1. Introduction
With the rapid advancement of urbanization and the continued expansion of the outdoor advertising market, placement optimization for billboards—a critical visual medium—has attracted growing attention from both academia and industry. Billboard placement is a crucial problem in urban advertising, traffic exposure, and spatial resource allocation. In the context of smart cities and increasing data availability, optimizing billboard deployment not only improves marketing efficiency but also supports urban visual management and policy control. Billboard site selection not only influences the economic returns of advertising investments but also plays an important role in shaping the urban landscape and improving the visual quality of public spaces [
1,
2]. However, determining how to deploy billboards in a scientific and rational manner within complex urban environments, where effective communication must be achieved without causing excessive concentration or wasting resources, remains a significant challenge [
3].
Traditional approaches to billboard site selection have primarily relied on empirical judgment or simplistic traffic flow statistics [
4]; generally, they lack systematic spatial analysis and rigorous mathematical optimization methodologies. These methods often overlook the intricate topological structure of urban road networks, the spatial heterogeneity inherent in population distribution, and the mutual influences among billboards. Consequently, achieving global, optimal site selection decisions through conventional means proves difficult.
Driven by recent advancements in Geographic Information Systems (GISs) and spatial optimization techniques, a range of analytical methodologies for billboard site selection has emerged [
5,
6,
7]. Despite these advancements, existing approaches continue to present three critical limitations: (1) Firstly, these models frequently exhibit an absence of robust weighted coverage capable of incorporating spatial heterogeneity into population density. (2) Secondly, they neglect to quantitatively account for the diminishing marginal utility that arises from overlapping billboard coverage. This oversight may lead to inefficiencies in resource allocation. (3) Thirdly, the prevailing methodologies exhibit inadequate computational efficiency when implemented on substantial urban spatial datasets, thus constraining their scalability and practical applicability.
To address these challenges, this study first constructed a comprehensive optimization model incorporating population-weighted road coverage and diminishing returns of overlapping exposure. Two complementary solution methods—a greedy algorithm and a PPO-based reinforcement learning approach—were then developed to solve this model efficiently and robustly. Adopting a road coverage perspective, this method established a multi-objective optimization model that incorporates factors such as road segment length, population-derived weighting, and penalties for redundant coverage. Regarding algorithmic design, two distinct solution strategies were developed to address this optimization problem. The first is an enhanced greedy algorithm that leverages spatial indexing and parallel computing to achieve efficient large-scale computation. The second is a deep reinforcement learning (DRL) approach based on Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO), which formulates the problem as a sequential decision-making process. The agent learns adaptive deployment strategies through interacting with the environment, guided by a reward function that balances coverage effectiveness and redundancy minimization. The reason for selecting these two methods lies in their complementary characteristics. The greedy algorithm provides fast, interpretable solutions with theoretical performance guarantees under submodular conditions, making it ideal for large-scale spatial tasks. In contrast, the PPO-based reinforcement learning method enables adaptive and policy-driven decision making, offering greater flexibility in handling complex, dynamic environments. Together, these methods balance computational efficiency and adaptive strategy learning, ensuring the model’s applicability across different urban planning scenarios.
The contributions of this study can be summarized as follows:
A population density-based methodology is introduced for calculating road segment weights, enabling more accurate assessment of billboard influence by assigning differentiated importance to distinct road segments.
A geometric series-based summation approach is proposed to quantitatively model the diminishing marginal returns associated with overlapping billboard coverage.
An enhanced greedy algorithm is developed, which integrates spatial indexing and parallel-computing techniques to significantly improve the solution efficiency for large-scale multi-objective billboard site selection problems.
A DRL approach based on PPO is designed, modeling billboard placement as a sequential decision-making process and enabling adaptive and intelligent deployment strategies in complex urban environments.
The remainder of this study is organized as follows:
Section 2 introduces the research background and reviews the relevant literature.
Section 3 presents the detailed methodology, including data preprocessing, multi-objective model construction, the enhanced greedy algorithm, and the PPO-based DRL method.
Section 4 describes the experimental design and analyzes the results.
Section 5 concludes the study and discusses potential avenues for future research.
2. Related Work
2.1. Research on Billboard Site Selection
The billboard site selection problem, a significant branch of spatial location optimization research, has witnessed an evolution in its theoretical development from simple to complex approaches. Early studies primarily concentrated on the relationship between billboards and traffic flow, proposing value assessment models predicated on traffic volume and utilizing road traffic metrics as the principal indicator of billboard value [
8,
9,
10,
11]. Subsequently, this assessment framework was expanded to incorporate the duration of billboard visibility, culminating in a comprehensive evaluation structure that integrates “traffic flow + visibility duration” [
12,
13].
With advances in Geographic Information Systems (GISs) technology, GIS-based methodologies for billboard visibility analysis have progressively developed. These methods assess the advertising effectiveness of different locations by simulating the visual scenes experienced by drivers. Furthermore, research integrating eye-tracking technology has delved deeper into the correlation between billboard positioning and the allocation of driver attention, thereby furnishing a more nuanced cognitive science foundation for billboard site selection [
14,
15,
16,
17].
A key limitation of earlier research efforts was their predominant focus on evaluating the positioning of individual billboards, lacking a holistic consideration of the optimal layout of the entire billboard network. As algorithms and computational capabilities have advanced, research focus has gradually pivoted toward challenges in the comprehensive optimization of billboard networks. A notable breakthrough in this domain was the framing of billboard site selection as a Maximal Covering Location Problem (MCLP). This model seeks to maximize road traffic coverage utilizing the minimal number of billboards. Following this, the development of spatial interaction models, which account for competitive and synergistic effects between billboards, further enriched the theoretical underpinnings of billboard network optimization [
18,
19]. This theoretical progress has helped establish a robust foundation for contemporary research endeavors in billboard location optimization.
Compared with earlier works, our approach focuses on optimizing the billboard network as a whole, combining population-weighted road coverage with redundancy control.
2.2. Facility Location Problem
The problem of billboard location can essentially be viewed as a special case of the Facility Location Problem (FLP). Within this theoretical framework, the classical Maximal Covering Location Problem (MCLP) [
20,
21] centers on maximizing demand point coverage with limited facility resources. As research has developed, introducing the Maximum Expected Covering Location Problem (MEXCLP) has expanded the foundational theory; this model innovatively considers the realistic scenario of potential facility failure, rendering optimization results more robust.
Another significant milestone in theoretical development was the introduction of the concept of partial coverage [
22,
23]. This innovation allows coverage effectiveness to gradually diminish with increasing distance, rather than adhering to the “all-or-nothing” coverage pattern characteristic of traditional models. This feature aligns remarkably well with the actual situation where billboard influence diminishes with viewing distance, thus providing a more practical theoretical foundation for billboard location research.
In recent years, research emphasis has progressively shifted toward facility location optimization problems based on road networks. Road network-based coverage maximization models have transcended traditional point-based coverage conceptualization by treating continuous road segments as coverage objects. This transformation better corresponds with billboards’ real-world coverage characteristics. Further theoretical advancement has been seen in the proposed weighted road coverage models [
24,
25,
26], which comprehensively consider factors such as travel time and traffic flow within road networks, enabling a more thorough and precise evaluation of coverage effectiveness. These theoretical progressions have systematically constructed a framework transitioning from point to line coverage, from binary to continuous attenuation coverage, and from static to dynamic coverage, thus providing a solid methodological foundation for road network-based billboard coverage models.
Our method extends classical FLP models by introducing continuous road coverage and diminishing effects, making billboard influence modeling more realistic.
2.3. Application of Greedy Algorithms in Location Problems
Owing to their simplicity and efficiency, greedy algorithms have been widely applied in facility location problems [
27,
28]. Early research confirmed that greedy algorithms could guarantee fixed-ratio approximation solutions to global optima in specific location problems, providing a theoretical foundation for their application. Subsequent theoretical breakthroughs demonstrated that for objective functions with submodular properties greedy algorithms could guarantee a
approximation solution. This significant conclusion has provided robust theoretical support for applying greedy algorithms in coverage-type problems.
Greedy algorithm improvements have progressed through several critical stages. First was the introduction of Lazy Evaluation techniques [
29], which significantly enhanced algorithm efficiency by dispensing with redundant calculations, making them particularly suitable for large-scale location problems. Second was the integration of greedy algorithms with submodular function optimization theory, forming adaptive algorithms that further improve adaptability and effectiveness in complex scenarios. With the development of big data technologies and parallel-computing architectures in recent years, greedy algorithms have encountered new development opportunities. The proposal of parallel greedy algorithms based on the MapReduce framework [
30] significantly improved solution efficiency for large-scale problems, making it possible to process location problems containing millions of candidate points. These technological advancements have provided efficient and feasible algorithmic tools for solving billboard location problems in practical applications.
Achieving a balance between algorithm complexity and optimization effectiveness represents the core issue in greedy algorithm research. Theoretical studies have demonstrated that these algorithms can reduce time complexity—from exponential to polynomial—in many practical scenarios while ensuring solution quality, making them the preferred algorithms for large-scale location problems. These theoretical and technological advancements have provided an important foundation for developing efficient billboard location optimization algorithms.
Beyond the traditional greedy approaches, we incorporate submodular optimization with PPO-based learning to enhance adaptability in complex urban environments.
2.4. Application of Reinforcement Learning in Location Problems
In recent years, reinforcement learning (RL), a learning method based on the interaction between agents and environments, has been widely applied to various optimization problems. Particularly in Facility Location Problems (FLPs), the application of reinforcement learning has demonstrated tremendous potential [
7,
31,
32]. Traditional facility location methods typically rely on heuristic algorithms or mathematical programming, but these approaches are often constrained by problem scale and computational complexity. Through simulating agents’ decision-making processes in an environment, reinforcement learning can provide more flexible and efficient optimization solutions when dealing with complex constraints and dynamic environments.
The application of reinforcement learning in location problems typically proceeds through the following steps: First, the state space of the problem is established, which represents the different situations in which the agent finds itself. In location problems, states can represent the current positions of billboards or facilities, areas already covered, resource allocation status, and so forth. Next, the action space is defined, encompassing the actions available to the agent. In billboard location problems, actions might involve selecting a new location or adjusting existing layouts. Subsequently, a reward function is designed to measure the contribution of current actions toward objectives. For location problems, reward functions are typically designed according to objectives such as maximizing coverage area, minimizing costs, or maximizing advertising effectiveness [
33,
34,
35,
36].
During the reinforcement learning process, agents continuously interact with the environment, obtain feedback signals, and update their strategies based on these signals. Agents gradually learn how to maximize returns from the environment through policy gradient or value function methods. For example, in billboard location problems, when selecting positions at each step, agents not only consider current coverage effectiveness but also determine whether existing choices might lead to resource waste or coverage redundancy, thereby optimizing selection strategies. Through multiple iterations, reinforcement learning can identify globally optimal solutions within large-scale spatial data, avoiding the local optima issues that traditional methods might encounter.
Compared to traditional methods, the advantage of reinforcement learning lies in its ability to address location problems with complex constraints and non-linear objectives. Reinforcement learning models do not need to rely on manually established rules or prior knowledge; they can self-learn through interaction with the environment, gradually discovering optimal solutions. Furthermore, reinforcement learning can handle dynamically changing environments, adapting to future demand variations and resource allocation adjustments, demonstrating strong adaptability and flexibility.
Although the application of reinforcement learning in location problems is still being researched, its potential, both in theory and practice, has gained widespread recognition [
37,
38]. Through reinforcement learning, location problems can achieve optimization across broader ranges and more complex environments, providing more intelligent and efficient decision support for advertising resource allocation, urban facility construction, and related domains.
2.5. Research Gaps and Contributions of This Paper
Despite certain advancements having been achieved in billboard location optimization research, the following gaps persist: (1) The majority of studies concentrate on either traffic flow or population distribution, yet rarely consider both factors concurrently. (2) There is also a lack of systematic quantification of the marginal effects associated with overlapping billboard coverage. (3) Algorithm computational efficiency requires enhancement, particularly when processing large-scale urban road networks.
Addressing these gaps, the primary contributions of this research are as follows: (1) We propose a comprehensive optimization model based on both road networks and population distribution, integrating road coverage with population weights. (2) We design a geometric series summation formula to quantify the diminishing marginal effects characteristic of overlapping coverage. (3) We develop an efficient greedy algorithm incorporating spatial indexing and parallel computation, suitable for processing large-scale urban spatial data. (4) We empirically validate the effectiveness of the proposed methodology through case studies, thereby providing scientific decision support for urban advertising resource planning.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Mathematical Modeling
The optimization problem addressed in this study was to determine the optimal placement of a fixed number of billboards from a set of candidate locations, in order to maximize the total population-weighted road coverage. This objective considered both the physical length of each road segment and the population density of its surrounding area, while also accounting for the diminishing marginal effectiveness of repeated exposures through overlapping coverage.
This research constructed a mathematical model for billboard location optimization based on road networks and population distribution. The model aims to select the optimal billboard layout from candidate locations to maximize weighted road coverage effectiveness. This weighted road coverage maximization problem with diminishing returns is a generalization of the classical Maximum Coverage Problem (MCP), which is known to be NP-hard. Our formulation introduces additional complexity through population-based weighting and geometric decay penalties for redundant exposure. Consequently, finding an exact solution becomes computationally infeasible for large-scale instances, which motivates the use of heuristic or learning-based optimization strategies. The key parameters and variables in the model are defined as follows:
R: Set of all road segments, ;
: Length of road segment r (in meters);
: Population weight of road r, reflecting population density in surrounding areas;
P: Set of all candidate billboard locations, ;
k: Number of billboards to be selected;
: Binary variable indicating whether a road segment r is covered by the i-th billboard, valued as 0 or 1;
: Repeated coverage penalty factor, , used to quantify the diminishing marginal effect characteristic;
d: Effective coverage radius of billboards, set as 300 m in this study.
The objective function constructed in this research aims to maximize the weighted coverage effect of the billboard network while considering the diminishing marginal effect of repeated coverage:
Note: The summation applies only to road segments actually covered by at least one billboard. For segments not covered by any billboard (i.e., all ), the contribution to the objective is defined as zero. Furthermore, the indices are assumed to be ordered according to coverage sequence and only valid when . In practice, this formulation is implemented as an ordered list of actual coverage events for each road segment.
When , the model completely ignores repeated coverage; when , the model considers repeated coverage as fully effective. In practical applications, the penalty factor is typically set between 0.3 and 0.8; this research selected as the standard value, based on experimental analysis.
For each road segment
r, its contribution to the objective function can be expressed as
This expression can be interpreted as follows: the first coverage obtains the full value ; the second coverage obtains a value of ; the third coverage obtains a value of ; and so forth. This design reflects the marginal diminishing property of repetitive coverage on advertising effectiveness; initial exposure exerts the maximum impact on the audience, with subsequent repeated exposures progressively diminishing in effect.
The mathematical transformation of the objective function formula can be simplified into a geometric series summation form. Assuming road segment
r is covered
c times, its contribution to the objective function can be expressed as follows:
Utilizing the geometric series summation formula, this can be further simplified to
When
(i.e., when marginal diminishing effects are not considered), the formula simplifies to a linear form:
This simplification renders the computation of the objective function significantly more efficient, particularly when processing large-scale road networks. However, in this study, we adopted in all our experiments to retain the diminishing-return effect of repeated exposures. The simplified form with is presented only to illustrate the model’s flexibility and potential for improved computational efficiency in future large-scale deployments.
The constraints of the model are as follows:
- (1)
The total number of selected billboards shall not exceed the predetermined value
k:
where
is the binary decision variable indicating whether candidate location
p is chosen for a billboard.
- (2)
Billboards may only be placed at predefined locations within the candidate set:
- (3)
Road segment
r is considered covered by billboard
p if the distance between
r and
p does not exceed the coverage radius
d:
where
indicates whether billboard
p covers road segment
r, and where
denotes the distance from point
x on road segment
r to billboard
p.
This mathematical model comprehensively considers road length, population distribution, and the marginal effects of repeated coverage, providing a theoretical foundation for billboard location optimization. Through the introduction of the population weight factor , the model more accurately evaluates the potential influence of billboards in different areas; through the introduction of the repeated coverage penalty factor , it reasonably quantifies the diminishing marginal effect characteristic of when multiple billboards repeatedly cover the same road segment.
To better illustrate the overall process,
Figure 1 presents a workflow diagram outlining the key components of our approach, including data preparation, model construction, and optimization via two algorithms.
3.2. Modeling Assumptions
This model adopts the following assumptions:
- (1)
Each billboard exerts full influence on road segments within a 300 m radius;
- (2)
Road segments are treated as homogeneous units with no internal spatial variation;
- (3)
The effect of multiple overlapping billboards is modeled as diminishing returns using a geometric series formulation. While this study modeled diminishing returns via a geometric penalty for repeated coverage, it did not incorporate explicit distance-based partial coverage. This simplification was adopted to maintain computational tractability in large-scale settings. Future work may consider integrating continuous decay functions to further refine spatial influence modeling;
- (4)
Population distribution remains static during deployment.
3.3. Greedy Algorithm
This research employed an improved greedy algorithm to solve the billboard location optimization problem. With its simplicity and efficiency, the greedy algorithm has become a common method for addressing combinatorial optimization problems [
39,
40]. In the application scenario of this research, the standard greedy algorithm was extended and optimized to process large-scale spatial data and complex coverage calculations. The core concept of the greedy algorithm is to select the current optimal candidate point at each step—specifically, the billboard location that provides the maximum coverage gain. The overall workflow is illustrated in
Figure 2. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
Pre-calculation phase: To reduce repetitive calculations, coverage situations for all candidate points are initially calculated. Spatial indexing technology is utilized to rapidly determine the road segments potentially covered by each candidate point. The road and weighted coverage lengths covered by each candidate point are calculated, with results cached to avoid subsequent redundant calculations.
Greedy selection phase: Candidate points that provide the maximum marginal gain are iteratively selected. The coverage situation of already-selected billboards is considered for each candidate point, applying the repeated coverage penalty factor. The candidate point providing the current maximum effective coverage gain is selected, the new road coverage is calculated, and the selected location is removed from the candidate set.
Final calculation phase: The geometric series summation formula is employed to calculate the final value of the objective function.
This research repeatedly optimized the greedy algorithm to address the characteristics of large-scale spatial data processing:
Batch processing and parallel computation: During the pre-computation phase, candidate points were divided into small batches for processing, with parallel-computing techniques employed to accelerate the processing of each batch. The implementation specifically utilized Python’s joblib library, leveraging multi-core CPUs for parallel task execution. The batch processing mechanism reduced memory pressure, while parallel computation significantly enhanced processing speed.
In the Wuhan case study, when processing 3971 candidate points and 25,251 road segments, the optimized implementation reduced computation time by approximately 80% compared to a baseline version that performed all calculations sequentially, without batch processing, parallelism, or result caching. The baseline was a naïve single-threaded approach using standard Python loops. These performance gains were observed under the same hardware and data conditions. While the full codebase has not been publicly released, we are happy to share the implementation upon request to support reproducibility.
Caching and fault-tolerance mechanisms: To enhance algorithm robustness, multi-level caching and fault-tolerance mechanisms were implemented: the calculation results were stored in JSON cache files to avoid recalculation after the program restarted; a temporary progress-saving mechanism enabled long-running calculations to resume from interruption points; and backup file strategies prevented data loss due to unexpected interruptions during file writing operations.
Memory optimization: Efficient data structures were employed to reduce memory consumption. NumPy arrays stored the road lengths and coverage counts, improving numerical calculation efficiency; dictionary structures stored the sparse coverage relationships, reducing memory usage; and periodic garbage collection was implemented to release memory resources that were no longer required.
Notably, although the greedy algorithm does not guarantee a globally optimal solution it is known to achieve a
approximation (approximately 63.2%) of the global optimum for problems with monotone submodular objective functions [
41,
42]. In this research, while the objective function—population-weighted road coverage with diminishing returns—exhibited marginal gain behavior resembling submodularity, we have not formally proved that it satisfies submodular or approximately submodular properties. Therefore, we do not claim a theoretical approximation guarantee. The greedy algorithm is employed as a practical heuristic that performs well empirically and supports large-scale spatial optimization through computational enhancements.
3.4. Proximal Policy Optimization
Reinforcement learning methods have been increasingly applied to optimization problems. The Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm, a common policy gradient method in deep reinforcement learning, has achieved excellent results across multiple domains, due to its stability and efficiency [
43,
44,
45]. This research attempted to apply the PPO algorithm to the billboard location optimization problem.
We modeled the billboard location problem as a reinforcement learning problem. The environment consists of the city’s road network, population distribution, and candidate billboard locations, while the agent’s task is to select billboard positions to maximize weighted advertising coverage effectiveness. The objective of reinforcement learning is to learn optimal policies through agent–environment interactions.
In our implementation, the PPO-based optimization framework consists of four main components. First, the environment is constructed, using spatial data on candidate billboard locations and road segments, with coverage relationships pre-computed. Second, the state representation includes features such as current coverage status, population distribution, and spatial distance measures. Third, the action space is defined as the remaining candidate locations, from which the agent selects a new billboard at each step. Finally, the reward function is designed to reflect the marginal gain in weighted coverage, penalized by redundant exposure. The agent interacts with the environment in multiple episodes, iteratively refining its policy via gradient ascent to maximize cumulative reward.
State space: The state space consists of three elements: the currently selected billboard locations, the coverage status of individual road segments, and the redundancy in coverage across billboards. Specifically, each state encompasses the coverage status of candidate billboard locations, the weighted coverage status of road segments, and the number of road segments covered by each billboard.
Action space: The action space involves selecting a new candidate billboard location. If a location has already been chosen, its action value is set to 0 (indicating an invalid action). Otherwise, the agent selects an unoccupied candidate location.
Reward function: The reward function is designed to capture the weighted coverage gain from the selected billboard location while incorporating a redundancy penalty factor to discourage over-exposure. This function prioritizes higher gains for newly covered road segments and imposes diminishing returns for repeated coverage, meaning that the incremental utility decreases as the frequency of overlap increases. When selecting a new billboard location, the reward function is defined by the weighted road length coverage and the potential impact of the chosen billboard:
Policy and value networks: The PPO algorithm employs policy and value networks, updating policies by optimizing objective functions. The policy network outputs a probability distribution for selecting billboard locations, while the value network estimates the value of the current state. The PPO algorithm uses a clipped objective function for updates, ensuring that each update does not cause excessive policy changes, thereby guaranteeing a stable training process.
PPO training: Through multiple training iterations, the agent learns to select optimal billboard locations across various states, aiming to maximize the effectiveness of weighted road coverage while avoiding excessive redundancy and resource over-concentration. The training process employs reward signals to update the policy, allowing the agent to adaptively choose the most suitable billboard locations based on real-time coverage conditions.
3.5. Model Innovations and Limitations
Innovations. The proposed model introduces several innovations. First, it integrates population-weighted road segment coverage into the billboard location problem, allowing for finer-grained influence estimation based on spatial population heterogeneity. Second, it incorporates a geometric decay function to reflect the diminishing marginal utility of overlapping billboard exposure, enhancing resource allocation efficiency. Third, the model supports dual-path optimization using both greedy approximation and reinforcement learning, combining interpretability with adaptability.
Limitations. Despite its strengths, the model also has limitations. It assumes a static population distribution and does not account for temporal variations in urban mobility. The geometric decay formulation may oversimplify more complex viewer behavior responses to repeated exposure. Additionally, visibility constraints and occlusions are not explicitly modeled, which may affect the real-world applicability of the deployment results.
4. Experiments and Results
This study focused on the area within the third ring road of Wuhan, China. The experimental dataset included road network, candidate billboard location, administrative boundary, and population distribution data. The experiments were performed on a computational system equipped with an Intel Core i7 processor and 32 GB of RAM. The implementation relied on Python libraries, including GeoPandas, NumPy, Matplotlib, Rasterio, and Joblib. To manage large-scale spatial data, the experimental design incorporated both batch processing and parallel-computing techniques, as well as pre-computation result caching mechanisms and memory optimization strategies.
To verify the effectiveness of the PPO algorithm in billboard location optimization problems, we employed the same experimental data used for the greedy algorithm: Wuhan city’s road network, population distribution, and candidate billboard locations. We performed billboard location optimization using the improved greedy and PPO algorithms, comparing their results.
Greedy algorithm experiment: In accordance with the steps outlined in the previous section, the greedy algorithm iteratively selects the billboard location that maximizes immediate coverage gain at each step, ultimately producing an optimized billboard layout.
PPO algorithm experiment: The PPO algorithm is utilized to train an agent that interacts with its environment, learning an optimal strategy for billboard placement guided by a reward function. Upon completing training, the agent is evaluated in a testing environment to select and optimize billboard locations based on the learned policy.
Although this study focused on greedy and reinforcement learning methods, future research could incorporate comparisons with other established optimization techniques, such as Genetic Algorithms or Mixed Integer Programming, to further validate the model’s generalizability.
4.1. Data Preparation and Preprocessing
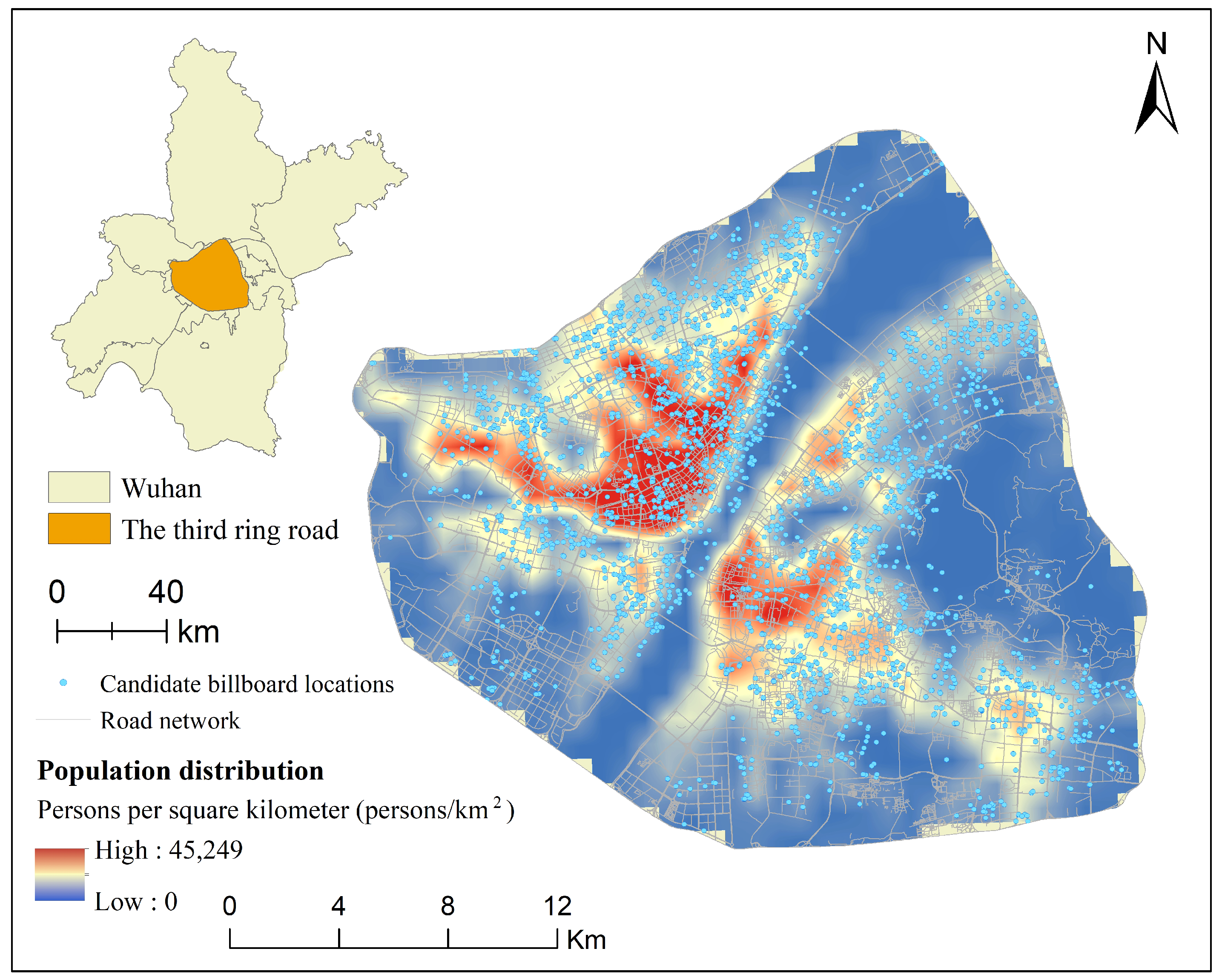
Our study area was located within the third ring road in Wuhan, China (as shown in
Figure 3). We constructed a spatial database comprising three essential categories: road network, population distribution, and candidate billboard locations. The road network data were derived from the Wuhan Transportation Department’s 2023 road network spatial database, which contains 25,251 road line features stored in ESRI Shapefile format. During data preprocessing, topological relationship repairs were implemented to ensure network integrity, and a delayed loading mechanism for spatial indexing was designed, effectively reducing memory consumption during system initialization.
Population distribution data were acquired from the LandScan population density raster data for Wuhan in 2023, which were provided by the Cubic Data Society, with a spatial resolution of 100 m. The values represent population density (persons/km
2), and the value “45,249” in the legend of
Figure 3 refers to the maximum observed population density in the study area. This study proposes a road weight calculation method based on population density, employing logarithmic normalization to convert population density values into weights ranging from 1 to 10. Specifically, regions with zero population density are assigned a baseline weight of 1, areas with median population density receive weights of approximately 5.5, and regions reaching or exceeding three times the median are assigned weights of 10. This design ensures reasonable weight allocation for road segments across different population density areas, more accurately reflecting the potential influence of billboards in various regions.
The candidate billboard location data, totaling 3971 candidate points, were based on potential advertising site information provided by Wuhan’s Planning Department. During data processing, areas unsuitable for advertising placement were excluded according to urban planning regulations and advertising standards, and an effective coverage radius of 300 m was determined for each billboard, based on advertising visibility research. This parameter setting was founded on research findings regarding optimal visual perception distances for pedestrians and drivers, balancing advertisement content readability and coverage range. While this study used a fixed value of 300 m, for experimental consistency, the model itself supports flexible adjustment of the coverage radius parameter. The 300 m value was, thus, not embedded in the mathematical formulation but was treated as an empirical setting that could be adapted or tested in future applications.
We designed a multi-level data-integration-and-optimization strategy to process large-scale spatial data efficiently. First, spatial reference systems for all data are unified to eliminate projection errors in calculations. Second, efficient data structures are employed to store road lengths, candidate point coordinates, and population weights to address memory usage concerns, while lightweight structures are designed to represent coverage relationships. Regarding computational efficiency, we implemented data batch processing, spatial index optimization, and parallel-computing techniques, significantly enhancing the system’s capacity to process large-scale spatial data. Additionally, multi-level caching mechanisms and progressive computation strategies were designed to effectively address potential interruption issues during extended computation processes.
The aforementioned data preparation and preprocessing work provided high-quality input data for subsequent billboard location optimization algorithms, establishing a solid foundation for solving large-scale spatial optimization problems.
4.2. Optimization Results
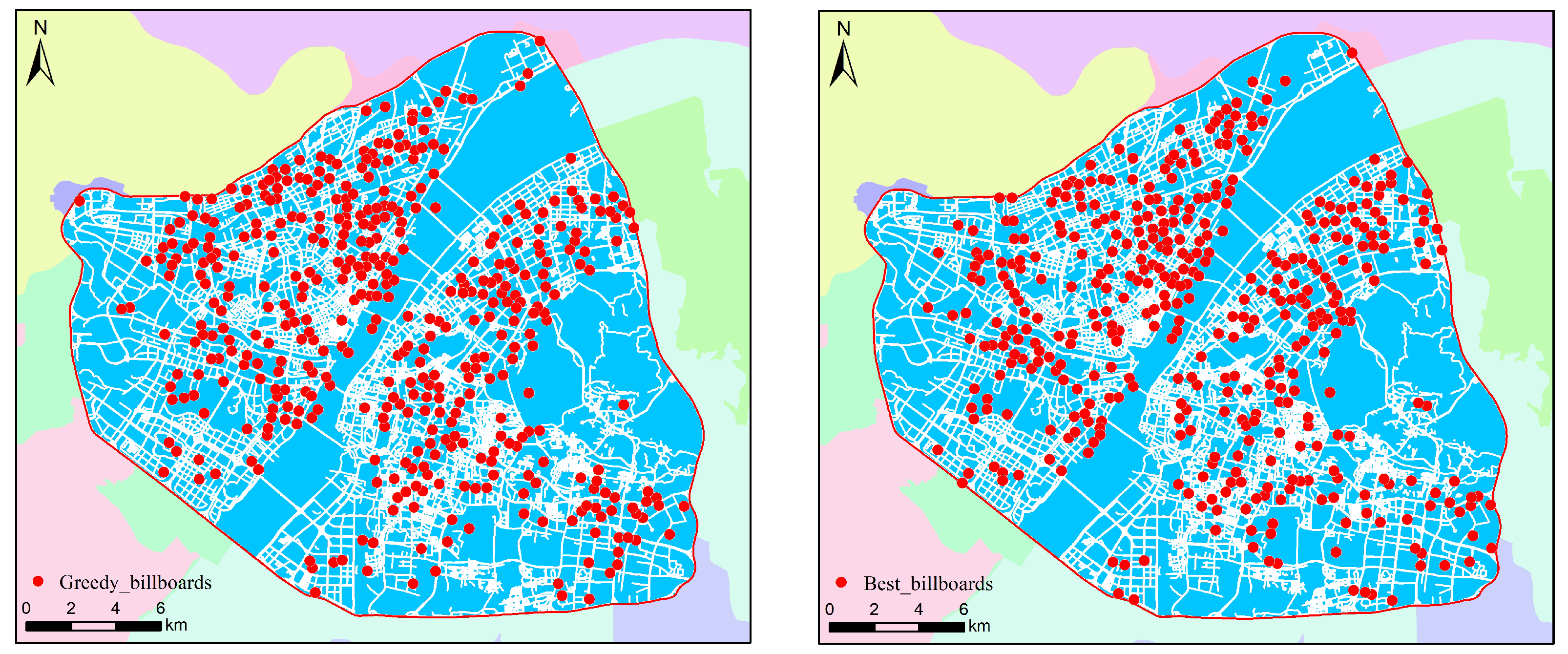
This research optimized the billboard location problem using the greedy and PPO algorithms. We implemented a constraint prohibiting repeated coverage within 300 m and selected 500 billboard locations. The greedy algorithm ultimately selected 500 billboard positions, covering the city’s road network while maximizing the weighted road length. The total weighted population was 388,864,270.75, with the results indicating that the greedy algorithm prioritized areas of higher population density, thereby effectively enhancing weighted road coverage effectiveness. Among the 500 selected billboard locations, the minimum weighted population was 714,254.31, the maximum was 877,264.69, and the average was 777,728.54. These data demonstrate that the greedy algorithm concentrates more resources in high-population-density areas when selecting billboards, yielding notably optimized effectiveness.The computed results are illustrated in
Figure 4, where
Figure 4a presents the spatial distribution obtained by the greedy algorithm, and
Figure 4b shows the layout generated by the PPO algorithm.
When performing billboard location optimization, the PPO algorithm adopts a reinforcement learning approach, continuously adjusting selection strategies through multiple training rounds. During PPO’s optimization process, the algorithm considers coverage benefits and repeated coverage penalties, learning optimal strategies through feedback mechanisms. Unlike the greedy algorithm, the PPO algorithm aims to achieve a more balanced billboard distribution, avoiding excessive concentration in particular areas. The PPO algorithm can better address repeated coverage issues through multiple training rounds while covering weighted road length, optimizing the overall billboard layout. Although this algorithm requires a longer computation time, its optimization effectiveness surpasses that of the greedy algorithm, achieving a more balanced billboard distribution.
4.3. Spatial Distribution Characteristics
The spatial distribution characteristics of the billboards differed between the two algorithms. As the greedy algorithm prioritized road segments with a greater current gain during each selection, the billboard locations it selected were often concentrated in areas of higher population density. This observed spatial concentration of billboard placement—particularly under the greedy strategy—reflects the inherent spatial heterogeneity of urban structure. Prior studies have shown that both population and street networks in cities often exhibit power-law or heavy-tailed distributions [
46]. Such non-uniformity may reinforce spatial inequality in resource allocation when using purely gain-driven optimization methods. Our results align with this theoretical insight, as the greedy algorithm tended to over-concentrate billboards in highly populated or central areas.
While this strategy maximizes weighted road coverage, it can lead to an over-concentration in specific zones, potentially causing imbalanced coverage effectiveness. For example, billboard density may become disproportionately high in city centers or densely populated regions, while remaining sparse in remote or low-population areas. Although this distribution may yield short-term advertising efficiency, it compromises long-term equitable resource allocation.
In contrast, through reinforcement learning approaches, the PPO algorithm can balance billboard selection across multiple training cycles, resulting in more uniform billboard distribution. Through repeated interactions with the environment, the PPO algorithm can avoid excessive concentration when selecting billboard locations and effectively utilize the potential influence of different areas, thereby achieving more balanced coverage. Due to the long-term optimization capabilities of reinforcement learning algorithms, the PPO algorithm can cover more areas and enhance overall advertising dissemination effectiveness, avoiding the resource waste phenomena that can occur in local optima with the greedy algorithm.
4.4. Algorithm Performance Analysis
For performance analysis, we focused on two key aspects: computational time and optimization effectiveness. The following evaluation examines the results of both the greedy and PPO algorithms, in these regards, using empirical data.
The greedy algorithm’s computation time is relatively short. In the experiments, it required approximately 7 min to select 500 billboard locations, primarily because it only performs local selection at each step, without requiring multiple rounds of optimization and training.
In contrast, the PPO algorithm requires multiple training sessions and iterative optimization to reach the optimal solution, resulting in a significantly longer computation time that that of the greedy algorithm. In this experiment, the PPO algorithm’s computation time was 1 h, as it not only needed to complete the model training but also required strategy adjustment and optimization based on environmental feedback.
The total weighted population is a crucial indicator for measuring billboard optimization effectiveness. The greedy algorithm prioritized areas with a larger current weighted population when selecting billboards, resulting in a total weighted population of 388,864,270.75. Although this algorithm can quickly provide a good solution, its excessive concentration in high-population-density areas leads to insufficient coverage in some low-population areas.
Through multiple rounds of training and optimization, the PPO algorithm was able to consider a broader range of areas, outperforming the greedy algorithm, in terms of weighted population coverage. The PPO algorithm’s final total weighted population was 392,115,423.52, slightly higher than the greedy algorithm. This indicates that the PPO algorithm not only improves coverage effectiveness in high-population areas during the optimization process but also optimizes coverage in low-population areas, resulting in more balanced overall weighted population coverage.
To quantitatively evaluate the spatial distribution balance, we computed the Gini coefficient of billboard locations across 1 km
2 grid cells covering the study area. A lower Gini value (closer to 0) indicates greater spatial equity. As shown in
Table 1, the PPO algorithm achieved a significantly lower Gini coefficient (0.41) compared to the greedy approach (0.62), confirming its ability to distribute billboards more evenly across urban spaces while avoiding over-concentration in high-density zones.
From
Table 1, it can be observed that both the greedy and PPO algorithms selected 500 billboards. However, the PPO algorithm had a slightly better performance, in terms of weighted population coverage effectiveness, particularly in total, average, minimum, and maximum weighted population. This indicates that the PPO algorithm not only improves coverage effectiveness in high-population areas but also maintains high coverage levels in low-population areas, optimizing billboard layout balance.
5. Conclusions
Research conclusion. This study addresses the billboard site selection problem in urban environments by constructing a multi-objective optimization framework that integrates road network topology and population distribution data. Two independent optimization methods were developed. The first is an enhanced greedy algorithm that significantly improves scalability and computational efficiency in solving large-scale spatial optimization problems through the integration of spatial indexing, batch processing, parallel computation, and caching mechanisms. The second is a DRL approach based on PPO, which formulates billboard placement as a sequential decision-making task and enables the agent to learn optimal deployment strategies through cumulative reward maximization. Empirical experiments conducted in Wuhan validated the effectiveness of the proposed methods. The enhanced greedy algorithm successfully selected 200 billboard sites from 3971 candidate locations, achieving a substantial reduction in resource redundancy and improving the spatial equity of advertising coverage. Meanwhile, the PPO-based DRL method demonstrated the ability to dynamically adjust deployment strategies based on simulated environmental feedback, showing potential for future application in real-time adaptive billboard planning. The experimental results indicate that the greedy algorithm excels in fast, high-impact deployment in dense urban zones, while PPO demonstrates superior adaptability and coverage balance across varied population regions. These findings highlight a practical trade-off between computational efficiency and long-term spatial equity, suggesting that hybrid strategies combining both paradigms may offer promising avenues for future deployment frameworks.
Advantage and limitation. The key advantages of the proposed approach include its population-sensitive design, explicit handling of redundant exposure through diminishing return modeling, and adaptability via two complementary optimization paths. However, the current model assumes static population distribution and does not account for billboard visibility or dynamic traffic flows. These simplifications may limit real-world accuracy in certain deployment scenarios.
Application scope. The proposed framework is applicable to billboard placement and similar resource deployment problems in urban spatial planning, especially in data-rich environments. It can be extended to applications such as public facility siting, environmental sensor placement, or electric vehicle charging station layout, where spatial coverage and demand heterogeneity are key concerns.
Future work. Future research should consider incorporating real-time or dynamic population data, extending the framework to handle multi-objective trade-offs (e.g., cost, equity, and coverage, simultaneously) and exploring more advanced optimization algorithms, such as metaheuristic methods or more sophisticated DRL architectures. Expanding the application of the proposed framework to broader facility locations and resource deployment problems also presents promising directions. With the continuous advancement of computing technologies and urban data infrastructures, billboard site optimization research is expected to evolve toward more intelligent, adaptive, and comprehensive systems.