A Data-Driven Framework for Analyzing Spatial Distribution of the Elderly Cardholders by Using Smart Card Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Study Area and Data Sources
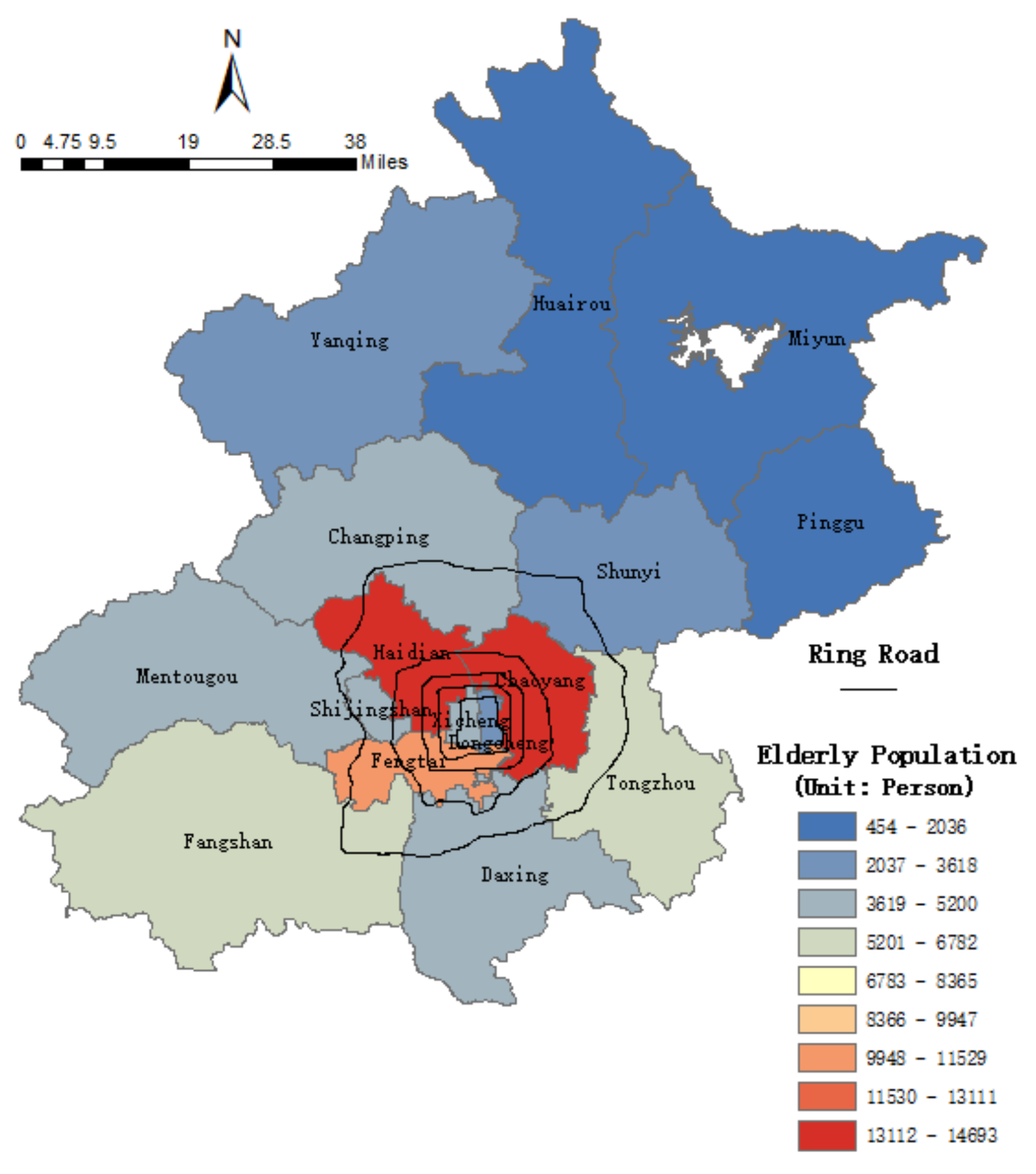
3.1. Statistical Distribution of the Elderly Population in Beijing
3.2. Smart Card Data
3.3. Point of Interest Data
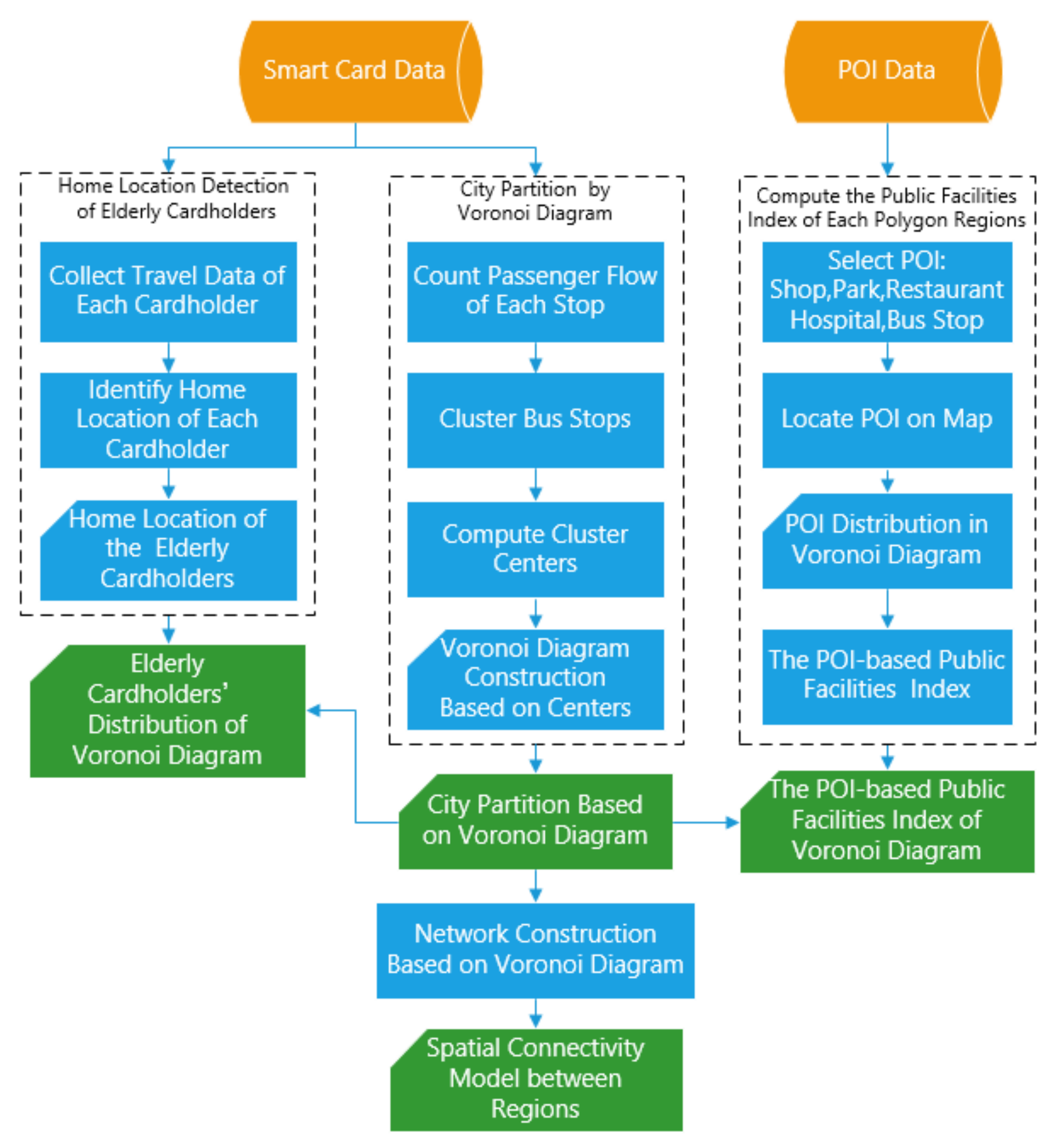
4. Methodologies
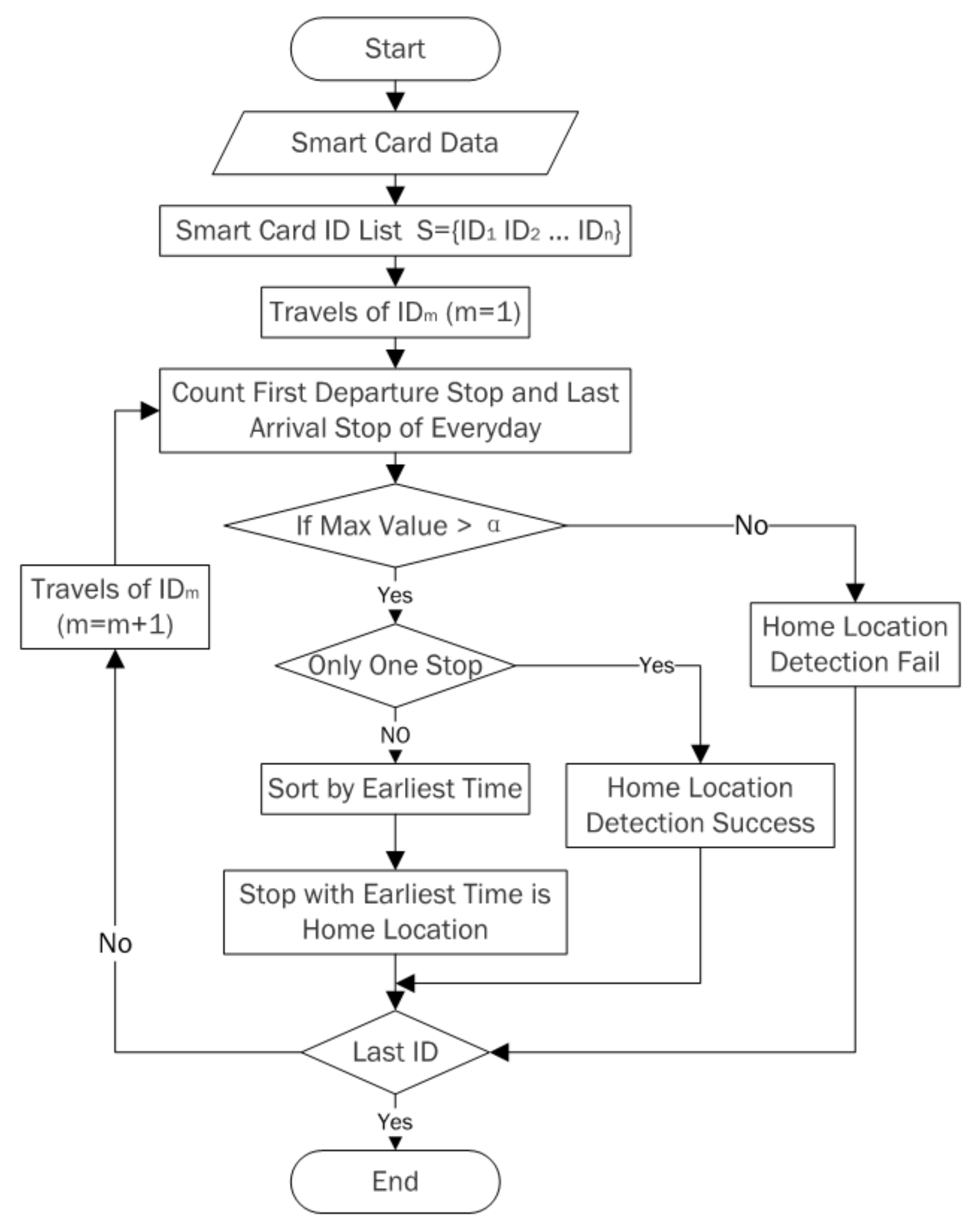
4.1. Home Location Identification of the Elderly Cardholders
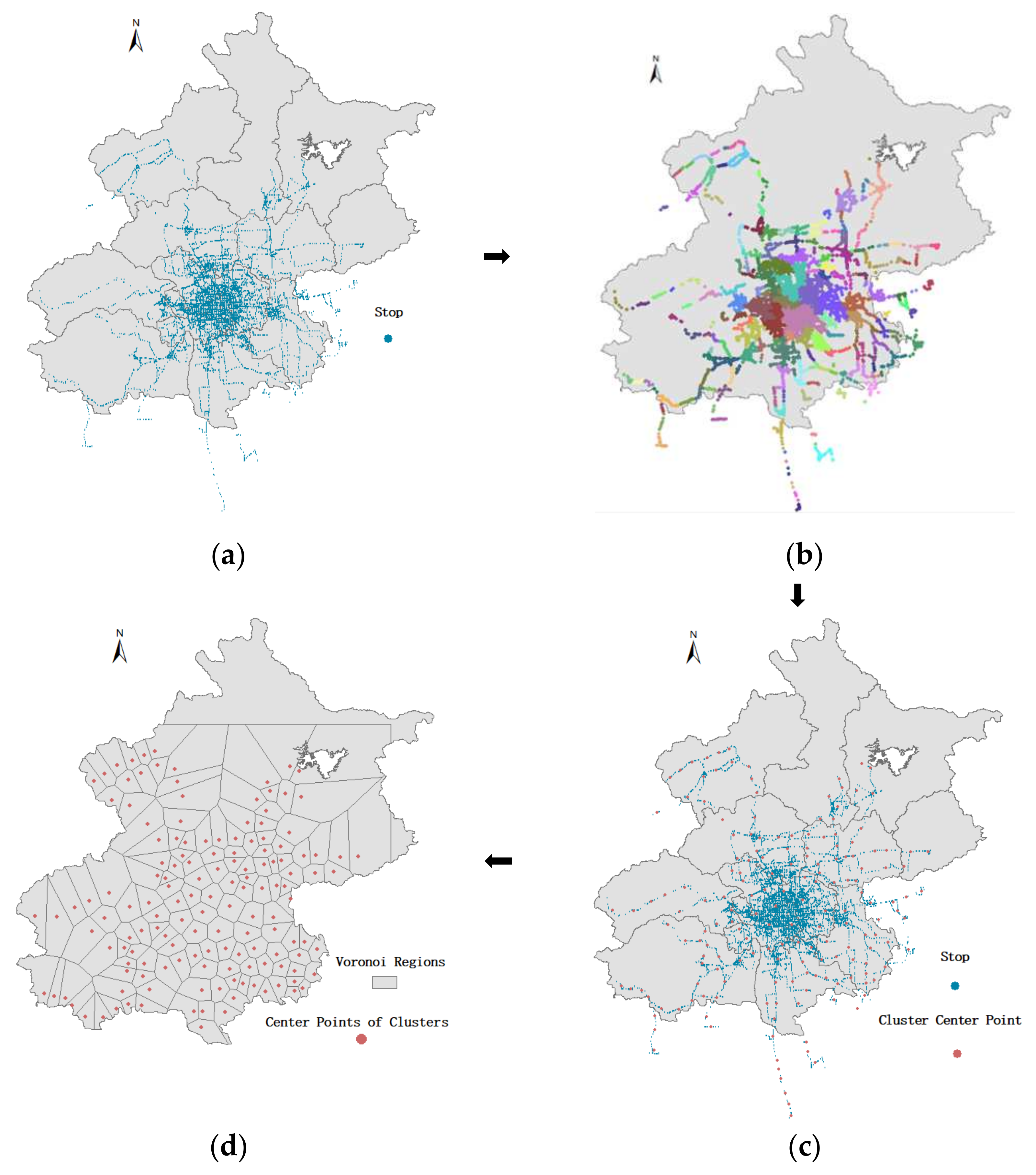
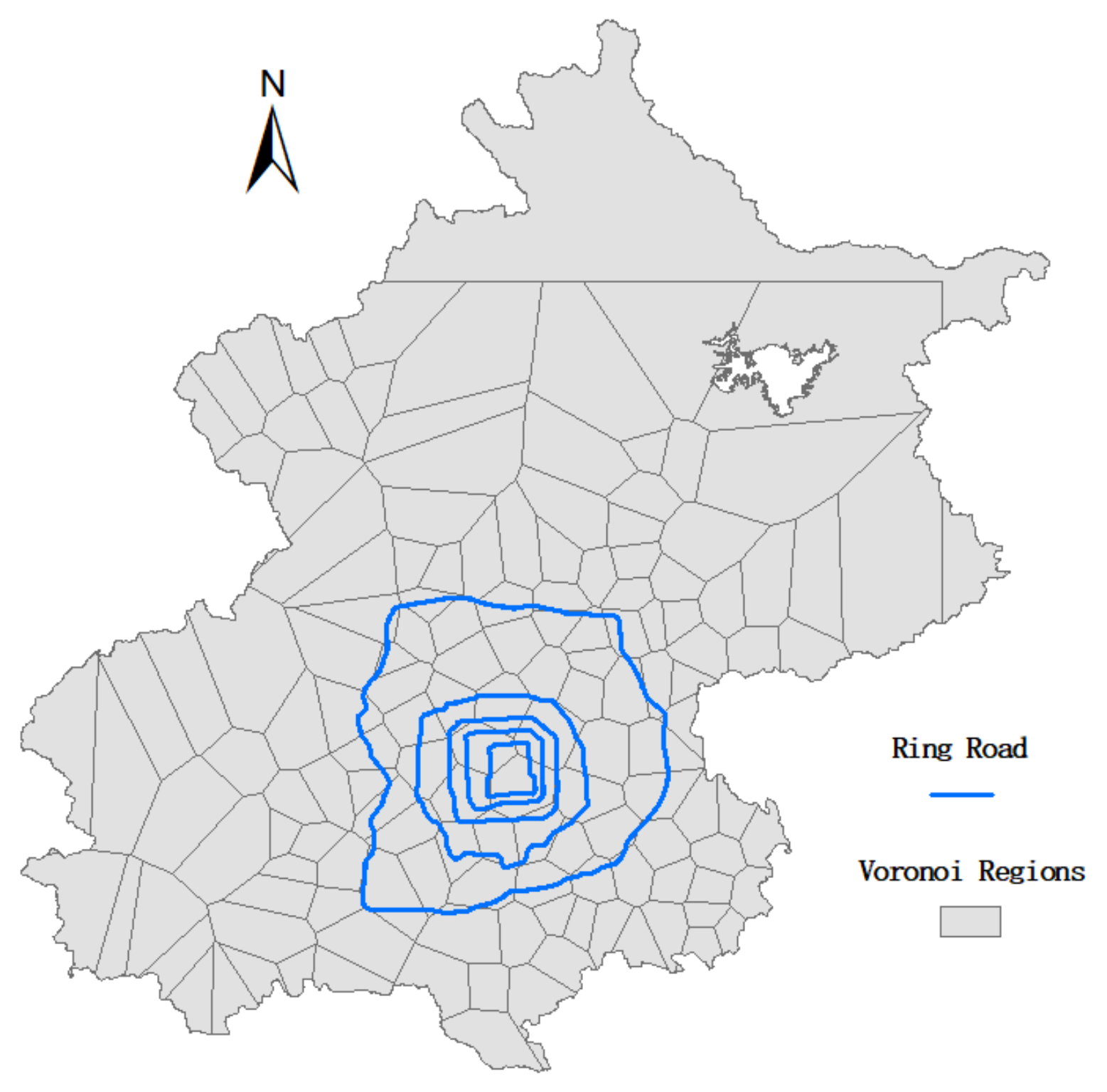
4.2. Voronoi Diagram Construction by Clustering Method
| Algorithm 1. Clustering method based on high frequency and distance |
| Data: Smart card data Input: Distance threshold Cluster indicator Output: Cluster number Set of cluster Count passage flow of each stop and sort these by descent based on the number For to .length If = 0 then Stop is new cluster core, insert into Else Let is new array For in do Sort by ascending If Stop and are in the same cluster, insert into Else Stop is new cluster core, insert into |
4.3. The Elderly Mobility Model Based on Gravity Model
5. Application Study and Results Analyses
5.1. Spatial Distribution of the Elderly Cardholders
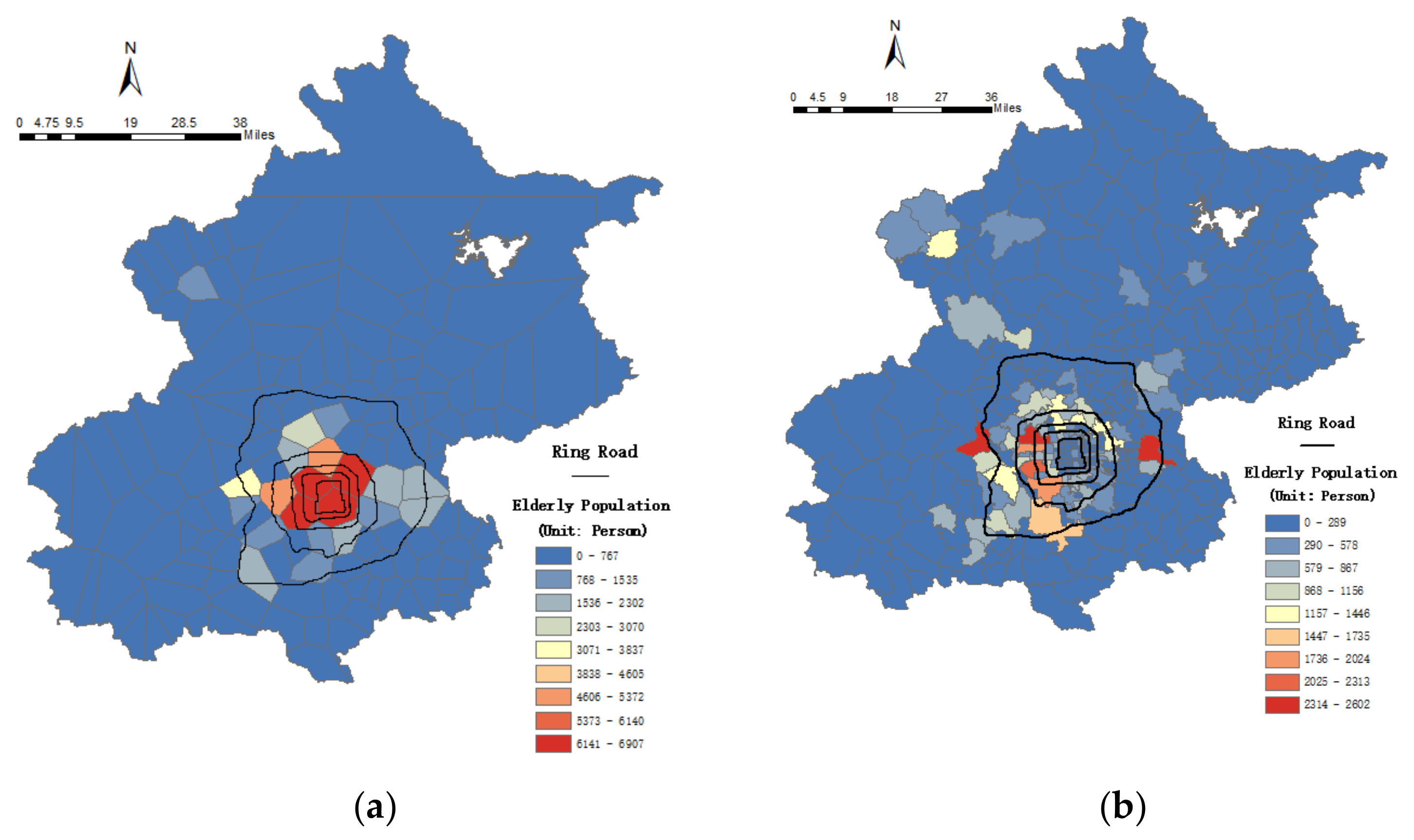
5.1.1. Home Location Spatial Distribution of the Elderly Cardholders
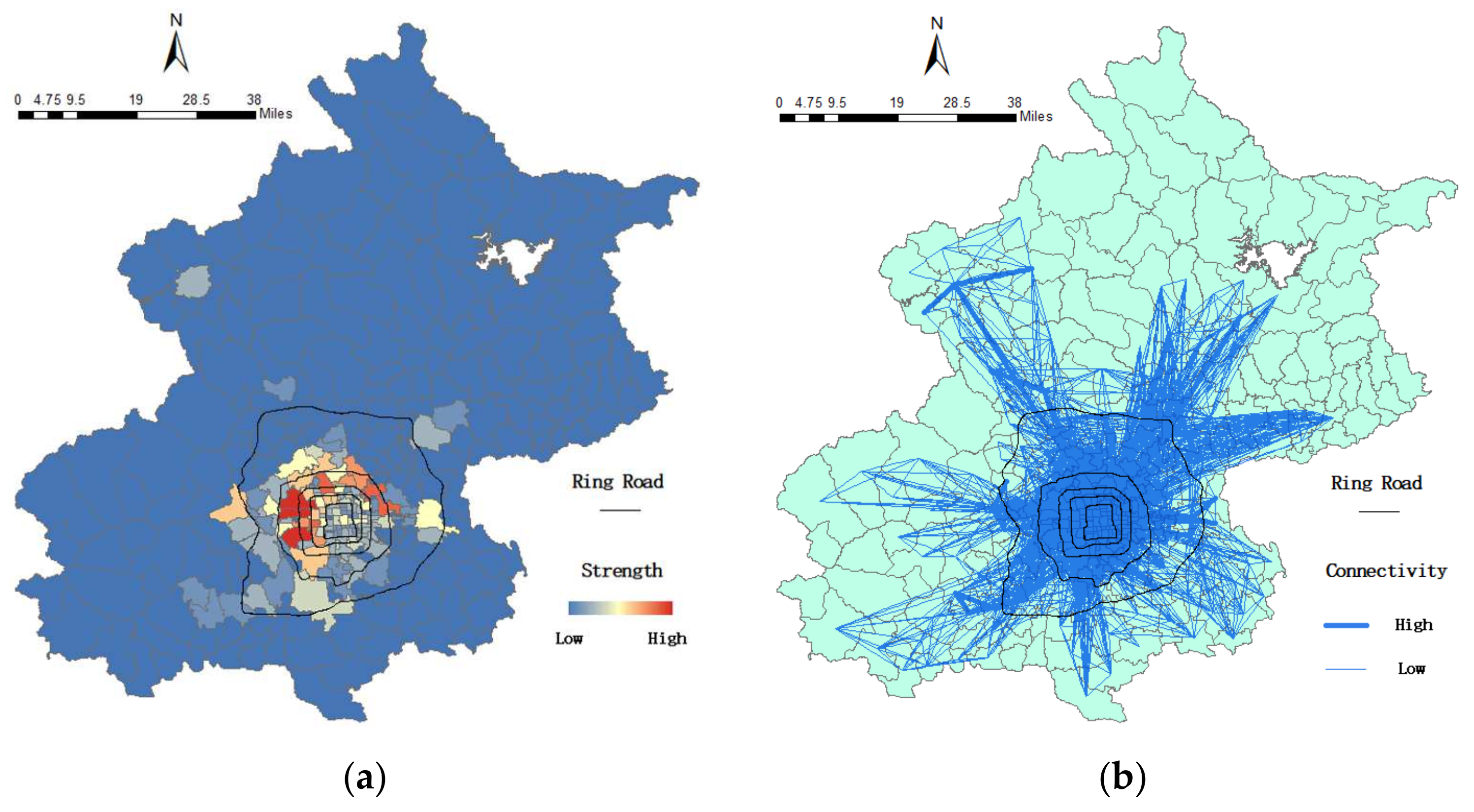
5.1.2. Spatial Distribution of the Elderly Cardholders Constructed by Voronoi Diagram
5.2. Mobility Model of the Elderly Cardholders in Beijing
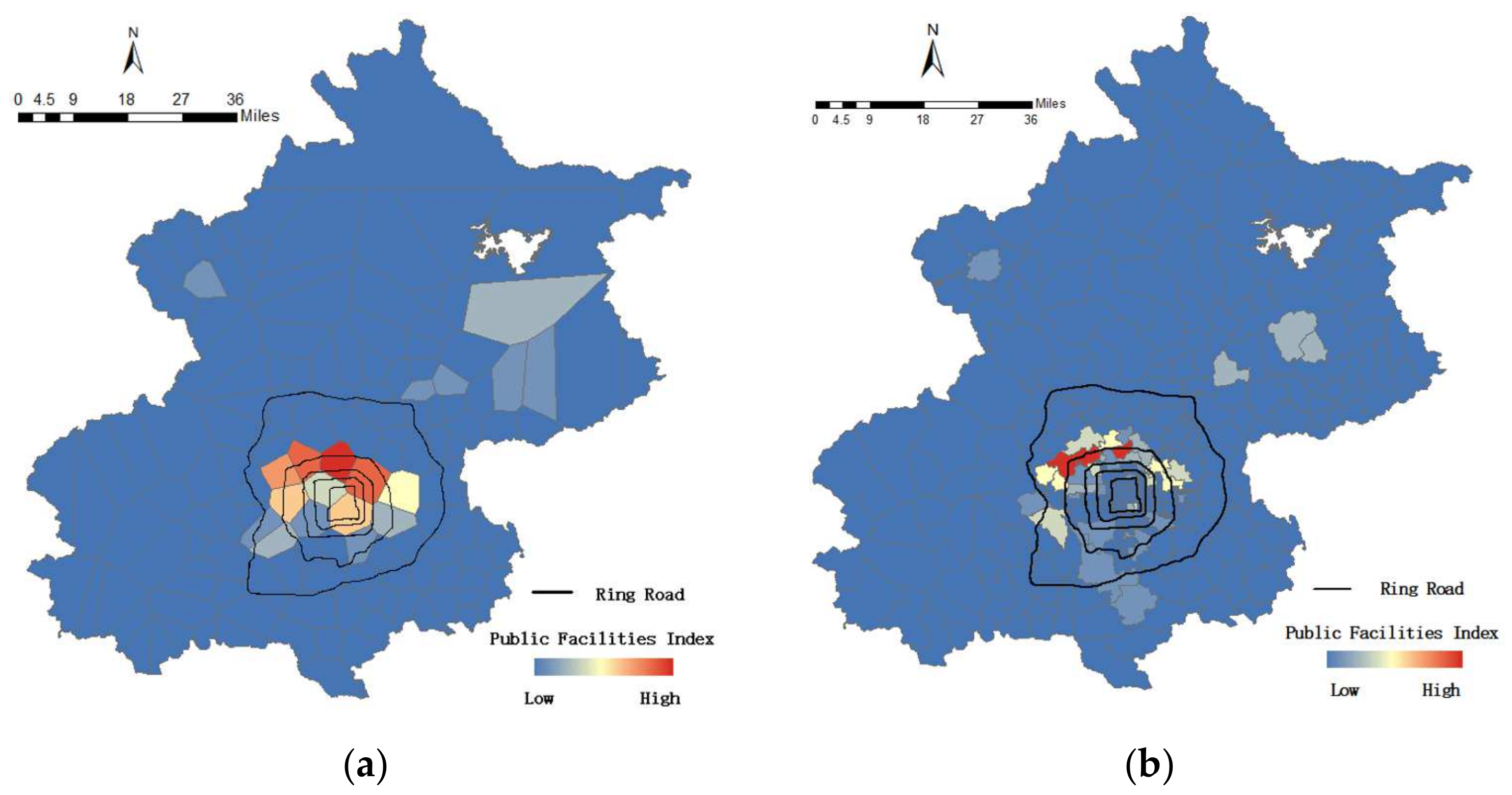
5.2.1. Spatial Distribution Public Facilities Index
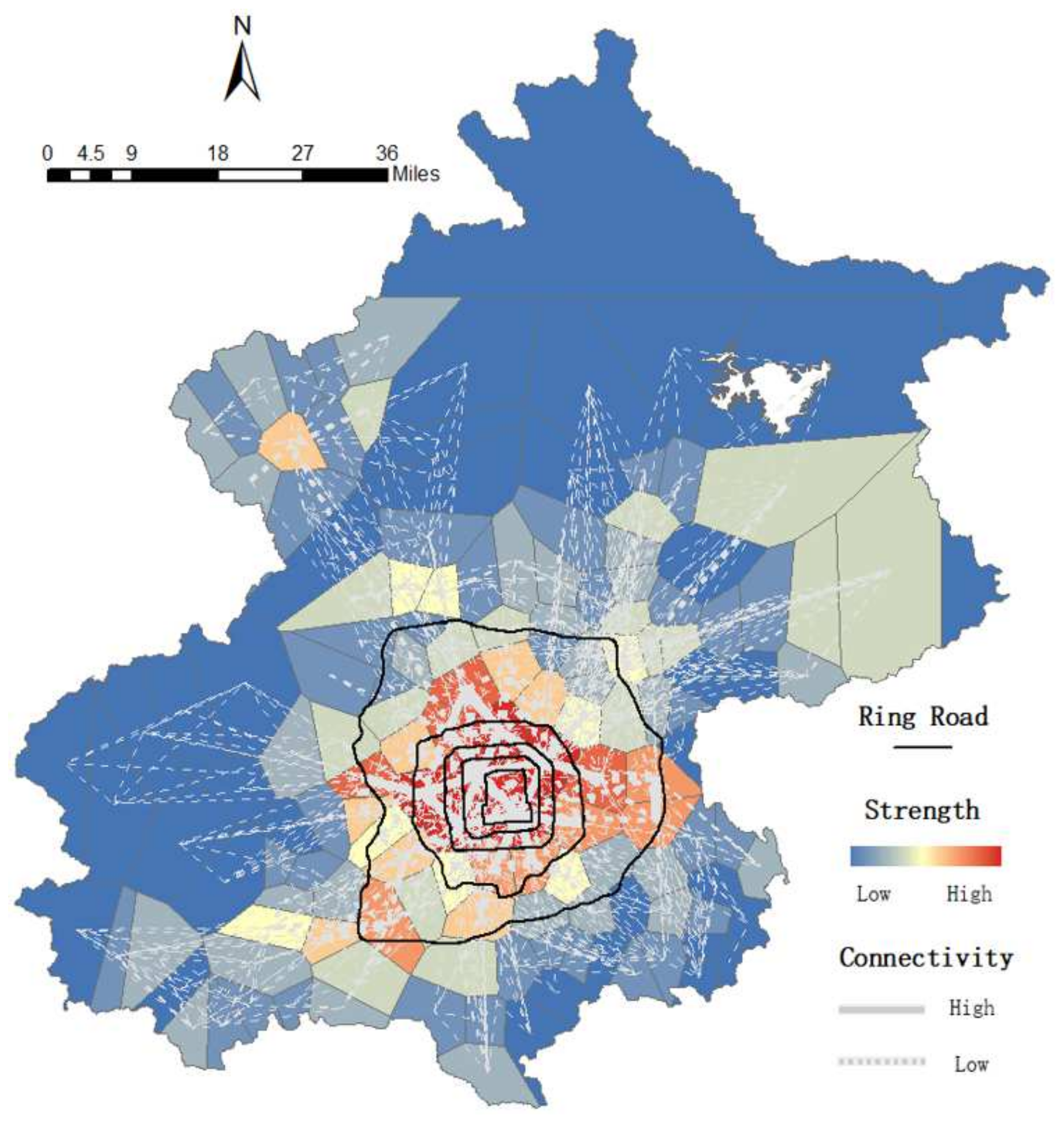
5.2.2. Mobility Model of the Elderly Cardholders
6. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. World Population Prospects 2019: Highlights (ST/ESA/SER.A/423); Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division, United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S. Assessing mobility in an aging society: Personal and built environment factors associated with older people’s subjective transportation deficiency in the US. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2011, 14, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtless, G. The impact of population aging and delayed retirement on workforce productivity. In SSRN; Boston College: Chestnut Hill, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, R.; Szeto, W.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Wong, S. Public transport policy measures for improving elderly mobility. Transp. Policy 2018, 63, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boschmann, E.E.; Brady, S.A. Travel behaviors, sustainable mobility, and transit-oriented developments: A travel counts analysis of older adults in the Denver, Colorado metropolitan area. J. Transp. Geogr. 2013, 33, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kong, X.; Xia, F.; Sun, L. Urban Human Mobility: Data-Driven Modeling and Prediction. ACM Sigkdd Explor. Newsl. 2019, 21, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, K.; Côme, E.; Oukhellou, L.; Verleysen, M. Clustering smart card data for urban mobility analysis. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 18, 712–728. [Google Scholar]
- Beijing Committee on Aging. White Papers of Development of Aging Service and Care System Construction in Beijing; Beijing Committee on Aging: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Erwig, M. The graph Voronoi diagram with applications. Networks 2000, 36, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.C.; Hidalgo, C.A.; Barabasi, A.-L. Understanding individual human mobility patterns. Nature 2008, 453, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Thill, J.-C. Combining smart card data and household travel survey to analyze jobs–housing relationships in Beijing. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2015, 53, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, S.; Ferreira, J.; Gonzalez, M.C. Activity-based human mobility patterns inferred from mobile phone data: A case study of Singapore. IEEE Trans. Big Data 2017, 3, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, C.; Batty, M.; Manley, E.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, F.; Schmitt, G. Variability in regularity: Mining temporal mobility patterns in London, Singapore and Beijing using smart-card data. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Lee, D.-H.; Erath, A.; Huang, X. Using smart card data to extract passenger’s spatio-temporal density and train’s trajectory of MRT system. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD International Workshop on Urban Computing, Beijing, China, 12 August 2012; pp. 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.-S.; Eom, J.K.; Lee, J.; Ko, S. Analysis of the Activity and Travel Patterns of the Elderly Using Mobile Phone-Based Hourly Locational Trajectory Data: Case Study of Gangnam, Korea. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3025. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, H.; Barthelemy, M.; Ghoshal, G.; James, C.R.; Lenormand, M.; Louail, T.; Menezes, R.; Ramasco, J.J.; Simini, F.; Tomasini, M. Human mobility: Models and applications. Phys. Rep. 2018, 734, 1–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, Q.; Yao, X.; Zhao, P.; Wei, H.; Ren, H. Detecting home location and trip purposes for cardholders by mining smart card transaction data in Beijing subway. Transportation 2018, 45, 919–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Loo, B.P.; Lin, D. Travel behaviour and mobility needs of older adults in an ageing and car-dependent society. Int. J. Urban Sci. 2017, 21, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, L.T.; Somenahalli, S.V. Exploring frequency of public transport use among older adults: A study in Adelaide, Australia. Travel Behav. Soc. 2015, 2, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.; Sui, Y.; Yu, X.; Sun, R. Spatio-temporal travel patterns of elderly people—A comparative study based on buses usage in Qingdao, China. J. Transp. Geogr. 2019, 76, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. Understanding the travel behavior of elderly people in the developing country: A case study of Changchun, China. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 96, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Lu, H.; Sun, Z.; Liu, J. Elderly’s travel patterns and trends: The empirical analysis of Beijing. Sustainability 2017, 9, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, E.; Zhang, R.; Xu, H. Analysis of elderly people’s travel behaviours during the morning peak hours in the context of the free bus programme in Beijing, China. J. Transp. Geogr. 2019, 76, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L. Modeling the mobility choices of older people in a transit-oriented city: Policy insights. Habitat Int. 2018, 76, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, W.; Yang, L.; Wong, R.; Li, Y.; Wong, S. Spatio-temporal travel characteristics of the elderly in an ageing society. Travel Behav. Soc. 2017, 9, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Song, C.; Pei, T.; Liu, Y.; Ma, T.; Du, Y.; Chen, J.; Fan, Z.; Tang, X.; Peng, Y. Accessibility to urban parks for elderly residents: Perspectives from mobile phone data. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 191, 103642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Chen, X.; Yang, S.; Cao, Z.; De Vos, J.; Witlox, F. Active travel for active ageing in China: The role of built environment. J. Transp. Geogr. 2019, 76, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titheridge, H.; Achuthan, K.; Mackett, R.; Solomon, J. Assessing the extent of transport social exclusion among the elderly. J. Transp. Land Use 2009, 2, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahern, A.; Hine, J. Rural transport–Valuing the mobility of older people. Res. Transp. Econ. 2012, 34, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, A.M.; Stockdale, A.; Findlay, A.; Short, D. Mobility as a driver of change in rural Britain: An analysis of the links between migration, commuting and travel to shop patterns. Int. J. Popul. Geogr. 2001, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.G.; Xia, J.C.; Robinson, T.P.; Goulias, K.G.; Church, R.L.; Olaru, D.; Tapin, J.; Han, R. Spatial analysis of access to and accessibility surrounding train stations: A case study of accessibility for the elderly in Perth, Western Australia. J. Transp. Geogr. 2014, 39, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goins, R.T.; Williams, K.A.; Carter, M.W.; Spencer, S.M.; Solovieva, T. Perceived barriers to health care access among rural older adults: A qualitative study. J. Rural Health 2005, 21, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Yang, M.; Wu, J.; Rasouli, S.; Lei, D. Assessing bus transit service from the perspective of elderly passengers in Harbin, China. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2019, 13, 761–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plazinić, B.R.; Jović, J. Mobility and transport potential of elderly in differently accessible rural areas. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 68, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, Z.; Ke, Z.; Xiaoyang, L.; Jian, Z.; Yan, L.; Lian, Z. Characterisation of elderly daily travel behaviour in Tianjin using a space–time cube. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, G.A.; Sampaio, R.R.; Nascimento Filho, A.S.; Moret, M.A.; Murari, T.B. Sustainable urban mobility analysis for elderly and disabled people in São Paulo. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, N.P.; Bastardo, R.; Pavão, J.; Santinha, G.; Rodrigues, M.; Rodrigues, C.; Queirós, A.; Dias, A. Smart Cities’ Applications to Facilitate the Mobility of Older Adults: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paiva, F.T.F.; Stival, M.M.; De Lima, L.R.; De Oliveira Silva, A.; De Sousa Barbalho, Y.G.; Da Costa, M.V.G.; Da Silva, I.C.R.; Funghetto, S.S. Predictive factors for reduced functional mobility in elderly diabetics and non-diabetics. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries. 2021, 41, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, S.; Emami, A.; Mirsaeedie, L. Elderly Mobility and Architectural Factors in Apartment Units: A Hierarchical Regression Analysis. J. Aging Environ. 2021, 35, 273–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Yu, Z. Investigating mobility in rural areas of China: Features, equity, and factors. Transp. Policy 2020, 94, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghinejad, H.; Abdi, A.; Kikhavani, S.; Ebrahimi, A. Assessment of care needs of the elderly living in Kermanshah province in 2020. Med. Sci. 2021, 25, 1955–1962. [Google Scholar]
- Barry, J.J.; Newhouser, R.; Rahbee, A.; Sayeda, S. Origin and destination estimation in New York City with automated fare system data. Transp. Res. Rec. 2002, 1817, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, K.; Ver Hoef, J.M.; Krivoruchko, K.; Lucas, N. Using ArcGIS Geostatistical Analyst; Esri Redlands: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 380. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Y.; Shen, Z. Discovering functional zones using bus smart card data and points of interest in Beijing. In Geospatial Analysis to Support Urban Planning in Beijing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 193–217. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Han, Y. Identification of Urban Functional Areas Based on POI Data: A Case Study of the Guangzhou Economic and Technological Development Zone. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fortune, S. A sweepline algorithm for Voronoi diagrams. Algorithmica 1987, 2, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Shop | Park | Restaurant | Hospital | Stop | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voronoi diagram | r | 0.924 | 0.686 | 0.941 | 0.921 | 0.996 |
| p value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| 328 counties | r | 0.677 | 0.349 | 0.708 | 0.605 | 0.899 |
| p value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 147 Voronoi Diagrams | 328 Counties | |
|---|---|---|
| Nodes | 147 | 328 |
| Edges | 972 | 5260 |
| Average degree | 25 | 74 |
| Average strength | 20,633 | 17,913 |
| Graph density | 0.09 | 0.15 |
| (a) | 156 | 2.6 | 0.3694 |
| (b) | 389.4 | 2.7 | 0.3703 |
| (c) | 970 | 2.8 | 0.3706 |
| (d) | 2412 | 2.9 | 0.3702 |
| (e) | 5988 | 3.0 | 0.3692 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Z.; Liu, X.; Lai, J.; Tong, C.; Zhang, A.; Shi, W. A Data-Driven Framework for Analyzing Spatial Distribution of the Elderly Cardholders by Using Smart Card Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10110728
Shi Z, Liu X, Lai J, Tong C, Zhang A, Shi W. A Data-Driven Framework for Analyzing Spatial Distribution of the Elderly Cardholders by Using Smart Card Data. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2021; 10(11):728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10110728
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Zhicheng, Xintao Liu, Jianhui Lai, Chengzhuo Tong, Anshu Zhang, and Wenzhong Shi. 2021. "A Data-Driven Framework for Analyzing Spatial Distribution of the Elderly Cardholders by Using Smart Card Data" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 10, no. 11: 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10110728
APA StyleShi, Z., Liu, X., Lai, J., Tong, C., Zhang, A., & Shi, W. (2021). A Data-Driven Framework for Analyzing Spatial Distribution of the Elderly Cardholders by Using Smart Card Data. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 10(11), 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10110728







