Model-Based Design of the 5-DoF Light Industrial Robot
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. MBD: Robot Design Preparation
2.1. Robot Structure Design
2.2. Robot 3D Model Design
3. MBD: Robot Design Methods
3.1. MBD: Rapid Prototyping
3.1.1. Joint Components Verification
3.1.2. Joint Components Selection
3.2. MBD: Robot Kinematics Algorithm
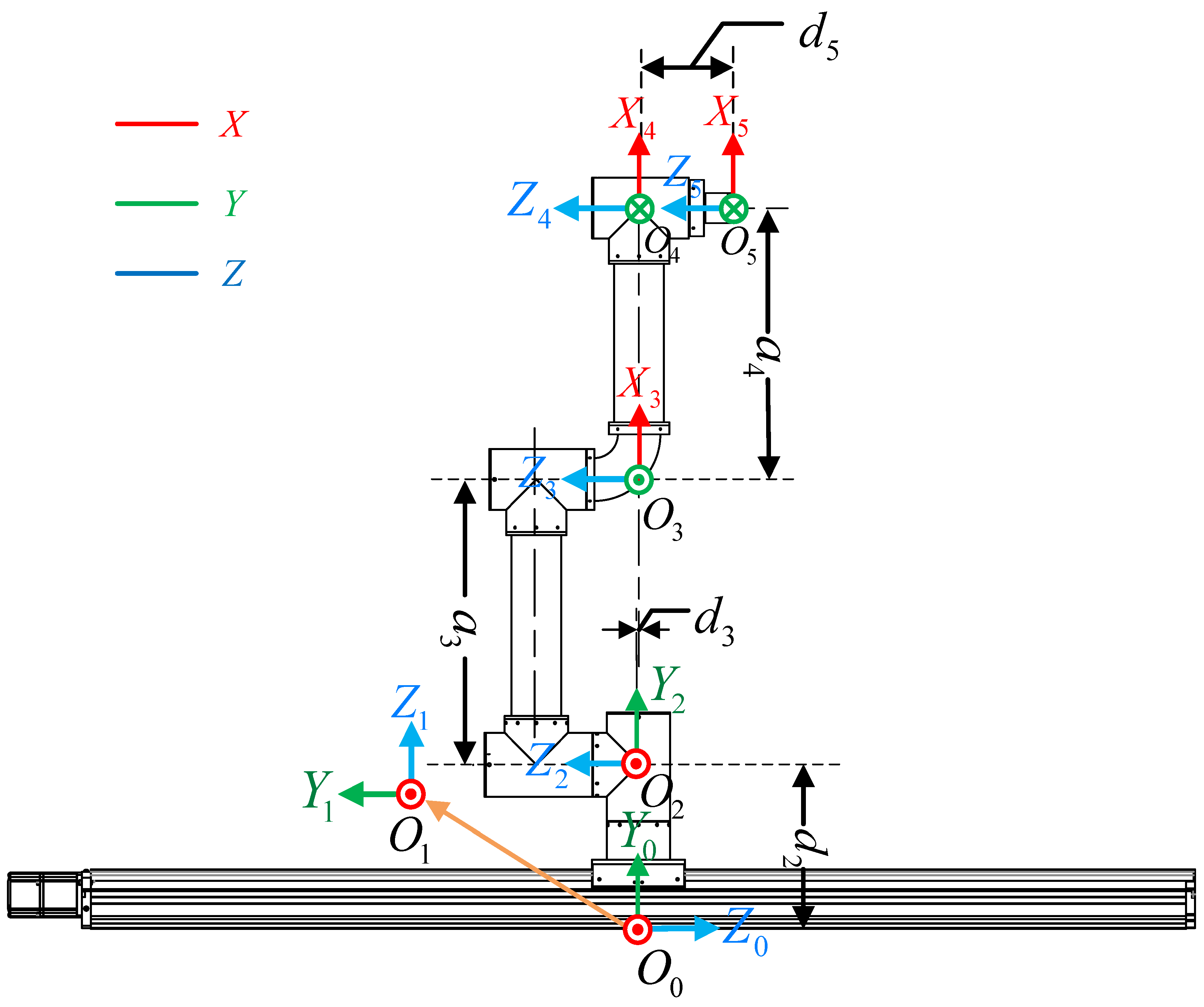
3.2.1. Kinematics Analysis
- Establishment of the coordinate system
- B.
- Forward kinematic analysis
- C.
- Inverse kinematic analysis
- (1)
- Solve joint variable 2 as follows:
- (2)
- Solve joint variable 4 as follows:
- (3)
- Solve joint variable 3 as follows:
- (4)
- Solve joint variable 5 as follows:
- (5)
- Solve joint variable 1 as follows:
3.2.2. Trajectory Planning
- Workspace analysis of the robot
- B.
- Joint space trajectory planning
- C.
- Cartesian space trajectory planning
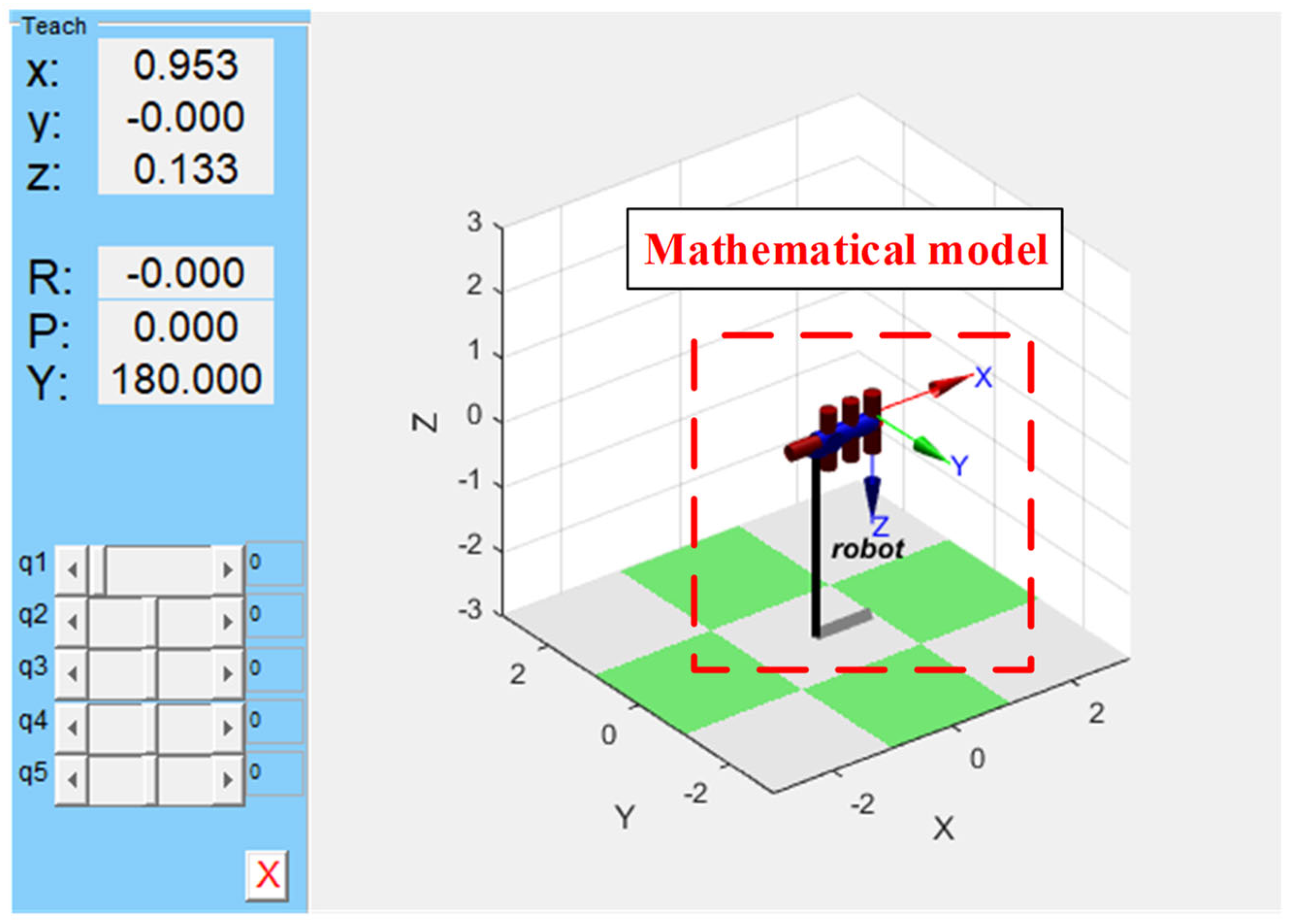
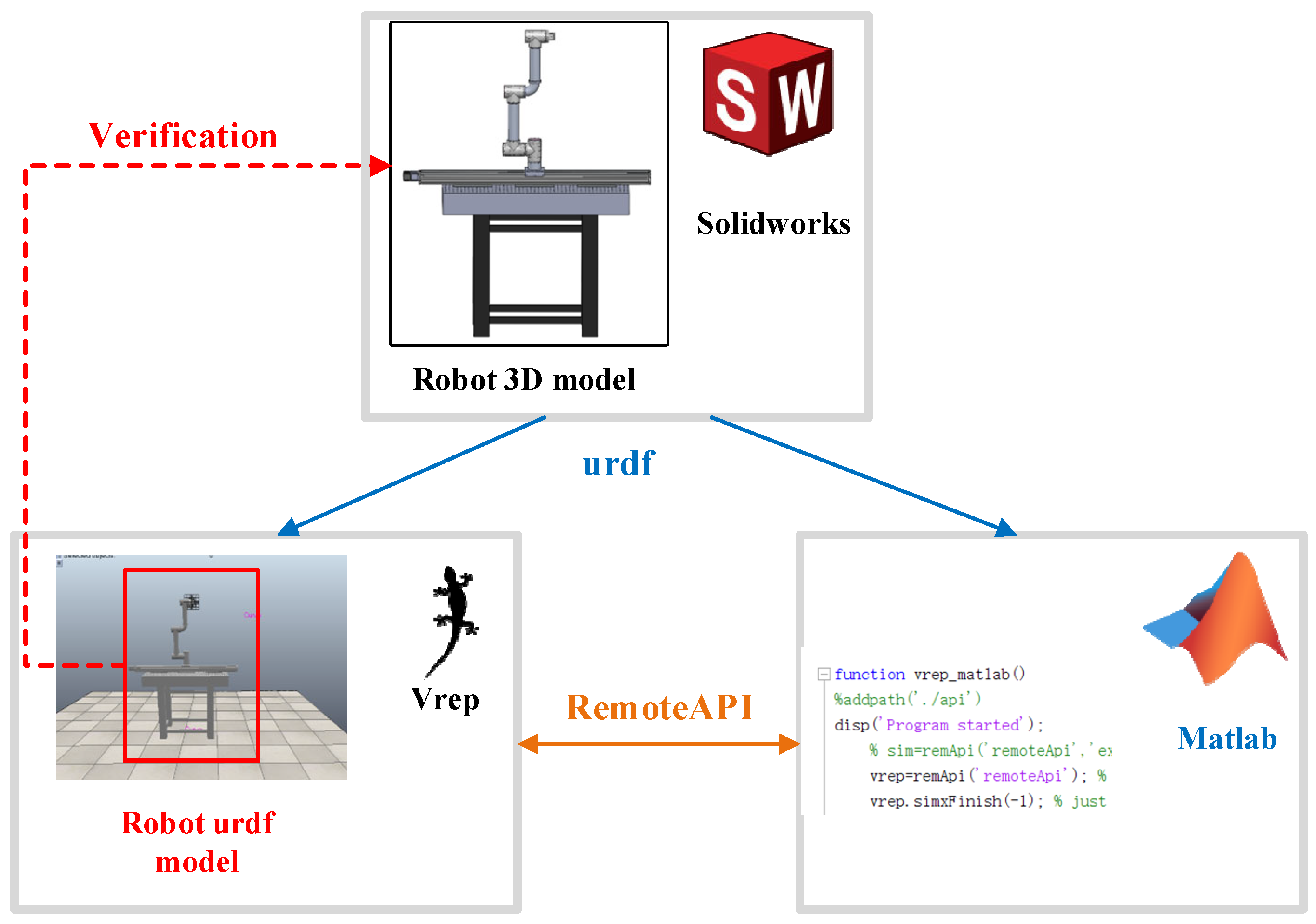
3.3. MBD: Robot Kinematics Simulation
3.3.1. Co-Simulation Platform of Matlab 2018b and Vrep Edu
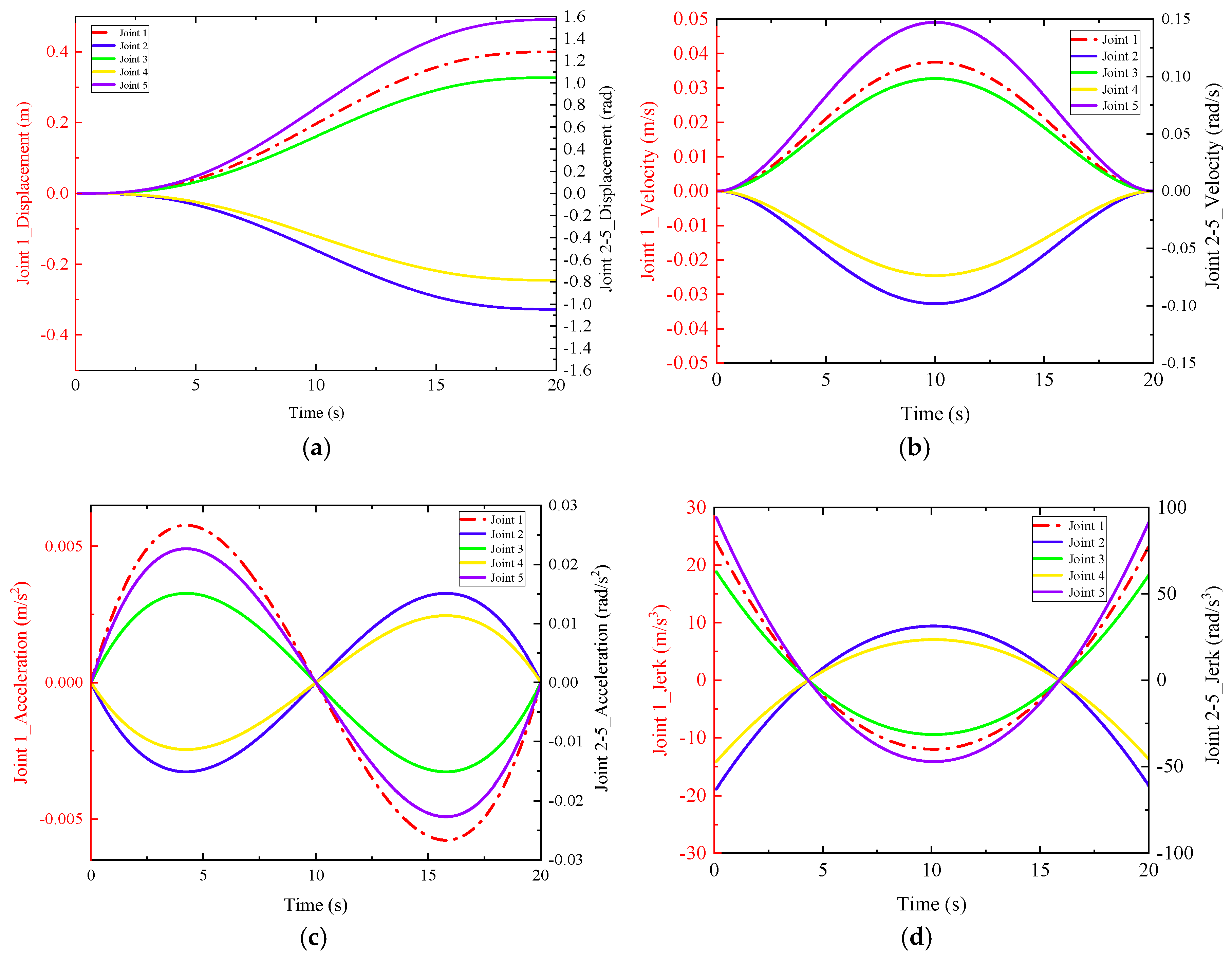
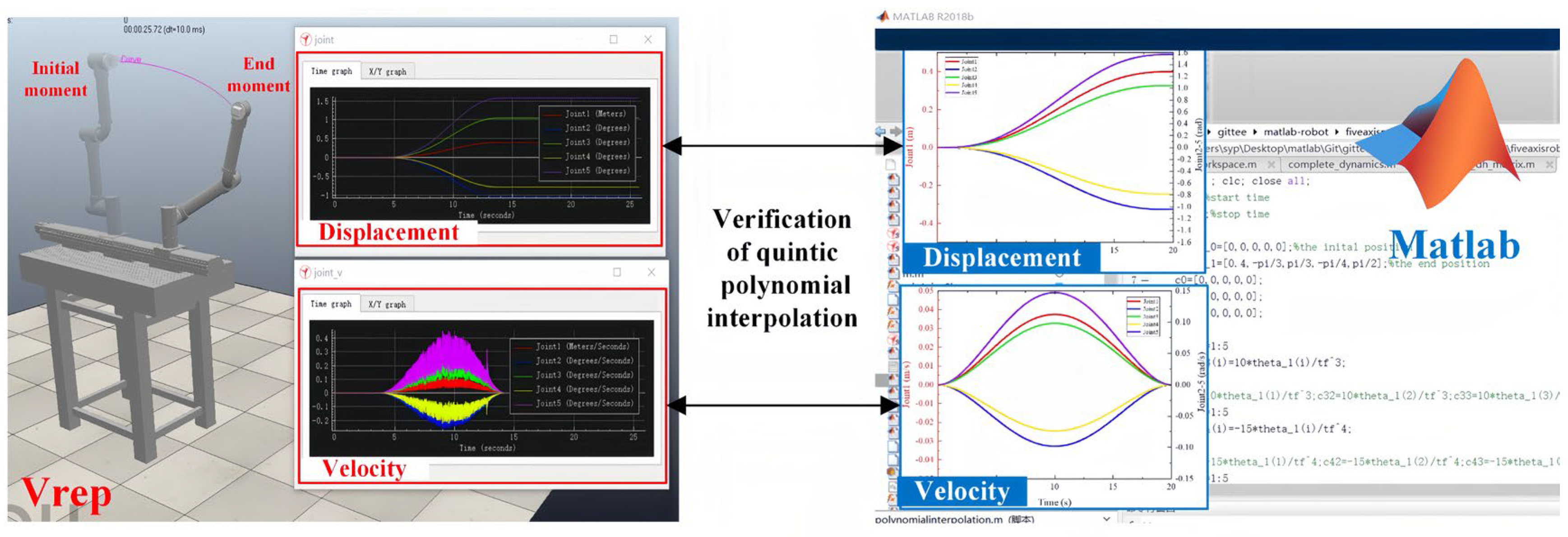
3.3.2. Simulation Verification of Trajectory Planning
- Simulation verification of joint space trajectory planning
- B.
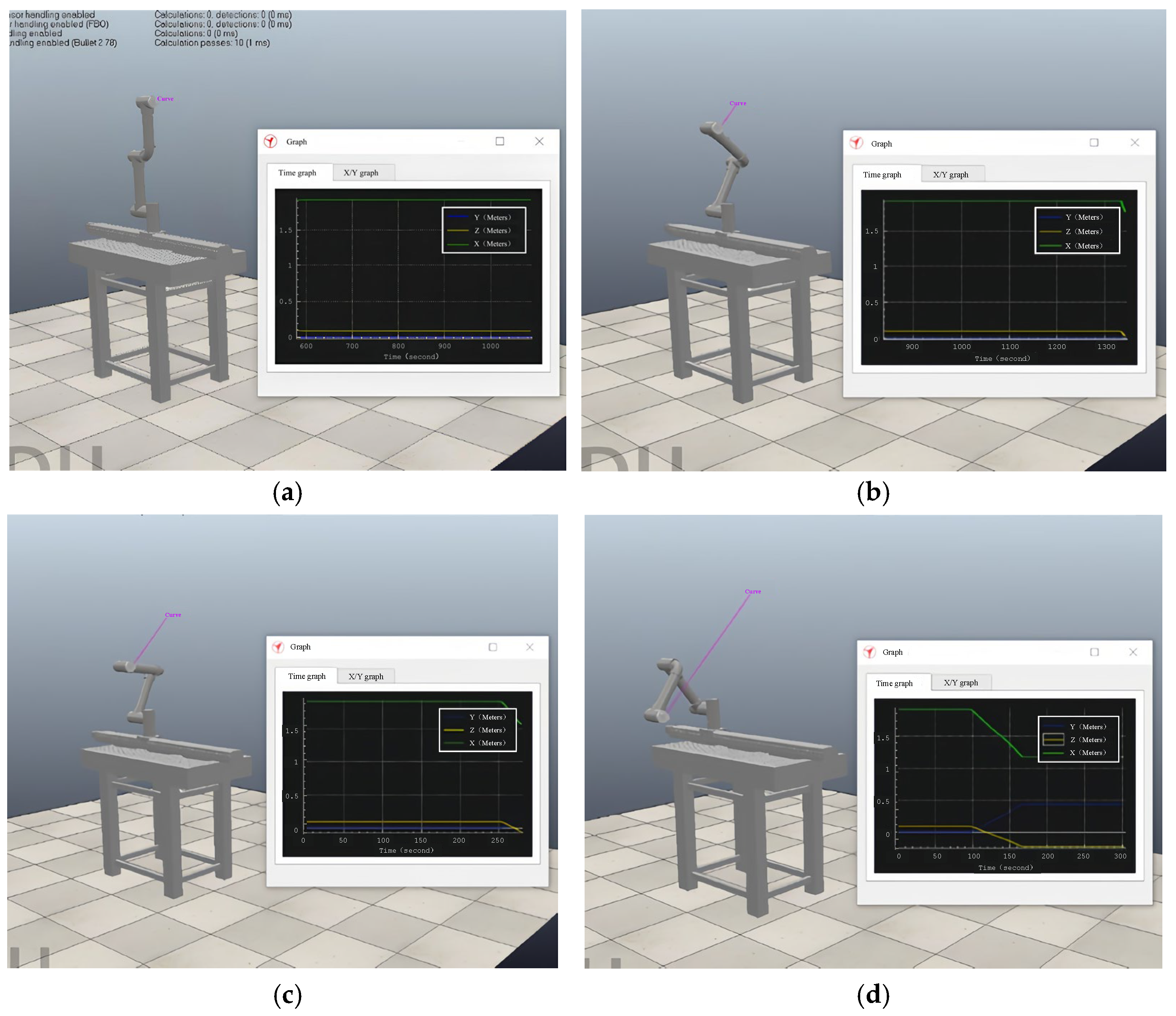
- Simulation verification of Cartesian space trajectory planning
4. Results and Discussion
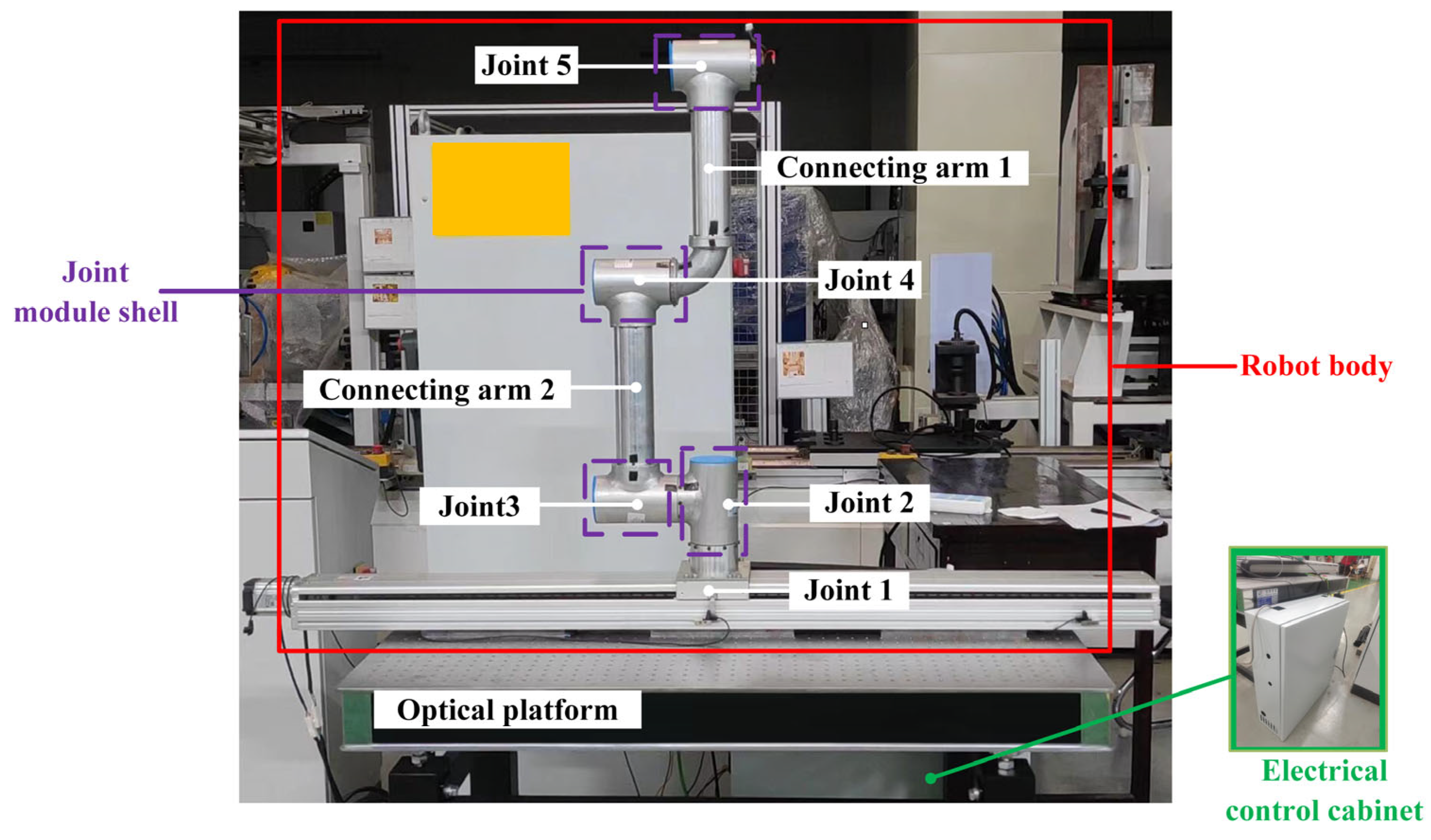
4.1. MBD: Robot Prototype
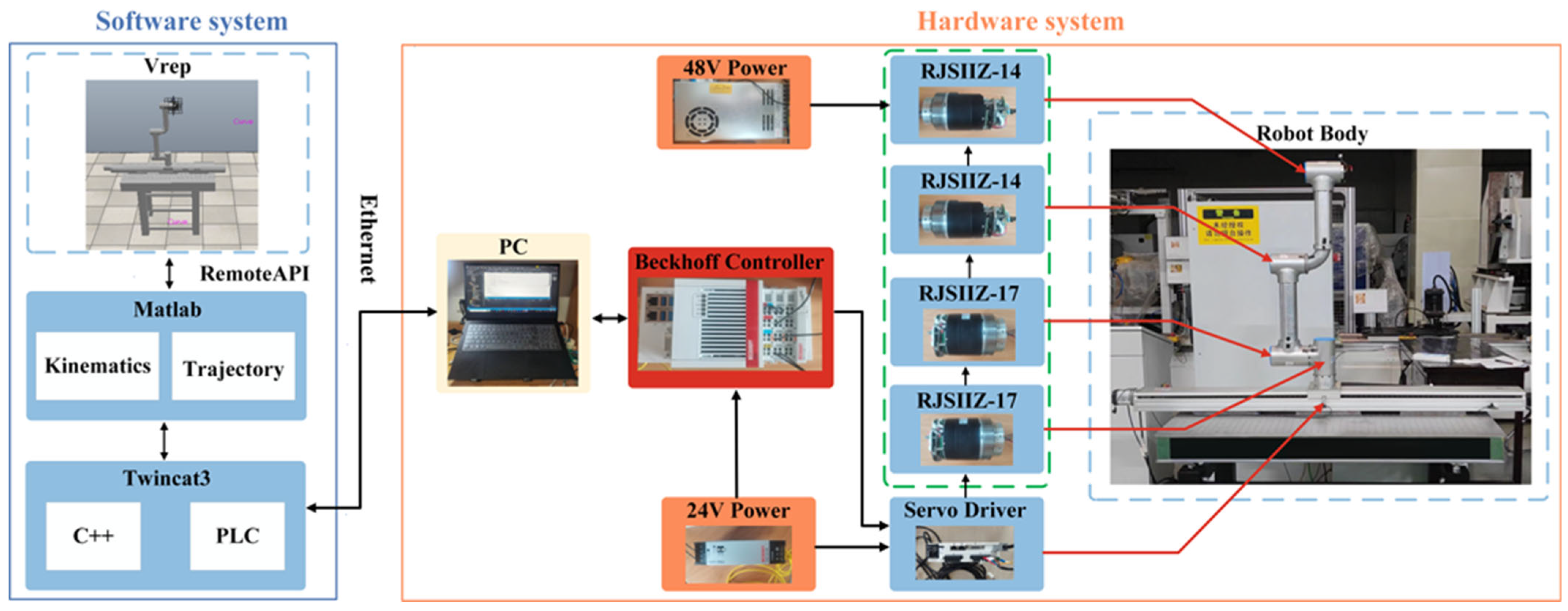
4.2. MBD: Robot Motion Control System and Test
4.2.1. Robot Motion Control System
4.2.2. Robot Test
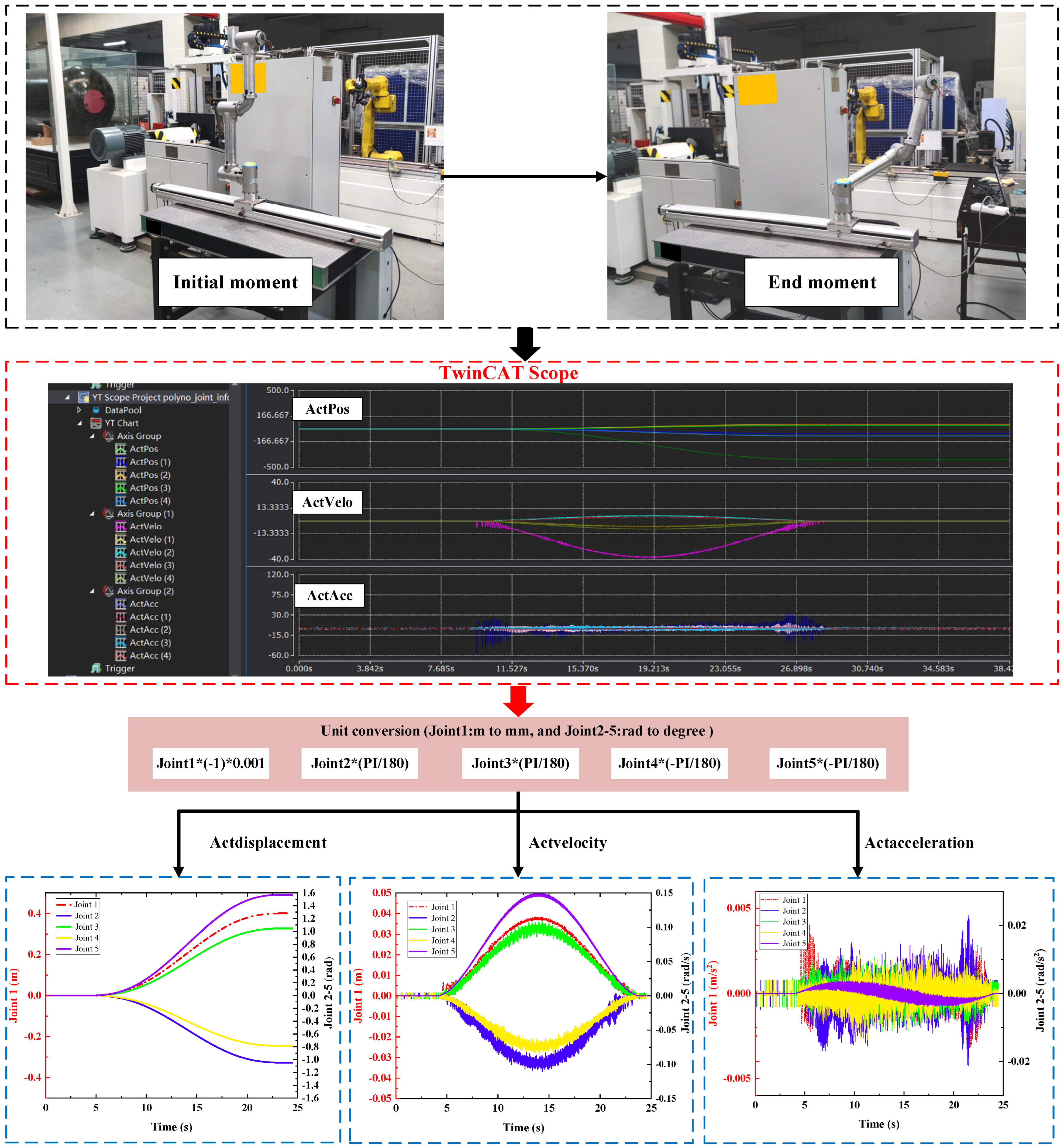
- Experiment with joint space trajectory planning
- B.
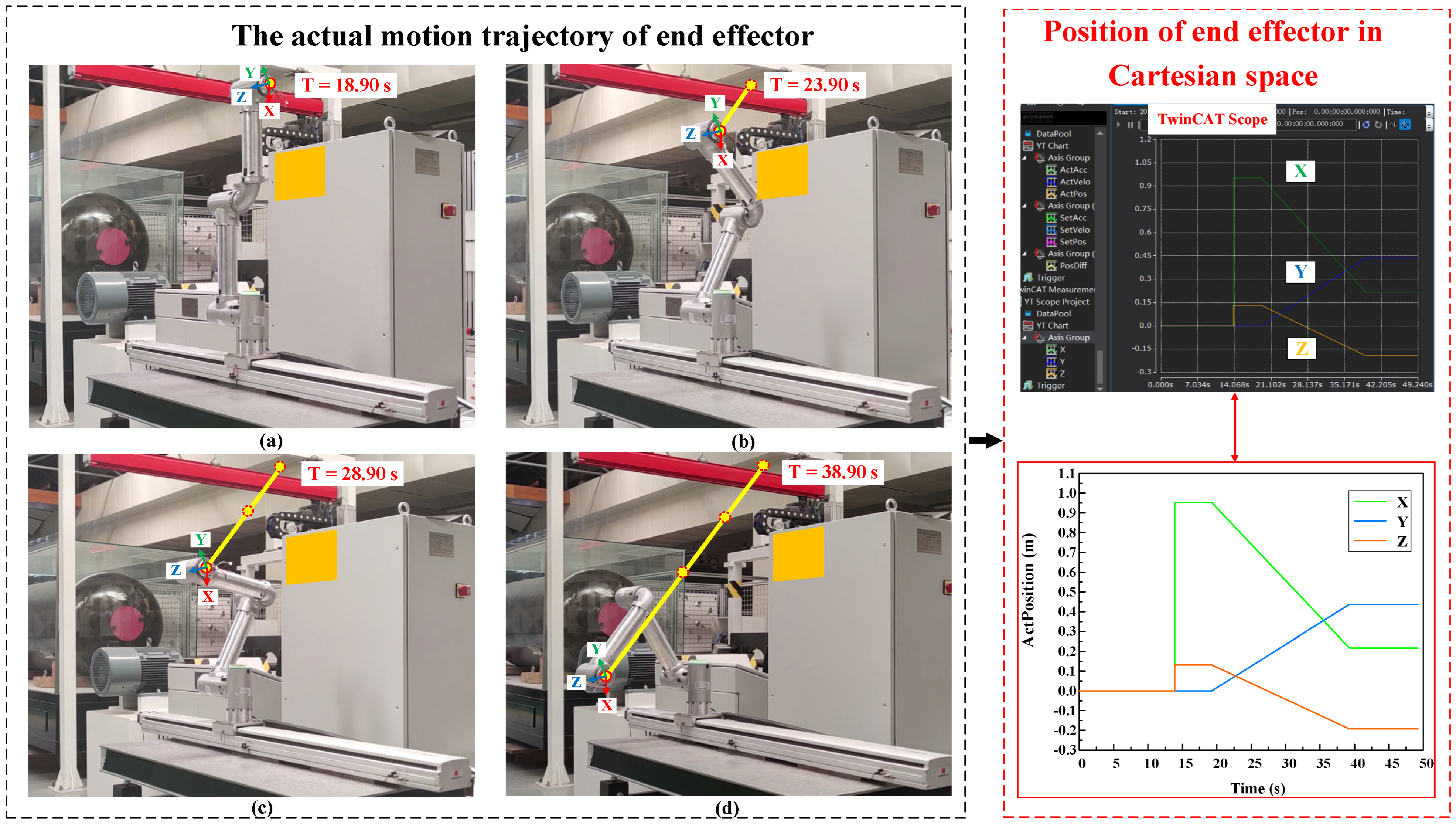
- Experiment of Cartesian space trajectory planning
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alghazzawi, T.F. Advancements in CAD/CAM technology: Options for practical implementation. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2016, 60, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Bona, A.; Nogueira, A.D.; Pecho, O.E. Optical properties of CAD–CAM ceramic systems. J. Dent. 2014, 42, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derby, S. Workcell Based Robot Design Methodologies. In Proceedings of the International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Atlanta, GA, USA, 13–16 September 1998; p. USAV01BT01A016. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, L.G.; Wu, H.T.; Liu, H.B. The Design of Mechanical Arm of Hot Extruding and Upsetting Machine Based on SolidWorks. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 655–657, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekhnacha, K.; Mazer, E.; Bessière, P. The design and implementation of a Bayesian CAD modeler for robotic applications. Adv. Robot. 2001, 15, 45–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, D.; Hao, W.; Wei, Y. Research on kinematic modeling and analysis methods of UR robot. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 4th Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC), Chongqing, China, 14–16 December 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Ponsà Cobas, S. Strategies for Remote Control and Teleoperation of a UR Robot; Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya: Barcelona, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zafra Navarro, A.; Guillén Pastor, J. UR Robot Scripting and Offline Programming in a Virtual Reality Environment; Universidad de Alicante: Alicante, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Arbo, M.; Eriksen, I.; Sanfilippo, F.; Gravdahl, J. Comparison of KVP and RSI for controlling KUKA robots over ROS. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 9841–9846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, G.; Stemmer, A.; Bischoff, R. The fast research interface for the kuka lightweight robot. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Innovative Robot Control Architectures for Demanding (Research) Applications How to Modify and Enhance Commercial Controllers (ICRA 2010), Anchorage, Alaska, 3 May 2010; pp. 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, S.; Buchstab, A. Kuka robots on-site. In Robotic Fabrication in Architecture, Art and Design 2014; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 373–380. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, H. Research and Application of Spacecraft Pipeline Digital Development Mode Based on MBD Technology. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1865, 032028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Li, J. Research on three-dimensional digital process planning based on MBD. Kybernetes 2018, 47, 816–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S. Using model-based design for hybrid electric vehicle systems. Electron. Wkly. 2010, 2416. [Google Scholar]
- Steinbauer, T.; Leiprecht, G.; Havraneck, W. High performance HIL real time for the Airbus A380 electrical backup hydraulic actuators. In Proceedings of the UKACC Control 2004 Mini Symposia, Bath, UK, 8 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yim, M.; Shen, W.M.; Salemi, B.; Rus, D.; Moll, M.; Lipson, H.; Klavins, E.; Chirikjian, G.S. Modular self-reconfigurable robot systems [grand challenges of robotics. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2007, 14, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamani-Saico, A.; Yanyachi, P.R. Implementation and performance study of the micro-ros/ros2 framework to algorithm design for attitude determination and control system. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 128451–128460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, C.S.; Dominguez, E.G.; Fryman, J.D.; Lewandowski, M.L. Collaborative robotics: New era of human–robot cooperation in the workplace. J. Saf. Res. 2020, 74, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, A.K.-Y.; Yang, Y.-H.; Lin, T.-C.; Chu, C.-W.; Lin, P.-C. Model-based design and evaluation of a brachiating monkey robot with an active waist. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel Alamsyah, M.I.; Erwin Tan, S. Serpentine Robot Model and Gait Design Using Autodesk Inventor and Simulink SimMechanics. EPJ Web Conf. 2014, 68, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Song, Y.; Dai, J.S. Reconfigurability of the origami-inspired in-tegrated 8R kinematotropic metamorphic mechanism and its evolved 6R and 4R mechanisms. Mech. Mach. Theory 2021, 161, 104245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabnis, C.; Anjana, N.; Talli, A.; Giriyapur, A.C. Modelling and simulation of industrial robot using SolidWorks. In Advances in Industrial Machines and Mechanisms: Select, Proceedings of the IPROMM 2020, Telangana, India, 21–22 December 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Cheraghpour, F.; Vaezi, M.; Jazeh, H.E.S.; Moosavian, S.A.A. Dynamic modeling and kinematic simulation of Stäubli© TX40 robot using MATLAB/ADAMS co-simulation. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics, Istanbul, Turkey, 13–15 April 2011; pp. 386–391. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L. Research on SDH Model Calibration Algorithm for Robotic Arm Based on Differential Transform. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Ge, L.; Li, R.; Liu, Z. Research on the kinematic parameter calibration method of industrial robot based on LM and PF algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2020 Chinese Control And Decision Conference (CCDC), Hefei, China, 22–24 August 2020; pp. 2198–2203. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, G.; Li, B.; Dai, J.S. Oriblock: The origami-blocks based on hinged dissection. Mech. Mach. Theory 2024, 203, 105826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yan, Z.; Xiao, J. Pose error prediction and real-time compensation of a 5-DOF hybrid robot. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 170, 104737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Yiren, Z.; Nan, Y. An Inverse Solution Algorithm for Industrial Robot. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2173, 469. [Google Scholar]
- Janson, L.; Schmerling, E.; Pavone, M. Monte Carlo motion planning for robot trajectory optimization under uncertainty. In Robotics Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 343–361. [Google Scholar]
- Long, D.T.; Binh, T.; Hoa, R.; Anh, L.; Toan, N. Robotic arm simulation by using matlab and robotics toolbox for industry application. Int. J. Electron. Commun. Eng. 2020, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, H.-J.; Son, Y.; Kim, J.-M. A Trapezoidal Velocity Profile Generator for Position Control Using a Feedback Strategy. Energies 2019, 12, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z. Cubic Polynomial Smooth Support Vector Machine Used in Intrusion Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 3rd International Conference on Materials Engineering, Manufacturing Technology and Control, Taiyuan, China, 27–28 February 2016; pp. 1236–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Ding, B.; Li, Y. Minimum-jerk trajectory planning pertaining to a translational 3-degree-of-freedom parallel manipulator through piecewise quintic polynomials interpolation. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2020, 12, 1687814020913667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanelli, G.A.; Selvaggio, M.; Ferro, M.; Ficuciello, F.; Vendittelli, M.; Siciliano, B. A v-rep simulator for the da vinci research kit robotic platform. In Proceedings of the 2018 7th IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (Biorob), Enschede, The Netherlands, 26–29 August 2018; pp. 1056–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Lovrec, D.; Tič, V.J.I. Comparison of different position controllers implemented with a Beckhoff controller and TwinCAT 3 software. Elektron. Viri 2022, 10, 83–86. [Google Scholar]







| Component | Output | Maximum Speed | Weight | Positioning Accuracy | Communication Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RJSIIZ-14 joint module | 13.5 (Nm) | 47.5 (rpm) | 1.0 (kg) | 0.015 (°) | EtherCAT |
| RJSIIZ-17 joint module | 49.0 (Nm) | 35.0 (rpm) | 1.9 (kg) | ||
| Linear slide table | 367(N) | 1.0 (m/s) | / | ±0.005 (mm) |
| 1 | 0 | |||
| 2 | 209 | 0 | ||
| 3 | −5.89 | 379.5 | 0 | |
| 4 | 0 | 364 | 0 | |
| 5 | −126.89 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Y.; Ma, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Wu, H.; Li, M. Model-Based Design of the 5-DoF Light Industrial Robot. Robotics 2025, 14, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics14080103
Shi Y, Ma T, Wang H, Zhang T, Zhang X, Wu H, Li M. Model-Based Design of the 5-DoF Light Industrial Robot. Robotics. 2025; 14(8):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics14080103
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Yongping, Tianbing Ma, Hao Wang, Tao Zhang, Xin Zhang, Huapeng Wu, and Ming Li. 2025. "Model-Based Design of the 5-DoF Light Industrial Robot" Robotics 14, no. 8: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics14080103
APA StyleShi, Y., Ma, T., Wang, H., Zhang, T., Zhang, X., Wu, H., & Li, M. (2025). Model-Based Design of the 5-DoF Light Industrial Robot. Robotics, 14(8), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics14080103






