Modeling Diurnal Changes in Land Surface Temperature in Urban Areas under Cloudy Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Concept for Modeling Land Surface Temperature
2.2. Implementation in GRASS GIS
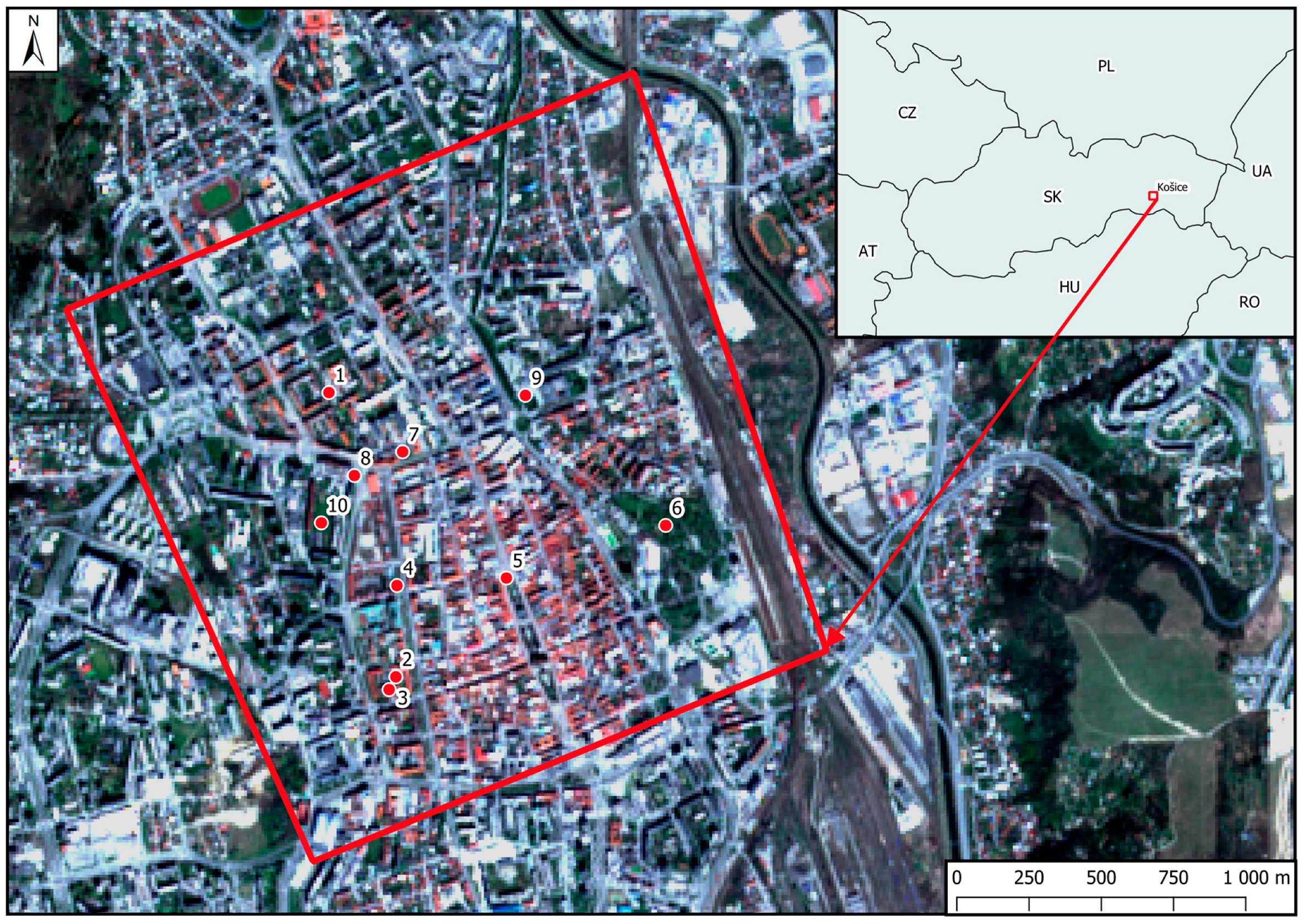
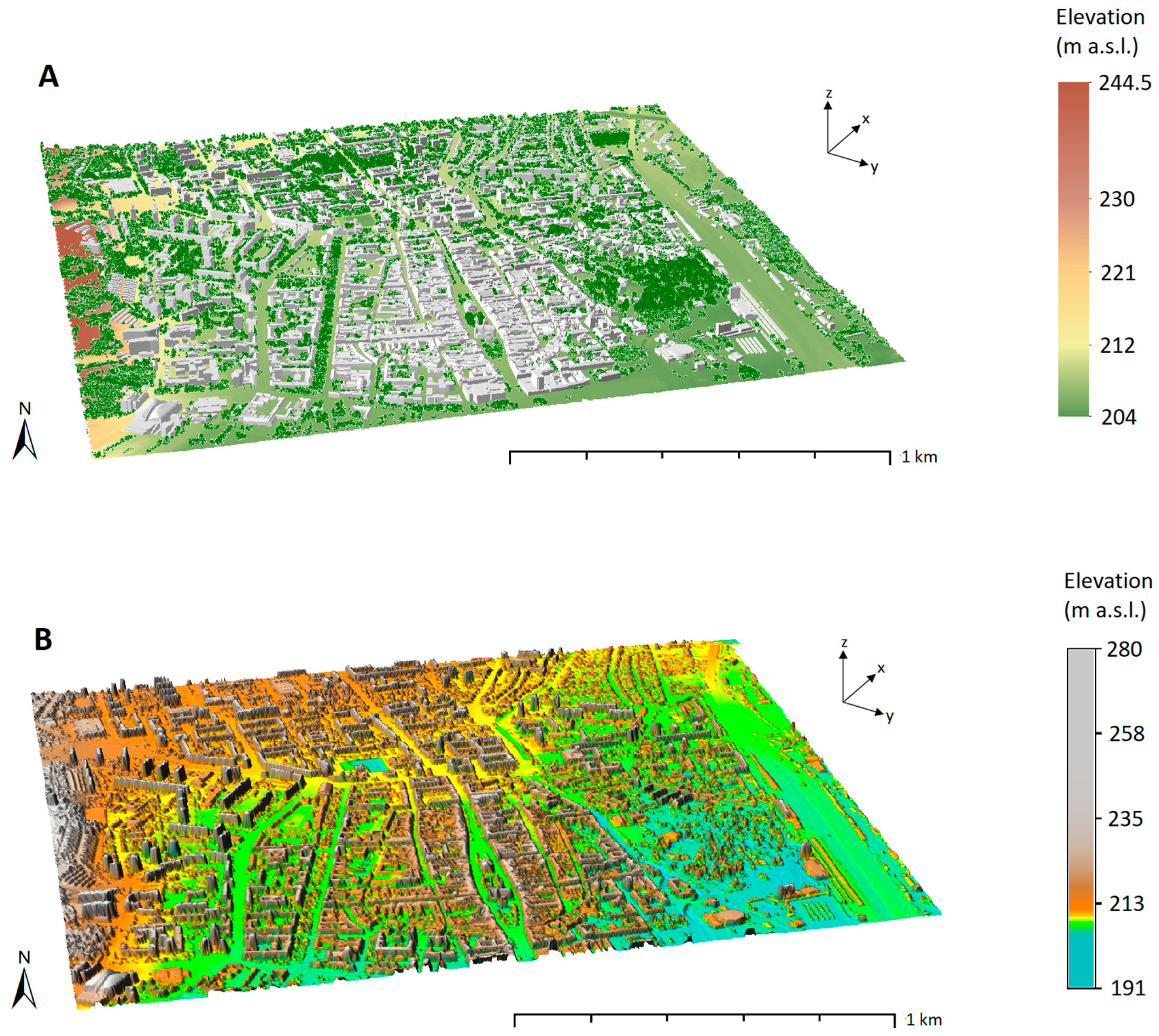
2.3. The Study Area and Data Collection
2.4. Input Data
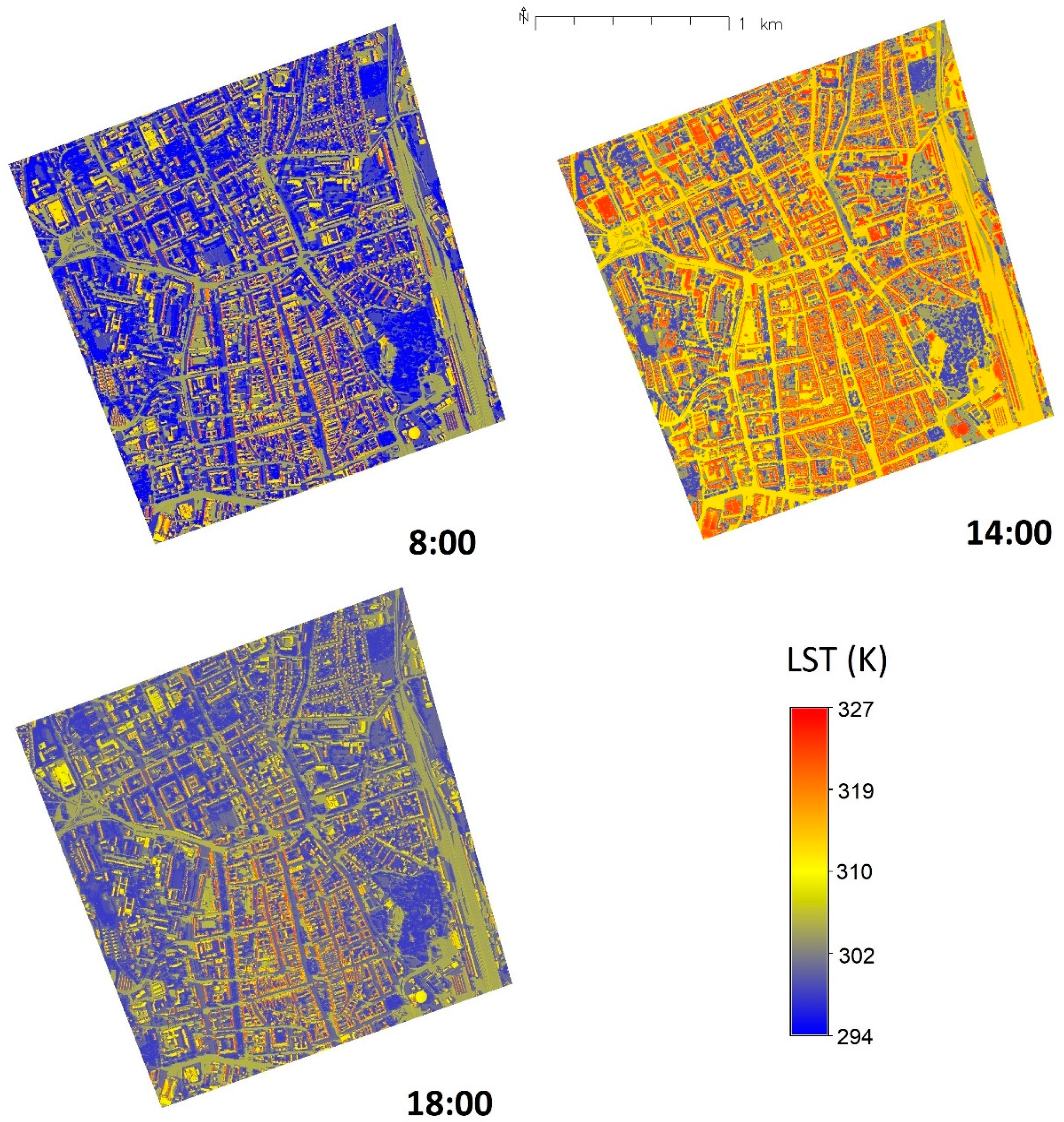
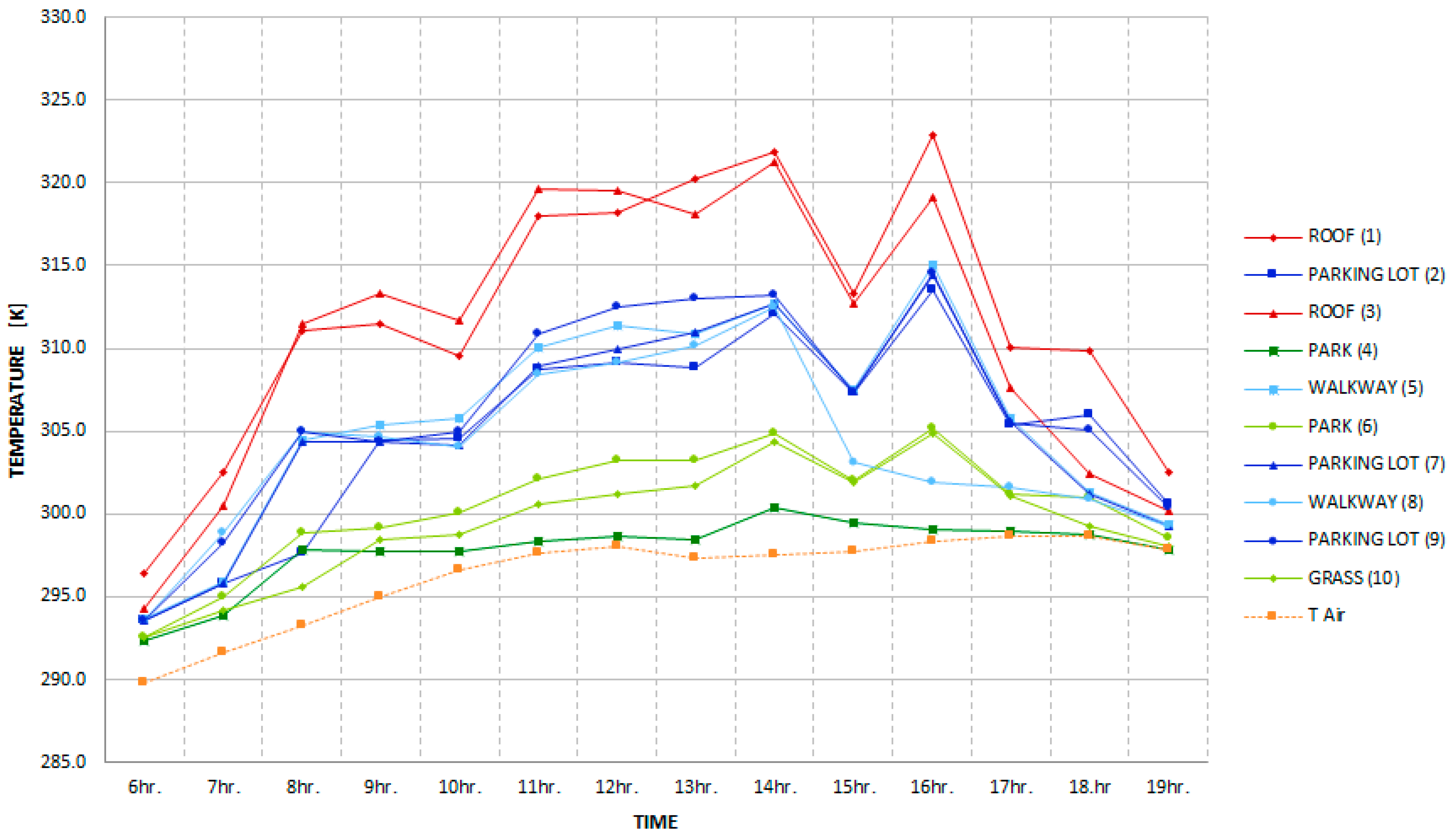
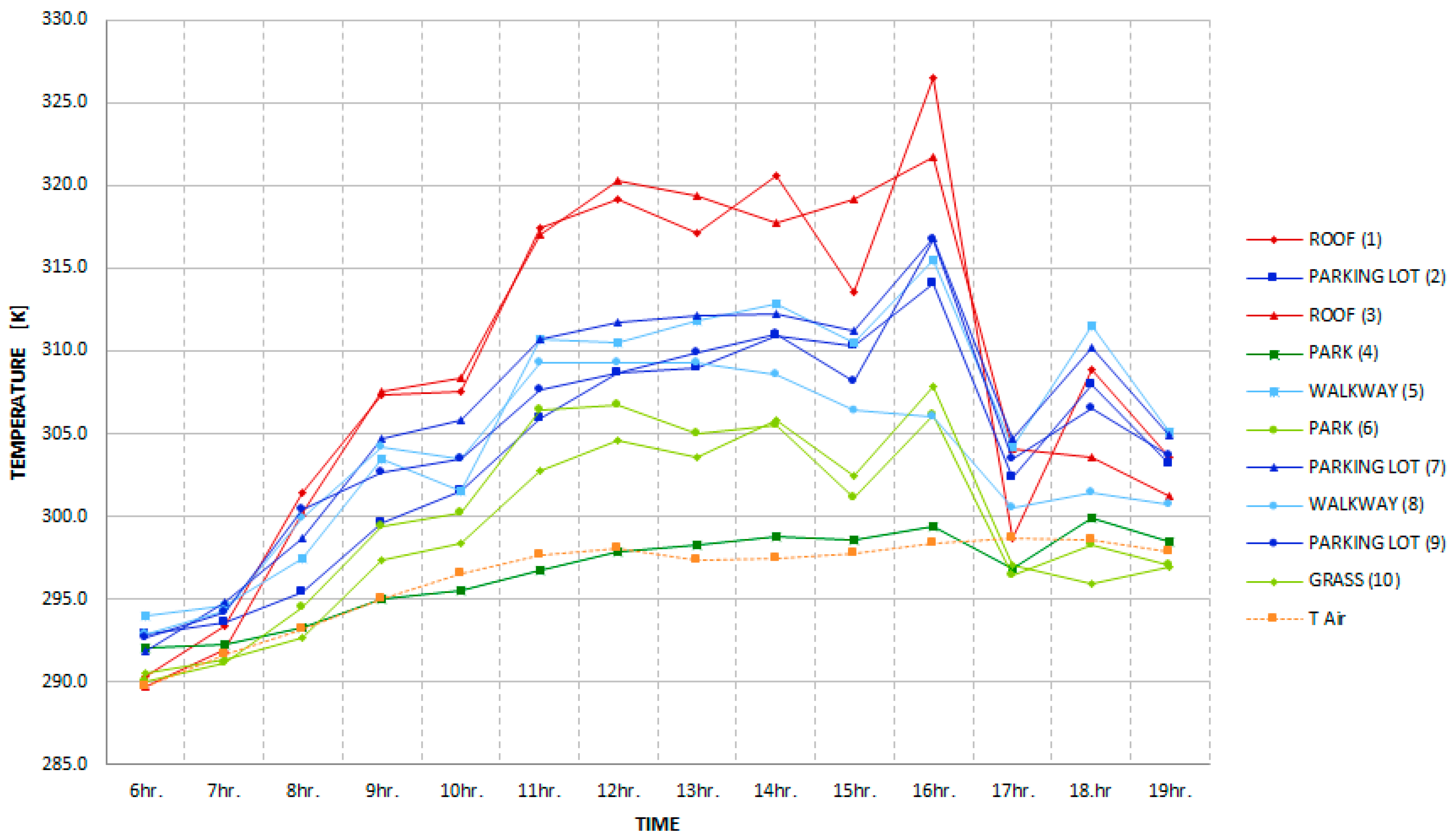
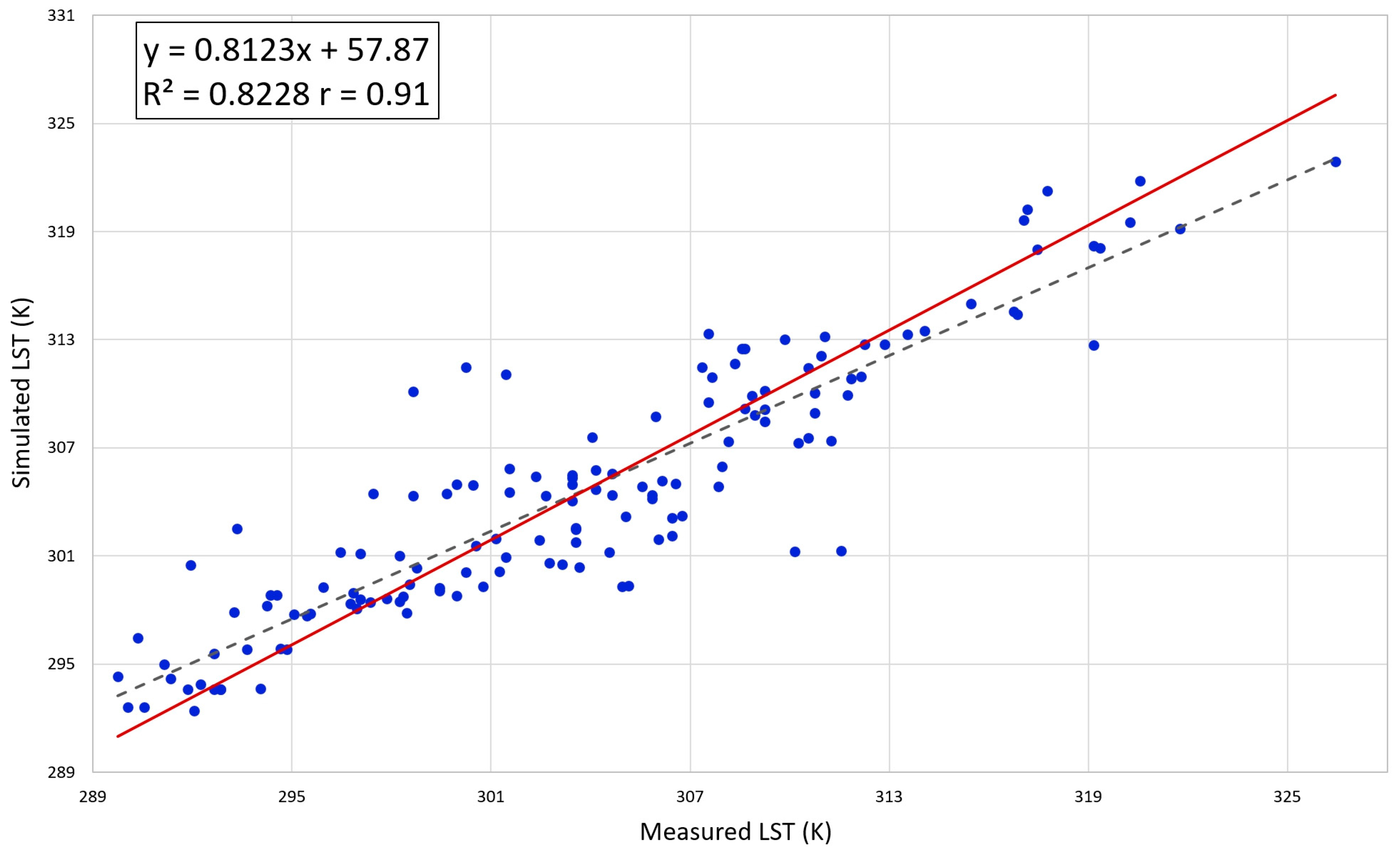
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y. Remote sensing retrieval of urban land surface temperature in hot-humid region. Urban Clim. 2018, 24, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y.; Myint, S.W. Effects of landscape composition and pattern on land surface temperature: An urban heat island study in the megacities of Southeast Asia. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 577, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, A.; Sharifi, E. Daily variation of urban heat island effect and its correlations to urban greenery: A case study of Adelaide. Front. Arch. Res. 2017, 6, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, J.E. A GIS-Based Approach to Microclimate Monitoring in Singapore’s High-Rise Housing Estates. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1994, 60, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar]
- The Urban Heat Island (UHI) Effect. Available online: http://www.urbanheatislands.com (accessed on 26 January 2019).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Reducing urban heat islands: Compendium of strategies. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/heat-islands/heat-island-compendium (accessed on 26 January 2019).
- Chen, Y.-C.; Chiu, H.-W.; Su, Y.-F.; Wu, Y.-C.; Cheng, K.-S. Does urbanization increase diurnal land surface temperature variation? Evidence and implications. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 157, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdahl, P.; Bretz, S.E. Preliminary survey of the solar reflectance of cool roofing materials. Energy Build. 1997, 25, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirsadeghi, M.; Costola, D.; Blocken, B.; Hensen, J. Review of external convective heat transfer coefficient models in building energy simulation programs: Implementation and uncertainty. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 56, 134–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Wendel, J. Analysis of urban surface morphologic effects on diurnal thermal directional anisotropy. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2019, 148, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Tang, B.-H.; Wu, H.; Ren, H.; Yan, G.; Wan, Z.; Trigo, I.F.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite-derived land surface temperature: Current status and perspectives. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voogt, J.; Oke, T. Thermal remote sensing of urban climates. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, T.; Miřijovský, J.; Purket, T. Airborne thermal remote sensing: The case of the city of Olomouc, Czech Republic. Eur. J. Remote. Sens. 2019, 52, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofierka, J.; Kaňuk, J. Assessment of photovoltaic potential in urban areas using open-source solar radiation tools. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 2206–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofierka, J.; Zlocha, M. A New 3-D Solar Radiation Model for 3-D City Models. Trans. GIS 2012, 16, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, S.; Catita, C.; Redweik, P.; Brito, M.C. Modelling solar potential in the urban environment: State-of-the-art review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biljecki, F.; Stoter, J.; LeDoux, H.; Zlatanova, S.; Çöltekin, A. Applications of 3D City Models: State of the Art Review. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2015, 4, 2842–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redweik, P.; Catita, C.; Brito, M.C. Solar energy potential on roofs and facades in an urban landscape. Sol. Energy 2013, 97, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogl, M.; Moudrý, V. Influence of vegetation canopies on solar potential in urban environments. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 66, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingberg, J.; Konarska, J.; Lindberg, F.; Johansson, L.; Thorsson, S. Mapping leaf area of urban greenery using aerial LiDAR and ground-based measurements in Gothenburg, Sweden. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 26, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofierka, J.; Gallay, M.; Onačillová, K.; Hofierka, J., Jr. Physically-based land surface temperature modeling in urban areas usinga 3-D city model and multispectral satellite data. Urban Clim. 2020, 31, 100566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GRASS GIS. Available online: http://grass.osgeo.org/ (accessed on 4 June 2020).
- Bretz, S.; Akbari, H.; Rosenfeld, A. Practical issues for using solar-reflective materials to mitigate urban heat islands. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ASHRAE. Handbook: Fundamentals; American Society of Heating, Refrigeration, and Air-Conditioning Engineers: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Grimmond, S.; Oke, T.R. Heat Storage in Urban Areas: Local-Scale Observations and Evaluation of a Simple Model. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1999, 38, 922–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R.; Cleugh, H.A. Urban heat storage derived as energy balance residuals. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1987, 39, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šúri, M.; Hofierka, J. A New GIS-based Solar Radiation Model and Its Application to Photovoltaic Assessments. Trans. GIS 2004, 8, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neteler, M.; Mitasova, H. Open Source GIS: A GRASS GIS Approach, 3rd ed.; The International Series in Engineering and Computer Science; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Onačillová, K.; Gallay, M. Spatio-temporal analysis of surface urban heat island based on LANDSAT ETM+ and OLI/TIRS imagery in the city of Košice, Slovakia. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 13, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofierka, J.; Gallay, M.; Kaňuk, J.; Šupinský, J.; Sasak, J. High-resolution urban greenery mapping for micro-climate modelling based on 3-D city models. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, XLII-4/W7, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neteler, M.; Bowman, M.H.; Landa, M.; Metz, M. GRASS GIS: A multi-purpose open source GIS. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 31, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Algarni, S.A. Modeling Radiation Heat Transfer for Building’s Cooling and Heating Loads: Considering the Role of Clear, Cloudy, and Dusty Conditions in Hot and Dry Climates. Ph.D. Thesis, King Khalid University, Abha, Asir, Saudi Arabia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Whillier, A. Design Factors Influencing Solar Collectors in Low Temperature Engineering Applications of Solar Energy; ASHRAE: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Vanino, S.; Nino, P.; De Michele, C.; Bolognesi, S.F.; D’Urso, G.; Di Bene, C.; Pennelli, B.; Vuolo, F.; Farina, R.; Pulighe, G.; et al. Capability of Sentinel-2 data for estimating maximum evapotranspiration and irrigation requirements for tomato crop in Central Italy. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 452–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneer, T.; Guymard, C.; Kambezidis, H. Solar Radiation and Daylight Models, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Grimmond, S.; Cleugh, H.; Oke, T. An objective urban heat storage model and its comparison with other schemes. Atmos. Environ. Part B. Urban Atmos. 1991, 25, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.-M.; Wang, Y.-L.; Ma, Z.-G.; Liu, Y. Simulating the Regional Impacts of Urbanization and Anthropogenic Heat Release on Climate across China. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 7187–7203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, A.; Vogt, R. Energy and radiation balance of a central European city. Int. J. Clim. 2004, 24, 1395–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
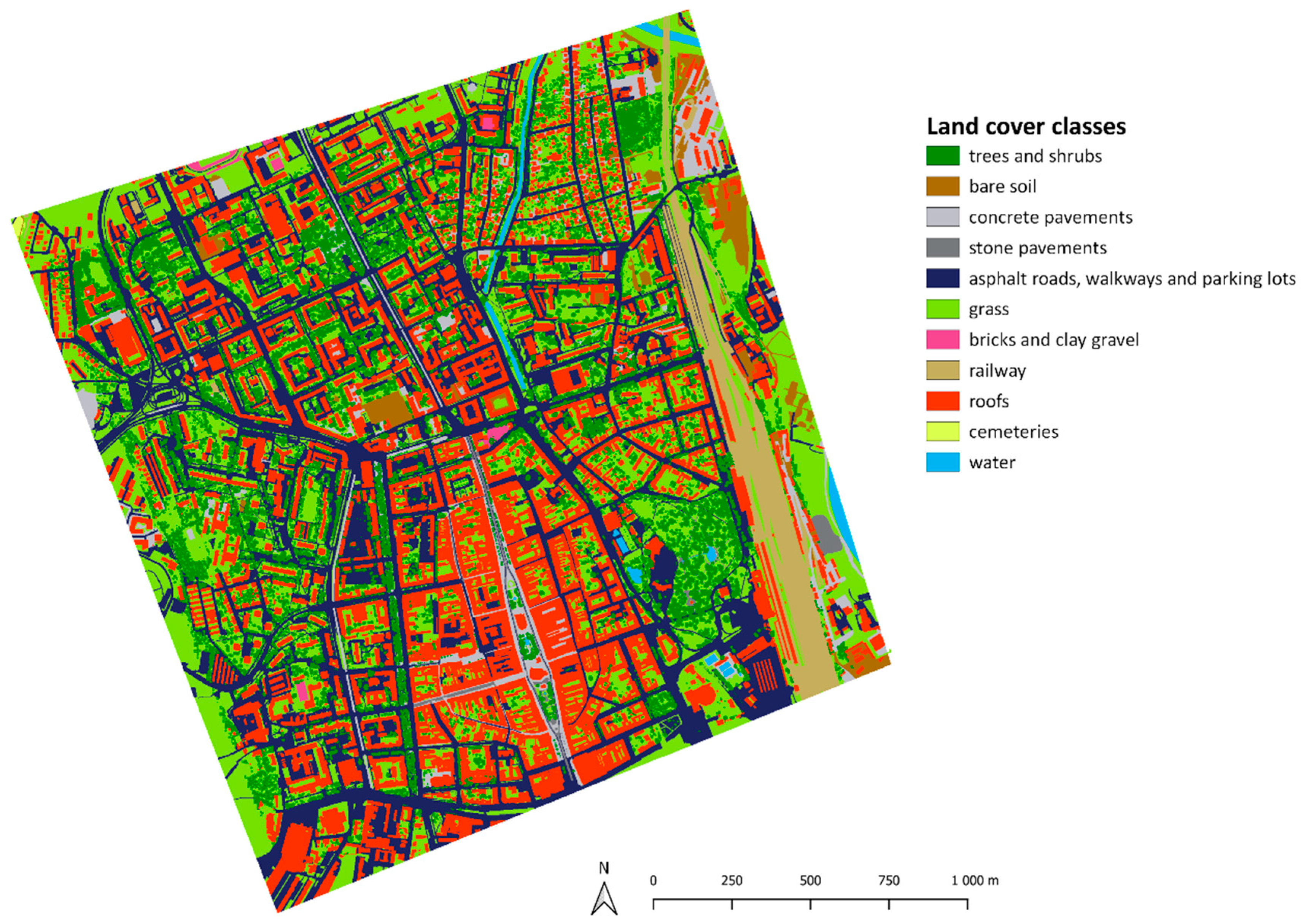
| Land Cover Class | Convective Heat Transfer Coefficient [W.m−2.K−1] |
|---|---|
| roofs | 10 |
| concrete pavements, stone pavements, asphalt roads, walkways and parking lots, bricks and clay gravel, railway, roofs, cemeteries | 20 |
| grass, bare soil | 50 |
| trees and shrubs | 60 |
| water | 80 |
| Time | Roof (1) | Parking Lot (2) | Roof (3) | Park (4) | Walkway (5) | Park (6) | Parking Lot (7) | Walkway (8) | Parking Lot (9) | Grass (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 h | SCL | SCD | SCD | CD | SCD | CD | SCD | SCD | SCD | SCD |
| 7 h | SCD | SCD | SCD | CD | CD | CD | SCD | SCL | SCD | SCL |
| 8 h | SCL | SCL | SCL | SCL | SCL | SCL | SCL | SCL | SCL | SCL |
| 9 h | SCL | SCD | SCD | CD | SCL | SCD | CD | CD | CD | SCD |
| 10 h | CD | CD | CD | CD | SCD | SCD | CD | CD | CD | CD |
| 11 h | SCL | SCD | SCD | CD | SCL | SCD | CD | CD | SCL | SCD |
| 12 h | SCD | CD | SCD | CD | SCL | SCD | CD | CD | SCL | SCD |
| 13 h | SCD | CD | SCD | CD | SCD | SCD | CD | SCL | SCL | CD |
| 14 h | SCD | SCD | SCD | CD | SCD | SCD | SCD | SCD | SCD | SCD |
| 15 h | CD | CD | CD | CD | CD | CD | CD | CD | CD | CD |
| 16 h | SCL | SCL | SCL | CL | CL | SCL | CL | SCL | CL | SCL |
| 17 h | CD-rain | CD-rain | CD-rain | CD-rain | CD-rain | CD-rain | CD-rain | CD-rain | CD-rain | CD-rain |
| 18 h | SCD | CL | SCD | CL | CL | SCD | CL | CL | SCD | SCD |
| 19 h | CD | CD | CD | CD | CD | CD | CD | CD | CD | CD |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hofierka, J.; Bogľarský, J.; Kolečanský, Š.; Enderova, A. Modeling Diurnal Changes in Land Surface Temperature in Urban Areas under Cloudy Conditions. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9090534
Hofierka J, Bogľarský J, Kolečanský Š, Enderova A. Modeling Diurnal Changes in Land Surface Temperature in Urban Areas under Cloudy Conditions. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2020; 9(9):534. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9090534
Chicago/Turabian StyleHofierka, Jaroslav, Jozef Bogľarský, Štefan Kolečanský, and Anastasia Enderova. 2020. "Modeling Diurnal Changes in Land Surface Temperature in Urban Areas under Cloudy Conditions" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 9, no. 9: 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9090534
APA StyleHofierka, J., Bogľarský, J., Kolečanský, Š., & Enderova, A. (2020). Modeling Diurnal Changes in Land Surface Temperature in Urban Areas under Cloudy Conditions. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 9(9), 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9090534






