Abstract
Spatial autocorrelation describes the interdependent relationship between the realizations or observations of a variable that is distributed across a geographical landscape, which may be divided into different units/areas according to natural or political boundaries. Researchers of Geographical Information Science (GIS) always consider spatial autocorrelation. However, spatial autocorrelation research covers a wide range of disciplines, not only GIS, but spatial econometrics, ecology, biology, etc. Since spatial autocorrelation relates to multiple disciplines, it is difficult gain a wide breadth of knowledge on all its applications, which is very important for beginners to start their research as well as for experienced scholars to consider new perspectives in their works. Scientometric analyses are conducted in this paper to achieve this end. Specifically, we employ scientometrc indicators and scientometric network mapping techniques to discover influential journals, countries, institutions, and research communities; key topics and papers; and research development and trends. The conclusions are: (1) journals categorized into ecological and biological domains constitute the majority of TOP journals;(2) northern American countries, European countries, Australia, Brazil, and China contribute the most to spatial autocorrelation-related research; (3) eleven research communities consisting of three geographical communities and eight communities of other domains were detected; (4) hot topics include spatial autocorrelation analysis for molecular data, biodiversity, spatial heterogeneity, and variability, and problems that have emerged in the rapid development of China; and (5) spatial statistics-based approaches and more intensive problem-oriented applications are, and still will be, the trend of spatial autocorrelation-related research. We also refine the results from a geographer’s perspective at the end of this paper.
1. Introduction
Spatial autocorrelation (SA) is a concept employed by researchers in a wide range of disciplines and whose datasets have locational information. The essential cause of SA may be geographical or locational proximity. As the first law of geography [1] says: “everything is relating to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things”; hence, SA is a widely existing geographical characteristic. Thanks to the endeavors of pioneering quantitative geographers (e.g., the “Washington School” [2]), in the 1950–1960s, SA drew much attention and became the central part of quantified geography. However, the first mention of SA appeared in 1968 (i.e., [3,4]), before which it was called spatial association, spatial dependence, spatial interaction, etc. The seminal works of the geographer Cliff and the statistician Ord [5,6] lay the theoretical foundation of SA, which inspired its flourishing development (i.e., [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]) across the natural and social sciences. Therefore, SA is also a series of statistical theories and methods used to deal with the dependence among spatial variables.
Different from a purely statistical concept, SA has a geographical feature, which means it applies to a variety of disciplines. Research relating to locational information confronts the problem of SA, because the dependence between the observed values of a variable caused by SA leads to the invalidation of the classical independent assumption, so the results will not be reliable. For example, researchers may obtain incorrect Type I error rates and biased estimates [24] when employing traditional statistical methods. Therefore, SA is not only a problem of geography, the area in which it originated, but also a problem of many other disciplines, such as spatial econometrics [25], ecology [26], biology [27], etc. A series of challenges that come with SA are, for example, how to test it in a spatial process (e.g., [28]) so that a proper model can be specified, how to deal with it in a model (e.g., [29,30]) so that one can obtain reasonable results, and how to make use of it so that representative samples can be drawn (e.g., [31,32]).
These are problems caused by SA from the statistical or technical perspective, whereas SA also has very rich implications for empirical studies. For example, Liu et al. [33] employed SA analysis to explore whether or not foreign direct investment affects environmental pollution in China, and Zhang et al. [34] addressed the spatial interaction between ecosystem services and urbanization, while Wang et al. [35] conducted spatiotemporal analysis to discuss the transmission and influencing factors of COVID-19.
The problems as well as the benefits that SA brings have been addressed not only from a geographer’s perspective, but also from the perspectives of scholars from other domains. However, it is difficult to provide an overview for the multiple disciplines of SA simultaneously, because researchers may lack experience beyond their own fields. In addition, with the era of information exploration, thousands of papers are continuously being written, which brings even more challenges for scholars to follow research from other fields. To this end, this paper aims to present a global view for SA research in different fields by employing scientometric techniques, and thus tries to figure out: the leading countries and institutions, influential research communities, key topics and important references, and the development as well as future research trends of SA. These constitute basic knowledge and may help researchers to gain a comprehensive understanding of SA research so that they can efficiently decide upon their interested research directions or gain new views from unfamiliar domains.
As a key methodology that provides statistical and visualized results for this paper, scientometric analysis deserves to be reviewed here. This is a bibliographical data-driven analytical theory, and can eliminate personal bias introduced by authors’ preferences and knowledge limits. Different from a traditional literature review, a scientometric analysis treats articles as datasets, and shifts from solely comprehending the context of papers (by human researchers) to using them as indicators that quantitatively qualify research, and to graphics that depict the global traits of disciplinary trends. As discussed in papers published in the journals Science [36] and Physical Reports [37], scientometric analysis has become more important with the now highly available scientific literature, because it provides a method by which a researcher can gain an understanding of a field more objectively. In this paper, numerical scientometric indicators and three scientometric network mining methods, i.e., co-authorship analysis, co-word analysis, and citation relations methods [38], are applied to the collected papers that have SA as the research topic. The numerical indicator provides a rank for the publications, countries/regions, and institutions. The network-based methods provide structural information that illustrates co-occurrences (e.g., co-words and co-citations) and collaborative activities (i.e., writing papers with co-authors), which are important research topics, references, and some academic schools or communities.
This paper employs the scientometric technique to provide a broad view of SA research that covers various disciplines. We believe that the results have positive referential values for GIS researchers (as well as researchers from other fields relating to SA research). The subsequent sections are organized as follows: Section 2 presents the datasets and scientometric methodologies which are employed in this paper. Section 3 provides the results and analyses, where Section 3.1 and Section 3.2 present influential journals, countries, and institutions, respectively, and Section 3.3 explores SA research communities. Section 3.4 focuses on important topics and papers of SA research, and Section 3.5 analyzes the development trajectory and possible future research trends. Section 4 discusses the results and refines them from a GIS researcher’s perspective. Section 5 draws some conclusions.
2. Datasets and Methodologies
2.1. Datesets
The bibliographical datasets analyzed in this paper were retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection (WOSCC) database. The detailed search conditions are listed in Table 1. Specifically, the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-E) and the Social Science Citation Index (SSCI) databases were used, because they are the most recognized data sources. After setting these conditions, 8461 records were obtained.

Table 1.
Bibliography search conditions.
We chose the terminology “spatial autocorrelation” as the keyword when researching this topic because “spatial autocorrelation” may be more generic than other expressions, such as “spatial correlation”, “spatial covariogram”, “spatial association”, “spatial dependence”, “spatial interaction”, etc., which can also represent spatial autocorrelation. For example, spatial covariograms or spatial correlograms are often used in geostatistics, and spatial association and spatial dependence are chosen by some researchers of spatial econometrics, but spatial autocorrelation can cover them all. In fact, when we talk about spatial autocorrelation, we not only think of basic spatial autocorrelation statistics (global or local), but also of semivariograms in geostatistics, spatial autocorrelation-related regression models that are widely employed by spatial econometricians as well as scholars in other fields, and other methods in ecology and biology.
The overall disciplinary distribution of the top ten subjects is depicted in Figure 1, which shows that ecology accounted for more than 2000 papers and is the most active and productive discipline relating to SA research. Other highly productive disciplines include environmental sciences/studies, biodiversity conservation, geography, multidisciplinary geosciences, etc. Figure 1 also shows that the percentage of papers in the geographical domain is about 19%, which indicates that other disciplines account for around 80% of SA-related research.
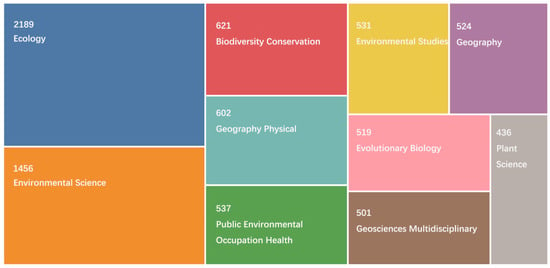
Figure 1.
Top ten most productive disciplines for SA research.
Except for the disciplinary information, the bibliographical datasets also contain the complete information of metadata, including authors, institutions, publication names, citation counts, and references. Hence, not only can the basic bibliography be extracted but also the network structures can be formed by picking the relevant information from the dataset. These items constitute original materials for scientometric analyses. In this paper, we employed several techniques, including scientometric indexes, co-authorship/words/citations analysis, to conduct our research.
2.2. Methodologies
2.2.1. Scientometric Indexes
For the datasets, three scientometrical indexes, the records (Recs), the Total Local Citation Score (TLCS), and the Total Global Citation Score (TGCS), were used to quantify the institutions as well as countries/regions. The Recs counts the frequency of an object (e.g., an institution) appearing in the dataset and thus describes the popularity of this object. The TLCS is the citation counts within the 8461 papers; it quantifies the SA-related domains impact. Additionally, the TGCS is the citation counts within papers in WOSCC; it measures the global impact. A phenomenon that has been observed is that some journals are so professional that they have a small audience, and thus their impact factors (IF) are relatively low, but they have good reputations among scholars within some domains; the TLCS is a metric that represents specialization. In contrast, the TGCS is a metric that represents universality. We used HistCite [39] to report the three counts.
2.2.2. Scientometric Network Mapping
- (1)
- Co-authorship analysis
Co-authorship analysis is often conducted to discover research/academic communities or schools by presenting cooperative relationship networks. There are three types of co-authorship analyses, i.e., authors analysis, institutions analysis, and countries/regions analysis [40]. We only focus on author analysis in this paper, aiming to find out scholars who have similar research interests. VOSviewer [41] was employed to carry out this work, with authors in the same community presented by the same color and connected by links. More specifically, each author is shown by a node, and co-authorship is expressed by links among the nodes. To visualize the co-author network and simultaneously reflect the leading scholar(s), we set the weight as “normalized citations”, which determines the size of a node. In other words, a node with a bigger size indicates that its corresponding author has been cited more frequently. Other types of weights include “links” and “total link strength”, which focus on the tightness of the co-authorship, and “documents” which represents the number of papers in which an author cooperated with other scholars.
- (2)
- Co-words analysis
The co-words (also called co-keyword or keywords co-occurrence) analysis enables researchers to gain knowledge of hot topics of their domain of interest. For beginners, it is helpful to have an overall impression of a research field, and thus to start his or her research by selecting a promising topic. For (relatively) mature scholars, it is also useful to obtain fresh ideas that may come up with the map of co-words networks. We still used VOSviewer to carry out the visualization. Being similar to the co-author networks, co-words networks consist of nodes and the links among them. To present the popularity of the words, we set weights as “occurrences”, a bigger node indicates more frequent occurrences of a word co-occurring with other words in the literature. The thickness between two words is determined by the number of their co-occurrences, and thicker links between two words signify stronger relevance. Other weights include “links” and “total link strength”, which emphasize the relevance of two keywords.
- (3)
- Co-citation analysis
Co-citation means that two articles are cited in one paper. Co-citation analysis builds co-cited relationships between articles, and then helps researchers to find important papers as well as their related researchers efficiently. It is a classic method in scientometrics [42]. We employed CiteSpace [43,44] to gain co-citation networks. Two important indices that CiteSpace can implement are “betweenness centrality” and “burst”. The former was first introduced by Freeman [45] to measure centrality based on the shortest path in a graph, and is used to show the pivotal nodes for information flow in a network (CiteSpace highlights the pivotal nodes with purplish red circles). Additionally, the latter was developed by Kleinberg [46], and is used to detect the burst of an event (citation, keyword, or publication) in CiteSpace with burst nodes colored with red circles. Another merit of CiteSpace is that it can generate the co-citation networks for different periods simultaneously, which is not only helpful for researchers to see the development of a research domain, but also helps one to infer the possible research trends.
Co-authorship, co-words, and co-citation analyses can be implemented by other scientometric mapping tools, not only those mentioned above. For a thorough overview of scientometric mapping tools, we refer the reader to the work of Li et al. [38]. The purpose of this paper is to gain knowledge of SA research on a macro-level, so we focus on the interpretation of the (visualized) results rather than the comparison of results output by different mapping tools.
3. Results and Analysis
SA research covers a wide range of disciplines because data with geographical or locational information have the feature of spatial autocorrelation. Additionally, SA research increased yearly over 1991–2021, which is shown in Figure 2 (i.e., Recs, the blue bars). Figure 2 also depicts the yearly changes of TLCS and TGCS for SA-related papers. Three significant peaks appear for 1993, 2007, and 2013, indicating that there were important contributions published in these years. There are also several moderate peaks between 1993 and 2007, showing that the SA methods and theories were continuously developed over these 15 years. The decreasing trend of the TLCS and TGCS after 2013 makes sense because there has not been enough time for newly published articles to be cited.
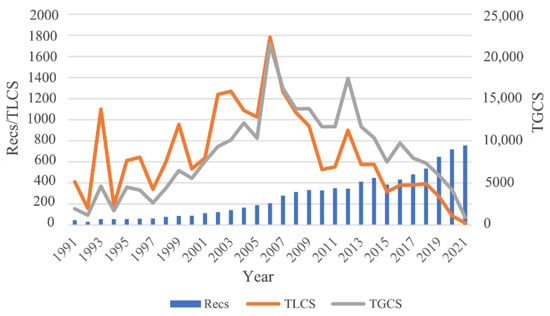
Figure 2.
Yearly counts of publications (Recs), total local citation scores (TLCS), and total global citation scores (TGCS) from 1991 to 2021. The left axis: counts of Recs and TLCS. The right axis: TGCS.
As mentioned in Section 2.1, the collected dataset contains complete metadata information which can tell a full story for each article. Therefore, compared to quantitative statistics, qualitative cognitions are more interesting. In this paper, we focus on influential journals, the main countries and institutions, representative research communities, hot topics and important references, and the evolution as well as possible research trends of SA research, which are discussed in the following subsections.
3.1. Influential Journals
An important element for scientific studies is the platform on which research findings are published and thus can be propagated. A formal platform can be academic journals which often are peer reviewed. It is necessary for researchers to know the influential journals in their research domains so that they can keep up to date with cutting-edge research. Table 2 presents ranks for journals in terms of Recs, TLCS, and TGCS. It shows that most productive journals relate to ecology. Specifically, Ecology, Global Ecology and Biogeography, and Ecography are the most representative journals with high TLCS values. These journals also have high TGCS values. In addition, as a geographical journal, Geographical Analysis is an outstanding geographical journal with TLCS 1002 and TGCS 4937. Except classic journals, open access journals such as PLoS ONE, Sustainability, and ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information appear in the Recs rank. For a research domain, important papers are probably published in journals with a high TLCS, so scholars typically pay more attention to these journals.

Table 2.
Top ten influential journals in terms of Recs, TLCS, and TGCS.
3.2. Main Countries and Institutions
For a scholar, conducting research includes not only reading and publishing articles in academic journals, but also conducting academic visits and communicating their research. Hence, knowing influential countries and institutions is necessary.
Table 3 shows different ranks Recs, TLCS, and TGCS. The top ten countries for each rank were extracted. USA ranks the first in all the three aspects, indicating that it has very big influence in SA research. Australia, Canada, and UK also have considerable impacts. As the only Asian country, China has the second largest amount of SA publications, and middling TLCS and TGCS ranks.

Table 3.
Top ten influential countries in terms of Recs, TLCS, and TGCS.
Table 4 presents the top ten institutions. Australian National University has the largest TLCS and TGCS values; University Montreal (Canada) and University Federal de Goiás (Brazil) also have high TLCS and TGCS values. Chinese Academy of Science and University of Chinese Academy of Science published the most SA research papers, but only has a rank of TGCS, indicating that ground-breaking works may be lacking somewhat. Except these institutions, the universities of USA make up a large proportion in this table, which is coincident with the result in Table 3.

Table 4.
Top ten influential institutions in terms of Recs, TLCS, and TGCS.
3.3. Representative Research Communities
The total number of authors for the 8461 papers is 27,752. In order to discover representative research communities, we conducted a co-authorship analysis for authors. Figure 3 shows the co-author networks of those authors who published more than five papers of SA research. Each node presents an author; the links between nodes indicate co-authorship between authors. A larger node means that papers of the respective author have more citations; a thicker link between two nodes means more collaborations of the authors. Two types of nodes can be recognized in the figure, grey ones which have rare co-authors that can hardly forms a community, and colored ones which have at least one co-author and indicate clusters. We focus on the colored clusters which are labeled by authors’ names and discuss the research communities according to the geographical locations of authors’ affiliations. Of note is that the figures shown in Section 3.3.1, Section 3.3.2, Section 3.3.3 and Section 3.3.4 (Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7) are zoomed in counterparts of Figure 3 with the scores of normalized citations of the leading authors listed in each figure caption.
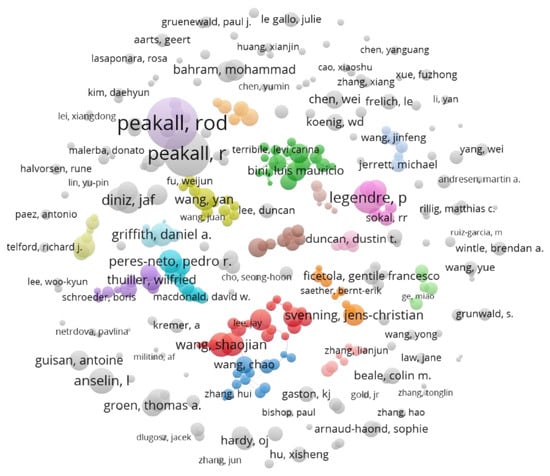
Figure 3.
Co-author networks of SA research. (The colored groups are detected SA research communities. The size of the node is weighted by normalized citations which can highlight the leading scholar(s) (i.e., the node(s) with bigger size(s)) of each community.)
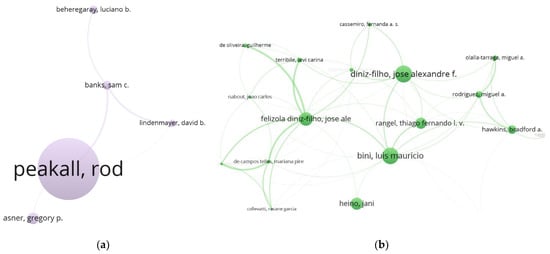
Figure 4.
Two research communities in the Southern Hemisphere: (a) Peakall’s GenAIEx community (Peakall, 139.71); (b) Diniz–Bini–Rangel community (Note: the node “diniz-filho” and the node “felizola diniz-filho” should be combined into one node. Diniz, 39.18 (=21.82 + 17.36); Bini, 21.46; Rangel, 14.36.)
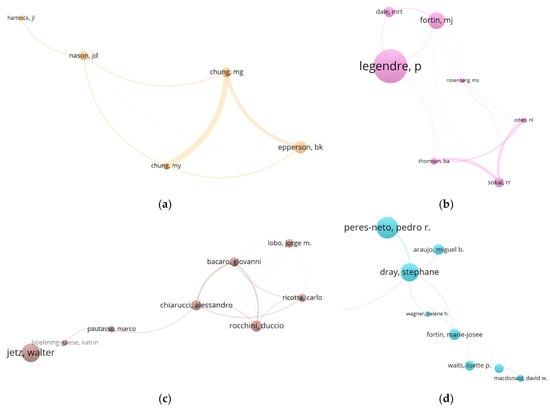

Figure 5.
Five research communities in northern America: (a) Epperson community (Epperson, 17.69); (b) Legendre–Fortin community (Legendre, 50.14; Fortin, 24.72); (c) Jetz community (Jetz, 20.55); (d) Peres Neto–Dray community (Peres Neto, 30.11; Dray, 25.38); and (e) Griffith community (Griffith, 30.43).
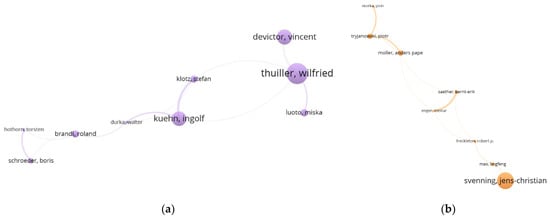
Figure 6.
Two research communities in Europe: (a) Thuiller–Kuehn community (Thuiller, 24.31; Kuehn, 16.73); and (b) Svenning community (Svenning, 26.21). (Note: Figure 6b is zoomed out to fit the typesetting. In fact, the node of Svenning is slightly bigger than the node of Thuiller in (a)).
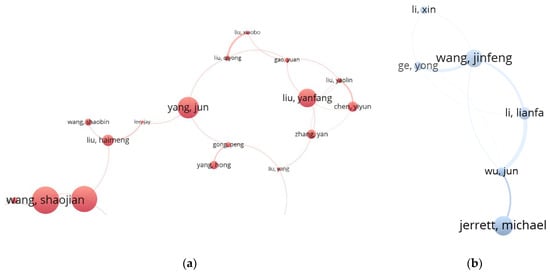
Figure 7.
Two research communities in China: (a) Wang–Yang–Liu community (Wang, 31.74; Yang, 24.88; Liu, 21.61); and (b) Wang community (Wang, 12.12). (Note: (b) is zoomed in to fit the typesetting).
3.3.1. Research Communities in the Southern Hemisphere
Two communities can be recognized in the southern hemisphere, as shown in Figure 4. The first is the Peakall community, and the second is the Diniz–Bini–Rangel community. Peakall’s GenAIEx, which is a “cross-platform package” [47] used to conduct population genetics analyses, contributes much to the TLCS and TGCS ranks of Australia and Australian National University (see Table 1 and Table 2). The package provides both frequency-based and distance-based methods to explore the spatial pattern of genetic structures; not only classical statistical analyses are available, but also spatial autocorrelation analyses, including spatial heterogeneity tests for genetic structures. In recent years, Peakall’s community pays much attention to the fine-scale genetic structure, which may offer new evolutionary insights that are overlooked by large-scale analyses [48,49,50].
The Diniz–Bini–Rangel community represents the Federal University Goiás (i.e., Univ Fed Goiás in Table 4) in Brazil. The SA research fruits of this community relate to multiple themes such as the geographical patterns of biodiversity and simulations [51], geographical genetics [52], and spatial statistics [53,54,55]. Compared to Peakall’s community, the Diniz–Bini–Rangel community is more connected and balanced. The Diniz–Bini–Rangel community consists of nodes with similar sizes, which indicates that the authors in these communities were cited at similar frequencies, whereas Peakall was cited far more frequently than other authors in Peakall’s community. The authors in the Diniz–Bini–Rangel community focus on spatial analysis and modelling for species distribution and patterns within macroecology [56,57].
These two communities constitute the main forces of SA research in the southern hemisphere. However, research communities in the northern hemisphere are more diverse, so in the following discussion, they are grouped at the continent level.
3.3.2. Research Communities in Northern America
Figure 5 presents five communities of SA research from northern America. The Epperson community is devoted to research of geographical genetics, developing probability and distribution theories of spatial statistics [58] and simulation processes to analyze population genetic data [59]; Epperson also considered the geographical scale problem, which is similar to the modifiable areal unit problem (MAUP) [60,61] in geography relating to the correlation among spatial statistics themselves [62]. The Jetz community (Yale University) addresses the geographical and environmental factors behind the distributions of biodiversity [63], and especially how the scale dependencies function on biodiversity [64]; in their studies, spatial autocorrelation always mingles with environmental variables, which impacts species distribution or co-occurrence [65].
Scholars from University of Montreal and University of Toronto constitute the Legendre–Fortin community, who study SA in the background of ecology. The beginning of Legendre’s SA work is the paper published in 1993 [28], which develops a frame within which SA can be described and measured, hypothesis testing can be conducted properly, and spatial structures can be introduced to ecological models explicitly. This paper led to the citation peaks in 1993 (see Figure 2). From then on, the SA works of Legendre and his team mainly emphasized exploring proper statistical methods for ecological studies [66]. Fortin’s team also focused on modelling ecological processes [67,68], however, from a perspective of conservation biology [69]. Sokal (1926–2012) is a pioneer who introduced SA to biology [70,71] and led studies of population genetics [27]; he collaborated extensively with authors in the Legendre–Fortin community. Another SA model-oriented research community is the Peres Neto–Dray community (Dray is from Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, France; his co-authorship with northern American authors groups him into this community), who are especially interested in exploring multi-scale and multivariate problems in ecological studies [72], and problems relating to the spatial weights matrices which represent spatial structures [73,74,75].
The Griffith community is devoted to spatial statistics and geographical information science (GIS) studies relating to the domain of geography. Griffith developed the Moran Eigenvector Spatial Filtering (MESF) technique to deal with the SA latent in the regressive model for spatial data [76,77], and this community develops a series of methods for solving mathematical or computational problems relating to SA (e.g., [78,79]).
3.3.3. Research Communities in Europe
Two research communities of SA research, presented in Figure 6, were discovered by VOSviwer. The Thuiller–Kuehn community focuses on species distribution modelling [80], uncovering the relationships between species distribution (in time series) and environmental factors [81]. Kuehn’s team developed an R package, “spind”, to improve prediction accuracy by selecting appropriate accuracy measures [82], and analysis lattice data at different spatial scales [83]. The Svenning community is focused on dealing with SA latent in spatial data in terms of regression models to conduct biodiversity studies [24].
3.3.4. Research Communities in Asia
The SA research forces of Asia are mainly in China. Figure 7 shows two communities: the Wang–Yang–Liu community, colored in red, and the Wang community, colored in pale blue. The common research object of the Wang–Yang–Liu community is cities. However, they concern different urban problems. Wang Shaojian and his co-workers study urban environmental pollution by spatial modelling, especially regression modelling with SA [33,84]. Yang Jun’s team use SA techniques to explore spatial factors that impact urban temperature [85,86]. Liu Yanfang’s research group is interested in urbanization [34] and urban public services, such as in Greenland [87], and medical facilities [88]. The Wang community is mainly made up of scholars from Chinese Academy of Science. Wang Jinfeng and his team developed “Sandwich Spatial Sampling” [31] and released “GD” (geographical detector or GeoDetector) [32,89] to handle spatial (stratified) heterogeneity latent in spatial/geographical datasets.
There are another two clusters of Chinese scholars in Figure 3: the blue cluster near the red community, and the green-yellow cluster near the Peakall community. We have not listed them out because the major nodes (i.e., Wang Chao, and Wang Yan) are made up of different scholars whose names are pronounced the same. As a summary, the blue cluster consists of researchers who apply SA analysis to spatial epidemic include the COVID-19 studies [35]; and authors in green-yellow cluster published papers about the spatial distribution of chemical elements in soil [90,91].
We discuss 11 SA research communities in total, except the Griffith community and two Chinese communities (Figure 7) belong to geography discipline, other 8 communities can be grouped in ecology and biology disciplines. Most of these 11 communities are methods originated so that they have great impacts.
3.4. Hot Topics and Important Papers
We analyze the research subject of SA in Section 3.2 and Section 3.3, and probe the research objects (hot topics) and important references in this part.
3.4.1. Hot Topics
A keywords co-occurrence map generated by VOSviewer is shown in Figure 8 (the co-occurrences of selected keywords are also listed); it provides evidence for picking out hot topics from more than 8000 references. Because “spatial autocorrelation” is a common topic in the literature, it has the largest size and is in the center of the co-occurrence map. In addition, other keywords still have significant sizes on which we focus to gain knowledge of the hot topics.
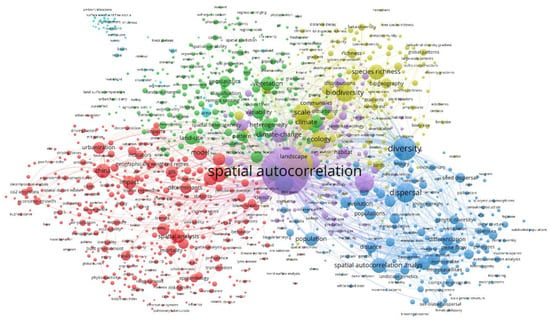
Figure 8.
SA keywords co-occurrence map by VOSviewer. (Co-occurrences: spatial autocorrelation, 3227; diversity, 657; dispersal, 461; climate change, 329; China, 329).
The blue cluster represents spatial autocorrelation analysis for molecular data, for the word “genetic” appears frequently in this group (e.g., landscape genetics, genetic structure, genetic diversity, etc.). The possible hot research topics include exploring the sources of diversity, e.g., seed dispersal [92,93], (isolation by) distance [94,95], (genetic) differentiation [96], and developing computer programs [97] for spatial genetic data analysis. The green-yellow cluster indicates studies pertaining to biodiversity, whose related topics include (species) richness [98], and beta-diversity [99]. Studies of this type consider factors such as scale [100] and climate [101], which impact biodiversity.
The green cluster highlights spatial heterogeneity and variability, for which geostatistical methods such as the use of variograms are frequently employed [87,102]. In addition, technologies including remote sensing and lidar are used to investigate topics related to land use [103], soil [104], and vegetation [105]. In this cluster, machine learning techniques [106], e.g., random forest, are applied to SA-related studies. The red cluster addresses topics such as urbanization, carbon emission, economic growth, health and epidemiology pertaining to China [107,108,109,110]. The spatial model selection, application, and improvement for specific research problems are frequently discussed by authors in this cluster [111,112,113]; in particular, the geographical weighted model is intensively developed and applied [114,115,116,117].
3.4.2. Important Papers
Figure 9 displays 959 papers whose nodes have larger sizes and are thus more influential. The biggest node is that of Peakall (2006) [20], who introduced GenAIEx 6 to the genetic analysis community, the popularity of this package may contribute to its convenience, i.e., that it can be used directly in Microsoft Excel. Another computer package used by this community is PopGenReport (Adamack (2014)) [118]. Hence, the purple cluster presents the main articles about packages that can conduct genetic data analyses. The green group suggests important works about geographical or environmental factors that impact genetic structure (e.g., Vekemans (2004) [119] and Streiff (1998) [120]).
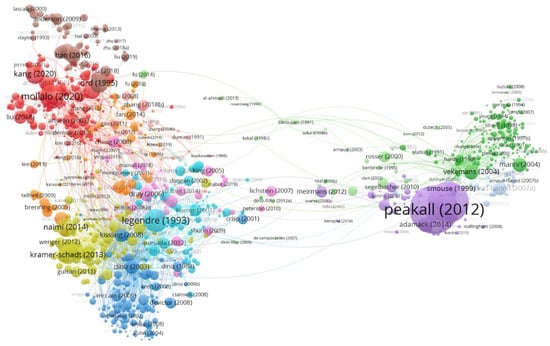
Figure 9.
Paper citations map by VOSviewer. (The weight for node size is still normalized citations).
The red and brown blocks emphasize important papers in spatial econometrics; these papers focus on local spatial autocorrelation indicators that describe spatial heterogeneity, e.g., Ord (1995) [121], and also focus on model building for spatial econometric analysis. The selected representative papers are Anselin (1996, 2002) [122,123], Griffith (2004) [124], and Leenders (2002) [125], etc. Papers of spatial model construction for ecological data are clustered into green-yellow, orange, and pink groups. Dray (2006) [75], Griffith (2006b) [30], Segurado (2004) [126], Naimi (2014) [127], Brenning (2005) [128], Telford (2005) [129], and Lichstein (2007) [130] are conspicuous. The (light) blue clusters are references relating to the demonstrations of the impacts of spatial autocorrelation in ecological modelling, e.g., Legendre (1993) [28], Diniz (2003) [51], and Kissling (2008) [131]; problems such as scale and spatial configuration (or weight matrix) are also addressed (Legendre (2002) [18], Jelinski (1996) [132], and Dungan (2002) [60]).
The important papers displayed in Figure 9 are in line with our reasoning: researchers prefer to cite references which are method-original or about user-friendly tools for implementing data analysis in their specific domains. Two other frequently used computer packages are GeoDa [133] and spdep [134,135], which are designed to handle spatial dependence hidden in geographical data. These references, however, are not presented in Figure 9.
3.5. Research Development and Trends
Section 3.4 discusses hot topics and important articles. However, the visualizations are for the whole time period so that papers which were published earlier have a bigger chance of being displayed, so we need to remove the intertwined knowledge so that the vein of the development of SA research from 1991 to 2021 can be clear. To gain information of the evolution of SA research, we need to consider the timeline, and CiteSpace [43,44] can meet this requirement. Figure 10 shows the co-keyword (or keywords co-occurrence) map and co-citation map with the timeline divided by six periods: 1991–1996, 1997–2002, 2003–2008, 2009–2014, 2015–2020, and 2021.
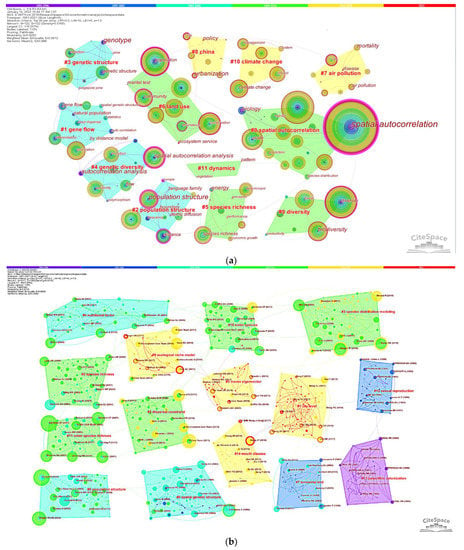
Figure 10.
Co-keyword and co-citation clusters. (a) co-keyword clusters and (b) co-citation clusters. (Representation of the timeline: 1991–1996 (the purple strip), 1997–2002 (the blue strip), 2003–2008 (the cyan strip), 2009–2014 (the light-green strip), 2015–2020 (the yellow strip), and 2021 (the red strip).) Convex hulls of different time periods are, respectively, colored; e.g., in the co-keyword clusters map, there are three clusters in 2015–2020, and in the co-citation clusters map, there are four clusters. A keyword’s color(s) is/are coincidence with its year(s) color(s), e.g., “spatial autocorrelation“ is colored purple, blue, cyan, light-green, yellow, and red like annual rings, indicating that it appears throughout 1991–2021. An article node is colored by color(s) of its citation year(s), e.g., Wang JF (2016) [32] was cited in 2015–2020 and 2021. These pivotal keywords have purplish red circles, and bursting cited papers are in red circles.
Table 5 presents the cluster labels of the co-keyword clusters map and co-citation clusters map. Although the CiteSpace extracted labels for co-citation clusters of 1991–1996 and 1997–2002, we can also summarize more accurate expressions through the representative papers displayed in the respective clusters. In the first period (1991–1996, purple), Sokal’s articles (e.g., [136,137]) were intensively cited; research in this period is mainly about SA analysis for biological data, which are pioneer works introducing SA in biology. In the second period (1997–2002, blue), studies were about spatial genetic structure [138] and diversity [139] considering SA in ecological modelling [140]. In the third period (2003–2008, cyan), SA studies also focused on spatial genetic structure and diversity, but publications pertaining to genetic population structure were emerging (e.g., [141,142]). In the fourth period, authors studied species richness, species distribution, etc.; “land use” appeared in this period, indicating that SA methodologies were applied to research more inclined to people. In the fifth period, except the “ecological niche model” and “moran eigenvector”, a large number of scholars employed SA methods to study city problems (air pollution [143], urbanization of China [144]), and problems of public health [145].

Table 5.
Label titles of clusters in Figure 10.
There seems to be a change that appeared in 2009–2014 after which SA research about studies in the geographical domain can be recognized in the global background, and SA studies began to cover problems pertaining to people and people’s lives. It can be inferred from the trajectory that more and more humanistic studies which employ SA methods will emerge in the future, so that SA may be a bridge which connects the observed phenomenon and its unobserved causes.
4. Discussion
4.1. Merits and Shortcomings of This Paper
In our research, we employed bibliographical-data-driven methods to explore the features of SA research which has several merits. Firstly, the results tell readers the general information of SA studies, such as those important journals, leading countries/regions, institutions, representative authors and articles. Secondly, the visualizations developed by scientometric tools suggest main research topics, and evolution of SA research. In a word, bibliographical analysis and visualization present objective results, and give researchers an overall view of SA research.
Although the results are objective, interpreting the results depends on people. For example, we organized the research communities in terms of countries/regions; however, it may be better to discuss these communities in terms of disciplines or research domains. Another point that needs to be explained is the division of time periods. The period 1991–2021 may be divided in a more “representative” manner rather than being equally divided (2021 is the single year left). The term “representative” means that topics in one period had better be different from the topics in its neighbor periods so that the development process can be presented more clearly. At last, as we mentioned in the very beginning of this paper, SA research covers to a wide range of disciplines within which geography-related domains counts small proportions, so works in geographical domains may be overlooked under such a huge base. To prevent this, we conducted co-keyword and co-citation analyses on papers within geographical domains.
4.2. Refine the Results from a Geographer’s Perspective
A total of 1699 records within geographical domains were extracted from the original dataset which have 8461 records. We conducted keywords co-occurrence analysis and co-citation analysis for the sub-dataset. Figure 11 shows topics highlighted in different time periods.
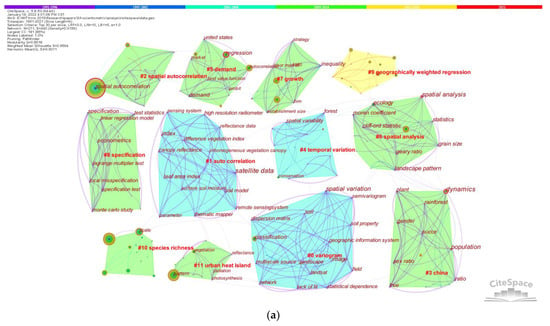
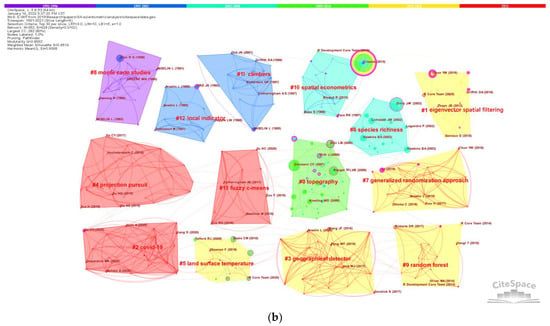
Figure 11.
Co-keyword and co-citation clusters for papers in geographical domains. (a) co-keyword clusters, and (b) co-citation clusters. (Interpretation of nodes, links, and colored convex hull are the same with those in Figure 10).
To interpret the co-keyword and co-citation map more efficiently and clearly, we condense the information to Figure 12. Instead of applying SA methods to specific research objects in Figure 10, topics in Figure 11 are more technical or method oriented. It can be seen from Figure 11 that, research often used Monte Carlo method to simulate SA in the early 1990s; in the middle-to-late 1990s and early 2000s, authors concentrated their attention to local SA, which is the variation (also called spatial heterogeneity) in a finer spatial scale comparing to the global scale on which global SA may not be significant. Classical SA methods developed in this period were Anselin’s LISA [146], Ord’s and Getis’ local SA statistics [121,147], and Fotheringham’s geographically weighted regression (GWR) [29]. Over 2003–2008, scholars considered temporal autocorrelation as well as spatial autocorrelation; related methods are thoroughly discussed in Cressie’s work [148]. Constructing proper models for data with different features is one of the hot topics in 2009–2014. Many social scientists employed regression models to explore econometric problems, and model specification tests are an important work during model-building processes. The Lagrange multiplier test for SA and spatial heterogeneity developed by Anselin [149] was frequently used to conduct specification tests. In 2015–2020, GWR, Wang’s geographical detector [89], and Griffith’s Moran Eigenvector Spatial Filtering (MESF) [15,76] were widely applied. Moreover, intensive developments and implementations [150] of these methods also contribute to their popularities. In 2021, SA methods were used to discover spatial or spatiotemporal distributions or patterns of COVID-19 (e.g., [151,152]); in addition, algorithms such as projection pursuit [153] and fuzzy c-means [154] were improved for spatial clustering in 2021.
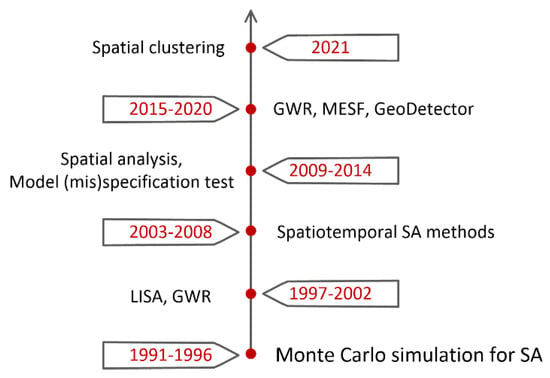
Figure 12.
Development of SA research in geographical domains 1991–2021.
Figure 12 also indicates a technical evolution of SA research. From the Monte Carlo simulation to combine typical clustering algorithm to spatial clustering, SA methods or techniques evolve with research needs and the features of datasets. Three main research trends of SA techniques may be: (1) developing faster-computing methods to handle massive spatial datasets; (2) exploring more intensive model building or parameter setting schemes to deal with finer-scale datasets as well as diversified research objects; and (3) improving model diagnosing methodologies to ensure the reliability of spatial models for datasets with huge sizes and multi-sources.
5. Conclusions
This paper employs scientometric methods, i.e., scientometric indicators and scientometric network techniques (co-author/word/citation analysis), to gain an all-encompassing perspective of SA research which covers a wide range of disciplines. Firstly, we used three indicators, Recs, TLCS, and TGCS, equipped in HistCite to evaluate the impacts of journals, countries/regions, and institutions relating to SA research. The results indicate that most of the top journals are of ecological and biological domains, among which geographical analysis ranks highly in terms of TLCS and TGCS. Northern American countries, European countries, Australia, Brazil, and China as well as institutions in these areas are influential. This gives general information about SA research.
Secondly, we employed VOSviewer to conduct an co-author analysis and identified 11 SA research communities. Griffith’s MESF community, Wang’s GeoDetecor community, and the Wang–Yang–Liu community are three groups contributing to SA research in the geographical domain. Anselin’s GeoDa group was not recognized. A reason for this may be that we did not include “spatial association”, which was the keyword of its seminar work [146] as a search topic.
Thirdly, we applied CiteSpace to conduct co-keyword and co-citation analyses and divided 1991–2021 into six time periods (2021 is the year single listed) so that the evolutionary path can be clearly presented. Global (the whole dataset with 8461 records) and local (the 1699 records relating to geographical domains) analyses were both conducted, from which research trends from two different views can be inferred. The first is from the view of all the related disciplines; SA research may be more humanistic, i.e., researchers may focus more on people and the natural as well as social environment within which they are living. SA models or SA analysis may better uncover the spatial pattern or key factors of the observed phenomena. The second is from the view of geography-related disciplines, and we make a technical summary. As the spatial datasets are becoming bigger, and their scales are finer, more efficient algorithms for computation are needed, and more intensive spatial model building or parameter setting schemes are also needed. In addition, improving model diagnosing methodology is very necessary for the reliable modelling of spatial data with huge sizes and multiple sources.
Although we have discussed SA-related research in geographical domains in the previous paragraph, it is still necessary to give an overall summary at the very end of this paper. As shown by the results of our analyses, SA-related research in geographical domains only makes up about 19% of the whole literature in which research of ecological and biological domains count the most. Before 2009, SA research in geographical domains can hardly be recognized in the global background, although fundamental works [4,5,6,15,29,146,147] were conducted by pioneering and later geographers. Hence, it may be after 2009 that these theoretical works of geographical domains are widely cited and deeply developed. Except the technical trends of SA research addressed in the above paragraph, the research trends of empirical studies should also be discussed. In fact, a very large portion of the detected research is applied research (e.g., the Wang–Yang–Liu community in Figure 7a and co-keywords clusters in Figure 11a) which implies that SA-related methodologies are potent to a wide range of research topics. Therefore, making geographers’ more visible and known is important for applying SA to more domains which use data with locational information as their research objects.
A last point that needs to be mentioned is that not all SA-related research is included in the 8461 records, because there are no searching strategies guaranteeing a collection without a single article left. However, these records should cover the majority of publications. Meanwhile, it does not mean that works not included in the datasets or not mentioned in this paper are not important. Although we cannot guarantee all SA papers to be included in the dataset, the results of this work still have referential value for SA researchers: not only for beginners to start a research topic more efficiently, but also for (relatively) mature researchers to gain new insights into their studies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijgi11050309/s1, Download 1–8461.
Author Contributions
Data curation, Kai Hu; methodology, Qing Luo and Kai Hu; formal analysis, Qing Luo and Kai Hu; visualization and writing—original draft, Qing Luo; validation, Wenxuan Liu; writing—review and editing, Kai Hu and Wenxuan Liu; resources and project administration, Huayi Wu. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 42001394; National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 71904064; National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 41930107; Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, grant number BK20190580; and Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering in Surveying, Mapping and Remote Sensing, Wuhan University, grant number 20I03.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The bibliographical data in .txt format that were analyzed in this paper can be found in the supplementary file.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tobler, W.R. A Computer Movie Simulating Urban Growth in the Detroit Region. Econ. Geograhy 1970, 46, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getis, A. A History of the Concept of Spatial Autocorrelation: A Geographer’s Perspective. Geogr. Anal. 2008, 40, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, B.J.L.; Marble, D.F. Spatial Analysis: A Reader in Statistical Geography; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Cliff, A.D.; Ord, J.K. The Problem of Spatial Autocorrelation. In Studies in Regional Science; Scott, A.J., Ed.; Pion: London, UK, 1969; pp. 25–55. [Google Scholar]
- Cliff, A.D.; Ord, J.K. Spatial Autocorrelation; Pion Limited: London, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Cliff, A.D.; Ord, J.K. Spatial Processes: Models & Applications; Pion: London, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Upton, G.J.G.; Fingleton, B. Spatial Data Analysis by Example: Point Pattern and Quantitative Data; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Haining, R. Spatial Data Analysis in the Social and Environmental Sciences; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Haining, R.P.; Haining, R. Spatial Data Analysis: Theory and Practice; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Anselin, L. Spatial Econometrics: Methods and Models; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Anselin, L.; Florax, R.; Rey, S.J. Advances in Spatial Econometrics: Methodology, Tools and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ripley, B.D. Statistical Inference for Spatial Processes; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, D.A. Spatial Autocorrelation: A Prime; Poin: London, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, D.A. Advanced Spatial Statistics; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, D.A. Spatial Autocorrelation and Spatial Filtering: Gaining Understanding through Theory and Scientific Visualization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, Y.; Griffith, D.A. Spatial Statistics and Geostatistics: Theory and Applications for Geographic Information Science and Technology; SAGE Publications: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, M.M.; Getis, A. Handbook of Applied Spatial Analysis: Software Tools, Methods and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, P.; Dale, M.R.T.; Fortin, M.; Gurevitch, J.; Hohn, M.; Myers, D.E. The consequences of spatial structure for the design and analysis of ecological field surveys. Ecography 2002, 25, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Dale, M.R.T.; Fortin, M.; Casgrain, P.; Gurevitch, J. Effects of spatial structures on the results of field experiments. Ecology 2004, 85, 3202–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GENALEX 6: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Ruibal, M.; Lindenmayer, D.B. Spatial autocorrelation analysis offers new insights into gene flow in the Australian bush rat, Rattus FuscipES. Comp. Study 2003, 57, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Smouse, P.E.; Peakall, R.; Gonzales, E. A heterogeneity test for fine-scale genetic structure. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 3389–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, M.J.; Dale, M.R.T. Spatial Analysis: A Guide for Ecologists; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, S.Q.N.; Xu, C.; Sandel, B.; Svenning, J.C. Effects of intrinsic sources of spatial autocorrelation on spatial regression modelling. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getis, A. Reflections on spatial autocorrelation. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2007, 37, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcu, M.; Kempenaers, B. Spatial autocorrelation: An overlooked concept in behavioral ecology. Behav. Ecol. 2010, 21, 902–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz-Filho, J.A.F.; Bini, L.M. Thirty-five years of spatial autocorrelation analysis in population genetics: An essay in honour of Robert Sokal (1926–2012). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2012, 107, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Legendre, P. Spatial autocorrelation—Trouble or new paradigm. Ecology 1993, 74, 1659–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Brunsdon, C.; Charlton, M. Geographically Weighted Regression: The Analysis of Spatially Varying Relationships; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, D.A.; Peresneto, P.R. Spatial modeling in ecology: The flexibility of eigenfunction spatial analyses. Ecology 2006, 87, 2603–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhuan, D.; Li, L.; Ge, Y. Spatial sampling design for monitoring the area of cultivated land. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Zhang, T.L.; Fu, B.J. A measure of spatial stratified heterogeneity. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Wang, S.J.; Zhang, W.Z.; Zhan, D.S.; Li, J.M. Does foreign direct investment affect environmental pollution in China’s cities? A spatial econometric perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.X.; Chen, Y.Y. On the spatial relationship between ecosystem services and urbanization: A case study in Wuhan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Dong, W.; Yang, K.; Ren, Z.D.; Huang, D.Q.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J. Temporal and spatial analysis of COVID-19 transmission in China and its influencing factors. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 105, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, S.; Bergstrom, C.T.; Borner, K.; Evans, J.A.; Helbing, D.; Milojevic, S.; Petersen, A.M.; Radicchi, F.; Sinatra, R.; Uzzi, B. Science of science. Science 2018, 359, eaao0185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, A.; Shen, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wu, J.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Stanley, H.E. The science of science: From the perspective of complex systems. Phys. Rep. 2017, 714-715, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Goerlandt, F.; Reniers, G. An overview of scientometric mapping for the safety science community: Methods, tools, and framework. Saf. Sci. 2021, 134, 105093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfield, E. Historiographic mapping of knowledge domains literature. J. Inf. Sci. 2004, 30, 119–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanzel, W. Coauthorship patterns and trends in the sciences (1980–1998): A bibliometric study with implications for database indexing and search strategies. Libr. Trends 2002, 50, 461–473. [Google Scholar]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, H. Co-citation in the scientific literature: A new measure of the relationship between two documents. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1973, 24, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 57, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Assoc Comp, M. Visualizing and Exploring Scientific Literature with CiteSpace. In Proceedings of the Chiir’18: Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Human Information Interaction & Retrieval, New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 11–15 March 2018; pp. 369–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, L.C. A Set of Measures of Centrality Based on Betweenness. Sociometry 1977, 40, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinberg, J. Bursty and hierarchical structure in streams. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2003, 7, 373–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research-an update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, R.E.; Banks, S.C.; Peakall, R. The impact of mating systems and dispersal on fine-scale genetic structure at maternally, paternally and biparentally inherited markers. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blyton, M.D.J.; Shaw, R.E.; Peakall, R.; Lindenmayer, D.B.; Banks, S.C. The role of relatedness in mate choice by an arboreal marsupial in the presence of fine-scale genetic structure. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2016, 70, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blyton, M.D.J.; Banks, S.C.; Peakall, R. The effect of sex-biased dispersal on opposite-sexed spatial genetic structure and inbreeding risk. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 1681–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz-Filho, J.A.F.; Bini, L.M.; Hawkins, B.A. Spatial autocorrelation and red herrings in geographical ecology. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2003, 12, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, J.A.F.; Barbosa, A.; Collevatti, R.G.; Chaves, L.J.; Terribile, L.C.; Lima-Ribeiro, M.S.; Telles, M.P.C. Spatial autocorrelation analysis and ecological niche modelling allows inference of range dynamics driving the population genetic structure of a Neotropical savanna tree. J. Biogeogr. 2016, 43, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, J.A.F.; Bini, L.M.; Rangel, T.F.; Morales-Castilla, I.; Olalla-Tarraga, M.A.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Hawkins, B.A. On the selection of phylogenetic eigenvectors for ecological analyses. Ecography 2012, 35, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, J.A.F.; Siqueira, T.; Padial, A.A.; Rangel, T.F.; Landeiro, V.L.; Bini, L.M. Spatial autocorrelation analysis allows disentangling the balance between neutral and niche processes in metacommunities. Oikos 2012, 121, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz-Filho, J.A.F.; Soares, T.N.; Lima, J.S.; Dobrovolski, R.; Landeiro, V.L.; de Campos Telles, M.P.; Rangel, T.F.; Bini, L.M. Mantel test in population genetics. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2013, 36, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, D.; Eduardo, A.A.; Oliveira, E.V.D.; Villalobos, F.; Dobrovolski, R.; Pereira, T.C.; Ribeiro, A.D.; Stropp, J.; Rodrigues, J.F.M.; Diniz, J.A.F.; et al. Unveiling geographical gradients of species richness from scant occurrence data. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2020, 29, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, J.M.; Tessarolo, G.; de Oliveira, G.; Souza, K.D.E.; Diniz, J.A.F.; Nabout, J.C. Geographical patterns in climate and agricultural technology drive soybean productivity in Brazil. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epperson, B.K. Geographical Genetics (MPB-38); Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Epperson, B.K.; Mcrae, B.H.; Scribner, K.T.; Cushman, S.A.; Rosenberg, M.S.; Fortin, M.; James, P.M.A.; Murphy, M.A.; Manel, S.; Legendre, P. Utility of computer simulations in landscape genetics. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 3549–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungan, J.L.; Perry, J.N.; Dale, M.R.T.; Legendre, P.; Citron-Pousty, S.; Fortin, M.J.; Jakomulska, A.; Miriti, M.; Rosenberg, M.S. A balanced view of scale in spatial statistical analysis. Ecography 2002, 25, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W.S. The Modifiable Areal Unit Problem (MAUP). In WorldMinds: Geographical Perspectives on 100 Problems: Commemorating the 100th Anniversary of the Association of American Geographers 1904–2004; Janelle, D.G., Warf, B., Hansen, K., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 571–575. [Google Scholar]
- Epperson, B.K. Spatial correlations at different spatial scales are themselves highly correlated in isolation by distance processes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.M.; Jetz, W. Remotely Sensed High-Resolution Global Cloud Dynamics for Predicting Ecosystem and Biodiversity Distributions. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertes, K.; Jetz, W. Disentangling scale dependencies in species environmental niches and distributions. Ecography 2018, 41, 1604–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domisch, S.; Wilson, A.M.; Jetz, W. Model-based integration of observed and expert-based information for assessing the geographic and environmental distribution of freshwater species. Ecography 2016, 39, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, F.G.; Legendre, P.; Borcard, D. Modelling directional spatial processes in ecological data. Ecol. Model. 2008, 215, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Minaya, J.; Conesa, D.; Fortin, M.J.; Alonso-Blanco, C.; Pico, F.X.; Marcer, A. A hierarchical Bayesian Beta regression approach to study the effects of geographical genetic structure and spatial autocorrelation on species distribution range shifts. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 929–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaak, D.J.; Peterson, E.E.; Hoef, J.M.V.; Wenger, S.J.; Falke, J.A.; Torgersen, C.E.; Sowder, C.; Steel, E.A.; Fortin, M.J.; Jordan, C.E.; et al. Applications of spatial statistical network models to stream data. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.-Water 2014, 1, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melles, S.J.; Fortin, M.J.; Lindsay, K.; Badzinski, D. Expanding northward: Influence of climate change, forest connectivity, and population processes on a threatened species’ range shift. Glob. Change Biol. 2011, 17, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokal, R.R.; Oden, N.L. Spatial autocorrelation in biology: 1. Methodology. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1978, 10, 199–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokal, R.R.; Oden, N.L. Spatial autocorrelation in biology: 2. Some biological implications and four applications of evolutionary and ecological interest. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1978, 10, 229–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dray, S.; Pelissier, R.; Couteron, P.; Fortin, M.; Legendre, P.; Peresneto, P.R.; Bellier, E.; Bivand, R.; Blanchet, F.G.; De Caceres, M. Community ecology in the age of multivariate multiscale spatial analysis. Ecol. Monogr. 2012, 82, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauman, D.; Drouet, T.; Fortin, M.J.; Dray, S. Optimizing the choice of a spatial weighting matrix in eigenvector-based methods. Ecology 2018, 99, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, D.A.; Arbia, G. Detecting negative spatial autocorrelation in georeferenced random variables. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 417–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dray, S.; Legendre, P.; Peres-Neto, P.R. Spatial modelling: A comprehensive framework for principal coordinate analysis of neighbour matrices (PCNM). Ecological Modelling 2006, 196, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, D.A. Spatial autocorrelation and eigenfunctions of the geographic weights matrix accompanying geo-referenced data. Can. Geogr./Le Géographe Can. 1996, 40, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, D.A. A linear regression solution to the spatial autocorrelation problem. J. Geogr. Syst. 2000, 2, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, D.A. Approximation of Gaussian spatial autoregressive models for massive regular square tessellation data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2015, 29, 2143–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, D.A.; Chun, Y.W.; Hauke, J. A Moran eigenvector spatial filtering specification of entropy measures. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2022, 101, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurell, D.; Franklin, J.; Konig, C.; Bouchet, P.J.; Dormann, C.F.; Elith, J.; Fandos, G.; Feng, X.; Guillera-Arroita, G.; Guisan, A.; et al. A standard protocol for reporting species distribution models. Ecography 2020, 43, 1261–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerasoli, F.; Thuiller, W.; Gueguen, M.; Renaud, J.; D’Alessandro, P.; Biondi, M. The role of climate and biotic factors in shaping current distributions and potential future shifts of European Neocrepidodera (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae). Insect Conserv. Divers. 2020, 13, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carl, G.; Kuhn, I. Spind: A package for computing spatially corrected accuracy measures. Ecography 2017, 40, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carl, G.; Levin, S.C.; Kuhn, I. spind: An R Package to Account for Spatial Autocorrelation in the Analysis of Lattice Data. Biodivers. Data J. 2018, 6, e20760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.J.; Huang, Y.Y.; Zhou, Y.Q. Spatial spillover effect and driving forces of carbon emission intensity at the city level in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.D.; Yang, J.; Sun, W.; Xiao, X.M.; Cecilia, J.X.; Jin, C.; Li, X.M. Impact of urban morphology and landscape characteristics on spatiotemporal heterogeneity of land surface temperature. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.D.; Yang, J.; Xiao, X.M.; Xia, J.H.; Jin, C.; Li, X.M. Influences of urban spatial form on urban heat island effects at the community level in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 53, 101972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Kong, X.S.; Jing, Y.; Cai, E.X.; Zhang, L.Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.L. Spatial Patterns and Driving Forces of Conflicts among the Three Land Management Red Lines in China: A Case Study of the Wuhan Urban Development Area. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.H.; He, Q.S.; Liu, Y.F.; Chen, W.Q.; Gao, Y. Inequality of public health and its role in spatial accessibility to medical facilities in China. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 92, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Geographical Detectors-Based Health Risk Assessment and its Application in the Neural Tube Defects Study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.J.; Zhao, K.L.; Zhang, C.S.; Wu, J.S.; Tunney, H. Outlier identification of soil phosphorus and its implication for spatial structure modeling. Precis. Agric. 2016, 17, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.Y.; Chen, Z.L.; Zhao, K.L.; Ye, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.Y.; Dong, J.Q.; Shao, Y.F.; Zhang, C.S.; Fu, W.F. Spatial Patterns of Potentially Hazardous Metals in Soils of Lin’an City, Southeastern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Wu, Y.C.; Serrao, E.A.; Zhang, J.P.; Jiang, Z.J.; Huang, C.; Cui, L.J.; Thorhaug, A.; Huang, X.P. Fine-scale genetic structure and flowering output of the seagrass Enhalus acoroides undergoing disturbance. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 5186–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, E.; Riofrio, M.L.; Iriondo, J.M. Complex fine-scale spatial genetic structure in Epidendrum rhopalostele: An epiphytic orchid. Heredity 2019, 122, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoe, A.L.; Nice, C.C.; Busbee, R.W.; Hood, G.R.; Egan, S.P.; Ott, J.R. Host plant associations and geography interact to shape diversification in a specialist insect herbivore. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 4197–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, Y.C.K.; Kristensen, N.P.; Gwee, C.Y.; Chisholm, R.A.; Rheindt, F.E. Bird diversity on shelf islands does not benefit from recent land-bridge connections. J. Biogeogr. 2022, 49, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacher, J.P.; Graitson, E.; Cauwenbergh, J.; Ursenbacher, S. Conservation genetics of a wide-ranged temperate snake: Same species, different locations, and different behaviour. Conserv. Genet. 2022, 23, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirmans, P.G. genodiveversion 3.0: Easy-to-use software for the analysis of genetic data of diploids and polyploids. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsukawa, H.; Yuasa, H.; Komuro, S.; Sergio, F. Raptor breeding sites indicate high plant biodiversity in urban ecosystems. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembicz, I.; Velev, N.; Boch, S.; Janisova, M.; Palpurina, S.; Pedashenko, H.; Vassilev, K.; Dengler, J. Drivers of plant diversity in Bulgarian dry grasslands vary across spatial scales and functional-taxonomic groups. J. Veg. Sci. 2021, 32, e12935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnott, A.; Emmerson, M.; Caplat, P.; Reid, N. Aerial invertebrate functional groups respond to landscape composition with only detritivores and predators responding to agri-environment scheme management. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 322, 107664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsianou, M.A.; Lazarina, M.; Michailidou, D.E.; Andrikou-Charitidou, A.; Sgardelis, S.P.; Kallimanis, A.S. The Effect of Climate and Human Pressures on Functional Diversity and Species Richness Patterns of Amphibians, Reptiles and Mammals in Europe. Diversity 2021, 13, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.W.; Wu, T.; Jiang, G.J.; Pu, L.J.; Zhang, J.Z.; Xu, F.; Yu, H.M.; Xie, X.F. Spatial Distribution, Environmental Risk and Safe Utilization Zoning of Soil Heavy Metals in Farmland, Subtropical China. Land 2021, 10, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.B.; Mao, W.L.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, L. Non-Linear Response of PM2.5 Pollution to Land Use Change in China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaum, M.; Walthert, L.; Fraefel, M.; Greiner, L.; Papritz, A. Mapping of soil properties at high resolution in Switzerland using boosted geoadditive models. Soil 2017, 3, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddeo, S.; Dronova, I.; Harris, K. Greenness, texture, and spatial relationships predict floristic diversity across wetlands of the conterminous United States. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 175, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, D.; Van Niekerk, A. Machine learning performance for predicting soil salinity using different combinations of geomorphometric covariates. Geoderma 2017, 299, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, Z.Q.; Chi, G.Q.; Wang, D.H.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zuo, D.Y. Differentiation and progress of urban regionalization in China: Perspectives of land use and geography. Appl. Geogr. 2021, 137, 102600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Y.; Dong, F.G.; Ji, Z.S. Research on coordination level and influencing factors spatial heterogeneity of China’s urban CO2 emissions. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Song, J.W. A comparative study of carbon tax and fuel tax based on panel spatial econometric model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 15931–15945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Chen, C.; Huang, C.Y.; Zhang, H.W.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Z.B.; Yang, S.G.; Li, L.J. Epidemiological features and spatial-temporal distribution of visceral leishmaniasis in mainland China: A population-based surveillance study from 2004 to 2019. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.C.; Li, B.; Nan, B. An analysis framework for the ecological security of urban agglomeration: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Geng, X.L.; Chen, W.X.; Fang, L.; Yao, R.; Wang, X.R.; Zhou, X. Inconsistency of Global Vegetation Dynamics Driven by Climate Change: Evidences from Spatial Regression. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, S.Q.; Wang, J.M. Applying the Super-EBM model and spatial Durbin model to examining total-factor ecological efficiency from a multi-dimensional perspective: Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 2183–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.B.; Brunsdon, C.; Charlton, M.; Harris, P. Geographically weighted regression with parameter-specific distance metrics. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 982–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.B.; Yang, W.B.; Ge, Y.; Harris, P. Improvements to the calibration of a geographically weighted regression with parameter-specific distance metrics and bandwidths. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2018, 71, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, X.L.; Lv, D.J.; Zhang, Y. Assessing the impact of land surface temperature on urban net primary productivity increment based on geographically weighted regression model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shen, J.Q.; Sun, F.H. Spatiotemporal differentiation of coupling coordination degree between economic development and water environment and its influencing factors using GWR in China’s province. Ecol. Model. 2021, 462, 109794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamack, A.T.; Gruber, B. PopGenReport: Simplifying basic population genetic analyses in R. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vekemans, X.; Hardy, O.J. New insights from fine-scale spatial genetic structure analyses in plant populations. Mol. Ecol. 2004, 13, 921–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streiff, R.; Labbe, T.; Bacilieri, R.; Steinkellner, H.; Glössl, J.; Kremer, A. Within-population genetic structure in Quercus robur L. and Quercus petraea (Matt.) Liebl. assessed with isozymes and microsatellites. Mol. Ecol. 1998, 7, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ord, J.K.; Getis, A. Local Spatial Autocorrelation Statistics: Distributional Issues and an Application. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L.; Bera, A.K.; Florax, R.; Yoon, M.J. Simple diagnostic tests for spatial dependence. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 1996, 26, 77–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Under the hood—Issues in the specification and interpretation of spatial regression models. Agric. Econ. 2002, 27, 247–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, D.A. A spatial filtering specification for the autologistic model. Environ. Plan. a-Econ. Space 2004, 36, 1791–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenders, R. Modeling social influence through network autocorrelation: Constructing the weight matrix. Soc. Netw. 2002, 24, 21–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segurado, P.; Araujo, M.B. An evaluation of methods for modelling species distributions. J. Biogeogr. 2004, 31, 1555–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimi, B.; Hamm, N.A.S.; Groen, T.A.; Skidmore, A.K.; Toxopeus, A.G. Where is positional uncertainty a problem for species distribution modelling? Ecography 2014, 37, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenning, A. Spatial prediction models for landslide hazards: Review, comparison and evaluation. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 5, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, R.J.; Birks, H.J.B. The secret assumption of transfer functions: Problems with spatial autocorrelation in evaluating model performance. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2005, 24, 2173–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichstein, J.W. Multiple regression on distance matrices: A multivariate spatial analysis tool. Plant Ecol. 2007, 188, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissling, W.D.; Carl, G. Spatial autocorrelation and the selection of simultaneous autoregressive models. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2008, 17, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelinski, D.E.; Wu, J.G. The modifiable areal unit problem and implications for landscape ecology. Landsc. Ecol. 1996, 11, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L.; Syabri, I.; Kho, Y. GeoDa: An Introduction to Spatial Data Analysis. Geogr. Anal. 2005, 38, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivand, R. Implementing spatial data analysis software tools in R. Geogr. Anal. 2006, 38, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivand, R.; Piras, G. Comparing Implementations of Estimation Methods for Spatial Econometrics. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 63, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokal, R.R.; Jacquez, G.M.; Wooten, M.C. Spatial autocorrelation analysis of migration and selection. Genetics 1989, 121, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokal, R.R.; Jacquez, G.M. Testing inferences about microevolutionary processes by means of spatial autocorrelation analysis. Evolution 1991, 45, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epperson, B.K.; Chung, M.G. Spatial genetic structure of allozyme polymorphisms within populations of Pinus Strobus (Pinaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2001, 88, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, B.A.; Porter, E.E. Relative influences of current and historical factors on mammal and bird diversity patterns in deglaciated North America. Global Ecology and Biogeography 2003, 12, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennon, J.J. Red-shifts and red herrings in geographical ecology. Ecography 2000, 23, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manel, S.; Schwartz, M.K.; Luikart, G.; Taberlet, P. Landscape genetics: Combining landscape ecology and population genetics. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, J.A.F.; Telles, M.P.D. Spatial autocorrelation analysis and the identification of operational units for conservation in continuous populations. Conserv. Biol. 2002, 16, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.R.; Wang, L.; Huang, W.Z.; Liu, S.; Yang, B.; Zheng, W.F. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Haze in Beijing Based on the Multi-Convolution Model. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.E.; Zhang, Z.K.; Ouyang, X.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, S.N.; Liu, B.L.; He, B.J. Delineating the spatial-temporal variation of air pollution with urbanization in the Belt and Road Initiative area. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 91, 106646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.Q.; Lv, Q.; Yin, F. Epidemiological and aetiological characteristics of hand, foot, and mouth disease in Sichuan Province, China, 2011-2017. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local Indicators of Spatial Association—LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getis, A.; Ord, J.K. The Analysis of Spatial Association by Use of Distance Statistics. Geogr. Anal. 1992, 24, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressie, N.; Wikle, C.K. Statistics for Spatio-Temporal Data; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Anselin, L. Lagrange Multiplier Test Diagnostics for Spatial Dependence and Spatial Heterogeneity. Geogr. Anal. 1988, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, Y.W.; Griffith, D.A.; Lee, M.; Sinha, P. Eigenvector selection with stepwise regression techniques to construct eigenvector spatial filters. J. Geogr. Syst. 2016, 18, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollalo, A.; Vahedi, B.; Rivera, K.M. GIS-based spatial modeling of COVID-19 incidence rate in the continental United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Choi, H.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, J. Spatial epidemic dynamics of the COVID-19 outbreak in China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Pan, H.Y.; Peng, L.; Chen, T.T.; Xu, J. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics of disaster resilience in Southwest China’s mountainous regions against the background of urbanization. Nat. Hazards 2020, 103, 3783–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grekousis, G. Local fuzzy geographically weighted clustering: A new method for geodemographic segmentation. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2021, 35, 152–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).