Network Patterns of Zhongyuan Urban Agglomeration in China Based on Baidu Migration Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
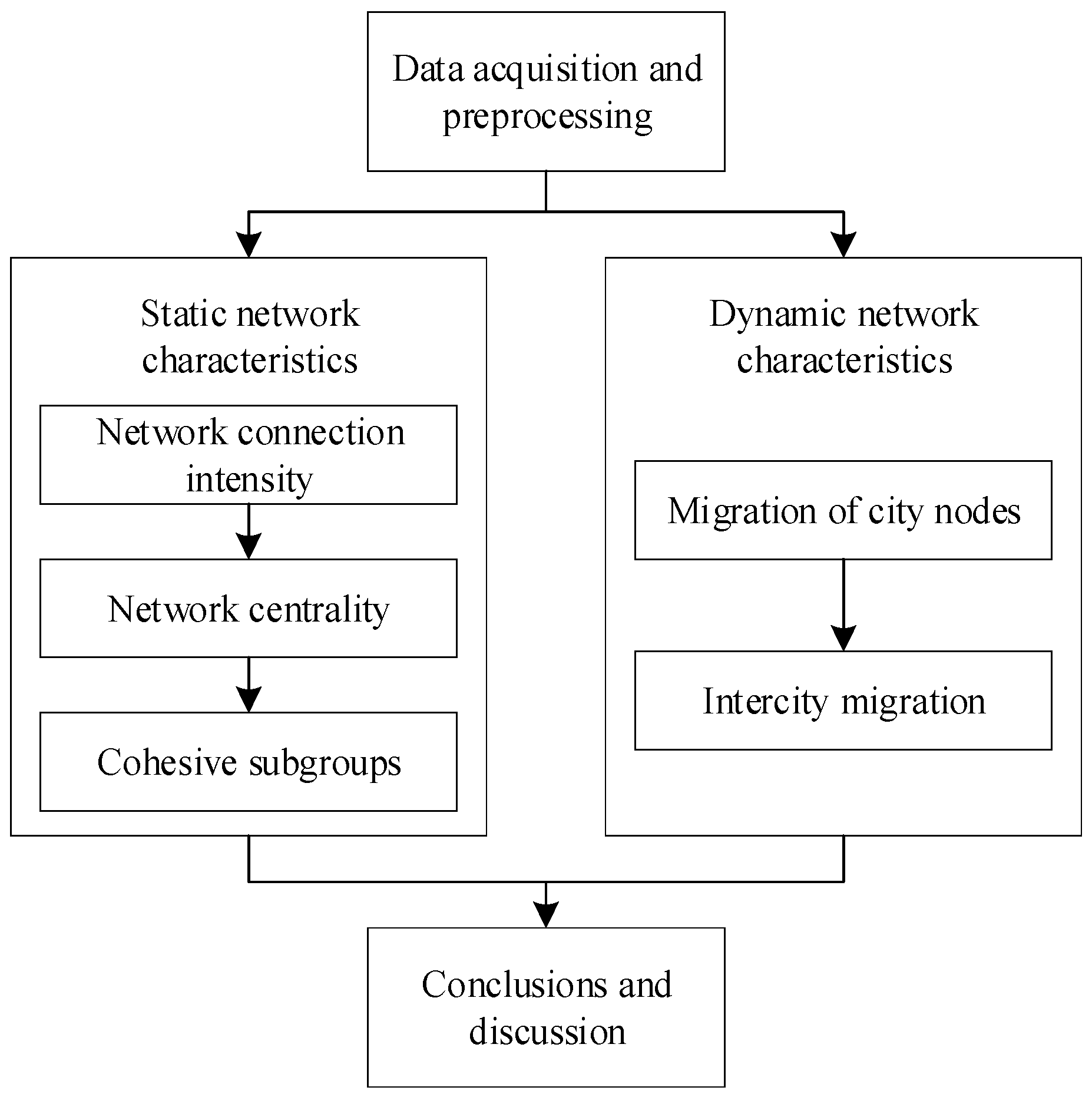
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Work Flow
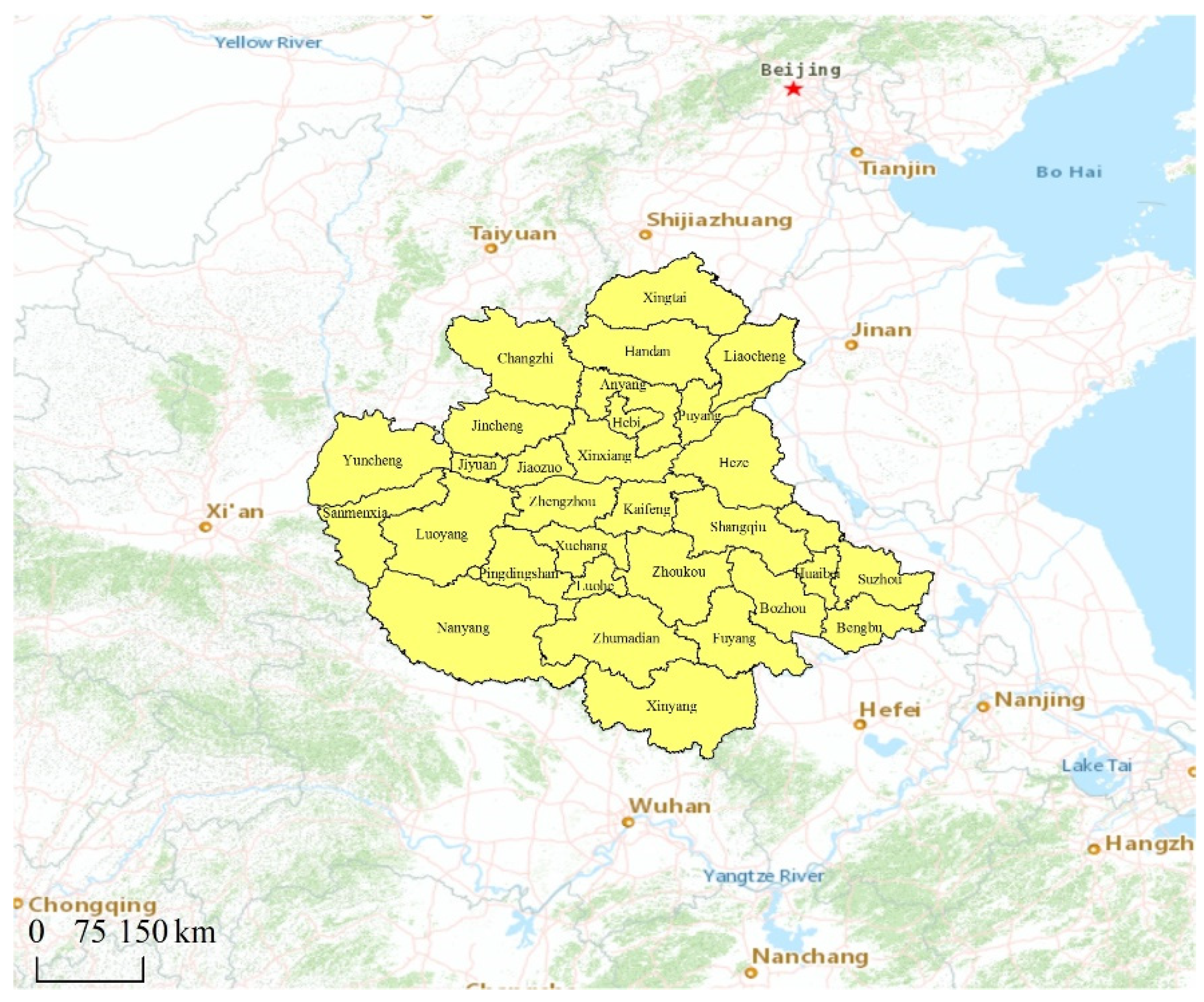
2.2. Data and Preprocessing
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Social Network Analysis
Point Weight
Centrality
Cohesive Subgroups
2.3.2. Dynamic Network Mining and Visualization
Time Series Clustering of the Point Weight Based on K-Means
Dynamic Visualization of the Edges Is Based on TimeCell
3. Results
3.1. Static Network Characteristics of Zhongyuan Urban Agglomeration Based on Social Network Analysis
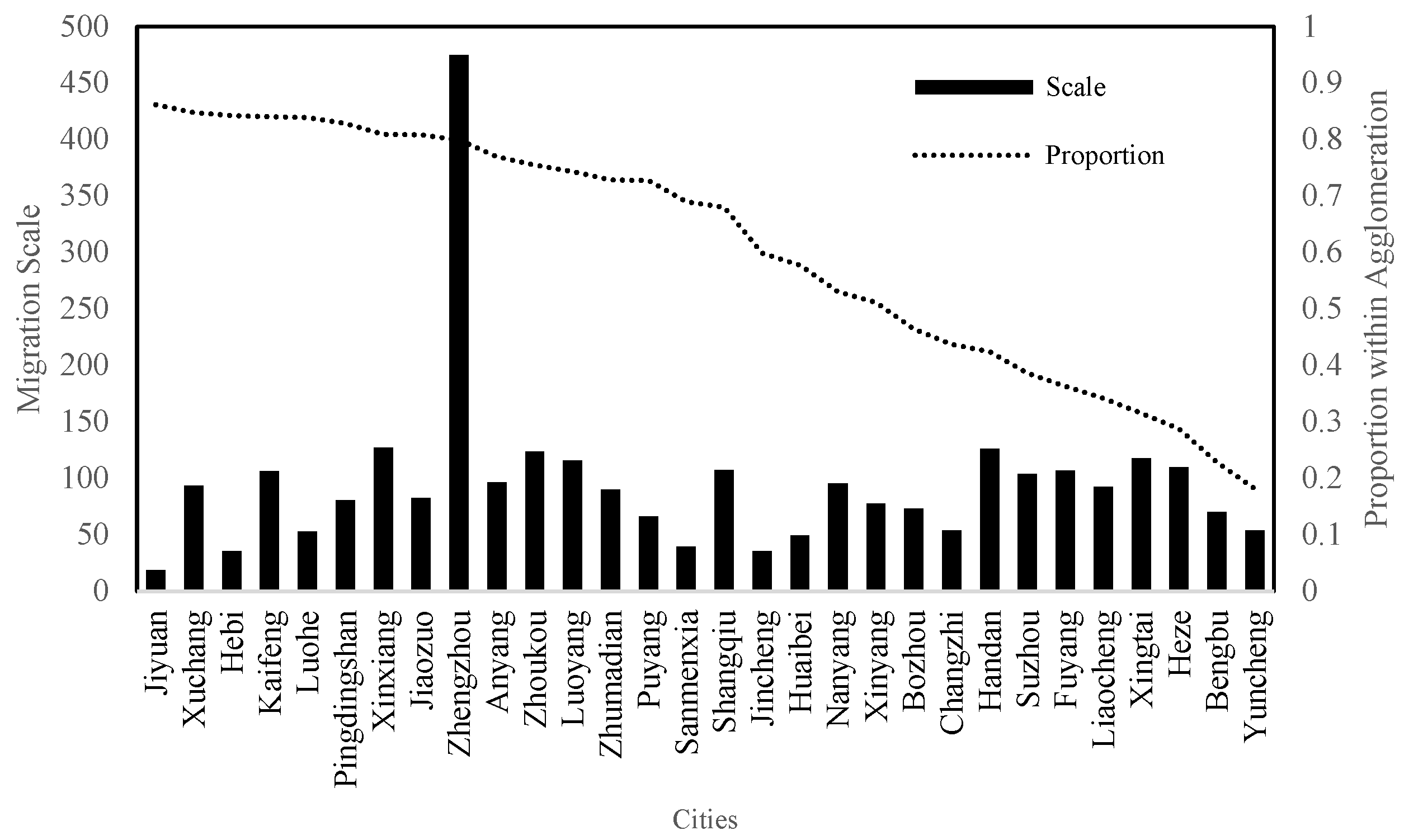
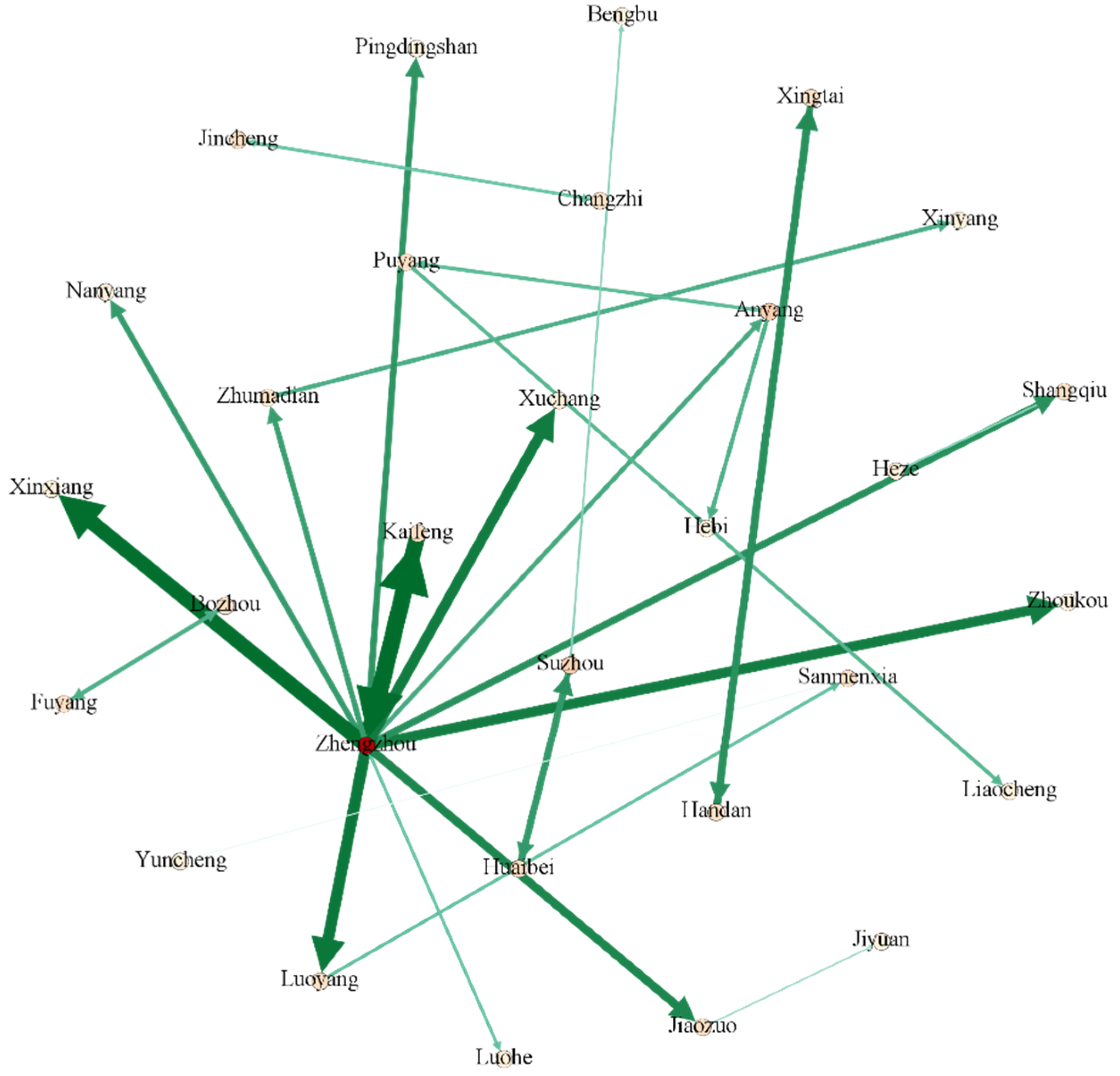
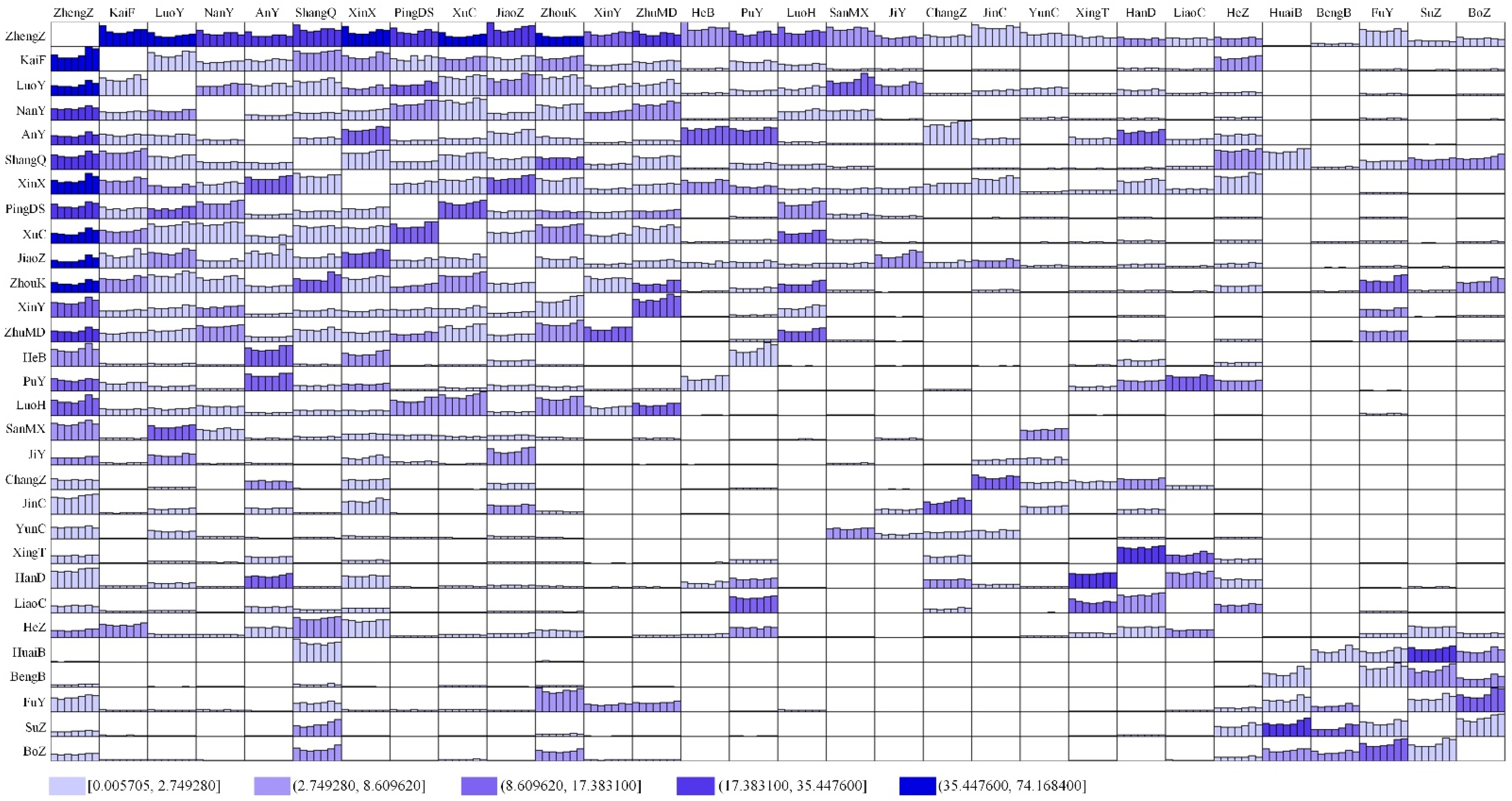
3.1.1. Network Connection Intensity
Levels of the Whole Network
City Point Weight
3.1.2. Network Centrality
3.1.3. Cohesive Subgroups
City Subgroup Division
Hierarchical Clustering Based on Subgroups
3.2. Dynamic Network Characteristics of Zhongyuan Urban Agglomeration in View of Periodicity
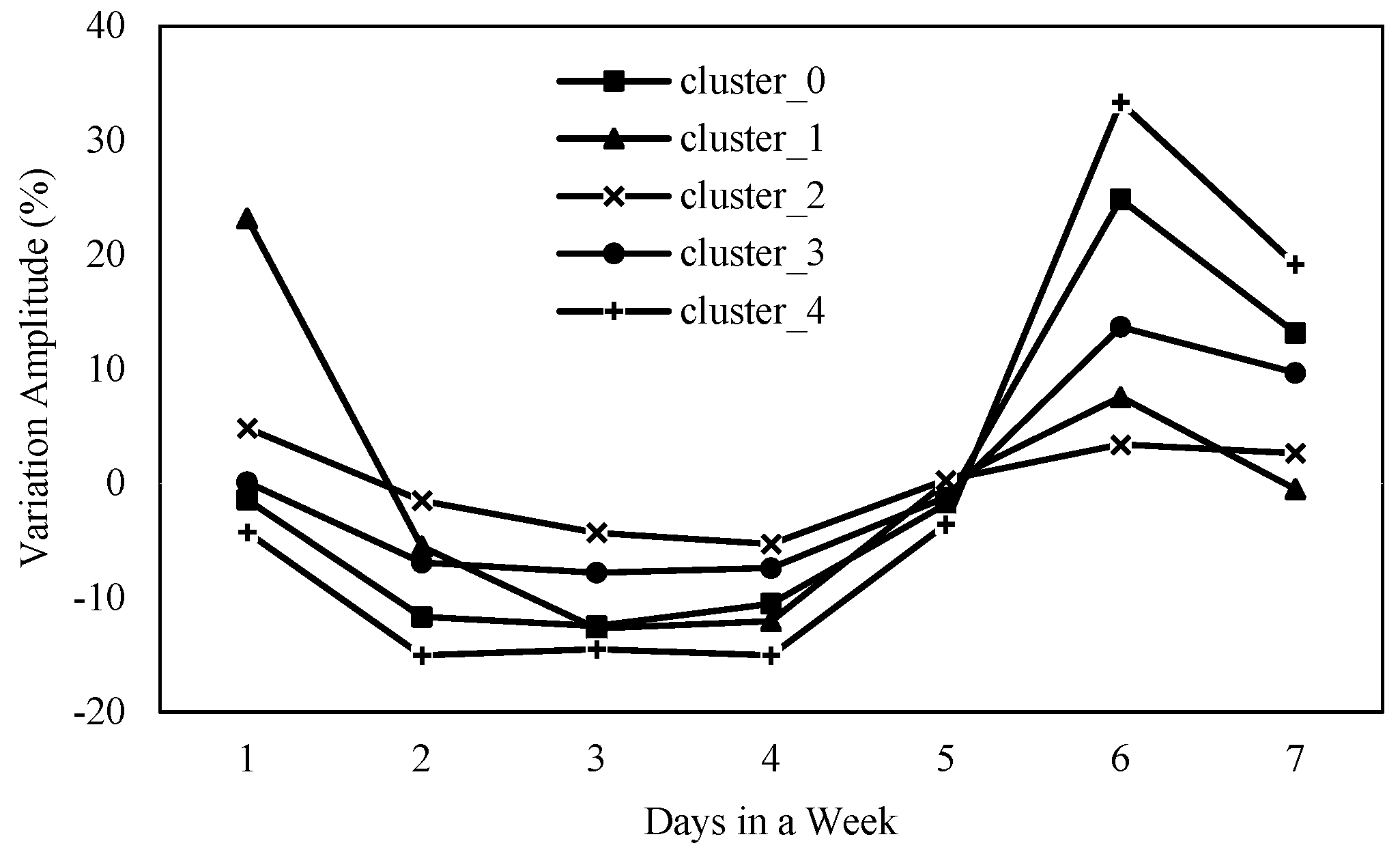
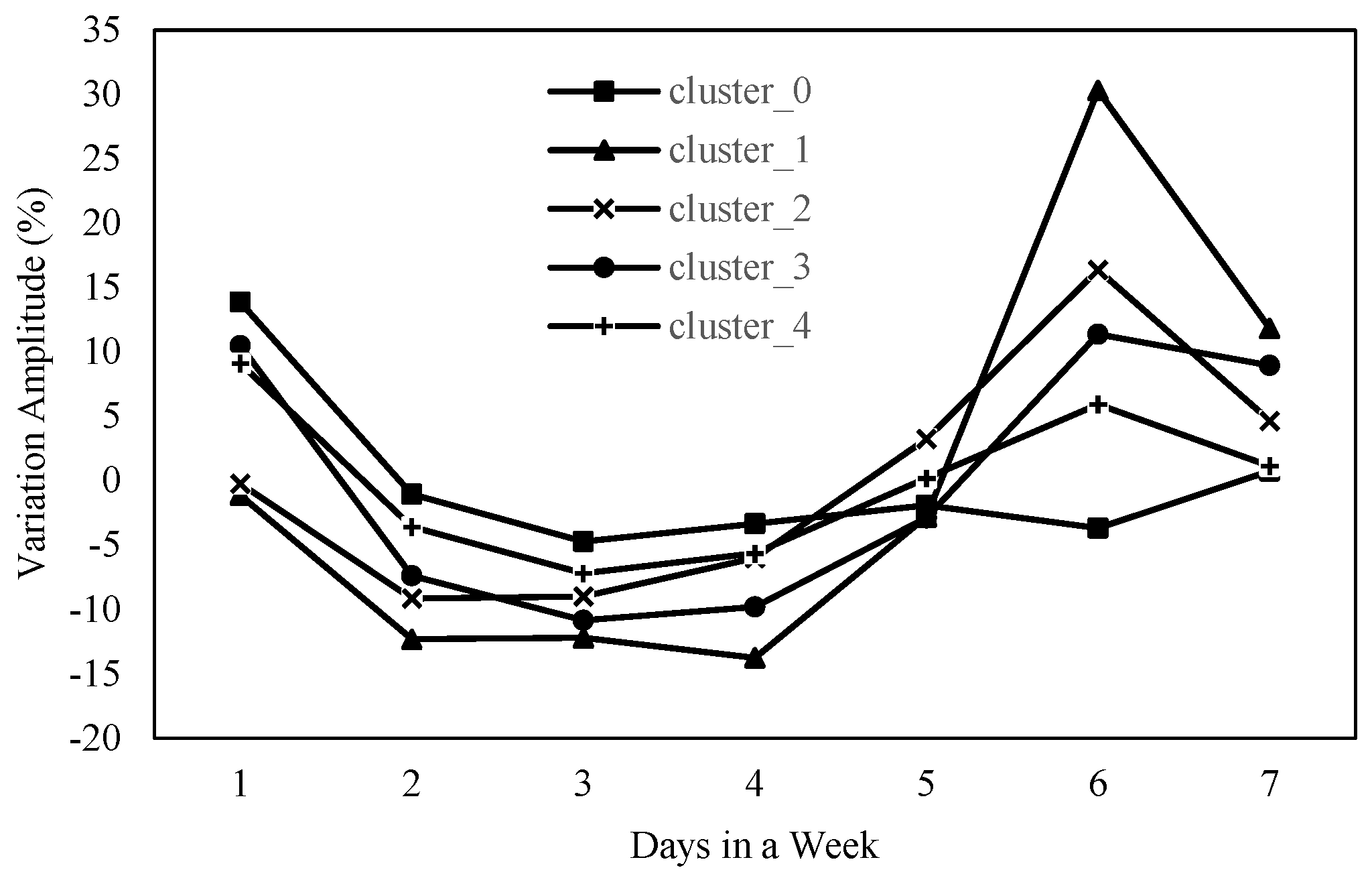
3.2.1. Dynamic Changes in the Migration Scale of City Nodes
Clustering Based on Immigration
Clustering Based on Emigration
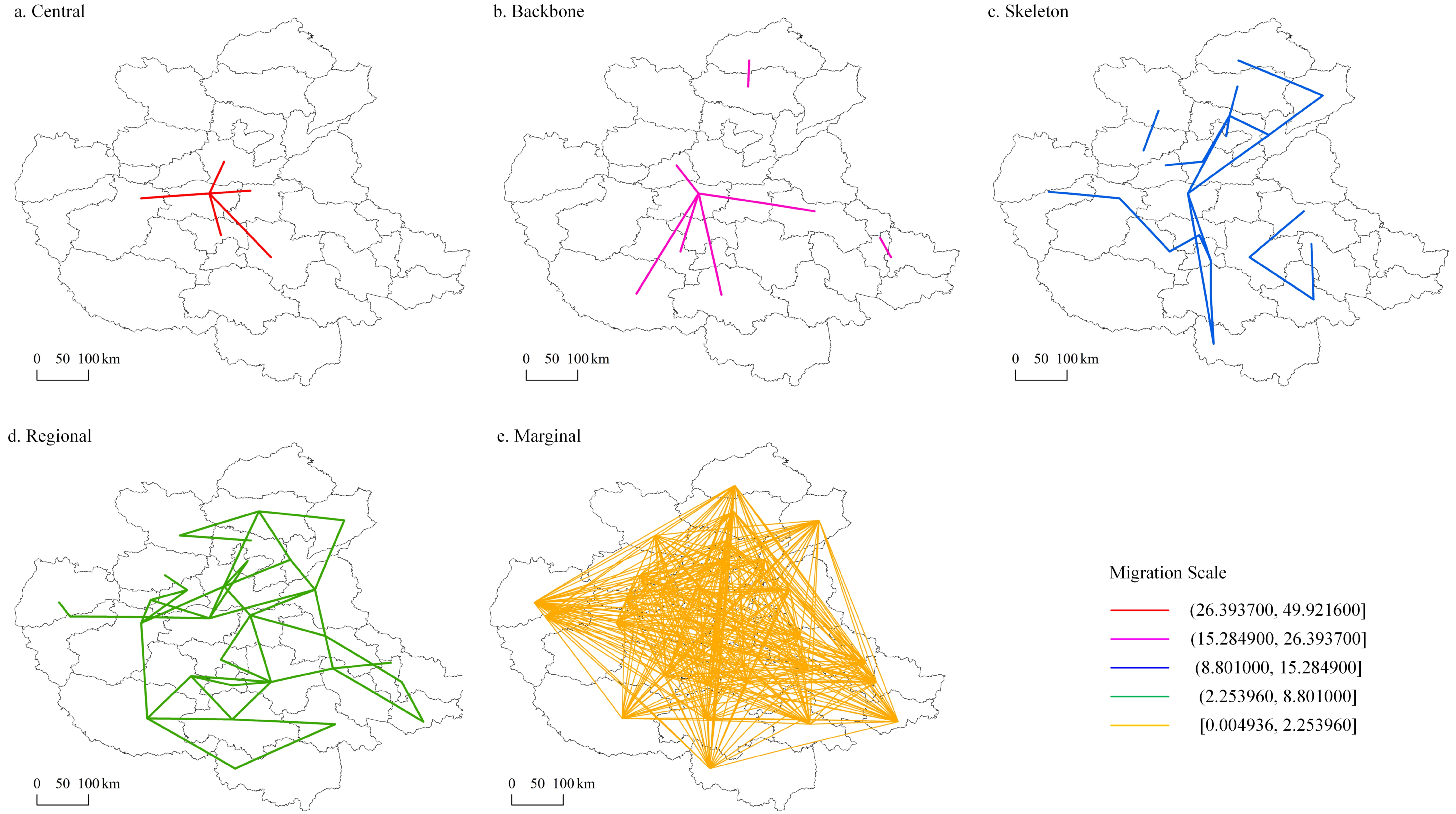
3.2.2. Dynamic Changes in the Intercity Migration Scale
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gottmann, J. Megalopolis: The Urbanized Northeastern Seaboard of the United States; The MIT Press: Cambridge, UK, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Gottmann, J. Megalopolitan systems around the world. Hrvat. Geogr. Glas. 1976, 38, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Li, C. Geographical discrimination for the urbanization response to upgrade of industry structure in Great Lakes industrial district. World Reg. Stud. 2006, 15, 71–77. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Murayama, Y.; Ichinose, T. Exploring the relationship between functional urban polycentricity and the regional characteristics of human mobility: A multi-view analysis in the Tokyo metropolitan area. Cities 2021, 111, 103109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Marshall, S.; Manley, E. Understanding the roles of rail stations: Insights from network approaches in the London metropolitan area. J. Transp. Geogr. 2021, 94, 103110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitz, A. The logistics dualization in question: Evidence from the Paris metropolitan area. Cities 2021, 119, 103407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. Mega–regions across the world and its experiences in China. Academics 2012, 6, 19–28, 269–273. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Castells, M. Local and global: Cities in the network society. Tijdschr. Voor Econ. En Soc. Geogr. 2002, 93, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q. China’s city network based on Tencent’s migration big data. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 853–869. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wang, M. Evolution of associated network characteristics between cities in Shandong province: Comparing central place and flow space theories. Geogr. Res. 2017, 36, 2197–2212. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B.; Zhong, Y. Study on spatial structure of population migration network of urban agglomeration in the middle Yangtze River based on complex network. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 118–128. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Hou, L. Research on characteristics of network structure of Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration based on Tencent population migration data. Mod. Urban Res. 2020, 9, 78–85. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhang, K.; Ma, F.; Guo, X.; Li, T. Spatial pattern of urban system based on gravity model and whole network analysis in eight urban agglomerations of China. Math. Probl. Eng. 2019, 9, 6509726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Huo, J.; Xue, J.; Cui, J.; Ma, B.; Liu, J. Comparative research of urban network structure of Zhongyuan Urban Agglomeration based on multivariate data. J. Henan Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2020, 50, 379–390. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Ding, Z.; Bu, S.; Wang, F. The network structure analysis of Zhongyuan Urban Agglomeration based on interactive and traffic flow relationship. Hum. Geogr. 2015, 30, 79–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Yu, Y.; Xie, L. Optimizing the spatial structure of urban agglomeration: Based on social network analysis. Qual. Quant. 2021, 55, 683–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Liu, J.; Qiao, D. Urban spatial connection and network structure in Zhongyuan Urban Agglomeration: A study based on integrated traffic and information flow. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2019, 39, 1929–1937. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mahutga, M.C.; Ma, X.; Smith, D.A.; Timberlake, M. Economic globalization and the structure of the world city system: The case of airline passenger data. Urban Stud. 2010, 47, 1925–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.J. The new geography of global civil society: NGOs in the world city network. Globalizations 2004, 1, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Shi, E. Spatial pattern of population daily flow among cities based on ICT: A case study of “Baidu Migration”. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 1667–1679. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, J. Study on the urban network connection of Chengdu-Chongqing Agglomeration based on Baidu Index. Areal Res. Dev. 2017, 36, 55–59, 129. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Krings, G.; Carabrese, F.; Ratti, C.; Blondel, V.D. Urban gravity: A model for inter-city telecommunication flows. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2009, 7, L07003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, S. Research on China’s urban population mobility network: Based on Baidu migration big data. Chin. J. Popul. Sci. 2017, 2, 35–46, 127. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Han, H.; Tang, Y.; Luo, G. Research on the characteristics of urban network structure in China based on Baidu migration data. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2021, 23, 1798–1808. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Yan, C. Spatial and temporal patterns of city connection networks in the Yellow River Basin based on Tencent’s big data of population migration. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 28–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ding, S.; Cao, W.; Fan, D.; Tang, B. Research on network patterns and influencing factors of population flow and migration in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Zhang, L.; Peng, P.; Huang, J. The network characteristics of urban agglomerations in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River based on Baidu migration data. Econ. Geogr. 2017, 37, 53–59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Lai, J. Research on spatial pattern of population mobility among cities: A case study of “Tencent Migration” big data in “National Day–Mid-Autumn Festival” vacation. Geogr. Res. 2019, 38, 1678–1693. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Notice of the National Development and Reform Commission on the Issuance of the Development Plan for Zhongyuan Urban Agglomeration. Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xxgk/zcfb/ghwb/201701/t20170105_962218_ext.html (accessed on 1 June 2021). (In Chinese)
- Liu, M.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Liang, L.; Qiao, D.; An, Y. The delimitation and evolution pattern of cities space attractive scopes in the Zhongyuan Urban Agglomeration. Areal Res. Dev. 2017, 36, 49–54. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H. Study on the Pattern and Optimization of Urban Network in Zhengzhou Urban Agglomeration from Space of Flows Viewpoint. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Yan, J. An inversion of the constitution of the Baidu migration scale index. J. Univ. Electron. Sci. Technol. China 2021, 50, 616–626. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J. Social Network Analysis; Sage Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. Whole Network Approach, 3rd ed.; Truth & Wisdom Press: Shanghai, China, 2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H. Cohesive subgroups and underlying factors in the urban network in China. Geogr. Res. 2019, 38, 2639–2652. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Qv, P.; Wang, X. DSNE: A new dynamic social network analysis algorithm. J. Jilin Univ. (Eng. Technol. Ed.) 2008, 38, 408–413. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Pei, T. Research progress in time series clustering methods based on characteristics. Prog. GeoGraphy 2012, 31, 1307–1317. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Shen, Z.; Tao, Y. Data Visualization, 2nd ed.; Publishing House of Electronics Industry: Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yi, J.S.; Elmqvist, N.; Lee, S. TimeMatrix: Analyzing temporal social networks using interactive matrix-based visualizations. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2010, 26, 1031–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Shen, L. Study on spatial-temporal characteristics of population mobility in the urban integration areas of three cities based on Tencent location big data. Mod. Urban Res. 2019, 11, 2–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]


| Point Centrality | Closeness Centrality | Between Centrality | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cities | Out Degree | In Degree | Cities | In Closeness | Out Closeness | Cities | Value |
| Zhengzhou | 20.000 | 18.000 | Zhengzhou | 69.048 | 74.359 | Zhengzhou | 423.522 |
| Luoyang | 9.000 | 8.000 | Shangqiu | 52.727 | 53.704 | Shangqiu | 127.813 |
| Zhoukou | 9.000 | 10.000 | Zhoukou | 52.727 | 54.717 | Zhoukou | 74.349 |
| Xinxiang | 8.000 | 7.000 | Kaifeng | 50.000 | 51.786 | Sanmenxia | 56.000 |
| Xuchang | 7.000 | 7.000 | Heze | 50.000 | 50.877 | Handan | 52.013 |
| Pingdingshan | 7.000 | 7.000 | Anyang | 49.153 | 49.153 | Anyang | 49.244 |
| Shangqiu | 7.000 | 8.000 | Xinxiang | 49.153 | 53.704 | Heze | 43.435 |
| Zhumadian | 7.000 | 7.000 | Handan | 49.153 | 36.709 | Puyang | 37.738 |
| Anyang | 6.000 | 6.000 | Puyang | 48.333 | 49.153 | Luoyang | 30.951 |
| Kaifeng | 6.000 | 6.000 | Zhumadian | 48.333 | 50.877 | Xinxiang | 30.820 |
| Nanyang | 6.000 | 6.000 | Xuchang | 47.541 | 50.000 | Fuyang | 30.559 |
| Puyang | 6.000 | 6.000 | Luoyang | 47.541 | 52.727 | Bozhou | 30.278 |
| Jiaozuo | 5.000 | 5.000 | Pingdingshan | 47.541 | 50.000 | Jiaozuo | 25.617 |
| Fuyang | 5.000 | 5.000 | Nanyang | 46.032 | 48.333 | Zhumadian | 21.807 |
| Heze | 5.000 | 5.000 | Luohe | 46.032 | 48.333 | Liaocheng | 21.479 |
| Luohe | 5.000 | 5.000 | Xinyang | 46.032 | 48.333 | Xinyang | 14.720 |
| Handan | 5.000 | 6.000 | Jincheng | 45.313 | 34.524 | Suzhou | 10.235 |
| Bozhou | 5.000 | 6.000 | Jiaozuo | 45.313 | 46.774 | Kaifeng | 10.204 |
| Liaocheng | 4.000 | 4.000 | Hebi | 44.615 | 45.313 | Jincheng | 9.808 |
| Xinyang | 4.000 | 4.000 | Jiyuan | 43.284 | 44.615 | Changzhi | 7.992 |
| Suzhou | 4.000 | 3.000 | Sanmenxia | 43.284 | 45.313 | Xuchang | 5.580 |
| Changzhi | 3.000 | 3.000 | Bozhou | 41.429 | 40.845 | Nanyang | 4.054 |
| Hebi | 3.000 | 3.000 | Fuyang | 39.189 | 40.278 | Pingdingshan | 3.849 |
| Bengbu | 3.000 | 3.000 | Liaocheng | 38.158 | 38.158 | Bengbu | 3.200 |
| Jiyuan | 3.000 | 3.000 | Huaibei | 36.709 | 37.179 | Luohe | 0.400 |
| Huaibei | 3.000 | 3.000 | Suzhou | 36.709 | 37.662 | Huaibei | 0.333 |
| Sanmenxia | 3.000 | 3.000 | Changzhi | 35.802 | 35.802 | Xingtai | 0.000 |
| Xingtai | 2.000 | 2.000 | Xingtai | 34.118 | 29.293 | Jiyuan | 0.000 |
| Jincheng | 2.000 | 3.000 | Bengbu | 31.183 | 31.183 | Yuncheng | 0.000 |
| Yuncheng | 1.000 | 1.000 | Yuncheng | 30.526 | 31.522 | Hebi | 0.000 |
| Subgroup Number | Cities |
|---|---|
| 1 | Zhengzhou, Kaifeng, Luoyang, Xinxiang, Xuchang |
| 2 | Zhengzhou, Kaifeng, Shangqiu, Xuchang, Zhoukou |
| 3 | Zhengzhou, Kaifeng, Shangqiu, Zhoukou, Heze |
| 4 | Zhengzhou, Kaifeng, Xinxiang, Puyang, Heze |
| 5 | Zhengzhou, Kaifeng, Pingdingshan, Xuchang, Zhoukou |
| 6 | Zhengzhou, Kaifeng, Xuchang, Zhoukou, Luohe |
| 7 | Zhengzhou, Luoyang, Nanyang, Pingdingshan, Xuchang |
| 8 | Zhengzhou, Luoyang, Nanyang, Pingdingshan, Zhumadian |
| 9 | Zhengzhou, Luoyang, Xinxiang, Jiaozuo, Jiyuan |
| 10 | Zhengzhou, Luoyang, Pingdingshan, Xuchang, Zhoukou |
| 11 | Zhengzhou, Luoyang, Pingdingshan, Xuchang, Luohe |
| 12 | Zhengzhou, Nanyang, Pingdingshan, Xuchang, Zhoukou, Zhumadian |
| 13 | Zhengzhou, Nanyang, Pingdingshan, Xuchang, Zhumadian, Luohe |
| 14 | Zhengzhou, Nanyang, Pingdingshan, Xinyang, Zhumadian |
| 15 | Zhengzhou, Anyang, Xinxiang, Hebi, Puyang |
| 16 | Zhengzhou, Pingdingshan, Xuchang, Zhoukou, Zhumadian, Luohe |
| 17 | Zhengzhou, Zhoukou, Xinyang, Zhumadian, Fuyang |
| Cluster Number | Max | Min | Cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster_0 | 24.86172 | –12.472807 | Bozhou, Xinyang, Zhoukou, Xinxiang, Luoyang, Jiyuan, Huaibei, Xuchang, Fuyang, Hebi |
| Cluster_1 | 23.1806 | –12.6821 | Zhengzhou |
| Cluster_2 | 4.8515374 | –5.296148 | Sanmenxia, Heze, Yuncheng, Handan, Changzhi |
| Cluster_3 | 13.671321 | –7.819742 | Nanyang, Shangqiu, Anyang, Pingdingshan, Jincheng, Luohe, Puyang, Liaocheng, Xingtai, Zhumadian |
| Cluster_4 | 33.3409 | –15.052 | Suzhou, Kaifeng, Jiaozuo, Bengbu |
| Cluster Number | Max | Min | Cities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster_0 | 13.89395 | –4.70248 | Zhoukou, Handan |
| Cluster_1 | 30.3182 | –13.7351 | Zhengzhou |
| Cluster_2 | 16.38534 | –9.140346 | Sanmenxia, Bozhou, Yuncheng, Changzhi, Fuyang |
| Cluster_3 | 11.39154 | –10.82296833 | Suzhou, Pingdingshan, Kaifeng, Xinxiang, Luoyang, Jiyuan, Huaibei, Luohe, Jiaozuo, Bengbu, Xuchang, Hebi |
| Cluster_4 | 9.109639 | –7.181792 | Xinyang, Nanyang, Shangqiu, Anyang, Jincheng, Puyang, Liaocheng, Heze, Xingtai, Zhumadian |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Hua, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, M. Network Patterns of Zhongyuan Urban Agglomeration in China Based on Baidu Migration Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11010062
Yang Z, Hua Y, Cao Y, Zhao X, Chen M. Network Patterns of Zhongyuan Urban Agglomeration in China Based on Baidu Migration Data. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2022; 11(1):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11010062
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zhenkai, Yixin Hua, Yibing Cao, Xinke Zhao, and Minjie Chen. 2022. "Network Patterns of Zhongyuan Urban Agglomeration in China Based on Baidu Migration Data" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 11, no. 1: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11010062
APA StyleYang, Z., Hua, Y., Cao, Y., Zhao, X., & Chen, M. (2022). Network Patterns of Zhongyuan Urban Agglomeration in China Based on Baidu Migration Data. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 11(1), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11010062





