Kisspeptin-10 Ameliorates Obesity-Diabetes with Diverse Effects on Ileal Enteroendocrine Cells and Pancreatic Islet Morphology in High-Fat Fed Female Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Tissue Processing
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
| Primary antibodies | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Target | Host | Dilution | Source |
| Insulin | Mouse | 1:500 | Abcam, ab6995 |
| Glucagon | Guinea pig | 1:200 | Raised in-house PCA2/4 |
| PYY | Rabbit | 1:500 | Abcam, ab22663 |
| GLP-1 | Rabbit | 1:200 | Raised in-house XJIC8 |
| GIP | Rabbit | 1:400 | RIC34/111J, kindly donated by Professor L Morgan, Guildford, UK |
| Ki-67 | Rabbit | 1:200 | Abcam, ab15580 |
| Secondary antibodies | |||
| Host and target | Reactivity | Dilution | Fluorescent dilution and source |
| Goat IgG | Mouse | 1:500 | Alexa Flour 594, Invitrogen, UK |
| Goat IgG | Guinea pig | 1:500 | Alexa Flour 488, Invitrogen, UK |
| Goat IgG | Rabbit | 1:500 | Alexa Flour 594, Invitrogen, UK |
2.4. Image Analysis
2.5. Biochemical Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
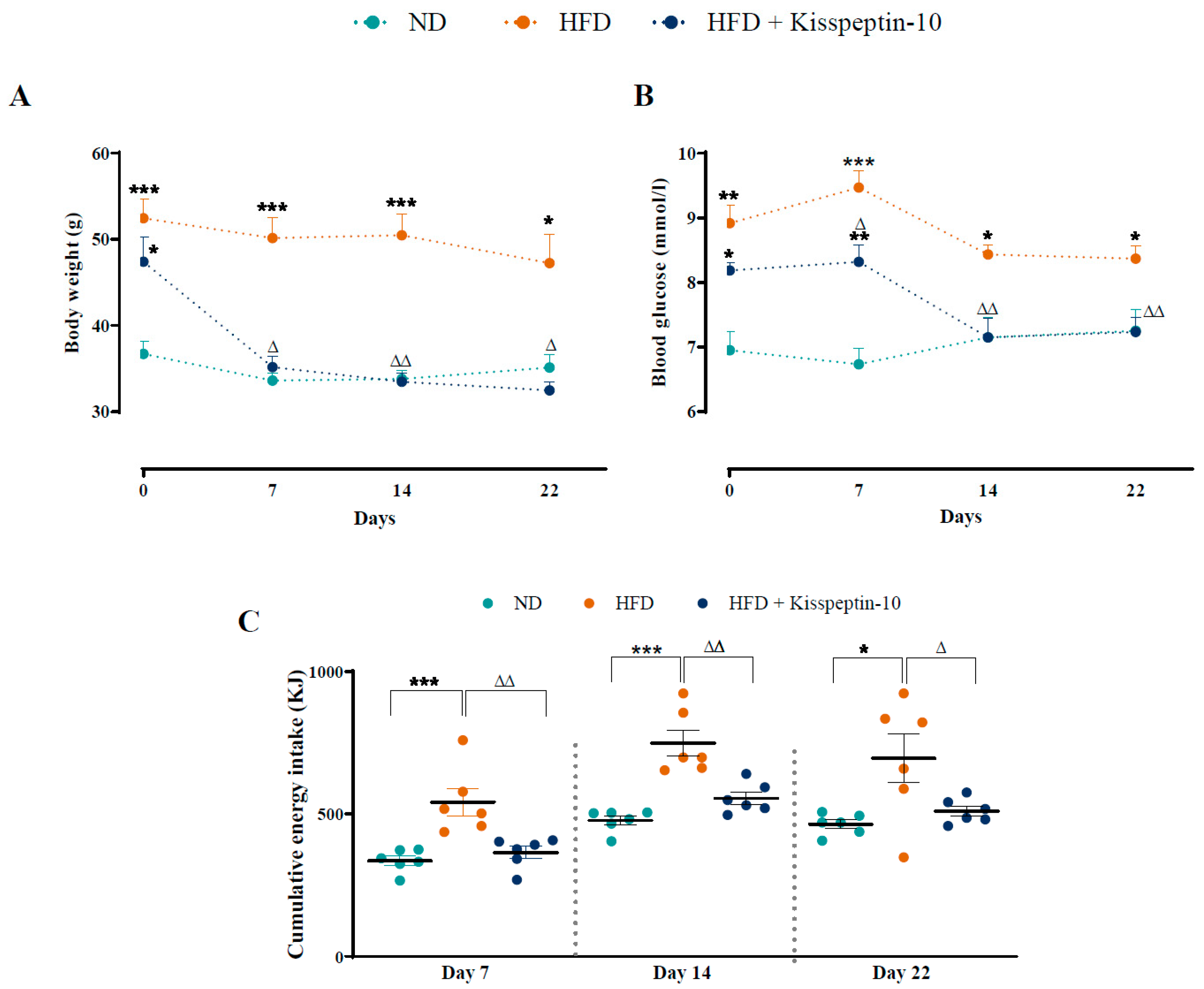
3.1. Effects of HFD and Kisspeptin-10 Treatment on Body Weight, Glucose and Energy Intake
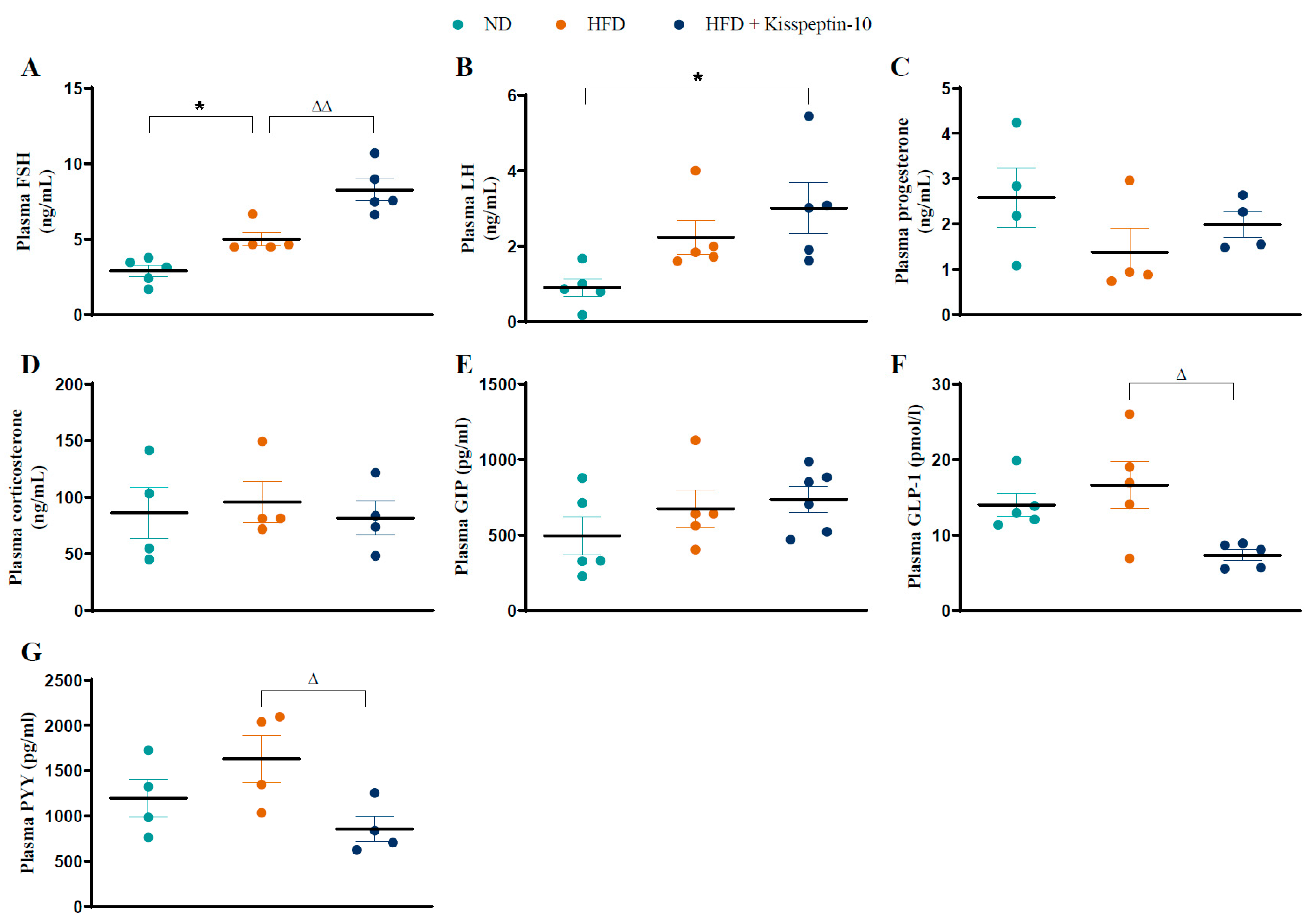
3.2. Effects of HFD and Kisspeptin-10 Treatment on Circulating Hormones
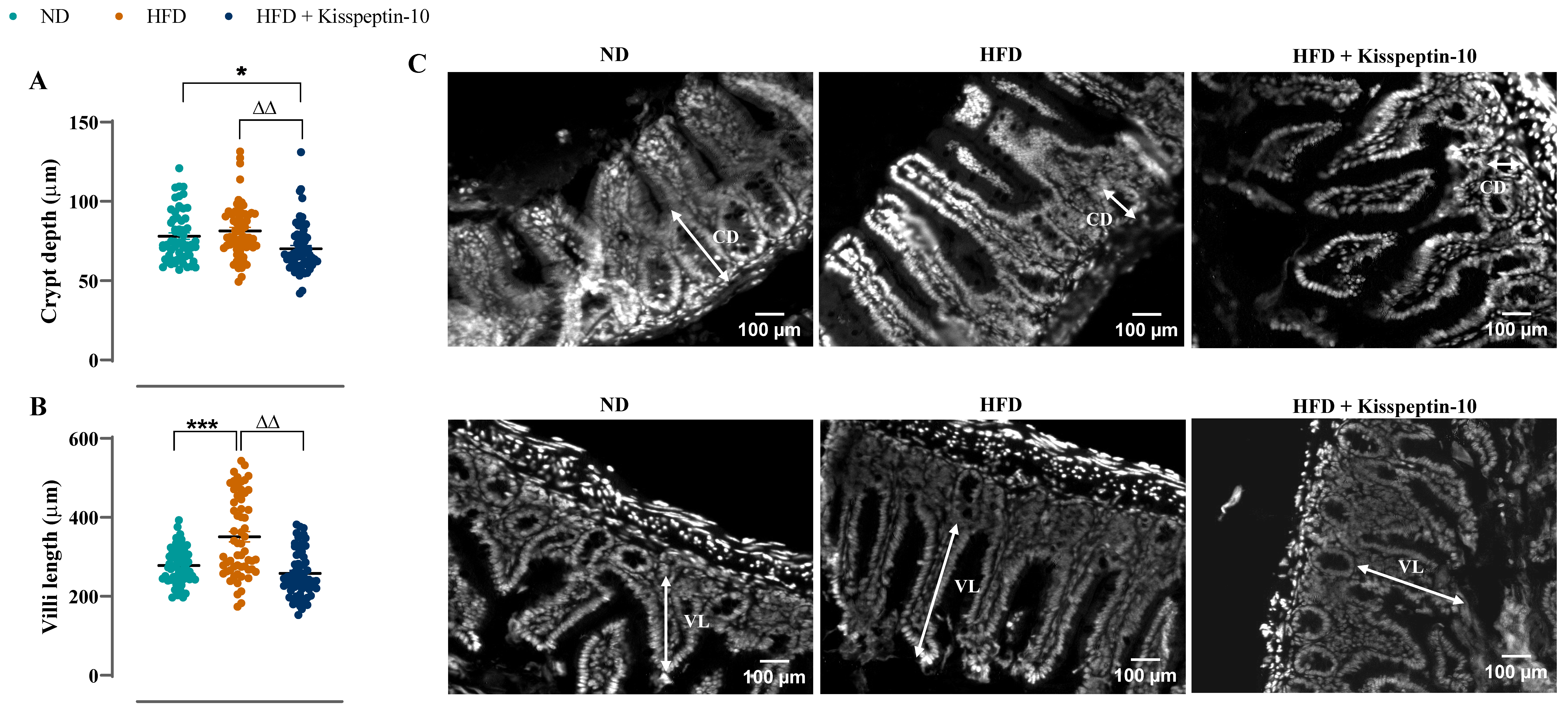
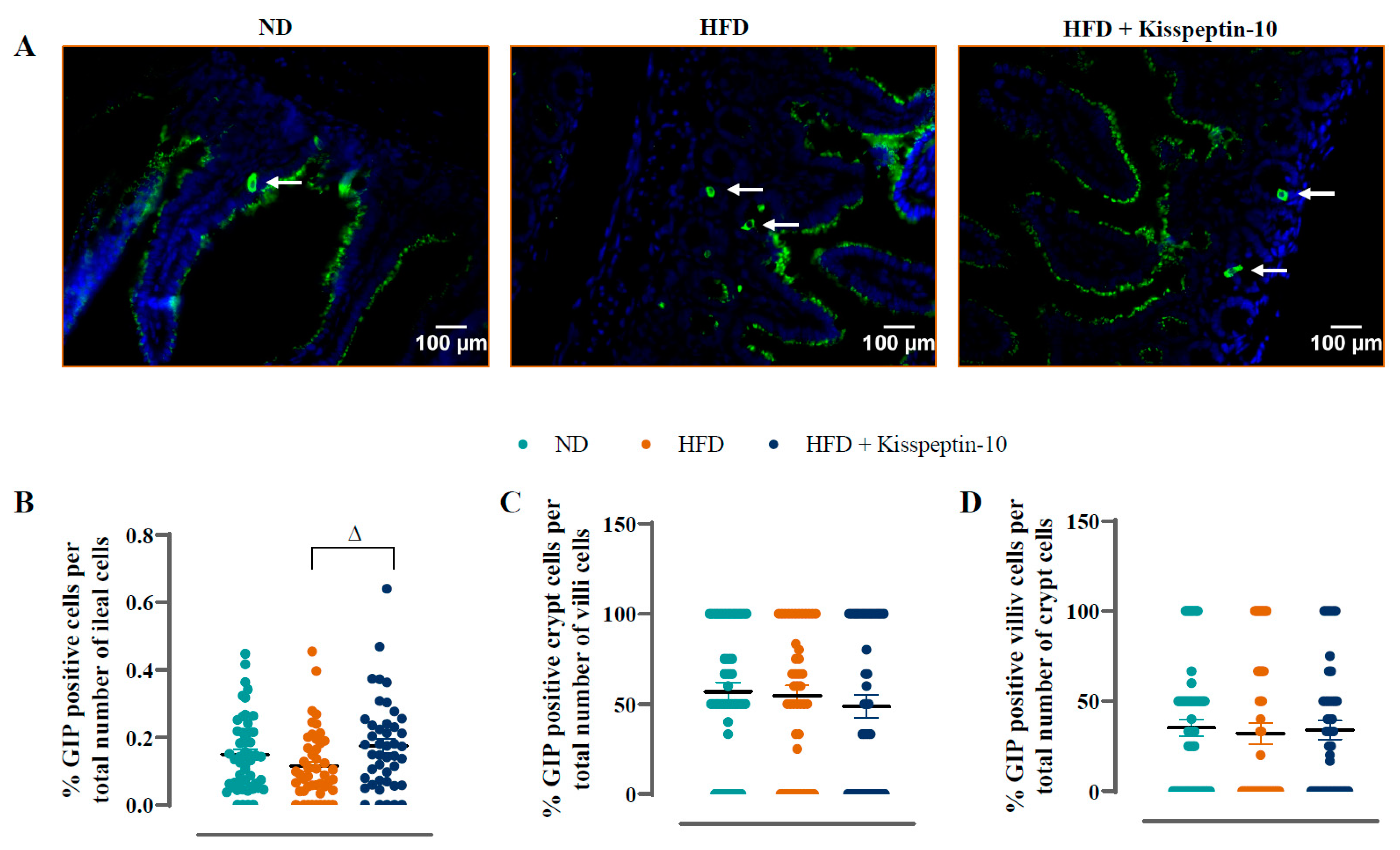
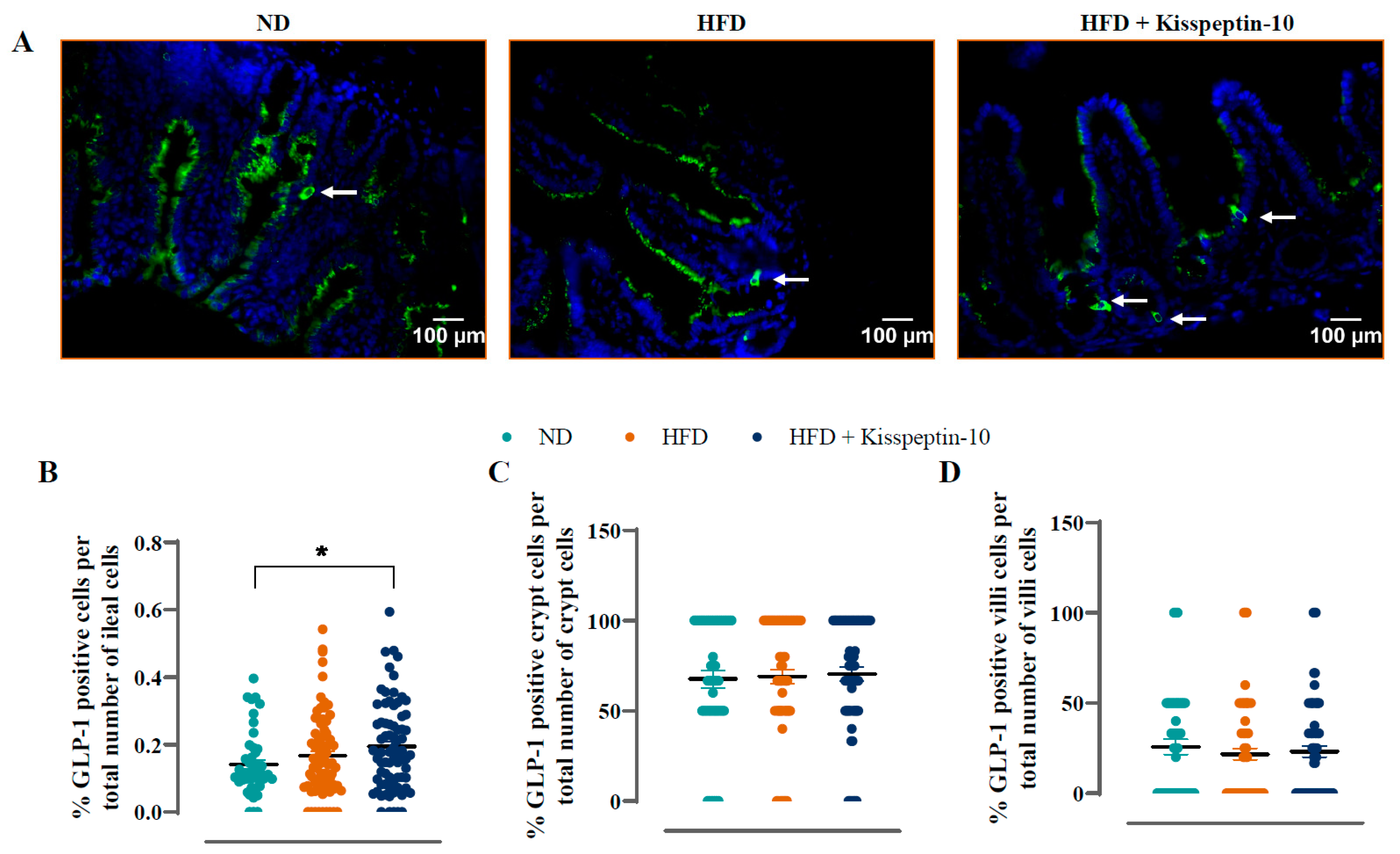
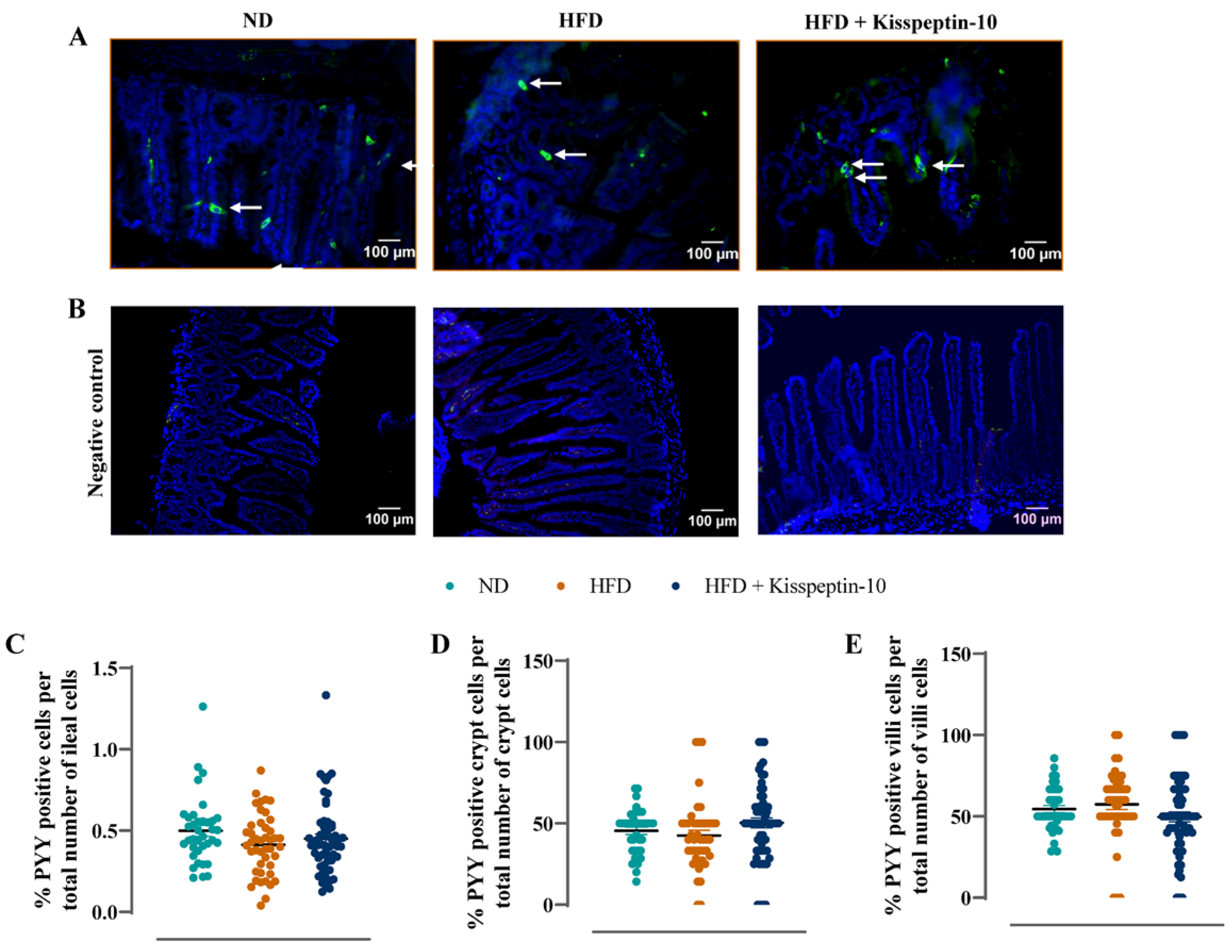
3.3. Effects of HFD and Kisspeptin-10 Treatment on Ileal Enteroendocrine Morphology and Cell Distribution
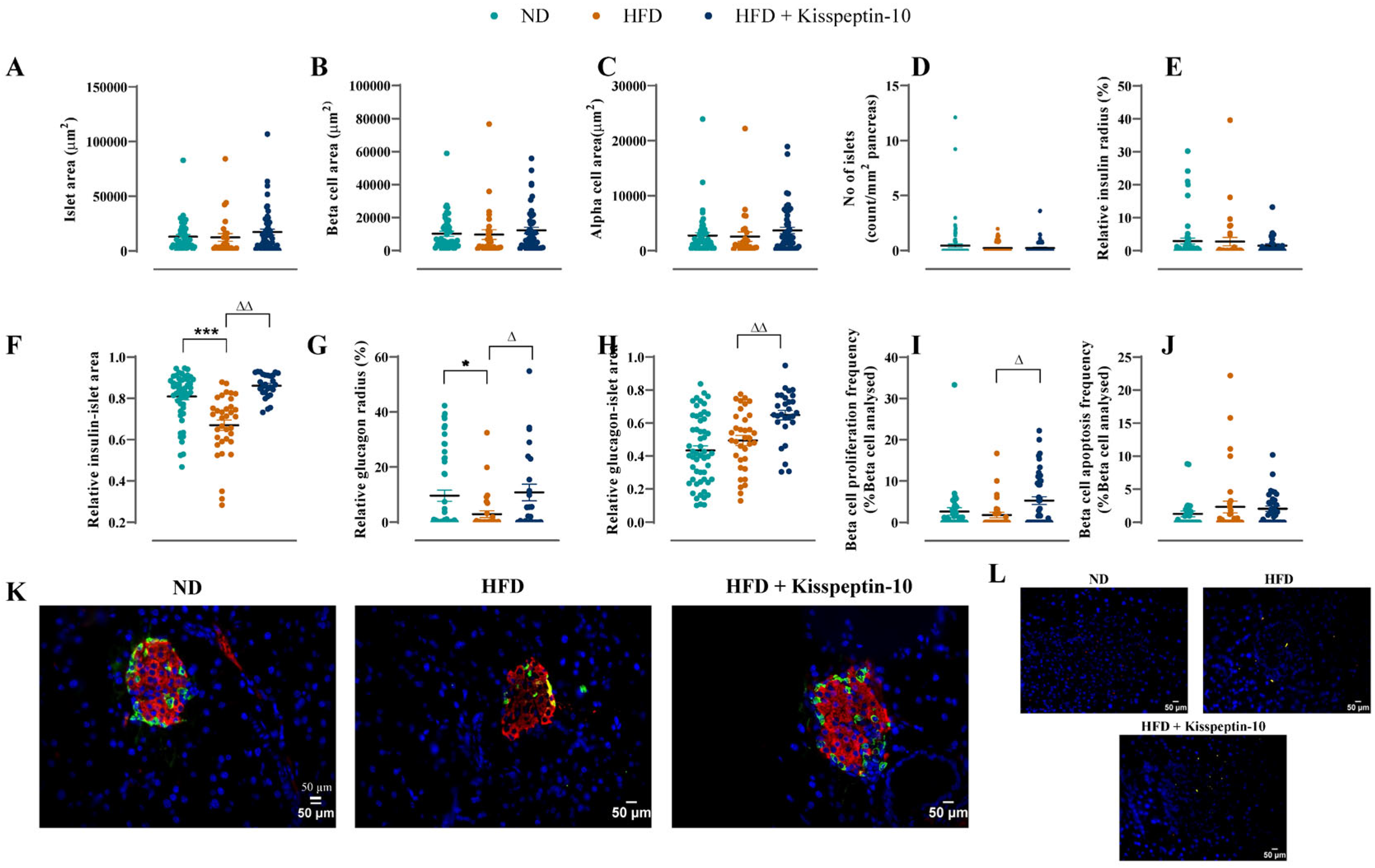
3.4. Effects of HFD and Kisspeptin-10 Treatment on Pancreatic Islet Morphology
3.5. Effects of HFD and Kisspeptin-10 Treatment on Pancreatic Beta-Cell Turnover
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torre, S.D.; Benedusi, V.; Fontana, R.; Maggi, A. Energy metabolism and fertility—A balance preserved for female health. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schon, S.B.; Cabre, H.E.; Redman, L.M. The impact of obesity on reproductive health and metabolism in reproductive-age females. Fertil. Steril. 2024, 122, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, A.; Khan, D.; Flatt, P.R.; Irwin, N.; Moffett, R.C. PYY (3-36) protects against high fat feeding induced changes of pancreatic islet and intestinal hormone content and morphometry. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Gen. Subj. 2023, 1867, 130359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Yu, C.; Zhao, H.; Huang, D. The role of kisspeptin in the control of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and reproduction. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 925206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotani, M.; Detheux, M.; Vandenbogaerde, A.; Communi, D.; Vanderwinden, J.M.; Le Poul, E.; Brézillon, S.; Tyldesley, R.; Suarez-Huerta, N.; Vandeput, F.; et al. The metastasis suppressor gene KiSS-1 encodes kisspeptins, the natural ligands of the orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR54. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 34631–34636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, V.M. Metabolic regulation of kisspeptin—The link between energy balance and reproduction. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzi-Engbeaya, C.; Comninos, A.N.; Clarke, S.A.; Jomard, A.; Yang, L.; Jones, S.; Abbara, A.; Narayanaswamy, S.; Eng, P.C.; Papadopoulou, D.; et al. The effects of kisspeptin on β-cell function, serum metabolites and appetite in humans. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 2800–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowe, J.E.; King, A.J.; Kinsey-Jones, J.S.; Foot, V.L.; Li, X.F.; O’Byrne, K.T.; Persaud, S.J.; Jones, P.M. Kisspeptin stimulation of insulin secretion: Mechanisms of action in mouse islets and rats. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.J.; Mondal, P.; Wolfe, A.; Alonso, L.C.; Stamateris, R.; Ong, B.W.T.; Lim, O.C.; Yang, K.S.; Radovick, S.; Novaira, H.J.; et al. Glucagon regulates hepatic kisspeptin to impair insulin secretion. Cell. Metab. 2014, 19, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, M.E.; Hsu, M.C.; Wu, Y.H.S.; Jiang, Y.-F.; Wu, L.-S.; Jong, D.-S.; Chiu, C.-H. Kisspeptin-activated autophagy independently suppresses non-glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, R.A.; Egido, E.M.; Hernández, R.; Marco, J. Kisspeptin-13 inhibits insulin secretion without affecting glucagon or somatostatin release: Study in the perfused rat pancreas. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 196, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Jin, W.; Peng, Y.; He, Z.; Wei, L.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Chang, M.; Wang, R. In vivo and vitro characterization of the effects of kisspeptin-13, endogenous ligands for GPR54, on mouse gastrointestinal motility. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 794, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Gao, Y.; Li, F.; Yuan, L. The role of gut–islet axis in pancreatic islet function and glucose homeostasis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2025, 27, 1676–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Cao, J.; Sun, C.; Yuan, L. The Regulation Role of the Gut-Islets Axis in Diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2024, 17, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosser, R.E.; Maulis, M.F.; Moullé, V.S.; Dunn, J.C.; Carboneau, B.A.; Arasi, K.; Pappan, K.; Poitout, V.; Gannon, M. High-fat diet-induced β-cell proliferation occurs prior to insulin resistance in C57Bl/6J male mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 308, E573–E582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, A.; Khan, D.; Flatt, P.R.; Moffett, C.R.; Irwin, N. GLP-1 receptor agonism and GIP receptor antagonism induce substantial alterations in enteroendocrine and islet cell populations in obese high fat fed mice. Peptides 2023, 169, 171093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Nemoto, Y.; Takei, Y.; Morikawa, R.; Oshima, S.; Nagaishi, T.; Okamoto, R.; Tsuchiya, K.; Nakamura, T.; Stutte, S.; et al. High-fat diet-derived free fatty acids impair the intestinal immune system and increase sensitivity to intestinal epithelial damage. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 522, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roch, G.J.; Busby, E.R.; Sherwood, N.M. Evolution of reproductive neurohormones. In Handbook of Neuroendocrinology; Fink, G., Pfaff, D.W., Levine, J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uenoyama, Y.; Inoue, N.; Nakamura, S.; Tsukamura, H. Kisspeptin neurons and estrogen–estrogen receptor α signaling: Unraveling the mystery of steroid feedback system regulating mammalian reproduction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glavas, M.M.; Lee, A.Y.; Miao, I.; Yang, F.; Mojibian, M.; O’Dwyer, S.M.; Kieffer, T.J. Developmental timing of high-fat diet exposure impacts glucose homeostasis in mice in a sex-specific manner. Diabetes 2021, 70, 2771–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, S.; Moffett, R.C.; Thomas, K.G.; Irwin, N.; Flatt, P.R. Vasopressin receptors in islets enhance glucose tolerance, pancreatic beta-cell secretory function, proliferation and survival. Biochimie 2019, 158, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, A.; Flatt, P.R.; Draper, M.; Tarasov, A.I.; Moffett, R.C.; Irwin, N.; Khan, D. Dopamine signalling in pancreatic islet cells and role in adaptations to metabolic stress. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2024, 76, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, I.; Qureshi, I.Z. Intraperitoneal kisspeptin-10 administration ameliorates sodium arsenite-induced reproductive toxicity in adult male mice. Andrologia 2022, 54, e14347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, T.S.; Vu, J.P.; Oh, S.; Sanford, D.; Pisegna, J.R.; Germano, P. Intraperitoneal treatment of kisspeptin suppresses appetite and energy expenditure and alters gastrointestinal hormones in mice. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 2254–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.; Vasu, S.; Moffett, R.C.; Irwin, N.; Flatt, P.R. Influence of neuropeptide Y and pancreatic polypeptide on islet function and beta-cell survival. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asuaje Pfeifer, M.; Langehein, H.; Grupe, K.; Müller, S.; Seyda, J.; Liebmann, M.; Rustenbeck, I.; Scherneck, S. PyCreas: A tool for quantification of localization and distribution of endocrine cell types in the islets of Langerhans. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1250023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.; Sridhar, A.; Flatt, P.R.; Moffett, R.C. Disturbed ovarian morphology, oestrous cycling and fertility of high fat fed rats are linked to alterations of incretin receptor expression. Reprod. Boil. 2023, 23, 100784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorupskaite, K.; George, J.T.; Anderson, R.A. The kisspeptin-GnRH pathway in human reproductive health and disease. Hum. Reprod. Update 2014, 20, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbara, A.; Ratnasabapathy, R.; Jayasena, C.N.; Dhillo, W.S. The effects of kisspeptin on gonadotropin release in non-human mammals. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 63–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakita, T.; Yasui, T.; Yoshida, K.; Matsui, S.; Iwasa, T. Associations of LH and FSH with reproductive hormones depending on each stage of the menopausal transition. BMC Women’s Health 2023, 23, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, J.M.; Navarro, V.M.; Fernandez-Fernandez, R.; Nogueiras, R.; Tovar, S.; Roa, J.; Vazquez, M.J.; Vigo, E.; Casanueva, F.F.; Aguilar, E.; et al. Changes in hypothalamic KiSS-1 system and restoration of pubertal activation of the reproductive axis by kisspeptin in undernutrition. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 3917–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasena, C.N.; Abbara, A.; Narayanaswamy, S.; Comninos, A.N.; Ratnasabapathy, R.; Bassett, P.; Mogford, J.T.; Malik, Z.; Calley, J.; Ghatei, M.A.; et al. Direct comparison of the effects of intravenous kisspeptin-10, kisspeptin-54 and GnRH on gonadotrophin secretion in healthy men. Hum. Reprod. 2015, 30, 1934–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, A.D.; Kauffman, A.S. Metabolic actions of kisspeptin signaling: Effects on body weight, energy expenditure, and feeding. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 231, 107974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambineri, A.; Pelusi, C.; Vicennati, V.; Pagotto, U.; Pasquali, R. Obesity and the polycystic ovary syndrome. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26, 883–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolson, K.P.; Garcia, C.; Delgado, I.; Marooki, N.; Kauffman, A.S. Metabolism and energy expenditure, but not feeding or glucose tolerance, are impaired in young Kiss1r KO female mice. Endocrinology. 2016, 157, 4192–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolson, K.P.; Marooki, N.; Wolfe, A.; Smith, J.T.; Kauffman, A.S. Cre/lox generation of a novel whole-body Kiss1r KO mouse line recapitulates a hypogonadal, obese, and metabolically-impaired phenotype. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2019, 498, 110559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, Z.; Ozcan, M.; Ozkaya, A.; Canpolat, S.; Kutlu, S.; Kelestimur, H. Percentages of serum, liver and adipose tissue fatty acids and body weight are affected in female rats by long-term Central kisspeptin treatments. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 129, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timper, K.; Brüning, J.C. Hypothalamic circuits regulating appetite and energy homeostasis: Pathways to obesity. Dis. Model. Mech. 2017, 10, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauge-Evans, A.C.; Richardson, C.C.; Milne, H.M.; Christie, M.R.; Persaud, S.J.; Jones, P.M. A role for kisspeptin in islet function. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 2131–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitha, M.; Reichardt, F.; Tabatabavakili, S.; Nezami, B.G.; Chassaing, B.; Mwangi, S.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Gewirtz, A.; Srinivasan, S. Intestinal dysbiosis contributes to the delayed gastrointestinal transit in high-fat diet fed mice. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 2, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreckley, E.; Murphy, K.G. The L-cell in nutritional sensing and the regulation of appetite. Front. Nutr. 2015, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, P.M.; Sun, R.C.; Guo, J.; Erwin, C.R.; Warner, B.W. High-fat diet enhances villus growth during the adaptation response to massive proximal small bowel resection. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2014, 18, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohin, N.; Keeley, T.M.; Carulli, A.J.; Walker, E.M.; Carlson, E.A.; Gao, J.; Aifantis, I.; Siebel, C.W.; Rajala, M.W.; ∙Myers, M.G., Jr.; et al. Rapid crypt cell remodeling regenerates the intestinal stem cell niche after Notch inhibition. Stem Cell Rep. 2020, 15, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Quast, D.R.; Wefers, J.; Pfeiffer, A.F. The evolving story of incretins (GIP and GLP-1) in metabolic and cardiovascular disease: A pathophysiological update. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thondam, S.K.; Cuthbertson, D.J.; Wilding, J.P. The influence of Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP) on human adipose tissue and fat metabolism: Implications for obesity, type 2 diabetes and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Peptides 2020, 125, 170208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, T.; Sun, Z.; Pan, Y.; Deng, X.; Yuan, G. Glucagon-like peptide-1: New regulator in lipid metabolism. Diabetes Metab. J. 2024, 48, 354–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliwowska, J.H.; Woods, N.E.; Alzahrani, A.R.; Paspali, E.; Tate, R.J.; Ferro, V.A. Kisspeptin a potential therapeutic target in treatment of both metabolic and reproductive dysfunction. J. Diabetes 2024, 16, e13541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.M.; Sun, E.W.; Keating, D.J. Mechanisms controlling hormone secretion in human gut and its relevance to metabolism. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 244, R1–R15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzi-Engbeaya, C.; Dhillo, W.S. Gut hormones and reproduction. Ann. Endocrinol. 2022, 83, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorga, A.; Cunningham, C.M.; Moazeni, S.; Ruffenach, G.; Umar, S.; Eghbali, M. The protective role of estrogen and estrogen receptors in cardiovascular disease and the controversial use of estrogen therapy. Biol. Sex Differ. 2017, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, U.S.; Waldén, T.B.; Carlsson, P.O.; Jansson, L.; Phillipson, M. Female mice are protected against high-fat diet induced metabolic syndrome and increase the regulatory T cell population in adipose tissue. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.E.; Chen, Y.C.; Esser, N.; Taylor, A.J.; van Raalte, D.H.; Zraika, S.; Verchere, C.B. The β cell in diabetes: Integrating biomarkers with functional measures. Endocr. Rev. 2021, 42, 528–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Tanday, N.; Flatt, P.R.; Irwin, N. The Beneficial Impact of a Novel Pancreatic Polypeptide Analogue on Islet Cell Lineage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanday, N.; Tarasov, A.I.; Moffett, R.C.; Flatt, P.R.; Irwin, N. Pancreatic islet cell plasticity: Pathogenic or therapeutically exploitable? Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, V.; Tanday, N.; Irwin, N.; Tarasov, A.I.; Flatt, P.R.; Moffett, R.C. Cafeteria diet compromises natural adaptations of islet cell transdifferentiation and turnover in pregnancy. Diabet. Med. 2025, 42, e15434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowe, J.E.; Hill, T.G.; Hunt, K.F.; Smith, L.I.; Simpson, S.J.; Amiel, S.A.; Jones, P.M. A role for placental kisspeptin in beta cell adaptation to pregnancy. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e124540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughton, C.K.; Munro, N.; Whyte, M. Targeting beta-cell preservation in the management of type 2 diabetes. Br. J. Diabetes 2017, 4, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sridhar, A.; Khan, D.; Muthukumar, R.; Sampathkumar, S.; Irwin, N.; Flatt, P.R.; Moffett, R.C. Kisspeptin-10 Ameliorates Obesity-Diabetes with Diverse Effects on Ileal Enteroendocrine Cells and Pancreatic Islet Morphology in High-Fat Fed Female Mice. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111591
Sridhar A, Khan D, Muthukumar R, Sampathkumar S, Irwin N, Flatt PR, Moffett RC. Kisspeptin-10 Ameliorates Obesity-Diabetes with Diverse Effects on Ileal Enteroendocrine Cells and Pancreatic Islet Morphology in High-Fat Fed Female Mice. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(11):1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111591
Chicago/Turabian StyleSridhar, Ananyaa, Dawood Khan, Rithiga Muthukumar, Swetha Sampathkumar, Nigel Irwin, Peter R. Flatt, and R. Charlotte Moffett. 2025. "Kisspeptin-10 Ameliorates Obesity-Diabetes with Diverse Effects on Ileal Enteroendocrine Cells and Pancreatic Islet Morphology in High-Fat Fed Female Mice" Biomolecules 15, no. 11: 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111591
APA StyleSridhar, A., Khan, D., Muthukumar, R., Sampathkumar, S., Irwin, N., Flatt, P. R., & Moffett, R. C. (2025). Kisspeptin-10 Ameliorates Obesity-Diabetes with Diverse Effects on Ileal Enteroendocrine Cells and Pancreatic Islet Morphology in High-Fat Fed Female Mice. Biomolecules, 15(11), 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111591






