1. Introduction
The global trend toward urbanization has driven urban sprawl in most metropolitan areas around the world. Thus, effective urban design strategies are required to provide citizens a prosperous, sustainable and safe living environment. To ensure the safety of residents, crime prevention has always been a crucial part of urban planning. The study and analysis of crime focus mainly on these two aspects: who are the persons that commit crime, and at what places do crimes occur [
1]. Regarding the first aspect, the great complex and diverse nature of human thinking can be an obstacle to analysis and control. Thus, to discover crime patterns, geography researchers focus on when and where crimes occur. As Ferreira et al. [
2] summarized, since the 1960s, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have been applied to a number of studies; meanwhile, digital crime mapping, developed significantly in the 1980s, has been widely applied to the criminology field. GIS technologies have been used in various ways including, but not limited to, monitoring alerts reported by citizens, providing visual aids for identifying crime distribution patterns, and identifying, modeling and predicting crime “hotspots”. Additionally, web mapping enables researchers, as well as the public, to obtain volunteer provided information for crime analysis and prevention.
Since the mid-nineteenth century, crime pattern studies, whether using paper or digital maps, have revealed, from a place perspective, that criminal activity is highly patterned, and thus, predictable [
3] In other words, incidents of crime are not randomly spatially distributed; crime “hotspots” do exist [
4]. Researchers also found that the “hotspots” are stable year after year [
5], thus suggesting that we can deal with crime problems by concentrating on the identified hotspots, which are within a small number of places. Based on the fact that the distribution of the incidents of crime follows a pattern, the concept of Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) has been proposed since the 1970s, which asserts that “the proper design and effective use of a built environment can lead to a reduction in the fear and incidence of crime and an improvement in the quality of life” [
6]. Discovering the characteristics of crime-concentrated places supports the planning of CPTED strategies. Empirical models are developed to summarize characteristics. Accordingly, predictive models are built to predict high-risk crime areas [
7,
8,
9].
Factors that affect crime rates. Various factors, including population density, poverty level, and the unemployment rate affect crime rates [
5]. The important factor most often included in crime research is population density. Although exhibiting different effects (positive or negative), population density is highly significant when predicting crime [
10,
11,
12,
13,
14]. Shaw and McKay [
15] introduced a social disorganization theory that suggests poverty, ethnic heterogeneity, and residential mobility are the three ecological predictors of crime, which promote crime by increasing social disorganization. Subsequent research has added several other factors to the list, including lone-parent families, structural density, urbanization, etc. [
16]. According to crime studies, most types of crime are positively related to the poverty level [
1,
12]. Troy et al. [
11], in their analysis, showed that the relationship between the percentage of single-parent families and crime is negative; whereas, in other regions, its influence is still uncertain. Wang and Minor [
17] found a strong negative relationship between employment and crime in Cleveland in 1990, and the effect on economic crimes was greater than the effect on violent crimes. A study [
10] conducted in Vancouver showed similar results. Also, researchers have examined the influences of educational attainment and a young population. Studies of crime and physical environment mostly focus on the presence, or absence, of structures, such as commercial buildings, parking lots, police stations, bus stops, etc. [
5,
18]. The number of street lights in prosperous regions, which provide more opportunities for property crime, serve as an indicator of the urbanization level of an area [
9]. The criminology of place study in Seattle [
5] revealed a positive relationship between lighting and crime. Riggs [
19] also suggested that street lights make it easier for criminals to see the contents of parked cars when stealing, or to make sure there is no one around when breaking into a house. Urban layout has also proved to be related to crime [
14]. The above factors have already shown they have an impact on crime. However, the following are also potential influential factors that can add to accuracy when predicting crime.
Relationship between vegetation density and crime. The relationship between vegetation density and crime has long been under debate. Studies find that criminals usually use dense vegetation as a shield when committing crimes; therefore, vegetation is positively related to the incidents of crime [
20]. On the other hand, some studies indicate that vegetation is related to a decrease in crime incidents. One of the possible reasons is that the green spaces attract people to spend time outdoors, thereby creating a natural surveillance around the area [
11,
21]. Providing A further reason comes from the attention restoration theory, which suggests that the mentally restorative effect of the vegetation may reduce violent crimes by restraining the psychological precursors to criminal acts [
12,
21,
22]. Another possible explanation is related to the broken windows theory, which suggests that the green spaces in an urban area indicate a well-managed society that creates an atmosphere of order and lawfulness, thereby preventing crime from occurring [
22].
Convenience of road networks. The convenience of road networks is another important factor that can influence a criminal’s selection of locations. Highly accessible areas are associated with higher property crime rates; whereas, complex road networks reduce this type of crime [
23]. This phenomenon can be explained by the routine activities theory that the convenient road network exposes attractive and unguarded targets to potential criminals. In addition, higher traffic flows create a natural surveillance that can reduce the crime rate to some extent [
23].
Studies conducted to discover the relationship between vegetation and crime in Canadian cities are limited. Likewise, few studies concerning the relationship between road networks and crime in Canada are documented. Urban crime is usually categorized by violent crime, also known as crime against persons. Non-violent crime is known as crime against property. Based on the available data, the purpose of our study is to discover the statistical relationships between urban property crime and high-vegetation coverage and urban property crime and road network density in the city of Vancouver. Types of non-violent property crimes, including breaking and entering (BNE), theft, and mischief, were analyzed. The objectives of our study are as follows: (1) to understand the spatial patterns of property crime; (2) to understand the spatial relationships between tree coverage and property crime, as well as road density and property crime; (3) to explore the spatial variation of the correlations between the two factors and property crime; and (4) to support decision making in urban property crime prevention and reduction strategies.
2. Literature Review
Various studies have been performed to examine the physical and social environment around crime hotspots. In terms of the surrounding physical environment, the presence of the following are found to be related to the concentration of crime: parking lots, commercial buildings, facilities (e.g., bus stops, police stations, street lighting, etc.), urban layout, and graffiti. However, few studies examined the effect of vegetation. In some of the studies, the presence of vegetation and buildings was used as an indicator to classify the land use of the study area [
18,
24,
25]. According to Chen et al. [
18], the percentage of non-vegetated areas increases the accuracy of predicting crime hotspots and is directly related to the occurrence of crime.
Relationship between vegetation and crime in U.S. cities. A few studies, most of which were conducted in the United States, concentrated on identifying the relationship between vegetation and crime. To understand the relationships among urban green space, violence, and crime in the U.S., Bogar and Beyer [
26] reviewed ten studies from 2001 to 2013. They found that the study methodology varies, and so do the results; thus, they suggested standardization in design and measurement. The most recent related studies are as follows:
Houston, TX and Philadelphia, PA. In their study of eleven community gardens and surrounding areas in Houston, TX, Gorham et al. [
27] compared the number of crime incidents in 2005 in the areas surrounding the gardens with randomly selected areas in the city. Results showed no significant difference between the number of property crimes in the areas surrounding the community gardens and other areas in the city. In other words, the community gardens, studied in Houston, do not have a strong effect on property crime. Garvin et al. [
21] evaluated the influence of green space on crime by conducting an experiment in Philadelphia, PA. The results of comparing the crime rate before and after the greening of chosen vacant lots suggested a reduction in crime, but this was not significantly related to the greening. However, the greening of vacant land does significantly increase the sense of security of the residents.
Baltimore, MD; Philadelphia, PA; Portland, OR; Minneapolis, MN. Troy et al. [
11] conducted a study in the greater Baltimore region, including Baltimore City and Baltimore County, MD. Their study took into account the different effects on crime of trees located in public or private land. Their analysis shows a reverse relationship between crime rate (robbery, burglary and shooting) and vegetation density. Roughly a twenty percent decrease in crime is expected when there is a ten percent increase in tree cover. Also, there is evidence that the effect of tree canopies varies between public and private land. Planting trees on public land results in higher crime-reduction benefits. However, in some areas there is a direct relationship between trees and crime, probably because the trees are mostly unmanaged, providing concealment for criminals. In a study performed in Philadelphia, Wolfe and Mennis [
12] conducted a spatial analysis of crime at the census tract level with similar results. The results indicate that robberies, burglaries and assaults are inversely related to vegetation coverage. Also, Wolfe and Mennis [
12] found that vegetation has a greater negative effect on assault than on other types of crimes. However, there is no significant association between thefts and vegetation coverage. According to Donovan and Prestemon [
22], in Portland, Oregon, the crown area of street trees demonstrates a negative effect on crime; whereas, the number of trees on the lot of a house is associated with an increase in crime. Eckerson [
13] found a negative relationship between vegetation and crime in Minneapolis, MN.
Relationship between vegetation and crime in Canadian cities. There is limited research examining the influence of vegetation on crime in Canadian cities. The most recent investigation applies Ordinary Least-Squares (OLS) and Spatial Lag models to different crime types in the Kitchener-Waterloo region, Ontario, [
28]. The results indicate a negative correlation between crime (both violent and non-violent) and vegetation density. A dissemination area, a standard geographic unit with census data and small enough to provide a large sample size, was used for the unit of analysis. Using Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR), Du [
28] also examined the spatial variation of the impacts from the two variables. However, Landsat imagery with a 30-m resolution is too coarse to capture the detailed spatial variations in vegetation [
29]. Moreover, the calculation of the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) does not separate trees and grass, which may affect crime differently.
Influence of road network on crime. Road network, which is less influential on crimes against persons, primarily influences property crime. Road network complexity may reduce property crime because criminals who are unfamiliar with an area may spend more time finding an escape route; the convenience of a road network, however, provides criminals opportunities to acquire suitable targets. Beavon et al. [
23], who concluded that the property crime rate is higher in more accessible and highly used areas, also suggested that traffic barriers and road closures can be used as potential effective crime prevention techniques by reducing accessibility. Copes [
30] performed a statistical analysis, which demonstrates that road density (calculated by dividing the number of roads passing through a tract by the area of the tract) directly influences the increase in motor vehicle theft. Copes’ results support the Beavon et al. [
23] study that the routine activity of a criminal is associated with the rate of property crime in an area, and road network is one of the methods to quantify the issue.
The relationship between road network patterns and crime has been analyzed in a few recent studies. A study, conducted in Tokyo, Japan, by Murakami et al. [
31], investigated the pattern of the road network around five robbed convenience stores. Murakami et al. [
31] found similarities in the road environment of the five crime scenes. However, their result is not convincing because of the small sample size, and, due to the absence of a control group, they failed to distinguish the characteristics from other road environments. Foster et al. [
32] conducted a survey in Perth, Australia that shows an inverse relationship between a perceived crime risk and the street connectivity of the area, represented by the number of three-way intersections. In other words, street connectivity actually increases the residents’ perception of safety within the area.
The study conducted in the Kitchener-Waterloo region [
28] also looked at the relationship between road network and crime. Du [
28] used road density as an explanatory variable in the crime regression models and concluded there is a positive correlation between crime and road density. Also, the impact is greater in the urban center of the region.
The number of studies on this topic is limited, and the results are restricted to the studied areas. To understand the impact of road networks on crime in a particular area, research must be performed using local data.
In summary, there has been extensive research conducted on crime spatial analysis. However, there is insufficient insight into how crime and vegetation/road networks are related. Research is inconsistently designed and focuses on particular cities or regions, thus providing a limited perspective on the impact that vegetation and road networks have on crime.
4. Results and Discussion
The percent of tree covered area is the investigated explanatory variable in this study. Thus the accuracy of the tree crown area extracted from the LiDAR datasets directly influences the performances of the regression models based on that percentage. Therefore, using the 2013 orthophoto, an accuracy assessment was conducted; the results show that the extracted tree covered area has producer’s and user’s accuracies of 96.9% and 99.9%, respectively. The overall accuracy of the tree extracted covered area is 98.4%. In conclusion, the results indicate a high accuracy for the tree covered area extracted from LiDAR datasets.
OSL regression was first applied to the three models (property crime, theft, and BNE); the results are shown in
Table 1. The percent of tree coverage and road density both demonstrate significant (with a 0.01 significance level) negative correlations with theft, BNE, and total property crime rates. However, the results show that the adjusted R
2 values of only 0.203, 0.171, and 0.140, for property crime, theft, and BNE, respectively, are all notably low. Also, the spatial lag regression results are shown in
Table 2 for comparison with the OLS results. The results also indicate a significant inverse relationship among the three outcome variables and both tree coverage and road density.
The performances of the regression models were estimated through the comparison of the log-likelihoods. Log-likelihood is used to estimate the fit of the model with a higher value (less negative), indicating a better fit. As shown in
Table 2, for all three models, the spatial lag regression increased the log-likelihood values from −10,277.4 to −10,139 for total property crime, from −5520.11 to −5378.38 for theft rate, and from −3357.24 to −3269.39 for BNE rate. The high significance of the spatially lagged dependent variable, “W_CrimeRate”, and the enhanced log-likelihood value confirm the better performance of the spatial lag models.
The next step involved applying GWR to the three models. Given the evidence that the independent variable, unemployment rate, did not show significant influence on crime, it was eliminated when applying GWR. Compared with the OLS regression results, the GWR results, with lower AICc statistics and enhanced adjusted R
2s, prove the significance of the spatial non-stationarity of the crime-tree and crime-road relationships. The GWR increased the adjusted R
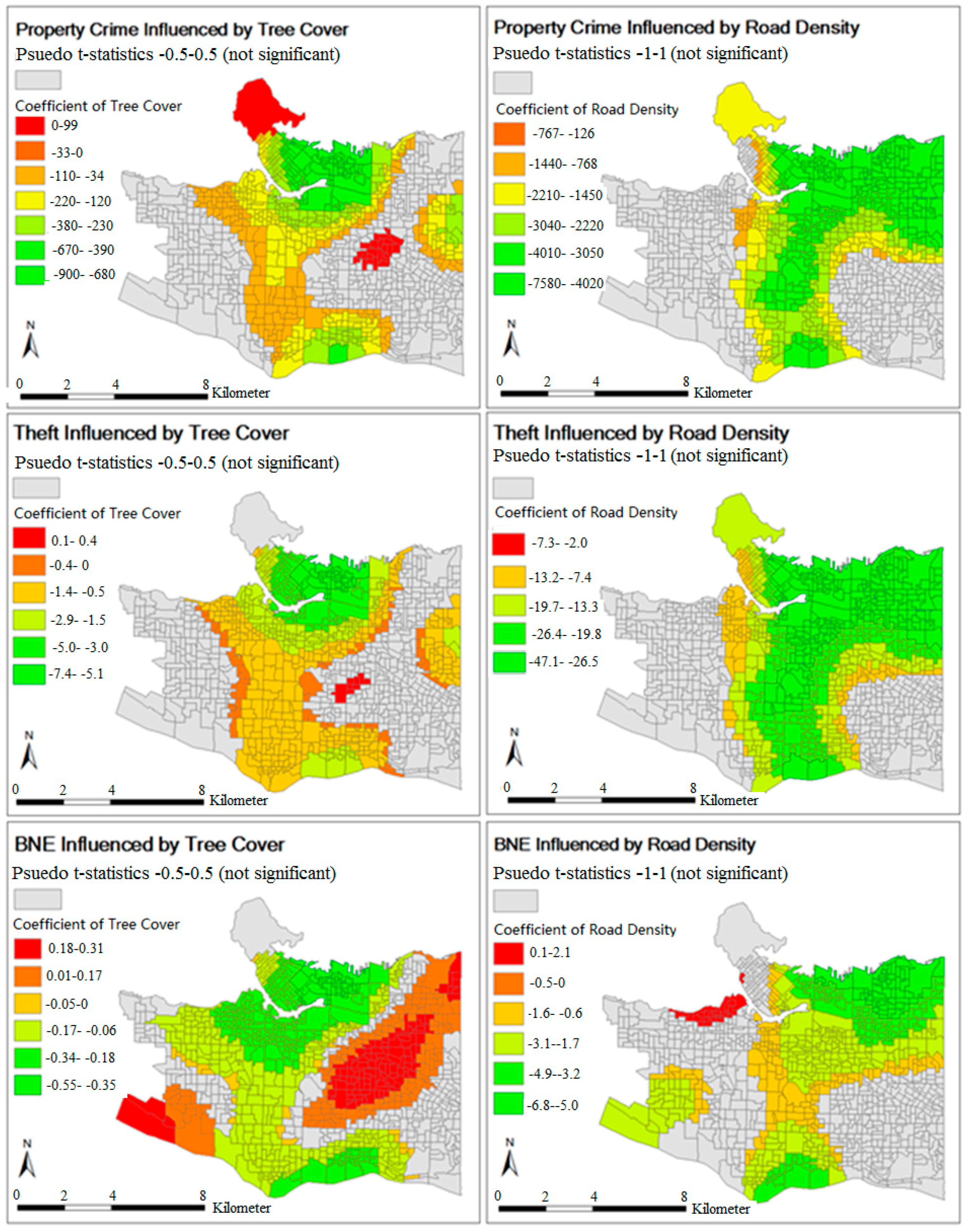
2s, from 0.266 to 0.444 for total property crime, from 0.242 to 0.372 for theft rate, and from 0.148 to 0.346 for the BNE rate. The output DA polygons from the GWR tool have their local coefficients for the tested explanatory variables; the variation of the local coefficients for the percentage of tree covered areas and road density in each model are mapped (see
Figure 2). Pseudo t-statistics were calculated, and the DAs having pseudo t-statistics near zero were regarded as having non-significant regression results as indicated by the colour grey in the maps.
As shown in the property crime GWR map, the coefficients of percent tree cover become more negative in the DAs that are closer to the downtown core of Vancouver, thereby expressing a stronger correlation between property crime rates in the downtown area and the Strathcona neighborhood. On the other hand, Stanley Park and some residential DAs in the Kensington-Cedar Cottage neighborhood show a positive, although weaker, correlation between tree coverage and the property crime rate. The theft GWR maps show similar trends, with relatively smaller actual values, for the coefficients. The BNE GWR map is different from the maps of property crime and theft. The negative relationship between percent tree cover and the BNE rate is still greater in downtown Vancouver and the Southern shoreline, but many more DAs demonstrate positive coefficients that are significant. Due to the low crime rate of BNE, the magnitude of the coefficients of tree coverage on BNE is much lower than that on theft and total property crime. Road density indicates a greater negative correlation also in the downtown area and the northeast region to the Hastings-Sunrise neighborhood, but the variation is relatively less than that of the coefficients of the tree coverage.
The regression results provide solid evidence of the inverse relationship between trees and the property crime rate, and between road density and property crime in Vancouver City. Firstly, airborne LiDAR data served as a reliable source for deriving tree crown areas and their spatial distribution in the city, with an overall accuracy of 98.4%. Compared with Landsat imagery, LiDAR data provides details of tree crowns beside buildings and along city streets. With a set parameter of 2 m when applying aggregate points, the extracted tree crown polygons from LiDAR points can be considered to have a spatial resolution of 2 m × 2 m. In addition to the use of a small unit of analysis, i.e., the dissemination area, high resolution and accuracy of the extracted tree covered area and calculations led to the precise estimate of the relationship of the tree covered area with property crime.
Spatial lag regression models prove the qualitative findings with significant negative coefficients in the regression results. As seen from the spatial lag regression results in
Table 2, BNE has a less negative coefficient in spatial lag, indicating a small magnitude of correlation with trees. Moreover, the explanatory power of the BNE model, denoted by pseudo R
2, is smaller than that for the other two models. The first finding could be due to the fact that, compared with theft, BNE has a smaller incident number. The possible cause of the smaller explanatory power of the BNE model is that the BNE rate is affected by other factor(s), which may have little influence on other types of property crime. For example, the BNE rate is more likely related to the distribution of the number and types of buildings, as well as average family income, security facilities, etc.
Most importantly, GWR, which provides more answers to the research questions, demonstrates the spatial variation of the correlation between trees and property crime. Significant negative correlations exist in the central area of the city, and the magnitude of the coefficient becomes greater in the downtown core of the city. However, unlike other DAs, Stanley Park DA and some of the Kensington-Cedar Cottage DAs demonstrate a positive correlation between property crime and trees.
According to the geoprocessing results, in 2013 the Kensington-Cedar Cottage neighborhood had a high tree coverage and a relatively high property crime rate. However, as one of the most ethnically diverse neighborhoods in east Vancouver, its high crime rate can be a result of a high level of social disorganization, rather than a high coverage of trees in the neighborhood. Most likely, Stanley Park had a high property crime rate because it is a tourist attraction, which makes it vulnerable to theft and mischief. Therefore, the high crime rates are the result of the above factors, rather than merely being the result of the trees and road network. Also reviewed were the standard residuals of the local regressions estimated using GWR. The under- and over-estimated results are randomly scattered over the map; clusters in the map indicate that there are factors that were not taken into account in the model [
41]. However, the high regression residuals are concentrated in the northern area of the city, including Stanley Park and the downtown area. Moreover, as seen from the local R
2 values of the GWR results of the property crime model, local R
2 values below 0.2 are clustered in the Renfrew-Collingwood and Kerrisdale neighborhoods. These are also the results of variations in the social aspect among different neighborhoods. Important factors, other than the included variables, may be involved.
Counter to the results of the study conducted in the Kitchener-Waterloo region, Ontario, a highly significant negative correlation was detected between road density and property crime [
28]. Because of the limited number of publications on this topic, we cannot conclude that this disagreement is the result of variations in the situation of different study areas. In addition, road density is somehow related to road complexity, with high road density probably suggesting a large number of road segments and a high level of complexity of the road network. For instance, as denoted by the research conducted in Tokyo [
31], residential areas usually have more roads and greater road densities than commercial areas. As mentioned, previous research on road networks and crime found that complex road networks can reduce the number of property crimes. The methodology in our study found only the statistical relationship between road density and property crime. More study on road characteristics is required to determine their effects on crime. The findings are the inspiration for planning the urban design strategies to prevent property crime. The inverse correlation between tree coverage and property crime suggests it is possible that the Greenest City Action Plan carried out in Vancouver not only creates beautiful views and clean air, but also reduces the city property crime rate and provides a safe living environment for residents. In addition, the downtown core of the city is usually a place with a high crime rate. According to the GWR maps, because there is a stronger correlation between the tree coverage and property crime in downtown Vancouver, to reduce the property crime rate, tree planting projects should be carried out in the downtown core commercial areas. The inverse relationship between road density and property crime suggests that, to reduce property crime, urban planners should design complex road networks with more road segments and higher road density within the urban areas. In regions with lower tree coverage and lower road density, which are regions likely to have high property crime rates, more police resources should be assigned for crime prevention.
Limitations to this study. First, this study was limited to the city of Vancouver, and some of the results (e.g., the spatial variation of the influence of trees on crime) are representative only of areas within the city. A study of the greater Vancouver area could possibly reveal more patterns and information. Also, similar research should be conducted in other municipalities in Canada to verify the hypotheses. Besides, this study did not differentiate urban trees along streets and beside buildings from trees in parks. The extent to which urban property crime can be reduced by planting trees in these different locations is still uncertain. There must be a detailed analysis of the relation of crime to urban parks and trees. More importantly, this study performed only a cross-sectional analysis. Further research is required to determine the causal relationship between the two variables and property crime. This can be done by performing a temporal crime trend analysis, focusing on areas with significant changes in vegetation coverage or road density.
Besides, in this study we focused only on property crime and aggregated some of the crime types. Aggregating different crime types is inappropriate in spatial pattern analysis [
43]. For instance, the spatial patterns of commercial BNE and residential BNE can be very different. Future studies are required if researchers are to be concerned with spatial patterns for specific crime types, such as thefts from vehicles, residential BNE, etc. Due to restrictions on the use of violent crime data, this study did not include an analysis of violent crime data. However, as previously noted, Vancouver also has a high Crime Severity Index (CSI) that takes into account the seriousness of crime incidents as well, and violent crime consequences are usually more serious than property crime. Therefore, future work should investigate the influence of vegetation and road network on violent crime as well. The newly launched GeoDash web application enables the collection of data regarding incidents of homicides and crimes against persons.
Furthermore, social and economic developments are changing rapidly and unexpectedly [
2]. The use of the 2006 unemployment rate data led to some errors in the regression models. Among the eight selected independent variables, the unemployment rate, insignificant in all three regression models, was eliminated in the GWR models. The 2011 census data is the most up to date demographic data used in this study; however, the actual statistics could have changed in 2013.
In this study, road density was calculated according to the definition provided by the World Bank. However, this calculation method ignores the other characteristics of a road network such as width and complexity, which are also correlated to road length. Therefore, the correlation between road density and property crime is a result of property crime being influenced by other road network factors. Further studies are needed to take these factors into consideration.
Lastly, the use of the LiDAR dataset in this study was limited to the extraction of classified tree points. The average height of high vegetation was derived from the dataset and used as another explanatory variable to investigate if the crime rate is related to tree height. In addition, such high-spatial resolution LiDAR data, with three-dimensional information, has the potential for the construction of 3D models for the further development of crime prevention applications.