The Relationship between Plasma Taurine Levels and Diabetic Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Blood Sample Processing
2.3. Measurement of Plasma Taurine Levels
2.4. Statistical Analysis
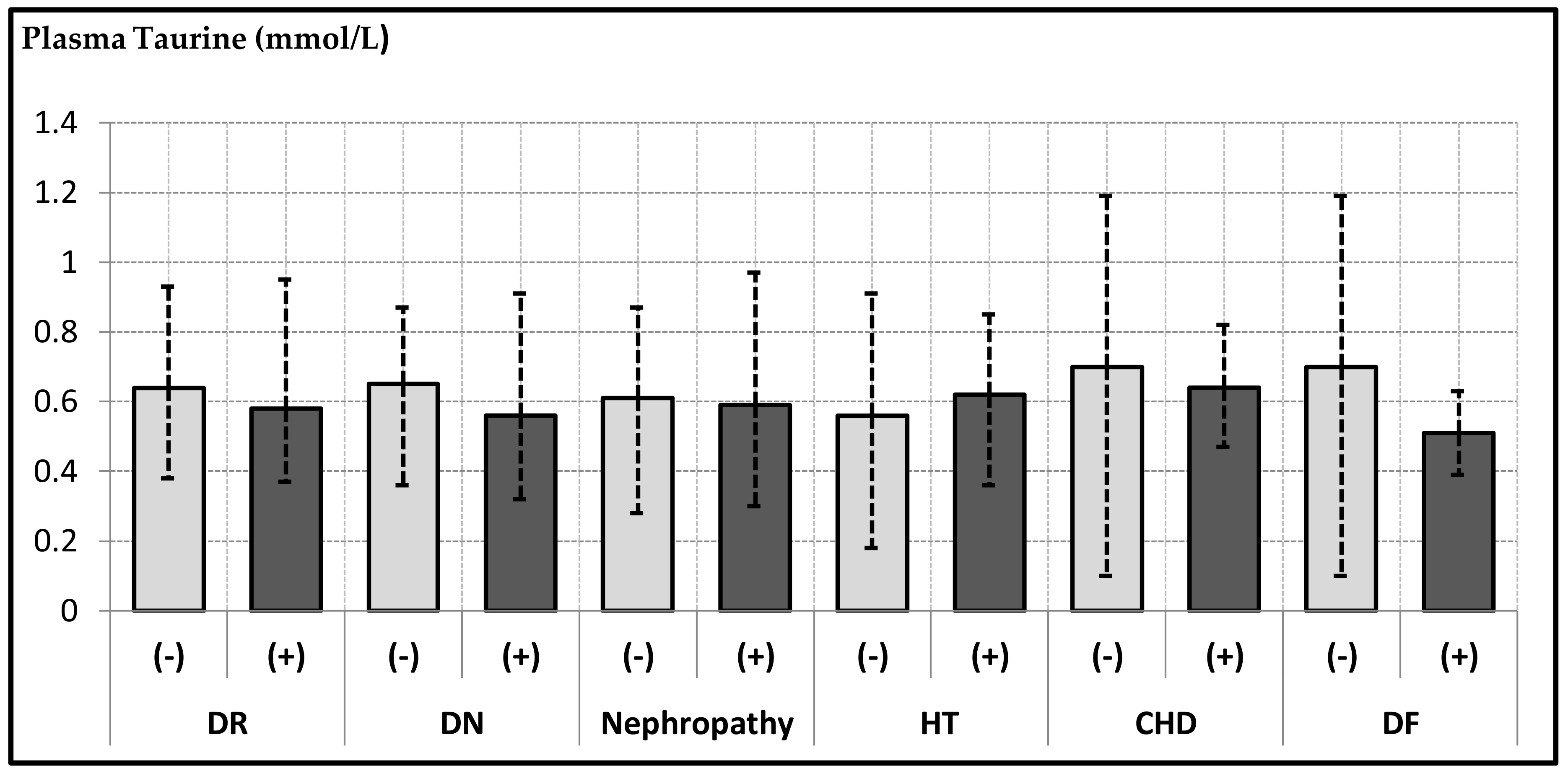
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2016: Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, S13–S22. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global report on diabetes; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- TURDEP-II Study Group. Diabetes epidemic in Turkey: results of the second population-based survey of diabetes and risk characteristics in Turkey (TURDEP-II). Diabetologia 2011, 54, 140. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, A.C. Diabetes mellitus. In Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine, Kasper, D.L.; Fauci, A.S., Hauser, S., Longo, D., Jameson, J.L., Loscalzo, J., Eds.; McGraw Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sirdah, M.M. Protective and therapeutic effectiveness of taurine in diabetes mellitus: A rationale for antioxidant supplementation. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2015, 9, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, J.; Roy, A.; Sil, P.C. Mechanism of the protective action of taurine in toxin and drug induced organ pathophysiology and diabetic complications: A review. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 1251–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Ceglarek, U.; Huang, T.; Wang, T.; Heianza, Y.; Ma, W.; Bray, G.A.; Thiery, J.; Sacks, F.M.; Qi, L. Plasma taurine, diabetes genetic predisposition, and changes of insulin sensitivity in response to weight-loss diets. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 3820–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huxtable, R.J. Physiological actions of Taurine. Physiol. Rev. 1992, 72, 101–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Schaffer, S.W.; Azuma, J. The potential usefulness of taurine on diabetes mellitus and its complications. Amino Acids. 2012, 42, 1529–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Silva, J.C.; Ribeiro, R.A.; Vettorazzi, J.F.; Irles, E.; Rickli, S.; Borck, P.C.; Porciuncula, P.M.; Quesada, I.; Nadal, A.; Boschero, A.C.; et al. Taurine supplementation ameliorates glucose homeostasis, prevents insulin and glucagon hypersecretion, and controls β, α, and δ-cell masses in genetic obese mice. Amino Acids. 2015, 47, 1533–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Puerta, C.; Arrieta, F.J.; Balsa, J.A.; Botella-Carretero, J.I.; Zamarrón, I.; Vázquez, C. Taurine and glucose metabolism: A review. Nutr. Hosp. 2010, 25, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murakami, S. Role of taurine in the pathogenesis of obesity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chobanian, A.V.; Bakris, G.L.; Black, H.R.; Cushman, W.C.; Green, L.A.; Izzo, J.L.; Jones, D.W. Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, detection, evaluation and treatment of high blood pressure. Hypertension 2003, 42, 1206–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merheb, M.; Daher, R.T.; Nasrallah, M.; Sabra, R.; Ziyadeh, F.N.; Barada, K. Taurine intestinal absorption and renal excretion test in diabetic patients: a pilot study. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 2652–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copeland, A.D.; Hendrich, C.E.; Porterfield, S.P. Distribution of free amino acids in streptozotocin-induced diabetic pregnant rats, their placentae and fetuses. Horm. Metab. Res. 1990, 22, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Yoshikawa, N.; Ito, H.; Schaffer, S.W. Impact of taurine depletion on glucose control and insulin secretion in mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 129, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anuradha, C.V.; Balakrishnan, S.D. Taurine attenuates hypertension and improves insulin sensitivity in the fructose-fed rat, an animal model of insulin resistance. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1999, 77, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, R.A.; Santos-Silva, J.C.; Vettorazzi, J.F.; Cotrim, B.B.; Mobiolli, D.D.; Boschero, A.C.; Carneiro, E.M. Taurine supplementation prevents morpho-physiological alterations in high-fat diet mice pancreatic beta-cells. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 1791–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vettorazzi, J.F.; Ribeiro, R.A.; Borck, P.C.; Branco, R.C.; Soriano, S.; Merino, B.; Boschero, A.C.; Nadal, A.; Quesada, I.; Carneiro, E.M. The bile acid TUDCA increases glucose-induced insulin secretion via the cAMP/PKA pathway in pancreatic beta cells. Metabolism 2016, 65, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Patters, A.B.; Ito, T.; Azuma, J.; Schaffer, S.W.; Chesney, R.W. Knockout of the TauT gene predisposes C57BL/6 mice to streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0117718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Ito, T.; Azuma, J.; Azuma, J.; Schaffer, S.W.; Chesney, R.W. The quest for an animal model of diabetic nephropathy and the role of taurine deficiency. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 803, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trachtman, H.; Futterweit, S.; Maesaka, J.; Ma, C.; Valderrama, E.; Fuchs, A.; Tarectecan, A.A.; Rao, P.S.; Sturman, J.A.; Boles, T.H.; et al. Taurine ameliorates chronic streptozocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 269, F429–F438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.N.; Parikh, M.; Lau-Cam, C.A. Impact of light ethanol intake and of taurine, separately and together, on pathways of glucose metabolism in the kidney of diabetic rats. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 803, 279–303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pandya, K.G.; Budhram, R.; Clark, G.J.; Lau-Cam, C.A. Taurine can enhance the protective actions of metformin against diabetes-induced alterations adversely affecting renal function. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 803, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koh, J.H.; Lee, E.S.; Hyun, M.; Kim, H.M.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, E.Y.; Yadav, D.; Chung, C.H. Taurine alleviates the progression of diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetic rat model. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 2014, 397307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripps, H.; Shen, W. Review: taurine: A "very essential" amino acid. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 2673–2686. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeng, K.; Ming, J.; Yang, N.; Wang, J.; Yu, X.; Song, Y.; Yang, Y. Taurine prevents high glucose-induced angiopoietin-2/tie-2 system alterations and apoptosis in retinal microvascular pericytes. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 396, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilchis, C.; Salceda, R. effect of diabetes on levels and uptake of putative amino acid neurotransmitters in rat retina and retinal pigment epithelium. Neurochem. Res. 1996, 21, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Mi, M.; Xu, H.; Chen, F.; Zeng, K. Taurine protects transformed rat retinal ganglion cells from hypoxia-induced apoptosis by preventing mitochondrial dysfunction. Brain Res. 2009, 1279, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froger, N.; Jammoul, F.; Gaucher, D.; Cadetti, L.; Lorach, H.; Degardin, J.; Pain, D.; Dubus, E.; Forster, V.; Ivkovic, I.; et al. Taurine is a crucial factor to preserve retinal ganglion cell survival. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 775, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farmer, K.L.; Li, C.; Dobrowsky, R.T. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Should a chaperone accompany our therapeutic approach? Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 880–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, M.J.; Lattimer, S.A.; Kamijo, M.; Van Huysen, C.; Sima, A.A.; Greene, D.A. Osmotically-induced nerve taurine depletion and the compatible osmolyte hypothesis in experimental diabetic neuropathy in the rat. Diabetologia 1993, 36, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askwith, T.; Zeng, W.; Eggo, M.C.; Stevens, M.J. Taurine reduces nitrosative stress and nitric oxide synthase expression in high glucose-exposed human Schwann cells. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 233, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, R. The nervous system and diabetes. In Joslin’s Diabetes Mellitus, 14th ed.; Khan, C.R., King, G.L., Moses, A.C., Weir, G.C., Jacobson, A.M., Smith, R.J., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 2968–3009. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. The beneficial effects of taurine in preventing metabolic syndrome. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1849–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nara, Y.; Yamori, Y.; Lovenberg, W. Effect of dietary taurine on blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1978, 27, 2689–2692. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fujita, T.; Ando, K.; Noda, H.; Ito, Y.; Sato, Y. Effects of increased adrenomedullary activity and taurine in young patients with borderline hypertension. Circulation 1987, 75, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, C.S. Effect of taurine supplementation on plasma homocysteine levels of the middle-aged Korean women. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2009, 643, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tappia, P.S.; Thliveris, J.; Xu, Y.J.; Tappia, P.S.; Thliveris, J.; Xu, Y.J. Effects of amino acid supplementation on myocardial cell damage and cardiac function in diabetes. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2011, 16, e17–e22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Diabetic Group | Control Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||||||
| Male | 28 | 12 | |||||
| Female | 31 | 16 | |||||
| Min | Max | Mean ± SD | Min | Max | Mean ± SD | p | |
| Age (years) | 37 | 82 | 58.6 ± 9.2 | 32 | 77 | 48.3 ± 8.9 | 0.001 |
| Height (cm) | 133 | 185 | 161.8 ± 9.9 | 138 | 180 | 164 ± 10.6 | 0.346 |
| Weight (kg) | 52 | 115 | 79.3 ± 13.8 | 60 | 117 | 81.5 ± 15.2 | 0.508 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.2 | 44.9 | 30.4 ± 5.6 | 22.1 | 41 | 29.8 ± 4.7 | 0.596 |
| WC (cm) | 70 | 130 | 96.1 ± 12 | 70 | 119 | 92.8 ± 13.1 | 0.245 |
| HC (cm) | 80 | 125 | 101.7 ± 9.8 | 90 | 130 | 102.1 ± 10.8 | 0.853 |
| SBP (mm × Hg) | 100 | 180 | 127 ± 15.3 | 100 | 160 | 125 ± 10 | 0.001 |
| DBP (mm × Hg) | 60 | 100 | 75.8 ± 8.1 | 60 | 90 | 74.6 ± 7.1 | 0.007 |
| FBG (mmol/L) | 4.38 | 24.64 | 10.16 ± 4.68 | 4.16 | 6.44 | 5.20 ± 0.63 | 0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 4.6 | 14.6 | 8.4 ± 2.1 | 5 | 6.5 | 5.7 ± 0.3 | 0.001 |
| Microalbuminuria (mg/dL) | 0.6 | 2367 | 209 ± 444.1 | 2 | 147 | 14.3 ± 28.4 | 0.023 |
| GFR (mL/min) | 8.56 | 118.89 | 86.05 ± 25.71 | 90.99 | 120.14 | 104.69 ± 8.05 | 0.001 |
| Taurine (mmol/L) | 0.2 | 0.9 | 0.60 ± 0.15 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 0.87 ± 0.22 | 0.001 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sak, D.; Erdenen, F.; Müderrisoglu, C.; Altunoglu, E.; Sozer, V.; Gungel, H.; Guler, P.A.; Sak, T.; Uzun, H. The Relationship between Plasma Taurine Levels and Diabetic Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9030096
Sak D, Erdenen F, Müderrisoglu C, Altunoglu E, Sozer V, Gungel H, Guler PA, Sak T, Uzun H. The Relationship between Plasma Taurine Levels and Diabetic Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(3):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9030096
Chicago/Turabian StyleSak, Duygu, Fusun Erdenen, Cuneyt Müderrisoglu, Esma Altunoglu, Volkan Sozer, Hulya Gungel, Pınar Akca Guler, Tuncer Sak, and Hafize Uzun. 2019. "The Relationship between Plasma Taurine Levels and Diabetic Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" Biomolecules 9, no. 3: 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9030096
APA StyleSak, D., Erdenen, F., Müderrisoglu, C., Altunoglu, E., Sozer, V., Gungel, H., Guler, P. A., Sak, T., & Uzun, H. (2019). The Relationship between Plasma Taurine Levels and Diabetic Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomolecules, 9(3), 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9030096





