Design of Multiple Spatial Context Detection Method Considering Elongated Top-Bounded Spaces Based on GPS Signal-To-Noise Ratio and Fuzzy Inference
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Design of Multiple Spatial Context Detection Method Considering ETBS
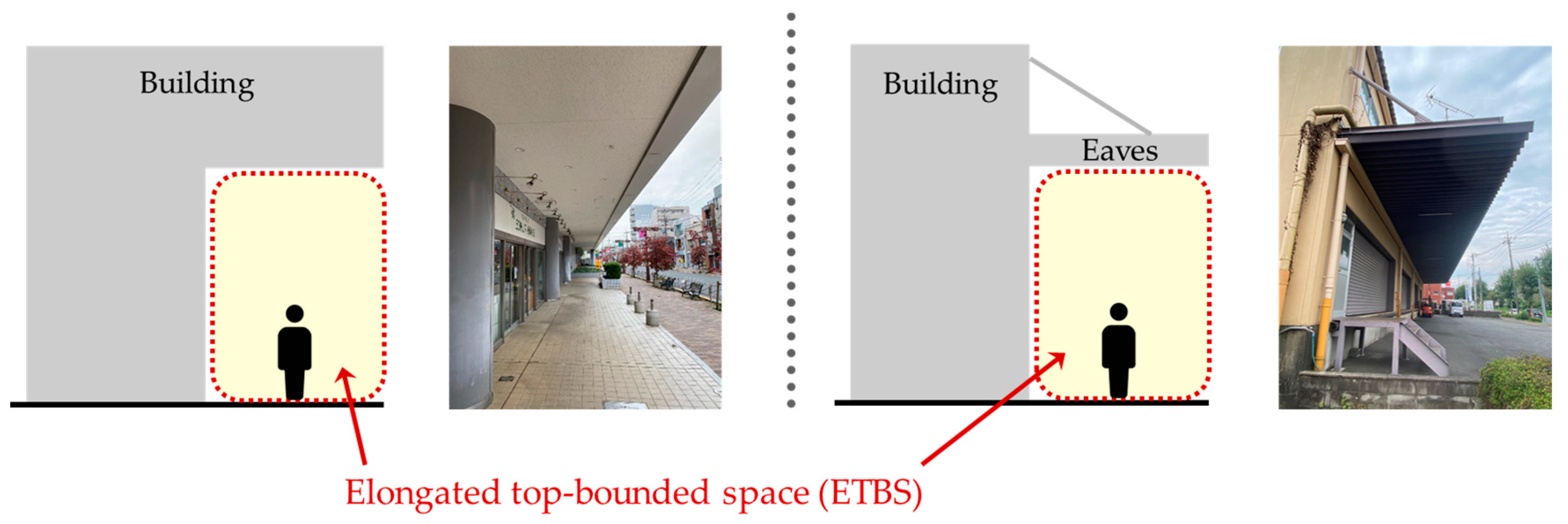
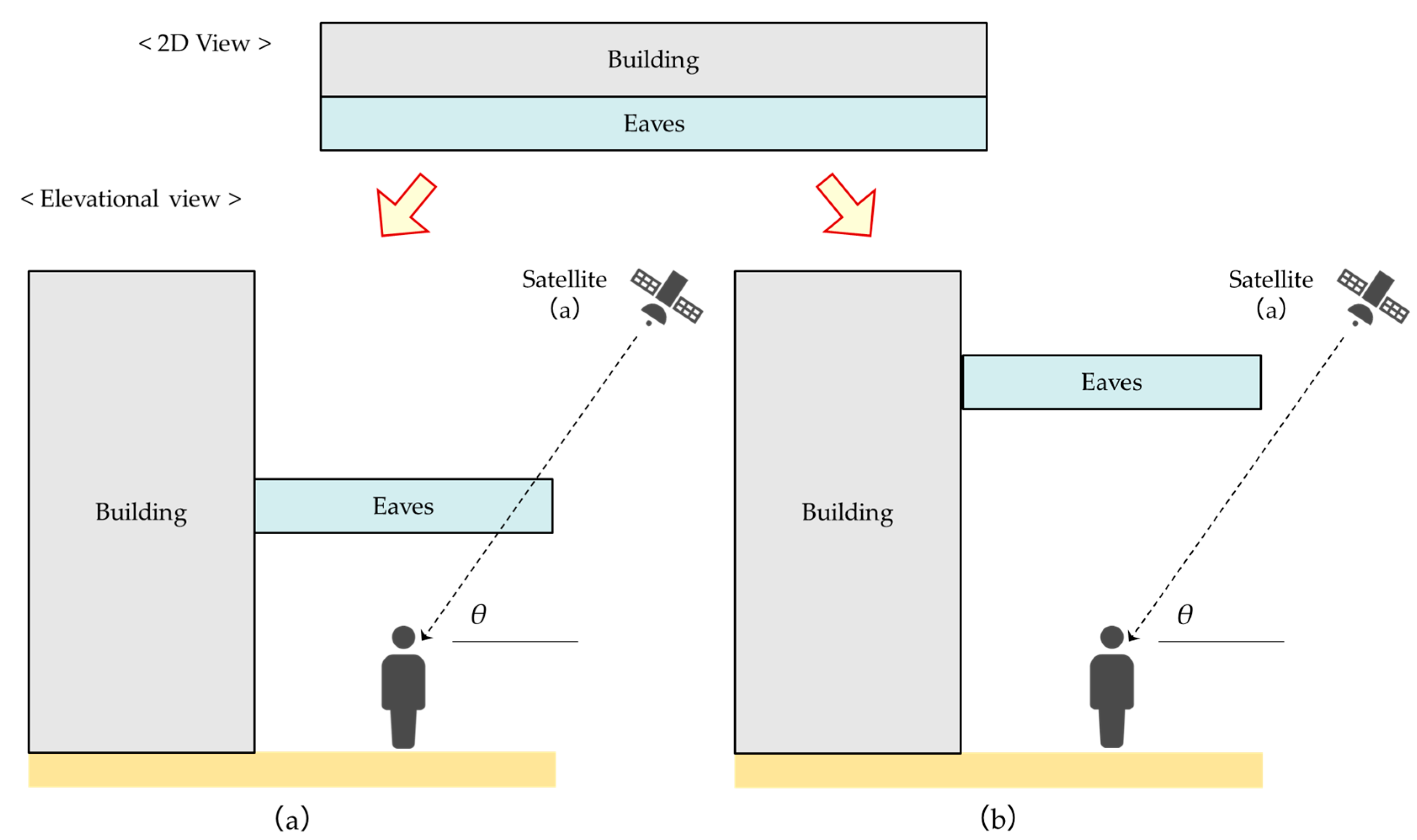
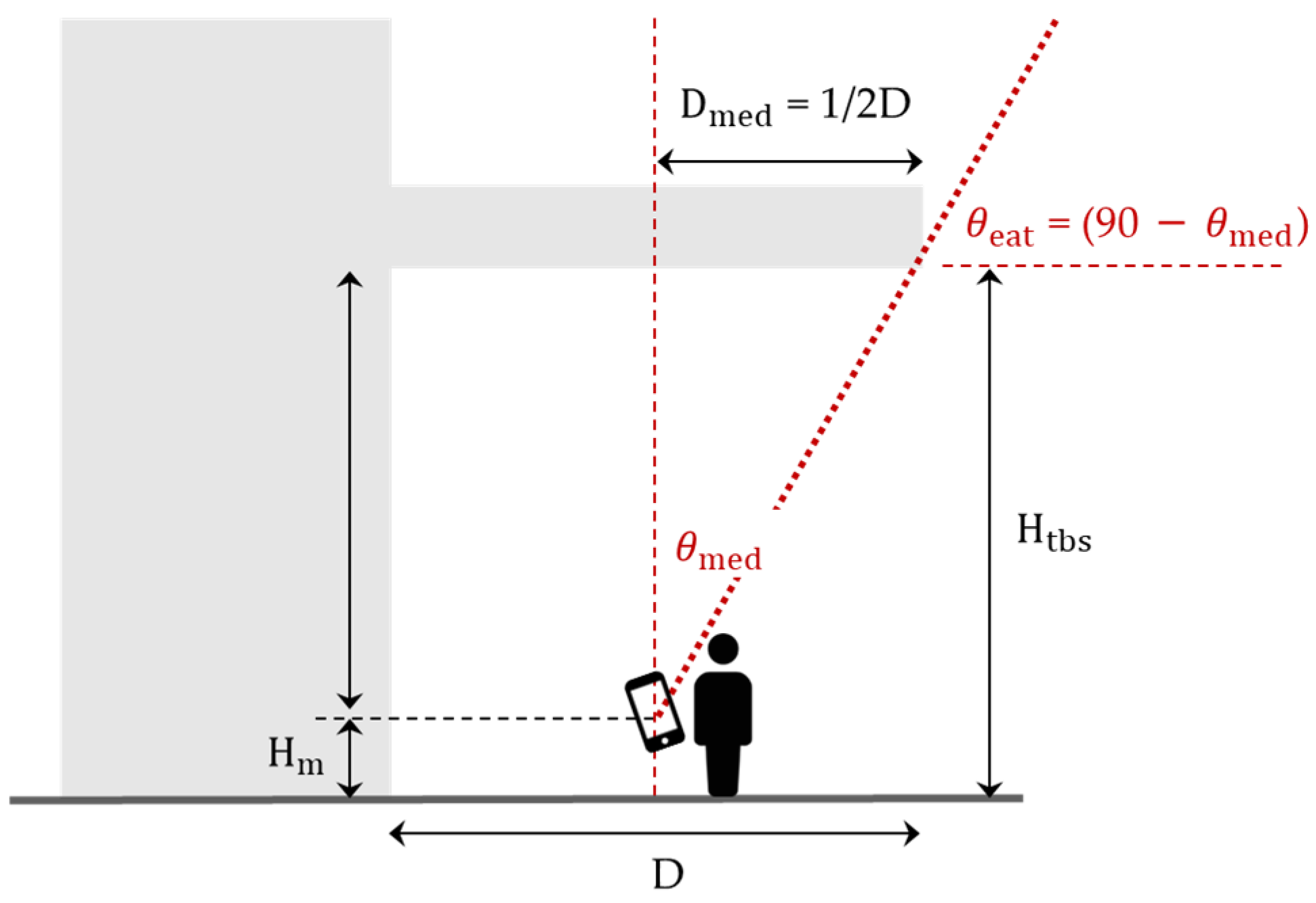
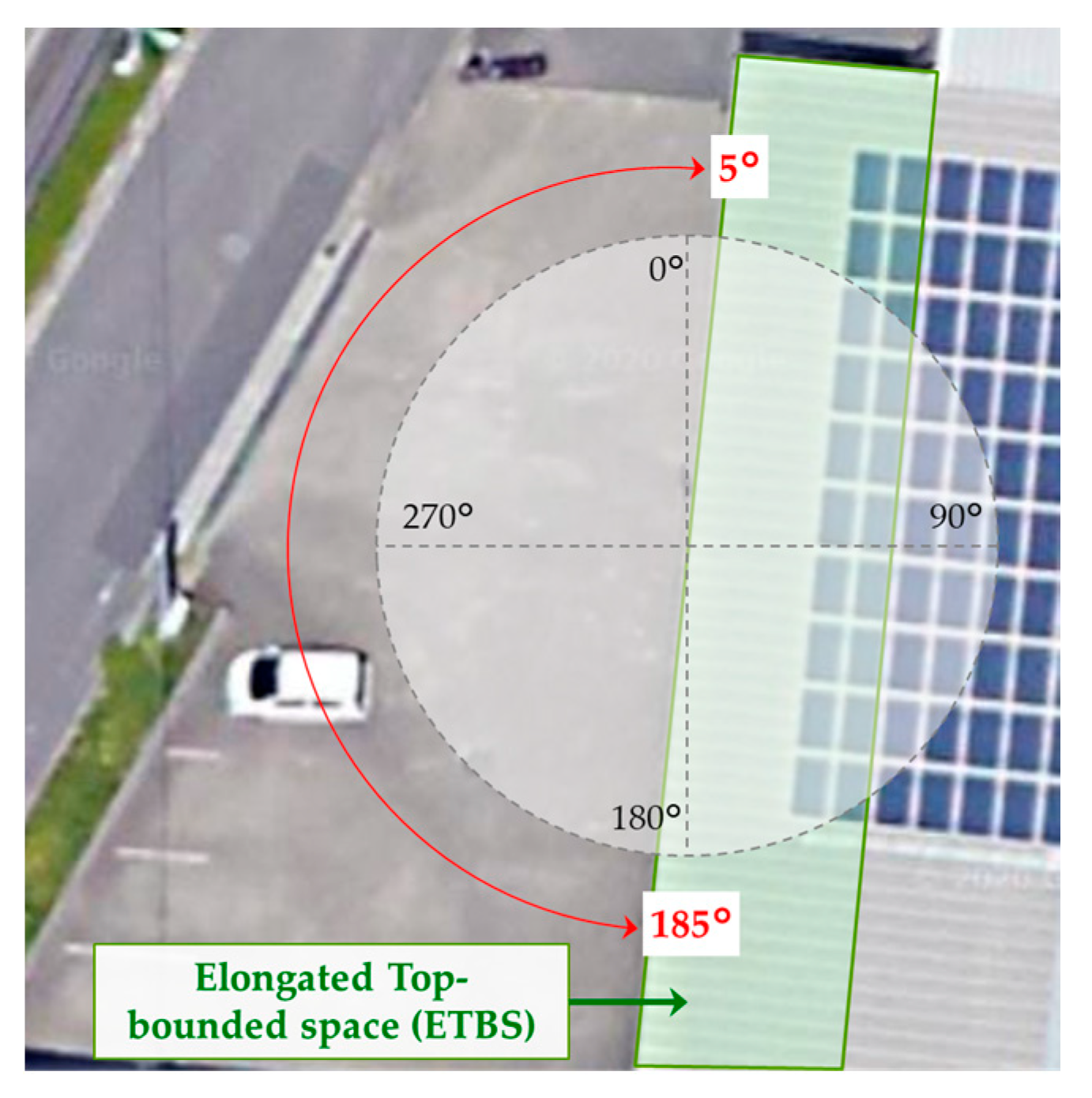
3.1. Requirements for ETBS Stay Detection
3.2. Design of Multiple Spatial Context Detection Method Considering ETBS
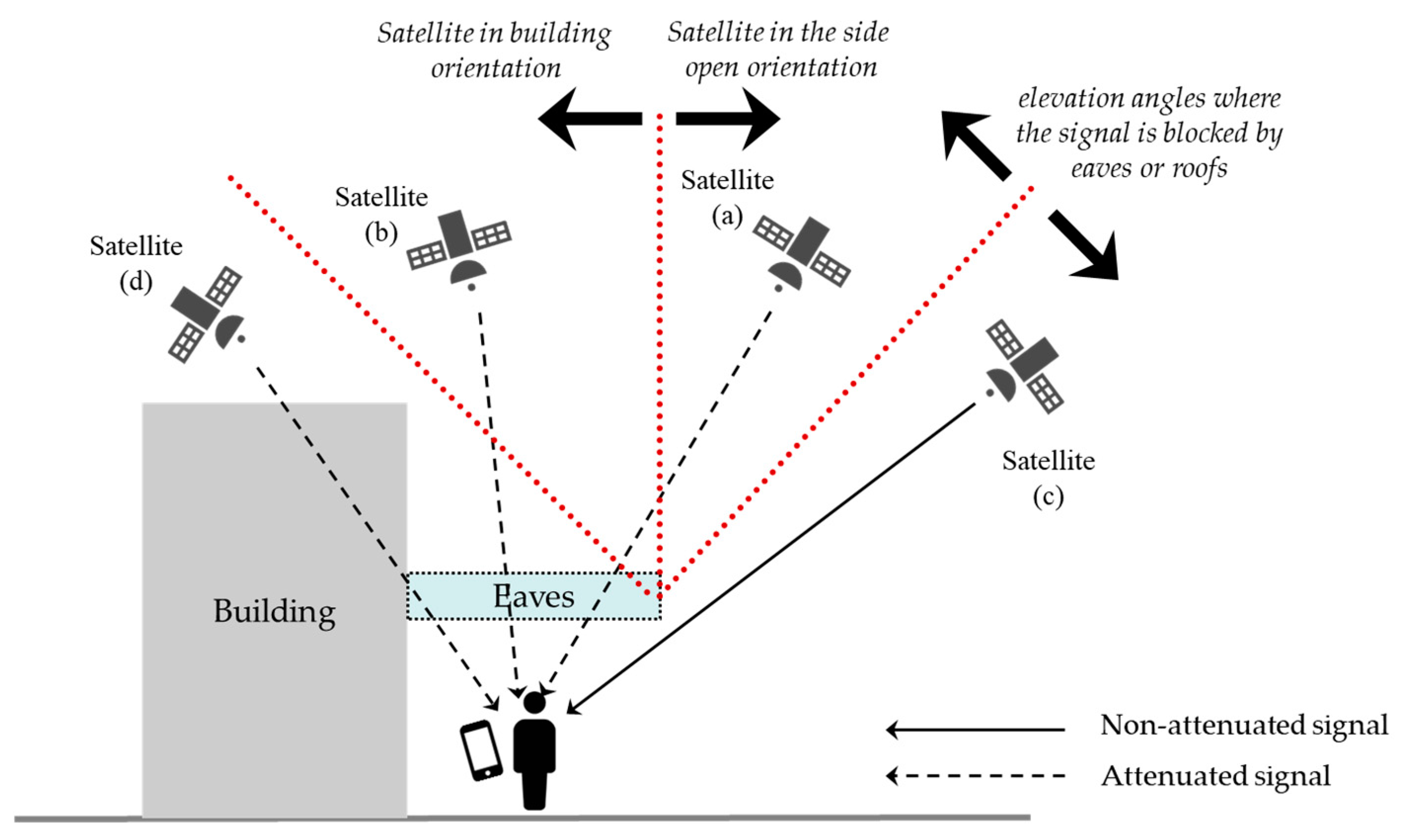
3.2.1. Overview
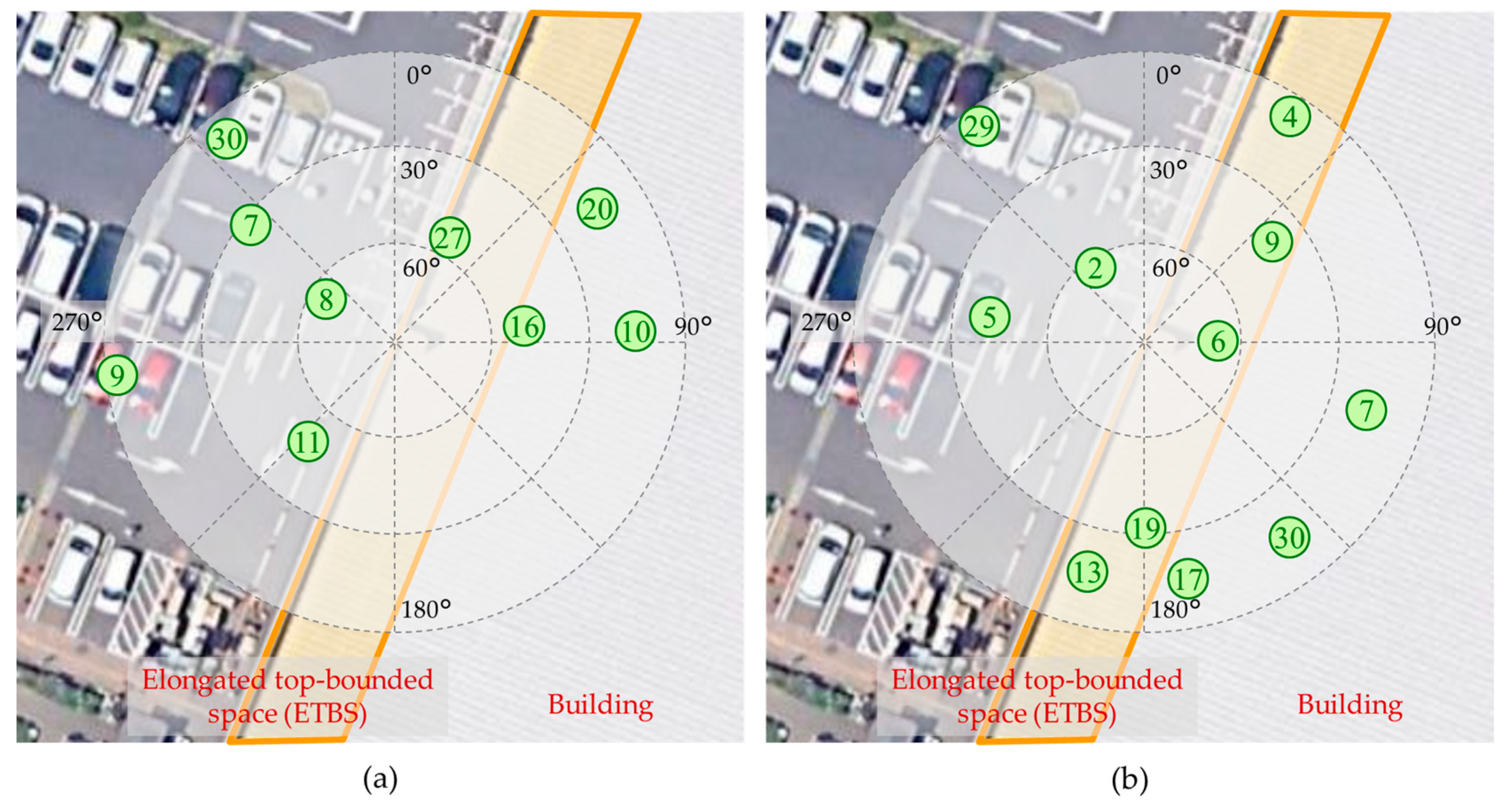
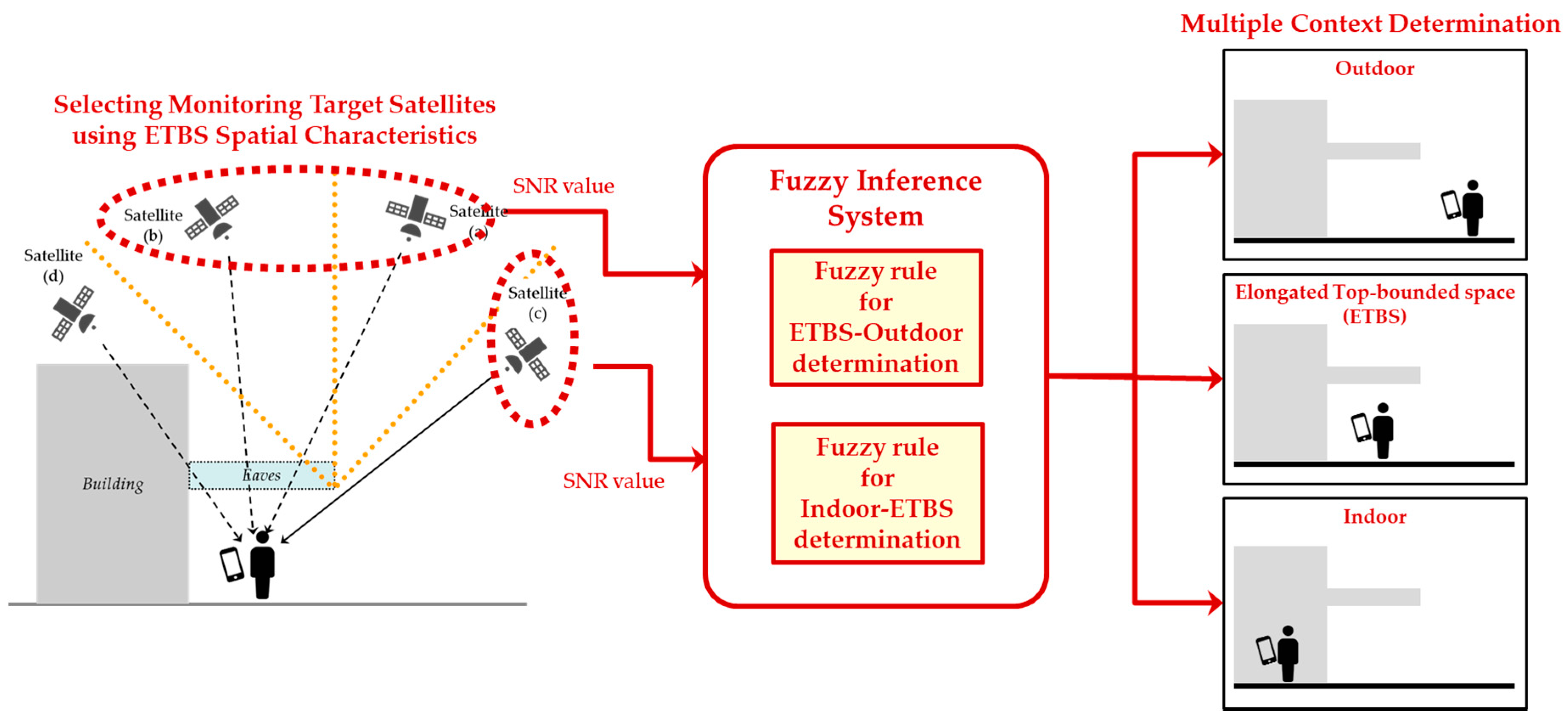
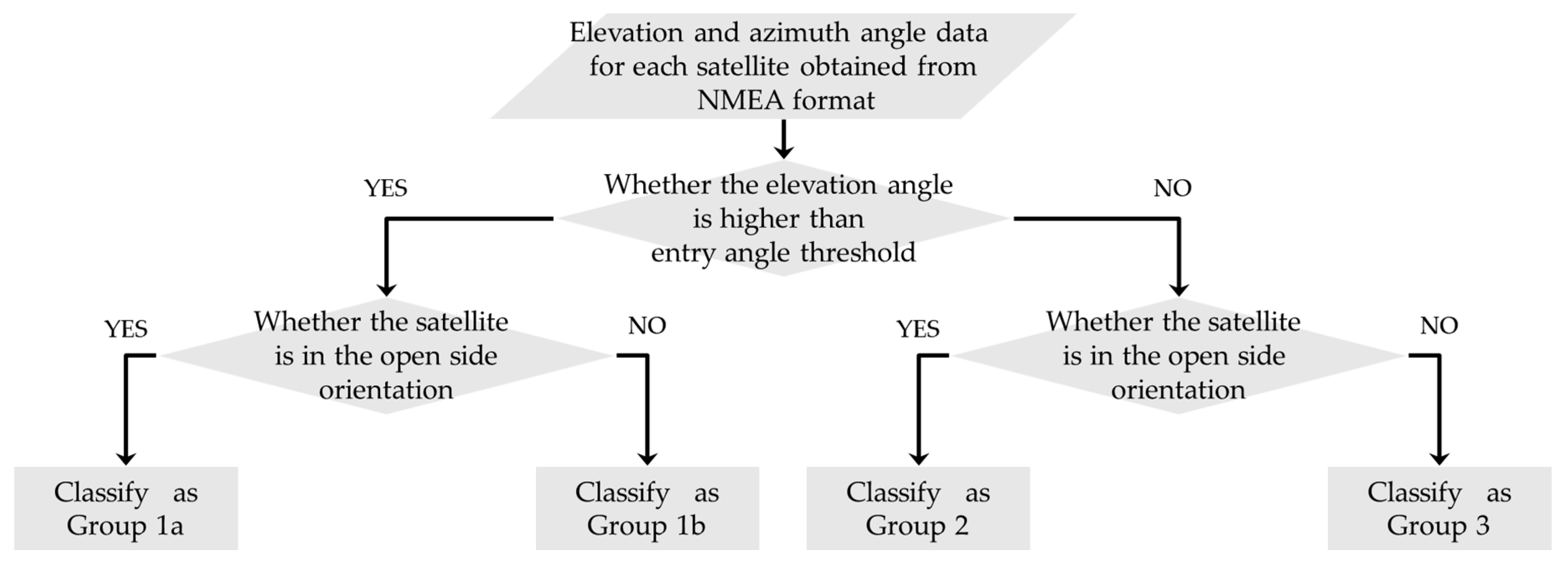
3.2.2. Satellite Classification Using the Entry Angle Threshold and Side Open Orientation
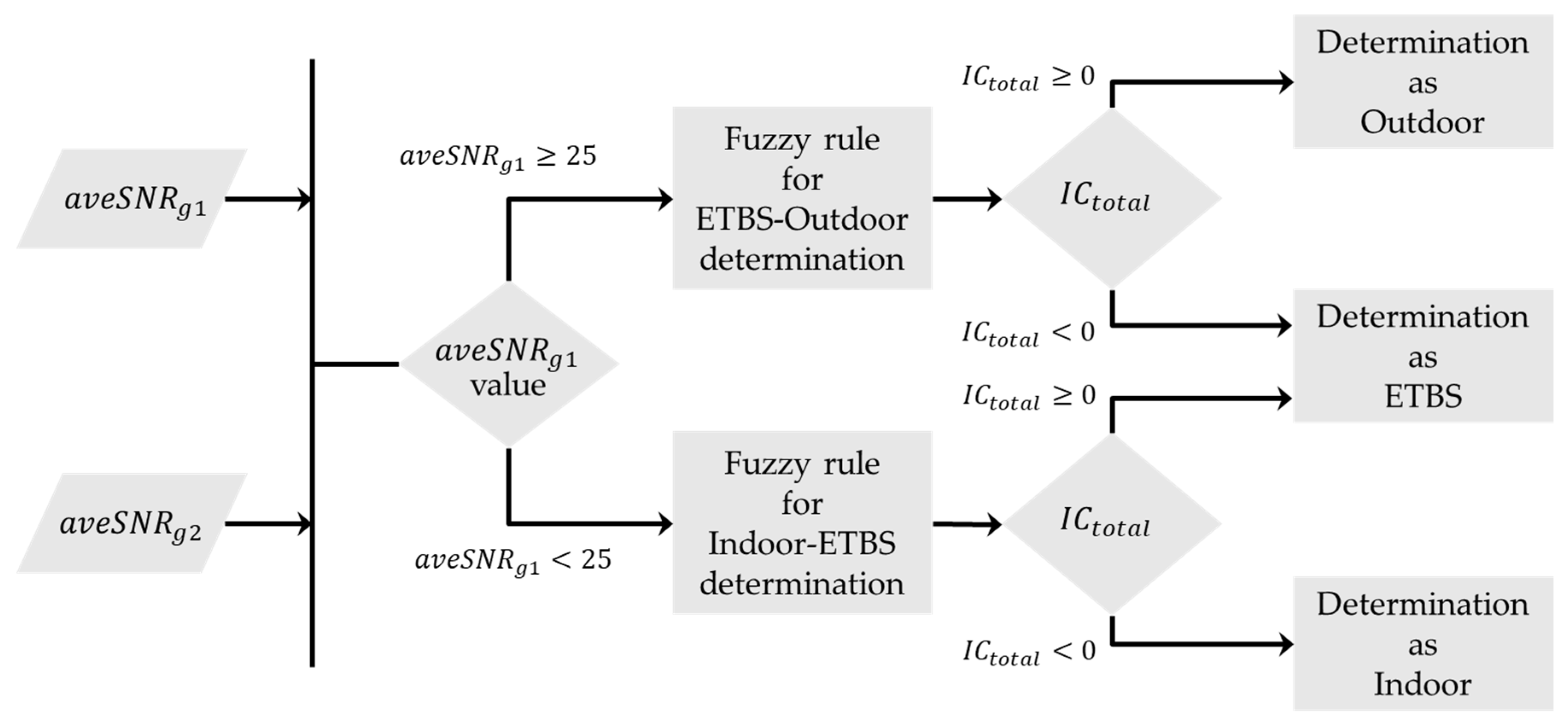
3.2.3. Design of the Decision Flow for Multiple Spatial Context Detection Using Fuzzy Inference
4. Evaluation Experiments
4.1. Evaluation for Multiple Spatial Context Detection Using Our Proposed Method
4.2. Evaluation of Differences in the Detection Accuracy by the Receiving Devices
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maghdid, H.S.; Lami, I.A.; Ghafoor, K.Z.; Lloret, J. Seamless outdoors-indoors localization solutions on smartphones: Implementation and challenges. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2016, 48, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, T.; Li, B.; Dempster, A.G.; Rizos, C. Power efficient indoor/outdoor positioning handover. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN11), Guimarães, Portugal, 21–23 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kohtake, N.; Morimoto, S.; Kogure, S.; Manandhar, D. Indoor and outdoor seamless positioning using indoor messaging system and GPS. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN2011), Guimarães, Portugal, 21–23 September 2011; pp. 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, R.S.; Hong, W.J.; Wang, J.S.; Lin, K.W. Seamless guidance system combining GPS, BLE beacon, and NFC technologies. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2016, 2016, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Wang, J.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, S. Seamless pedestrian navigation methodology optimized for indoor/outdoor detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 18, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, F.; Ning, B.; Ke, Q.; Zhang, C. A fast indoor/outdoor transition detection algorithm based on machine learning. Sensors 2019, 19, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatanova, S.; Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Diakité, A.; Isikdag, U.; Sithole, G.; Barton, J. Spaces in spatial science and urban applications—State of the art review. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Diakité, A.A.; Zlatanova, S.; Aleksandrov, M. Finding outdoor boundaries for 3D space-based navigation. Trans. GIS 2020, 24, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Diakité, A.A.; Zlatanova, S. An extraction approach of the top-bounded space formed by buildings for pedestrian navigation. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 4, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feriol, F.; Vivet, D.; Watanabe, Y. A Review of Environmental Context Detection for Navigation Based on Multiple Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Jiang, H.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, J.; Lu, X.; Xie, L. Bluedetect: An ibeacon-enabled scheme for accurate and energy-efficient indoor-outdoor detection and seamless location-based service. Sensors 2016, 16, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Groves, P.D. Environmental context detection for adaptive navigation using GNSS measurements from a smartphone. Navig. J. Inst. Navig. 2018, 65, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Shen, G. Iodetector: A generic service for indoor outdoor detection. In Proceedings of the 10th Acm Conference on Embedded Network Sensor Systems, Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–9 November 2012; pp. 113–126. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Diakité, A.A.; Zlatanova, S. A generic space definition framework to support seamless indoor/outdoor navigation systems. Trans. GIS 2019, 23, 1273–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.T. Analysis and modeling GPS NLOS effect in highly urbanized area. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Groves, P.D.; Ziebart, M.K. Smartphone shadow matching for better cross-street GNSS positioning in urban environments. J. Navig. 2015, 68, 411–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjrad, M.; Groves, P.D. Enhancing least squares GNSS positioning with 3D mapping without accurate prior knowledge. Navig. J. Inst. Navig. 2017, 64, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Bai, X.; Kan, Y.C.; Hsu, L.T. Tightly coupled GNSS/INS integration via factor graph and aided by fish-eye camera. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 10651–10662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyraud, S.; Bétaille, D.; Renault, S.; Ortiz, M.; Mougel, F.; Meizel, D.; Peyret, F. About non-line-of-sight satellite detection and exclusion in a 3D map-aided localization algorithm. Sensors 2013, 13, 829–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seco-Granados, G.; Lopez-Salcedo, J.; Jimenez-Banos, D.; Lopez-Risueno, G. Challenges in indoor global navigation satellite systems: Unveiling its core features in signal processing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2012, 29, 108–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, H.-J. Fuzzy set theory. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, T.; Sugeno, M. Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1985, 1, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaminpardaz, S.; Wang, K.; Teunissen, P.J.G. Australia-first high-precision positioning results with new Japanese QZSS regional satellite system. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chang, Q.; Li, Q.; Shi, Z.; Chen, W. Indoor-Outdoor Detection Using a Smart Phone Sensor. Sensors 2016, 16, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


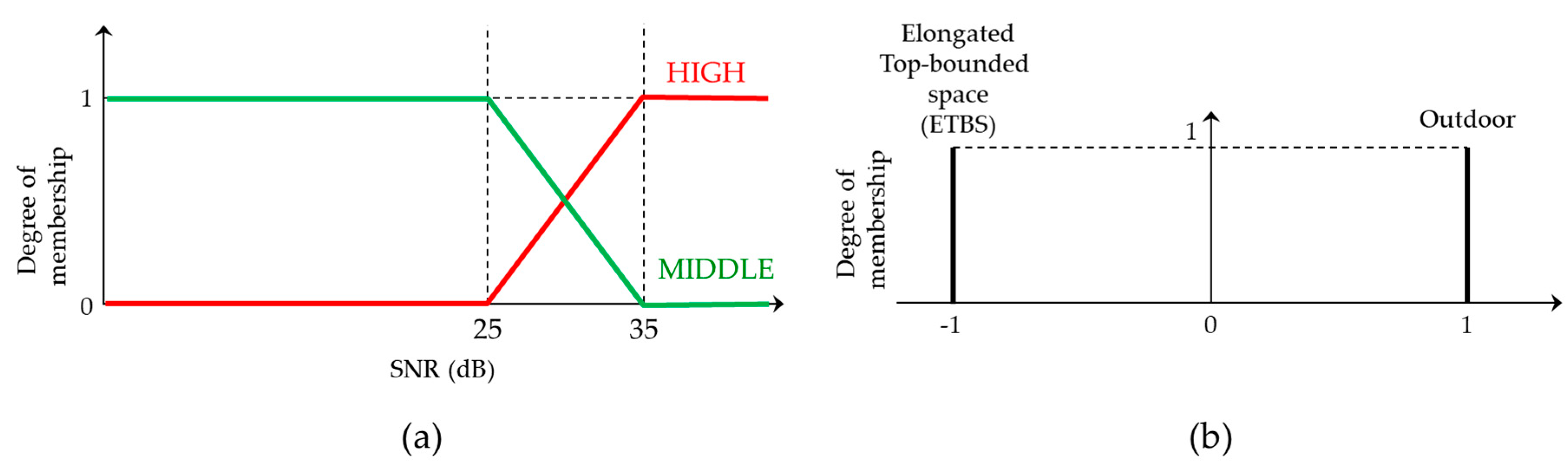


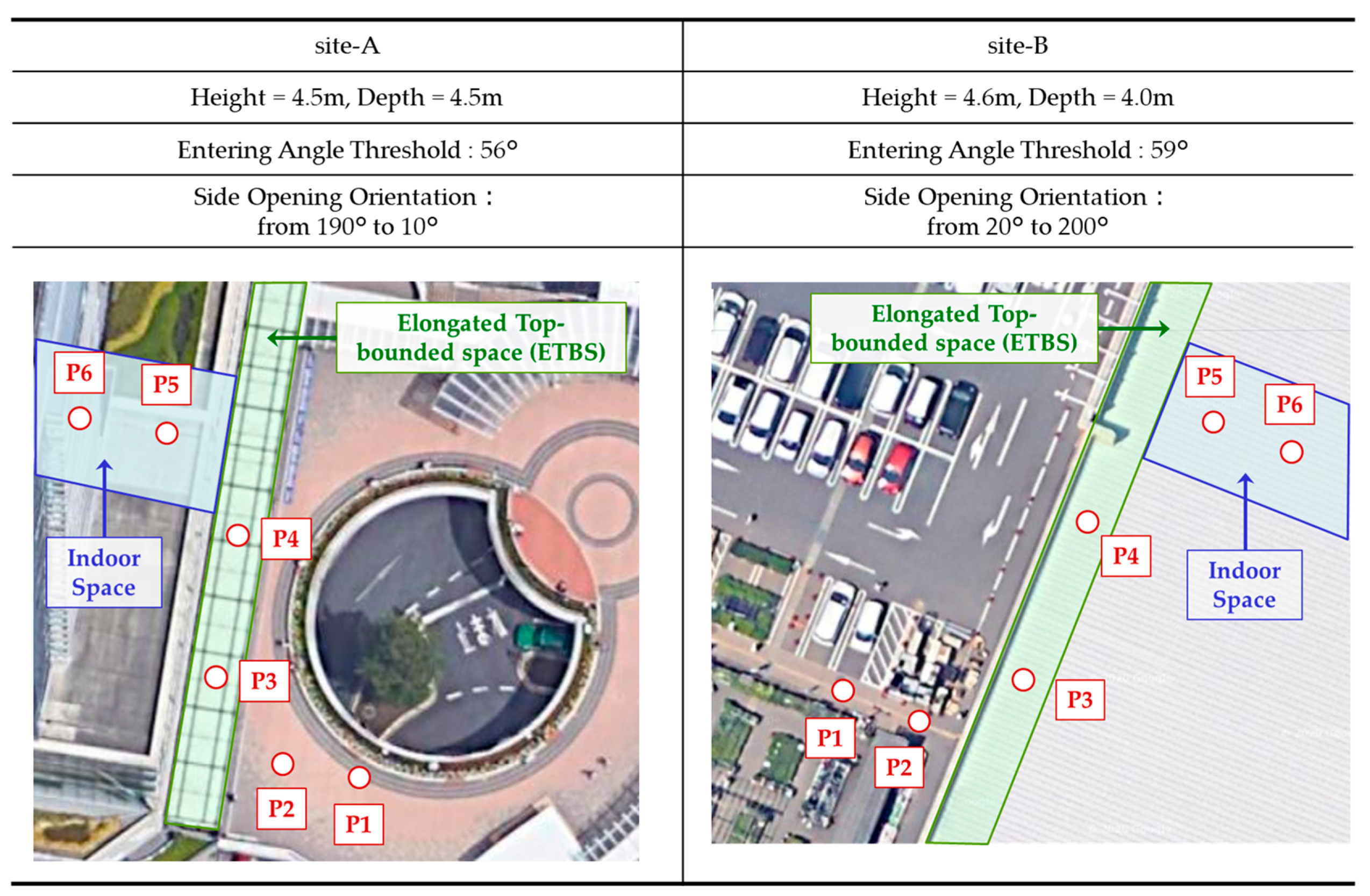
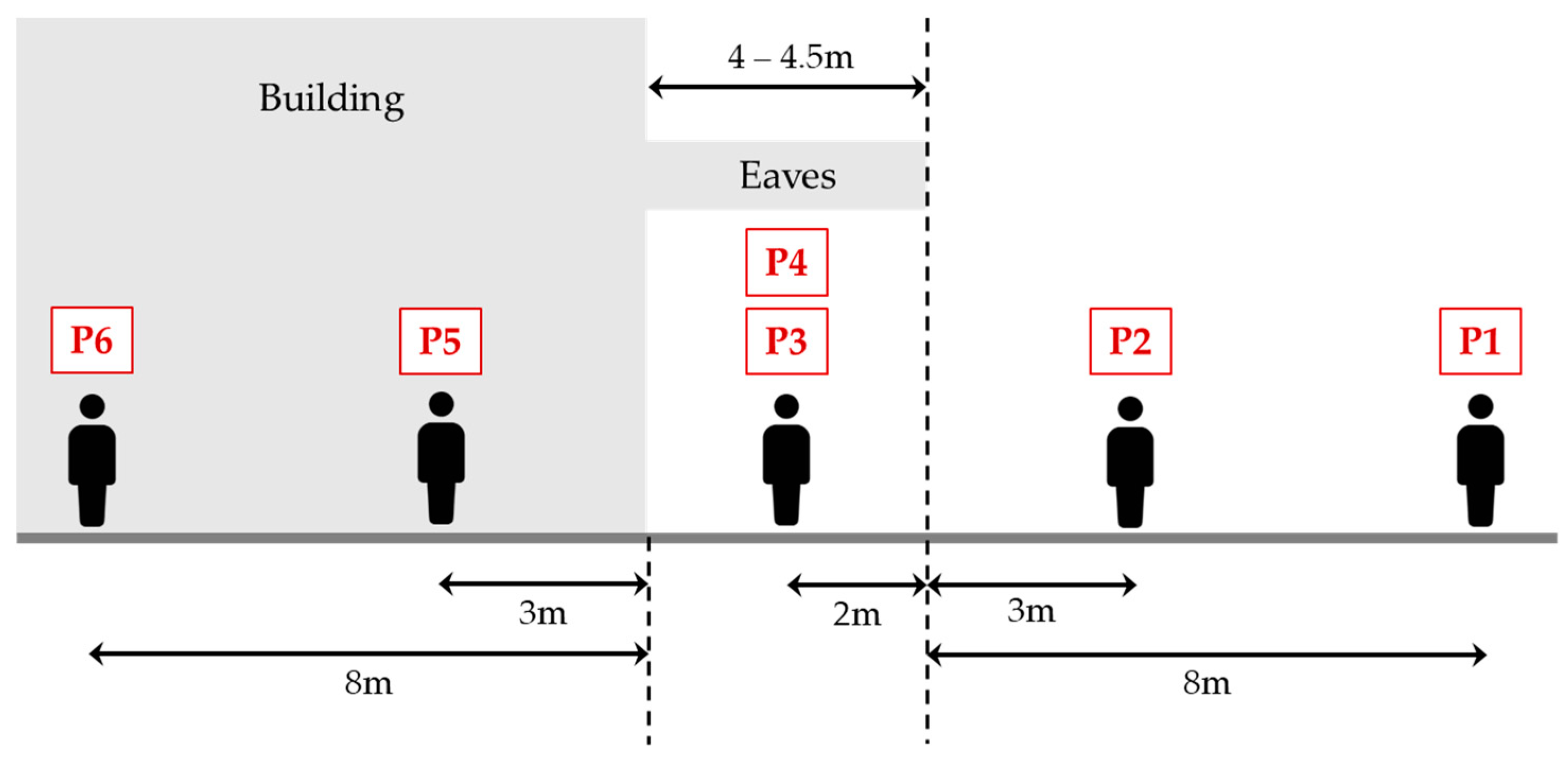
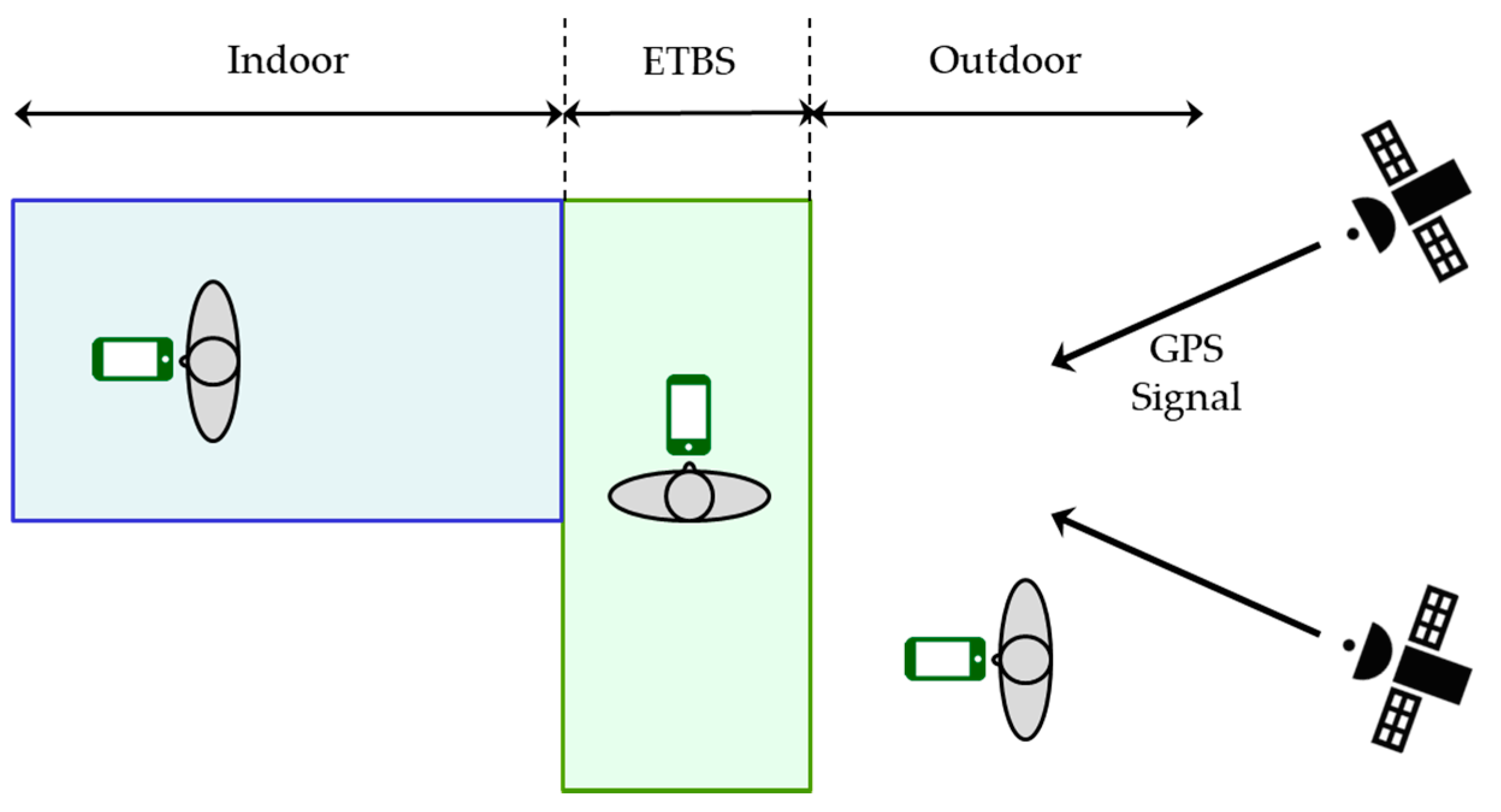

| ID | Contents |
|---|---|
| R1 | If is HIGH, and is HIGH, then = 1 |
| R2 | If is HIGH, and is MIDDLE, then =−1 |
| R3 | If is MIDDLE, and is HIGH, then =−1 |
| R4 | If is MIDDLE, and is MIDDLE, then =−1 |
| ID | Contents |
|---|---|
| R1 | If is MIDDLE, and is MIDDLE, then = 1 |
| R2 | If is MIDDLE, and is LOW, then = −1 |
| R3 | If is LOW, and is MIDDLE, then = −1 |
| R4 | If is LOW, and is LOW, then = −1 |
| aveSNR Value (dB-Hz) | P1 | P2 | P3 and P4 | P5 | P6 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 1 | Group 2 | |
| Average | 36.5 | 35.1 | 36.9 | 36.2 | 27.6 | 34.9 | 21.2 | 23.2 | 19.9 | 19.7 |
| Max | 40.6 | 40 | 38.4 | 39.6 | 35.4 | 40.6 | 24.2 | 26.6 | 24 | 21.2 |
| Min | 33.4 | 33 | 35.4 | 33.8 | 20.8 | 28.8 | 19 | 20.2 | 16 | 18.2 |
| Standard Deviation | 2.02 | 1.95 | 1.11 | 1.55 | 3.92 | 2.92 | 1.57 | 1.86 | 2.45 | 0.92 |
| Number of Measurement | Number of Correct Detections | Detection Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outdoor | P1 | 12 | 12 | 100.0% |
| P2 | 12 | 12 | 100.0% | |
| Elongated top-bounded space (ETBS) | P3 and P4 | 24 | 21 | 87.5% |
| Indoor | P5 | 12 | 10 | 83.3% |
| P6 | 12 | 12 | 100.0% | |
| Total | 72 | 67 | 93.1% |
| Model A | Model B | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model Name | Fujitsu Arrows m4 | Google Pixel3a | |||
| OS version | Android 7.1.1 | Android 10 | |||
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 1 | Group 2 | ||
| Average of aveSNR (dB-Hz) | P1 | 37.2 | 35.9 | 36.9 | 40.6 |
| P2 | 36.8 | 36.5 | 35.7 | 41.5 | |
| P3 and P4 | 27.7 | 33 | 27.7 | 34.8 | |
| P5 | 21.4 | 22 | 22 | 25.2 | |
| P6 | 20.7 | 18.9 | 19.7 | 21.4 | |
| Model A | Model B | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Measurement | Number of Correct Detections | Number of Correct Detections | ||
| Outdoor | P1 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| P2 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| Elongated top-bounded space (ETBS) | P3 and P4 | 12 | 10 | 9 |
| Indoor | P4 | 6 | 5 | 3 |
| P5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| Total | 36 | 33 | 30 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tabata, K.; Nakajima, M.; Kohtake, N. Design of Multiple Spatial Context Detection Method Considering Elongated Top-Bounded Spaces Based on GPS Signal-To-Noise Ratio and Fuzzy Inference. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9120717
Tabata K, Nakajima M, Kohtake N. Design of Multiple Spatial Context Detection Method Considering Elongated Top-Bounded Spaces Based on GPS Signal-To-Noise Ratio and Fuzzy Inference. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2020; 9(12):717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9120717
Chicago/Turabian StyleTabata, Kenichi, Madoka Nakajima, and Naohiko Kohtake. 2020. "Design of Multiple Spatial Context Detection Method Considering Elongated Top-Bounded Spaces Based on GPS Signal-To-Noise Ratio and Fuzzy Inference" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 9, no. 12: 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9120717
APA StyleTabata, K., Nakajima, M., & Kohtake, N. (2020). Design of Multiple Spatial Context Detection Method Considering Elongated Top-Bounded Spaces Based on GPS Signal-To-Noise Ratio and Fuzzy Inference. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 9(12), 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9120717




