Image Segmentation Parameter Optimization Considering Within- and Between-Segment Heterogeneity at Multiple Scale Levels: Test Case for Mapping Residential Areas Using Landsat Imagery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Parameter Optimization for SS-GEOBIA and MS-GEOBIA
3. Methods
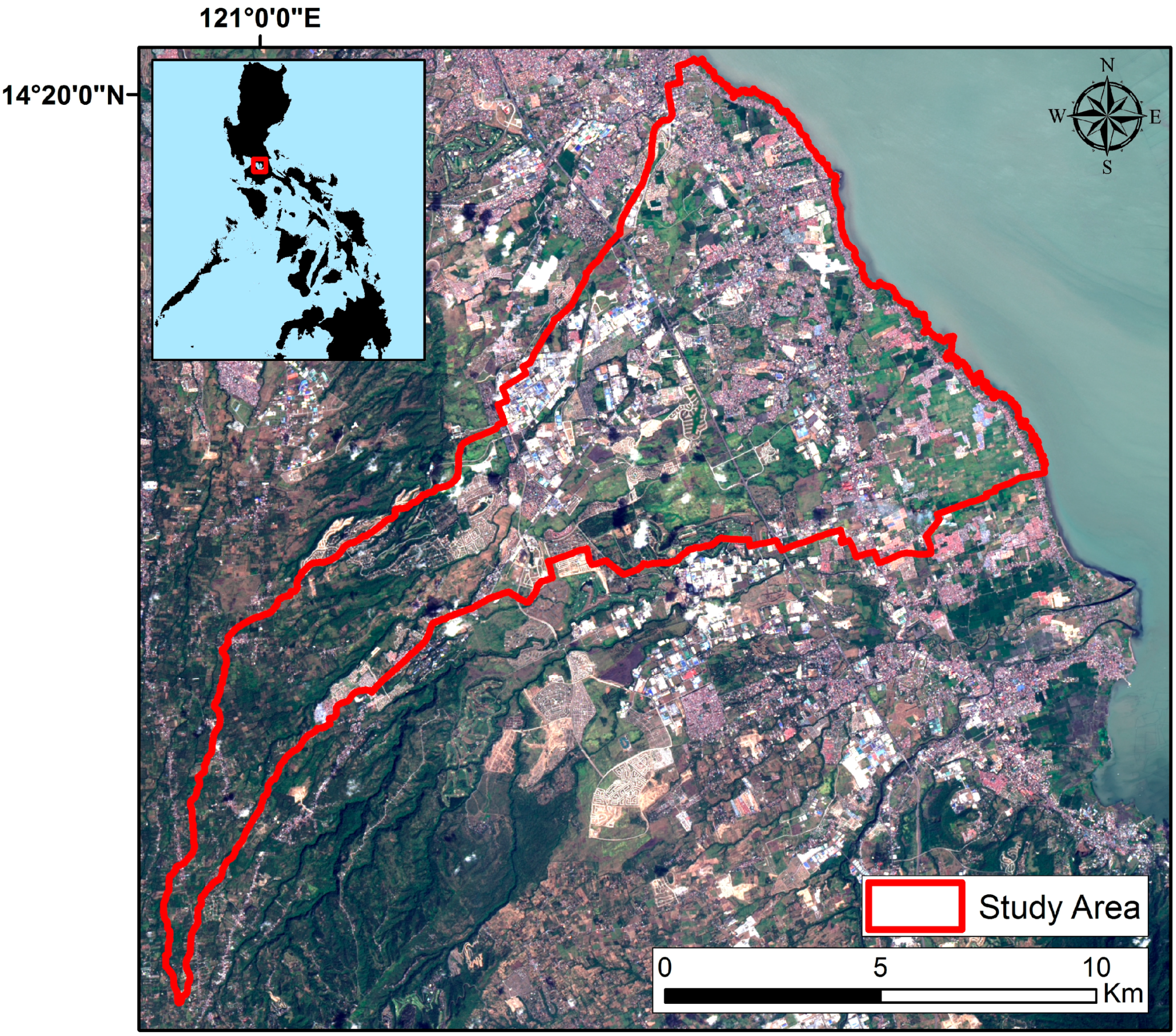
3.1. Study Area and Data
3.2. Image Pansharpening
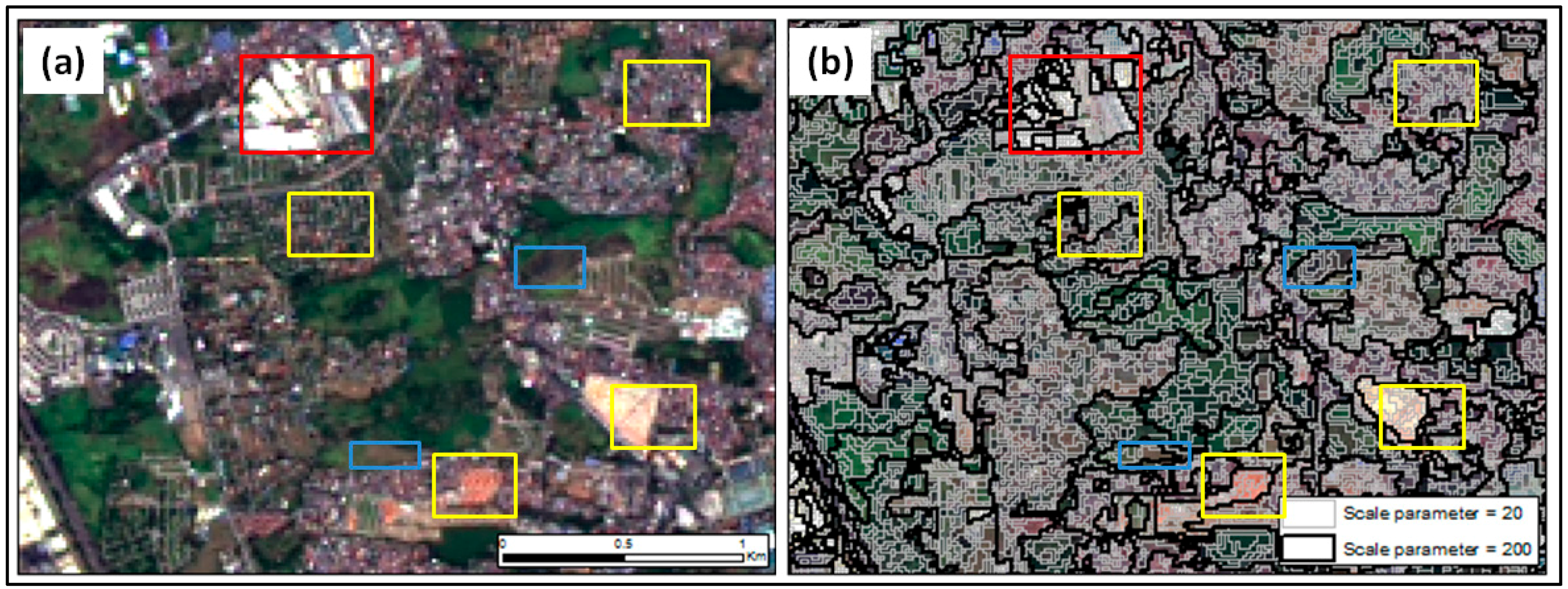
3.3. Image Segmentation Parameter Optimization
- a = 1 for SS-GEOBIA;
- a = 2 and a = 0.50 for segmentation levels 1–2, respectively, for two-level GEOBIA;
- a = 3, a = 1, and a = 0.33 for segmentation levels 1–3 for three-level GEOBIA; and
- a = 4, a = 2, a = 0.50, and a = 0.25 for segmentation levels 1–4 for four-level GEOBIA.
3.4. Image Classification
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Impact of Parameter Optimization on Classification Accuracy
| Number of Segmentation Levels | SP (Level 1) | SP (Level 2) | SP (Level 3) | SP (Level 4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 80 | - | - | - |
| 2 | 60 | 100 | - | - |
| 3 | 40 | 80 | 120 | - |
| 4 | 40 | 60 | 100 | 120 |
| SP(s) | PA “Residential” | UA “Residential” | Fclass “Residential” | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS-GEOBIA | 20 | 0.873 | 0.686 | 0.768 |
| 40 | 0.800 | 0.721 | 0.759 | |
| 60 | 0.909 | 0.735 | 0.813 | |
| 80 | 0.891 | 0.721 | 0.797 | |
| 100 | 0.927 | 0.680 | 0.785 | |
| 120 | 0.909 | 0.685 | 0.781 | |
| 140 | 0.891 | 0.754 | 0.817 | |
| 160 | 0.945 | 0.693 | 0.800 | |
| 180 | 0.909 | 0.658 | 0.763 | |
| 200 | 0.927 | 0.586 | 0.718 | |
| MS-GEOBIA | 60 + 100 | 0.945 | 0.722 | 0.819 |
| 40 + 80 + 120 | 0.945 | 0.765 | 0.846 | |
| 40 + 60 + 100 + 120 | 0.964 | 0.746 | 0.841 | |
| All-inclusive | 0.945 | 0.722 | 0.819 |

| One-Level GEOBIA | Two-Level GEOBIA | Three-Level GEOBIA | Four-Level GEOBIA | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP | OGf (a = 1) | OGf (a = 2) | OGf (a = 0.50) | OGf (a = 3) | OGf (a = 1) | OGf (a = 0.33) | OGf (a = 4) | OGf (a = 2) | OGf (a = 0.50) | OGf (a = 0.25) |
| 20 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 40 | 0.318 | 0.465 | 0.242 | 0.550 | 0.318 | 0.224 | 0.595 | 0.465 | 0.242 | 0.218 |
| 60 | 0.467 | 0.515 | 0.427 | 0.534 | 0.467 | 0.416 | 0.542 | 0.515 | 0.427 | 0.411 |
| 80 | 0.483 | 0.451 | 0.520 | 0.442 | 0.483 | 0.534 | 0.438 | 0.451 | 0.520 | 0.540 |
| 100 | 0.451 | 0.385 | 0.545 | 0.367 | 0.451 | 0.586 | 0.360 | 0.385 | 0.545 | 0.605 |
| 120 | 0.382 | 0.300 | 0.526 | 0.280 | 0.382 | 0.603 | 0.273 | 0.300 | 0.526 | 0.641 |
| 140 | 0.305 | 0.226 | 0.470 | 0.208 | 0.305 | 0.574 | 0.201 | 0.226 | 0.470 | 0.631 |
| 160 | 0.229 | 0.161 | 0.397 | 0.146 | 0.229 | 0.526 | 0.141 | 0.161 | 0.397 | 0.607 |
| 180 | 0.127 | 0.084 | 0.258 | 0.076 | 0.127 | 0.392 | 0.073 | 0.084 | 0.258 | 0.498 |
| 200 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
4.2. Comparison of SS-GEOBIA and MS-GEOBIA Classification Approaches
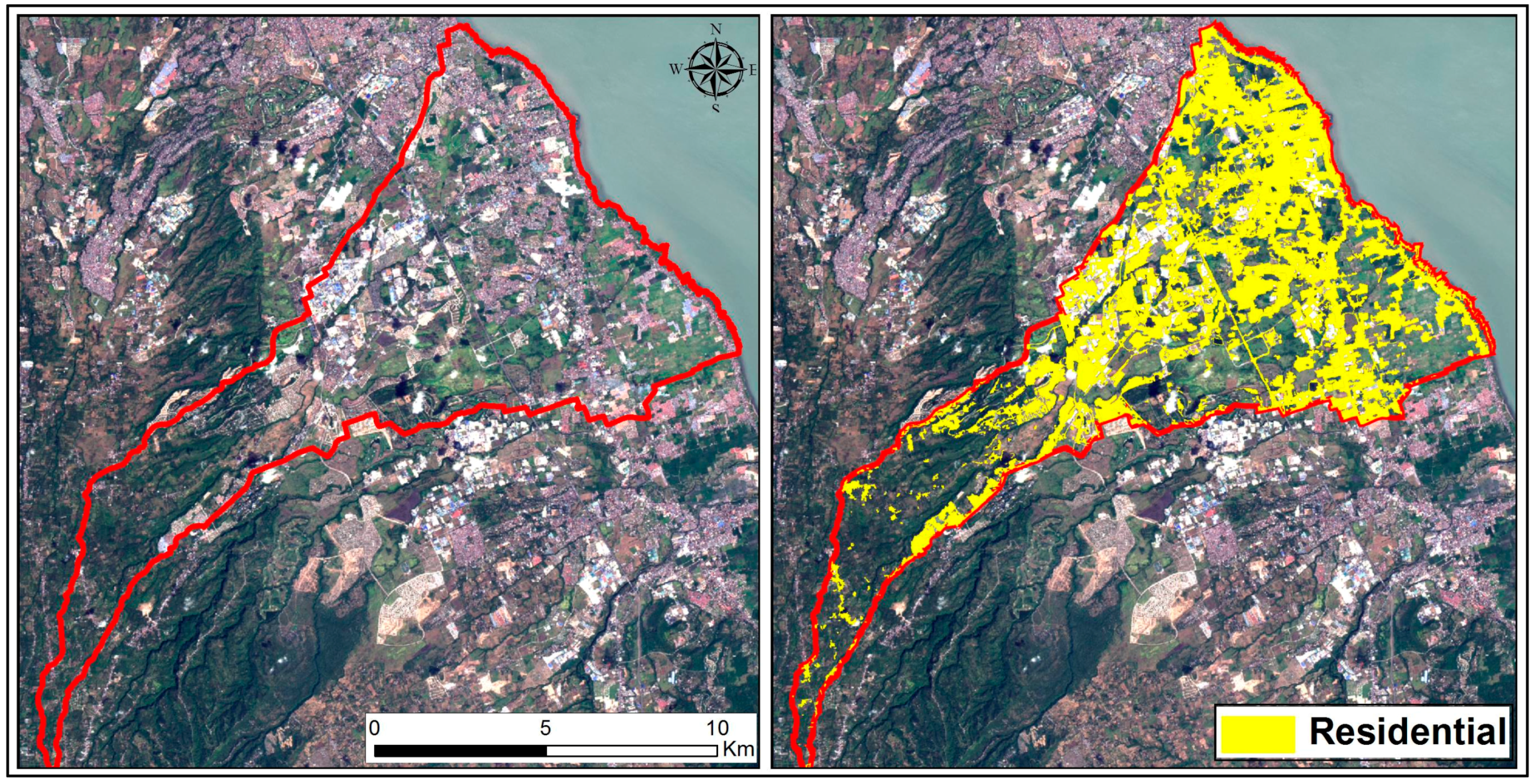
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crowell, M.; Coulton, K.; Johnson, C.; Westcott, J.; Bellomo, D.; Edelman, S.; Hirsch, E. An estimate of the U.S. population living in 100-year coastal flood hazard areas. J. Coast. Res. 2010, 26, 201–211. [Google Scholar]
- Eicher, C.L.; Brewer, C.A. Dasymetric mapping and areal interpolation: Implementation and evaluation. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2001, 28, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, P.F.; Langford, M. Modeling sensitivity to accuracy in classified imagery: A study of areal interpolation by dasymetric mapping. Prof. Geogr. 1996, 48, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, M.; Scepan, J.; Clarke, K.C. The use of remote sensing and landscape metrics to describe structures and changes in urban land uses. Environ. Plan. A 2002, 34, 1443–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, G.J.; Castilla, G. Geographic object-based image analysis (GEOBIA): A new name for a new discipline. In Object-Based Image Analysis; Blaschke, T., Lang, S., Hay, G., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 75–89. [Google Scholar]
- Blaschke, T. Object based image analysis for remote sensing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, M.; Liu, X.; Clarke, K.C. Spatial metrics and image texture for mapping urban land use. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Warner, T.A.; Madden, M.; Atkinson, D.S. Multi-scale GEOBIA with very high spatial resolution digital aerial imagery: Scale, texture and image objects. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 2825–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.A.; Xie, Z. Classifying a high resolution image of an urban area using super-object information. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 83, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waske, B.; van der Linden, S. Classifying multilevel imagery from SAR and optical sensors by decision fusion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.A. High resolution urban land cover classification using a competitive multi-scale object-based approach. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, S.W.; Gober, P.; Brazel, A.; Grossman-Clarke, S.; Weng, Q. Per-pixel vs. object-based classification of urban land cover extraction using high spatial resolution imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1145–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Roberts, C.; Johnson, B. Object-based target search using remotely sensed data: A case study in detecting invasive exotic Australian Pine in south Florida. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2008, 63, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, U.C.; Hofmann, P.; Willhauck, G.; Lingenfelder, I.; Heynen, M. Multi-resolution, object-oriented fuzzy analysis of remote sensing data for GIS-ready information. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2004, 58, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’OLEIRE-Oltmanns, S.; Eisank, C.; Draguţ, L.; Blaschke, T. An object-based workflow to extract landforms at multiple scales from two distinct data types. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.A.; Tateishi, R.; Hoan, N.T. A hybrid pansharpening approach and multiscale object-based image analysis for mapping diseased pine and oak trees. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 6969–6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fritts, J.E.; Goldman, S.A. Image segmentation evaluation: A survey of unsupervised methods. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2008, 110, 260–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Xia, F. Assessing object-based classification: Advantages and limitations. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 1, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espindola, G.M.; Camara, G.; Reis, I.A.; Bins, L.S.; Monteiro, A.M. Parameter selection for region-growing image segmentation algorithms using spatial autocorrelation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3035–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.A.; Xie, Z. Unsupervised image segmentation evaluation and refinement using a multi-scale approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Deng, M.; Mei, X.; Chen, T.; Shao, Q.; Hong, L. Optimal segmentation of a high-resolution remote-sensing image guided by area and boundary. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 6914–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, A.; Yang, J.; Zhang, C.; Su, W.; Yun, W.; Zhu, D.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z. The optimal segmentation scale identification using multispectral WorldView-2 images. Sens. Lett. 2012, 10, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, P.; Feng, X. An unsupervised evaluation method for remotely sensed imagery segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.; Brundson, C.; Charlton, M. Quantitative Geography: Perspectives on Spatial Analysis; SAGE Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E.; Hall, M. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques, 3rd ed.; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, X.; Xiao, P.; He, G.; Zhu, L. Segmentation quality evaluation using region-based precision and recall measures for remote sensing images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 102, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martha, T.R.; Kerle, N.; Westen, C.J.; van Jetten, V.; Kumar, K.V. Segment optimization and data-driven thresholding for knowledge-based landslide detection by object-based image analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4928–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikokou, G.B.; Smit, J. A technique for optimal selection of segmentation scale parameters for object-oriented classification of urban scenes. S. Afr. J. Geomat. 2013, 2, 358–369. [Google Scholar]
- USGS EarthExplorer. Available online: http://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 30 June 2015).
- Fasbender, D.; Radoux, J.; Bogaert, P. Bayesian data fusion for adaptable image pansharpening. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.A.; Tateishi, R.; Hoan, N.T. Satellite image pansharpening using a hybrid approach for object-based image analysis. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2012, 1, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baatz, M.; Schape, A. Multiresolution Segmentation—An Optimization Approach for High Quality Multi-Scale Image Segmentation. Available online: http://www.ecognition.com/sites/default/files/405_baatz_fp_12.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2015).
- Walker, J.S.; Blaschke, T. Object based land cover classification for the Phoenix metropolitan area: Optimization vs. transportability. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 2021–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drăguţ, L.; Tiede, D.; Levick, S.R. ESP: A tool to estimate scale parameter for multiresolution image segmentation of remotely sensed data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.R. Introductory Digital Image Processing—A Remote Sensing Perspective, 3rd ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolova, M.; Japkowicz, N.; Szpakowicz, S. Beyond accuracy, F-Score and ROC: A family of discriminant measures for performance evaluation. In AI 2006: Advances in Artificial Intelligence; Springer: Berlin, Geramny, 2006; pp. 1015–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, R.; Wood, S.; Sheley, R. Mapping invasive plants using hyperspectral imagery and breiman cutler classifications (RandomForest). Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.; Frank, E.; Holmes, G.; Pfahringer, B.; Reutemann, P.; Witten, I.H. The WEKA data mining software: An update. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2009, 11, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzone, L.; Carlin, L. A multilevel context-based system for classification of very high spatial resolution images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2587–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, G.J.; Marceau, D.J.; Bouchard, A. Modeling multi-scale landscape structure within a hierarchical scale-space framework. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2002, 34, 532–535. [Google Scholar]
- Drăguţ, L.; Csillik, O.; Eisank, C.; Tiede, D. Automated parameterisation for multi-scale image segmentation on multiple layers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 88, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Lin, C.; Cui, W.; Yao, J. Scale selection based on Moran’s I for segmentation of high resolution remotely sensed images. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARRS), Quebec, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 4895–4898.
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Johnson, B.A.; Bragais, M.; Endo, I.; Magcale-Macandog, D.B.; Macandog, P.B.M. Image Segmentation Parameter Optimization Considering Within- and Between-Segment Heterogeneity at Multiple Scale Levels: Test Case for Mapping Residential Areas Using Landsat Imagery. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2015, 4, 2292-2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi4042292
Johnson BA, Bragais M, Endo I, Magcale-Macandog DB, Macandog PBM. Image Segmentation Parameter Optimization Considering Within- and Between-Segment Heterogeneity at Multiple Scale Levels: Test Case for Mapping Residential Areas Using Landsat Imagery. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2015; 4(4):2292-2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi4042292
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohnson, Brian A., Milben Bragais, Isao Endo, Damasa B. Magcale-Macandog, and Paula Beatrice M. Macandog. 2015. "Image Segmentation Parameter Optimization Considering Within- and Between-Segment Heterogeneity at Multiple Scale Levels: Test Case for Mapping Residential Areas Using Landsat Imagery" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 4, no. 4: 2292-2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi4042292
APA StyleJohnson, B. A., Bragais, M., Endo, I., Magcale-Macandog, D. B., & Macandog, P. B. M. (2015). Image Segmentation Parameter Optimization Considering Within- and Between-Segment Heterogeneity at Multiple Scale Levels: Test Case for Mapping Residential Areas Using Landsat Imagery. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 4(4), 2292-2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi4042292







