Construction of a WebGIS Tool Based on a GIS Semiautomated Processing for the Localization of P2G Plants in Sicily (Italy)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
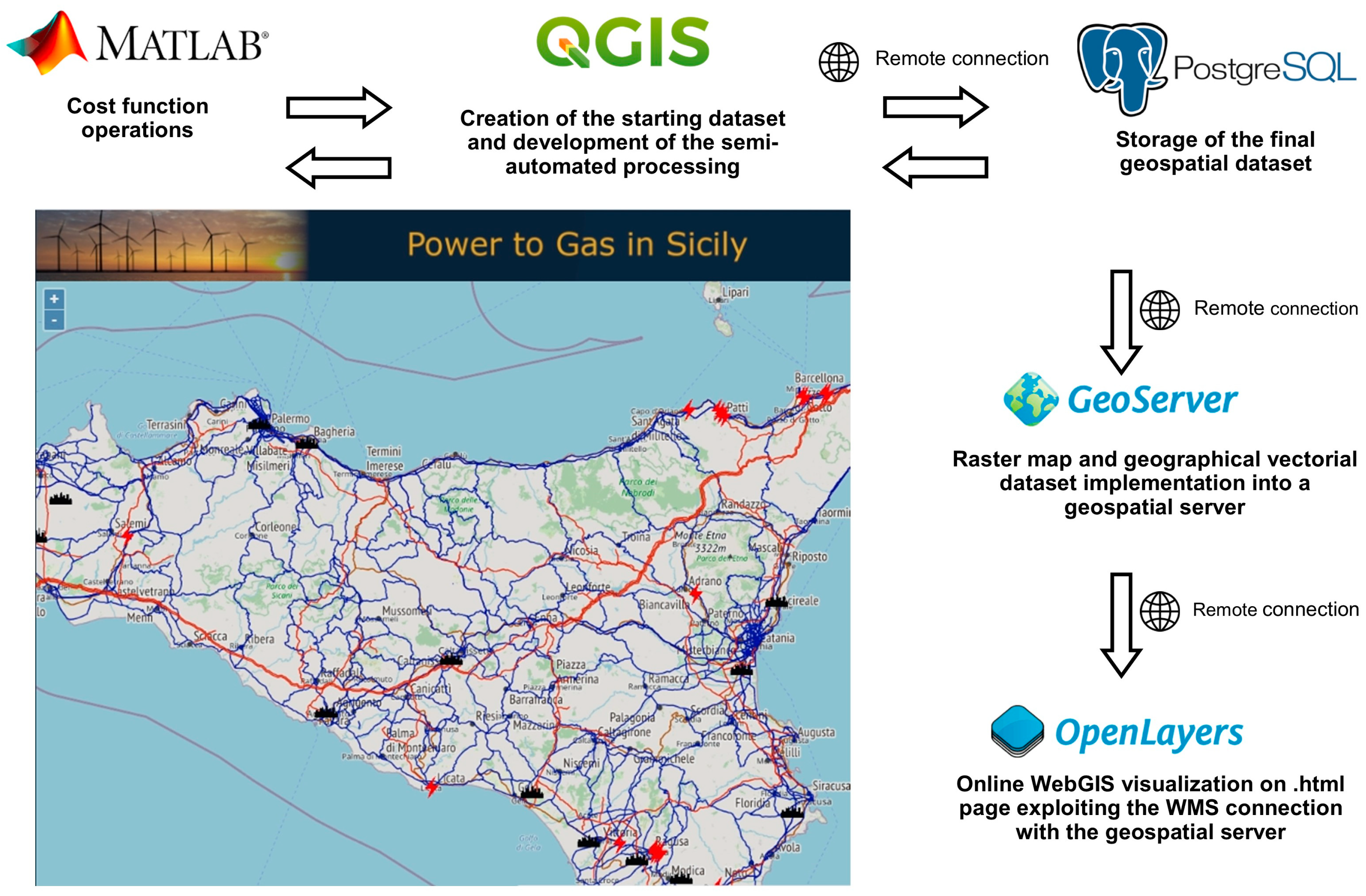
2. GIS-Based Processing for Localization of Power Plants
3. Semi-Automated GIS Processing
- The hydrogen demand, considered proportional to the population of the main inhabited centers.
- The supply energy from the existing photovoltaic and wind facilities settled in Sicily.
- The distances between the hydrogen demand nodes and supply energy nodes considering different networks (main roads, railway, and pipeline).
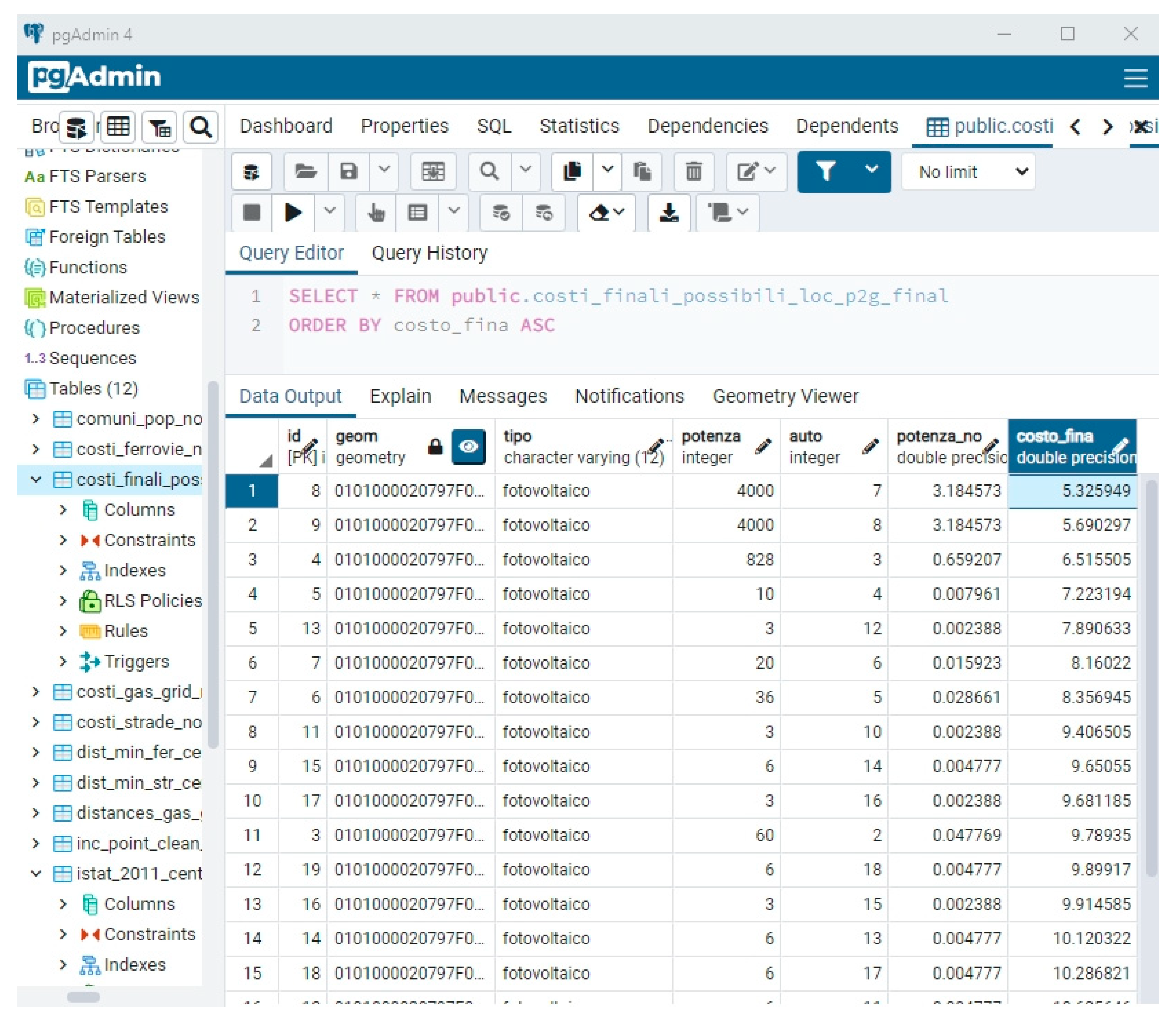
- The cost function is calculated for every possible solution within the domain of possible localizations.
4. Final Results: The WebGIS Platform
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simonis, B.; Newborough, M. Sizing and operating power-to-gas systems to absorb excess renewable electricity. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 21635–21647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, S.; O’Shea, R.; Wall, D.M.; Deane, J.P.; Murphy, J.D. Modelling of a power-to-gas system to predict the levelised cost of energy of an advanced renewable gaseous transport fuel. Appl. Energy 2018, 215, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thema, M.; Bauer, F.; Sterner, M. Power-to-Gas: Electrolysis and methanation status review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 112, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götz, M.; Lefebvre, J.; Mörs, F.; McDaniel Kock, A.; Graf, F.; Bajohr, S.; Reinmert, R.; Kolb, T. Renewable Power-to-Gas: A technological and economic review. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 1371–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gahleitner, G. Hydrogen from renewable electricity: An international review of power-to-gas pilot plants for stationary applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38.5, 2039–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodchild, M. Geographic information systems and science: Today and tomorrow. Ann. GIS 2009, 15, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Resch, B.; Sagl, G.; Törnros, T.; Bachmaier, A.; Eggers, J.-B.; Herkel, S.; Narmsara, S.; Gündra, H. GIS-Based Planning and Modeling for Renewable Energy: Challenges and Future Research Avenues. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2014, 3, 662–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Fast, V.; Teri, P.; Calvert, K. Integrating Land-Use and Renewable Energy Planning Decisions: A Technical Mapping Guide for Local Government. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.; Li, R. A Geospatial Approach for Prioritizing Wind Farm Development in Northeast Nebraska, USA. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2014, 3, 968–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viana, H.; Cohen, W.B.; Lopes, D.; Aranha, J. Assessment of forest biomass for use as energy. GIS-based analysis of geographical availability and locations of wood-fired power plants in Portugal. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 2551–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahma, A.; Saikia, K.; Hiloidhari, M.; Baruah, D.C. GIS based planning of a biomethanation power plant in Assam, India. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 62, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atici, K.B.; Simsek, A.B.; Ulucan, A.; Tosun, M.U. A GIS-based Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis approach for wind power plant site selection. Util. Policy 2015, 37, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyzi, S.; Khanmohammadi, M.; Abedinzadeh, N.; Aalipour, M. Multi- criteria decision analysis FANP based on GIS for siting municipal solid waste incineration power plant in the north of Iran. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 47, 101513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Garni, H.Z.; Awasthi, A. Solar PV power plant site selection using a GIS-AHP based approach with application in Saudi Arabia. Appl. Energy 2017, 206, 1225–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albraheem, L.; Alabdulkarim, L. Geospatial Analysis of Solar Energy in Riyadh Using a GIS-AHP-Based Technique. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zlatanova, S.; Diakite, A.A.; Aleksandrov, M.; Yan, J. Towards Integrating Heterogeneous Data: A Spatial DBMS Solution from a CRC-LCL Project in Australia. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noskov, A. Smart City Webgis Applications: Proof of Work Concept For High-Level Quality-Of-Service Assurance. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci 2018, IV-4/W7, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grippa, T.; Lennert, M.; Beaumont, B.; Vanhuysse, S.; Stephenne, N.; Wolff, E. An Open-Source Semi-Automated Processing Chain for Urban Object-Based Classification. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neteler, M.; Bowman, M.H.; Landa, M.; Metz, M. GRASS GIS: A multi-purpose open source GIS. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 31, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neteler, M.; Beaudette, D.; Cavallini, P.; Lami, L.; Cepicky, J. GRASS GIS. In Open Source Approaches in Spatial Data Handling. Advances in Geographic Information Science; Hall, G.B., Leahy, M.G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 2, pp. 171–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graser, A.; Olaya, V. Processing: A Python Framework for the Seamless Integration of Geoprocessing Tools in QGIS. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2015, 4, 2219–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquaré Mariotto, F.; Antoniou, V.; Drymoni, K.; Bonali, F.L.; Nomikou, P.; Fallati, L.; Karatzaferis, O.; Vlasopoulos, O. Virtual Geosite Communication through a WebGIS Platform: A Case Study from Santorini Island (Greece). Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, D.; Zichar, M.; Tóth, R.; Kiss, E.; Karancsi, G.; Mester, T. Geovisualization Techniques of Spatial Environmental Data Using Different Visualization Tools. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scianna, A.; Gaglio, G.F.; La Guardia, M.; Nuccio, G. Development of a Virtual CH Path on WEB: Integration of a GIS, VR, and Other Multimedia Data. In Digital Heritage. Progress in Cultural Heritage: Documentation, Preservation, and Protection. EuroMed 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Ioannides, M., Fink, E., Cantoni, L., Champion, E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 12642, pp. 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell-Carrera, C.; Saorin, J.L.; Melián Díaz, D. User VR Experience and Motivation Study in an Immersive 3D Geovisualization Environment Using a Game Engine for Landscape Design Teaching. Land 2021, 10, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.; Acuna, M.; Moroni, M.; Taskhiri, M.S.; Turner, P. Optimizing the Location of Biomass Energy Facilities by Integrating Multi-Criteria Analysis (MCA) and Geographical Information Systems (GIS). Forests 2018, 9, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tahvanainen, T.; Anttila, P. Supply chain cost analysis of long-distance transportation of energy wood in Finland. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 3360–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kurdi, N.; Pillot, B.; Gervet, C.; Linguet, L. Towards Robust Scenarios of Spatio-Temporal Renewable Energy Planning: A GIS-RO Approach. In Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming. CP 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Schiex, T., de Givry, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11802, pp. 729–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Xu, F.; Lin, S. Site selection of photovoltaic power plants in a value chain based on grey cumulative prospect theory for sustainability: A case study in Northwest China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janke, J.R. Multicriteria GIS modeling of wind and solar farms in Colorado. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 2228–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lozano, J.M.; Antunes, C.H.; García-Cascales, M.S.; Dias, L.C. GIS-based photovoltaic solar farms site selection using ELECTRE-TRI: Evaluating the case for Torre Pacheco, Murcia, Southeast of Spain. Renew. Energy 2014, 66, 478–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosgerau, H.; Mathiesen, A.; Sparre Andersen, M.; Boldreel, L.O.; Hjuler, M.L.; Kamla, E.; Kristensen, L.; Brogaard Pedersen, C.; Pjetursson, B.; Nielsen, L.H. A WebGIS portal for exploration of deep geothermal energy based on geological and geophysical data. GEUS Bull. 2016, 35, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffeis, G.; Roncolato, D.; Cherubini, A.; Bernardoni, A.; Boccardi, S.; Greco, A.; Chiesa, A.; Brolis, M.; Fasano, M. BIOPOLE: WebGIS-Based Decision Support System (DSS) in Bio-Energy Plant Localization. Int. Congr. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 278. Available online: https://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/iemssconference/2012/Stream-B/278/ (accessed on 25 July 2021).
- Raffler, C. QNEAT3—QGIS Network Analysis Toolbox, 2018, Vienna. Available online: https://root676.github.io/ (accessed on 21 July 2021).




| Step | Shapefiles | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Buffering | square grid | point |
| railway network | line | |
| main roads network | line | |
| wind and photovoltaic plants | point | |
| Intersection | square grid | point |
| railway network main roads network | line line | |
| wind and photovoltaic plants | point | |
| Cleaning | domain of possible localizations | multipoint |
| domain of possible localizations | point | |
| Cost of distances definition | domain of possible localizations | point |
| main urban centers | point | |
| main roads network | line | |
| railway network | line | |
| gas network | line | |
| gas network | point |
| Shapefile | Type | Geospatial Operation | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| square grid | point | grid creation | 1 * 1 km ext. |
| railway network | line | buffering | 0.5 * 0.5 km ext. |
| main roads network | line | buffering | 0.5 * 0.5 km ext. |
| wind and photovoltaic plants | point | buffering | 1 * 1 km ext. |
| square grid | point | intersection in order of density | |
| railway network | line | ||
| main roads network | line | ||
| wind and photovoltaic plants | point | ||
| domain of possible localizations | multipoint | multipoint to point conversion | |
| domain of possible localizations | point | multiple geometries removal | |
| domain of possible localizations | point | auto-incremental field addiction | |
| domain of possible localizations | point | Origin-destination matrix (QNEAT) | Shortest path optimization |
| main urban centers | point | ||
| main roads network | line | ||
| railway network | line | ||
| gas network | line | line to point conversion | 5 m dist. |
| gas network | point | distance from the nearest node |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
La Guardia, M.; D’Ippolito, F.; Cellura, M. Construction of a WebGIS Tool Based on a GIS Semiautomated Processing for the Localization of P2G Plants in Sicily (Italy). ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10100671
La Guardia M, D’Ippolito F, Cellura M. Construction of a WebGIS Tool Based on a GIS Semiautomated Processing for the Localization of P2G Plants in Sicily (Italy). ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2021; 10(10):671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10100671
Chicago/Turabian StyleLa Guardia, Marcello, Filippo D’Ippolito, and Maurizio Cellura. 2021. "Construction of a WebGIS Tool Based on a GIS Semiautomated Processing for the Localization of P2G Plants in Sicily (Italy)" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 10, no. 10: 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10100671
APA StyleLa Guardia, M., D’Ippolito, F., & Cellura, M. (2021). Construction of a WebGIS Tool Based on a GIS Semiautomated Processing for the Localization of P2G Plants in Sicily (Italy). ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 10(10), 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10100671








