Spatial Distribution of Pension Institutions in Shanghai Based on the Perspective of Wisdom Grade
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Spatial Distribution of Pension Institutions
2.2. Intelligent Pension Institutions
3. Materials and Methods
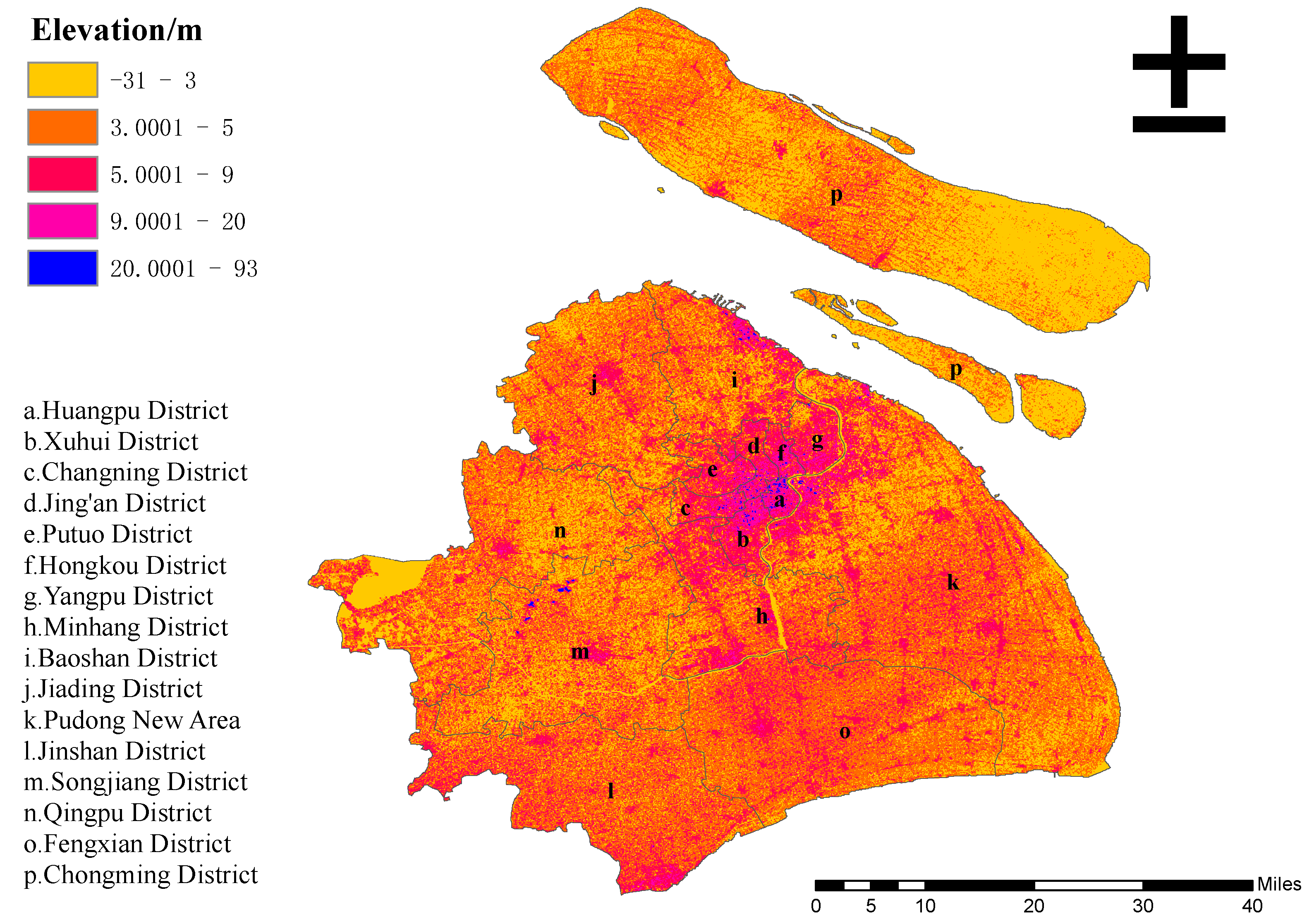
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Multi-Source Data Acquisition and Processing
3.2.1. Index Construction
3.2.2. Data Source
3.2.3. The Wisdom Grade Distribution of the Pension Institutions in Shanghai
3.3. Research Methods
3.3.1. Spatial Density Analysis
3.3.2. Spatial Cluster Analysis
3.3.3. Spatial Inequality Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
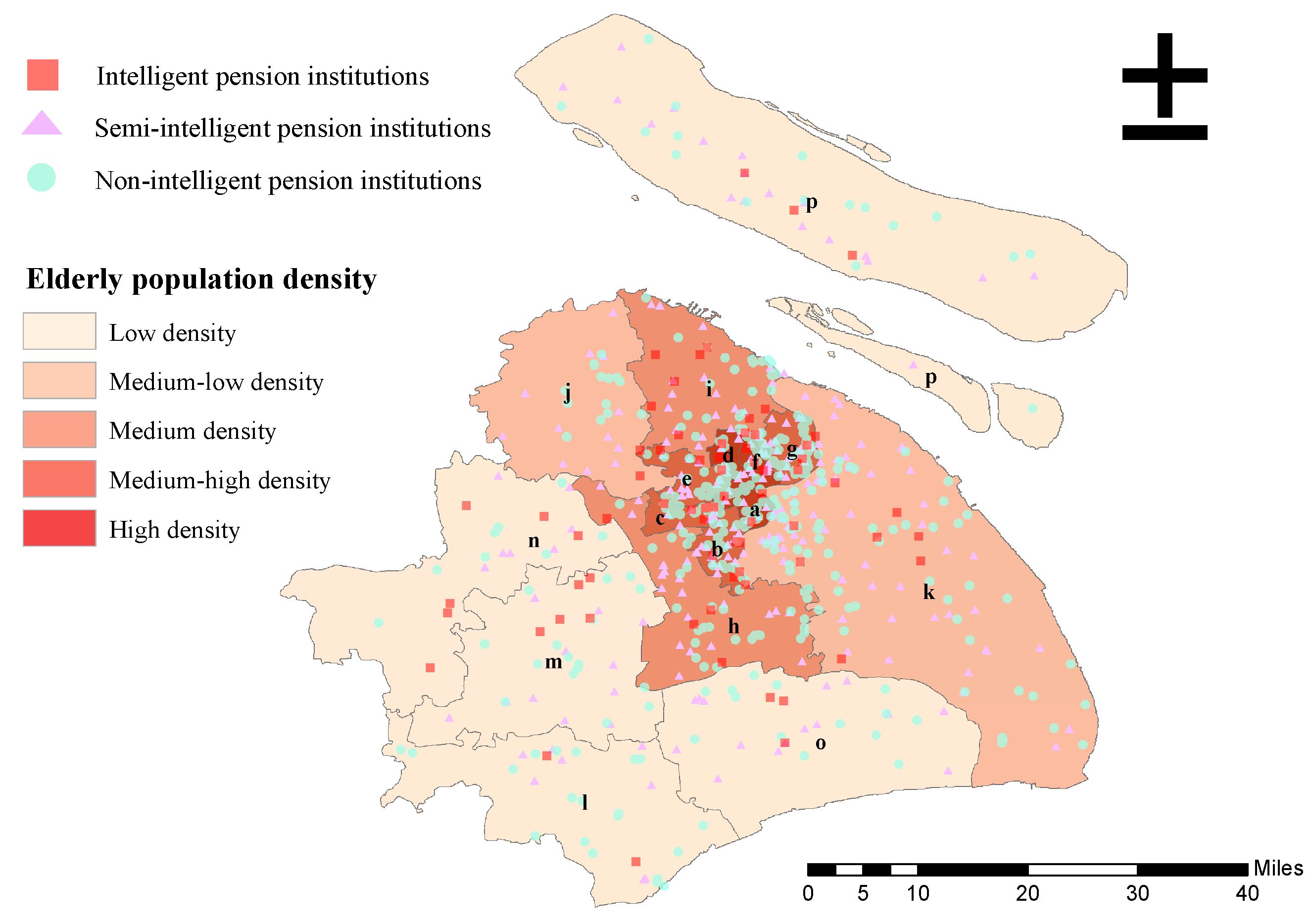
4.1. Spatial Scale Distribution
4.2. Spatial Clustering Distribution
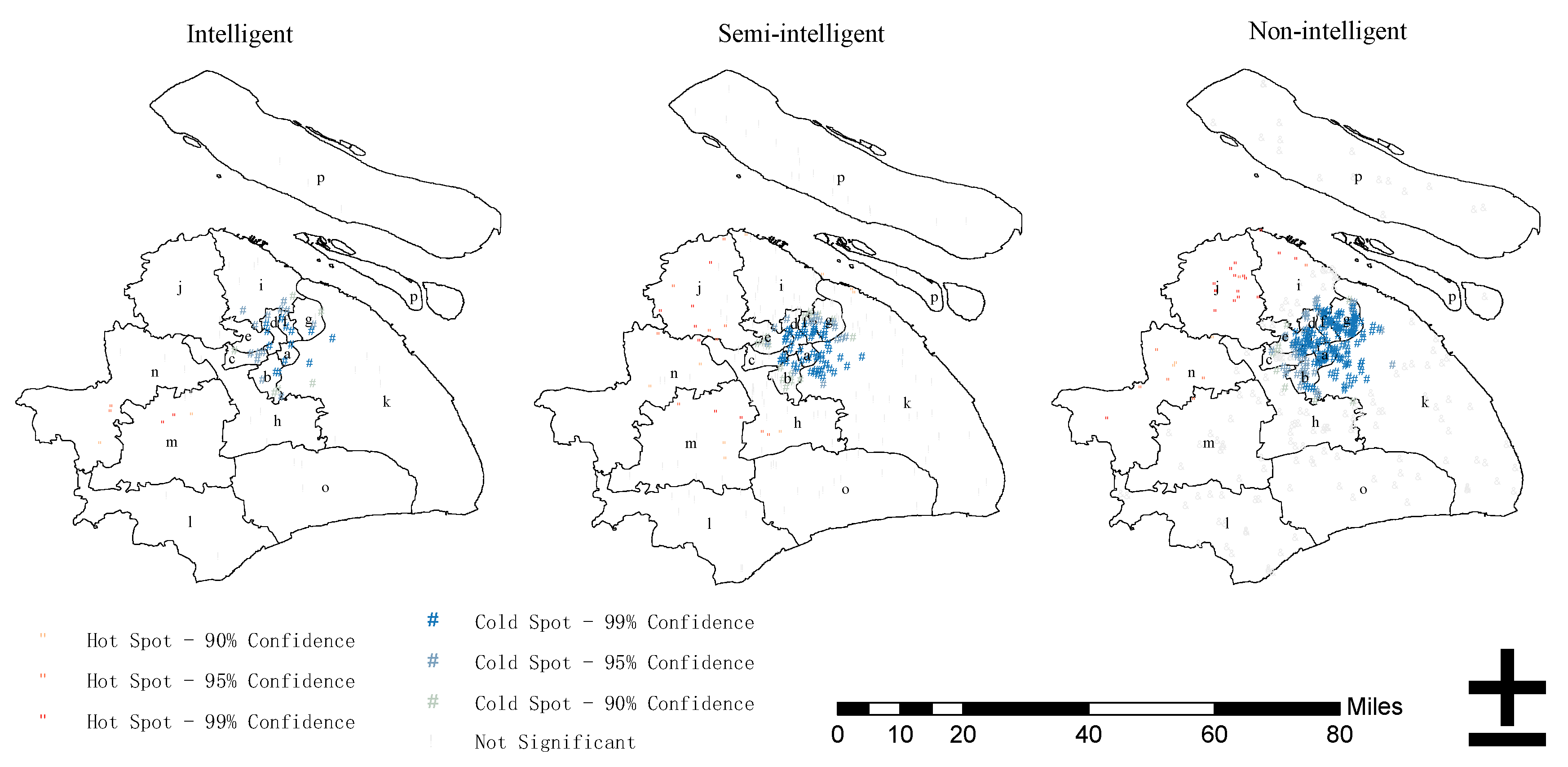
4.2.1. Standard Deviation Ellipse and Kernel Density Estimation Analysis
4.2.2. Spatial Correlation Analysis
4.3. Spatial Fairness Distribution
4.3.1. Gini Coefficient
4.3.2. Correlation Coefficient
4.3.3. Resource Allocation Analysis
5. Conclusions, Recommendations, and Limitations of Study
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Recommendations
5.3. Limitation of Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, K.; Han, J.; Zhao, S.; Cao, J. Geographical Pattern Evolution of Health Resources in China: Spatio-Temporal Dynamics and Spatial Mismatch. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Chen, L.; Pu, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, L. Current situation investigation of the internal medical institutions and the providing of health services in the elderly care institutions in a community in Shanghai. Chin. Health Resour. 2018, 21, 323–328. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q.; Li, Y. Analysis on optimal allocation strategy of intelligent medical space for community home care. Acad. Bimest. 2020, 03, 63–65. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Tan, J.; Chen, Y. Research on Demand Forecast of Social Pension Facilities: A Case Study of Chongqing. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Symposium on Advancement of Construction Management and Real Estate, Guiyang, China, 24–27 August 2018; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 457–475. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Gong, P.; White, M. Study on Spatial Distribution Equilibrium of Elderly Care Facilities in Downtown Shanghai. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.; Liu, S. Study on Spatial Distribution and Accessibility of Elderly Care Institutions in Shanghai. Mod. Urban Res. 2021, 06, 17–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Yao, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, C. Study on the Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Pension Service Institutions in Shijiazhuang City of China. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2022, 41, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Yang, Y. Research on Spatial Pattern of Henan Pension Institutions Based on Accessibility. Int. J. Educ. Humanit. 2023, 8, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Jiang, W.; Shi, J.; Xin, S.; Peng, J.; Liu, H. A Method for Assessing the Fairness of Health Resource Allocation Based on Geographical Grid. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2020, 64, 1171–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Zhang, H. Study on the spatial equilibrium in pension combined with medicalcare resources allocation in Beijing. Chin. J. Health Policy 2020, 13, 7–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qin, L.; Zhou, Y. Research on the Configuration of Healthcare Space in Elderly Care Facilities under the Background of Medical-Nursing Combination. Archit. J. 2021, S1, 74–79. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, R.; Qian, L.; Yang, X.; Dong, L.; Zhang, G. Supply-demand balance and spatial distribution optimization of primary care facilities in highland cities from a resilience perspective: A study of Lhasa, China. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, K.; Wang, Z. Spatial distribution of community pension facilities from the perspective concept of health equity: A case study of the central city of Shanghai. Hum. Geogr. 2021, 36, 48–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, K. Analysis of fairness and trends in the allocation of medical and health resources in Shanghai from 1995 to 2018. Chin. J. Evid.-Based Med. 2021, 21, 1016–1023. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Song, W.; Li, C.; Lu, J. The Spatial Equity of Nursing Homes in Changchun: A Multi-Trip Modes Analysis. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Wang, J.; Hu, N. Equity Performance Evaluation for Resource Allocation in Urban Senior Care Organization from the Perspective of Health Equity: A Case Study of Wuhan. Mod. Urban Res. 2022, 08, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kang, R.; Wang, Z.; Lv, X. Does Private Sector Participation Enhance the Fairness of Elderly Care Service Supply—Based on Beijing. Soc. Secur. Stud. 2022, 03, 29–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, P.; Liu, Z.; Lan, J. Equity and efficiency in spatial distribution of basic public health facilities: A case study from Nanjing metropolitan area. Urban Policy Res. 2018, 37, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Liu, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, N.; Liu, Y. From service capacity to spatial equity: Exploring a multi-stage decision-making approach for optimizing elderly-care facility distribution in the city centre of Tianjin, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 85, 104076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, D.; Peng, Q. Constructing basic analysis about the “Internet + Community Home-Based Care” service model in China’s city. Soc. Secur. Stud. 2017, 39, 18–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S. Internet of Things and Smart Elderly Care. Video Eng. 2014, 38, 24–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sui, D.; Peng, Q. “Internet + Home-based care for Senior Citizens”: Research in Service Model of Intellectual Home-based Care for Senior Citizens. J. Xinjiang Norm. Univ. (Ed. Philos. Soc. Sci.) 2016, 37, 128–135. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pires, P.; Mendes, L.; Mendes, J.; Rodrigues, R.; Pereira, A. Integrated e-Healthcare System for Elderly Support. Cogn. Comput. 2016, 8, 368–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; Aghayi, E.; Noferesti, M.; Memarzadeh-Tehran, H.; Mondal, T.; Pang, Z.; Deen, M. Smart Homes for Elderly Healthcare—Recent Advances and Research Challenges. Sensors 2017, 17, 2483–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Wu, Y. Smart home for elderly care: Development and challenges in China. BMC Geriatr. 2020, 20, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Zhao, M. Spatial difference of intelligent pension service in China. J. North Minzu Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci.) 2022, 05, 117–123. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wu, L.; Liu, L.; Zhao, T. Research progress of smart elderly care system in nursing home. Chin. Nurs. Res. 2023, 37, 1011–1014. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tong, F. Construction and Application Strategies of Multi-system Interactive Elderly Care System. J. Nantong Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 37, 89–96. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Zhao, M. Research on the Evaluation Index System of Smart Elderly Care. J. Northeast. Univ. (Soc. Sci.) 2022, 24, 88–94. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Hu, J.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Liang, M. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Pro-Poor Tourism Villages in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ouyang, W.; Zhang, D. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Traditional Villages in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. Sustainability 2022, 15, 15953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, P.; Sprenger, C.; van Veen, F. On Extreme Values of Moran’s I and Geary’s c. Geogr. Anal. 1984, 16, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, F.; Zech, W.C.; Nazari, R.; Karimi, M.; Bacchus, A. Developing a Geospatial Framework for Severe Occupational Injuries Using Moran’s I and Getis-Ord Gi* Statistics for Southeastern United States. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2022, 23, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Gong, P.; White, M.; Zhang, B. Research on Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Pension Resources in Shanghai Community-Life Circle. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Li, R.; Ma, S. Research on the equity of health resource allocation in TCM hospitals in China based on the Gini coefficient and agglomeration degree: 2009–2018. Int. J. Equity Health 2022, 21, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, K.; Tan, M.; Yang, Z.; Shi, S. Modeling of Feature Selection Based on Random Forest Algorithm and Pearson Correlation Coefficient. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2219, 012046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, L. A Study on the Characteristics of Spatial Distribution of Care Facilities and Capacities for the Elderly in Shanghai. Archit. J. 2018, 02, 90–94. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Yao, S.; Wu, J.; Huang, L.; Ren, Z. Study on spatial Distribution of residential care facilities in Shanghai. J. East China Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2018, 05, 157–169. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]



| Category | Variable | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure (A1) | Smart Devices (B1) | Intelligent testing equipment, automatic washing and maintenance equipment, and other equipment installation. |
| Network facilities (B2) | Coverage of wireless networks, optical fiber, imaging equipment, and other facilities. | |
| Environmental facilities (B3) | Installation of barrier-free facilities, intelligent temperature sensing equipment, fresh air system, etc. | |
| Emergency facilities (B4) | Improvement of water/fuel/smoke leakage detection system, automatic alarm system, etc. | |
| Medical facilities (B5) | Installation of physical examination all-in-one machine, guided inquiry machine, nursing equipment, and other facilities. | |
| Management (A2) | Intelligent Supervision (B6) | Coverage of facilities, such as IP cameras and real-time positioning systems. |
| Health data (B7) | Establishment, update, and data visualization of health file information | |
| Service (A3) | Human Resources (B8) | Number of professional doctors and professional nursing staff. |
| Medical Services (B9) | The advanced degree of medical services, such as telemedicine system and monitoring physiological indicators. | |
| Psychological Services (B10) | The arrangement of psychological services, such as online psychological counseling and education for the elderly. | |
| Life Services (B11) | Convenience of life styles, such as medical care, shopping, diet, entertainment, etc. |
| District | Pension Institution | Types of Pension Institutions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Sample (n, %) | Intelligent (n, %) | Semi-Intelligent (n, %) | Non-Intelligent (n, %) | |
| a | 28 | 23 (82.14) | 1 (4.35) | 6 (26.09) | 16 (69.57) |
| b | 56 | 48 (85.71) | 7 (14.58) | 16 (33.33) | 25 (52.08) |
| c | 40 | 36 (90.00) | 5 (13.89) | 9 (25.00) | 22 (61.11) |
| d | 37 | 32 (86.49) | 5 (15.63) | 11 (34.38) | 16 (50.00) |
| e | 58 | 46 (79.31) | 4 (8.70) | 15 (32.61) | 27 (58.70) |
| f | 47 | 41 (87.23) | 4 (9.76) | 16 (39.02) | 21 (51.22) |
| g | 74 | 59 (79.73) | 4 (6.78) | 15 (25.42) | 40 (67.80) |
| h | 71 | 59 (83.10) | 4 (6.78) | 24 (40.68) | 31 (52.54) |
| i | 56 | 49 (87.50) | 8 (16.33) | 18 (36.73) | 23 (46.94) |
| j | 34 | 31 (91.18) | 2 (6.45) | 13 (41.94) | 16 (51.61) |
| k | 151 | 128 (84.77) | 8 (6.25) | 59 (46.09) | 61 (47.66) |
| l | 34 | 30 (88.24) | 2 (6.67) | 8 (26.67) | 20 (66.67) |
| m | 36 | 33 (91.67) | 5 (15.15) | 11 (33.33) | 17 (51.52) |
| n | 25 | 22 (88.00) | 6 (27.27) | 7 (31.82) | 9 (40.91) |
| o | 35 | 32 (91.43) | 3 (9.38) | 15 (46.88) | 14 (43.75) |
| p | 43 | 41 (95.35) | 3 (7.32) | 19 (46.34) | 19 (46.34) |
| Average | 51.56 | 44.38 (86.06) | 4.44 (10.00) | 16.38 (36.90) | 23.56 (53.10) |
| District | Area | Elderly Population | Number of Institutions Adoptions | Number of Beds in Pension Institutions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Intelligent | Semi-Intelligent | Non-Intelligent | ||||
| a | 20.52 | 32.62 | 1921 | 2362 | 412 | 997 | 953 |
| b | 54.93 | 33.44 | 4043 | 5752 | 853 | 2314 | 2585 |
| c | 37.18 | 22.38 | 4291 | 5213 | 682 | 1388 | 3143 |
| d | 37 | 36.25 | 3315 | 4221 | 1306 | 1816 | 1727 |
| e | 55.53 | 36.6 | 5241 | 5612 | 428 | 2789 | 2106 |
| f | 23.48 | 29.49 | 4903 | 6953 | 1224 | 2193 | 3536 |
| g | 61.61 | 40.95 | 7305 | 8248 | 961 | 3714 | 3573 |
| Urban | 289 | 231.73 | 31,019 | 38,361 | 5866 | 15,211 | 17,623 |
| h | 372.56 | 37.76 | 8860 | 12,698 | 1634 | 7036 | 4028 |
| i | 365.3 | 37.98 | 7242 | 11,409 | 3283 | 3933 | 4193 |
| j | 463.16 | 23.44 | 4995 | 9623 | 411 | 5036 | 4176 |
| k | 1210 | 102.48 | 15,326 | 20,953 | 2822 | 10,473 | 7658 |
| l | 586.05 | 17.78 | 3155 | 5513 | 1144 | 1422 | 2947 |
| m | 606.64 | 20.04 | 4961 | 9556 | 3354 | 2802 | 3400 |
| n | 668.54 | 16.49 | 2040 | 6685 | 2389 | 2203 | 2093 |
| o | 773.38 | 18.66 | 2956 | 6019 | 1198 | 3243 | 1578 |
| p | 1413 | 26.07 | 3893 | 6674 | 590 | 3150 | 2934 |
| Suburban | 6050 | 300.70 | 53,428 | 89,130 | 16,825 | 39,298 | 33,007 |
| Shanghai | 6339 | 532.43 | 84,447 | 127,491 | 22,691 | 54,509 | 50,630 |
| Types of Pension Institutions | Moran’s I | Z | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 0.053 | 8.488 | 0.000 |
| Intelligent | −0.007 | 0.177 | 0.859 |
| Semi-intelligent | 0.082 | 3.373 | 0.001 |
| Non-intelligent | 0.018 | 1.641 | 0.101 |
| District | G1 | G2 | G3 | District | G1 | G2 | G3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 0.486 | 0.529 | 0.646 | h | 0.406 | 0.500 | 0.471 |
| b | 0.412 | 0.476 | 0.407 | i | 0.347 | 0.481 | 0.516 |
| c | 0.452 | 0.537 | 0.503 | j | 0.418 | 0.435 | 0.491 |
| d | 0.426 | 0.531 | 0.512 | k | 0.318 | 0.421 | 0.449 |
| e | 0.454 | 0.455 | 0.461 | l | 0.323 | 0.367 | 0.526 |
| f | 0.346 | 0.515 | 0.480 | m | 0.350 | 0.521 | 0.534 |
| g | 0.461 | 0.515 | 0.472 | n | 0.324 | 0.454 | 0.409 |
| Urban | 0.440 | 0.518 | 0.500 | o | 0.345 | 0.398 | 0.474 |
| p | 0.259 | 0.341 | 0.391 | ||||
| Shanghai | 0.387 | 0.495 | 0.513 | Suburban | 0.350 | 0.466 | 0.509 |
| Economy, Population, Income, Housing, and Health Status | Value | Correlation Coefficient | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | G2 | G3 | |||
| Economy and population of Shanghai | GDP per capita | 199,543.2 | 0.460 | 0.422 | 0.348 |
| Per capita disposable income | 76,066.19 | 0.766 | 0.806 | 0.323 | |
| Total service assets | 6885.52 | 0.555 | 0.570 | 0.461 | |
| Elderly population density | 357.29 | 0.607 | 0.639 | 0.282 | |
| The elderly are the main source of income | Labor income ratio | 3.19% | −0.546 | −0.582 | −0.179 |
| Pension ratio | 94.07% | 0.578 | 0.497 | 0.141 | |
| The proportion of the rest of the family | 2.09% | −0.427 | −0.184 | −0.055 | |
| Subsistence allowance ratio | 0.36% | −0.321 | −0.353 | 0.091 | |
| Proportion of property income | 0.06% | 0.165 | 0.076 | −0.003 | |
| Living conditions of the elderly | Proportion living with spouse and children | 27.41% | 0.556 | 0.739 | 0.331 |
| Proportion living with a spouse | 44.41% | −0.646 | −0.813 | −0.434 | |
| Proportion living with children | 12.67% | 0.376 | 0.525 | 0.395 | |
| Proportion living alone (with a nanny) | 0.32% | 0.559 | 0.601 | 0.132 | |
| Proportion living alone (without nanny) | 9.78% | −0.348 | 0.525 | −0.231 | |
| Proportion of pension institutions | 1.96% | 0.084 | 0.192 | 0.012 | |
| Health status of the elderly | Healthy ratio | 61.80% | −0.252 | −0.173 | 0.171 |
| Basic health ratio | 28.54% | 0.290 | 0.216 | −0.149 | |
| Unhealthy but self-care | 6.48% | 0.106 | 0.013 | −0.248 | |
| Unhealthy and non-self-care | 3.17% | 0.302 | 0.245 | −0.080 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Tian, Q. Spatial Distribution of Pension Institutions in Shanghai Based on the Perspective of Wisdom Grade. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12070265
Li Q, Tian Q. Spatial Distribution of Pension Institutions in Shanghai Based on the Perspective of Wisdom Grade. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2023; 12(7):265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12070265
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qiaoxing, and Qinrui Tian. 2023. "Spatial Distribution of Pension Institutions in Shanghai Based on the Perspective of Wisdom Grade" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 12, no. 7: 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12070265
APA StyleLi, Q., & Tian, Q. (2023). Spatial Distribution of Pension Institutions in Shanghai Based on the Perspective of Wisdom Grade. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 12(7), 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12070265





