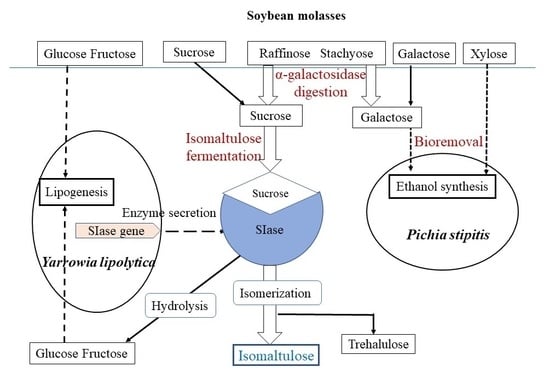
Whole Conversion of Soybean Molasses into Isomaltulose and Ethanol by Combining Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Successive Selective Fermentations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains, Plasmids and Media
2.2. Expression of RMgase Gene in Y. lipolytica
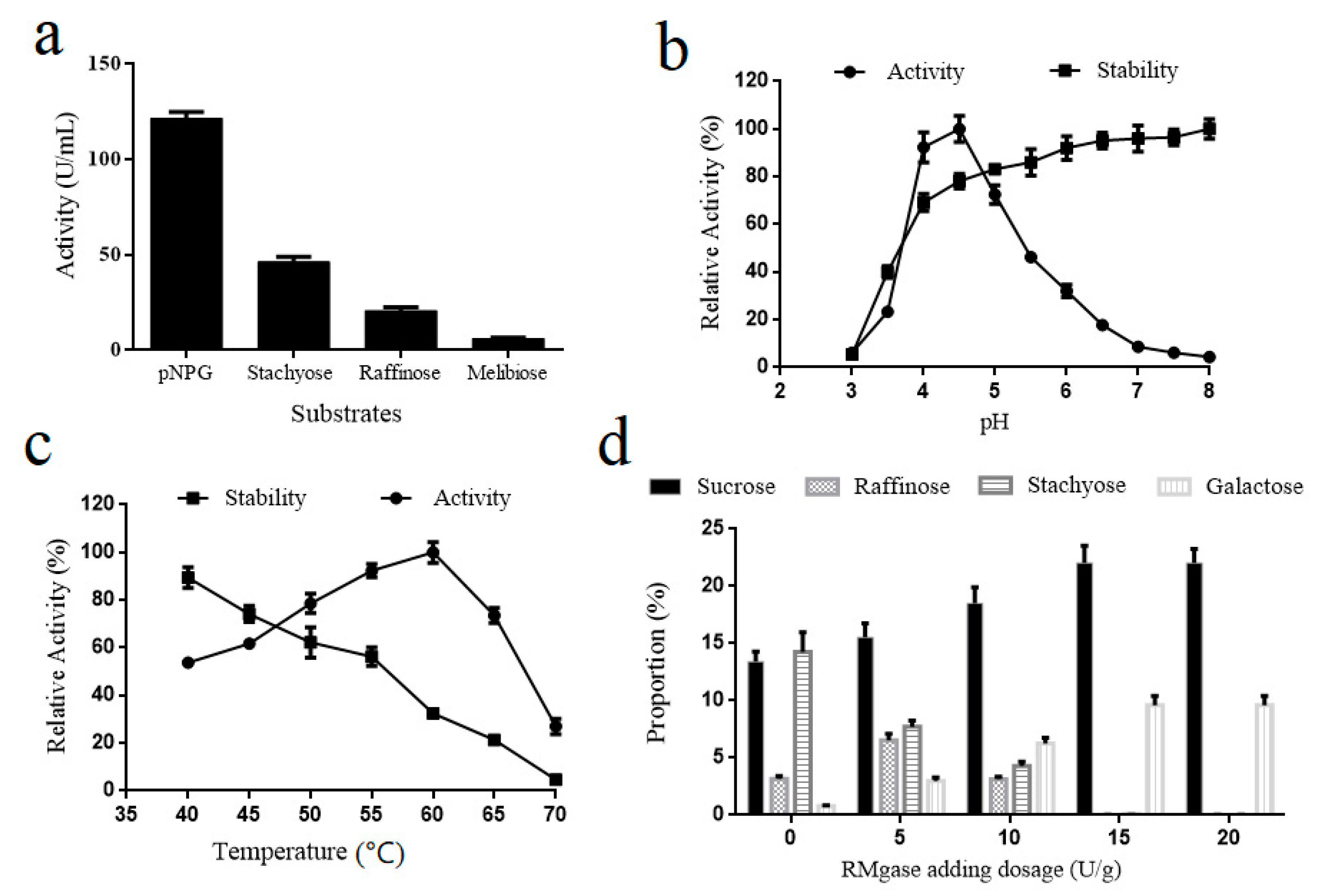
2.3. Enzymatic Activity Assay and Sugar Detection
2.4. Effects of pH and Temperature on Purified α-Galactosidase Activity and Stability
2.5. Sucrose Generation from Soy Molasses by α-Galactosidase Hydrolysis
2.6. Optimization of SMH Supplementation at the Flask Level
2.7. Isomaltulose Production in 10-L Fermenter
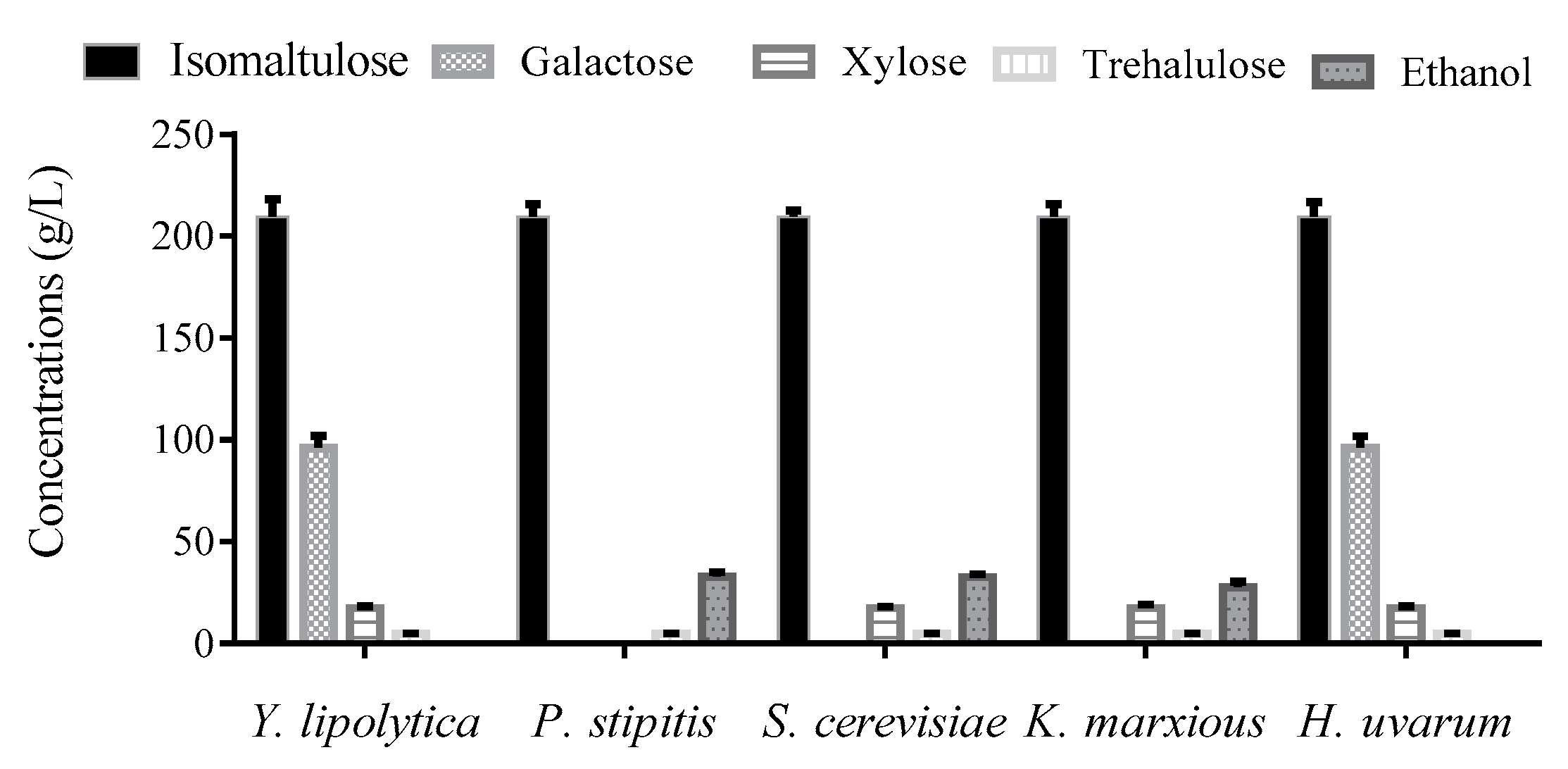
2.8. Isomaltulose Biopurification with Ethanol-Producing Yeast Strain
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Secretory Expression of α-Galactosidase in Y. lipolytica
3.2. Sucrose Generation from Soy Molasses by α-Galactosidase Hydrolysis
3.3. Isomaltulose Production from SMH in a Two-Stage Bioprocess
3.4. Removing Sugar Byproducts Using Yeast Strains
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Achten, J.; Jentjens, R.F.; Jeukendrup, A. Exogenous oxidation of isomaltulose is lower than that of sucrose during exercise in men. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleddermann, M.; Rauh-Pfeiffer, A.; Demmelmair, H.; Holdt, L.; Teupser, D.; Koletzko, B. Effects of a Follow-On Formula Containing Isomaltulose (Palatinose™) on Metabolic Response, Acceptance, Tolerance and Safety in Infants: A Randomized-Controlled Trial. PloS ONE 2016, 11, e0151614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lina, B.A.; Jonker, D.; Kozianowski, G. Isomaltulose (Palatinose): A review of biological and toxicological studies. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.H.; Park, S.E.; Lim, J.K.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, D.Y.; Park, C.S. Conversion of sucrose into isomaltulose by Enterobacter sp. FMB1, an isomaltulose-producing microorganism isolated from traditional Korean food. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenthaler, F.W.; Peters, S. Carbohydrates as green raw materials for the chemical industry. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2004, 7, 65–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawale, P.D.; Shendurse, A.M.; Mohan, M.S.; Patil, G.R. Isomaltulose (Palatinose)—An emerging carbohydrate. Food Biosci. 2017, 18, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, N.I.H.; Sporns, P.E. Analysis and Quantitation of Minor Di- and Trisaccharides in Honey, Using Capillary Gas Chromatography. J. Food Sci. 2010, 53, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wu, S.; Qiu, J.; Xu, C.; Li, S.; Xu, H. Green synthesis of isomaltulose from cane molasses by Bacillus subtilis WB800-pHA01-palI in a biologic membrane reactor. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, B. Current studies on sucrose isomerase and biological isomaltulose production using sucrose isomerase. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 6569–6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.Y.; Jung, J.H.; Seo, D.H.; Hansin, J.; Ha, S.J.; Cha, J.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, C.S. Isomaltulose production via yeast surface display of sucrose isomerase from Enterobacter sp. FMB-1 on Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9179–9184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morello, E.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Llull, D.; Solé, V.; Miraglio, N.; Langella, P.; Poquet, I. Lactococcus lactis, an efficient cell factory for recombinant protein production and secretion. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 14, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Jung, J.H.; Seo, D.H.; Ha, S.J.; Yoon, J.W.; Kim, Y.C.; Shim, J.H.; Park, C.S. Microbial production of palatinose through extracellular expression of a sucrose isomerase from Enterobacter sp. FMB-1 in Lactococcus lactis MG1363. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8828–8833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, Z.P.; Sheng, J.; Zheng, Y.; Ji, X.F.; Zhou, H.X.; Liu, X.Y.; Chi, Z.M. High and efficient isomaltulose production using an engineered Yarrowia lipolytica strain. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braunegg, G.; Bona, R.; Koller, M. Sustainable Polymer Production. Journal of Macromolecular Science: Part D-Rev. Polym. Process. 2004, 43, 1779–1793. [Google Scholar]
- Solaiman, D.K.Y.; Ashby, R.D.; Nunez, A. Production of sophorolipids by Candida bombicola grown on soy molasses as substrate. Biotechnol. Lett. 2004, 26, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, M.; Wei, P.; Yang, S.T. Polymalic acid fermentation by Aureobasidium pullulans for malic acid production from soybean hull and soy molasses: Fermentation kinetics and economic analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 223, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Du, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, S. Butanol Production from Soybean Hull and Soy Molasses by Acetone-Butanol-Ethanol Fermentation. ACS Symp. 2014, 1178, 25–41. [Google Scholar]
- Lynd, L.R.; Wyman, C.E.; Gerngross, T.U. Biocommodity Engineering. Biotechnol. Prog. 1999, 15, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; Lin, M.; Yang, S.T. Propionic acid production from soy molasses by Propionibacterium acidipropionici: Fermentation kinetics and economic analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, R.; Yong, K.P. Production of Fungal α-Galactosidase and Its Application to the Hydrolysis of Galactooligosaccharides in Soybean Milk. J. Food Sci. 2010, 47, 1973–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.N.; Yuan, T.Z.; Shi, P.J.; Luo, H.Y.; Ning, L.; Meng, K.; Bai, Y.G.; Yang, P.L.; Zhou, Z.G.; Zhang, Z.F. Properties of a novel α-galactosidase from Streptomyces sp. S27 and its potential for soybean processing. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2010, 47, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, S.; Rooke, J.A.; Galbraith, H. Improvement of the nutritive value of soybean meal by protease and a-galactosidase treatment in broiler cockerels and broiler chicks. Br. Poult. Sci. 2003, 44, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madzak, C. Yarrowia lipolytica: Recent achievements in heterologous protein expression and pathway engineering. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 4559–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gietz, R.D.; Schiestl, R.H. High-efficiency yeast transformation using the LiAc/SS carrier DNA/PEG method. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, H.; Cheng, H.; Deng, Z. Isomaltulose production by yeast surface display of sucrose isomerase from Pantoea dispersa on Yarrowia lipolytica. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 32, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Cheng, H.; Liu, D.; Cheng, H.; Deng, Z. Integrated approach to producing high-purity trehalose from maltose by the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica displaying trehalose synthase (TreS) on the cell surface. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6179–6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baik, S.H.; Saito, K.; Yokota, A.; Asano, K.; Tomita, F. Molecular cloning and high-level expression in Escherichia coli of fungal alpha-galactosidase from Absidia corymbifera IFO 8084. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2000, 90, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Meng, K.; Bai, Y.; Shi, P.; Luo, H.; Yang, P.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, B. A novel protease-resistant alpha-galactosidase with high hydrolytic activity from Gibberella sp. F75: Gene cloning, expression, and enzymatic characterization. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 83, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katrolia, P.; Jia, H.; Yan, Q.; Song, S.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, H. Characterization of a protease-resistant alpha-galactosidase from the thermophilic fungus Rhizomucor miehei and its application in removal of raffinose family oligosaccharides. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, S.; Meng, K.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Yuan, T.; Luo, H.; Yao, B. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel a-galactosidase gene from Penicillium sp. F63 CGMCC 1669 and expression in Pichia pastoris. Enzym. Microb. Tech. 2007, 40, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Seitl, I.; Mu, W.; Zhang, T.; Stressler, T.; Fischer, L.; Jiang, B. Biotechnical production of trehalose through the trehalose synthase pathway: Current status and future prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 2965–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simila, J.; Gernig, A.; Murray, P.; Fernandes, S.; Tuohy, M.G. Cloning and expression of a thermostable alpha-galactosidase from the thermophilic fungus Talaromyces emersonii in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 1653. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferretti, A.; Flanagan, V.P.; Ruth, J.M. Nonenzymatic browning in a lactose-casein model system. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1970, 18, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.G.; Melton, L.D. Nonenzymatic browning of lactose and caseinate during dry heating at different relative humidities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 10036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hymowitz, T.; Collins, F.I.; Panczner, J.; Walker, W.M. Relationship Between the Content of Oil, Protein, and Sugar in Soybean Seed. Agron. J. 1972, 64, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, V.M.; de Rezende, S.T.; Moreira, M.A.; de Barros, E.G.; Felix, C.R. Characterization of alpha-galactosidases from germinating soybean seed and their use for hydrolysis of oligosaccharides. Phytochemistry 2001, 58, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalabrini, P.; Rossi, M.; Spettoli, P.; Matteuzzi, D. Characterization of Bifidobacterium strains for use in soymilk fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1998, 39, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaiman, D.K.; Ashby, R.D.; Hotchkiss, A.T., Jr.; Foglia, T.A. Biosynthesis of medium-chain-length poly(hydroxyalkanoates) from soy molasses. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira-Leitão, V.S.; Cammarota, M.C.; Aguieiras, E.C.G.; de Sá, L.R.V.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Freire, D.M.G. The protagonism of biocatalysis in green chemistry and its environmental benefits. Catalysts 2017, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, Y.; Chi, B.; Xu, Z.; Feng, X.; Li, S.; Xu, H. An innovative method for immobilizing sucrose isomerase on e-poly-L-lysine modified mesoporous TiO2. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Digested Soy Molasses (g/L) | Isomaltulose Production (g/L) | Residual Sucrose (g/L) | Yield (g/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 400 | 84.7 ± 7.6 | 0 | 0.96 |
| 500 | 106.3 ± 8.2 | 0 | 0.96 |
| 600 | 126.2 ± 7.2 | 0 | 0.96 |
| 700 | 135.9 ± 12.1 | 11.6 ± 1.3 | 0.95 |
| 800 | 144.8 ± 10.9 | 7.9 ± 0.6 | 0.86 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.-P.; Zhang, L.-L.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.-Y.; Yu, X.-J. Whole Conversion of Soybean Molasses into Isomaltulose and Ethanol by Combining Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Successive Selective Fermentations. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9080353
Wang Z-P, Zhang L-L, Liu S, Liu X-Y, Yu X-J. Whole Conversion of Soybean Molasses into Isomaltulose and Ethanol by Combining Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Successive Selective Fermentations. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(8):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9080353
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhi-Peng, Lin-Lin Zhang, Song Liu, Xiao-Yan Liu, and Xin-Jun Yu. 2019. "Whole Conversion of Soybean Molasses into Isomaltulose and Ethanol by Combining Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Successive Selective Fermentations" Biomolecules 9, no. 8: 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9080353
APA StyleWang, Z.-P., Zhang, L.-L., Liu, S., Liu, X.-Y., & Yu, X.-J. (2019). Whole Conversion of Soybean Molasses into Isomaltulose and Ethanol by Combining Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Successive Selective Fermentations. Biomolecules, 9(8), 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9080353