Post-War Urban Damage Mapping Using InSAR: The Case of Mosul City in Iraq
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
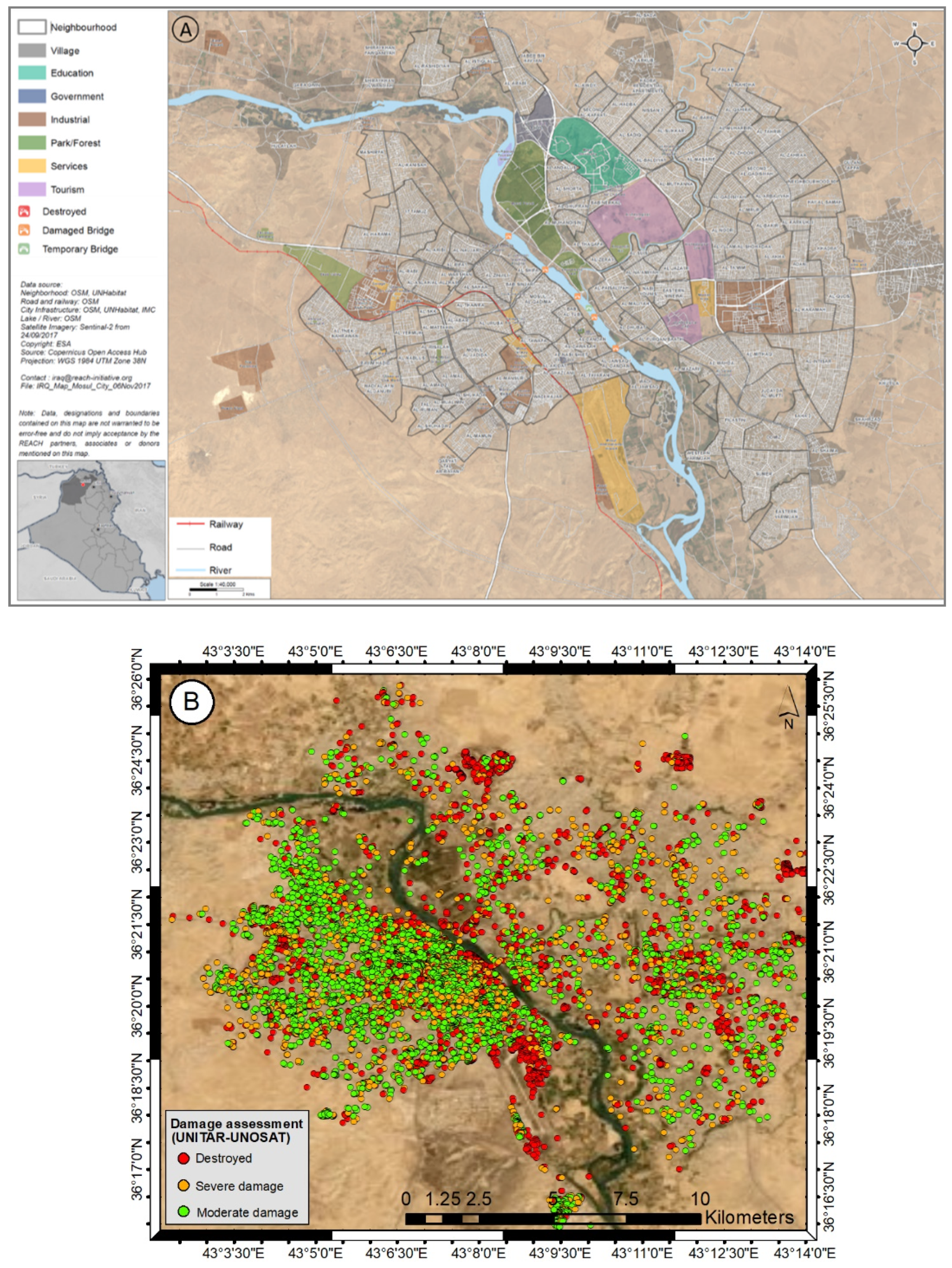
2.1. Study Area and Data
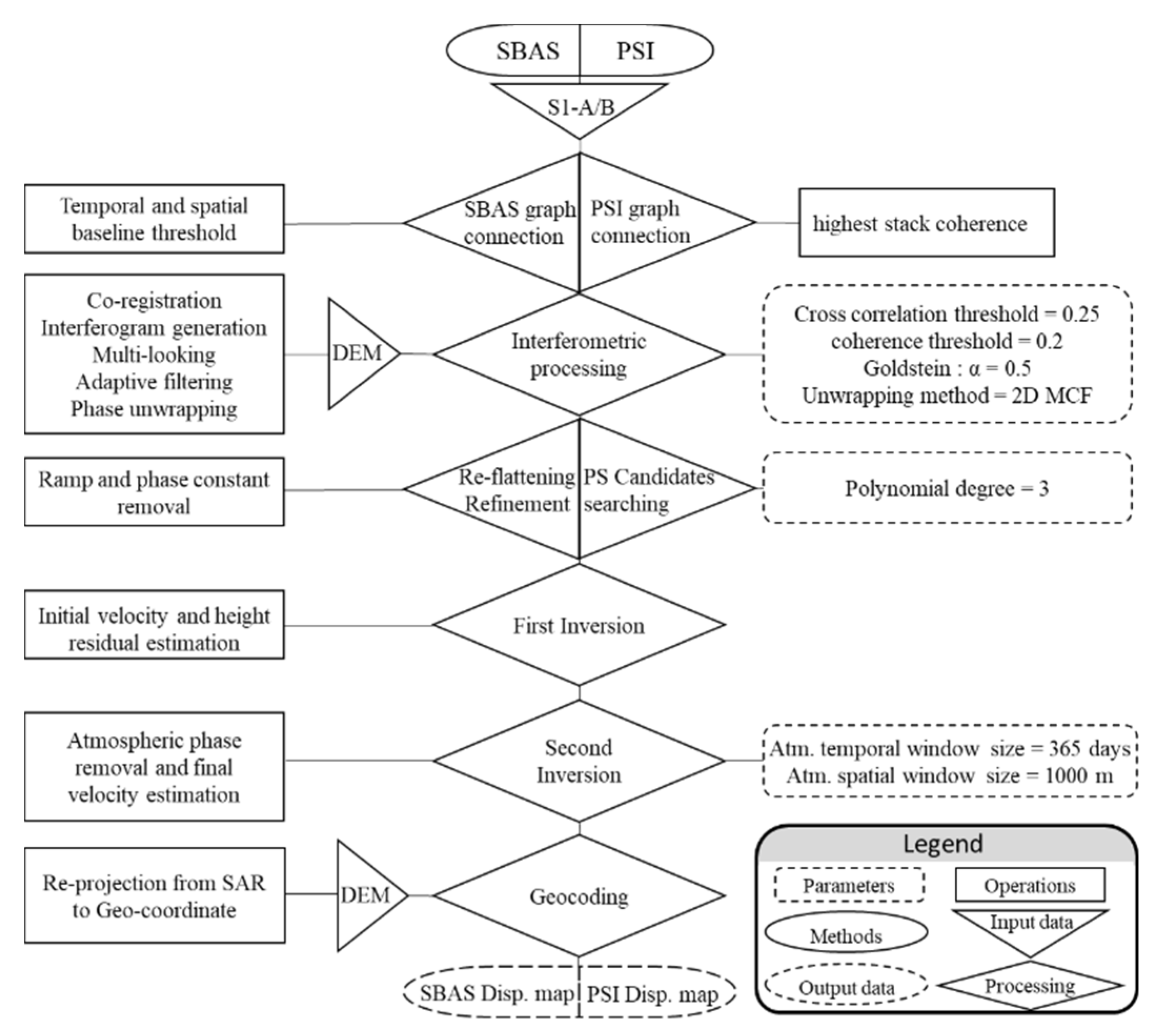
2.2. SBAS- and PSI-Based Deformation Detection
2.3. Coherence-Based Change Detection
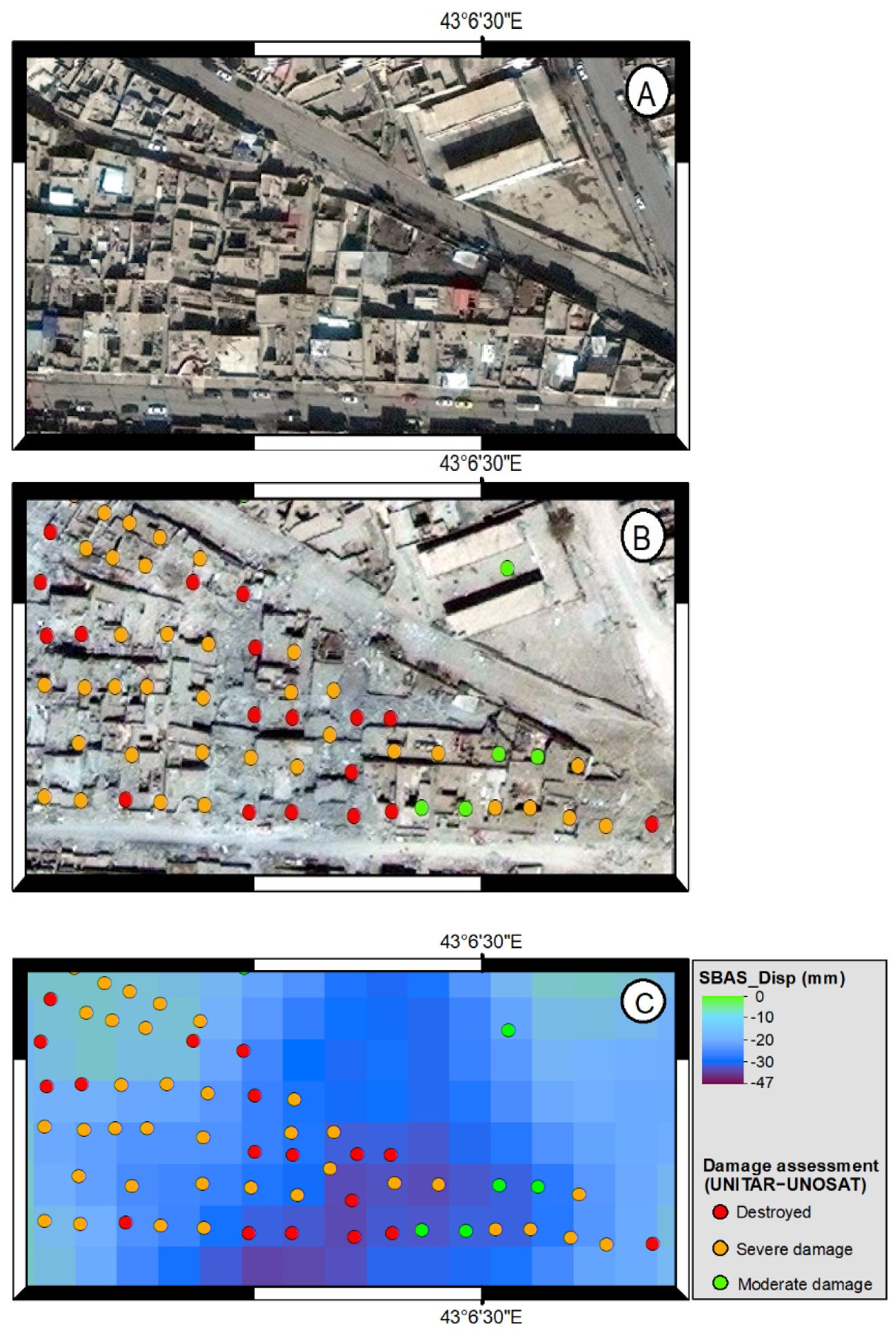
3. Results
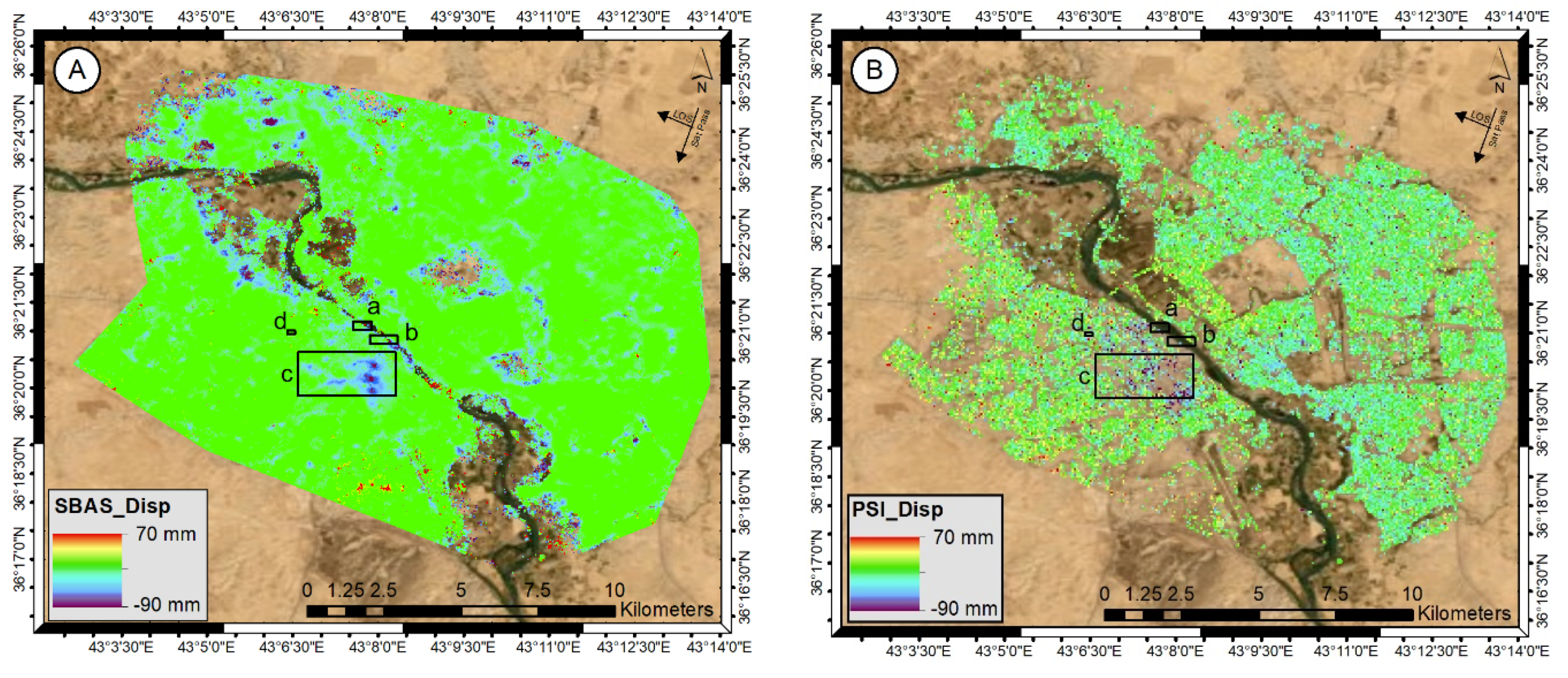
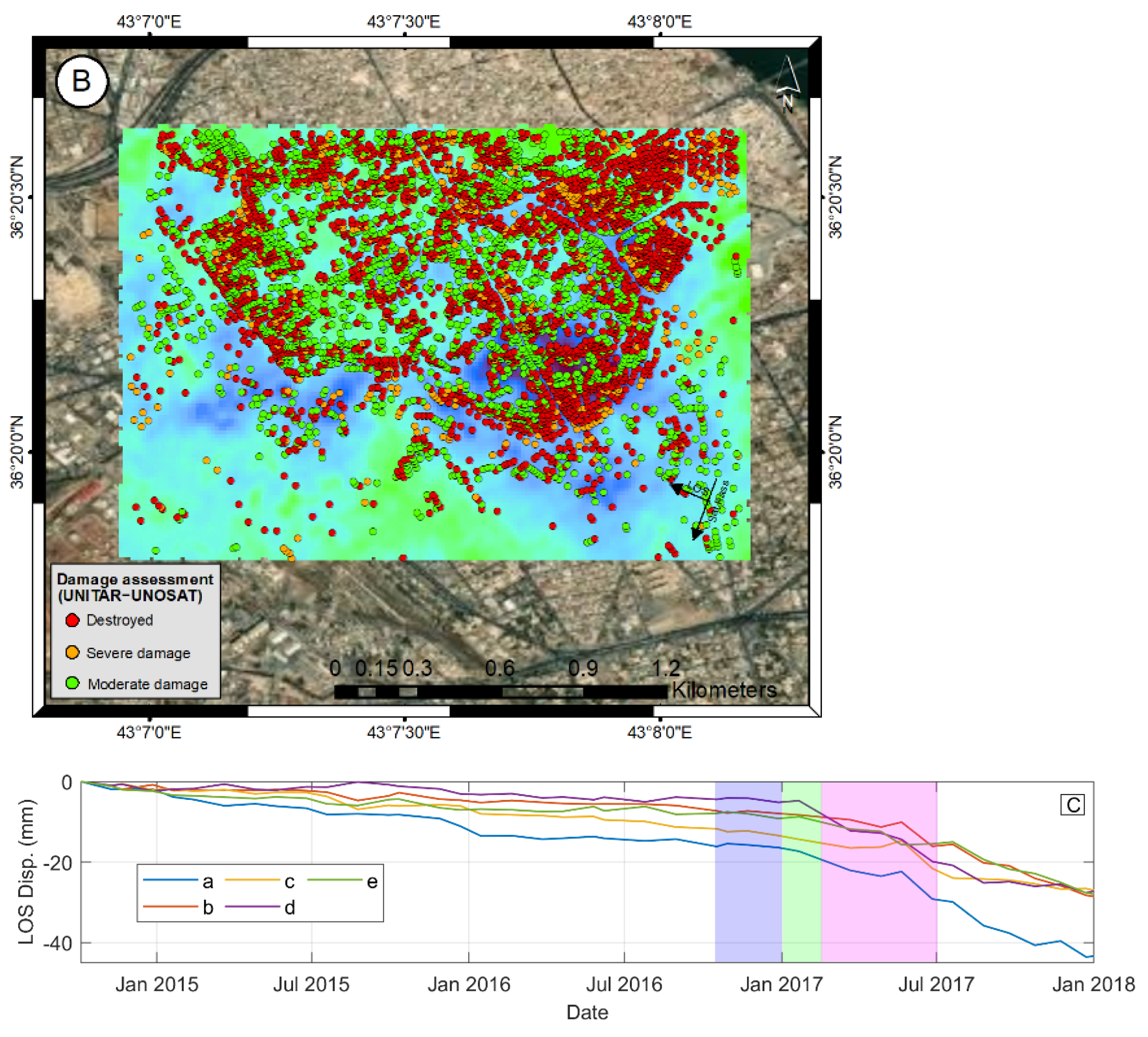
3.1. DInSAR City Monitoring (SBAS–PSI)
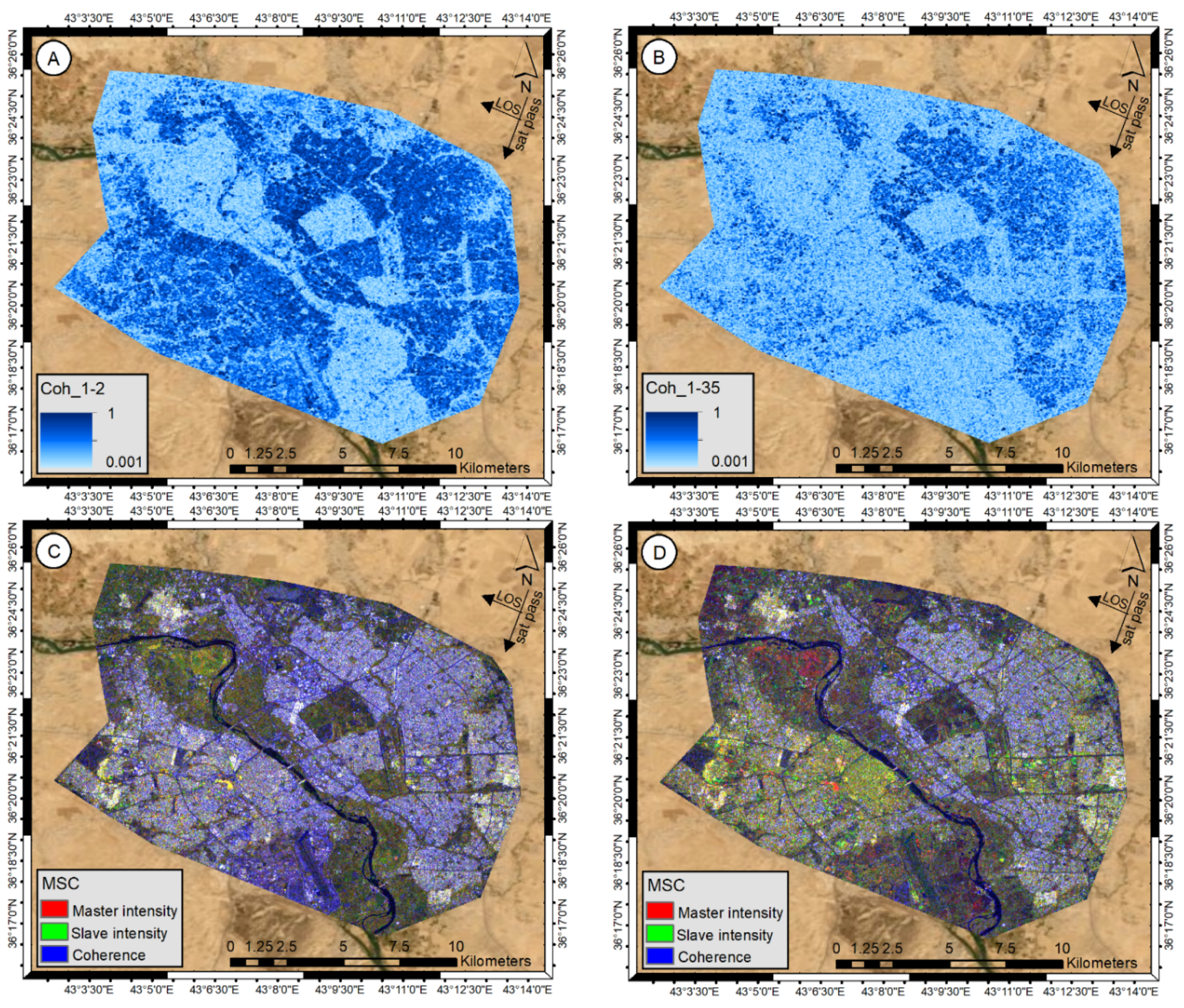
3.2. Coherence-Based Change Detection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruiz-Armenteros, A.M.; Lazecky, M.; Hlaváčová, I.; Bakoň, M.; Manuel Delgado, J.; Sousa, J.J.; Lamas-Fernández, F.; Marchamalo, M.; Caro-Cuenca, M.; Papco, J.; et al. Deformation monitoring of dam infrastructures via spaceborne MT-InSAR. The case of La Viñuela (Málaga, southern Spain). Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 138, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Susaki, J. Optical and SAR data integration for automatic change pattern detection. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, II, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramondo, S.; Bignami, C.; Pierdicca, N.; Chini, M. SAR and optical remote sensing for urban damage detection and mapping: Case studies. 2007 Urban Remote Sens. Jt. Event URS 2007, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noviello, C.; Verde, S.; Zamparelli, V.; Fornaro, G.; Pauciullo, A.; Reale, D.; Nicodemo, G.; Ferlisi, S.; Gullà, G.; Peduto, D. Monitoring buildings at landslide risk with SAR: A methodology based on the use of multipass interferometric data. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Mag. 2020, 8, 91–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, M.; Pierdicca, N.; Emery, W.J. Exploiting SAR and VHR optical images to quantify damage caused by the 2003 Bam earthquake. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 47, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, M.; Saroli, M.; Stramondo, S.; Bignami, C.; Albano, M.; Falcucci, E.; Gori, S.; Doglioni, C.; Polcari, M.; Tallini, M.; et al. New insights into earthquake precursors from InSAR. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubin, A.; Saleem, A. Remote sensing-based mapping of the destruction to Aleppo during the Syrian Civil War between 2011 and 2017. Appl. Geogr. 2019, 108, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Gong, L.; Zhang, J. A correlation change detection method integrating PCA and multi-texture features of SAR image for building damage detection. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 52, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nex, F.; Duarte, D.; Tonolo, F.G.; Kerle, N. Structural building damage detection with deep learning: Assessment of a state-of-the-art cnn in operational conditions. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-E.; Jung, Y.T. Detection of Earthquake-Induced Building Damages Using Polarimetric SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulain, V.; Inglada, J.; Spigai, M.; Tourneret, J.-Y.; Marthon, P. High-resolution optical and SAR image fusion for building database updating. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2900–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Shan, J. A comprehensive review of earthquake-induced building damage detection with remote sensing techniques. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 84, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, T.W.; Chu, J.; Frankenberg, E.; Thomas, D. Assessment and prediction of natural hazards from satellite imagery. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2007, 31, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washaya, P.; Balz, T.; Mohamadi, B. Coherence change-detection with Sentinel-1 for natural and anthropogenic disaster monitoring in urban areas. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandour, A.; Jezzini, A. Post-War Building Damage Detection. Proceedings 2018, 2, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, M.; Yamazaki, F. Characteristics of satellite SAR images in the areas damaged by earthquakes. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2000 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Taking the Pulse of the Planet: The Role of Remote Sensing in Managing the Environment. (Cat. No. 00CH37120), Elizabeth City, NC, USA, 24–28 July 2000; Volume 6, pp. 2693–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, M.; Jeong, B.; Takizawa, O. Earthquake damage detection using remote sensing data. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–27 July 2007; pp. 2989–2991. [Google Scholar]
- Yonezawa, C.; Takeuchi, S. Decorrelation of SAR data by urban damages caused by the 1995 Hyogoken-nanbu earthquake. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 1585–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, C.; Tomiyama, N.; Takeuchi, S. Urban damage detection using decorrelation of SAR interferometric data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2002; Volume 4, pp. 2051–2053. [Google Scholar]
- Bamler, R.; Hartl, P. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Inverse Probl. 1998, 14, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Rosen, P.A.; Hensley, S. Atmospheric effects in interferometric synthetic aperture radar surface deformation and topographic maps. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 7547–7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, M.; Schlögel, R.; Bruzzone, L.; Cuozzo, G. Integration of PSI, MAI, and intensity-based sub-pixel offset tracking results for landslide monitoring with X-band corner reflectors-Italian Alps (Corvara). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, M.; Schlögel, R.; Kofler, C.; Cuozzo, G.; Rutzinger, M.; Zieher, T.; Toschi, I.; Remondino, F.; Mejia-Aguilar, A.; Thiebes, B.; et al. Sentinel-1 and Ground-Based Sensors for Continuous Monitoring of the Corvara Landslide (South Tyrol, Italy). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, M.; Cuozzo, G.; Bruzzone, L.; Nilfouroushan, F. Performance evaluation of phase and weather-based models in atmospheric correction with Sentinel-1data: Corvara landslide in the Alps. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 1332–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, G.; D’Agostino, N.; Giuliani, R.; Noviello, C.; Reale, D.; Verde, S. Assimilation of GPS-derived atmospheric propagation delay in DInSAR data processing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 784–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafta, R.; Al-Nuaimi, M.A.; Burnham, G. Injury and death during the ISIS occupation of Mosul and its liberation: Results from a 40-cluster household survey. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme. Environmental Issues in Areas Retaken From Isil Mosul, Iraq Rapid Scoping Mission; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. Iraq Reconstruction and Investment; Part 2; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Habitat for Humanity. Initial Planning Framework for the Reconstruction of Mosul; HH: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pepe, A.; Lanari, R. On the Extension of the Minimum Cost Flow Algorithm for Phase Unwrapping of Multitemporal Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boloorani, A.D.; Darvishi, M.; Weng, Q.; Liu, X. Post-War Urban Damage Mapping Using InSAR: The Case of Mosul City in Iraq. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10030140
Boloorani AD, Darvishi M, Weng Q, Liu X. Post-War Urban Damage Mapping Using InSAR: The Case of Mosul City in Iraq. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2021; 10(3):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10030140
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoloorani, Ali Darvishi, Mehdi Darvishi, Qihao Weng, and Xiangtong Liu. 2021. "Post-War Urban Damage Mapping Using InSAR: The Case of Mosul City in Iraq" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 10, no. 3: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10030140
APA StyleBoloorani, A. D., Darvishi, M., Weng, Q., & Liu, X. (2021). Post-War Urban Damage Mapping Using InSAR: The Case of Mosul City in Iraq. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 10(3), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10030140






