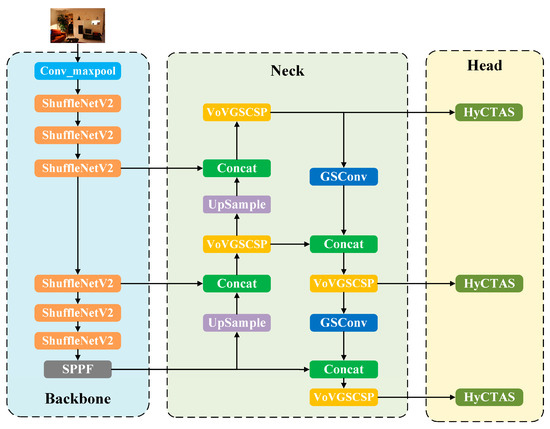
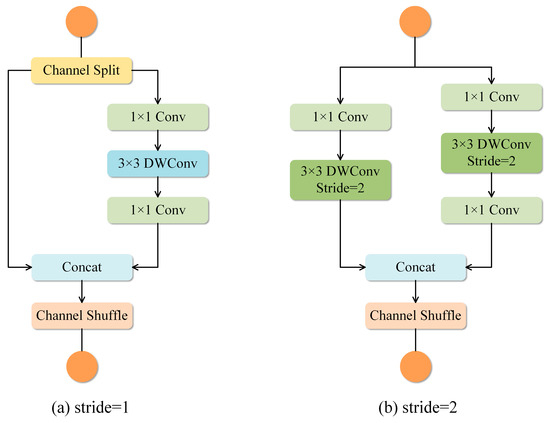
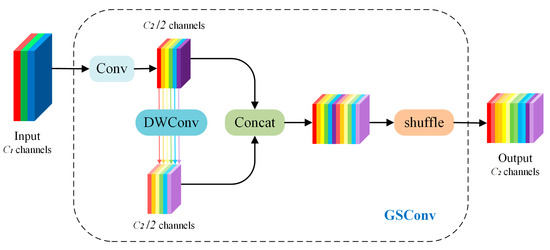
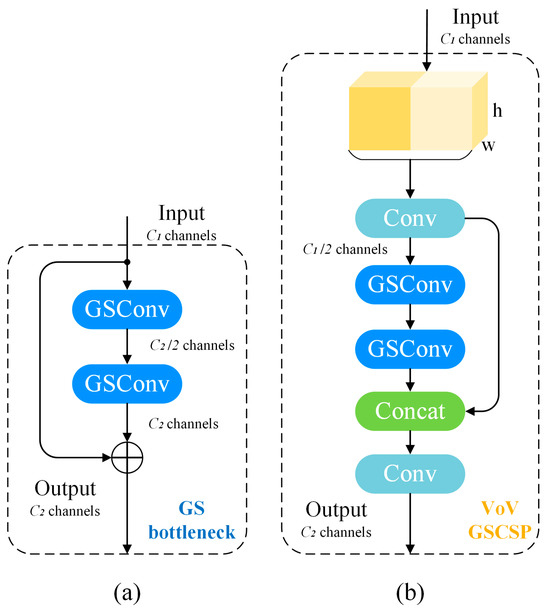
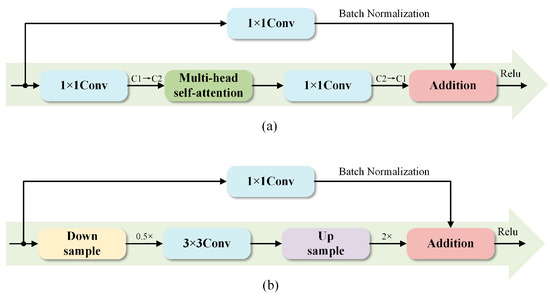
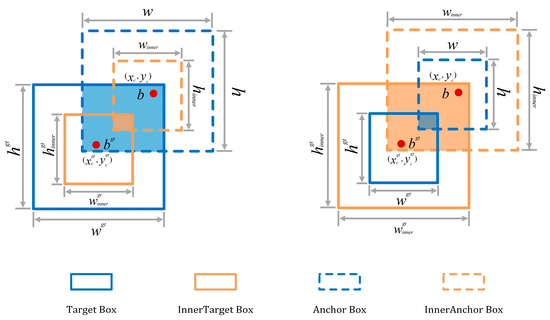
Abstract
Precise object detection is fundamental to robust indoor navigation and localization. However, the practical deployment of deep learning-based detectors on mobile platforms is frequently impeded by their extensive parameter counts, substantial computational overhead, and prolonged inference latency, rendering them impractical for real-time and GPU-independent applications. To overcome these limitations, this paper presents Nav-YOLO, a highly optimized and lightweight architecture derived from YOLOv8n, specifically engineered for navigational tasks. The model’s efficiency stems from several key improvements: a ShuffleNetv2-based backbone significantly reduces model parameters; a Slim-Neck structure incorporating GSConv and GSbottleneck modules streamlines the feature fusion process; the VoV-GSCSP hierarchical network aggregates features with minimal computational cost; and a compact detection head is designed using Hybrid Convolutional Transformer Architecture Search (HyCTAS). Furthermore, the adoption of Inner-IoU as the bounding box regression loss accelerates the convergence of the training process. The model’s efficacy is demonstrated through a purpose-built Android application. Experimental evaluations on the VOC2007 and VOC2012 datasets reveal that Nav-YOLO substantially outperforms the baseline YOLOv8n, achieving mAP50 improvements of 10.3% and 5.0%, respectively, while maintaining a comparable parameter footprint. Consequently, Nav-YOLO demonstrates a superior balance of accuracy, model compactness, and inference speed, presenting a compelling alternative to existing object detection algorithms for mobile systems.
1. Introduction
The rapid development of deep learning technology in recent years has provided novel approaches and ideas for visual navigation. These methods are being increasingly adopted by researchers to enhance overall living standards, particularly benefiting individuals with visual impairments [1]. The challenges are the lack of landmark recognition, object detection, and hazard identification for the visually impaired in research on navigation and positioning [2]. Overcoming perceptual challenges in scenes remains particularly difficult for individuals who are visually impaired. Recognizing objects from the input images constitutes a critical task for computational systems to achieve environmental understanding [3]. Object detection is a fundamental task in computer vision, which involves classifying and localizing objects within image data. Object detection has been extensively deployed across diverse applications, encompassing a range of tasks, including visual navigation, immersive environments such as VR and AR, as well as object retrieval tasks [4,5].
There has been a significant increase in work applying deep learning models, particularly for object detection, within navigation assistance systems [6]. Many studies have utilized pre-trained object detection models based on neural network algorithms for navigation, such as DeepCNN (Deep Convolutional Neural Networks) and YOLO (You Only Look Once). Notably, significant research focuses on mobile applications and assistive technologies; for example, Dosi et al. [7] developed an Android application that utilized MobileNet’s architecture to recognize objects for visually impaired people. Similarly, Vaidya et al. [8] utilized the pre-trained YOLOv3 model on MSCOCO for real-time object detection. Shariatinezhad et al. [9] explored obstacle detection using YOLOv5 and transfer learning, while Ashiq et al. [10] implemented a deep CNN framework for object detection and recognition tasks. Kuriakose et al. [11] developed a portable smartphone navigation assistant based on deep learning for obstacle identification and scene understanding. Further emphasizing the efficiency of mobile deployment, Afif et al. [12] developed an integrated lightweight convolutional neural network based on CSPNet and EfficientNetv2 for indoor object detection systems on edge devices. In summary, a prominent application area for object detection in navigation systems is assisting visually impaired individuals, such as In-out YOLO Glass [13] and Third Eye [14]. Increasing advances in efficient and real-time target detection algorithms highlight their great potential for wider navigation applications and market adoption.
In general, there are two types of object detection methods based on CNN architectures: the two-stage approach, which involves generating candidate bounding boxes and subsequently classifying objects contained within them, and the one-stage approach, which performs object detection and classification in a unified process without generating proposals. Representative two-step detection models, including R-CNN [15] and Fast-RCNN [16], are known for strong robustness and low error rates. However, their extended inference time limits their suitability for real-time use cases. In contrast, one-stage models, such as SSD [17] and YOLO [18], achieve comparable accuracy while significantly improving processing speed, thereby enhancing their suitability for real-time detection applications. Despite the wide variety of available object detection frameworks, choosing an appropriate model for real-time navigation requires rigorous design and analysis, as these scenarios demand low inference latency and minimal memory footprint. The computational efficiency of one-stage detectors proves indispensable for vision-based navigation systems, demanding real-time obstacle detection and environmental perception capabilities to ensure reliable autonomous decision-making [19].
In addition, device portability and model lightweight design are fundamental considerations in navigation assistance system development [20]. Mobile phones present considerable promise due to their sensors, cameras, continuously enhanced processing capabilities, and broadening availability for navigation. While one-stage detectors have achieved notable accuracy improvements in recent years, their mobile deployment remains challenging due to large model sizes, high parameter counts, heavy computational demands, and prolonged processing time. These constraints include real-time deployment of powerful models, such as YOLO, on mobile computing platforms.
Lightweight networks are a key focus in computer vision research, aiming to minimize model size and computational demands while maintaining accuracy. Current approaches to lightweight models are categorized into lightweight architecture design and model compression. The former category encompasses series such as SqueezeNet [21], MobileNet [22], ShuffleNet [23], and GhostNet [24], which aim to develop novel convolutional methods and structures for more efficient CNNs. Previous studies replace the entire YOLO backbone with lightweight networks, effectively reducing model size while still achieving real-time processing speeds; however, they exhibit considerably lower accuracy compared to the original algorithm [25]. When deploying models in practice, several key factors must be considered, including computational resource requirements, model complexity, real-time inference capability, and detection accuracy. Researchers have studied compression strategies, including pruning and knowledge distillation, to optimize model efficiency. Replacing standard convolution offers an effective pathway for parameter reduction, typically implemented via depth-wise separable convolution or dilated convolution. These lightweight modeling techniques play a crucial role in selecting the optimal model tailored to specific application requirements.
Current research on the lightweight YOLO-based object detector is focused on applications such as real-time autonomous driving [26], UAV object detection [27], road object detection [28], and indoor-outdoor object detection [13]. Although numerous lightweight modifications exist for YOLO-based object detectors, they are not optimized for object detection in mobile navigation scenarios. Furthermore, there is a lack of research explicitly demonstrating the viability of end-to-end applications using these developed models.
To address these issues, this study introduces a lightweight Nav-YOLO model to support real-time object detection for navigation purposes. The main contributions of this paper are as follows.
- To develop a lightweight detection framework for navigation, where ShuffleNetv2, Slim-Neck with VoV-GSCSP, a HyCTAS-based detection head, and the Inner-IoU loss function are not merely combined but systematically co-designed to complement each other, enabling both structural efficiency and enhanced feature representation, thereby achieving an optimal trade-off between accuracy, speed, and computational cost.
- To validate the effectiveness of the proposed Nav-YOLO by comparing its detection accuracy, inference speed, and resource efficiency against YOLOv8n and other state-of-the-art object detection frameworks.
- To demonstrate real-time applicability through mobile deployment, verifying that Nav-YOLO maintains high inference speed and efficient resource utilization on smartphones, thus confirming its suitability for practical navigation scenarios.
The structure of this study is presented as follows: Section 2 reviews the theoretical foundations of the detection approach. Section 3 presents the technical implementation of the Nav-YOLO model and its improved components, while Section 4 discusses the experimental setup and provides detailed results. Section 5 discusses the efficiency of the designed framework. Finally, Section 6 presents the conclusions.
2. Related Work
2.1. YOLOv8 Network Architecture
As a one-stage detection model, YOLO performs object localization and classification in a unified step, formulating detection as a regression task [18]. YOLO relies on a convolutional neural network for the entire process, jointly estimating class labels and bounding box parameters, which greatly improves detection speed due to its end-to-end architecture. The YOLO series has evolved from YOLOv1 to YOLOv13. YOLOv8, introduced by Ultralytics in early 2023, represents a notable improvement within the YOLO model series, offering enhanced detection performance and faster inference compared to its predecessors, such as YOLOv5. YOLOv8 consists of four main modules: input, backbone for extracting features, neck network, and detection head. The architecture of YOLOv8 is illustrated in Figure 1.
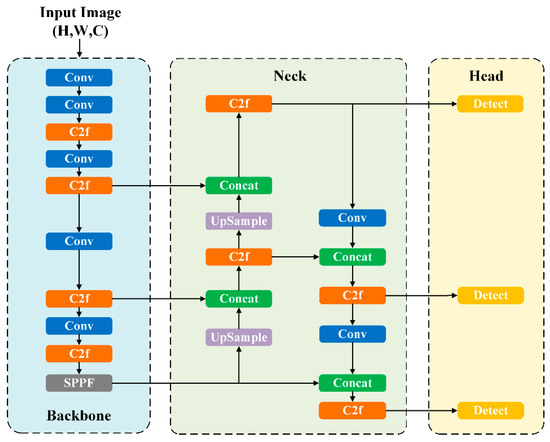
Figure 1.
Structure of YOLOv8.
The input layer standardizes input images by applying operations such as image resizing and pixel normalization, making them suitable for processing by the network.
The backbone uses a modified CSPDarknet53 architecture [29], incorporating CBL (Conv + BatchNorm + SiLU), C2f (Cross Stage Partial Network with two convolutions and fusions), and SPPF (Spatial Pyramid Pooling Fast) modules for feature extraction. The YOLO architecture processes the input image through stacked Conv and C2f modules to generate multi-scale feature maps. The C2f module functions as an optimized residual learning block, improving upon the original C3 design. These feature maps then pass through an SPPF module, which applies multi-kernel pooling to fuse feature representations across scales before transferring them to the neck network.
In the neck, a hybrid structure of FPN (Feature Pyramid Networks) [30] and PAN (Pyramid Attention Network) [31] is employed to enhance the fusion of features across various object scales. Concat denotes combining feature maps along a particular axis, often utilized to join two maps and enable upsampling through deconvolution.
The detection head follows the conventional practice of decoupling the classification head and the regression head, which involves loss computation and bounding box filtering.
2.2. Performance Comparison of YOLOv8 Variants
YOLOv8 controls the depth and layer quantity through tunable parameters, including depth (d), width (w), and ratio (r). The framework comprises five model scales: YOLOv8s, YOLOv8n, YOLOv8m, YOLOv8l, and YOLOv8x, which vary in computational complexity and architectural scale. Key distinctions among variants are reflected in their convolutional depth, parameter count, and suitability for deployment. Deeper models typically achieve higher detection accuracy at the cost of increased size and reduced inference speed. These dimensional characteristics critically determine storage overhead and computational load, particularly for resource-constrained edge or mobile devices. Consequently, this study conducts preliminary performance measurements of the YOLOv8 variants on the PASCAL VOC 2007 dataset [32] for accurate and efficient object detection, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Performance comparison of YOLOv8 variants.
Results demonstrate that while YOLOv8x achieves the highest mAP of 64.94%, it requires the largest model size of 130 MB. Conversely, YOLOv8n maintains a minimal model size of 5.95 MB but has the lowest mAP of 52.18%. As the foundational variant, YOLOv8n has the minimum depth and minimum width architecture within this series, while subsequent models (s/m/l/x) are progressively scaled versions with increased parametric complexity. The architectural expansion consistently enhances detection accuracy through the addition of extra layers, albeit at the cost of extended training duration and increased computational demands. For mobile deployment, inference latency and hardware constraints must be prioritized.
To provide insight into the training dynamics of the network, Figure 2 illustrates the curves for bounding box loss, precision, mAP, and recall across the YOLOv8 series. These four curves converge and stabilize after 80 epochs, indicating successful model training without overfitting. Considering the importance of real-time efficiency and detection precision, this work adopts YOLOv8n as the foundational model for further improvement.
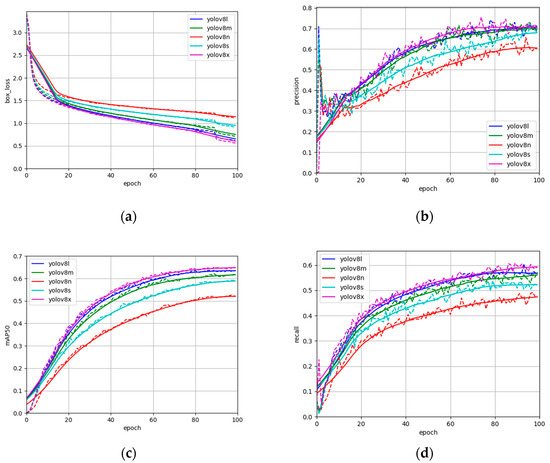
Figure 2.
Training performance curves of the YOLOv8 variants. (a) Bounding box loss, (b) Precision, (c) mAP, and (d) Recall.
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Experimental Details
4.1.1. Dataset
Training and ablation studies utilized the PASCAL VOC dataset. The VOC 2007 dataset, widely adopted for validating computer vision tasks, such as object detection and semantic segmentation, comprises 9963 images across 20 classes. These were split into 5011 training images and 4952 validation images. The VOC2012 dataset shares class definitions with VOC2007 but contains 5716 training images and 5823 validation images.
4.1.2. Environment and Training Parameters
The experiment was conducted on a Windows 11 (64-bit) system with an Intel Core i7-13700KF CPU, 64 GB of RAM, and an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4080 GPU. Model development leveraged PyTorch (v1.10.0, CUDA 10.2, cuDNN 7.5.0), Visual Studio Code (v1.85), and Python (v3.9). Optimization employed Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) with a momentum value of 0.9. Some training hyperparameters included an initial learning rate of 0.01, a weight decay of 0.0005, a batch size of 32, and a training duration of 100 epochs. A cosine annealing learning rate scheduler was employed to gradually reduce the learning rate from its initial value to near zero, thereby ensuring stable convergence in the later stages of training. To avoid unstable updates in the early phase, a linear warmup strategy was applied for the first 3 epochs, during which the learning rate increased linearly from 0 to the target value. Additionally, mosaic augmentation was disabled during the final 10 epochs to enhance the model’s ability to generalize to real-world image distributions.
4.1.3. Evaluation Metrics
Model performance was assessed using Precision (P), Recall (R), Mean Average Precision (mAP), model size, F1-score, computational complexity (FLOPs), and Composite Optimization Score (COS).
Precision (P) is the proportion of correct positive predictions among all positive predictions. The calculation process is shown in Equation (15).
Recall (R) refers to the proportion of actual positives correctly identified and is mathematically denoted as Equation (16).
F1-score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall, indicating overall accuracy and stability. The calculation process is illustrated in Equation (17).
Average Precision (AP) is the area under the precision-recall curve for a single class. The calculation process is outlined in Equation (18).
mAP is the mean of the AP scores across all classes, providing a holistic performance measure. It can be calculated as Equation (19).
where is true positive and represents correctly detected positive samples, is false positive and refers to the negative samples incorrectly classified as positive, is false negative and refers to positive samples incorrectly classified as negative. is the total number of object classes.
To provide a more comprehensive evaluation of Nav-YOLO, we propose a COS that jointly considers detection performance and computational efficiency. This score integrates Precision (P), Recall (R), F1-score (F1), mAP50 (mAP), model size (S), and FLOPs (F).
where are the normalized detection metrics through division by 100. While are the normalized efficiency metrics are defined as:
where denote the model size and FLOPs of the YOLOv8n. is a weighting factor that balances the relative importance of detection performance and efficiency. In the experiments, we set to give equal weight to both aspects. A higher COS indicates a model that achieves superior performance while maintaining low computational cost and compact size, making it particularly suitable for mobile and real-time applications.
4.2. Comparative Analysis of Lightweight Backbones
The backbone network has a significant influence on model size and computational demands. To achieve greater compactness and enhance feature extraction, this study replaces the original YOLOv8 backbone with lightweight CNN structures, including ShuffleNetv2 [23], GhostNet [24], MobileNetv3 [22], and FasterNet [41]. Compared to heavier counterparts, such as CSPDarknet53, these architectures offer fewer parameters and lower computational costs.
As shown in Table 2, MobileNetv3 and ShuffleNetv2 outperform the baseline YOLOv8n in Precision, Recall, F1-score, and mAP50. ShuffleNetv2 demonstrates the most significant gains, increasing these metrics by 7.22%, 11.39%, 9.74%, and 10.82%, respectively, while reducing FLOPs by 0.2 GFLOPs and maintaining a comparable model size. Although MobileNetv3 also improves detection accuracy, its larger size hinders mobile deployment. Conversely, GhostNet and FasterNet showed inferior performance across all metrics.

Table 2.
The results of backbone feature networks of different lightweight models.
ShuffleNetv2 achieves the highest COS value of 0.2952, driven by robust detection performance with a Performance Score of 0.6310 while maintaining computational efficiency comparable to the baseline. YOLOv8n ranks second with a COS of 0.2666, demonstrating that its extreme compactness and low FLOPs effectively offset slightly lower detection metrics, thereby rendering it highly suitable for deployment on resource-constrained platforms. In contrast, GhostNet, MobileNetv3, and FasterNet exhibit negative efficiency scores due to substantially increased model sizes and computational demands relative to YOLOv8n, which adversely impacts their overall COS despite achieving reasonable detection performance. These results substantiate that Nav-YOLO, when integrated with lightweight backbones such as ShuffleNetv2, achieves an optimal balance between accuracy and efficiency. Accordingly, the COS metric serves as a comprehensive evaluation framework, underscoring the practical benefits of models tailored for mobile and real-time navigation applications.
4.3. Comparative Experiments and Analysis of Bottleneck Structures
The neck module refines feature outputs from the backbone. To evaluate the efficacy of bottleneck architectures in feature fusion, four models were assessed: the Asymptotic Feature Pyramid Network (AFPN) [42], the Bi-directional Feature Pyramid Network (BiFPN) [43], the Cross-Scale Feature Fusion Module (CCFM) [44], and the Slim-Neck [33].
The results are shown in Table 3. All structures improved the Precision and F1-score over baseline YOLOv8n. SlimNeck improves precision by 5.17%, recall by 1.76%, F1-score by 3.02%, and mAP50 by 3.57%, while reducing model size by 0.34 MB and FLOPs by 0.8 G. While CCFM achieved the most lightweight design with a Model Size of 3.97 MB and FLOPs of 6.7 G, its accuracy improvement was relatively limited. The SlimNeck configuration achieves the highest COS value of 0.3321, primarily due to its superior detection performance, with a Performance Score of 0.5669, while also maintaining competitive computational efficiency, as evidenced by an Efficiency Score of 0.0774. The CCFM variant ranks second with a COS of 0.3264, distinguished by the highest efficiency score among the compared models, achieving an Efficiency Score of 0.1078. BiFPN demonstrates a balanced trade-off, yielding a COS of 0.2679; it slightly outperforms the baseline YOLOv8n by enhancing detection performance while incurring only minimal efficiency losses. In contrast, AFPN exhibits a negative efficiency score due to its increased model size and elevated FLOPs, which outweigh the corresponding performance improvements and lead to a diminished overall COS. Therefore, considering both the lightweight efficiency and model detection accuracy, this study selected SlimNeck to optimize the neck module of YOLOv8n.

Table 3.
The results of neck module of different models.
4.4. Ablation Test
Ablation experiments assessed the contributions of individual modules within Nav-YOLO using consistent evaluation metrics. Results are detailed in Table 4.

Table 4.
The results of head module of different models.
Integrating ShuffleNetv2 alone increased recall by 11.39% and mAP50 by 10.82%, while model size increased by 10.6%. Adding Slim-Neck resulted in a trade-off between precision and recall. Precision surged to 71.35%, but recall decreased by 7.02% to 52.15% compared to ShuffleNetv2. The YOLOv8n-ShuffleNetv2-SlimNeck configuration also reduced FLOPs by 12.2% to 7.2 G versus baseline. The observed trade-off between precision and recall following the integration of the Slim-Neck module can be attributed to its structural influence on feature aggregation. Specifically, the Slim-Neck implements a more selective and compact feature fusion mechanism through VoV-GSCSP, which enhances the discriminability of salient object features while effectively suppressing background noise. This refined feature representation enables the detector to generate higher-confidence positive predictions, thereby elevating precision. Conversely, the increased selectivity and condensation inherent in this approach may inadvertently filter out weaker or partially occluded object signals, diminishing the model’s capacity to identify all true positives and resulting in a marginal reduction in recall. Fundamentally, the Slim-Neck induces a bias toward high-confidence detections, prioritizing precision at the expense of recall, thus exemplifying a classical precision-recall trade-off characteristic of feature-compressed architectures.
In addition, four detection heads were then evaluated on this base architecture, as shown in Table 4, including RFADetection [45], RepDetection [46], Diverse Branch Block (DBB) Head [47], and HyCTAS [36]. As shown in Table 4, RFADetection achieved the highest precision of 75.71% but the lowest recall of 55.60%. RepDetection offered a balanced performance with a 64.38% F1 score. DBBHead achieved a maximum mAP50 of 64% at a prohibitive computational expense, requiring FLOPs of 13.6 G, representing an 88.90% increase compared to the SlimNeck. Meanwhile, HyCTAS achieved 64% mAP50 accuracy, equivalent to DBBHead, while achieving radical efficiency enhancements and reducing computation to FLOPs of 6.9 G, a 15.9% reduction relative to the SlimNeck configuration. Additionally, it compressed the model size to 5.90 MB, achieving 4.3% compression compared to the original YOLOv8n. The final YOLOv8n-ShuffleNetv2-SlimNeck-HyCTAS configuration achieved an 11.82% absolute improvement in mAP50 over the original YOLOv8n while simultaneously reducing computational demands.
The YOLOv8n-ShuffleNetv2-SlimNeck-HyCTAS variant achieves the highest COS value of 0.3637, indicating an optimal balance between enhanced detection performance, with a Performance Score of 0.6440, and maintained computational efficiency, as reflected by an Efficiency Score of 0.0835. Notably, the SlimNeck variant achieves a competitive COS of 0.3231 independently, demonstrating that its neck design effectively improves precision without imposing excessive computational costs. In contrast, although the RFADetection and RepDetection variants exhibit modest improvements in raw detection metrics with Performance Scores ranging from approximately 0.646 to 0.649, their substantial increases in model size and floating-point operations lead to markedly negative efficiency scores near −0.43, thereby diminishing their overall COS values to approximately 0.10. Similarly, the DBBHead variant delivers strong detection performance with a Performance Score of 0.6478 but suffers the greatest efficiency penalty, as indicated by an Efficiency Score of –0.9973, due to drastic increases in model size and FLOPs, resulting in a negative COS.
To verify the effectiveness of loss functions for bounding box regression, PowerfulIoU and InnerIoU were evaluated within the optimized YOLOv8n-ShuffleNetv2-SlimNeck-HyCTAS framework, as shown in Table 5. The experimental results indicate that the YOLOv8n-ShuffleNetv2-SlimNeck-HyCTAS-InnerIoU model attained the highest COS value of 0.3650. Its Performance Score of 0.6565 corresponds to a 23.1% enhancement relative to the baseline score of 0.5331, which can be attributed primarily to significant improvements in precision, recall, and F1. Furthermore, by leveraging a redesigned, lightweight network architecture, the model demonstrates superior computational efficiency, reducing FLOPs by 15.9% from 8.2 G to 6.9 G, thereby contributing positively to the Efficiency Score. Although a marginal increase in model size was observed, the substantial gains in detection performance, combined with significantly decreased computational complexity, culminate in an optimized balance between accuracy and efficiency.

Table 5.
Performance comparison of loss function.
Based on comprehensive experimental validation and the performance requirements, YOLOv8n-ShuffleNetv2-SlimNeck-HyCTAS-InnerIoU was selected as the enhanced design for real-time object detection in navigation systems.
5. Discussion
This section analyzes detection metrics on the VOC 2007/2012 benchmarks, deployment efficiency, and real-time inference results for Nav-YOLO and comparative models.
5.1. Comparison of Detection Performance Between Different Models on the VOC2007 Dataset
Nav-YOLO was compared to YOLOv3, YOLOv3-tiny, YOLOv5, and YOLOv6 under identical hardware, datasets, data augmentation techniques, and balanced training and testing set ratios on the VOC2007. The training process spanned 100 epochs, with the best-performing results chosen for evaluation. Results are shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
The comparison results of different models on VOC2007 dataset.
While YOLOv3 achieved a slightly higher mAP50 of 64.25% compared to Nav-YOLO’s 62.52%, the solution delivers critical advantages, including the highest recall-precision harmony with a 65.71% F1-score, which exceeds YOLOv3 by 1.08% and YOLOv6 by 12.85%. It is achieved alongside radical efficiency gains, evidenced by a 6.02 MB model size representing 96.96% compression compared to YOLOv3 and a 6.9 GFLOPs computational load equivalent to a 97.56% reduction relative to YOLOv3. Furthermore, Nav-YOLO attains 58.40% recall, outperforming YOLOv3 by 1.16%. Notably, Nav-YOLO surpasses contemporary efficient models, achieving a 12.18% F1-score advantage over YOLOv3-tiny, a 15.87% advantage over YOLOv5, and a 12.85% advantage over YOLOv6, while maintaining a competitive precision of 75.09%, second only to YOLOv3’s 74.01%.
Figure 9 comparatively visualizes Precision, mAP, and Recall curves alongside model size metrics across evaluated architectures. The comparative analysis on VOC 2007 shows that Nav-YOLO demonstrates the most favorable compromise between accuracy and runtime performance.
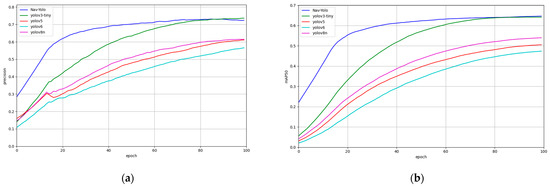
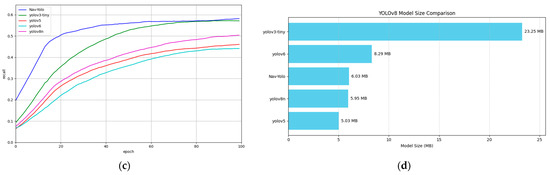
Figure 9.
Model training process on VOC2007 dataset. (a) Precision; (b) mAP; (c) Recall; (d) Model size.
5.2. Comparison of Detection Performance Between Different Models on VOC2012 Dataset
To validate the effectiveness of Nav-YOLO in complex scenes, comparative experiments were conducted on the VOC2012 dataset. Performance was evaluated against YOLOv3-tiny, YOLOv5, YOLOv6, and YOLOv8n, as shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
The comparison results of different models on VOC2012 dataset.
Both YOLOv8n and Nav-YOLO achieved an mAP50 of over 58% on VOC2012. Nav-YOLO outperforms YOLOv8n in terms of mAP50, achieving the highest scores with a 5% advantage and performing very well. Nav-YOLO achieves the second smallest model size at 6.02 MB, representing a 3.2% reduction compared to YOLOv8n. Its computational load of 7.8 GFLOPs constitutes a 59.2% reduction compared to YOLOv3-tiny despite delivering a 9.71% higher mAP50.
Training results of Nav-YOLO on the VOC2012 dataset are illustrated in Figure 10. After 50 epochs of training, Nav-YOLO demonstrates a rapid convergence and ultimately attains superior performance, particularly in Precision (Figure 10a), mAP50 (Figure 10b), and Recall (Figure 10c).
Figure 10.
Model training process on the VOC2012 dataset. (a) Precision; (b) mAP; (c) Recall; (d) Model size.
5.3. Model Deployment and Real-Time Detection
To further validate the effectiveness of the proposed model in real-world scenarios, we developed and deployed an Android application based on Nav-YOLO and conducted tests in typical indoor navigation environments such as offices and laboratory settings. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves real-time detection and inference on mobile devices, while maintaining high detection accuracy for navigation-relevant objects such as chairs and bottles. Moreover, Nav-YOLO achieves inference speeds comparable to those of YOLOv8n, while maintaining superior detection accuracy. These findings confirm the suitability of our lightweight design for mobile deployment and highlight its potential for practical indoor navigation applications.
The Android application was developed using the Nano Computer Neural Network (NCNN) framework, an optimized open-source inference engine designed for mobile platforms.
The deployment workflow includes four key stages (Figure 11). First, the server-trained PyTorch model (.pt file) is exported to Open Neural Network Exchange (ONNX) format to ensure cross-platform compatibility. Second, the ONNX model is transformed into NCNN format using the onnx2ncnn tool. This process produces ‘.param’ and ‘.bin’ files that store the model’s architecture and weights for efficient execution on mobile devices. Third, the model is deployed to Android terminals through Gradle-managed dependency resolution, ensuring compatibility with the library and toolchain. Finally, leveraging the Java Development Kit (JDK) with Android-specific stability optimizations enables efficient model inference on mobile devices.
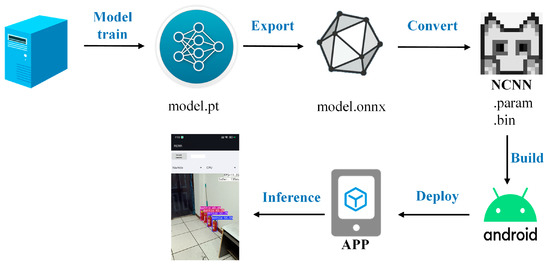
Figure 11.
Description of deployment process.
Figure 12 presents the results of object detection for navigation using this mobile application. Qualitative observations indicate that the Nav-YOLO model achieves significantly improved detection performance compared to the original YOLOv8n, detecting more objects with higher precision. Table 8 quantifies the real-time detection performance of YOLOv8n and Nav-YOLO across three navigation scenarios, with a focus on two key metrics for mobile deployment: inference speed (FPS) and inference delay. The quantitative evaluations performed on a mobile platform demonstrate that the proposed model achieves inference speeds comparable to the baseline and even surpasses it in specific scenarios, as evidenced by closely matched frame rates and latency metrics. Notably, this speed performance advantage is sustained without compromising the model’s superior detection accuracy. These empirical findings collectively and robustly affirm the practical viability of the proposed model in real-time mobile deployment scenarios.
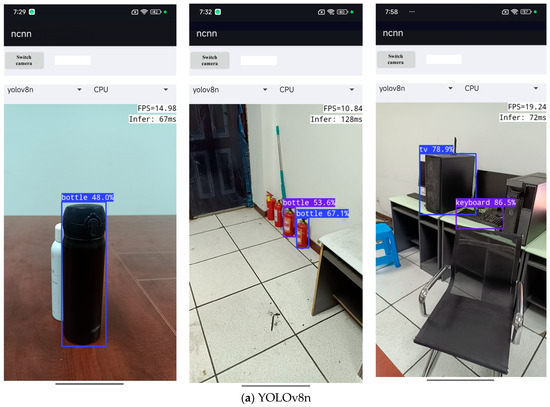

Figure 12.
Application implementation display. (a) Detection results using YOLOv8n; (b) Detection results using Nav-YOLO.

Table 8.
Comparison of Real-Time Detection Performance Between YOLOv8n and Nav-YOLO.
A critical aspect of successful mobile deep learning deployment lies in addressing the practical engineering challenges encountered during Android application development and model optimization. This study deployed an improved YOLOv8-based model incorporating non-standard modules such as Slim-Neck and HyCTAS, and encountered significant challenges throughout the conversion pipeline. The transition from PyTorch to ONNX and subsequently to the NCNN format proved particularly problematic due to limited support for custom operators, often resulting in computational graphs with redundant operations, which ultimately led to compatibility issues with the C++ inference interface. To achieve real-time performance, a multi-faceted optimization strategy for NCNN was implemented, including FP16 quantization for reduced memory usage, Vulkan backend integration for GPU acceleration, and selective use of highly optimized operators. Furthermore, considerable performance variability was observed across different Systems-on-Chip (SoCs), attributable to disparities in CPU architectures, the availability of specialized AI accelerators (NPUs), and differences in memory bandwidth. These findings underscore the critical influence of hardware fragmentation on consistent deployment outcomes and highlight the necessity of hardware-aware optimization strategies in real-world applications.
5.4. Limitations of Our Work
Although the PASCAL VOC 2007 and VOC 2012 datasets are widely recognized as standard benchmarks for object detection, their limited category diversity and inherent bias towards common scenes restrict their capacity to fully represent the complexity of real-world navigation environments. The relatively homogeneous nature of the imagery in these datasets inadequately reflects the challenging conditions encountered in practical navigation contexts, such as dynamic lighting variations, significant occlusions, and dense clutter. Therefore, models trained exclusively on these datasets may demonstrate diminished generalization capabilities when applied to diverse indoor settings that diverge from the VOC domain. To overcome this limitation, future research will focus on evaluating Nav-YOLO using more comprehensive and navigation-specific datasets that encompass varied illumination conditions, intentional obstructions, crowded scenes, and an expanded range of object categories. Such rigorous benchmarking is anticipated to provide a more robust validation of the model’s resilience and its practical effectiveness in real-world applications.
Furthermore, the model occasionally misclassifies visually similar objects, such as confusing a fire extinguisher with a bottle or identifying a portion of a table as a sink. This limitation primarily arises from dataset constraints, including the absence of certain object categories and the presence of coarse annotations, which impede the learning of fine-grained inter-class distinctions. The issue is exacerbated by architectural factors: the model’s design emphasizes local feature processing with limited integration of global contextual information and lacks explicit mechanisms to enforce semantic consistency across different parts of an object. Consequently, partially occluded or atypical object instances are particularly prone to misinterpretation. These findings highlight the inherent challenges in reliably discriminating semantically similar classes under real-world conditions and suggest avenues for improvement through enhanced data curation and architectural refinement.
6. Conclusions
This study introduces Nav-YOLO, an optimized lightweight architecture derived from YOLOv8n for real-time object detection in navigation systems, specifically designed for computationally constrained devices. To address the limitations of computational complexity and deployment constraints in existing methods, we propose a ShuffleNetv2-based backbone for efficient feature extraction, a Slim-Neck design with VoV-GSCSP structure to maintain accuracy while minimizing computational load, and a HyCTAS-optimized detection head with Inner-IoU loss for accelerated bounding box regression. The experiments demonstrate that Nav-YOLO achieves significant improvements over YOLOv8n, with notable increases of 10.3% and 10.6% in mAP50 and recall on VOC2007, respectively, along with 5% and 3.8% increases in mAP50 and recall on VOC2012, while maintaining comparable parameter efficiency.
The Nav-YOLO model proposed in this study provides an efficient and robust solution for real-time object detection in navigation systems. In future research, we will expand the training dataset to include more challenging navigation scenarios, such as complex urban obstacles and indoor environments, thereby enhancing the algorithm’s generalization capability across diverse real-world environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and Methodology, Litao Zhu; Experiment and data collection, Cheng Su and Jin Zhou; Writing—original draft, Litao Zhu, Wen Dai and Jialiang Wang; Writing—review and editing, Litao Zhu, Wen Dai, Yucheng Mao and Jiangbing Sun. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42301509), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2025T180082, 2024M761474), and the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (No. KYCX25_2107).
Data Availability Statement
The data and code are available from https://github.com/back2-thebasic/NavYolo (accessed on 15 September 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Alahmadi, T.J.; Rahman, A.U.; Alkahtani, H.K.; Kholidy, H. Enhancing object detection for VIPs using YOLOv4_Resnet101 and text-to-speech conversion model. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2023, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Nazir, S.; Khan, H.U. Analysis of navigation assistants for blind and visually impaired people: A systematic review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 26712–26734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masal, K.M.; Bhatlawande, S.; Shingade, S.D. An integrated region proposal and spatial information guided convolution network based object recognition for visually impaired persons’ indoor assistive navigation. Imaging Sci. J. 2024, 72, 884–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, Y.; Atri, M.; Albahar, M.A.; Ben Atitallah, A.; Alsariera, Y.A. Obstacle detection system for navigation assistance of visually impaired people based on deep learning techniques. Sensors 2023, 23, 5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, Y.; Jeong, H.; Choi, S.H.; Park, K.-B.; Lee, J.Y. Deep learning-based object detection in augmented reality: A systematic review. Comput. Ind. 2022, 139, 103661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Chen, K.; Shi, Z.; Guo, Y.; Ye, J. Object detection in 20 years: A survey. Proc. IEEE 2023, 111, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosi, S.; Sambare, S.; Singh, S.; Lokhande, N.; Garware, B. Android application for object recognition using neural networks for the visually impaired. In Proceedings of the 2018 Fourth International Conference on Computing Communication Control and Automation (ICCUBEA), Pune, India, 16–18 August 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Vaidya, S.; Shah, N.; Shah, N.; Shankarmani, R. Real-time object detection for visually challenged people. In Proceedings of the 2020 4th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 13–15 May 2020; pp. 311–316. [Google Scholar]
- Shariatinezhad, M.; Molaeezadeh, S.F.; Gholami, M. Outdoor navigation for visually impaired people using YOLOv5 and Transfer learning: An analytical study. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 84, 24521–24540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashiq, F.; Asif, M.; Ahmad, M.B.; Zafar, S.; Masood, K.; Mahmood, T.; Mahmood, M.T.; Lee, I.H. CNN-based object recognition and tracking system to assist visually impaired people. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 14819–14834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriakose, B.; Shrestha, R.; Sandnes, F.E. DeepNAVI: A deep learning based smartphone navigation assistant for people with visual impairments. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 212, 118720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afif, M.; Ayachi, R.; Said, Y.; Atri, M. Deep embedded lightweight CNN network for indoor objects detection on FPGA. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2025, 201, 105085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladis, K.A.; Madavarapu, J.B.; Kumar, R.R.; Sugashini, T. In-out YOLO glass: Indoor-outdoor object detection using adaptive spatial pooling squeeze and attention YOLO network. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 91, 105925. [Google Scholar]
- Guravaiah, K.; Bhavadeesh, Y.S.; Shwejan, P.; Vardhan, A.H.; Lavanya, S. Third eye: Object recognition and speech generation for visually impaired. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 218, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part I 14. pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Badrloo, S.; Varshosaz, M.; Pirasteh, S.; Li, J. Image-based obstacle detection methods for the safe navigation of unmanned vehicles: A review. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriakose, B.; Shrestha, R.; Sandnes, F.E. Smartphone navigation support for blind and visually impaired people-a comprehensive analysis of potentials and opportunities. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Copenhagen, Denmark, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 568–583. [Google Scholar]
- Iandola, F.N.; Han, S.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5 MB model size. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07360. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.-T.; Sun, J. Shufflenet v2: Practical guidelines for efficient cnn architecture design. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 116–131. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, C. Ghostnet: More features from cheap operations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 1580–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Bie, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Hong, J.; Li, J. Real-time vehicle detection algorithm based on a lightweight You-Only-Look-Once (YOLOv5n-L) approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 119108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaur, B.; Mishra, K.; Kumar, A. An improved lightweight small object detection framework applied to real-time autonomous driving. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 234, 121036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L. PS-YOLO: A Lighter and Faster Network for UAV Object Detection. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Ye, K.; Qiu, S. Study on lightweight strategies for L-YOLO algorithm in road object detection. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Xiong, P.; An, J.; Wang, L. Pyramid attention network for semantic segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.10180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everingham, M.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The pascal visual object classes (voc) challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2010, 88, 303–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Wei, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Ren, Q. Slim-neck by GSConv: A better design paradigm of detector architectures for autonomous vehicles. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.02424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, S.; Van der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Condensenet: An efficient densenet using learned group convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 2752–2761. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.M.; Wu, Y.-H.; Chen, P.-Y.; Hsieh, J.-W.; Yeh, I.-H. CSPNet: A new backbone that can enhance learning capability of CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 390–391. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Wan, C.; Dai, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, D.; Xiao, B.; Huang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, L. Real-time image segmentation via hybrid convolutional-transformer architecture search. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.10413. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Wu, L.; Chen, S.; Hu, X.; Li, J.; Tang, J.; Yang, J. Generalized focal loss: Learning qualified and distributed bounding boxes for dense object detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 21002–21012. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 12993–13000. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.; Zhong, Y.; Gao, Y.; Scott, M.R.; Huang, W. Tood: Task-aligned one-stage object detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3490–3499. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, C.; Zhang, S. Inner-iou: More effective intersection over union loss with auxiliary bounding box. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.02877. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Kao, S.-h.; He, H.; Zhuo, W.; Wen, S.; Lee, C.-H.; Chan, S.-H.G. Run, don’t walk: Chasing higher FLOPS for faster neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 12021–12031. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Lei, J.; Zhu, Z.; Cheng, S.; Feng, Z.; Liang, R. AFPN: Asymptotic feature pyramid network for object detection. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 1–4 October 2023; pp. 2184–2189. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Pang, R.; Le, Q.V. Efficientdet: Scalable and efficient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 10781–10790. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Lv, W.; Xu, S.; Wei, J.; Wang, G.; Dang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Detrs beat yolos on real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 16965–16974. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, D.; Song, T.; Ye, Y.; Li, K.; Song, Y. RFAConv: Innovating spatial attention and standard convolutional operation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.03198. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, N.; Han, J.; Ding, G.; Sun, J. Repvgg: Making vgg-style convnets great again. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13733–13742. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, X.; Han, J.; Ding, G. Diverse branch block: Building a convolution as an inception-like unit. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 10886–10895. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).