 mediates the TGF-β1+EGF-induced “scatter” response in transformed human keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 2179–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Providence, K.M.; Kutz, S.M.; Staiano-Coico, L.; Higgins, P.J. PAI-1 gene expression is regionally induced in wounded epithelial cell monolayers and required for injury repair. J. Cell. Physiol. 2000, 182, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romer, J.; Lund, L.R.; Eriksen, J.; Ralfkiaer, E.; Zeheb, R.; Gelehrter, T.D.; Dano, K.; Kristensen, P. Differential expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its type-1 inhibitor during healing of mouse skin wounds. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 97, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortlever, R.M.; Higgins, P.J.; Bernards, R. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is a critical downstream target of p53 in the induction of replicative senescence. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortlever, R.M.; Nijwening, J.H.; Bernards, R. Transforming growth factor-β requires its target plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 for cytostatic activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 24308–24313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Wang, W.L.; Liu, J.; Li, W.B.; Bai, L.L.; Yuan, Y.D.; Song, S.X. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 promotes the proliferation and inhibits the apoptosis of pulmonary fibroblasts by Ca(2+) signaling. Thromb. Res. 2012, 131, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, D.K.; Zhang, J.Q. Pregnane X receptor: A double-edged sword. Chin. Med. J. 2009, 122, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bajou, K.; Peng, H.; Laug, W.E.; Maillard, C.; Noel, A.; Foidart, J.M.; Martial, J.A.; DeClerck, Y.A. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 protects endothelial cells from FasL-mediated apoptosis. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Kelm, R.J., Jr.; Budd, R.C.; Sobel, B.E.; Schneider, D.J. Inhibition of apoptosis and caspase-3 in vascular smooth muscle cells by plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1. J. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 92, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Placencio, V.R.; Declerck, Y.A. Protumorigenic activity of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 through an antiapoptotic function. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2012, 104, 1470–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes-Giacoia, E.; Miyake, M.; Goodison, S.; Rosser, C.J. Targeting plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in a human cancer xenograft model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2697–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czekay, R.P.; Loskutoff, D.J. Unexpected role of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 in cell adhesion and detachment. Exp. Biol. Med. 2004, 229, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Czekay, R.P.; Aertgeerts, K.; Curriden, S.A.; Loskutoff, D.J. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 detaches cells from extracellular matrices by inactivating integrins. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 160, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkawi, S.; Nassar, T.; Tarshis, M.; Cines, D.B.; Higazi, A.A. LRP and alphavbeta3 mediate tPA activation of smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. 2006, 291, H1351–H1359. [Google Scholar]
- Czekay, R.P.; Wilkins-Port, C.E.; Higgins, S.P.; Freytag, J.; Overstreet, J.M.; Klein, R.M.; Higgins, C.E.; Samarakoon, R.; Higgins, P.J. PAI-1: An integrator of cell signaling and migration. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 2011, 562481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkles, J.A. The TWEAK-Fn14 cytokine-receptor axis: Discovery, biology and therapeutic targeting. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Garcia, B.; Madrigal-Matute, J.; Moreno, J.A.; Martin-Ventura, J.L.; Lopez-Franco, O.; Sastre, C.; Ortega, L.; Burkly, L.C.; Egido, J.; Blanco-Colio, L.M. TWEAK-Fn14 interaction enhances plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and tissue factor expression in atherosclerotic plaques and in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 89, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Providence, K.M.; Higgins, S.P.; Mullen, A.; Battista, A.; Samarakoon, R.; Higgins, C.E.; Wilkins-Port, C.E.; Higgins, P.J. SERPINE1 (PAI-1) is deposited into keratinocyte migration “trails” and required for optimal monolayer wound repair. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2008, 300, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.C.; Duszczyszyn, D.A.; Castellino, F.J.; Ploplis, V.A. Accelerated skin wound healing in plasminogen activator inhibitor-1-deficient mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 1681–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romer, J.; Bugge, T.H.; Pyke, C.; Lund, L.R.; Flick, M.J.; Degen, J.L.; Dano, K. Impaired wound healing in mice with a disrupted plasminogen gene. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simone, T.M.; Longmate, W.M.; Law, B.K.; Higgins, P.J. Targeted inhibition of PAI-1 activity impairs epithelial migration and wound closure following cutaneous injury. Adv. Wound Care 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Murphy, S.B.; Kishore, R.; Vaughan, D.E. Global gene expression profiling in PAI-1 knockout murine heart and kidney: Molecular basis of cardiac-selective fibrosis. PLoS One 2013, 8, e63825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasek, J.J.; Gabbiani, G.; Hinz, B.; Chaponnier, C.; Brown, R.A. Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective tissue remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinz, B.; Phan, S.H.; Thannickal, V.J.; Galli, A.; Bochaton-Piallat, M.L.; Gabbiani, G. The myofibroblast: One function, multiple origins. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 1807–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmouliere, A.; Gabbian, G. Apoptosis mediates the decrease in cellularity during the transition between granulation tissue and scar. Exp. Nephrol. 1995, 3, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wipff, P.J.; Rifkin, D.B.; Meister, J.J.; Hinz, B. Myofibroblast contraction activates latent TGF-beta1 from the extracellular matrix. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 179, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Vaughan, D.E. PAI-1 in tissue fibrosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ann, D.K.; Akhondzadeh, A.; Duong, H.S.; Messadi, D.V.; Le, A.D. Increased vascular endothelial growth factor may account for elevated level of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 via activating ERK1/2 in keloid fibroblasts. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2004, 286, C905–C912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuan, T.L.; Wu, H.; Huang, E.Y.; Chong, S.S.; Laug, W.; Messadi, D.; Kelly, P.; Le, A. Increased plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in keloid fibroblasts may account for their elevated collagen accumulation in fibrin gel cultures. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ly, C.M.; Ko, C.Y.; Meyers, E.E.; Lawrence, D.A.; Bernstein, A.M. UPA binding to PAI-1 induces corneal myofibroblast differentiation on vitronectin. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 4765–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroja, B.S.; Kang, L.E.; Imas, A.O.; Carmeliet, P.; Bernstein, A.M. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 regulates integrin alphavbeta3 expression and autocrine transforming growth factor β signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 20708–20717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diebold, I.; Kraicun, D.; Bonello, S.; Gorlach, A. The “PAI-1 paradox” in vascular remodeling. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 100, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balsara, R.D.; Ploplis, V.A. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1: The double-edged sword in apoptosis. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 100, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Longmate, W.M.; Monichan, R.; Chu, M.L.; Tsuda, T.; Mahoney, M.G.; DiPersio, C.M. Reduced fibulin-2 contributes to loss of basement membrane integrity and skin blistering in mice lacking integrin alpha3beta1 in the epidermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, J.C.; Rogers, D.S.; Simon, R.H.; Sisson, T.H.; Thannickal, V.J. Plasminogen activation induced pericellular fibronectin proteolysis promotes fibroblast apoptosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
