Built-Up Surface Ensemble Model for Romania Based on OpenStreetMap, Microsoft Building Footprints, and Global Human Settlement Layer Data Sources Using Triple Collocation Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
- –
- Preprocess: We align the data sources on the common 10 m grid and settlement mask, rasterize the OSM/MSBF sources, and center each source by removing its settlement mean. Centering isolates covariation around the local signal and prevents mean offsets from biasing scale/variance estimates.
- –
- Estimate scaling: Using ETC on the centered triplet, we estimate per-source scale factors that map each input to a common latent signal scale. These factors correct systematic amplitude differences (e.g., under/overestimation) before any weighting.
- –
- Estimate errors with correlation: We then apply CTC to the rescaled triplet to obtain error variances and the cross-covariance term that captures known dependence between the GHS and MSBF datasets. This yields a settlement-specific error covariance matrix.
- –
- Compute BLUE weights: for pixels where all three sources are non-zero, we compute BLUE weights by inverting the error covariance. This provides data-driven weights and a combined built-up estimate on the common scale.
- –
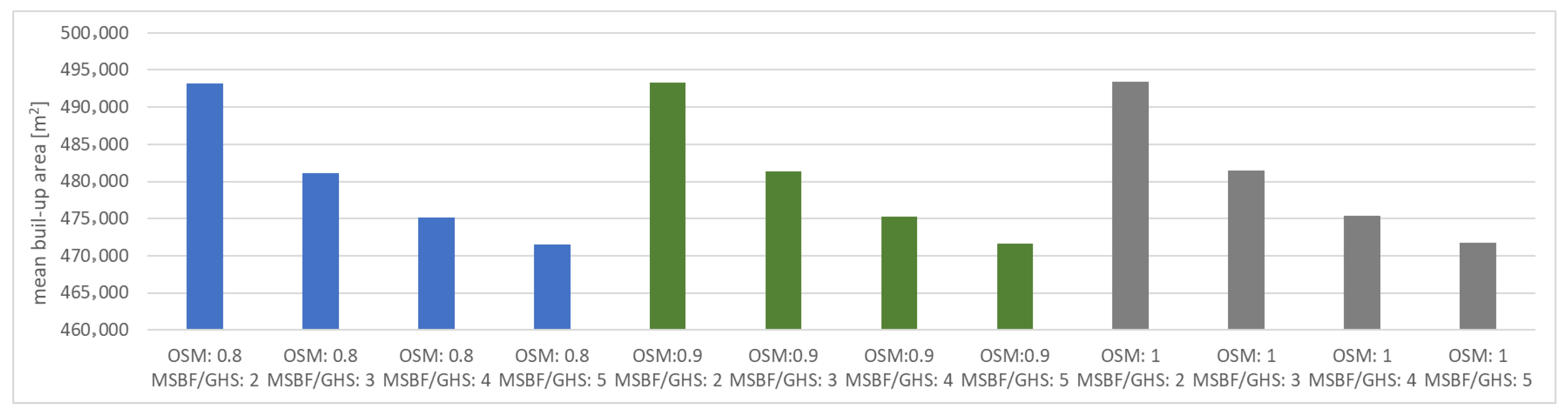
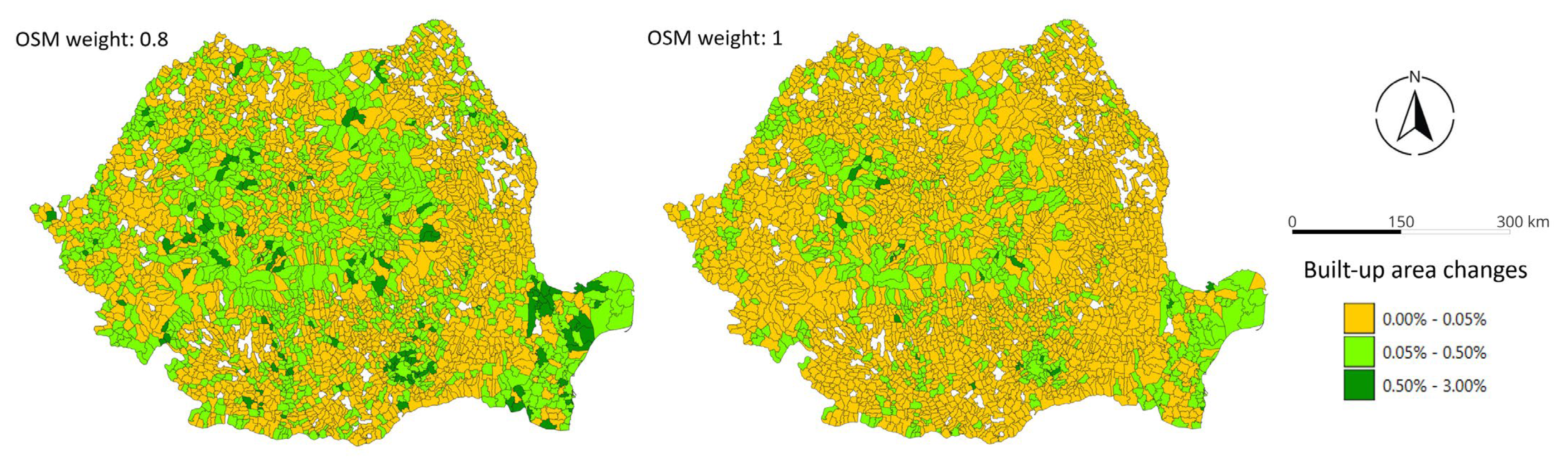
- Handle zeros and missingness: When an input is zero while peers are non-zero, we treat it as missing for weight estimation. When one of the sources does not show built-up coverage in a given cell, but the other two do, the existence of the building is still probable (e.g., an OSM absence may reflect unmapped buildings; a GHS absence may reflect acquisition timing). In such cases, the original TCA-based weights are rescaled. Because OSM generally offers high positional accuracy where present, its weight is explicitly constrained in the algorithm in two-source cases. When built-up is indicated by a single remote-sensing-based source (GHS or MSBF), considered as a more error-prone situation, we treat presence as uncertain and reduce the TCA-derived contribution by a preset division factor, remaining conservative until corroborated by additional sources. Although the used parameter values have empirical motivation, they remain partly subjective. We therefore assess their impact using a Morris sensitivity analysis.
- –
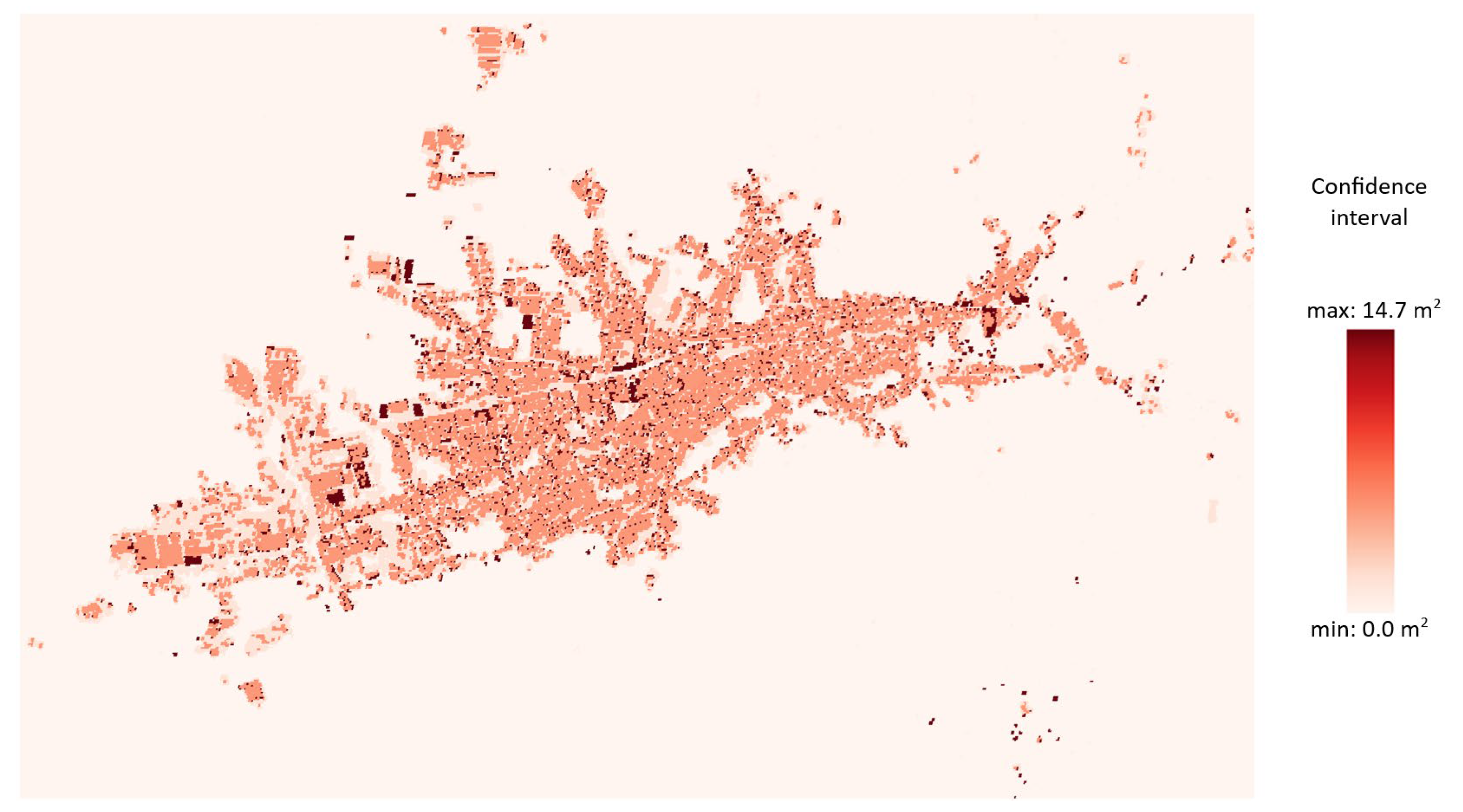
- Propagate uncertainty to confidence intervals. For each pixel, we combine the weights with the estimated error variances to compute the standard error and report confidence intervals for the ensemble estimate, enabling uncertainty-aware interpretation and downstream use.
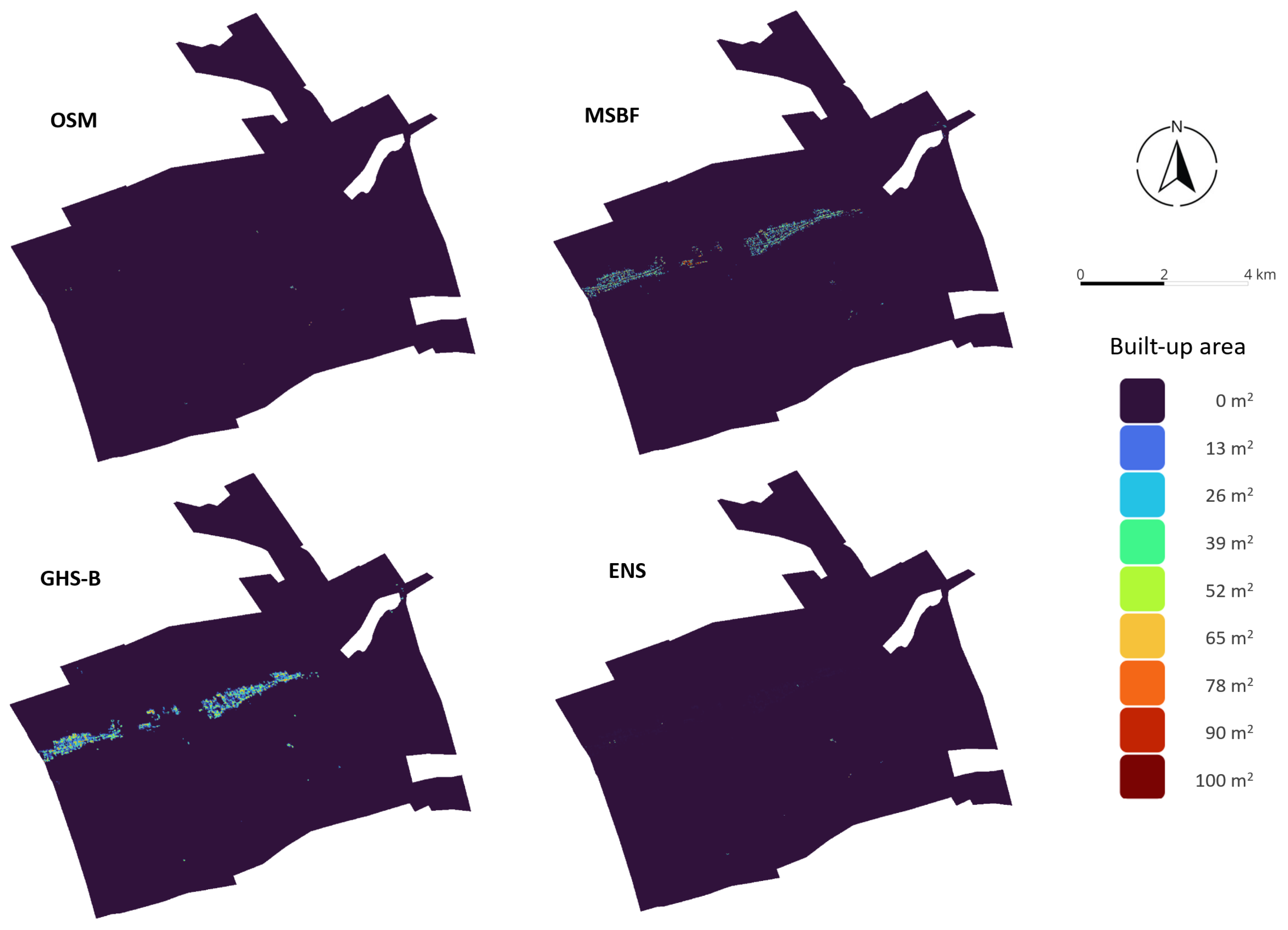
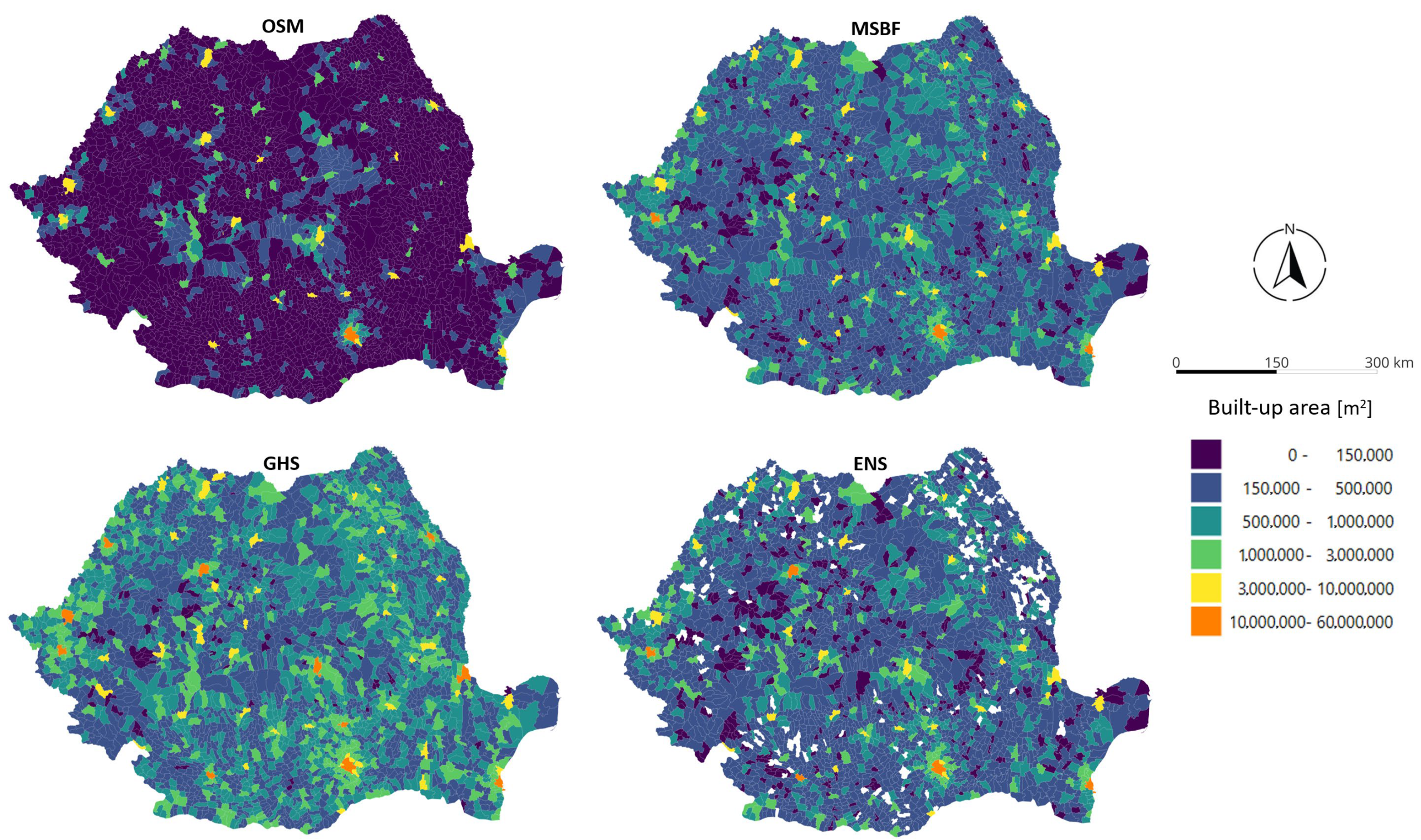
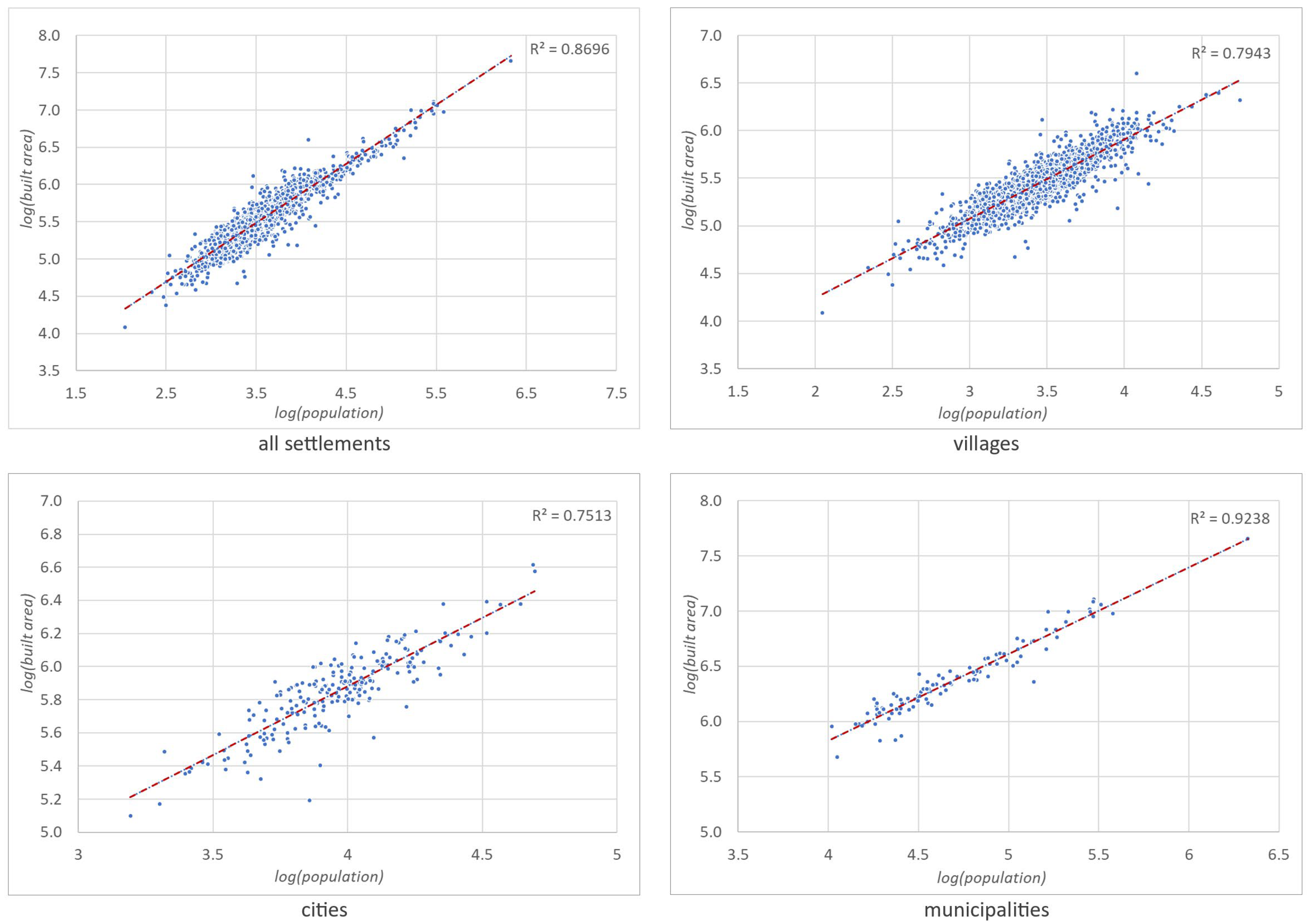
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BLUE | Best Linear Unbiased Estimate |
| CTC | Correlated Triple Collocation |
| GERS | Global Entity Reference System |
| ENS | Ensemble model |
| ETC | Extended Triple Collocation |
| GHS | Global Human Settlement Layer Built-S |
| RNSO | Romanian National Statistical Office |
| LAU | Local Administrative Units |
| MCDA | Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis |
| MSBF | Microsoft Building Footprint |
| OSM | OpenStreetMap |
| TCA | Triple Collocation Analysis |
References
- de Arruda, H.F.; Reia, S.M.; Ruan, S.; Atwal, K.S.; Kavak, H.; Anderson, T.; Pfoser, D. An OpenStreetMap Derived Building Classification Dataset for the United States. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biljecki, F.; Chow, Y.S. Global Building Morphology Indicators. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2022, 95, 101809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, H.R.; Pollard, D.; Winters, A.; Renn, S.; Borkovska, O.; Musuka, C.A.; Membele, G.; Lazar, A.N.; Tatem, A.J. Assessing the Impact of Building Footprint Dataset Choice for Health Programme Planning: A Case Study of Indoor Residual Spraying (IRS) in Zambia. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2025, 24, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liao, W.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Shi, Q.; Zhu, J.; et al. 3D-GloBFP: The First Global Three-Dimensional Building Footprint Dataset. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2024, 16, 5357–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, H.R.; Darin, E.; Adewole, W.A.; Jochem, W.C.; Lazar, A.N.; Tatem, A.J. Building Footprint Data for Countries in Africa: To What Extent Are Existing Data Products Comparable? Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2024, 110, 102104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boo, G.; Darin, E.; Leasure, D.R.; Dooley, C.A.; Chamberlain, H.R.; Lázár, A.N.; Tschirhart, K.; Sinai, C.; Hoff, N.A.; Fuller, T.; et al. High-Resolution Population Estimation Using Household Survey Data and Building Footprints. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebakula, V.; Sims, K.; Reith, A.; Rose, A.; McKee, J.; Coleman, P.; Kaufman, J.; Urban, M.; Jochem, C.; Whitlock, C.; et al. LandScan Global 30 Arcsecond Annual Global Gridded Population Datasets from 2000 to 2022. Sci. Data 2025, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herfort, B.; Lautenbach, S.; Porto De Albuquerque, J.; Anderson, J.; Zipf, A. A Spatio-Temporal Analysis Investigating Completeness and Inequalities of Global Urban Building Data in OpenStreetMap. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedmann, T.; Allen, C. City Footprints and SDGs Provide Untapped Potential for Assessing City Sustainability. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bono, A.; Mora, M.G. A Global Exposure Model for Disaster Risk Assessment. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2014, 10, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, H.; Fu, C.; Miller, C. Ten Questions Concerning Data-Driven Modelling and Forecasting of Operational Energy Demand at Building and Urban Scale. Build. Environ. 2023, 239, 110407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milojevic-Dupont, N.; Wagner, F.; Nachtigall, F.; Hu, J.; Brüser, G.B.; Zumwald, M.; Biljecki, F.; Heeren, N.; Kaack, L.H.; Pichler, P.-P.; et al. EUBUCCO v0.1: European Building Stock Characteristics in a Common and Open Database for 200+ Million Individual Buildings. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherheș, V.; Grecea, C.; Vilceanu, C.-B.; Herban, S.; Coman, C. Challenges in Systematic Property Registration in Romania: An Analytical Overview. Land 2025, 14, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Păunescu, V.; Kohli, D.; Iliescu, A.-I.; Nap, M.-E.; Șuba, E.-E.; Sălăgean, T. An Evaluation of the National Program of Systematic Land Registration in Romania Using the Fit for Purpose Spatial Framework Principles. Land 2022, 11, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistor, C.; Vîrghileanu, M.; Cârlan, I.; Mihai, B.-A.; Toma, L.; Olariu, B. Remote Sensing-Based Analysis of Urban Landscape Change in the City of Bucharest, Romania. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y. GlobalBuildingAtlas: An Open Global and Complete Dataset of Building Polygons, Heights and LoD1 3D Models. arXiv 2025, arXiv:10.48550/arXiv.2506.04106. [Google Scholar]
- Albulescu, A.-C.; Grozavu, A.; Larion, D.; Burghiu, G. Assessing the Earthquake Systemic Vulnerability of the Urban Centres in the South-East Region of Romania. The Tale of Galați and Brăila Cities, Romania. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2022, 13, 1106–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paunescu, M.; Luca, O.; Stanescu, A.A.; Gaman, F. Digital Mapping and Resilience Indicators, as Pillars of Bucharest’s Seismic Resilience Strategy. Infrastructures 2025, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, R.; Samela, C.; Crăciun, I.; Manfreda, S.; Adamowski, J.; Sole, A.; Sivertun, Å.; Ozunu, A. Large Scale Flood Risk Mapping in Data Scarce Environments: An Application for Romania. Water 2020, 12, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ţîncu, R.; Zêzere, J.L.; Lazar, G. Identification of Elements Exposed to Flood Hazard in a Section of Trotus River, Romania. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2018, 9, 950–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biljecki, F.; Chow, Y.S.; Lee, K. Quality of Crowdsourced Geospatial Building Information: A Global Assessment of OpenStreetMap Attributes. Build. Environ. 2023, 237, 110295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, T.; Lautenbach, S.; Herfort, B.; Reinmuth, M.; Schorlemmer, D. Assessing Completeness of OpenStreetMap Building Footprints Using MapSwipe. ISPRS Int. J. Geoinf. 2023, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Fan, H.; Jia, Q.; Ma, M.; Zhong, Z.; Li, J.; Jing, N. How Do Contributions of Organizations Impact Data Inequality in OpenStreetMap? Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2024, 109, 102077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, P.; Giovando, C.; Goch, K.; Pesaresi, M.; Politis, P.; Martinez, A. Towards a Pan-EU Building Footprint Map Based on The Hierarchical Conflation of Open Datasets: The Digital Building Stock Model—DBSM. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 48, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, J.J. Building-Level Comparison of Microsoft and Google Open Building Footprints Datasets (Short Paper). In Proceedings of the Leibniz International Proceedings in Informatics (LIPIcs), International Conference on Geographic Information Science (GIScience), Leeds, UK, 12–15 September 2023; Volume 277, pp. 35:1–35:6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwintschik, M. Microsoft’s 1.4 Billion Global ML Building Footprints. 2024. Available online: https://tech.marksblogg.com/microsofts-global-ml-building-footprints.html (accessed on 8 October 2025).
- Pesaresi, M. GHS-BUILT-S R2023A—GHS Built-Up Surface Grid, Derived from Sentinel2 Composite and Landsat, Multitemporal (1975–2030); European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pesaresi, M.; Schiavina, M.; Politis, P.; Freire, S.; Krasnodębska, K.; Uhl, J.H.; Carioli, A.; Corbane, C.; Dijkstra, L.; Florio, P.; et al. Advances on the Global Human Settlement Layer by Joint Assessment of Earth Observation and Population Survey Data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2024, 17, 2390454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Ying, Q.; Yang, F.; Qin, Y. Accuracy Assessment of Global Human Settlement Layer (GHSL) Built-up Products over China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, S.; Fang, C.; Guan, L.; Liu, M. Global Urban and Rural Settlement Dataset from 2000 to 2020. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, J.; Thapa, B.R. Bayesian Model Averaging for Satellite Precipitation Data Fusion: From Accuracy Estimation to Runoff Simulation. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Chaudhari, O.; Chandra, R. A Review of Ensemble Learning and Data Augmentation Models for Class Imbalanced Problems: Combination, Implementation and Evaluation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 244, 122778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Wen, J.; Pedrycz, W.; Aritsugi, M. Complex Evidence Theory for Multisource Data Fusion. Chin. J. Inf. Fusion 2024, 1, 134–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Anwar, S. Paradox Elimination in Dempster–Shafer Combination Rule with Novel Entropy Function: Application in Decision-Level Multi-Sensor Fusion. Sensors 2019, 19, 4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoni, S.; Jahmunah, V.; Salvi, M.; Barua, P.D.; Molinari, F.; Acharya, U.R. Application of Uncertainty Quantification to Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: A Review of Last Decade (2013–2023). Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 165, 107441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, R.; Devillers, R.; Luther, J.E.; Eddy, B.G. GIS-Based Multiple-Criteria Decision Analysis. Geogr. Compass 2011, 5, 412–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffelen, A. Toward the True Near-Surface Wind Speed: Error Modeling and Calibration Using Triple Collocation. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1998, 103, 7755–7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.T.; Crow, W.T. Evaluation of Assumptions in Soil Moisture Triple Collocation Analysis. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, A.; Su, C.-H.; Zwieback, S.; Crow, W.; Dorigo, W.; Wagner, W. Recent Advances in (Soil Moisture) Triple Collocation Analysis. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 45, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Jia, L.; Menenti, M.; Hu, G. Global Soil Moisture Data Fusion by Triple Collocation Analysis from 2011 to 2018. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pataki, A.; Bertalan, L.; Pásztor, L.; Nagy, L.A.; Abriha, D.; Liang, S.; Singh, S.K.; Szabó, S. Soil Moisture Satellite Data Under Scrutiny: Assessing Accuracy Through Environmental Proxies and Extended Triple Collocation Analysis. Earth Syst. Environ. 2025, 9, 801–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Huang, P.; Chen, X.; Jin, H.; Zhu, Q.; Luo, H. Triple Collocation-Based Model Error Estimation of VIC-Simulated Soil Moisture at Spatial and Temporal Scales in the Continental United States in 2010–2020. Water 2024, 16, 3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Huang, H.; Shi, W.; Chen, R. A Reference-Free Method for the Thematic Accuracy Estimation of Global Land Cover Products Based on the Triple Collocation Approach. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, K.; Chen, X.; Sun, R. Evaluation and Fusion of Multi-Source Sea Ice Thickness Products with Limited in-Situ Observations. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1464391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Vermeulen, A.; Dong, J.; Duan, Z. Triple Collocation-Based Merging of Multi-Source Gridded Evapotranspiration Data in the Nordic Region. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 335, 109451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; He, M.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Duan, Z. Triple Collocation-Based Error Estimation and Data Fusion of Global Gridded Precipitation Products over the Yangtze River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Lei, F.; Wei, L. Triple Collocation Based Multi-Source Precipitation Merging. Front. Water 2020, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Jiang, S.; Dong, J.; Ren, L.; Yong, B.; Yang, B.; Li, X.; Duan, Z. A Combined Extended Triple Collocation and Cumulative Distribution Function Merging Framework for Improved Daily Precipitation Estimates over Mainland China. J. Hydrol. 2024, 641, 131757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, K.A.; Vogelzang, J.; Konings, A.G.; Entekhabi, D.; Piles, M.; Stoffelen, A. Extended Triple Collocation: Estimating Errors and Correlation Coefficients with Respect to an Unknown Target. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 6229–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gambau, V.; Turiel, A.; González-Haro, C.; Martínez, J.; Olmedo, E.; Oliva, R.; Martín-Neira, M. Triple Collocation Analysis for Two Error-Correlated Datasets: Application to L-Band Brightness Temperatures over Land. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.D. Factorial Sampling Plans for Preliminary Computational Experiments. Technometrics 1991, 33, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Dhanya, C.T. Influence of Spatial Heterogeneity in Error Characterization Using Triple Collocation; Copernicus GmbH: Göttingen, Germany, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, T.W.; Quiring, S.M.; Zhao, C.; Leasor, Z.T.; Landry, C. Triple Collocation Evaluation of In Situ Soil Moisture Observations from 1200+ Stations as Part of the U.S. National Soil Moisture Network. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 2537–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Park, J. The Use of Triple Collocation Approach to Merge Satellite- and Model-Based Terrestrial Water Storage for Flood Potential Analysis. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammedshum, A.A.; Maathuis, B.H.P.; Mannaerts, C.M.; Teka, D. Using a Triple Sensor Collocation Approach to Evaluate Small-Holder Irrigation Scheme Performances in Northern Ethiopia. Water 2024, 16, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhl, J.H.; Leyk, S. Spatially Explicit Accuracy Assessment of Deep Learning-Based, Fine-Resolution Built-up Land Data in the United States. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 123, 103469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heris, M.P.; Foks, N.L.; Bagstad, K.J.; Troy, A.; Ancona, Z.H. A Rasterized Building Footprint Dataset for the United States. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



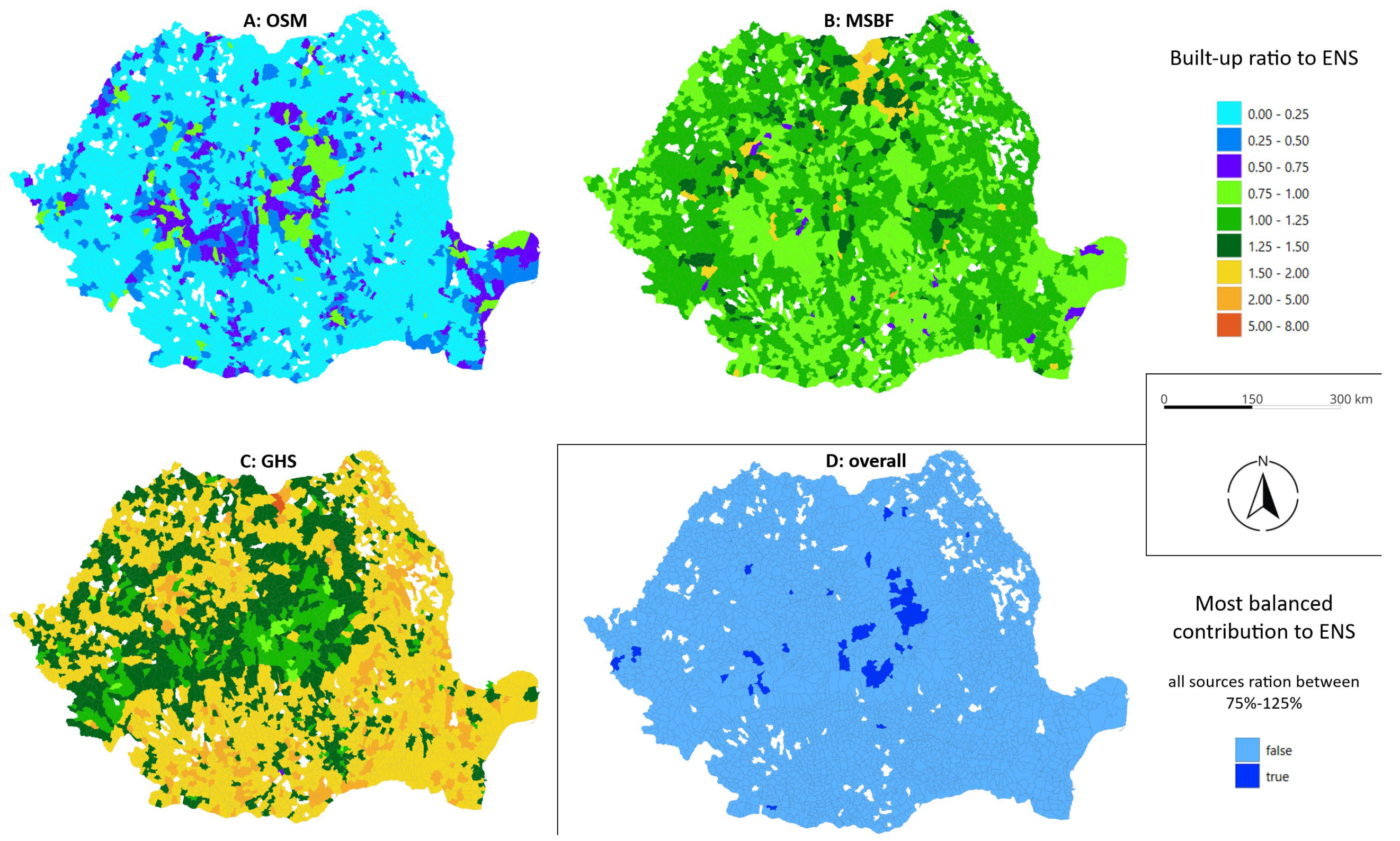

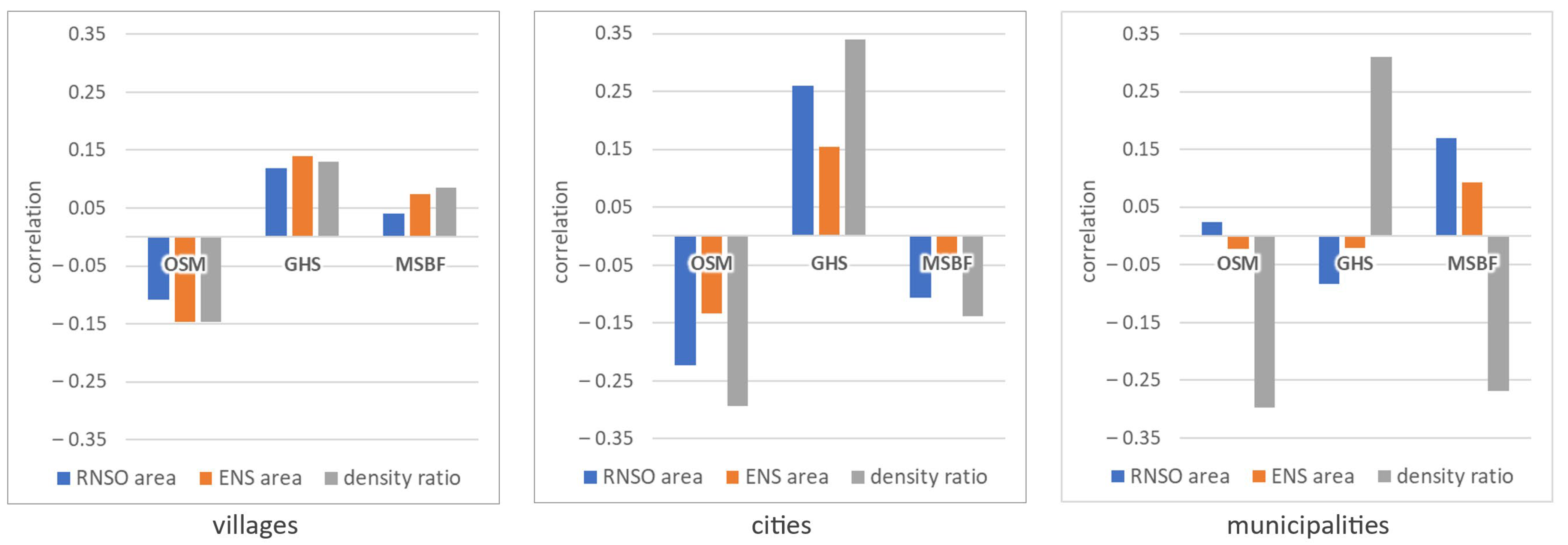

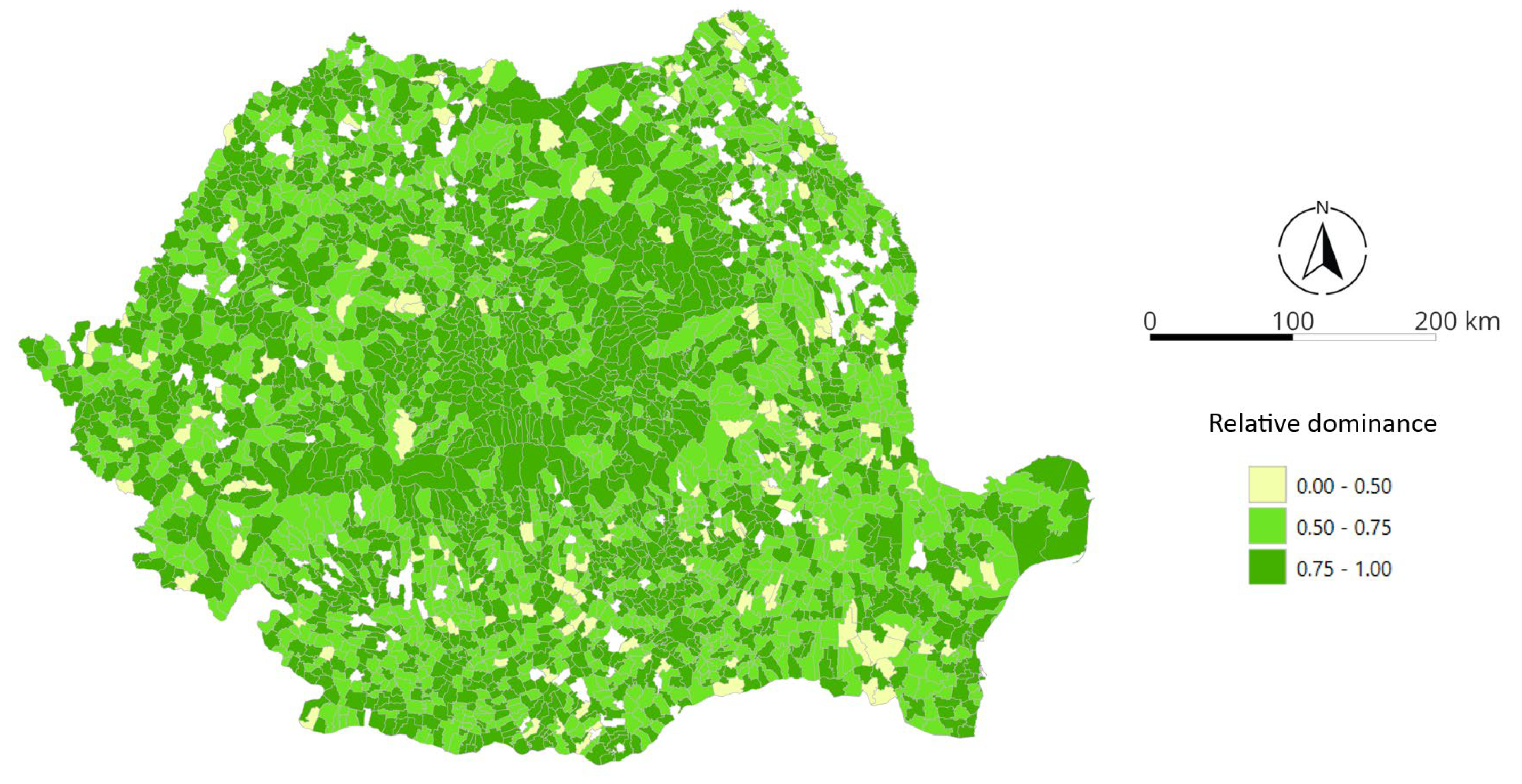
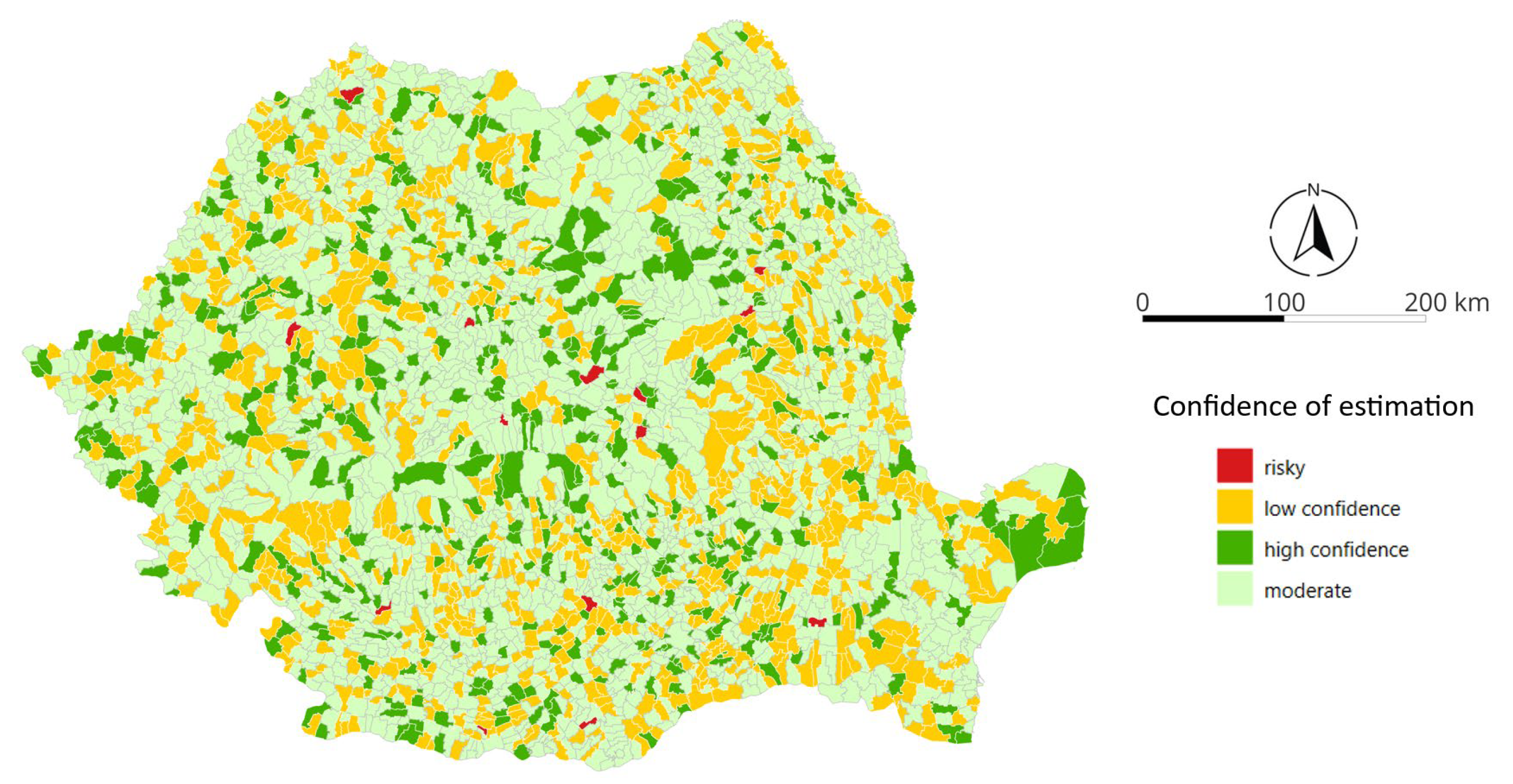
| Name | Data Source | Release Date | Data Format | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSM | https://download.geofabrik.de/europe/romania.html | 18 June 2025 | vector → raster | 10 m |
| MSBF | https://minedbuildings.z5.web.core.windows.net/global-buildings/dataset-links.csv | 2 January 2025 | vector → raster | 10 m |
| GHS | https://human-settlement.emergency.copernicus.eu/download.php | 2018 | raster | 10 m |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magyari-Sáska, Z.; Haidu, I. Built-Up Surface Ensemble Model for Romania Based on OpenStreetMap, Microsoft Building Footprints, and Global Human Settlement Layer Data Sources Using Triple Collocation Analysis. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2025, 14, 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14110420
Magyari-Sáska Z, Haidu I. Built-Up Surface Ensemble Model for Romania Based on OpenStreetMap, Microsoft Building Footprints, and Global Human Settlement Layer Data Sources Using Triple Collocation Analysis. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2025; 14(11):420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14110420
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagyari-Sáska, Zsolt, and Ionel Haidu. 2025. "Built-Up Surface Ensemble Model for Romania Based on OpenStreetMap, Microsoft Building Footprints, and Global Human Settlement Layer Data Sources Using Triple Collocation Analysis" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 14, no. 11: 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14110420
APA StyleMagyari-Sáska, Z., & Haidu, I. (2025). Built-Up Surface Ensemble Model for Romania Based on OpenStreetMap, Microsoft Building Footprints, and Global Human Settlement Layer Data Sources Using Triple Collocation Analysis. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 14(11), 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14110420









