Generation of Lamprey Monoclonal Antibodies (Lampribodies) Using the Phage Display System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
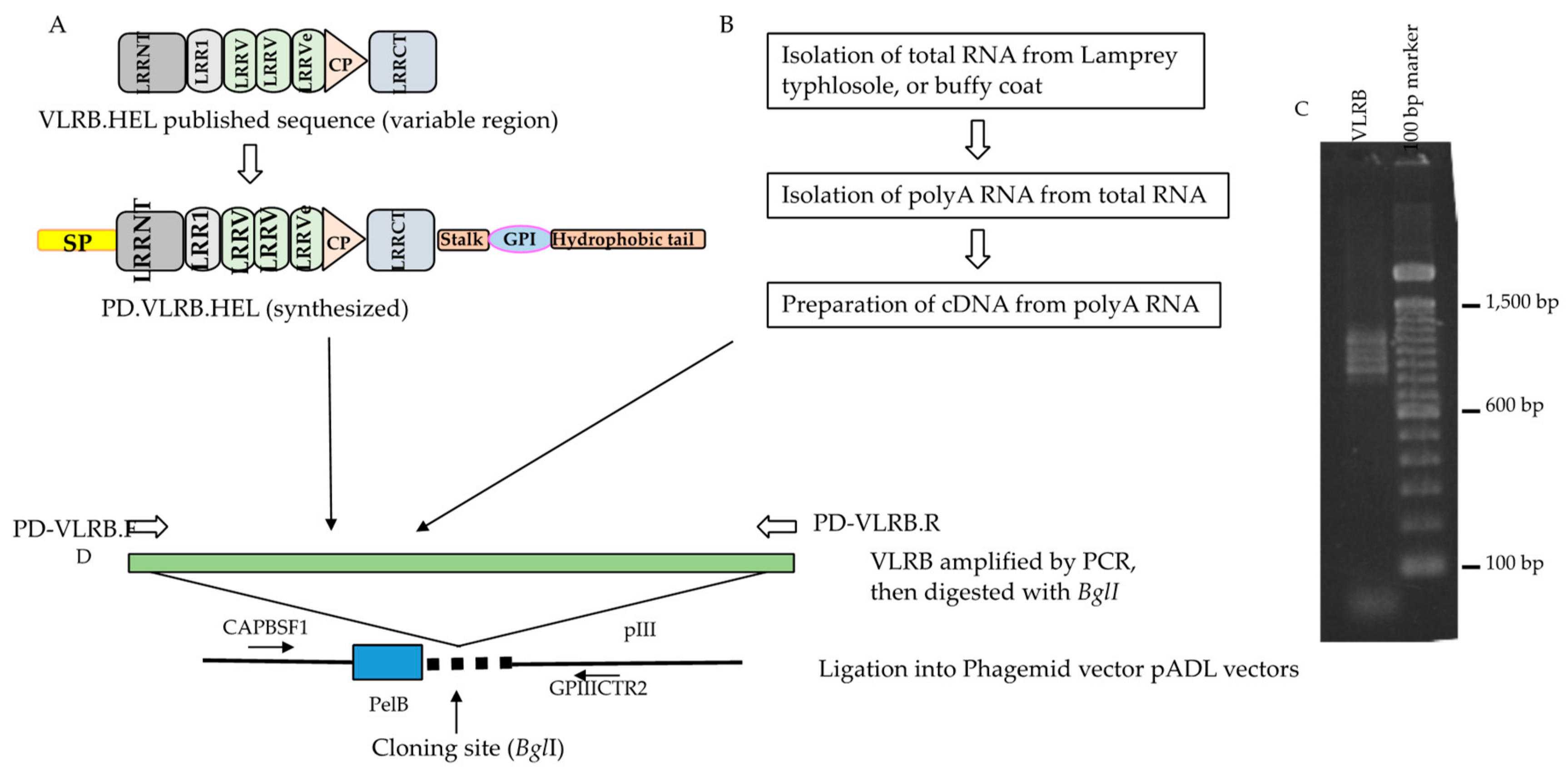
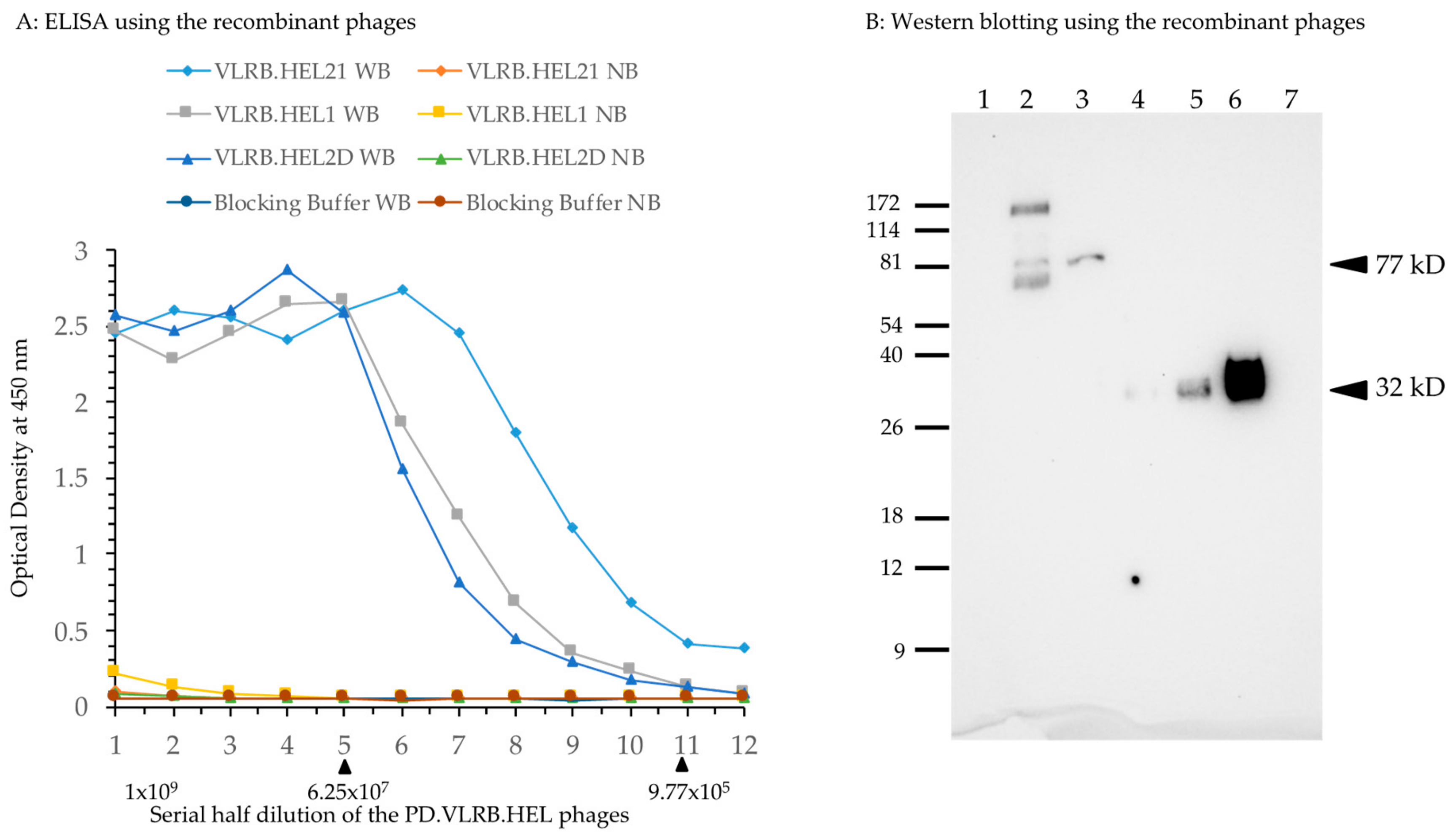
2.1. Testing the Driver VLRB Molecules in M13 Phage Display System
2.2. Construction and Characterization of a Competitor Phage Display Library
2.3. Subtraction Experiment for Recovery of the Driver Phage by Panning
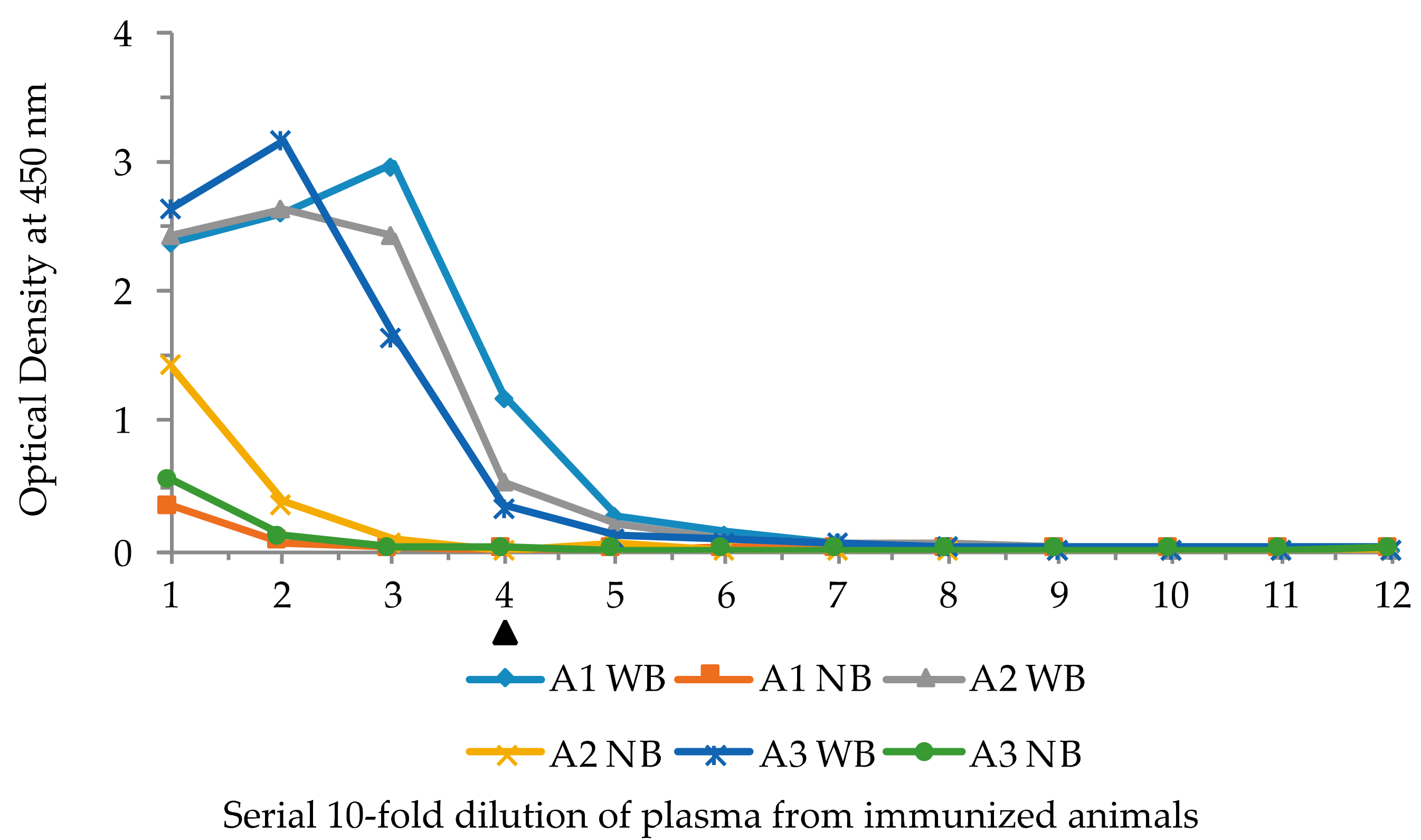
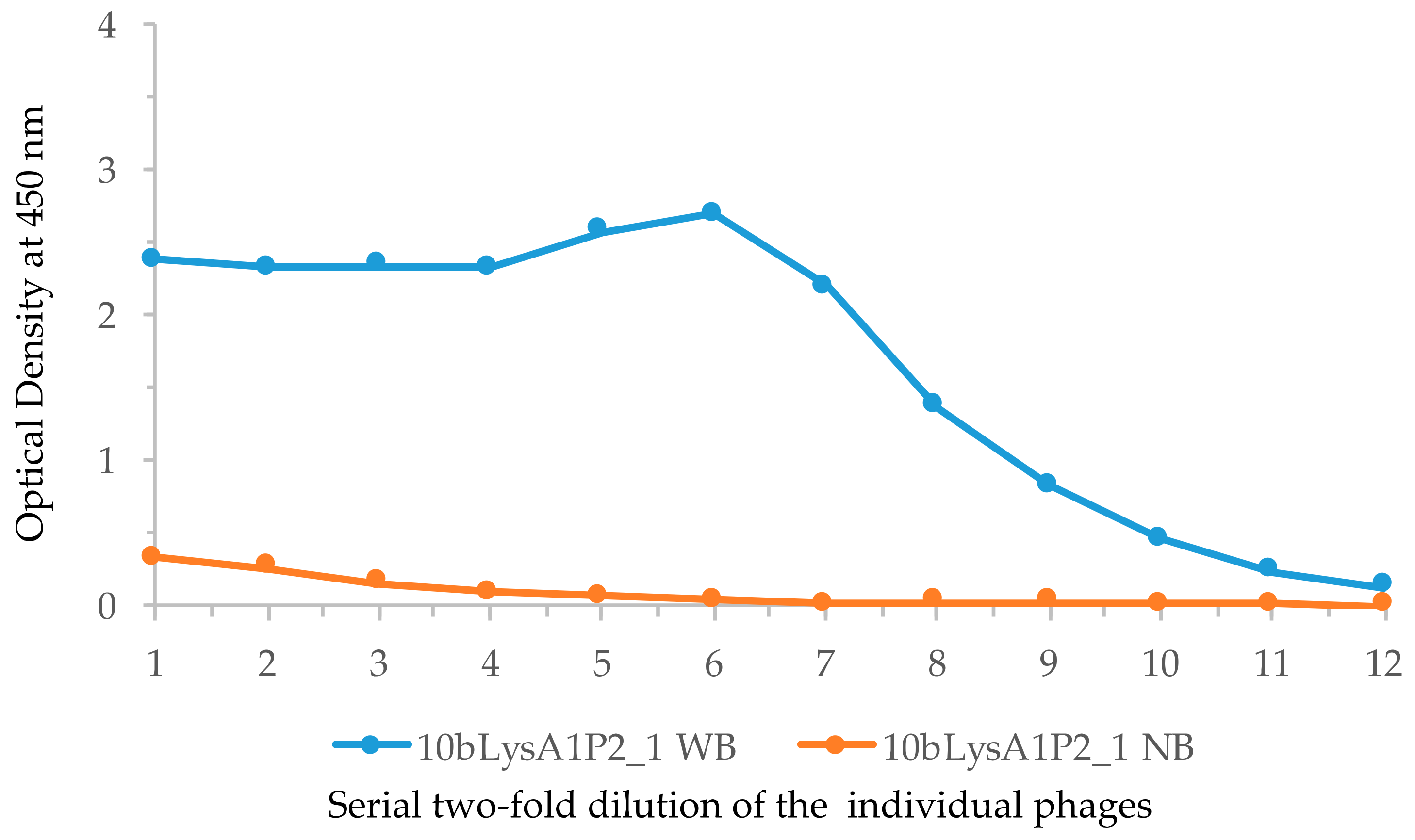
2.4. Immunization of Lamprey Larvae with Lysozyme and Isolation of Anti-Lysozyme VLRB Clones
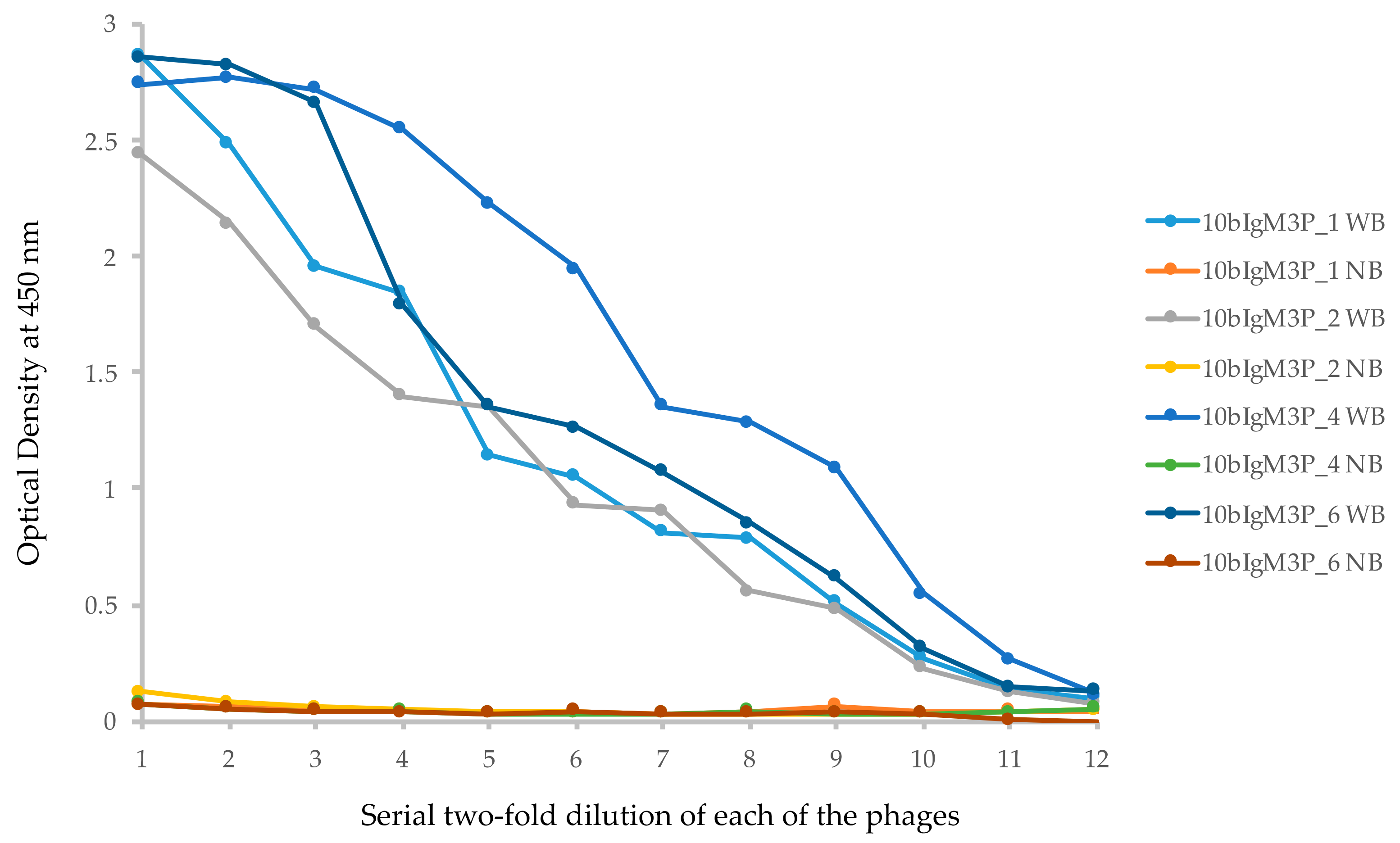
2.5. Isolation of VLRB Against Human IgM Protein
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Immunizations
4.3. Naive VLRB Phage Display Library Construction
4.4. Subcloning of Anti-Hen Egg Lysozyme (HEL) VLRB Molecules for Phage Display
4.5. Phage Preparation from the VLRB Phage Display Libraries and the VLRB HEL Phage Display Clones
4.6. Titering the VLRB Phage Display Libraries and Individual VLRB.HEL Phage
4.7. Biotinylation of the Bait and ELISA Screening
4.8. Panning, Rescue, and Superinfection
4.9. ELISA Test of the Candidate Phage Clones
4.10. PCR, Enzyme Digestion and Sequence Analysis of the Phagemid Clones
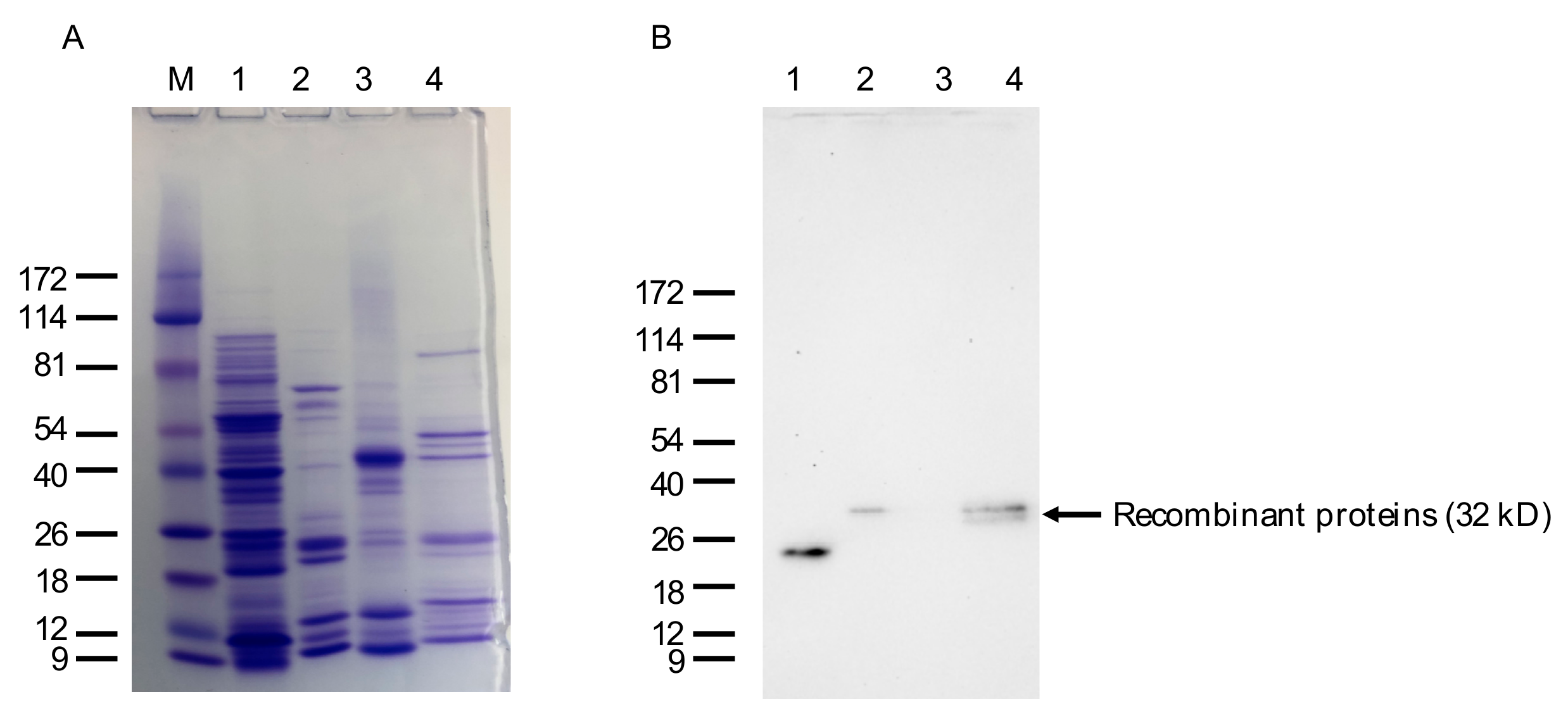
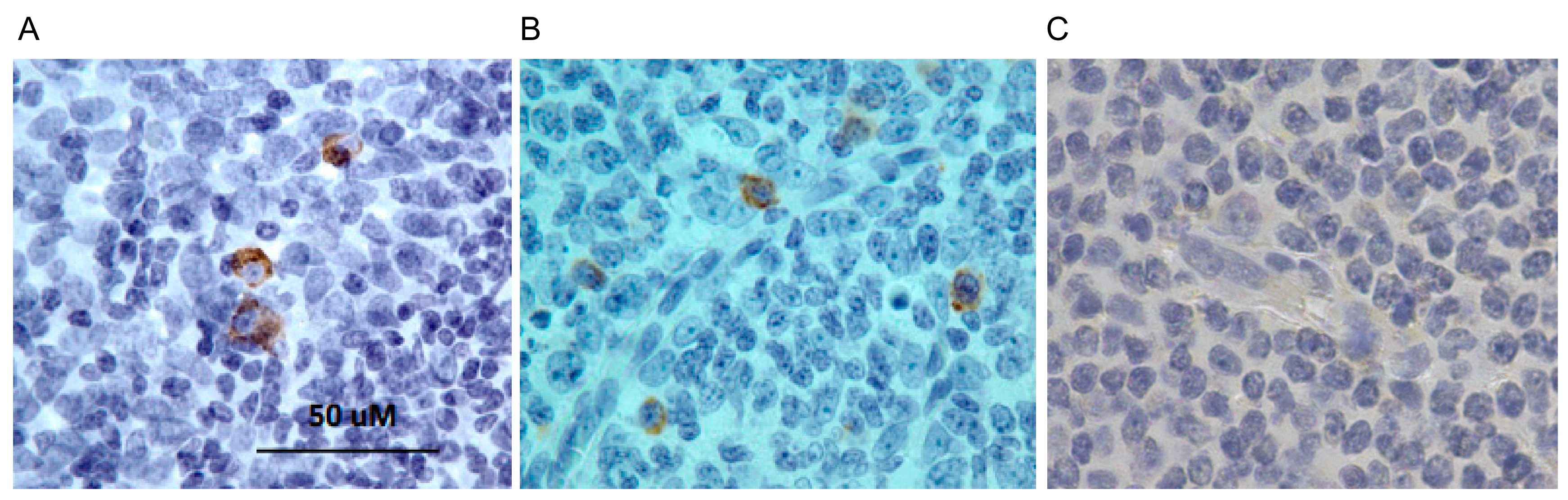
4.11. Isolation of Bacterially Expressed VLRB Recombinant Proteins, Western Blotting, and Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Janvier, P. Facts and fancies about early fossil chordates and vertebrates. Nature 2015, 520, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancer, Z.; Amemiya, C.T.; Ehrhardt, G.R.; Ceitlin, J.; Gartland, G.L.; Cooper, M.D. Somatic diversification of variable lymphocyte receptors in the agnathan sea lamprey. Nature 2004, 430, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancer, Z.; Saha, N.R.; Kasamatsu, J.; Suzuki, T.; Amemiya, C.T.; Kasahara, M.; Cooper, M.D. Variable lymphocyte receptors in hagfish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9224–9229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagawa, F.; Kishishita, N.; Shimizu, K.; Hirose, S.; Miyoshi, M.; Nezu, J.; Nishimura, T.; Nishizumi, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; et al. Antigen-receptor genes of the agnathan lamprey are assembled by a process involving copy choice. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alençon, E.; Petranovic, M.; Michel, B.; Noirot, P.; Aucouturier, A.; Uzest, M.; Ehrlich, S.D. Copy-choice illegitimate DNA recombination revisited. EMBO J. 1994, 102, 9224–9229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, M.N.; Rogozin, I.B.; Iyer, L.M.; Glazko, G.V.; Cooper, M.D.; Pancer, Z. Diversity and function of adaptive immune receptors in a jawless vertebrate. Science 2005, 310, 1970–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrin, B.R.; Alder, M.N.; Roux, K.H.; Sina, C.; Ehrhardt, G.R.; Boydston, J.A.; Turnbough, C.L.; Cooper, M.D. Structure and specificity of lamprey monoclonal antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2040–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, M.N.; Herrin, B.R.; Sadlonova, A.; Stockard, C.R.; Grizzle, W.E.; Gartland, L.A.; Gartland, G.L.; Boydston, J.A.; Turnbough, C.L., Jr.; Cooper, M.D. Antibody responses of variable lymphocyte receptors in the lamprey. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasumi, S.; Velikovsky, C.A.; Xu, G.; Gai, S.A.; Wittrup, K.D.; Flajnik, M.F.; Mariuzza, R.A.; Pancer, Z. High-affinity lamprey VLRA and VLRB monoclonal antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12891–12896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.P.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, S.W.; Yu, J.E.; Kim, Y.R.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, T.S. Investigation of variable lymphocyte receptors in the alternative adaptive immune response of hagfish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 55, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Liu, Y.; Chan, J.T.; Tong, J.; Li, Z.; Shi, M.; Davani, D.; Parsons, M.; Khan, S.; Zhan, W.; et al. Identification of human plasma cells with a lamprey monoclonal antibody. JCI Insight 2016, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasquez, A.C.; Nomura, K.; Cooper, M.D.; Herrin, B.R.; He, S.Y. Leucine-rich-repeat-containing variable lymphocyte receptors as modules to target plant-expressed proteins. Plant Methods. 2017, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umlauf, B.A.-O.; Clark, P.A.-O.; Lajoie, J.M.; Georgieva, J.V.; Bremner, S.A.-O.; Herrin, B.A.-O.; Kuo, J.A.-O.; Shusta, E.A.-O. Identification of variable lymphocyte receptors that can target therapeutics to pathologically exposed brain extracellular matrix. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.; Ma, M.Z.; Gildersleeve, J.C.; Chowdhury, S.; Barchi, J.J., Jr.; Mariuzza, R.A.; Murphy, M.B.; Mao, L.; Pancer, Z. Sugar-binding proteins from fish: Selection of high affinity “lambodies” that recognize biomedically relevant glycans. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, H.; Herrin, B.R.; Alder, M.N.; Catera, R.; Yan, X.J.; Chiorazzi, N.; Cooper, M.D. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia monitoring with a Lamprey idiotope-specific antibody. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2013, 1, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.J.; Kim, H.J.; Yang, C.S.; Kyeong, H.H.; Choi, J.M.; Hwang, D.E.; Yuk, J.M.; Park, K.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.G.; et al. A high-affinity protein binder that blocks the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway effectively suppresses non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Ther. 2014, 77, 1254–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.; Choi, H.J.; Yun, M.; Kang, Y.; Jung, J.E.; Ryu, Y.; Kim, T.Y.; Cha, Y.J.; Cho, H.S.; Min, J.J.; et al. Enzymatic prenylation and oxime ligation for the synthesis of stable and homogeneous protein-drug conjugates for targeted therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 12020–12024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, N.; Heo, W.D.; Kim, H.S. Tracking protein-protein interaction and localization in living cells using a high-affinity molecular binder. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 470, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.E.; Ryou, J.H.; Oh, J.R.; Han, J.W.; Park, T.K.; Kim, H.S. Anti-Human VEGF Repebody Effectively Suppresses Choroidal Neovascularization and Vascular Leakage. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.E.; Choi, J.M.; Yang, C.S.; Lee, J.J.; Heu, W.; Jo, E.K.; Kim, H.S. Effective suppression of C5a-induced proinflammatory response using anti-human C5a repebody. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 477, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moot, R.; Raikar, S.S.; Fleischer, L.; Querrey, M.; Tylawsky, D.E.; Nakahara, H.; Doering, C.B.; Spencer, H.T. Genetic engineering of chimeric antigen receptors using lamprey derived variable lymphocyte receptors. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics. 2016, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.W.; Herrin Br Fau-Cooper, M.D.; Cooper Md Fau-Wilson, I.A.; Wilson, I.A. Antigen recognition by variable lymphocyte receptors. Science 2008, 321, 1834–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.P. Filamentous fusion phage: Novel expression vectors that display cloned antigens on the virion surface. Science 1985, 228, 1315–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-C.; Park, K.; Han, J.; Lee, J.-J.; Kim, H.J.; Hong, S.; Heu, W.; Kim, Y.J.; Ha, J.-S.; Lee, S.-G. Design of a binding scaffold based on variable lymphocyte receptors of jawless vertebrates by module engineering. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3299–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondot, S.; Koch J Fau-Breitling, F.; Breitling F Fau-Dubel, S.; Dubel, S. A helper phage to improve single-chain antibody presentation in phage display. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.J.; Kuraku, S.; Holt, C.; Sauka-Spengler, T.; Jiang, N.; Campbell, M.S.; Yandell, M.D.; Manousaki, T.; Meyer, A.; Bloom, O.E.; et al. Sequencing of the sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus) genome provides insights into vertebrate evolution. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassan, K.M.A.; Hansen, J.D.; Herrin, B.R.; Amemiya, C.T. Generation of Lamprey Monoclonal Antibodies (Lampribodies) Using the Phage Display System. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9120868
Hassan KMA, Hansen JD, Herrin BR, Amemiya CT. Generation of Lamprey Monoclonal Antibodies (Lampribodies) Using the Phage Display System. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(12):868. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9120868
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassan, Khan M. A., John D. Hansen, Brantley R. Herrin, and Chris T. Amemiya. 2019. "Generation of Lamprey Monoclonal Antibodies (Lampribodies) Using the Phage Display System" Biomolecules 9, no. 12: 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9120868
APA StyleHassan, K. M. A., Hansen, J. D., Herrin, B. R., & Amemiya, C. T. (2019). Generation of Lamprey Monoclonal Antibodies (Lampribodies) Using the Phage Display System. Biomolecules, 9(12), 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9120868





