MART: Ship Trajectory Prediction Model Based on Multi-Dimensional Attribute Association of Trajectory Points
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Problem Statement
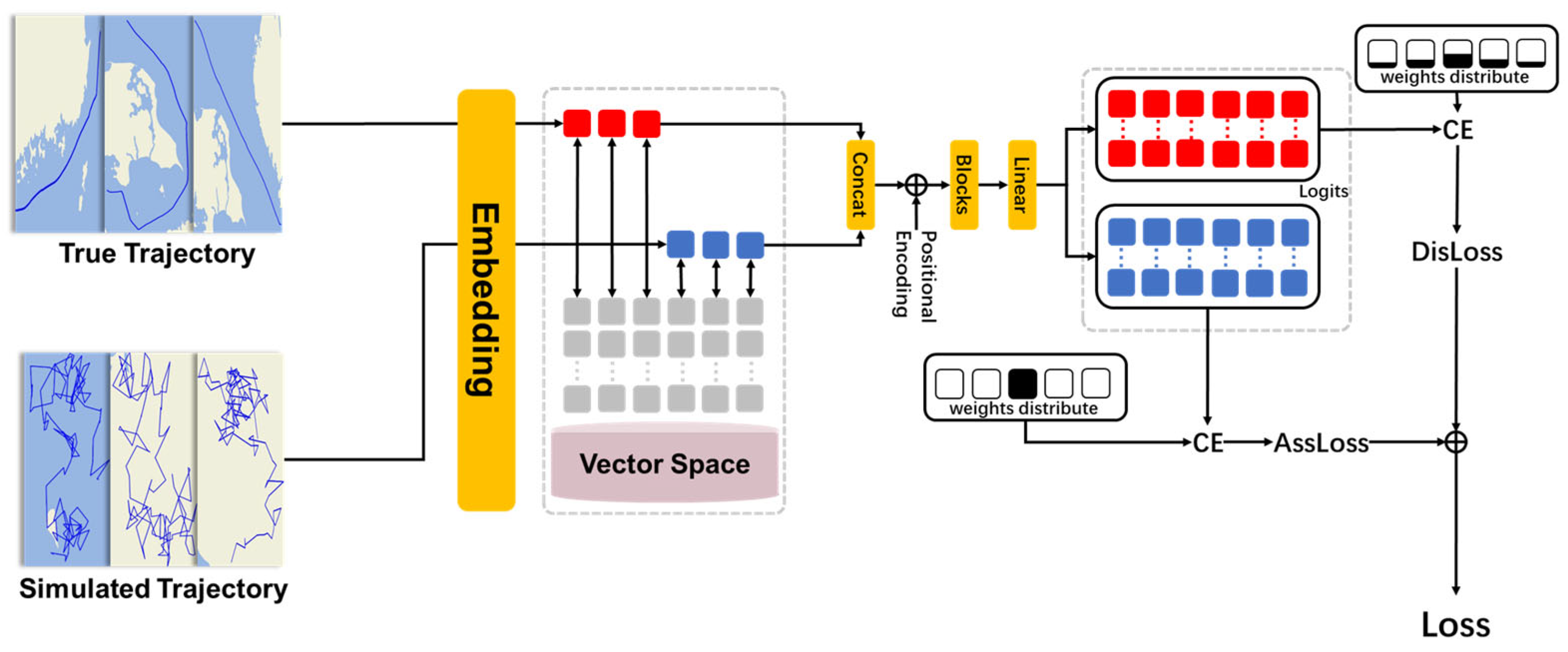
2.2. Model Structure
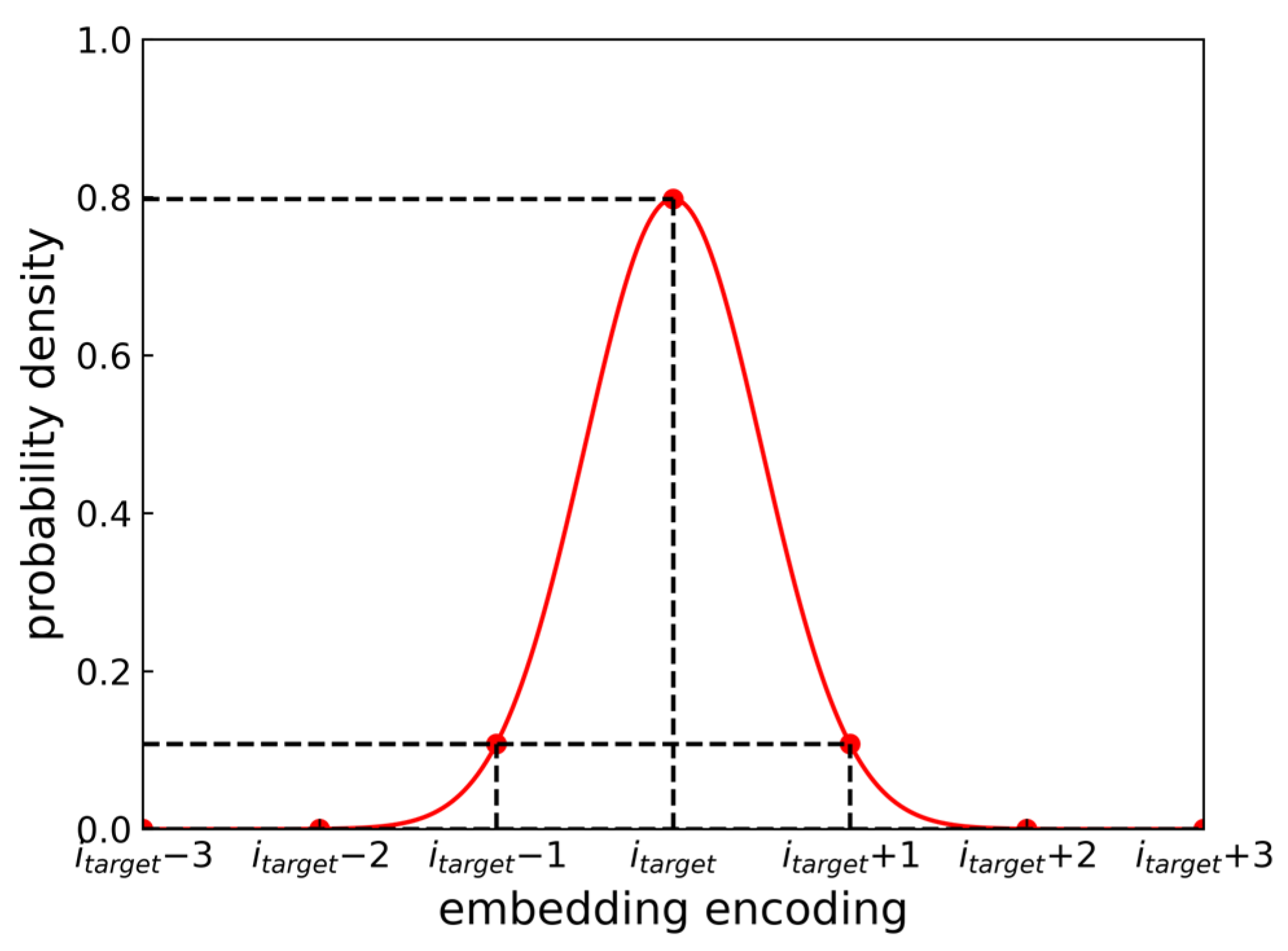
2.3. Distance Loss
2.4. Association Loss
- Randomly initialize the position, speed, and heading of the starting trajectory point;
- Calculate the position of the next trajectory point at the next moment based on the speed and heading, while randomly generating its new speed and heading;
- Repeat step 2 until the generated trajectory reaches the set length.
| Algorithm 1: Generate_Simulated_Traj () |
| Description: Generate simulated trajectories . Input: the boundary of area , the maximum of sog = 30, the maximum of cog = 360, the length of trajectory . Output: . // Generate the origin position = random_point() // Generate the others point for i in 0: −1 do // Randomly generate the speed and direction = random_motion() = cal_point() ) end Return |
- In terms of application: DisLoss is used for real trajectory prediction, while AssLoss is used for simulated trajectory prediction.
- In terms of weight assignment: The weight distribution of DisLoss adopts a normal distribution, whereas for AssLoss, the weight corresponding to the true value is 1 and the weights for all other values are 0.
- In terms of purpose: DisLoss aims to teach the model about the relative distances between attribute values, while AssLoss aims to force the model to learn the physical association between motion attributes (SOG, COG) and the resulting position change.
3. Experiment
3.1. Datasets
3.2. Model Parameters
3.3. Evaluation Criteria
3.3.1. Haversine Distance
3.3.2. Fréchet Distance
- Based on the probability distribution output by the model, random sampling is performed to obtain a predicted trajectory point.
- This newly predicted point is used as input to continue predicting the probability distribution of the next point, and sampling is conducted again.
- Repeat this process until a complete predicted trajectory is generated.
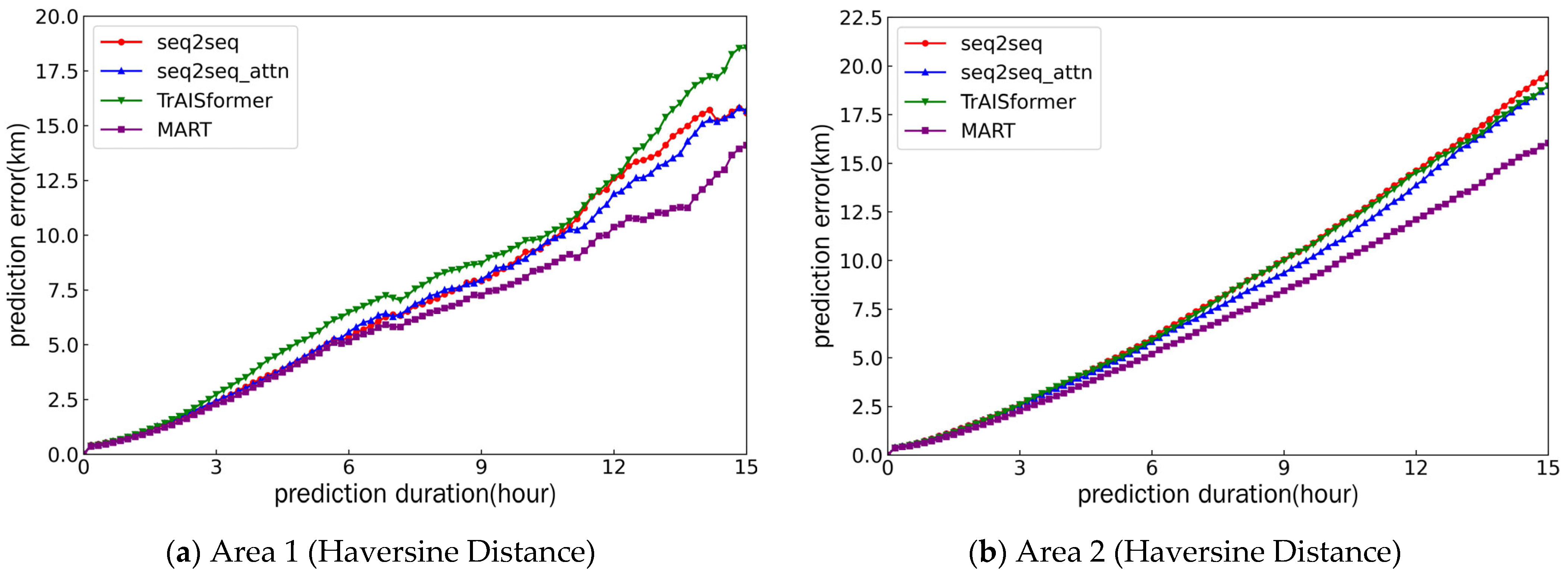
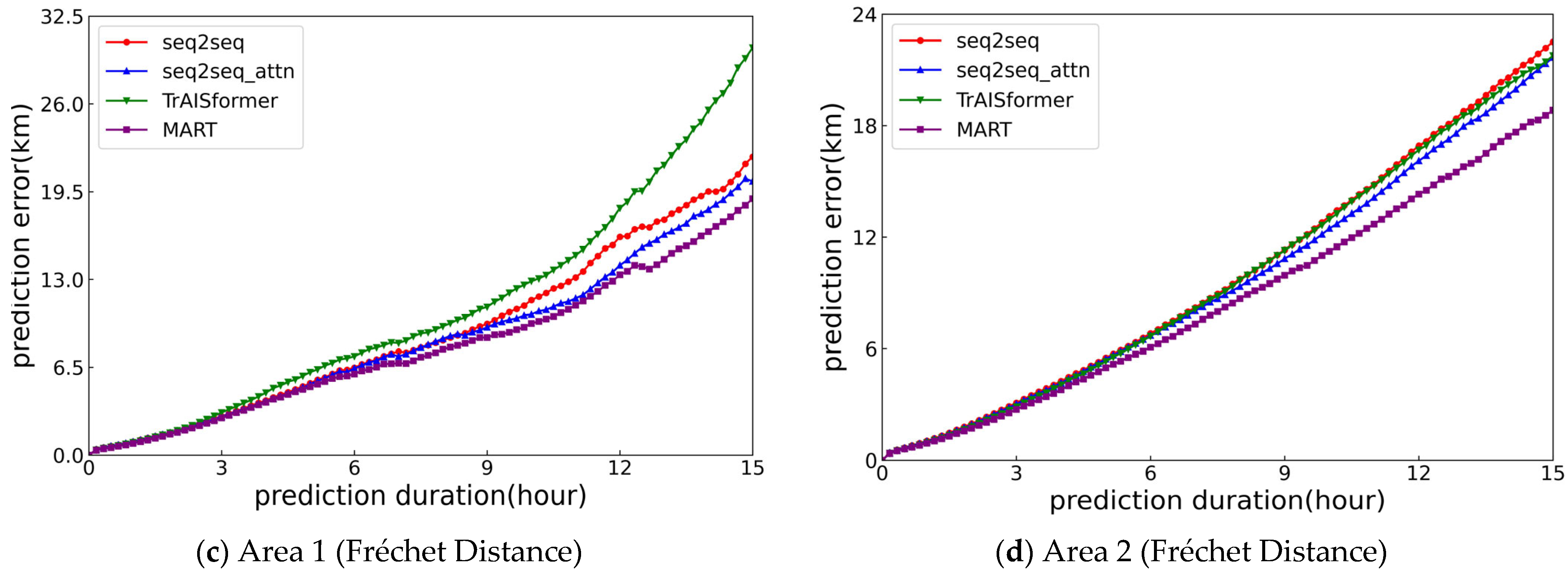
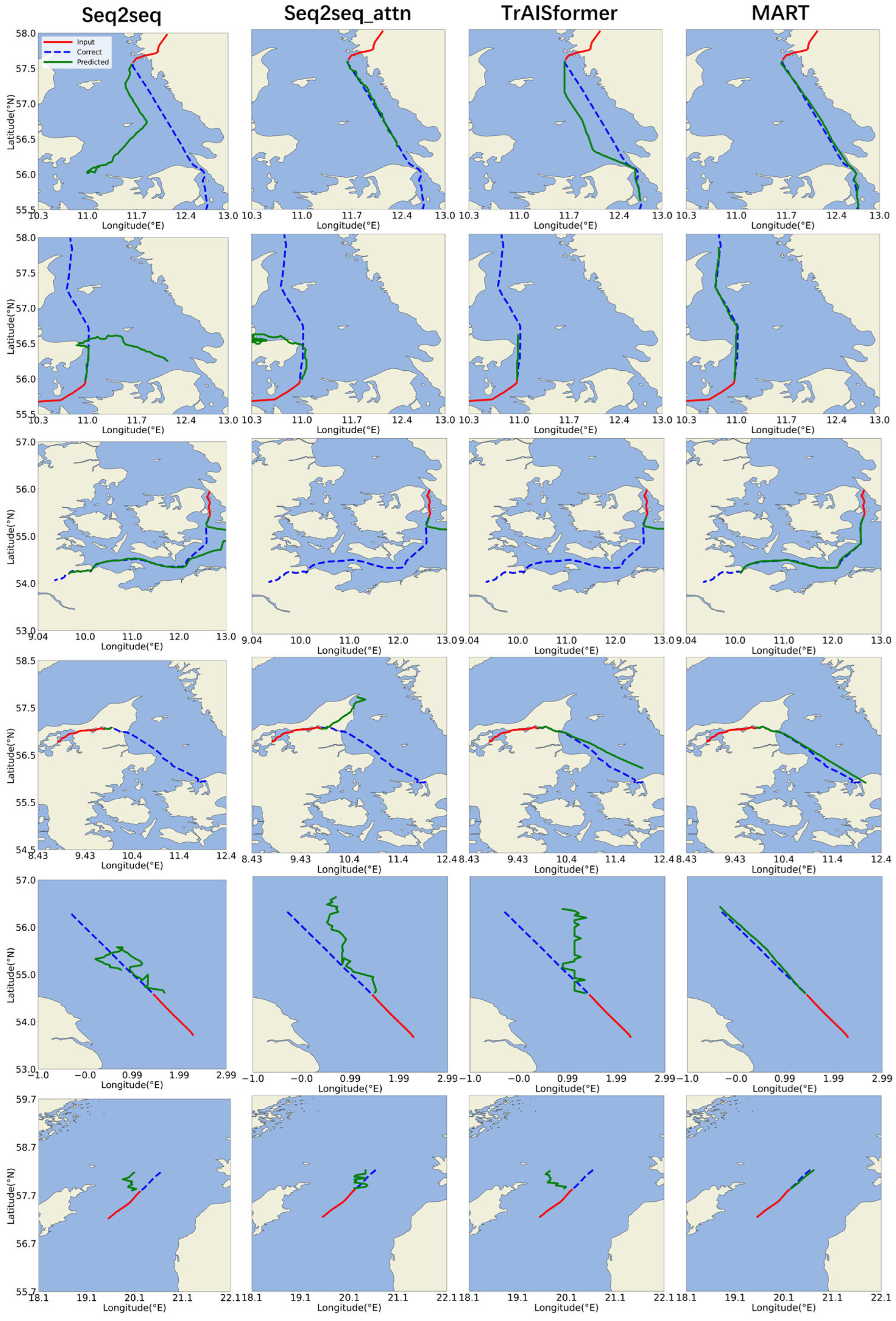
3.4. Comparative Experiment
3.5. Ablation Experiment
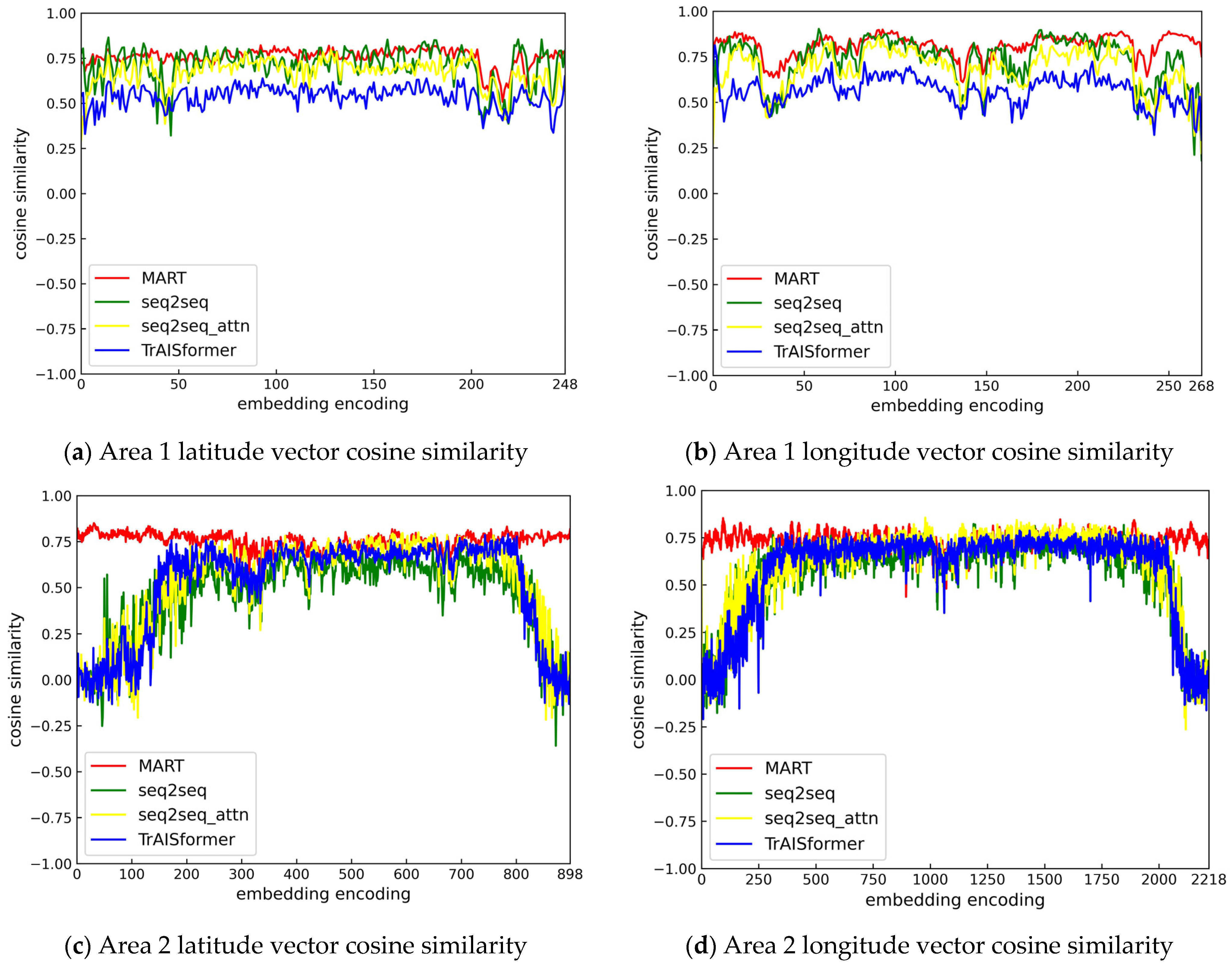
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIS | Automatic Identification System |
| MART | Multi-dimensional Attribute Relationship Transformer |
| AssLoss | Association Loss |
| IMO | International Maritime Organization |
| lat | Latitude |
| lon | Longitude |
| sog | Speed over ground |
| cog | Course over ground |
| MMSI | Maritime Mobile Service Identity |
| NCV | Nearly Constant Velocity |
| KDE | Kernel Density Estimation |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| CE | Cross Entropy Loss |
| FFN | Feed Forward Network |
| GNN | Graph Neural Network |
| OOD Generalization | Out-of-Distribution Generalization |
| MDNs | Mixture Density Networks |
References
- Chen, C.-H.; Khoo, L.P.; Chong, Y.T.; Yin, X.F. Knowledge Discovery Using Genetic Algorithm for Maritime Situational Awareness. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 2742–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, E.; Zhang, G.; Mao, S.; Rachmawati, L.; Huang, G.-B. Modeling Historical AIS Data for Vessel Path Prediction: A Comprehensive Treatment. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.01592. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Jiang, R.; Du, Y.; Lu, Q.; Guo, Z. TPR-DTVN: A Routing Algorithm in Delay Tolerant Vessel Network Based on Long-Term Trajectory Prediction. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2021, 2021, 6630265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, X.-P.; Dang, X.-K.; Do, V.-D.; Corchado, J.M.; Truong, H.-N. Robust Adaptive Fuzzy-Free Fault-Tolerant Path Planning Control for a Semi-Submersible Platform Dynamic Positioning System with Actuator Constraints. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 12701–12715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, W.; Bao, K.; Wang, P. Artificial Intelligence in Ship Trajectory Prediction. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, X.K.; Truong, H.N.; Do, V.D. A Path Planning Control for a Vessel Dynamic Positioning System Based on Robust Adaptive Fuzzy Strategy. Automatika 2022, 63, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Cao, Y.; Cheng, X. Research of AIS Data-Driven Ship Arrival Time at Anchorage Prediction. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 12740–12746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Z.; Zhu, J. AIS Database Powered by GIS Technology for Maritime Safety and Security. J. Navig. 2008, 61, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlamis, I.; Tserpes, K.; Sardianos, C. Detecting Search and Rescue Missions from AIS Data. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 34th International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops (ICDEW), Paris, France, 16–20 April 2018; pp. 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Venskus, J.; Treigys, P.; Markevičiūtė, J. Unsupervised Marine Vessel Trajectory Prediction Using LSTM Network and Wild Bootstrapping Techniques. Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control. 2021, 26, 718–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, K.V.; Boubekki, A.; Kampffmeyer, M.C.; Jenssen, R.; Christensen, A.N.; Hørlück, S.; Clemmensen, L.H. A Contextually Supported Abnormality Detector for Maritime Trajectories. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkus, R.; Venskus, J.; Markevičiūtė, J.; Treigys, P. Enhancing Maritime Safety: Estimating Collision Probabilities with Trajectory Prediction Boundaries Using Deep Learning Models. Sensors 2025, 25, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fu, X.; Xiao, Z.; Xu, H.; Qin, Z. Vessel Trajectory Prediction in Maritime Transportation: Current Approaches and Beyond. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 19980–19998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong Li, X.; Jilkov, V.P. Survey of Maneuvering Target Tracking. Part I. Dynamic Models. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2003, 39, 1333–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristic’, B.; Scala’, B.L.; Morelande’, M.; Gordon, N. Statistical Analysis of Motion Patterns in AIS Data: Anomaly Detection and Motion Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2008 11th International Conference on Information Fusion, Cologne, Germany, 30 June–3 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzarella, F.; Arguedas, V.F.; Vespe, M. Knowledge-Based Vessel Position Prediction Using Historical AIS Data. In Proceedings of the 2015 Sensor Data Fusion: Trends, Solutions, Applications (SDF), Bonn, Germany, 6–8 October 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, H.; Teixeira, A.P.; Guedes Soares, C. Ship Trajectory Uncertainty Prediction Based on a Gaussian Process Model. Ocean Eng. 2019, 182, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zuo, Y.; Li, T. Vessel Navigation Behavior Analysis and Multiple-Trajectory Prediction Model Based on AIS Data. J. Adv. Transp. 2022, 2022, 6622862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jeong, J.; Park, Y. Ship Trajectory Prediction Based on Bi-LSTM Using Spectral-Clustered AIS Data. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forti, N.; Millefiori, L.M.; Braca, P.; Willett, P. Prediction Oof Vessel Trajectories from AIS Data via Sequence-to-Sequence Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 8936–8940. [Google Scholar]
- Capobianco, S.; Millefiori, L.M.; Forti, N.; Braca, P.; Willett, P. Deep Learning Methods for Vessel Trajectory Prediction Based on Recurrent Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2021, 57, 4329–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Fablet, R. A Transformer Network with Sparse Augmented Data Representation and Cross Entropy Loss for AIS-Based Vessel Trajectory Prediction. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 21596–21609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lam, J.S.L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, R.W.; Liang, M.; Li, Y. Unsupervised Hierarchical Methodology of Maritime Traffic Pattern Extraction for Knowledge Discovery. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2022, 143, 103856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jiao, H.; Yang, Z. Ship Trajectory Prediction Based on Machine Learning and Deep Learning: A Systematic Review and Methods Analysis. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126, 107062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, S.; Shi, C.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ke, R.; Zhao, J. Sensing Data Supported Traffic Flow Prediction via Denoising Schemes and ANN: A Comparison. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 14317–14328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Piao, L.; Zang, X.; Luo, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Rong, J. Analyzing Differences of Highway Lane-Changing Behavior Using Vehicle Trajectory Data. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2023, 624, 128980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Xing, H.; Zhang, Z. Vessel Trajectory Prediction Based on Spatio-Temporal Graph Convolutional Network for Complex and Crowded Sea Areas. Ocean Eng. 2024, 298, 117232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, X.; Ye, L.; Yu, W.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J. Predicting Vessel Trajectories Using ASTGCN with StemGNN-Derived Correlation Matrix. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.Z.; Zhang, X.D.; Tang, H.N. STGDPM:Vessel Trajectory Prediction with Spatio-Temporal Graph Diffusion Probabilistic Model. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.08065. [Google Scholar]
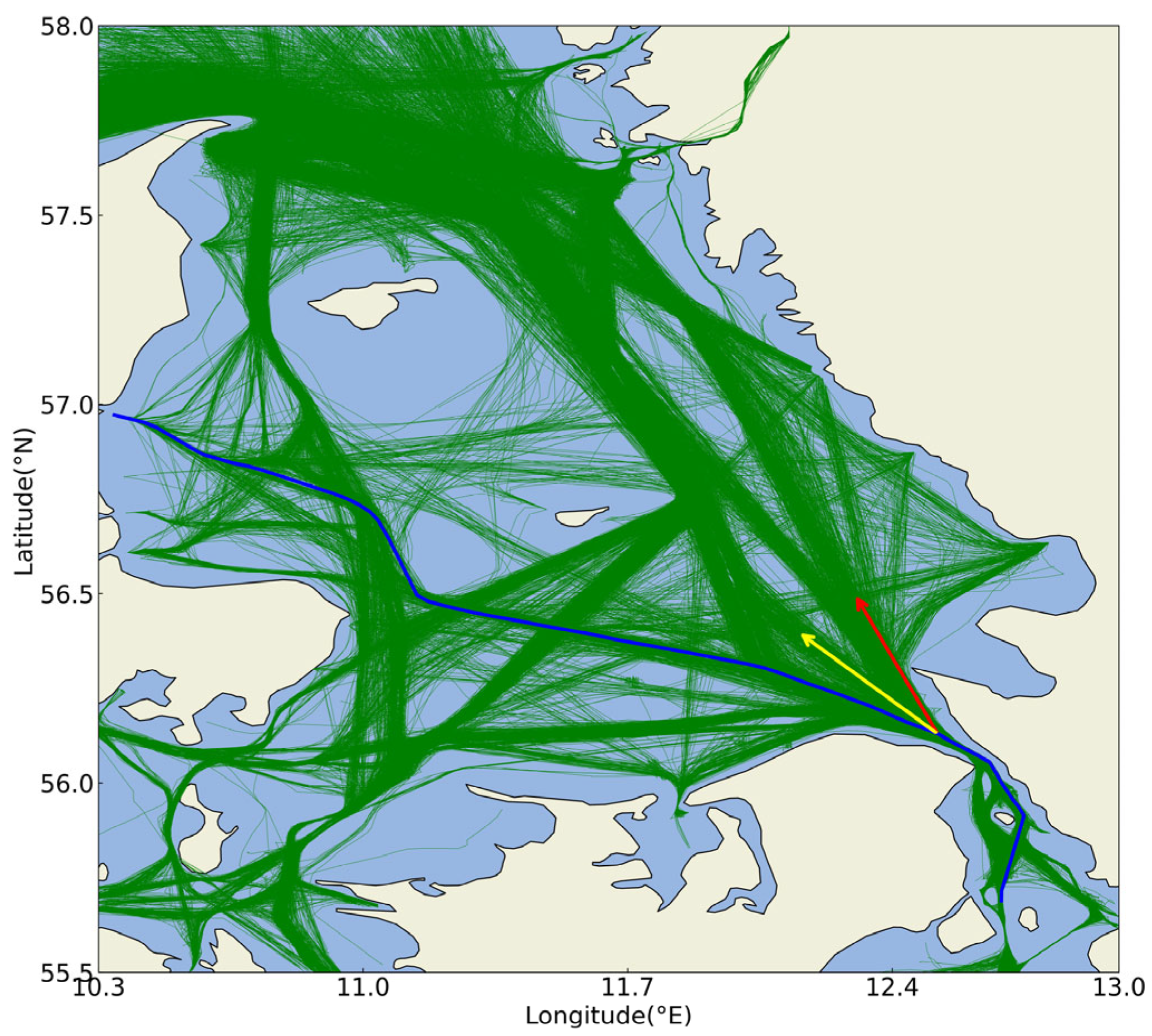
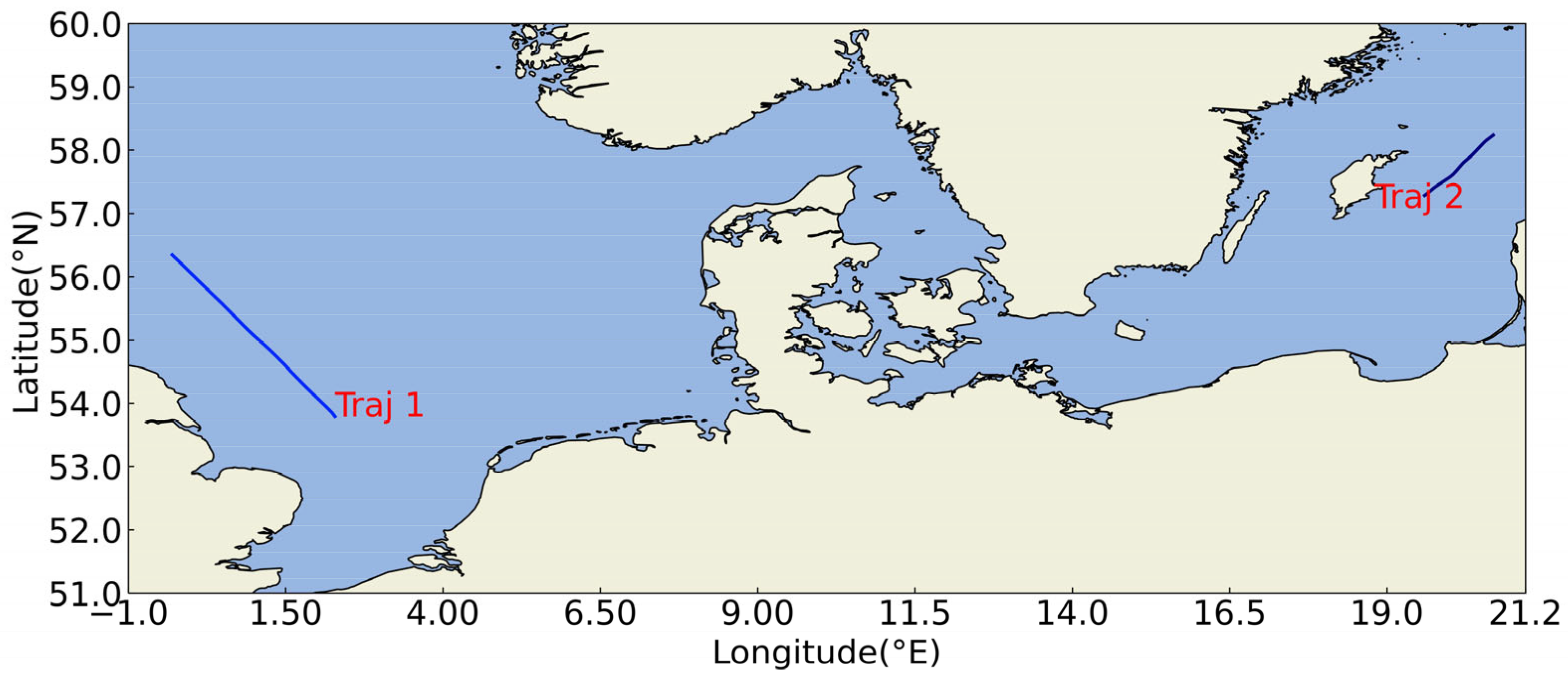
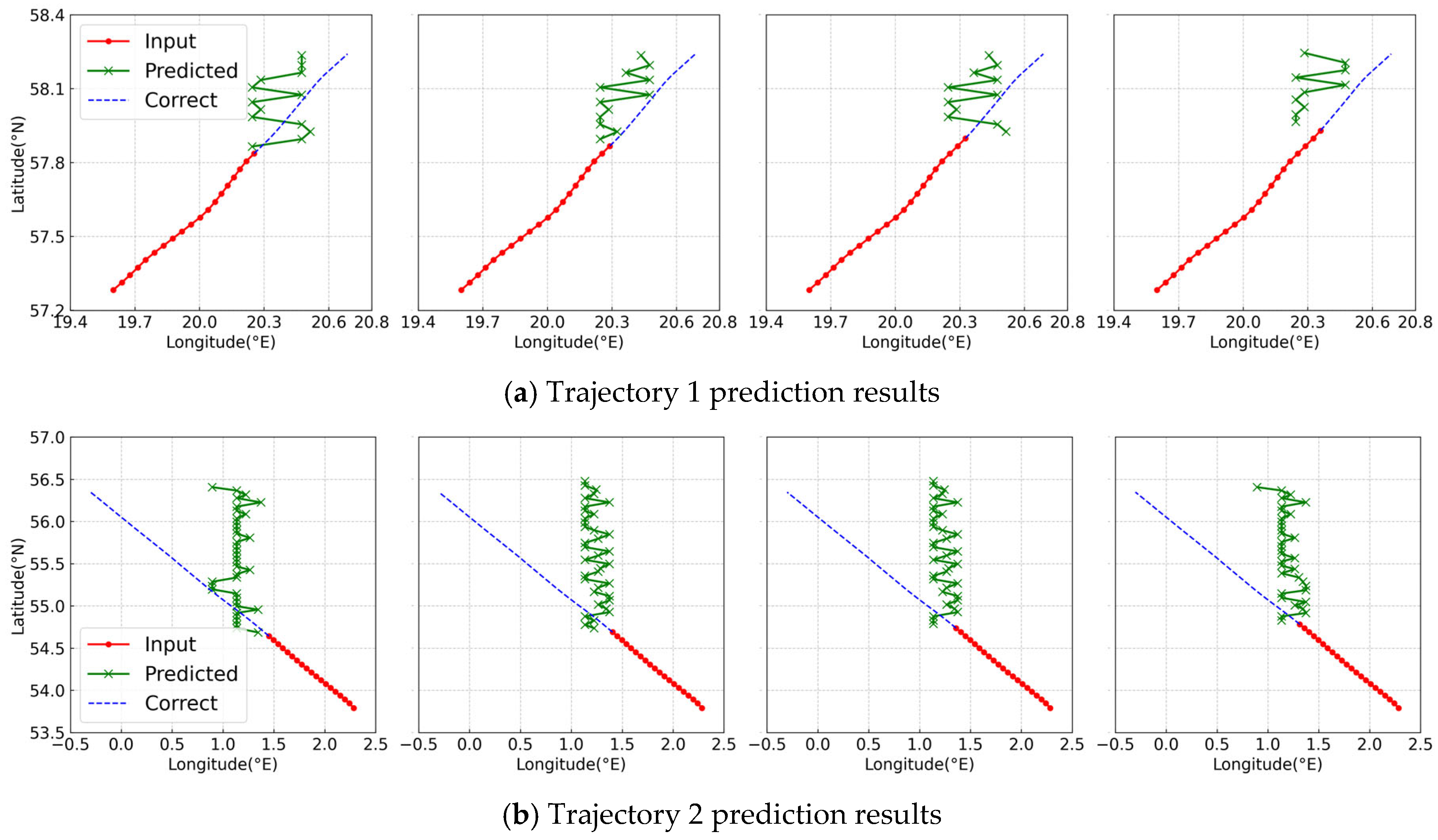
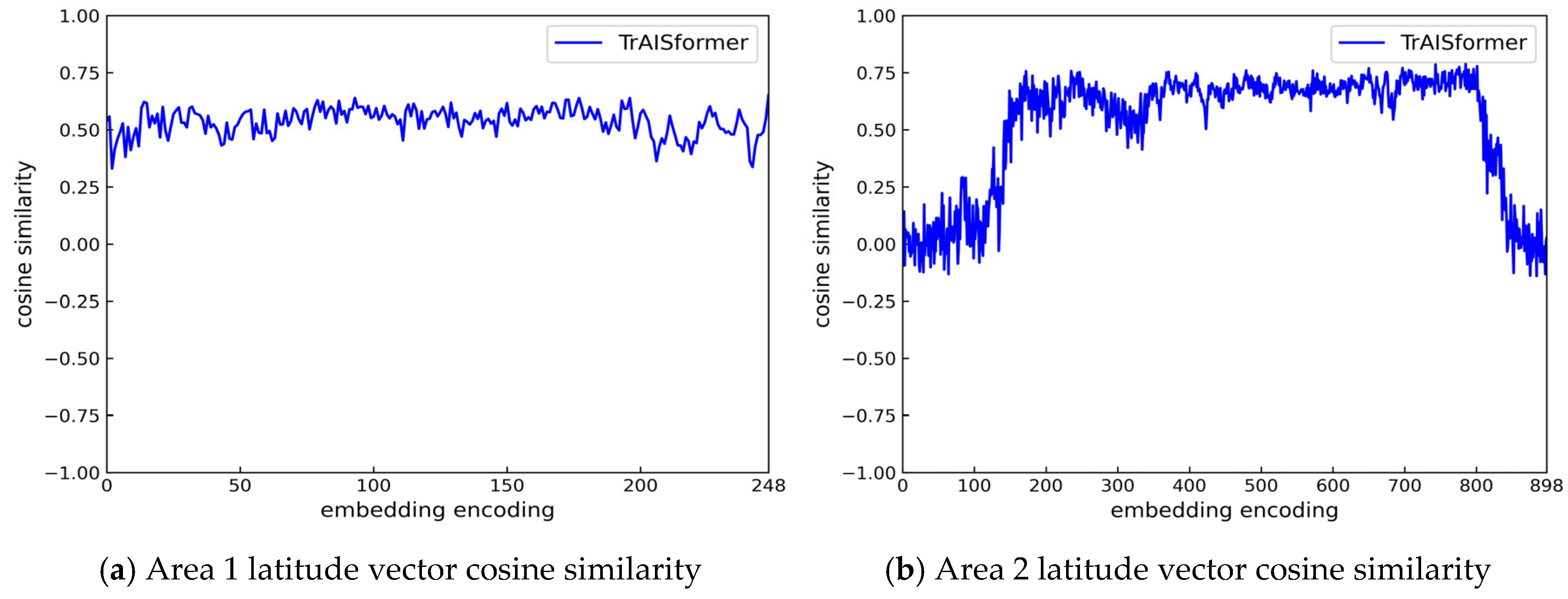


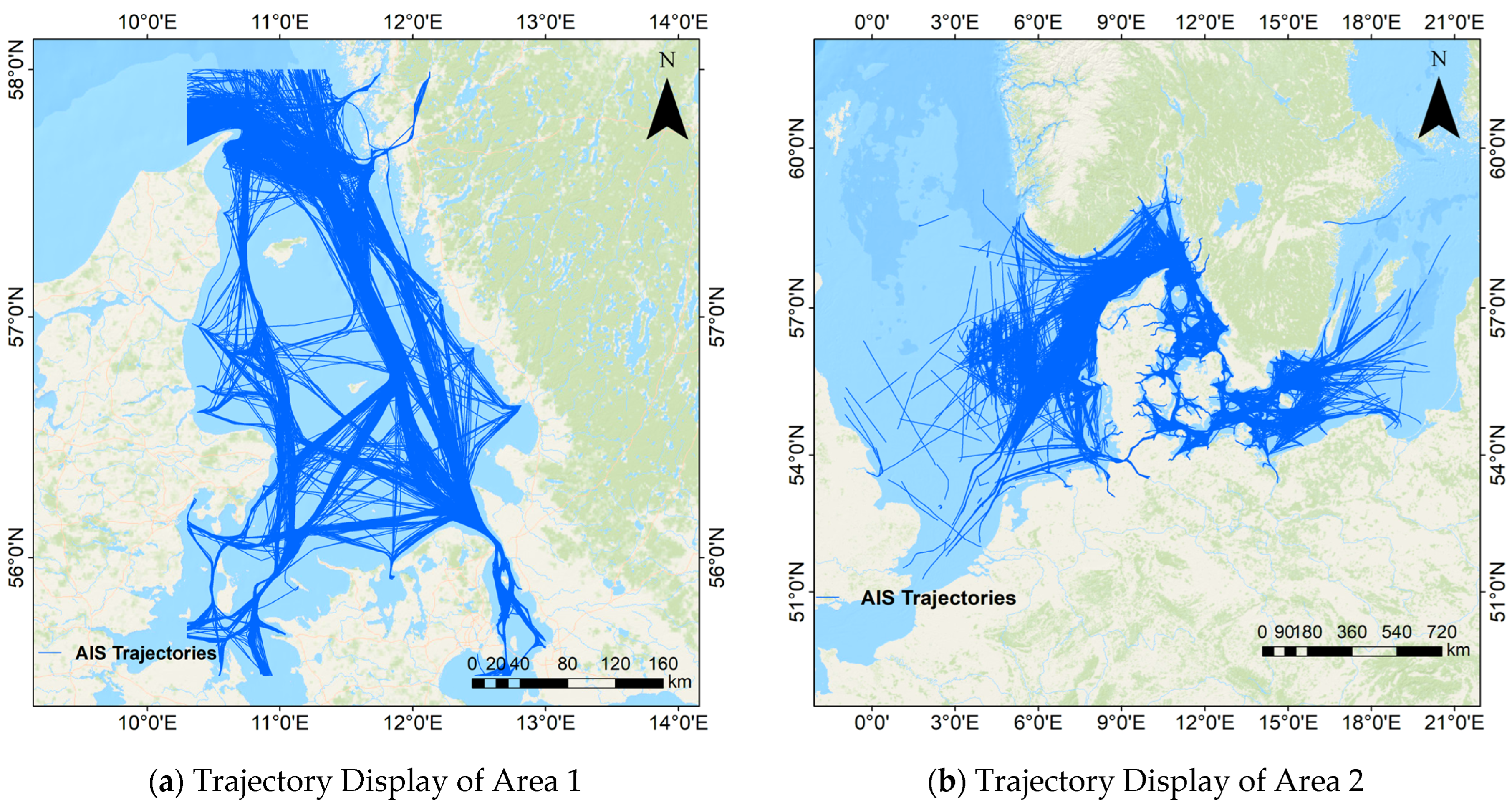

| Datasets | Time Range | Spatial Range | Data Volume |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area 1 | 2019.1.1–2019.3.31 | (55.5°, 10.3°)–(58°, 13°) | 13,679 |
| Area 2 | 2023.9.1–2024.2.29 | (51°, −1°)–(60°, 21.2°) | 78,647 |
| Model | 5 h (Area 1) | 10 h (Area 1) | 15 h (Area 1) | 5 h (Area 2) | 10 h (Area 2) | 15 h (Area 2) | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| seq2seq | 4.43 | 9.24 | 15.58 | 4.83 | 11.49 | 19.64 | Haversine |
| 5.31 | 11.48 | 22.10 | 5.50 | 13.13 | 22.51 | Fréchet | |
| seq2seq_attn | 4.46 | 8.93 | 15.68 | 4.64 | 10.72 | 18.99 | Haversine |
| 5.22 | 10.41 | 20.27 | 5.43 | 12.47 | 21.66 | Fréchet | |
| TrAISformer | 5.22 | 9.76 | 18.56 | 4.74 | 11.40 | 18.97 | Haversine |
| 6.13 | 12.88 | 30.17 | 5.31 | 12.97 | 21.76 | Fréchet | |
| MART | 4.30 | 8.07 | 14.10 | 4.19 | 9.57 | 16.04 | Haversine |
| 5.06 | 9.74 | 18.99 | 4.97 | 11.24 | 18.82 | Fréchet |
| Model | seq2seq | seq2seq_attn | TrAISformer |
|---|---|---|---|
| MART | YES | YES | YES |
| seq2seq | NO | YES | |
| seq2seq_attn | YES |
| Model | seq2seq | seq2seq_attn | TrAISformer |
|---|---|---|---|
| MART | YES | YES | YES |
| seq2seq | NO | NO | |
| seq2seq_attn | YES |
| Model | 5 h (Area 1) | 10 h (Area 1) | 15 h (Area 1) | 5 h (Area 2) | 10 h (Area 2) | 15 h (Area 2) | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Improvement | 5.22 | 9.76 | 18.56 | 4.74 | 11.40 | 18.97 | Haversine |
| 6.13 | 12.88 | 30.17 | 5.31 | 12.97 | 21.76 | Fréchet | |
| Only With DisLoss | 4.62 | 8.81 | 13.14 | 4.35 | 10.33 | 17.20 | Haversine |
| 5.27 | 9.41 | 20.51 | 5.33 | 12.90 | 22.42 | Fréchet | |
| Only With AssLoss | 4.64 | 9.26 | 20.64 | 4.67 | 10.40 | 16.74 | Haversine |
| 5.62 | 13.11 | 21.55 | 5.04 | 11.77 | 19.43 | Fréchet | |
| MART | 4.30 | 8.07 | 14.10 | 4.19 | 9.57 | 16.04 | Haversine |
| 5.06 | 9.74 | 18.99 | 4.97 | 11.24 | 18.82 | Fréchet |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, S.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y. MART: Ship Trajectory Prediction Model Based on Multi-Dimensional Attribute Association of Trajectory Points. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2025, 14, 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14090345
Zhao S, Guo W, Liu Y. MART: Ship Trajectory Prediction Model Based on Multi-Dimensional Attribute Association of Trajectory Points. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2025; 14(9):345. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14090345
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Senyang, Wei Guo, and Yi Liu. 2025. "MART: Ship Trajectory Prediction Model Based on Multi-Dimensional Attribute Association of Trajectory Points" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 14, no. 9: 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14090345
APA StyleZhao, S., Guo, W., & Liu, Y. (2025). MART: Ship Trajectory Prediction Model Based on Multi-Dimensional Attribute Association of Trajectory Points. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 14(9), 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14090345







