Dot Symbol Auto-Filling Method for Complex Areas Considering Shape Features
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Existing Dot Symbols Filling Method
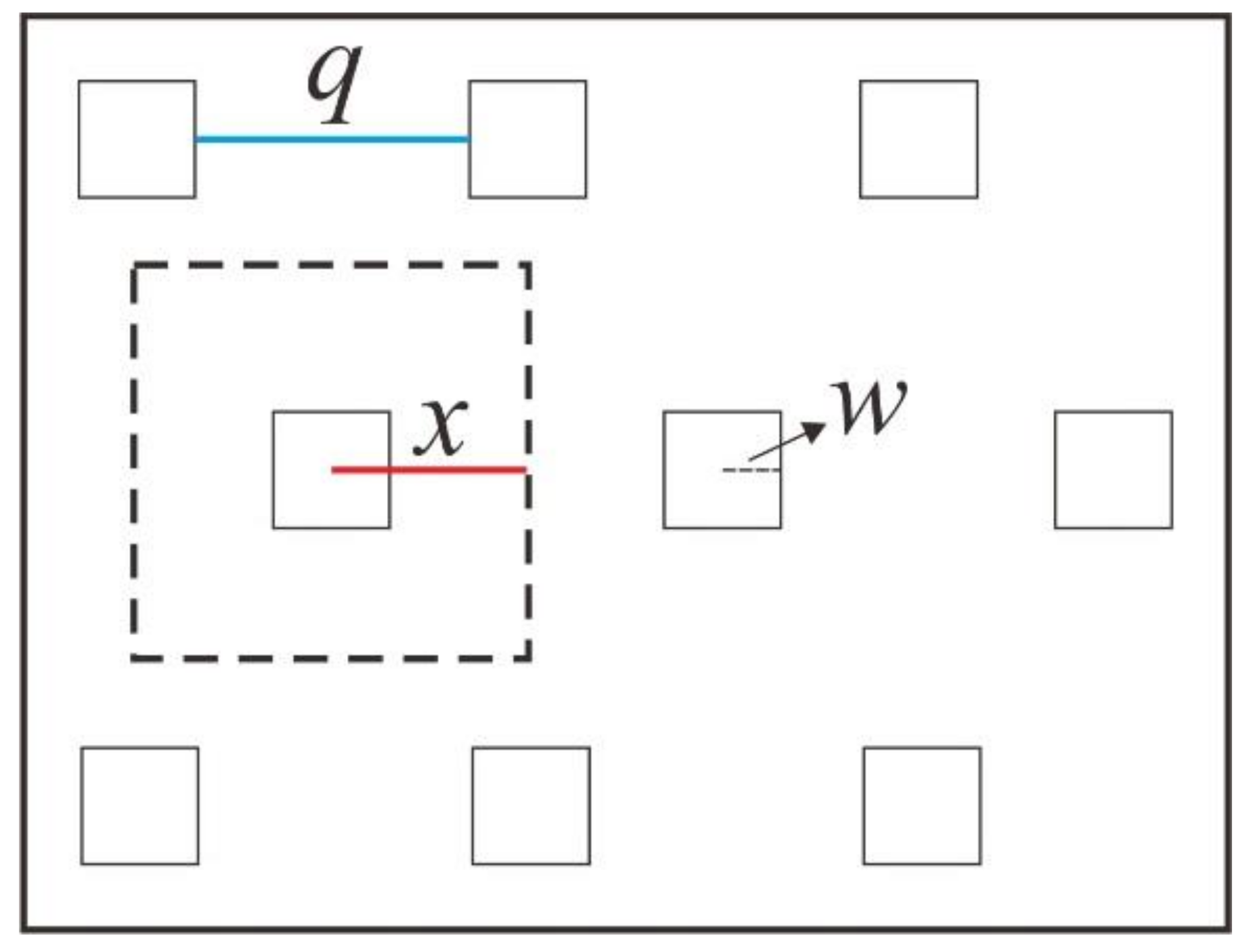
2.1.1. Three-Square Type Symbol
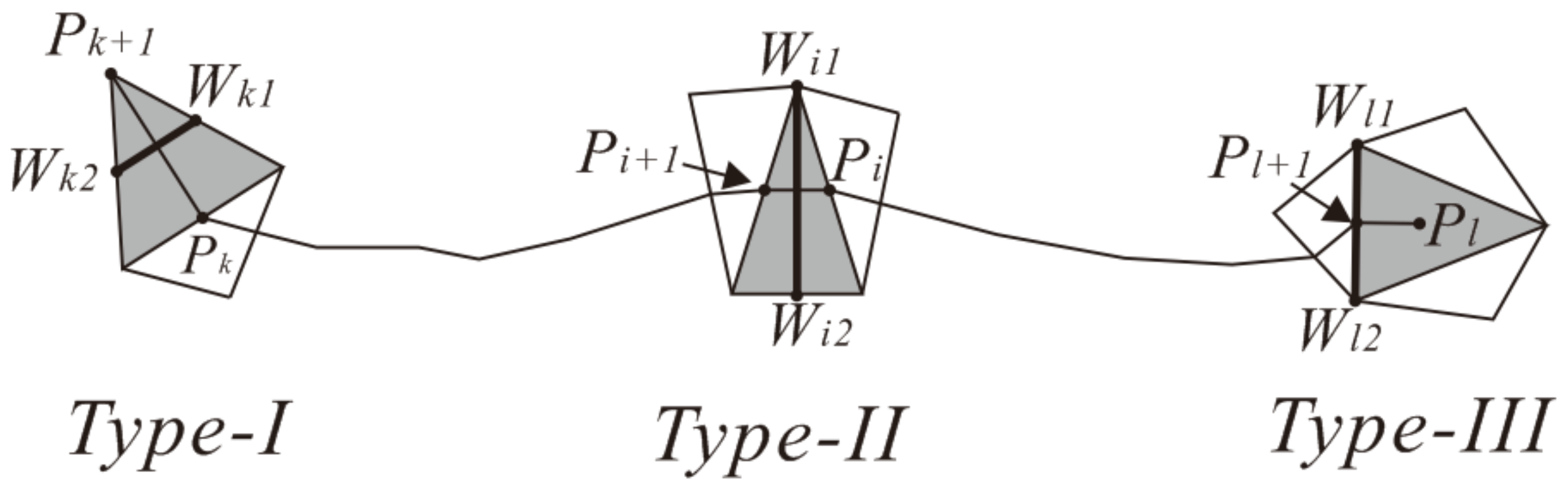
2.1.2. Average Width of a Triangle Set
- Type-I triangle: There is only one adjacent triangle, and the two sides of the triangle are the boundaries of the polygon.
- Type-II triangle: There are two adjacent triangles, which is the backbone structure of the skeleton line and describes the extension direction of the skeleton line.
- Type-III triangle: There are three adjacent triangles, which are the intersections of the skeleton line branches as the starting points for stretching in three directions.
2.2. Deficiencies of the Existing Method
3. Methodology
3.1. Fine Division of Internal Structure
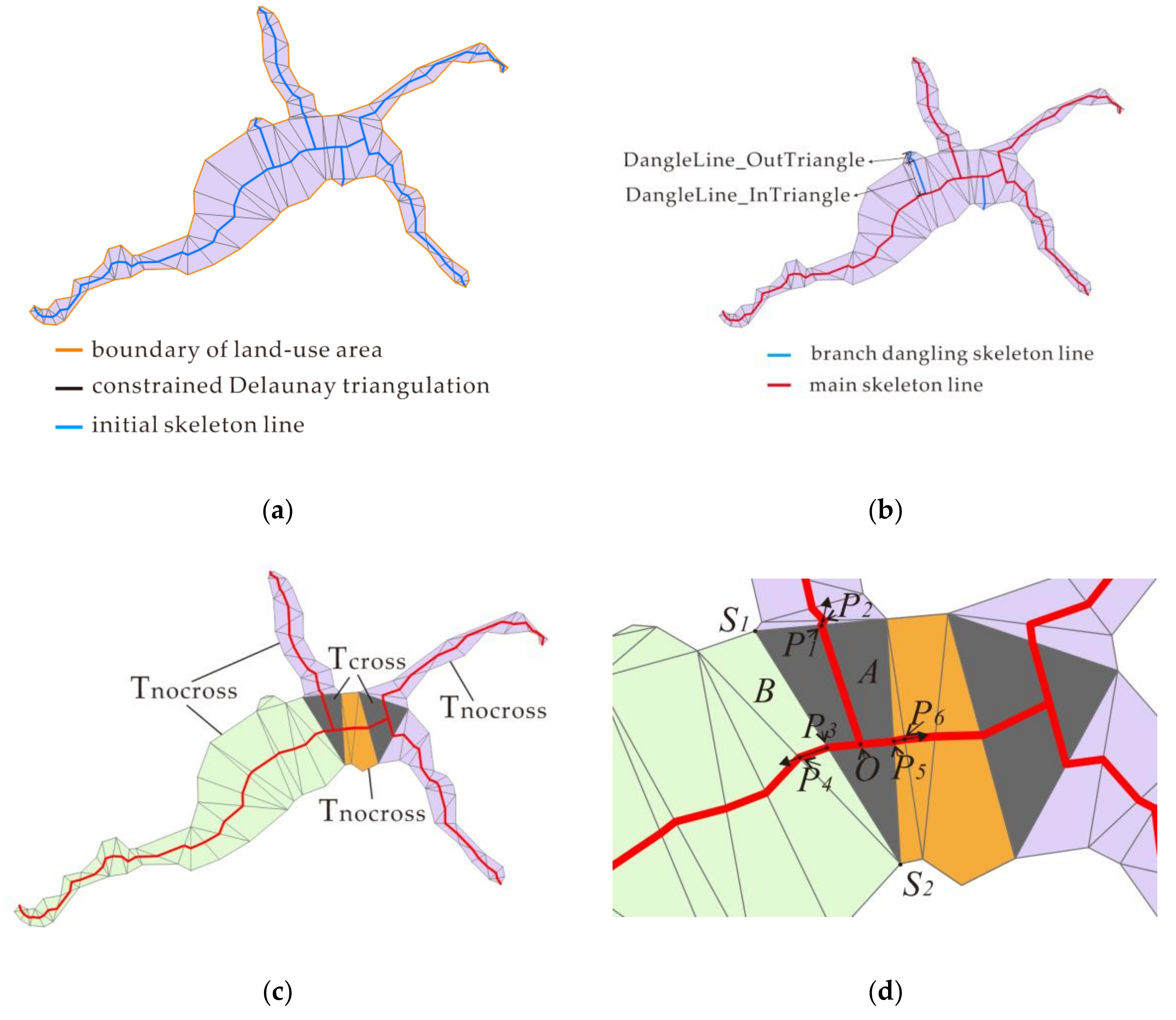
3.1.1. Branch Extraction
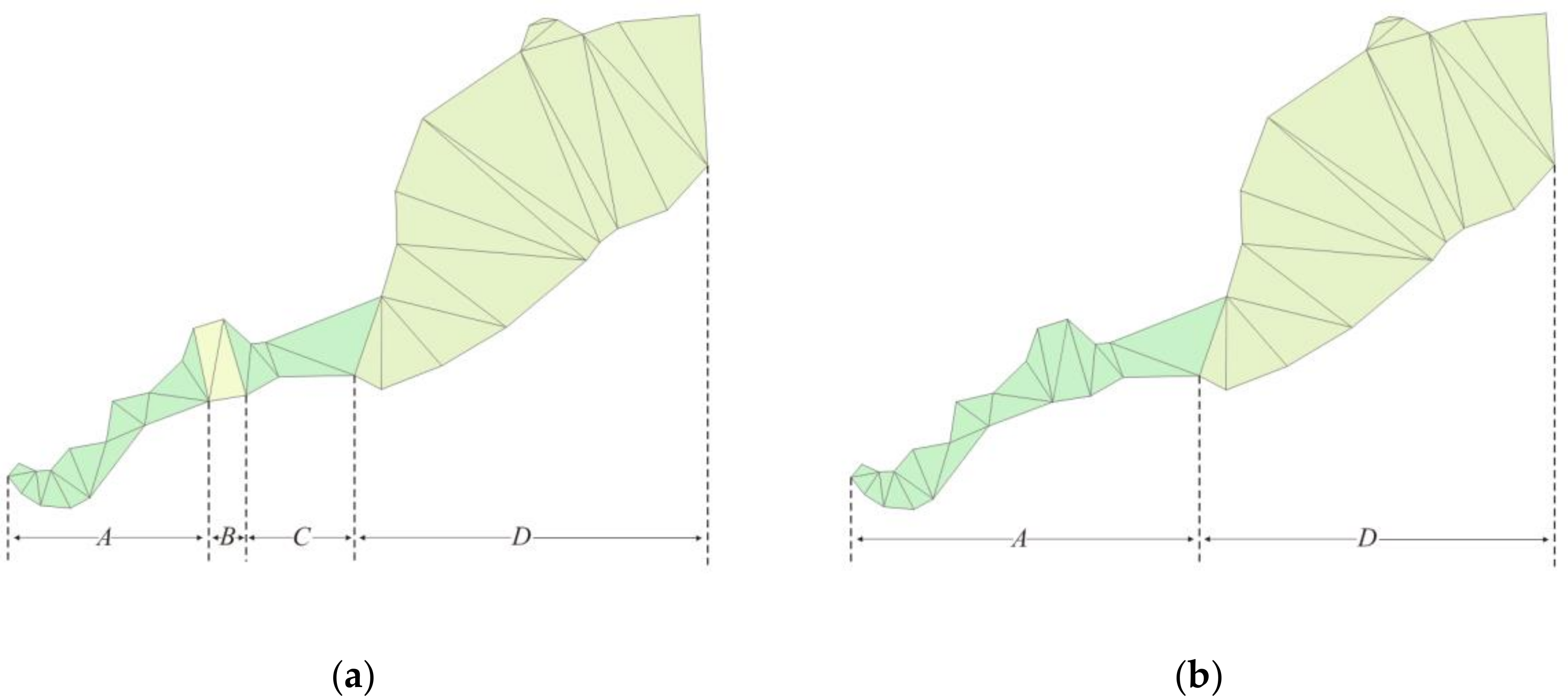
3.1.2. Segment Extraction
3.2. Symbol Filling
- If WS ≥ WT and AS ≥ AT, the segment belongs to tile type.
- If WS < WT and AS ≥ AT, the segment belongs to narrow type.
- If WS ≥ WT and AS < AT, the segment belongs to point type.
- If WS < WT and AS < AT, the segment does not need to fill.
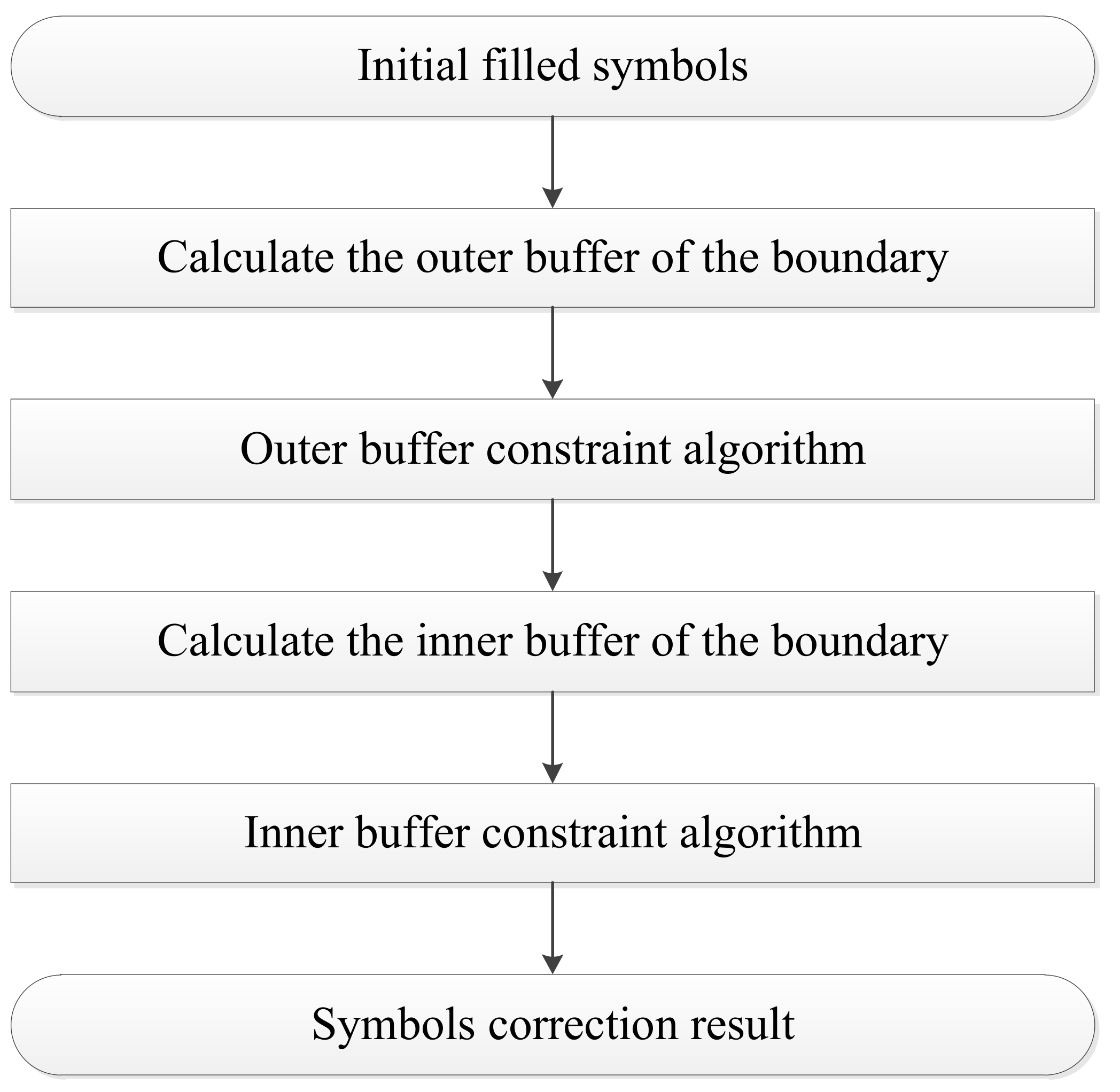
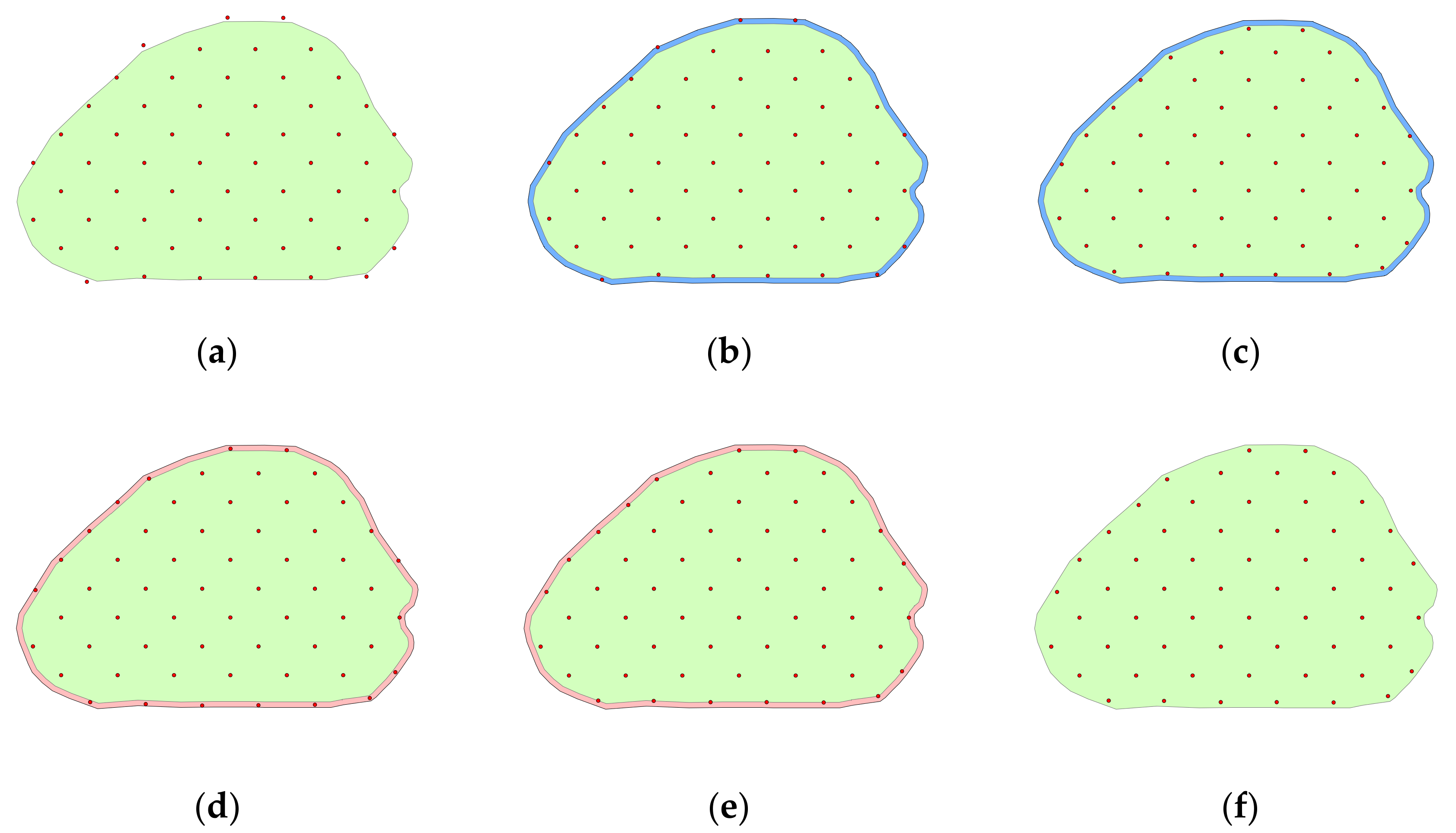
3.3. Symbol Correction under Boundary Constraint
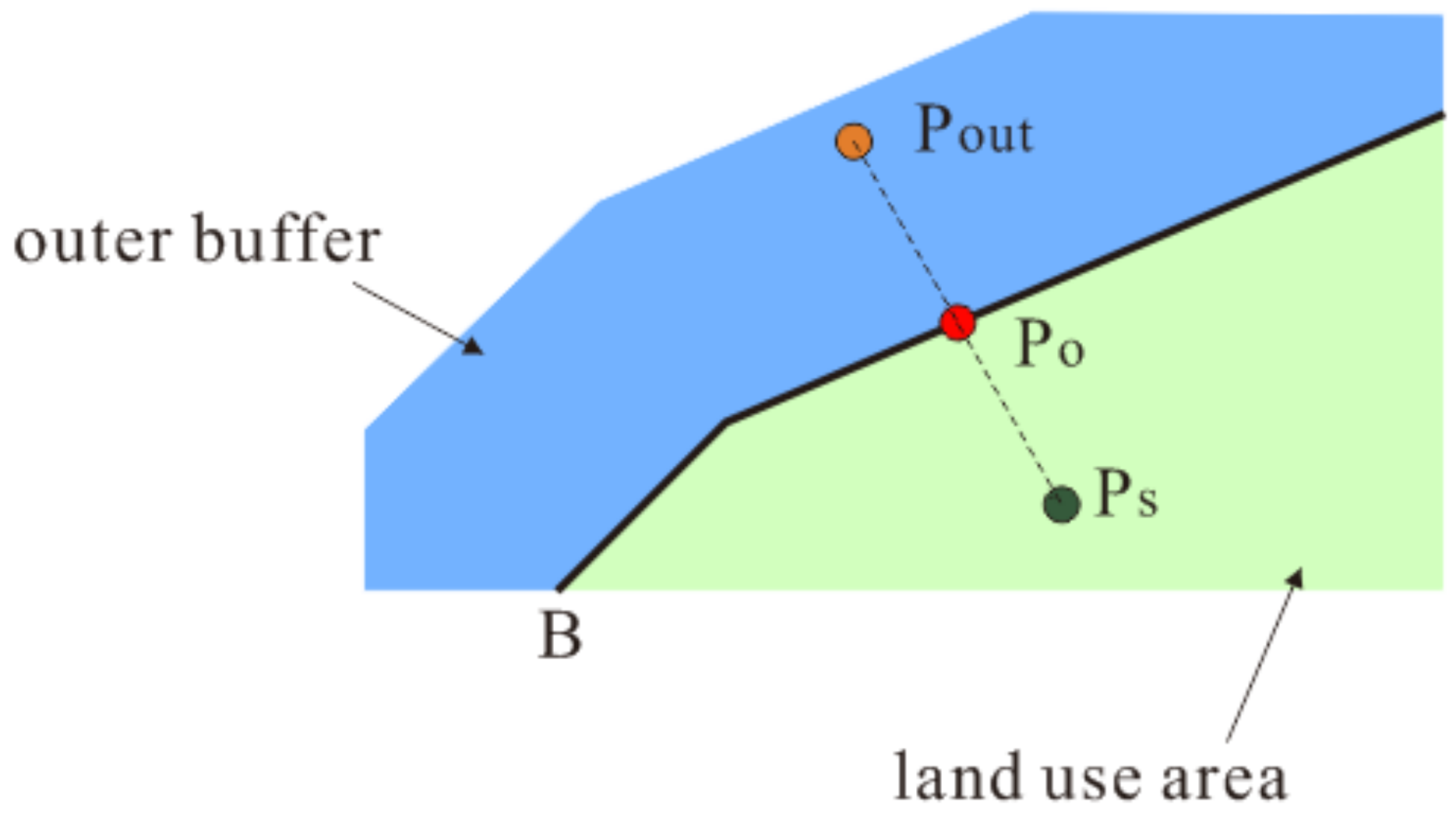
3.3.1. Outer Buffer of Boundary Constraint
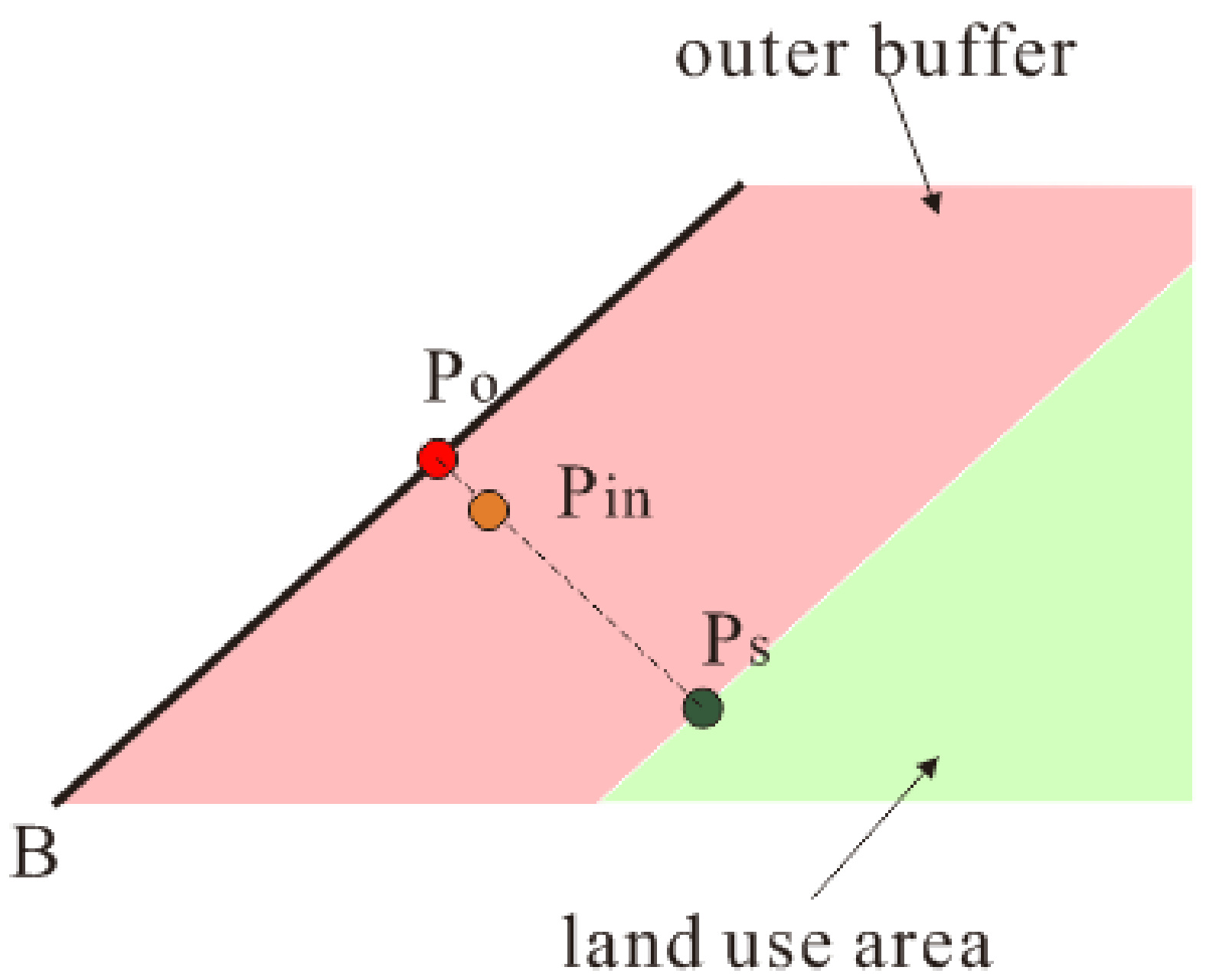
3.3.2. Inner Buffer of Boundary Constraint
4. Experiment and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Data and Environment
4.2. Typical Data Analysis
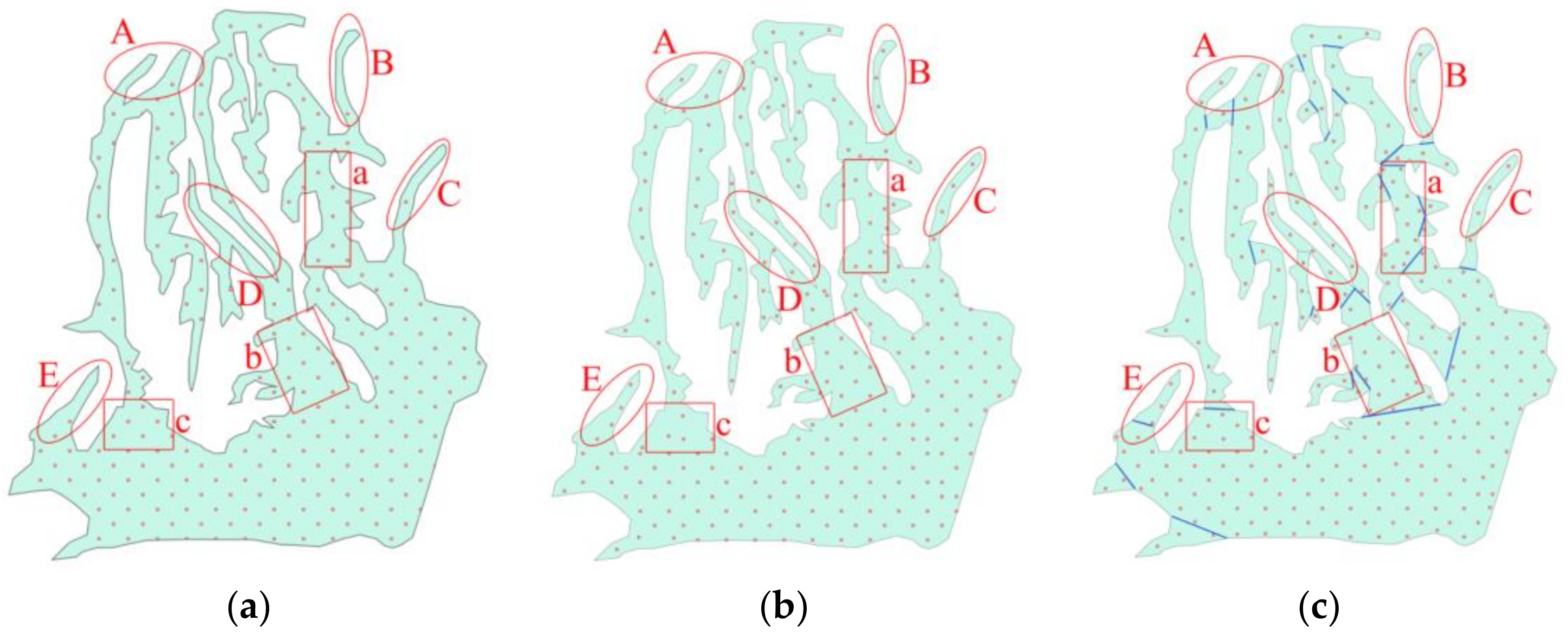
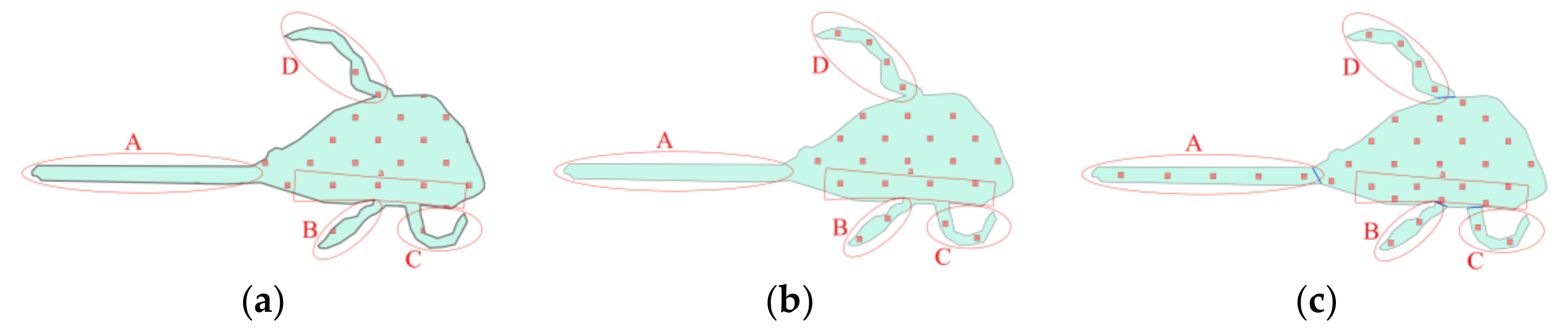
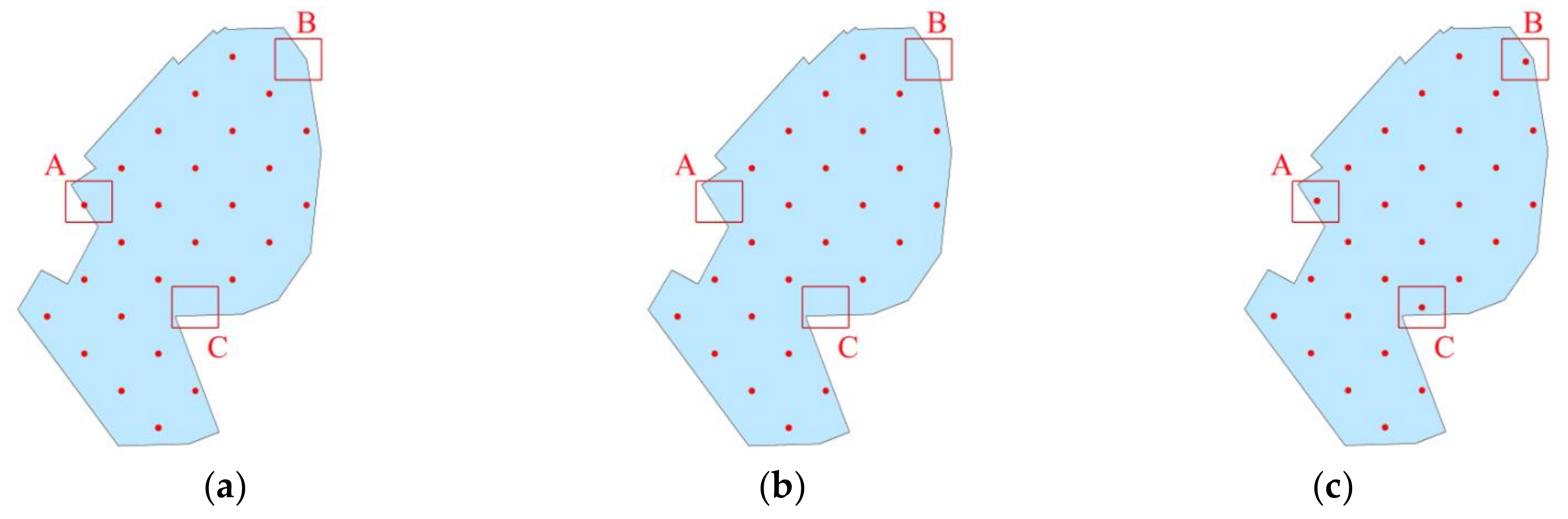
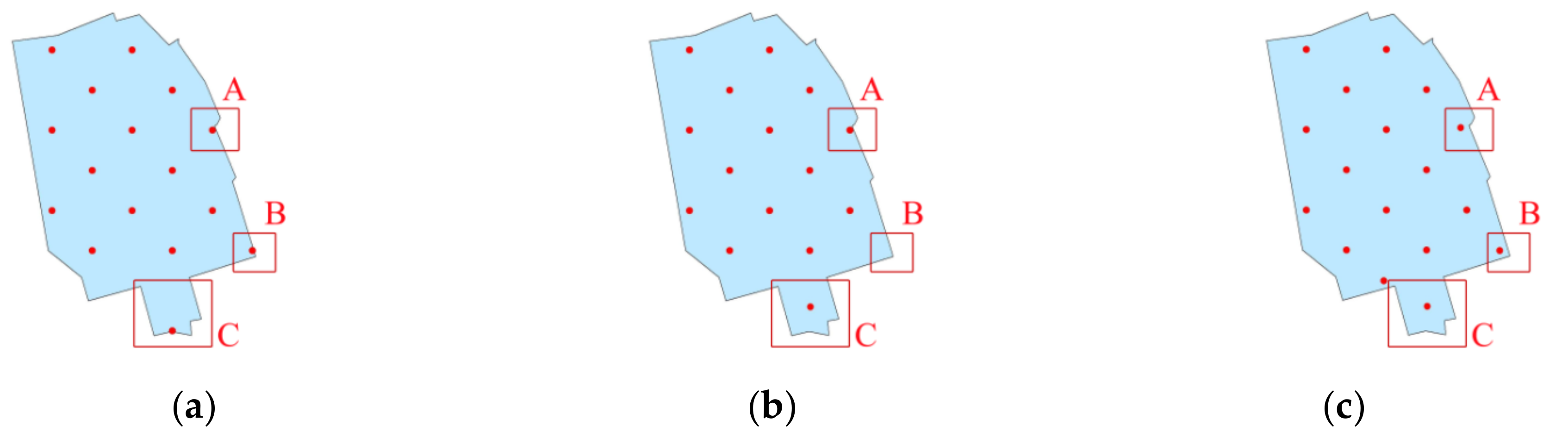
4.2.1. Rational Filling of Complex Areas
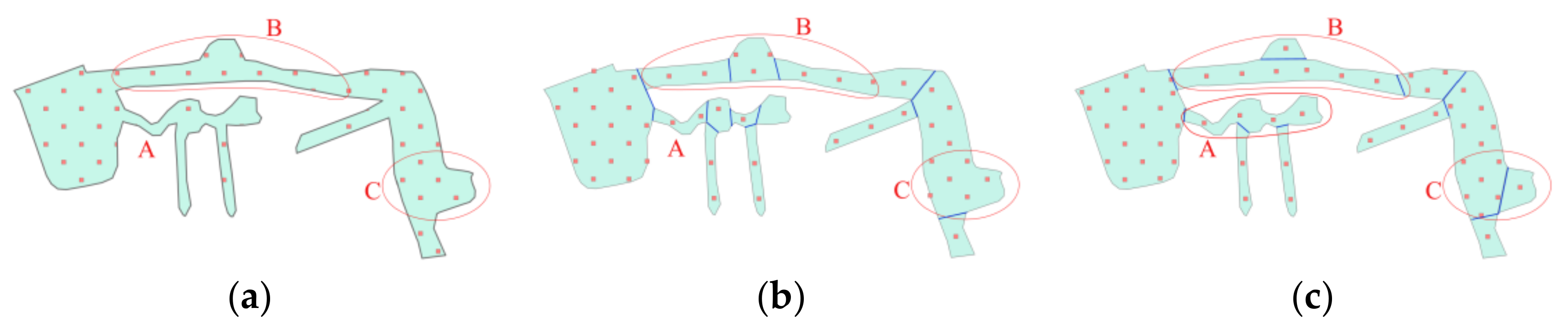
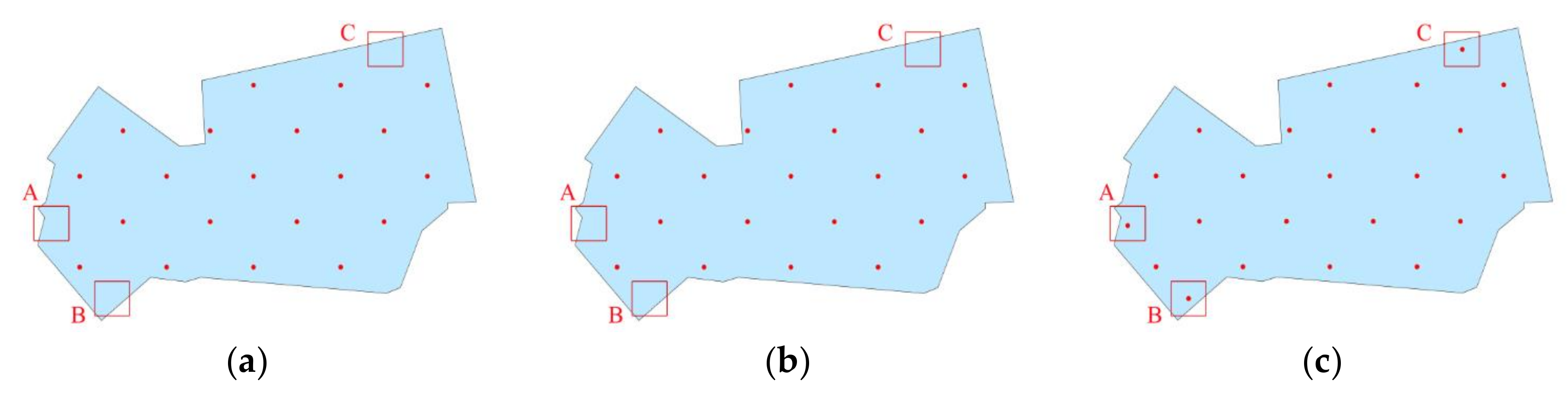
4.2.2. Rational Filling of Regular Areas
4.3. Mass Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arthur Robinson, H. Elements of Cartography; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Slocum, T.A.; McMaster, R.M.; Kessler, F.C.; Howard, H.H.; Mc Master, R.B. Thematic Cartography and Geographic Visualization; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Millett, M.E. The Egocentric Map Perspective in Thematic Choropleth Maps. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Oregon, Eugene, OR, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hey, A.; Bill, R. Placing dots in dot maps. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 2417–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.E.; Groop, R.E. Regional portrayal with multi-pattern color dot maps. Cartogr. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Geovis. 1981, 18, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, W.L. Semiology of Graphics. Psyccritiques 1985, 30, 78. [Google Scholar]
- DiBiase, D.; MacEachren, A.M.; Krygier, J.B.; Reeves, C. Animation and the role of map design in scientific visualization. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1992, 19, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N. Frequency histogram legend in the choropleth map: A substitute to traditional legends. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2004, 31, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavin, S. Mapping continuous geographical distributions using dot-density shading. Am. Cartogr. 1986, 13, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimerling, A.J. Dotting the dot map, revisited. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2009, 36, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, J.R. Dotting the dot map: An analysis of dot size, number, and visual tone density. Surv. Mapp. 1949, 9, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Harrie, L.; Revell, P. Automation of Vegetation Symbol Placement on Ordnance Survey® 1:50 000 Scale Maps. Cartogr. J. 2007, 44, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, A. Automated dot mapping: How to dot the dot map. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2012, 39, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, B.; Jenny, H.; Räber, S. Map Design for the Internet; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dent, B.D.; Torguson, J.S.; Hodler, T.W. Cartography, Thematic Map Design, 6th ed.; McGraw-Hill: Dubuque, IA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- De Berg, M.; Bose, P.; Cheong, O.; Morin, P. On simplifying dot maps. Comput. Geom. 2004, 27, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Ai, T.; Yang, W. A Map Symbol Filling Method for Complex Land Patch Based on Simplex Partition. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2018, 34, 1–6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meijers, M.; Savino, S.; Van Oosterom, P. SPLITAREA: An algorithm for weighted splitting of faces in the context of a planar partition. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2016, 30, 1522–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.T.; Zuo, X.Q.; Zhang, L.T.; Huang, L. An algorithm for symbol configuration of land type. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2012, 37, 100–103. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Szombara, S. Unambiguous collapse operator of digital cartographic generalization process. In Proceedings of the 16th ICA Workshop on Generalisation and Map Production, Dresden, Germany, 23–24 August 2013; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Krygier, J.; Wood, D. Making Maps: A Visual Guide to Map Design for GIS, 2nd ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H.; Park, H.W. Fast view interpolation of stereo images using image gradient and disparity triangulation. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2003, 18, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewchuk, J.R.; Brown, B.C. Fast segment insertion and incremental construction of constrained Delaunay triangulations. Comput. Geom. 2015, 48, 554–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Edelsbrunner, H.; Tan, T. Proof of correctness of the digital Delaunay triangulation algorithm. Comput. Geom. Theory Appl. 2015, 48, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Filling Method | Number of Dot Symbols | Sufficiency | Symbol Overlap | Number of Spatial Conflicts |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional three-square shaped filling method | 14,032 | 0.67 | 0.64 | 1148 |
| The filling method based on simple segmentation | 17,650 | 0.88 | 0.78 | 745 |
| The method proposed in this paper | 20,034 | 0.95 | 1 | 0 |
| Filling Method | Dataset 1 | Dataset 2 | Dataset 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of polygons processed | 174 | 3050 | 5296 |
| Total area of polygons (km2) | 432 | 1211 | 1632 |
| Total computing time (s) | 2.12 | 27.69 | 59.95 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, Y.; Li, C.; Wu, P. Dot Symbol Auto-Filling Method for Complex Areas Considering Shape Features. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8030158
Yin Y, Li C, Wu P. Dot Symbol Auto-Filling Method for Complex Areas Considering Shape Features. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2019; 8(3):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8030158
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Yong, Chengming Li, and Pengda Wu. 2019. "Dot Symbol Auto-Filling Method for Complex Areas Considering Shape Features" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 8, no. 3: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8030158
APA StyleYin, Y., Li, C., & Wu, P. (2019). Dot Symbol Auto-Filling Method for Complex Areas Considering Shape Features. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 8(3), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8030158




