Spatiotemporal Influence of Urban Environment on Taxi Ridership Using Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Geographically Weighted Regression Model
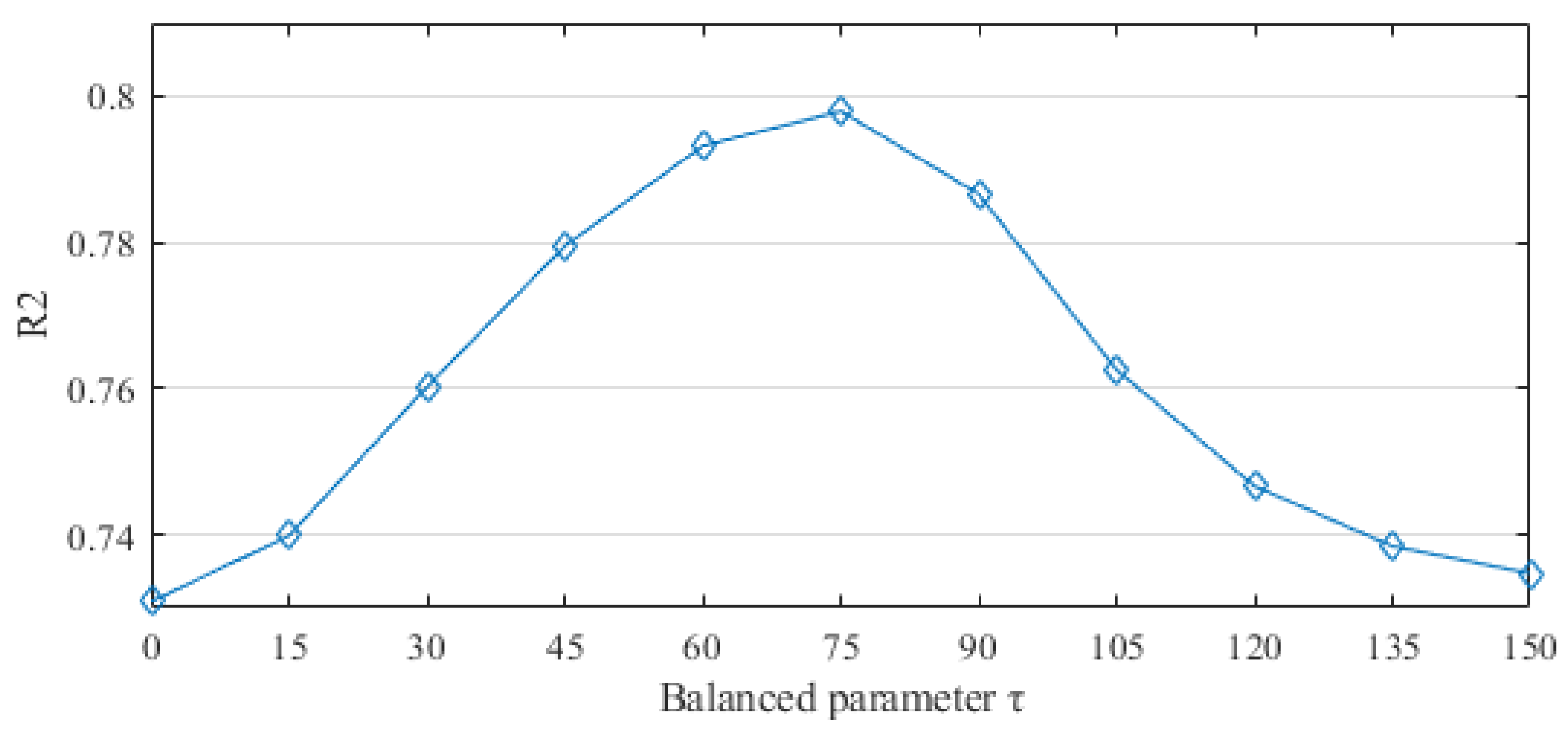
2.2. Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression Model
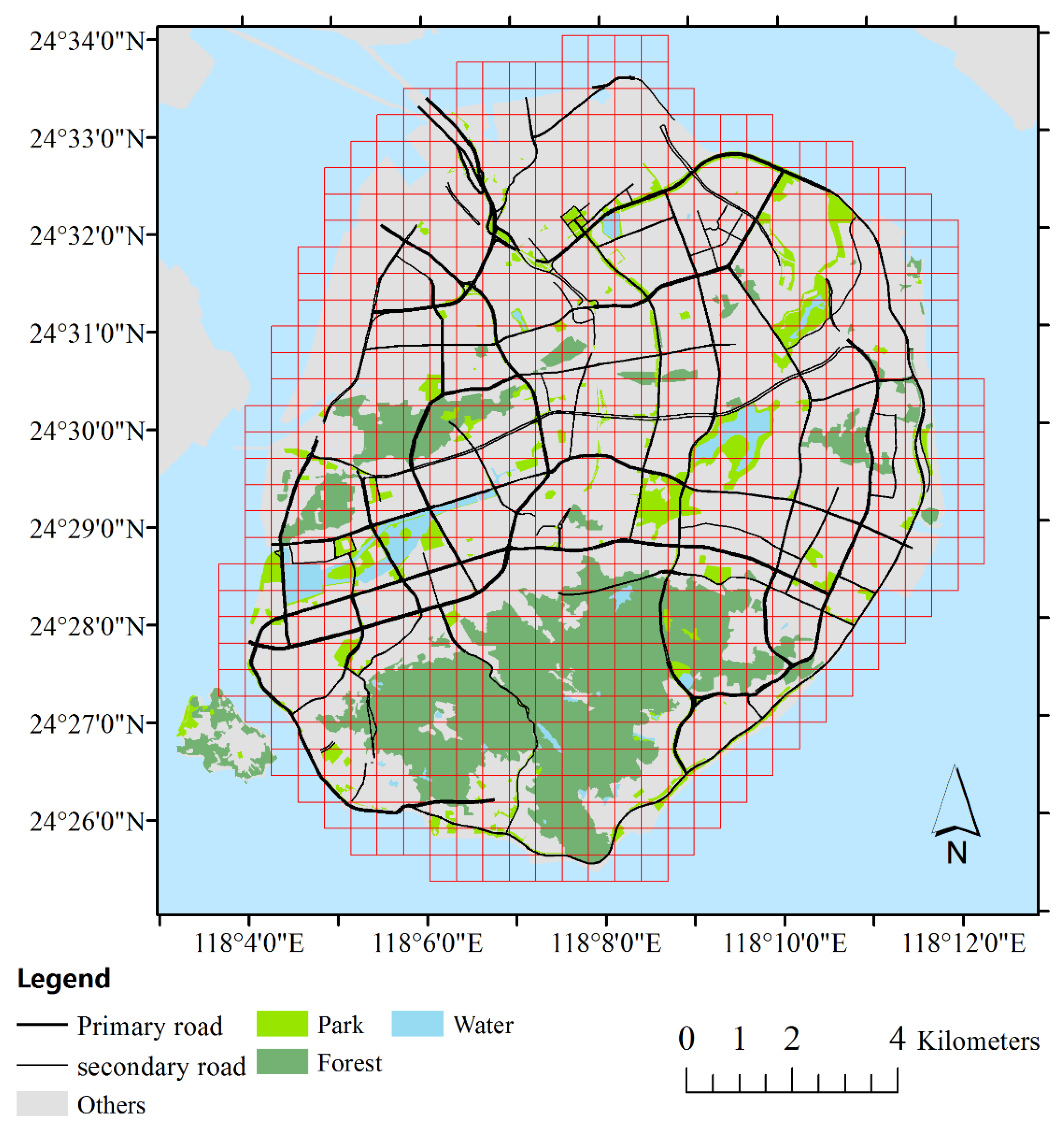
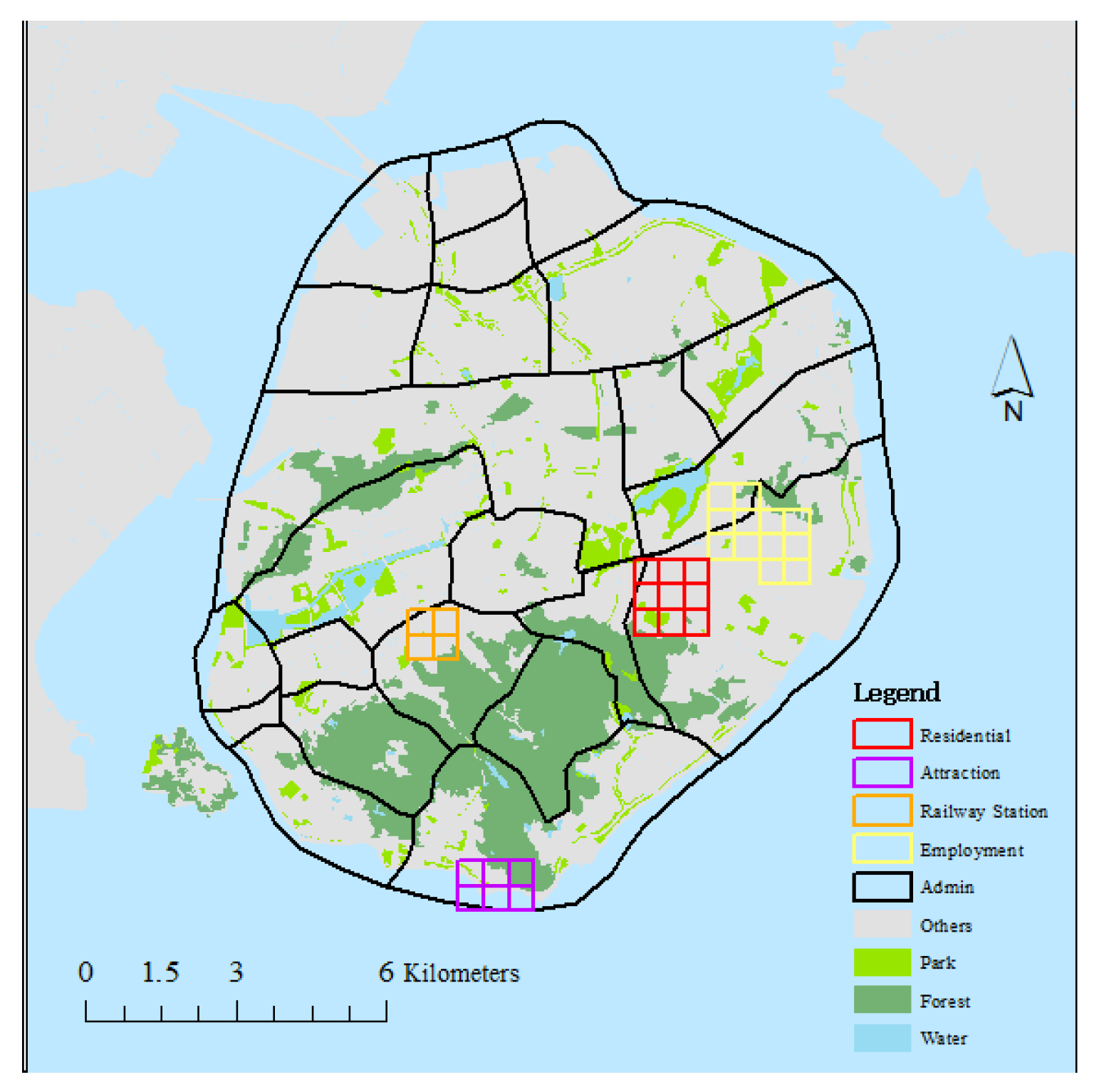
3. Study Area and Data
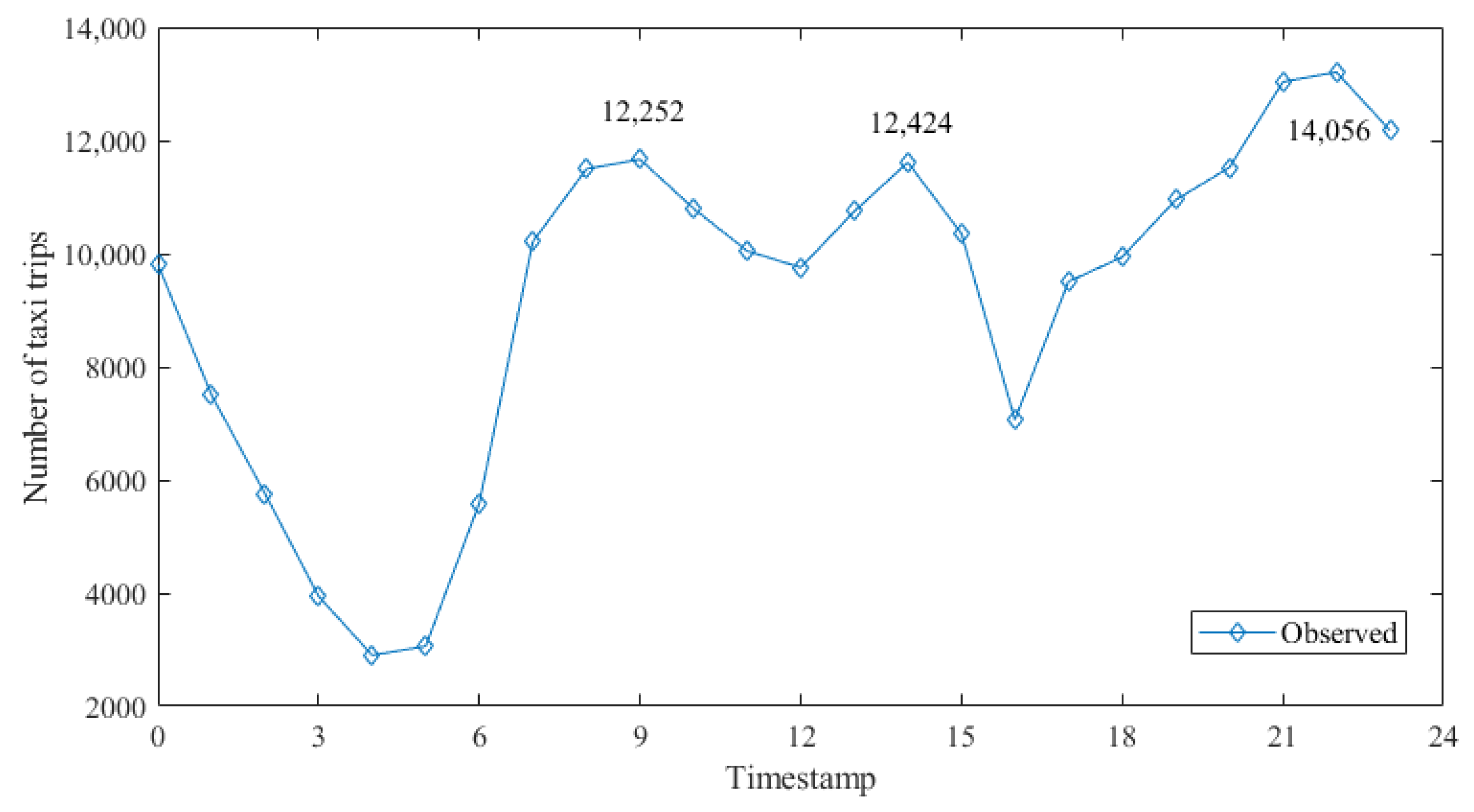
3.1. Taxi Ridership Data
- Missing coordinates for OD location or location outside the study area.
- Missing trip distance d or d <300 m or d >40 km.
- Missing trip time t or t <1 min or t >4 h.
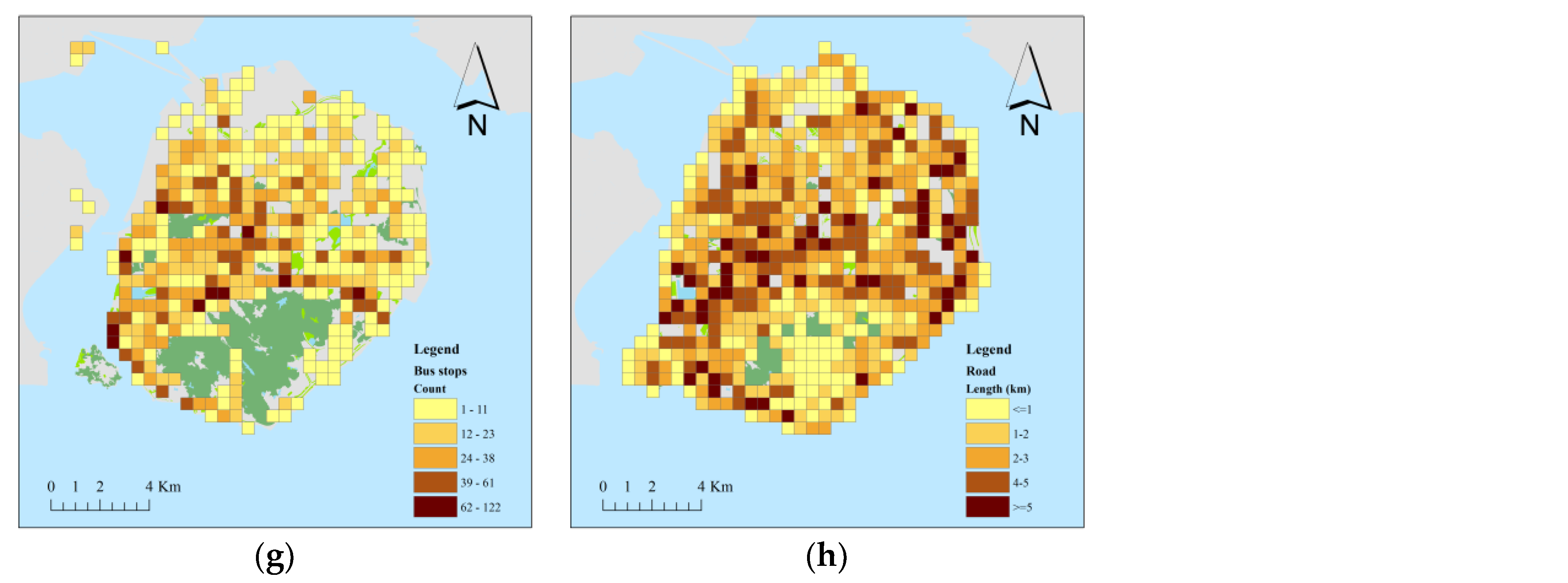
3.2. Urban Environment Assessment
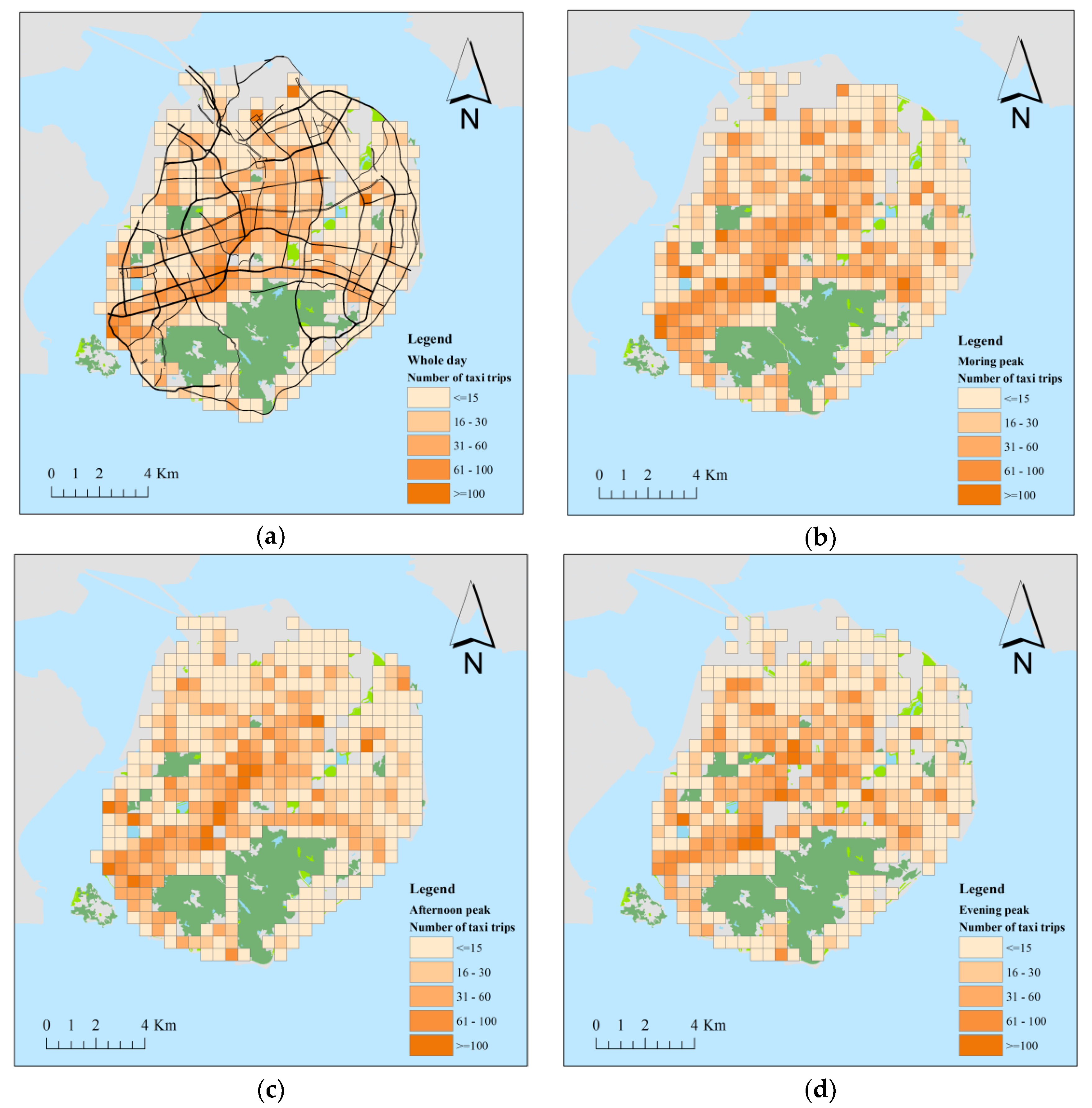
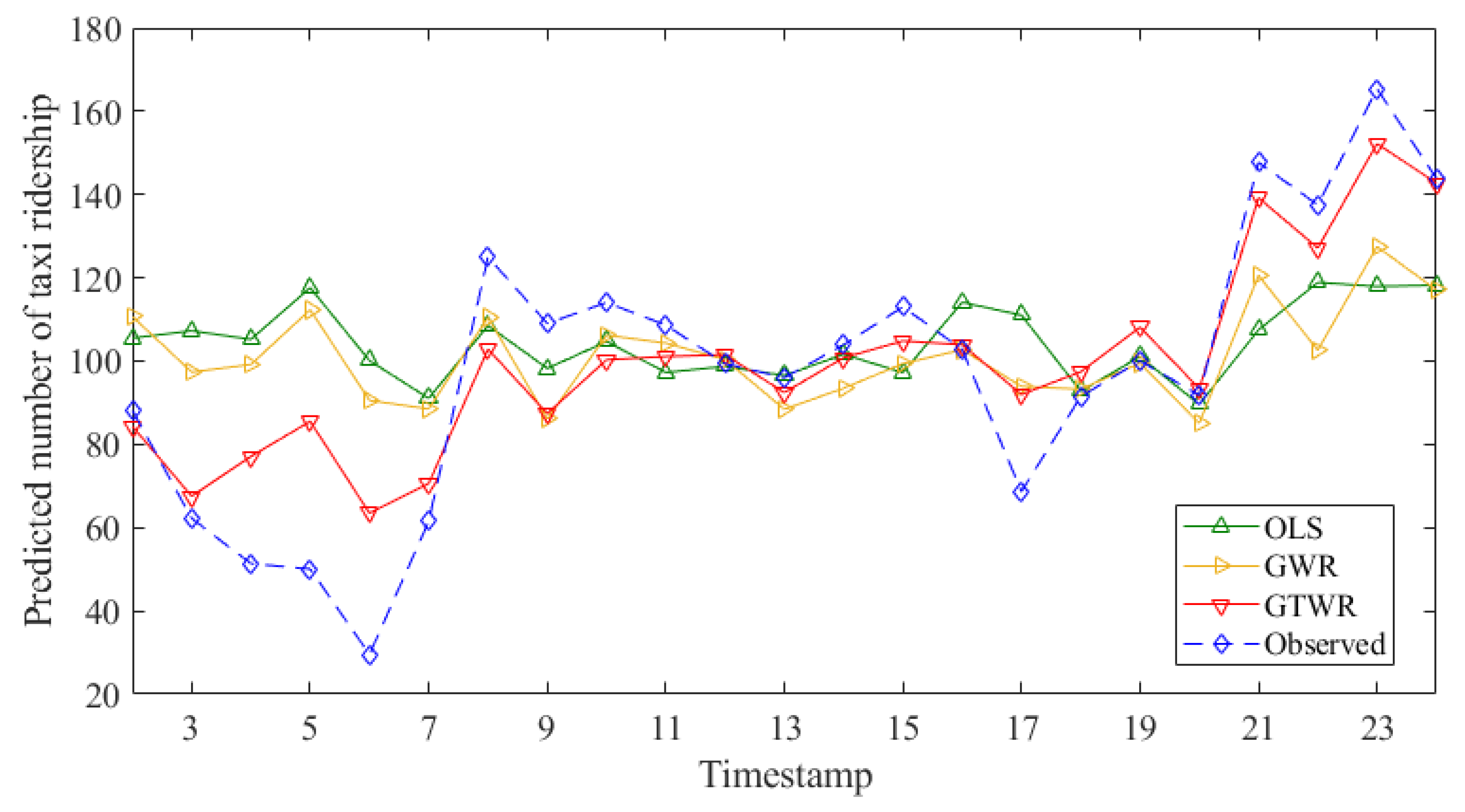
4. Model Results
5. Discussion
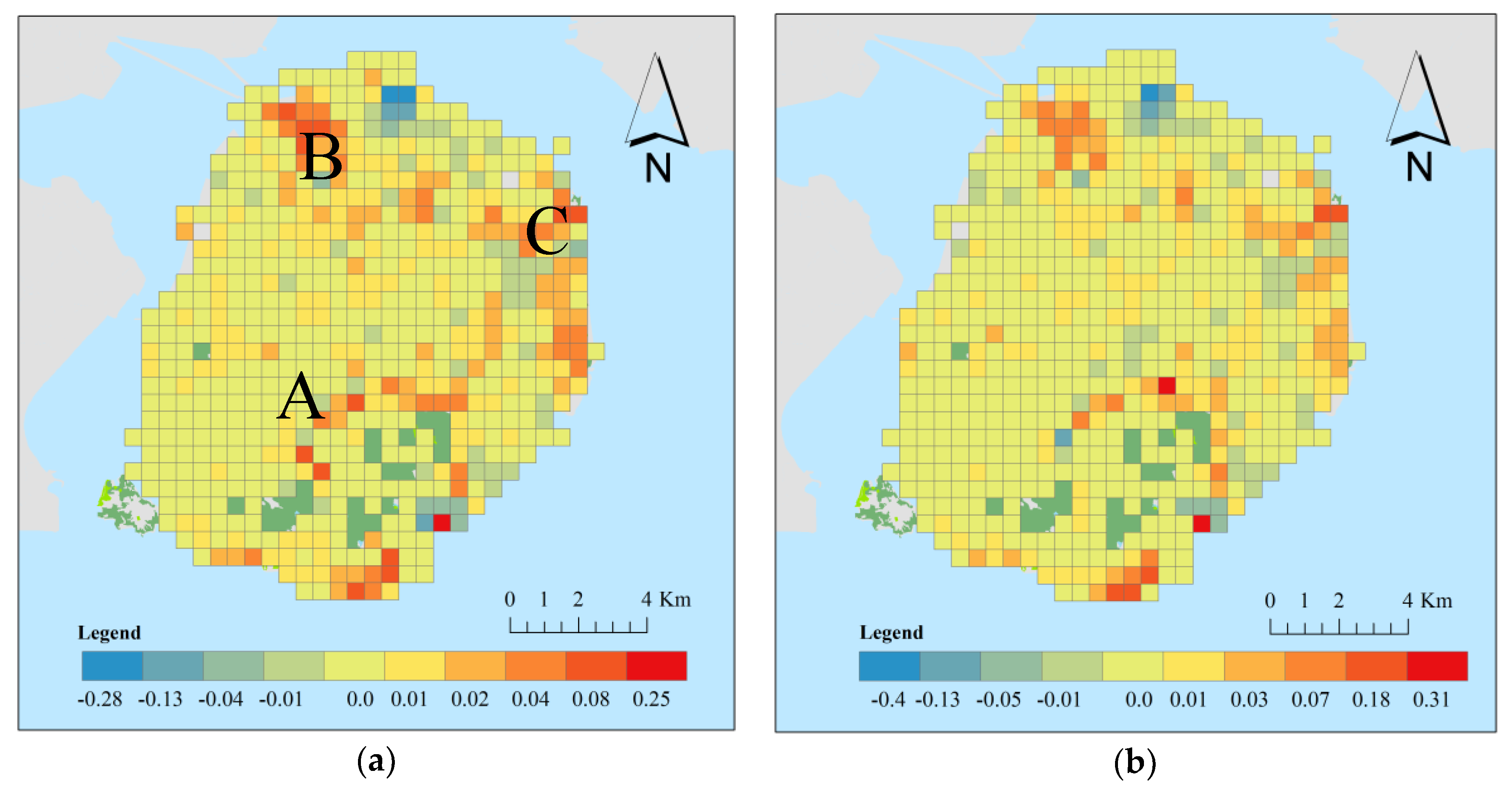
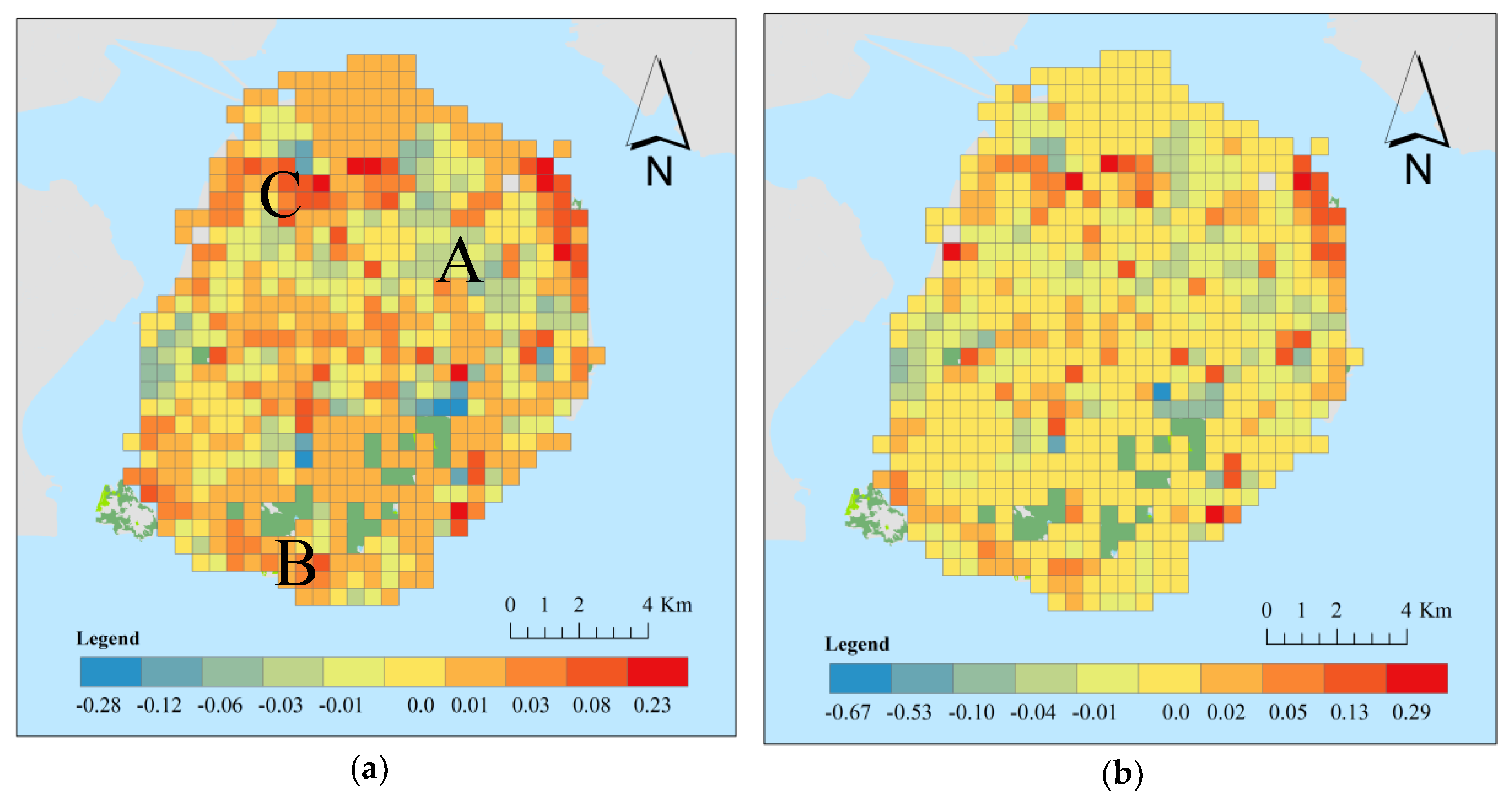
5.1. Spatial Variations of the Coefficients
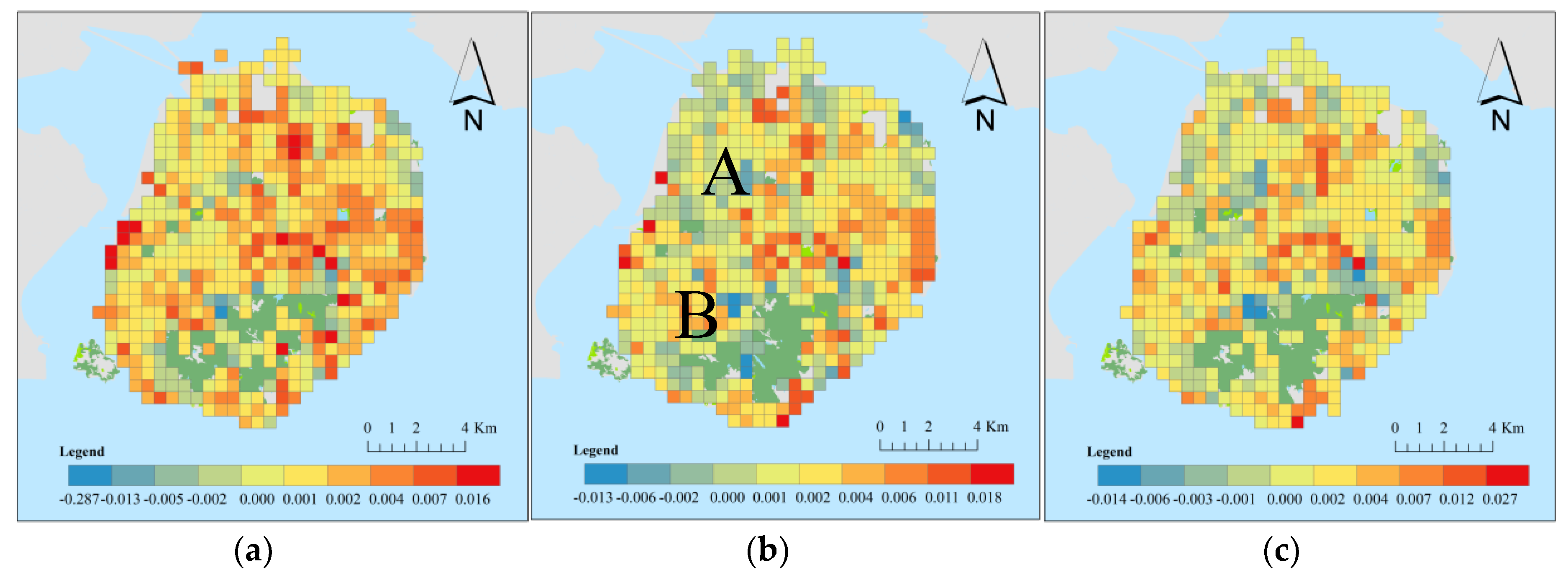
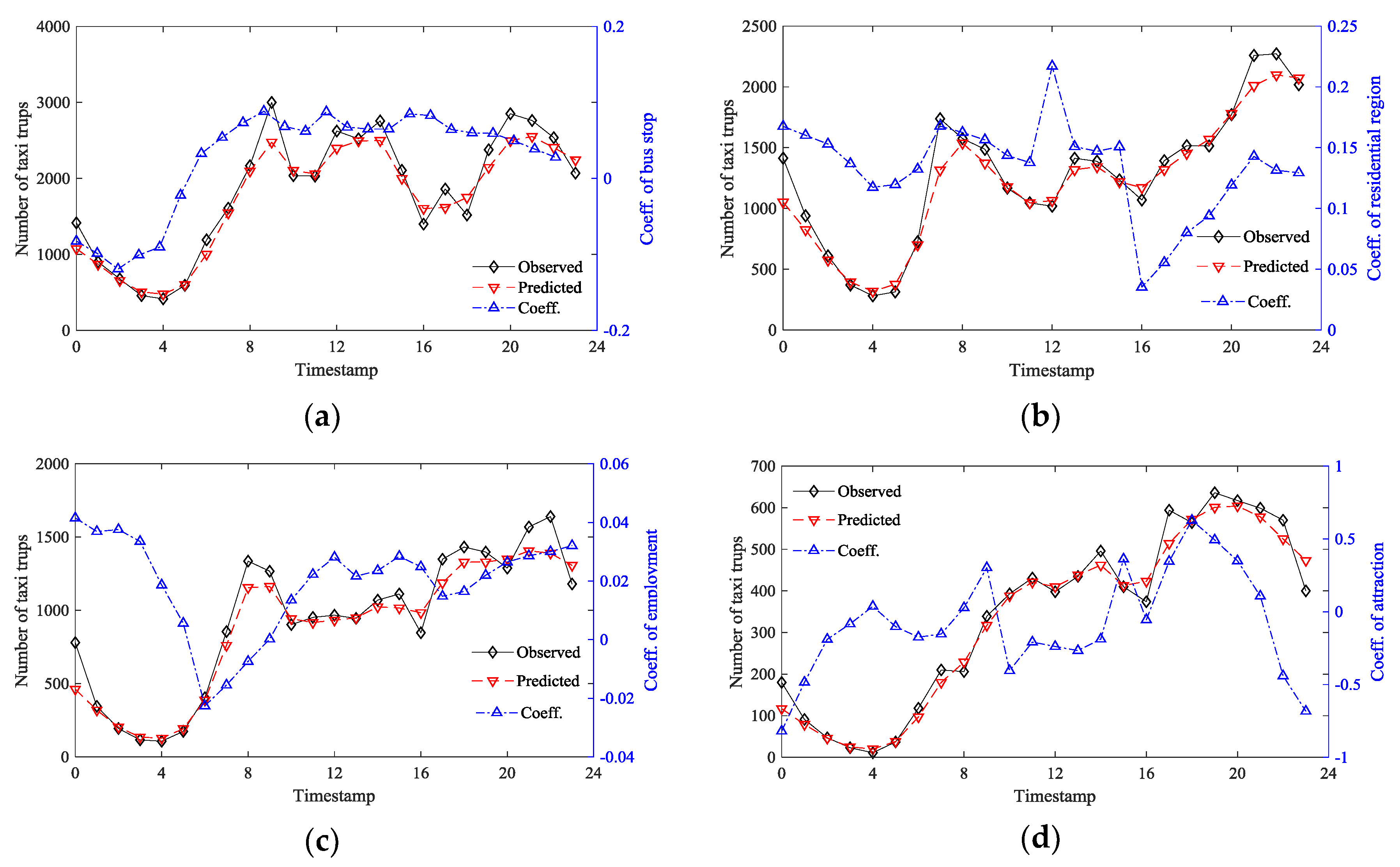
5.2. Temporal Variations of the Coefficients
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- King, D.A.; Peters, J.R.; Daus, M.W. Taxicabs for Improved Urban Mobility: Are We Missing an Opportunity? Presented at the Transportation Research Board 91st Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 22–26 January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Y.M. How can the taxi industry survive the tide of ridesourcing? Evidence from Shenzhen, China. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2017, 79, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Mishra, S. Land use and transit ridership connections: Implications for state-level planning agencies. Land Use Policy 2013, 30, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.D.; Miller, D.; Iseki, H.; Fink, C. Nature and/or nurture? Analyzing the determinants of transit ridership across us urbanized areas. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2009, 43, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Ding, C.; Wang, Y. A geographically and temporally weighted regression model to explore the spatiotemporal influence of built environment on transit ridership. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2018, 70, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinelli, F.; Nair, R.; Calabrese, F.; Berlingerio, M.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Sbodio, M.L. Data-driven transit network design from mobile phone trajectories. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 1724–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Franz, M.L.; Zhu, S.; Mahmoudi, J.; Nasri, A.; Zhang, L. Analysis of Washington, DC taxi demand using GPS and land-use data. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 66, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, S. Urban land uses and traffic ‘source-sink areas’: Evidence from gps-enabled taxi data in Shanghai. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 106, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Qu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Xu, C.; Liu, S. Spatio-temporal analysis of passenger travel patterns in massive smart card data. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 18, 3135–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.W. The effect of driving restrictions on air quality in Mexico city. J. Political Econ. 2008, 116, 38–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Ukkusuri, S.V. Exploring Spatial Variation of Urban Taxi Ridership Using Geographically Weighted Regression. Presented at the 94th Annual Meeting of the Transportation Research Board, Washington, DC, USA, 11–15 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- O’Sullivan, D. Geographically Weighted Regression: The Analysis of Spatially Varying Relationships; Fotheringham, A.S., Brunsdon, C., Charlton, M., Eds.; The Ohio State University: Columbus, OH, USA, 2003; Volume 35, pp. 272–275. [Google Scholar]
- Cardozo, O.D.; García-Palomares, J.C.; Gutiérrez, J. Application of geographically weighted regression to the direct forecasting of transit ridership at station-level. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 34, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, L.F.; Zhao, F.; Liu, X.; Li, M.T.; Ubaka, I. Transit ridership model based on geographically weighted regression. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2006, 1972, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, Y.-C.; Jou, R.-C.; Yang, C.-H. Factors affecting public transportation usage rate: Geographically weighted regression. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2015, 78, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Varley, D.; Chen, J. What affects transit ridership? A dynamic analysis involving multiple factors, lags and asymmetric behaviour. Urban Stud. 2011, 48, 1893–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Motta, G.; Liu, K. Delivering real-time information services on public transit: A framework. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 18, 2642–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wu, B.; Barry, M. Geographically and temporally weighted regression for modeling spatio-temporal variation in house prices. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Li, R.; Huang, B. A geographically and temporally weighted autoregressive model with application to housing prices. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 1186–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Crespo, R.; Yao, J. Geographical and temporal weighted regression (GTWR). Geogr. Anal. 2015, 47, 431–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wu, L.; Qin, K.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, Y. A geographically and temporally weighted regression model for ground-level PM2. 5 estimation from satellite-derived 500 m resolution AOD. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tang, Q.; Gong, D.-Y.; Zhang, Z. Estimating ground-level pm2. 5 concentrations in beijing using a satellite-based geographically and temporally weighted regression model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.-J.; Kong, S.-J.; Chang, C.-H. Spatio-temporal water quality mapping from satellite images using geographically and temporally weighted regression. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lam, K.-F.; Wu, J.T.; Lam, T.T.-Y. Geographically weighted temporally correlated logistic regression model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peruggia, M. Model selection and multimodel inference: A practical information-theoretic approach (2nd ed.).(telegraphic reviews)(book review). J. Wildl. Manag. 2002, 67, 175–196. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, X.; Qian, X.; Ukkusuri, S.V. A graph-based approach to measuring the efficiency of an urban taxi service system. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 2479–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Wu, S.; Zhang, F.; Liu, R.; Zhou, Y. Extending geographically and temporally weighted regression to account for both spatiotemporal heterogeneity and seasonal variations in coastal seas. Ecol. Inform. 2018, 43, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

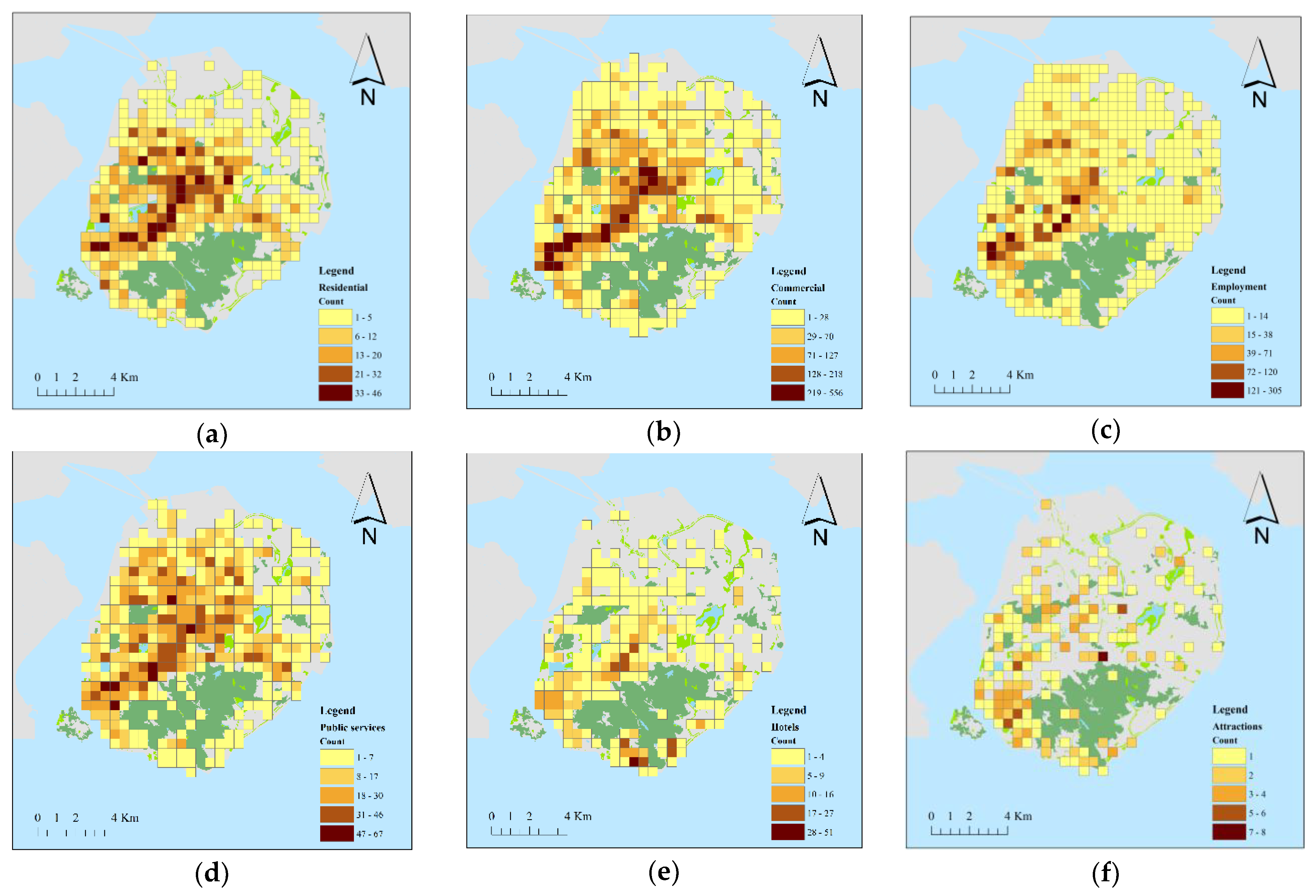
| Type | Variable | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Urban environment | Residential | Number of residential records in each cell |
| Commercial | Number of retail stores, shopping malls, restaurants and entertainment centres in each cell | |
| Employment | Number of companies, education and government offices in each cell | |
| Public service | Number of financial, telecommunication, automobile and medical services in each cell | |
| Hotel | Number of hotels in each cell | |
| Attraction | Number of tourist attractions in each cell | |
| Transport | Bus stop | Number of bus stops in each cell |
| Road | Length of road in each cell |
| Res. | Com. | Emp. | Public Services | Hotel | Att. | Bus | Road | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residential | 1 | |||||||
| Commercial | 0.752 | 1 | ||||||
| Employment | 0.528 | 0.627 | 1 | |||||
| Public services | 0.757 | 0.779 | 0.503 | 1 | ||||
| Hotel | 0.272 | 0.415 | 0.372 | 0.335 | 1 | |||
| Attraction | 0.194 | 0.159 | 0.113 | 0.209 | 0.202 | 1 | ||
| Bus stop | 0.475 | 0.474 | 0.373 | 0.504 | 0.322 | 0.188 | 1 | |
| Road | 0.150 | 0.191 | 0.173 | 0.154 | 0.084 | 0.121 | 0.274 | 1 |
| Variable | Coefficient | t-statistic | t-probability | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 1.834 | 20.100 | 0.000 | -- |
| Residential | 0.053 | 10.075 | 0.000 | 1.651 |
| Employment | −0.001 | −0.317 | 0.751 | 1.556 |
| Hotel | 0.062 | 6.122 | 0.000 | 1.258 |
| Attraction | −0.032 | −0.764 | 0.444 | 1.084 |
| Bus stop | 0.036 | 12.943 | 0.000 | 1.517 |
| Road | 0.216 | 7.933 | 0.000 | 1.125 |
| Diagnostic Information | ||||
| R2 | 0.4691 | |||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.4662 | |||
| AIC | 110,806.15 | |||
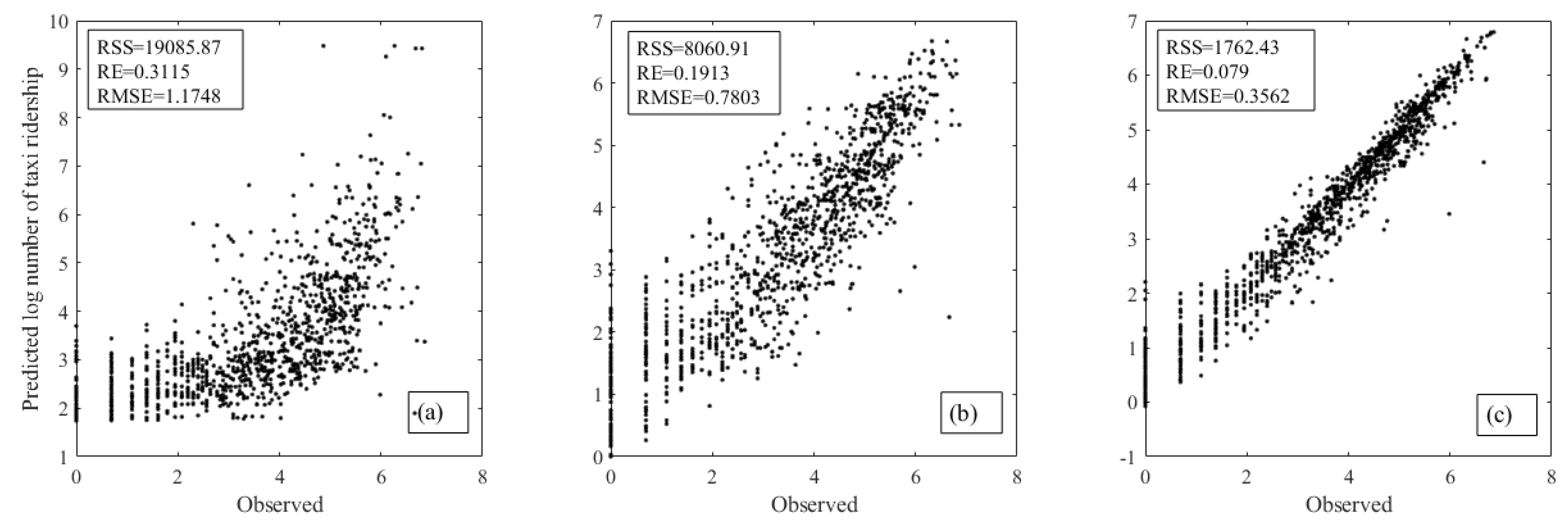
| RSS | 19,085.87 | |||
| Variable | AVG | MIN | MAX | LQ | MED | UQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 1.877 | 0.0100 | 5.5974 | 1.1780 | 1.6947 | 2.4620 |
| Residential | 0.069 | −0.4256 | 1.1324 | 0.0243 | 0.0531 | 0.0905 |
| Employment | 0.020 | −0.1162 | 0.5169 | −0.0048 | 0.0020 | 0.0302 |
| Hotel | 0.213 | −0.8061 | 1.8083 | 0.0970 | 0.1790 | 0.2806 |
| Attraction | −0.100 | −1.3732 | 1.5520 | −0.3395 | 0.0958 | 0.0806 |
| Bus stop | 0.044 | −0.0537 | 0.3449 | 0.0149 | 0.0343 | 0.0730 |
| Road | 0.177 | −0.4226 | 1.3716 | 0.0215 | 0.1560 | 0.2915 |
| Diagnostic Information | ||||||
| R2 | 0.7805 | |||||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.7793 | |||||
| AIC | 101,115.35 | |||||
| RSS | 8060.91 | |||||
| Variable | AVG | MIN | MAX | LQ | MED | UQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 1.8463 | −3.2832 | 7.4410 | 0.8118 | 1.7029 | 2.6531 |
| Residential | 0.0760 | −1.6402 | 2.4488 | 0.0102 | 0.0505 | 0.1134 |
| Employment | 0.0216 | −0.4920 | 1.0506 | −0.0087 | 0.0027 | 0.0323 |
| Hotel | 0.2414 | −12.1476 | 3.7126 | 0.0695 | 0.1974 | 0.3782 |
| Attraction | −0.1390 | −4.8221 | 3.4925 | −0.4156 | −0.1002 | 0.1653 |
| Bus stop | 0.0460 | −0.1327 | 0.7814 | 0.0107 | 0.0385 | 0.0723 |
| Road | 0.1746 | −1.8823 | 3.1798 | −0.0358 | 0.1711 | 0.3821 |
| Diagnostic Information | ||||||
| R2 | 0.9527 | |||||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.9524 | |||||
| AIC | 84,026.81 | |||||
| RSS | 1762.43 | |||||
| Proportion | 100% | 70% | 50% | 30% | 10% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 (GTWR) | 0.9783 | 0.9803 | 0.9837 | 0.9873 | 0.9389 |
| R2 (GWR) | 0.8091 | 0.8360 | 0.8379 | 0.7824 | 0.7806 |
| R2 (OLS) | 0.4699 | 0.4707 | 0.4890 | 0.4523 | 0.4478 |
| Variable | Period | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Morning Peak | Afternoon Peak | Evening Peak | |
| Residential | 0.048 | 0.102 | 0.121 |
| Employment | 0.136 | 0.050 | 0.046 |
| Hotel | 0.093 | 0.013 | 0.057 |
| Attraction | −0.294 | −0.155 | −0.215 |
| Bus stop | 0.054 | 0.053 | 0.045 |
| Road | 0.008 | 0.173 | 0.230 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Huang, B.; Zhu, S. Spatiotemporal Influence of Urban Environment on Taxi Ridership Using Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8010023
Zhang X, Huang B, Zhu S. Spatiotemporal Influence of Urban Environment on Taxi Ridership Using Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2019; 8(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xinxin, Bo Huang, and Shunzhi Zhu. 2019. "Spatiotemporal Influence of Urban Environment on Taxi Ridership Using Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 8, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8010023
APA StyleZhang, X., Huang, B., & Zhu, S. (2019). Spatiotemporal Influence of Urban Environment on Taxi Ridership Using Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 8(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8010023





