Effectiveness of School Site Decisions on Land Use Policy in the Planning Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
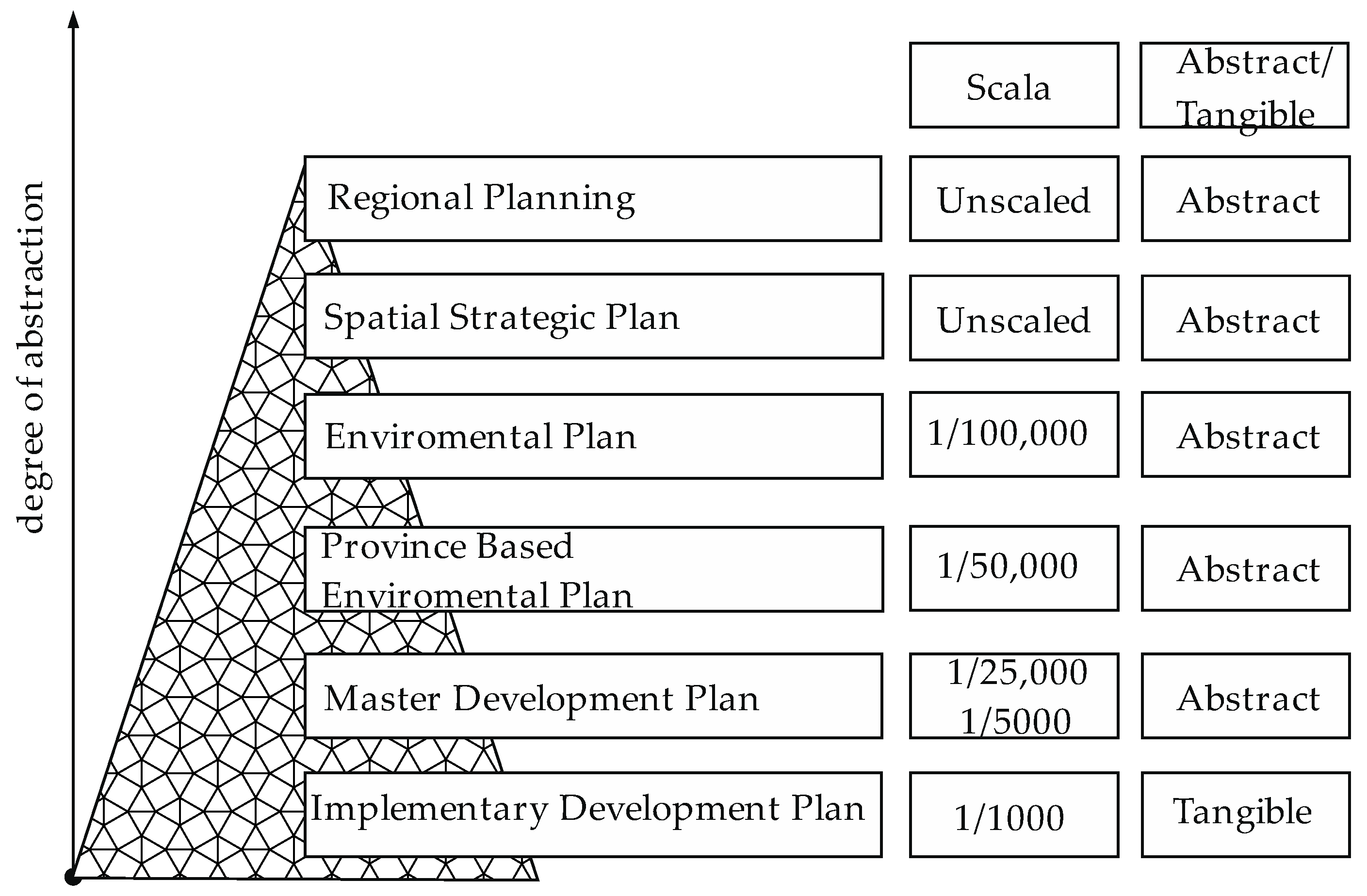
2.1. City Planning
2.2. Study Area
2.2.1. Educational Facility Area Size
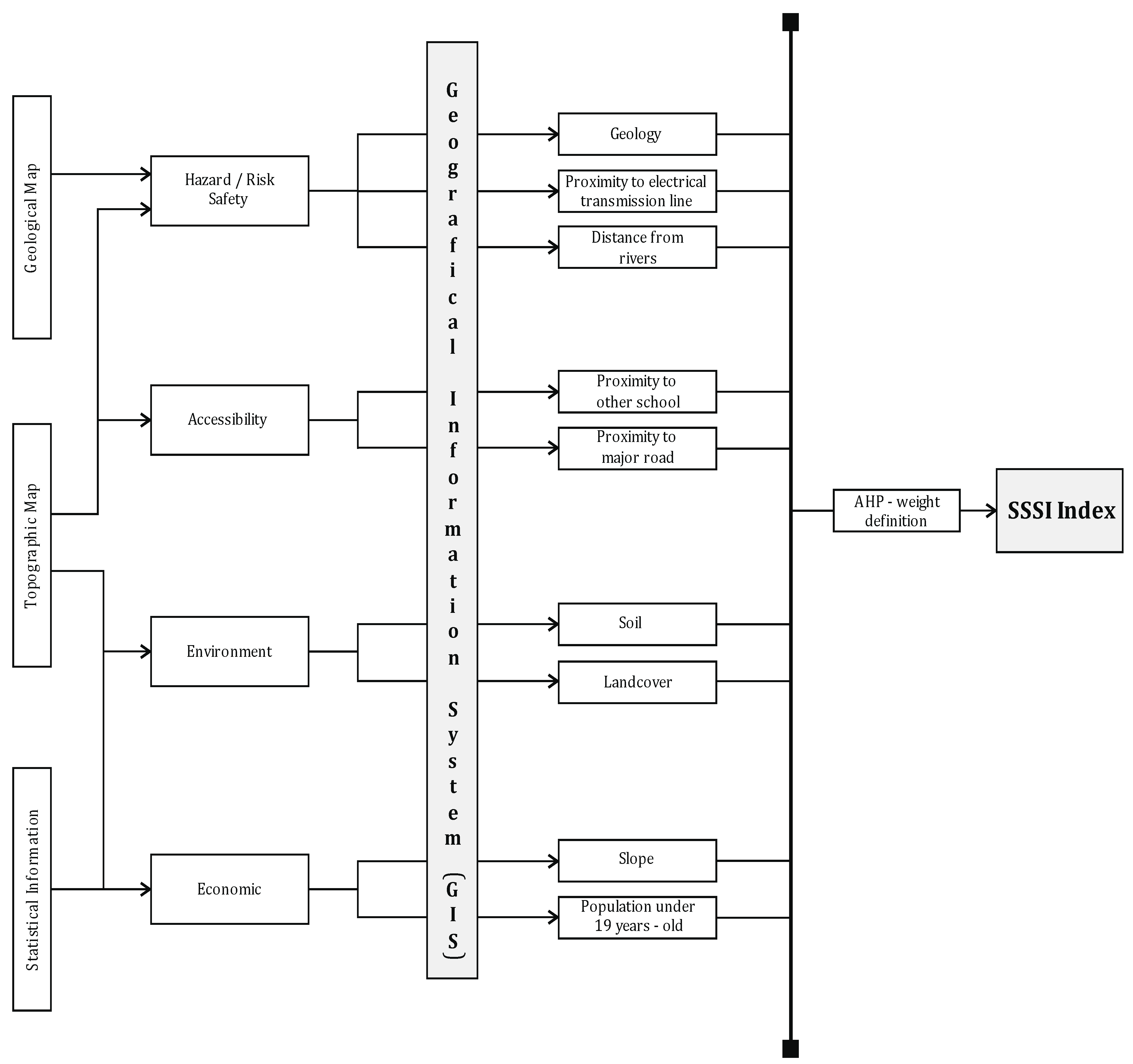
2.2.2. School Site Selection Index
2.2.3. Parameters in SSSI
2.2.4. Analytical Hierarchy Process
2.3. School Site Selection Index Parameters
2.3.1. Population Aged under 19 Years (per Pixel)
2.3.2. Distance from Existing Schools
2.3.3. Proximity to Main Roads
2.3.4. Distance (m) from Rivers
2.3.5. Land Use
2.3.6. Slope (°)
2.3.7. Soil
- Absolute protected areas: Class I, Class II, and Class III farmland;
- Priority protected areas: Class IV, Class V, and Class VI farmland;
- Areas that can be settled: Class VII and Class VIII farmland.
2.3.8. Proximity (m) to Electrical Transmission Lines
2.3.9. Geology
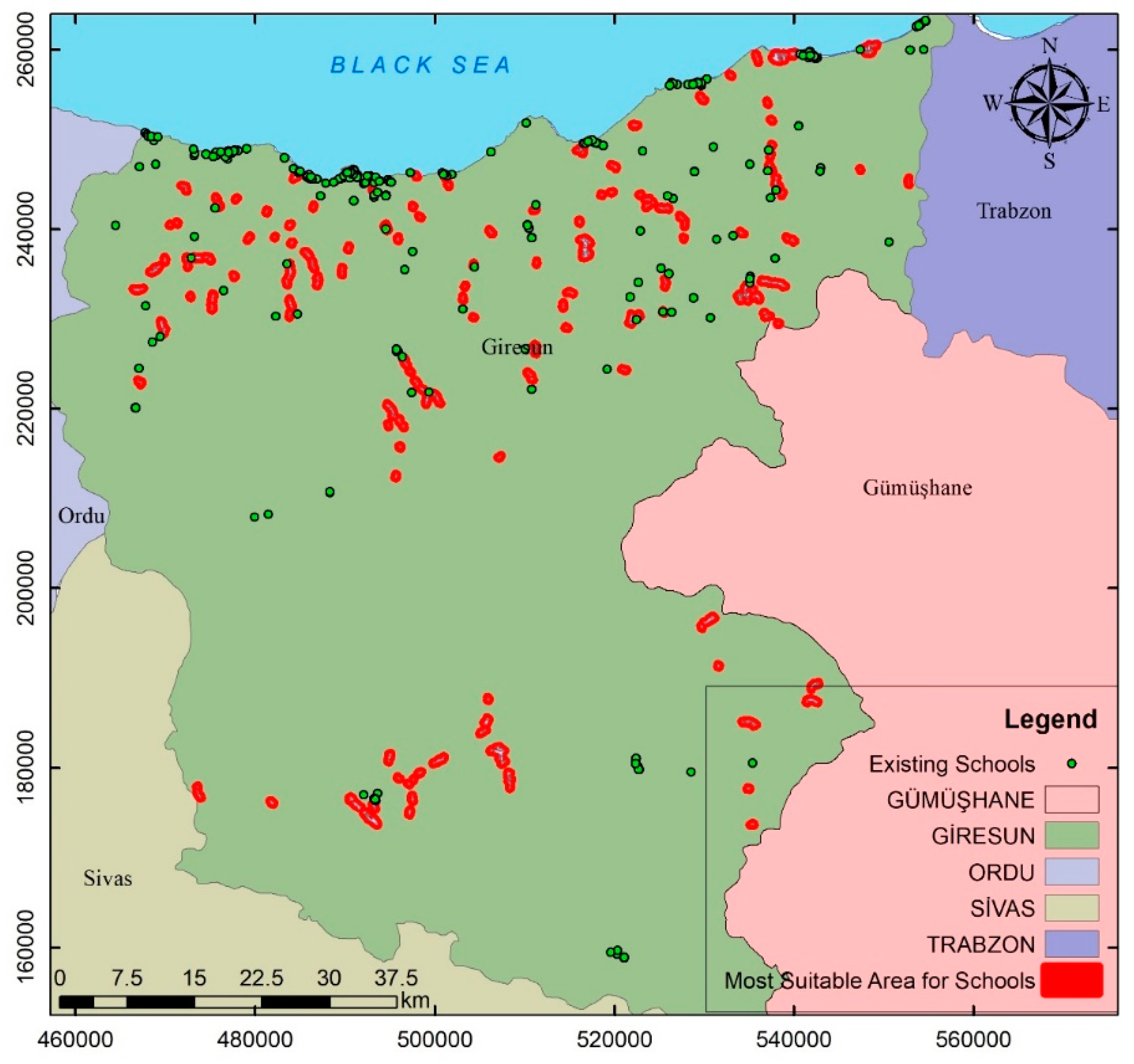
3. Results
3.1. Interpolation of Maps
3.2. Validation—Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Category | Criteria | Literature Review | Frequency | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [65] | [16] | [66] | [18] | [67] | [68] | [69] | [12] | [20] | [21] | [70] | [24] | [26] | Total | ||
| Hazard/Risk/Safety | Avalanche (snow/ice) | 3 | |||||||||||||
| Bank erosion | 5 | ||||||||||||||
| Flood areas | 12 | ||||||||||||||
| Landslide | 5 | ||||||||||||||
| Rockfall | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Underground flooding | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Earthquake zones | - | ||||||||||||||
| Geology | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Proximity to high voltage power lines | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Hazardous waste | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Enviromental/Geographic | Distance from streams | 11 | |||||||||||||
| Elevation and slope | 11 | ||||||||||||||
| Land cover | 7 | ||||||||||||||
| Natural heritage areas | 4 | ||||||||||||||
| Noise level | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Air Pollution | 5 | ||||||||||||||
| Vegetation type | - | ||||||||||||||
| Visibility | - | ||||||||||||||
| Presence of sensitive ecosystem | - | ||||||||||||||
| Land use type | 6 | ||||||||||||||
| Rainfall Intensity | - | ||||||||||||||
| Economic | Medical facility | 4 | |||||||||||||
| Emergency communication | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Safe haven | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Transformers | 6 | ||||||||||||||
| Proximity to residential areas | 7 | ||||||||||||||
| Proximity to tourist areas | 4 | ||||||||||||||
| Proximity to agricultural areas | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Population density | 10 | ||||||||||||||
| Social/Accessibility/ Infrastructure | Distance from existing schools | 11 | |||||||||||||
| Distance from roads | 13 | ||||||||||||||
| Existing fire stations | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Existing police stations | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Existing libraries | 2 | ||||||||||||||
| Industrial areas | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Commercial areas | 2 | ||||||||||||||
| Category | Criteria | Sub-Criteria | Rating Score | Weight (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard/Risk/Safety | Distance from rivers (m) (D) | <150 150–300 301–450 451–600 >600 | 10 8 6 4 2 | 0.119 |
| Proximity to electrical transmission lines (m) (H) | <150 150–300 301–450 451–600 >600 | 10 8 6 4 2 | 0.028 | |
| Geology (I) | The most suitable Suitable Unsuitable Restricted | 0 2 4 6 | 0.019 | |
| Accessibility | Distance from schools (m) (A) | <800 801–1300 1301–1800 1801–2400 >2400 | 10 8 6 4 2 | 0.240 |
| Proximity to main roads (C) | <150 150–300 301–450 451–600 >600 | 10 6 2 4 8 | 0.157 | |
| Environmental | Land use (E) | Forest Seasonal agriculture Agricultural areas Wetlands Rocky areas Open areas Other | 9 2 1 10 5 6 0 | 0.078 |
| Soil (G) | Class I Soil (Good agricultural land) Class II Soil Class III Soil Class IV Soil Class V Soil Class VI Soil Class VII Soil Class VIII Soil | 10 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 | 0.043 | |
| Economic | Population aged under 19 years (per pixel) (B) | 0 0.01–0.03 0.04–0.07 0.08–0.17 >0.17 | 10 8 6 4 2 | 0.237 |
| Slope (°) (F) | <10 10–15 16–20 21–25 >25 | 2 4 6 8 10 | 0.078 |
| Giresun/Center (Primary, Middle, High School) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| School Name | Building Area (m²) | Annex (m²) | Garden Area (m²) | Total Area (m²) | Location (m) | |
| AKSU District | Y (m) | X (m) | ||||
| ABACIBÜKÜ PRIMARY SCHOOL | 780.0 | - | 4525.55 | 5305.55 | 452,652.78 | 4,530,933.59 |
| ZÜBEYDE HANIM VOCATIONAL AND TECHNICAL ANATOLIAN HIGH SCHOOL | 1720.0 | 630 | 3812.02 | 6162.02 | 452,866.79 | 4,531,008.40 |
| ANATOLIAN IMAM HATIP HIGH SCHOOL | 1540.0 | - | 3780.00 | 5320.00 | 452,924.74 | 4,530,900.71 |
| 15 TEMMUZ ŞEHİTLER AKSU ANATOLIAN HIGH SCHOOL | 1000.0 | - | 2243.00 | 3243.00 | 452,771.27 | 4,530,620.74 |
| 15 TEMMUZ ŞEHİTLER SCHOOL | 550.0 | - | 835.79 | 1385.79 | 453,011.18 | 4,530,627.28 |
| ŞEHİT HAKAN GEMİCİ SECONDARY SCHOOL | 830.0 | 1345 | 5448.90 | 7623.90 | 452,672.33 | 4,530,159.97 |
| SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL | 1233.0 | 1660 | 41,176.09 | 49,085.09 | 452,440.96 | 4,529,198.62 |
| SOCIAL SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL | 880.0 | 2529 | 452,443.08 | 4,529,005.94 | ||
| FINE ARTS AND SPORTS HIGH SCHOOL | 1607.0 | - | 452,475.21 | 4,528,921.38 | ||
| ÇINARLAR District | ||||||
| GİRESUN HIGH SCHOOL | 800.0 | 300 | 4040.00 | 5140.00 | 448,846.85 | 4,532,061.79 |
| MEHMET AKİF ERSOY SECONDARY SCHOOL | 565.0 | 170 | 2365.00 | 3100.00 | 448,909.43 | 4,532,026.09 |
| HURŞİT BOZBAĞ GIRL ANADOLU IMAM HATIP HIGH SCHOOL | 1165.0 | - | 2160.00 | 3325.00 | 448,797.83 | 4,531,808.07 |
| ÇITLAKKALE District | ||||||
| ÇITLAKKALE İMAM HATİP SECONDARY SCHOOL | 880.0 | - | 2514.00 | 3394.00 | 445,733.51 | 4,530,541.47 |
| NAMIK KEMAL PRIMARY SCHOOL | 1100.0 | - | 1700.00 | 2800.00 | 446,207.77 | 4,530,679.50 |
| ÇITLAKKALE PRESCHOOL | 1165.0 | - | 3015.00 | 4180.00 | 446,750.53 | 4,530,457.27 |
| ERİKLİMAN District | ||||||
| YEŞİL GİRESUN VOCATIONAL AND TECHNICAL ANATOLIAN HIGH SCHOOL | 1385.0 | 625 | 4064.51 | 6074.51 | 442,328.64 | 4,532,567.19 |
| FEVZİ ÇAKMAK District | ||||||
| 23 NİSAN PRIMARY SCHOOL | 900.0 | - | 2440.00 | 3340.00 | 448,014.17 | 4,531,187.98 |
| GAZİLER District | ||||||
| GÜRE İMAM HATİP SECONDARY SCHOOL | 850.0 | - | 2950.00 | 3800.00 | 442,703.00 | 4,531,768.82 |
| ATATÜRK VOCATIONAL AND TECHNICAL ANATOLIAN HIGH SCHOOL | 500.0 | - | 650.00 | 1150.00 | 442,741.06 | 4,531,798.23 |
| HAMDİ BOZBAĞ ANATOLIAN HIGH SCHOOL | 3100.0 | - | 3500.00 | 6600.00 | 442,776.90 | 4,531,840.00 |
| MİMAR SİNAN ANATOLIAN HIGH SCHOOL | 630.0 | - | 2570.00 | 3200.00 | 442,832.51 | 4,531,791.06 |
| EDUCABLE DISABLED SCHOOL | 1400.0 | - | 1765.00 | 3165.00 | 442,916.19 | 4,531,984.68 |
| GEDİKKAYA District | ||||||
| GEDİKKAYA SECONDARY SCHOOL | 1140.0 | - | 4985.59 | 6125.59 | 450,756.75 | 4,531,350.29 |
| GEDİKKAYA PRESCHOOL | 365.0 | - | - | - | 451206.35 | 4,531,139.70 |
| ŞEHİT İSA YÜKSEL PRIMARY SCHOOL | 730.0 | - | 4206.15 | 4936.15 | 451,259.30 | 4,531,177.41 |
| 125. YIL VOCATIONAL AND TECHNICAL ANATOLIAN HIGH SCHOOL | 1450.0 | 2630 | 27,081.43 | 31,161.43 | 451,148.83 | 4,530,603.35 |
| GEMİLERÇEKEĞİ District | ||||||
| MİTHAT PAŞA SECONDARY SCHOOL | 690.0 | - | 2068.00 | 2758.00 | 449,324.38 | 4,531,478.12 |
| HACI HÜSEYİN District | ||||||
| YEŞİLGİRESUN PRIMARY SCHOOL | 920.0 | - | 1715.00 | 2635.00 | 448,997.94 | 4,531,719.48 |
| HACI MİKTAT District | ||||||
| VOCATIONAL AND TECHNICAL ANATOLIAN HIGH SCHOOL | 5100.0 | - | 3300.00 | 8400.00 | 448,089.49 | 4,531,461.26 |
| HACISİYAM District | ||||||
| ATATÜRK ANATOLIAN HIGH SCHOOL | 1605.0 | - | 7285.00 | 8890.00 | 447,246.62 | 4,531,054.71 |
| KANUNİ SECONDARY SCHOOL | 535.0 | - | 1995.00 | 2530.00 | 447,279.29 | 4,530,960.40 |
| HURŞİT BOZBAĞ GIRL ANATOLIAN IMAM HATIP HIGH SCHOOL | 645.0 | - | 965.00 | 1610.00 | 447,553.55 | 4,531,044.30 |
| ABDULLAH BOZBAĞ PRIMARY SCHOOL | 515.0 | - | 635.00 | 1150.00 | 447,602.38 | 4,531,084.13 |
| KAPU District | ||||||
| CUMHURİYET SECONDARY SCHOOL | 1100.0 | - | 2485.00 | 3585.00 | 448,496.05 | 4,531,807.12 |
| KAVAKLAR District | ||||||
| FATİH VOCATIONAL AND TECHNICAL ANATOLIAN HIGH SCHOOL | 680.0 | - | 3170.00 | 3850.00 | 448,908.06 | 4,531,262.83 |
| ŞEHİT İSMAİL BAY SPECIAL EDUCATION AND APPLICATION SCHOOL | 215.0 | - | 5155.00 | 5370.00 | 449,922.93 | 4,529,938.07 |
| 15 TEMMUZ ŞEHİTLER İMAM HATİP SECONDARY SCHOOL | 1120.0 | - | 11,740.00 | 12,860.00 | 450,023.73 | 4,530,501.40 |
| ÇOTANAK PRIMARY SCHOOL | 860.0 | - | 2458.00 | 3318.00 | 449,212.98 | 4,531,245.92 |
| 75. YIL PRESCHOOL | 1000.0 | - | 1420.00 | 2420.00 | 449,198.23 | 4,531,195.85 |
| KAYADİBİ District | ||||||
| KAYADİBİ PRIMARY SCHOOL | 500.0 | - | 2085.00 | 2585.00 | 448,844.65 | 4,528,630.05 |
| NİZAMİYE District | ||||||
| GAZİPAŞA PRIMARY SCHOOL | 860.0 | - | 2720.00 | 3580.00 | 448,513.52 | 4,531,542.91 |
| MUSTAFA KEMAL SECONDARY SCHOOL | 1145.0 | - | 6705.00 | 7850.00 | 448,463.79 | 4,531,282.79 |
| FINDIK YURDU PRESCHOOL | 700.0 | - | 300.00 | - | 448,476.81 | 4,531,228.86 |
| TEYYAREDÜZÜ District | ||||||
| 19 EYLÜL PRIMARY SCHOOL | 2200.0 | 580 | 5620.00 | 8400.00 | 443,912.28 | 4,531,545.42 |
| 24 KASIM PRESCHOOL | 250.0 | - | 650.00 | 900.00 | 444,666.29 | 4,530,995.51 |
| TEYYAREDÜZÜ SECONDARY SCHOOL | 740.0 | - | 2610.00 | 3350.00 | 444,719.95 | 4,531,000.21 |
References
- Coruhlu, Y.E.; Baser, V.; Yildiz, O. Object-based geographical data model for determination of the cemetery sites using SWOT and AHP integration. Surv. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, Z. Urban and Graveyard Sprawl: The Unsustainability of Death. In Theology and Urban Sustainability; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 37–52. [Google Scholar]
- Coruhlu, Y.E.; Uzun, B.; Yildiz, O. Zoning plan-based legal confiscation without expropriation in Turkey in light of ECHR decisions. Land Use Policy 2020, 95, 104598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baser, V.; Uzun, B.; Yildirim, V. An alternative method for expropriation for lane-like projects in planned area: A case study from Trabzon in Turkey. Surv. Rev. 2019, 51, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thériault, M.; Le Berre, I.; Dubé, J.; Maulpoix, A.; Vandersmissen, M.H. The effects of land use planning on housing spread: A case study in the region of Brest, France. Land Use Policy 2020, 92, 104428. [Google Scholar]
- Başer, V. Yaylalardaki arazi kullanım değişiminin coğrafi bilgi sistemi ile analizi: Giresun örneği. Bitlis Eren Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Dergisi 2019, 8, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yìldiz, O.; Coruhlu, Y.E.; Biyik, C. Registration of agricultural areas towards the development of a future Turkish cadastral system. Land Use Policy 2018, 78, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, I.; Enemark, S.; Wallace, J.; Rajabifard, A. Land Administration for Sustainable Development; ESRI Press Academic: Redlands, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ramamurthy, V.; Challa, O.; Naidu, L.G.K.; Kumar, K.S.A.; Singh, S.K.; Mamatha, D.; Ranjitha, K.; Mishra, B.B. Land Evaluation and Land Use Planning. In The Soils of India; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 191–214. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, H. Land use planning and health and well-being. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, S115–S123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockheed, M.E.; Verspoor, A.M. Improving Primary Education in Developing Countries; Oxford University Press for World Bank: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Jayaweera, K.N. Application of Geographic Information Systems for Government School Sites Selection. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Sri Jayewardenepura, Nugegoda, Sri Lanka, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Türkiye Nüfus Bilgileri. Available online: https://www.tuik.gov.tr/tr/# (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Başeğmez, M.; Taşdemir, İ.; Gül, Ç. Eğitim alanlarının yer seçim kriterlerinin belirlenmesinde yaşanan problemler ve çözüm önerileri. TMMOB Harita ve Kadastro Mühendisleri Odası 2017, 16, 188–194. [Google Scholar]
- Drobne, S.; Lisec, A. Multi-attribute decision analysis in GIS: Weighted linear combination and ordered weighted averaging. Informatica 2009, 33, 459–475. [Google Scholar]
- Bukhari, Z.; Rodzi, A.; Noordin, A. Spatial multi-criteria decision analysis for safe school site selection. Int. Geoinform. Res. Dev. J. 2010, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, N.C. School siting: Contested visions of the community school. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2010, 76, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, A.M.; Hifni, N.A.; Ghazali, R.; Hashim, K.A.; Disa, N.M.; Mahmud, S. A study on school location suitability using AHP in GIS approach. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 8th International Colloquium on Signal Processing and Its Applications, Melaka, Malaysia, 23–25 March 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ozdemir, B.; Tokyay, O. Multi Criteria Decision Support for the Best Allocation of the Primary School Area. Int. Multidiscip. Sci. GeoConference SGEM Surv. Geol. Min. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 1, 457. [Google Scholar]
- Dadfar, N.A. Suitablity Analysis of a New High School in the City of Calabasas. Ph.D. Thesis, California State University, Northridge, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Talam, P.K.; Ngigi, M.M. Integration of GIS and Multicriteria Evaluation for School Site Selection A Case Study of Belgut Constituency. In Proceedings of the Sustainable Research and Innovation Conference, Kenya School of Monetary Studies, Nairobi, Kenya, 6–8 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tervonen, T.; Barberis, G.F.; Figueira, J.R.; Escribano, M. Site Selection for a University Kindergarten in Madrid. In Evaluation and Decision Models with Multiple Criteria; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 201–214. [Google Scholar]
- Yıldız, M.S. Eğitim Tesislerinin Kuruluş Yeri Seçiminde Bulanık TOPSIS Yönetiminin Uygulanması: Düzce’de Bir Lokasyon Analizi. J. Int. Soc. Res. 2015, 8, 763. [Google Scholar]
- Jamal, I. Multi-criteria GIS analysis for school site selection in Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Oblast, Tajikistan. Master’s Thesis, Geographical Information Science, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Uslu, A.; Kızıloğlu, K.; İşleyen, S.K.; Kahya, E. Okul yeri seçiminde coğrafi bilgi sistemine dayalı AHP-TOPSIS yaklaşımı: Ankara ili örneği. Politeknik Dergisi 2017, 20, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.A. Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis for Primary School Site Selection in Al-Mahaweel district Using GIS Technique. J. Kerbala Univ. 2018, 16, 342–350. [Google Scholar]
- Vasiljević, T.Z.; Srdjević, Z.; Bajčetić, R.; Miloradov, M.V. GIS and the analytic hierarchy process for regional landfill site selection in transitional countries: A case study from Serbia. Environ. Manag. 2012, 49, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, V. Application of raster-based GIS techniques in the siting of landfills in Trabzon Province, Turkey: A case study. Waste Manag. Res. 2012, 30, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, V.; Memisoglu, T.; Bediroglu, S.; Colak, H.E. Municipal solid waste landfill site selection using multi-criteria decision making and GIS: Case study of Bursa province. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2018, 26, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyan, M. MSW landfill site selection by combining AHP with GIS for Konya, Turkey. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baser, V. Optimization oy Existing Solid Waste Landfill Sites Using GIS and MCDA: The Case of Giresun, Turkey. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2019, 28, 9033–9043. [Google Scholar]
- Joerin, F.; Thériault, M.; Musy, A. Using GIS and outranking multicriteria analysis for land-use suitability assessment. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2001, 15, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczewski, J. GIS-based land-use suitability analysis: A critical overview. Prog. Plan. 2004, 62, 3–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, J.; Khan, S. Spatial sensitivity analysis of multi-criteria weights in GIS-based land suitability evaluation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 1582–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sherbinin, A.; Bukvic, A.; Rohat, G.; Gall, M.; McCusker, B.; Preston, B.; Apotsos, A.; Fish, C.; Kienberger, S.; Muhonda, P.; et al. Climate vulnerability mapping: A systematic review and future prospects. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2019, 10, e600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.; Acuna, M.; Moroni, M.; Taskhiri, M.S.; Turner, P. Optimizing the location of biomass energy facilities by integrating Multi-Criteria Analysis (MCA) and Geographical Information Systems (GIS). Forests 2018, 9, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghajari, Y.E.; Alesheikh, A.A.; Modiri, M.; Hosnavi, R.; Abbasi, M.; Sharifi, A. Urban vulnerability under various blast loading scenarios: Analysis using GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis techniques. Cities 2018, 72, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, V.; Bediroglu, S. A geographic information system-based model for economical and eco-friendly high-speed railway route determination using analytic hierarchy process and least-cost-path analysis. Expert Syst. 2019, 36, e12376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbuSada, J.; Thawaba, S. Multi criteria analysis for locating sustainable suburban centers: A case study from Ramallah Governorate, Palestine. Cities 2011, 28, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erden, T.; Coşkun, M.Z. Coğrafi bilgi sistemleri ve analitik hiyerarşi yöntemi yardimiyla itfaiye istasyon yer seçimi. TMMOB Karita ve Kadastro Mühendisleri Odası 13. Türkiye Bilimsel ve Teknik Kurultayı 2011, 301–304. [Google Scholar]
- Stelzenmüller, V.; Gimpel, A.; Gopnik, M.; Gee, K. Aquaculture site-selection and marine spatial planning: The roles of GIS-based tools and models. In Aquaculture Perspective of Multi-Use Sites in the Open Ocean; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 131–148. [Google Scholar]
- Gumusay, M.U.; Koseoglu, G.; Bakirman, T. An assessment of site suitability for marina construction in Istanbul, Turkey, using GIS and AHP multicriteria decision analysis. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.M.; Suliman AE, R.E.; Al-Nahry, A.H.; Abd El Rahman, E.N. Spatial modeling for the optimum site selection of solar photovoltaics power plant in the northwest coast of Egypt. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 18, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colak, H.E.; Memisoglu, T.; Gercek, Y. Optimal site selection for solar photovoltaic (PV) power plants using GIS and AHP: A case study of Malatya Province, Turkey. Renew. Energy 2020, 149, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. The Analytic Hierarchy Process; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Wind, Y.; Saaty, T.L. Marketing applications of the analytic hierarchy process. Manag. Sci. 1980, 26, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragones-Beltran, P.; Chaparro-Gonzalez, F.; Pastor-Ferrando, J.; Pla-Rubio, A. An AHP/ANP-based multi-criteria decision approach for the selection of solar-thermal power plant investment projects. Energy 2014, 66, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Gazette; Zoning Law Prime Ministry Public House: Hong Kong, China, 1985; p. 378.
- Doebele, W.; Matsubara, J.; Nishiyama, Y. Conceptual Models of Land Readjustment; Land Readjustment: The Japanese System, A Lincoln Institute of Land Policy Book; Lincoln Institute of Land Policy: Boston, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Uzun, B.; Simsek, N.C. Land readjustment for minimizing public expenditures on school lands: A case study of Turkey. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baser, V.; Biyik, C. Coastal and marine zone legislation within the concept of land management in Turkey. Surv. Rev. 2019, 51, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coğrafi Durum Bilgisi. Available online: http://www.giresun.gov.tr/sehrimiz (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Mahmood, K.; Khalifa, S. Primary School Buildings Requirements and Design. Pak. Eng. Congr. Symp. Low-Cost Struct. 1978, XVI, 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Yenice, M.S. İlköğretim okulları için mekânsal yeterlilik analizi; Burdur örneği. Hacettepe Üniversitesi Eğitim Fakültesi Dergisi 2013, 28, 430–439. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Education and Skills. Available online: https://www.education.ie/en/School-Design/Design-Guidance/bu_tgd_025_rev1.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- Plan gösterimleri. Available online: https://mpgm.csb.gov.tr (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Ömürbek, N.; Şimşek, A. Analitik hiyerarşi süreci ve analitik ağ süreci yöntemleri ile online alişveriş site seçimi. Yönetim ve Ekonomi Araştırmaları Dergisi 2014, 12, 306–327. [Google Scholar]
- Pineda-Henson, R.; Culaba, A.B.; Mendoza, G.A. Evaluating environmental performance of pulp and paper manufacturing using the analytic hierarchy process and life-cycle assessment. J. Ind. Ecol. 2002, 6, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunschweig, T.; Becker, B. Choosing research priorities by using the analytic hierarchy process: An application to international agriculture. R&D Manag. 2004, 34, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- School Siting Guidelines. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-06/documents/school_siting_guidelines-2 (accessed on 27 October 2020).
- Amram, O.; Abernethy, R.; Brauer, M.; Davies, H.; Allen, R. Proximity of public elementary schools to major roads in Canadian urban areas. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2011, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- California Department of Education. Available online: https://www.cde.ca.gov/ls/fa/sf/schoolsiteguide (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Kazakis, N.; Kougias, I.; Patsialis, T. Assessment of flood hazard areas at a regional scale using an index-based approach and Analytical Hierarchy Process: Application in Rhodope–Evros region, Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toprak ve arazi siniflamasi standartlari teknik talimati. Available online: https://www.tarimorman.gov.tr/Belgeler/Mevzuat/Talimatlar/ToprakAraziSiniflamasiStandartlariTeknikTalimativeIlgiliMevzuat_yeni (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- School Site Selection Guide. Available online: https://www2.gov.bc.ca/assets/gov/education/administration/resource-management/capital-planning/siteselectionguide (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- Alaska Department Ofeducation & Early Development. Available online: https://education.alaska.gov/facilities/publications/siteselection (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- Available online: https://www.frederickcountymd.gov/DocumentCenter/View (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- School Facility Design. Available online: http://www.cde.ca.gov/ls/fa/sf/schoolsiteguide (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Liddle, P.G.A. A New Approach to School Site Suitability Assessment: A Case Study in Durham North Carolina; University of Minnesota: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Report an Environmental Violation. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ (accessed on 2 November 2020).
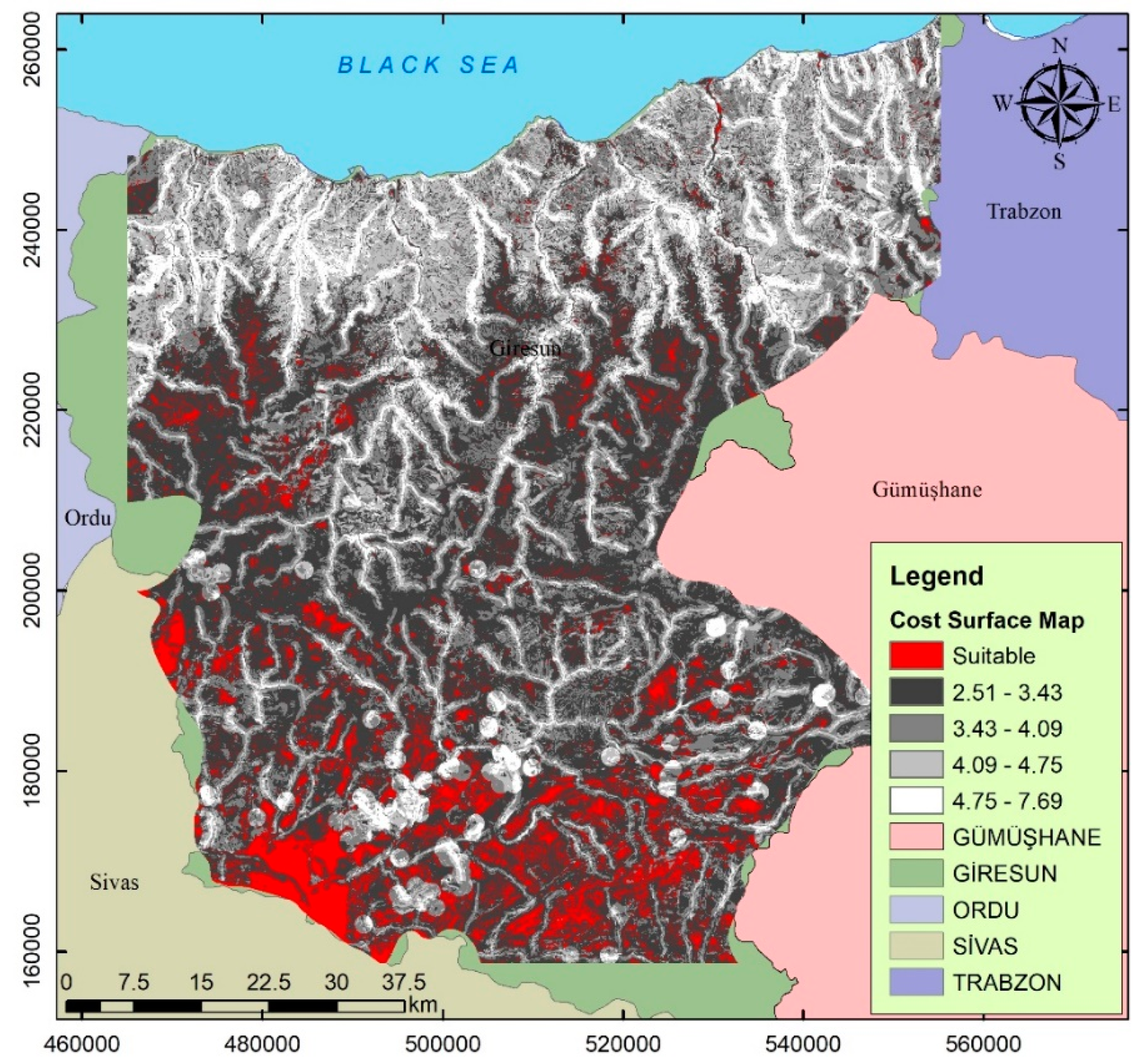
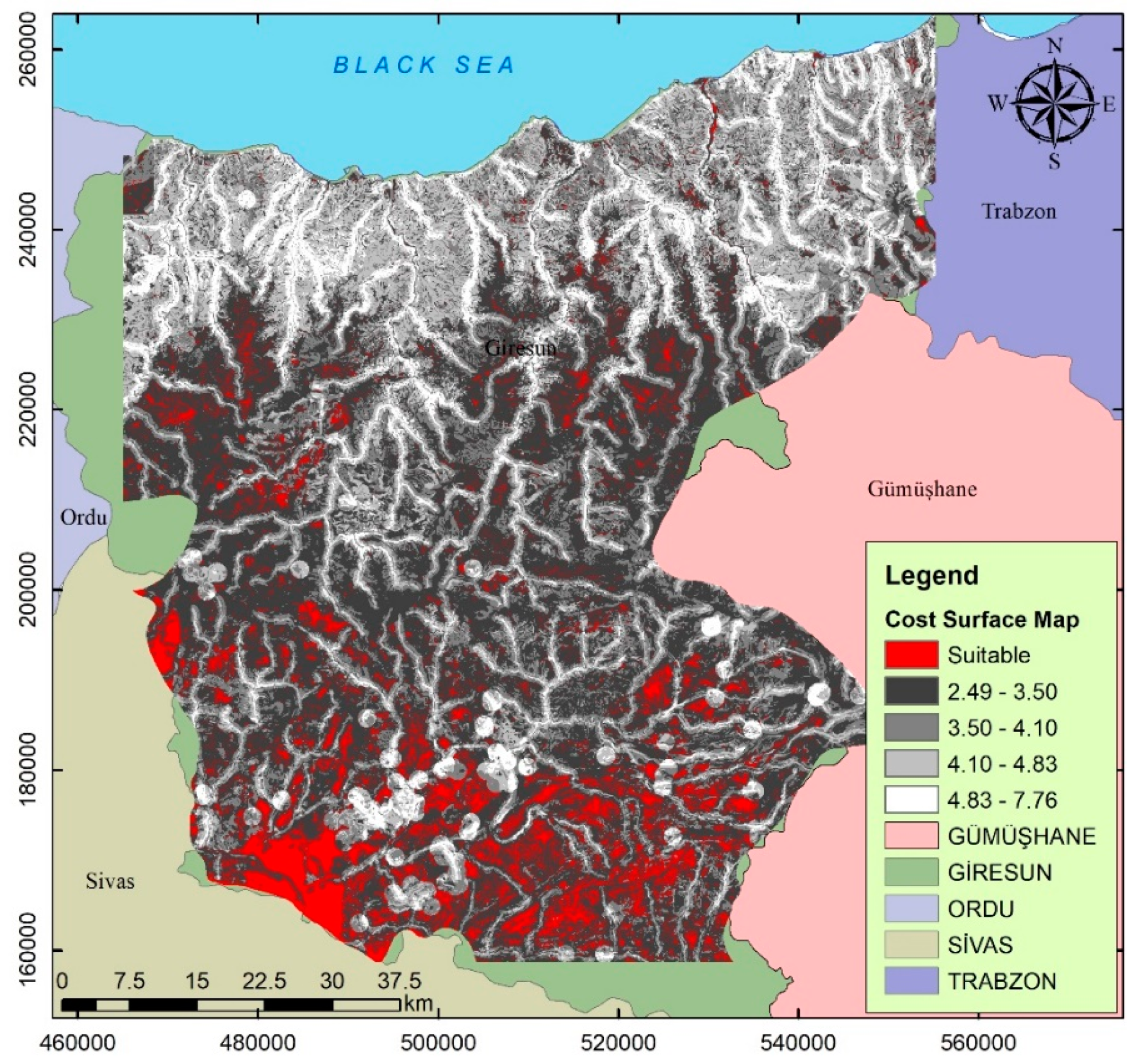
| Layer | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost Surface | 0.84740817 | 7.68693113 | 3.62420290 | 0.83396815 |
| Sensitivity 1 | 1.0565918 | 6.68393135 | 3.40203058 | 0.72953943 |
| Sensitivity 2 | 2.2271065 | 6.59693145 | 3.12012967 | 0.59817467 |
| Sensitivity 3 | 2.4906170 | 6.20693159 | 2.75260654 | 0.52469339 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baser, V. Effectiveness of School Site Decisions on Land Use Policy in the Planning Process. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9110662
Baser V. Effectiveness of School Site Decisions on Land Use Policy in the Planning Process. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2020; 9(11):662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9110662
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaser, Volkan. 2020. "Effectiveness of School Site Decisions on Land Use Policy in the Planning Process" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 9, no. 11: 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9110662
APA StyleBaser, V. (2020). Effectiveness of School Site Decisions on Land Use Policy in the Planning Process. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 9(11), 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9110662





