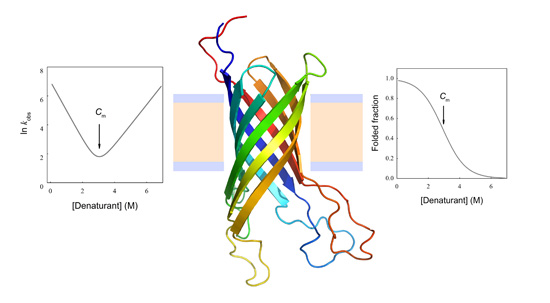
Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Membrane Protein Folding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Basic Strategies for Studying Protein Folding and Stability
 N→U), which is the accepted form to quantify the structural thermodynamic stability of a protein [27,28,29].
N→U), which is the accepted form to quantify the structural thermodynamic stability of a protein [27,28,29].
 N→U, which becomes negative for temperatures higher than the so-called thermal denaturation midpoint (Tm) or lower than the cold denaturation temperature (Tc). Convexity in Figure 1A is given by the heat capacity change upon unfolding (
N→U, which becomes negative for temperatures higher than the so-called thermal denaturation midpoint (Tm) or lower than the cold denaturation temperature (Tc). Convexity in Figure 1A is given by the heat capacity change upon unfolding (  ), which reports the difference between solvent interactions in the folded and unfolded states, and it has been found to correlate with the change in the solvent-accessible surface area (ΔASA) as a protein unfolds [30].
), which reports the difference between solvent interactions in the folded and unfolded states, and it has been found to correlate with the change in the solvent-accessible surface area (ΔASA) as a protein unfolds [30]. N→U on the denaturant concentration was empirically explored for many small globular proteins (Figure 1B), typically finding a linear relationship [31]:
N→U on the denaturant concentration was empirically explored for many small globular proteins (Figure 1B), typically finding a linear relationship [31]:

 N→U reaching a maximum value which corresponds to the maximal protein stability. Heating or cooling the sample will lead to a decrease in
N→U reaching a maximum value which corresponds to the maximal protein stability. Heating or cooling the sample will lead to a decrease in  N→U which will equal zero at the temperature of cold unfolding (Tc) and at the melting temperature (Tm). At both temperatures half the protein population is folded and the other half is unfolded; (B) Protein stability decrease following a linear function of the concentration of the chaotropic agent.
N→U which will equal zero at the temperature of cold unfolding (Tc) and at the melting temperature (Tm). At both temperatures half the protein population is folded and the other half is unfolded; (B) Protein stability decrease following a linear function of the concentration of the chaotropic agent.  N→U reaches the zero value at the mid-denaturant concentration (Cm) where 50% of the population is folded and the other 50% is unfolded.
N→U reaches the zero value at the mid-denaturant concentration (Cm) where 50% of the population is folded and the other 50% is unfolded.
 N→U reaching a maximum value which corresponds to the maximal protein stability. Heating or cooling the sample will lead to a decrease in
N→U reaching a maximum value which corresponds to the maximal protein stability. Heating or cooling the sample will lead to a decrease in  N→U which will equal zero at the temperature of cold unfolding (Tc) and at the melting temperature (Tm). At both temperatures half the protein population is folded and the other half is unfolded; (B) Protein stability decrease following a linear function of the concentration of the chaotropic agent.
N→U which will equal zero at the temperature of cold unfolding (Tc) and at the melting temperature (Tm). At both temperatures half the protein population is folded and the other half is unfolded; (B) Protein stability decrease following a linear function of the concentration of the chaotropic agent.  N→U reaches the zero value at the mid-denaturant concentration (Cm) where 50% of the population is folded and the other 50% is unfolded.
N→U reaches the zero value at the mid-denaturant concentration (Cm) where 50% of the population is folded and the other 50% is unfolded.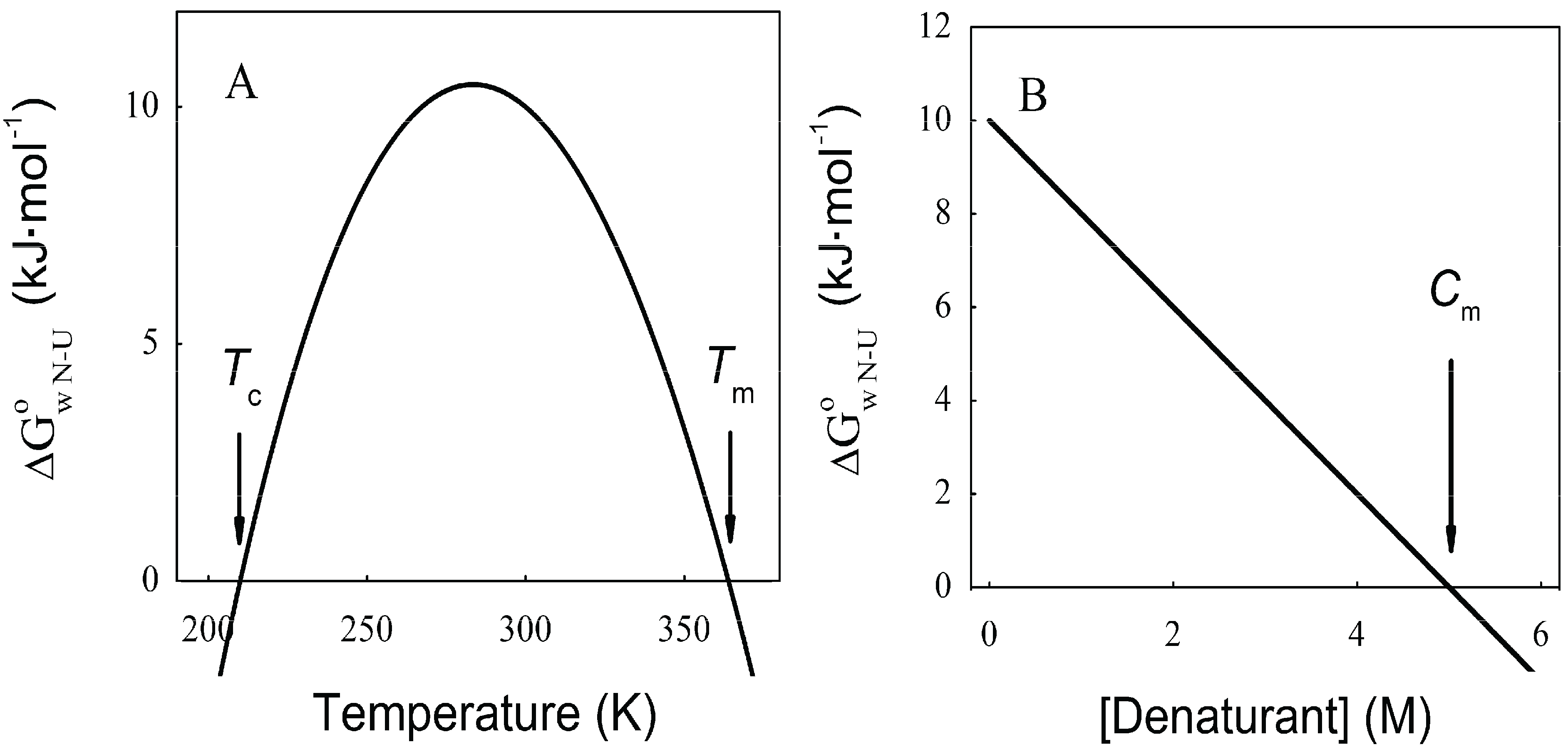
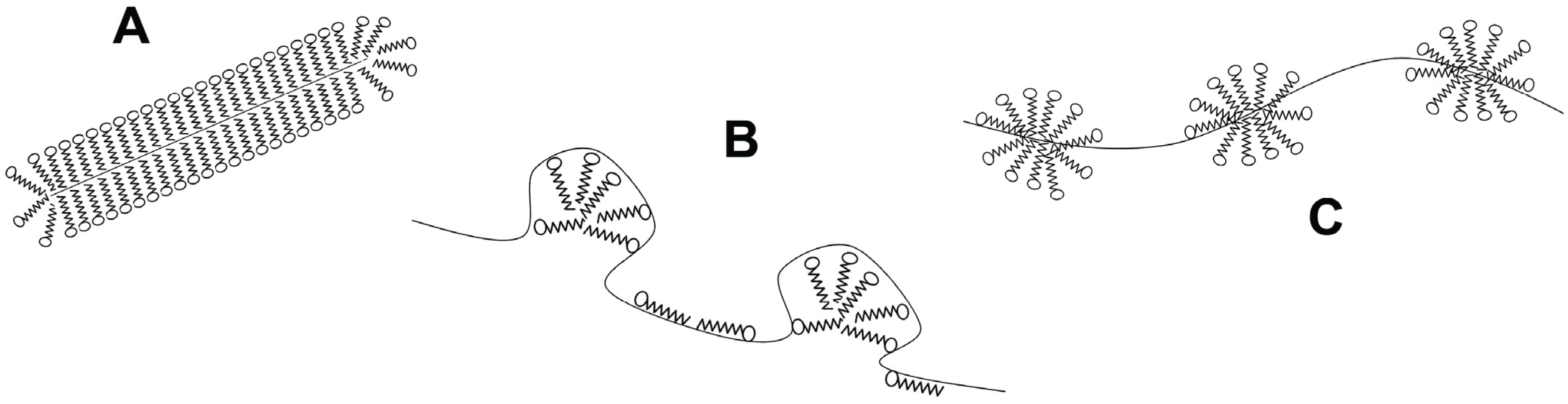
3. Temperature Induced Membrane Protein Denaturation
4. Solvent Denaturation of Membrane Proteins
4.1. The Two-State Model, a Paradigm for Small Globular Protein Folding




 N→U). When represented as a function of a combined size-stability variable, they fall within a narrow “golden triangle”, which also predicts a maximal allowed size for a protein domain that folds under thermodynamic control of about 500 residues [63,64].
N→U). When represented as a function of a combined size-stability variable, they fall within a narrow “golden triangle”, which also predicts a maximal allowed size for a protein domain that folds under thermodynamic control of about 500 residues [63,64].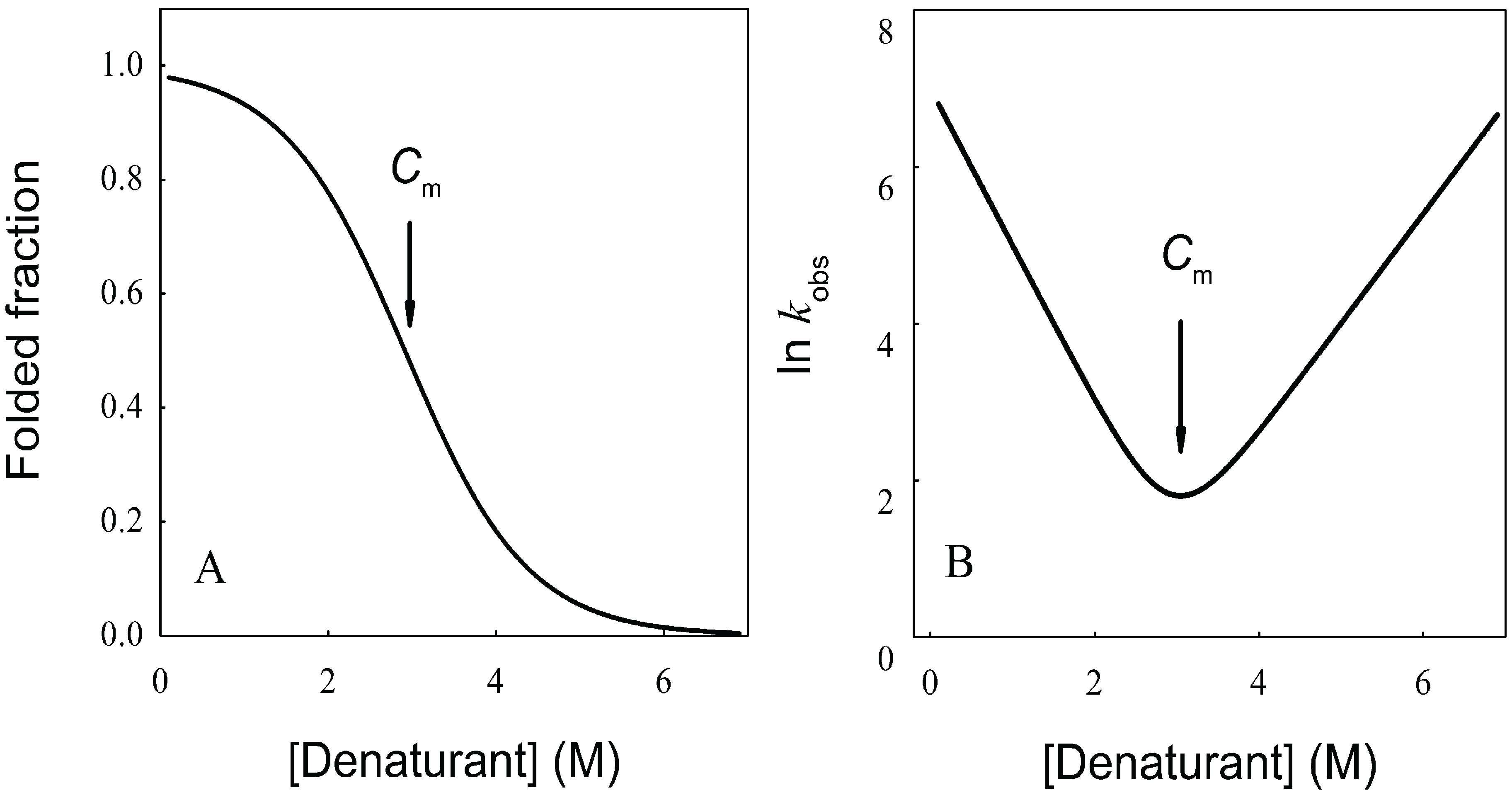

 N→U = 17 kJ·mol−1 and mnu = 6.7 kJ·mol−1·M−1. In addition, folding and unfolding kinetics can be well described by single exponential functions, indicating the lack of intermediates in the folding reaction. The dependence of ln kobs on [GndHCl] has the typical V-shape corresponding to a two-state process with kfº = 56.7 s−1, kuº = 0.1 s−1, mf = 4.2 kJ·mol−1·M−1 and mu = 1.9 kJ·mol−1·M−1. From these data it is possible to calculate an equilibrium
N→U = 17 kJ·mol−1 and mnu = 6.7 kJ·mol−1·M−1. In addition, folding and unfolding kinetics can be well described by single exponential functions, indicating the lack of intermediates in the folding reaction. The dependence of ln kobs on [GndHCl] has the typical V-shape corresponding to a two-state process with kfº = 56.7 s−1, kuº = 0.1 s−1, mf = 4.2 kJ·mol−1·M−1 and mu = 1.9 kJ·mol−1·M−1. From these data it is possible to calculate an equilibrium  N→U using Equation (6), obtaining a value of 16 kJ·mol−1, very close to the thermodynamically determined value. All these data allow the inclusion of the src SH3 domain on the list of single-domain proteins that fold without detectable populations of partially folded intermediates. Furthermore, it can be demonstrated that the ratio between mf and mnu gives an idea of the surface change between the transition state and the folded ensemble of conformations. In this case, mf/mnu = 0.6 suggesting that about two thirds of the buried surface area of the folded protein is excluded from the solvent in the transition state [67].
N→U using Equation (6), obtaining a value of 16 kJ·mol−1, very close to the thermodynamically determined value. All these data allow the inclusion of the src SH3 domain on the list of single-domain proteins that fold without detectable populations of partially folded intermediates. Furthermore, it can be demonstrated that the ratio between mf and mnu gives an idea of the surface change between the transition state and the folded ensemble of conformations. In this case, mf/mnu = 0.6 suggesting that about two thirds of the buried surface area of the folded protein is excluded from the solvent in the transition state [67].4.2. Membrane Protein Folding in Solution
4.2.1. Beta Barrel Bacterial Outer Membrane Proteins

4.2.2. Helical Membrane Proteins

 N→U of about 24 kJ·mol−1. However, the unfolding kinetics showed that the folding mechanism is indeed more complex including several intermediates, and that the pathways for unfolding and refolding are different [100]. The relation between the folding and unfolding rate constants and SDS concentration suggest a linear free energy relationship similar to that described for small globular proteins. Besides, the structure of the unfolding transition state was characterized using a set of single mutants, being closer to the SDS-unfolded state than to the native one. This behavior is clearly different from that described for most small globular proteins where the structure of the transition state is closer to that of the native state [101]. On the other hand kinetic studies suggested that the folding route is polarized: while SDS disrupts the helical packing of the outer helices, some of the internal ones are resistant, so that the protein conserves a large amount of secondary structure in the denatured state [102]. Further attempts to characterize this unfolded state showed that although the secondary structure contains significant amounts of native signatures, the tertiary structure was mainly disrupted [103]. These important differences with the unfolded state of soluble proteins open interesting questions about how to compare unfolding processes when the final unfolded states are very different.
N→U of about 24 kJ·mol−1. However, the unfolding kinetics showed that the folding mechanism is indeed more complex including several intermediates, and that the pathways for unfolding and refolding are different [100]. The relation between the folding and unfolding rate constants and SDS concentration suggest a linear free energy relationship similar to that described for small globular proteins. Besides, the structure of the unfolding transition state was characterized using a set of single mutants, being closer to the SDS-unfolded state than to the native one. This behavior is clearly different from that described for most small globular proteins where the structure of the transition state is closer to that of the native state [101]. On the other hand kinetic studies suggested that the folding route is polarized: while SDS disrupts the helical packing of the outer helices, some of the internal ones are resistant, so that the protein conserves a large amount of secondary structure in the denatured state [102]. Further attempts to characterize this unfolded state showed that although the secondary structure contains significant amounts of native signatures, the tertiary structure was mainly disrupted [103]. These important differences with the unfolded state of soluble proteins open interesting questions about how to compare unfolding processes when the final unfolded states are very different.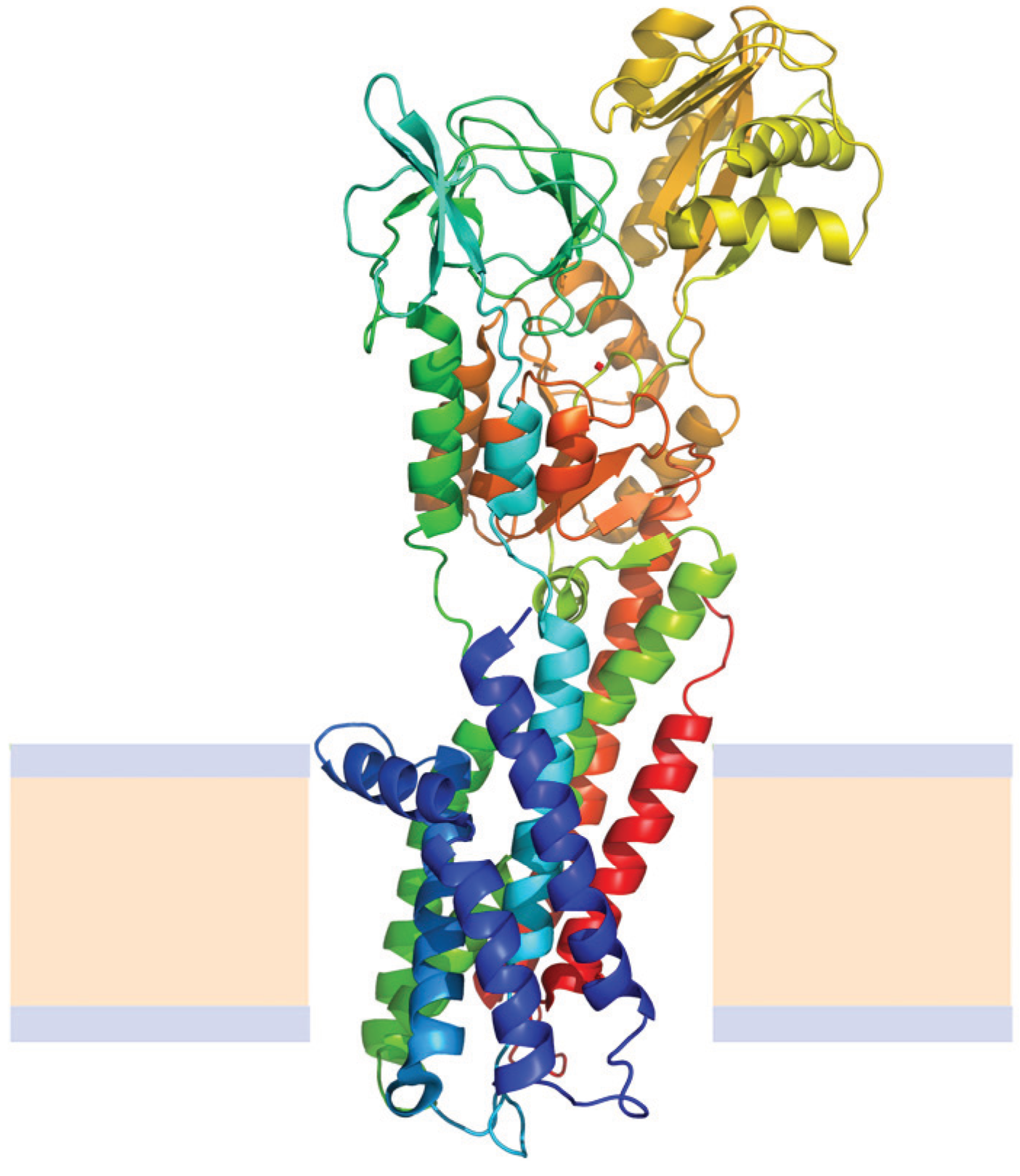
 = 12.9 kJ·mol−1, mnu = 4.1 kJ·mol−1·M−1 and
= 12.9 kJ·mol−1, mnu = 4.1 kJ·mol−1·M−1 and  = 0.93 kJ·mol−1·K−1. These values were relatively lower than those expected for mesophilic proteins of similar molecular mass that unfold according to a two-state model. An approximately linear dependence of
= 0.93 kJ·mol−1·K−1. These values were relatively lower than those expected for mesophilic proteins of similar molecular mass that unfold according to a two-state model. An approximately linear dependence of  on the number of protein residues is well established for the unfolding of small soluble monomeric proteins (smaller than 200 residues) [107]. Booth and Curnow have shown that bacteriorhodopsin, diacylglycerol kinase and the potassium channel KcsA, seem to fit within this trend [107]. On the contrary, CopA
on the number of protein residues is well established for the unfolding of small soluble monomeric proteins (smaller than 200 residues) [107]. Booth and Curnow have shown that bacteriorhodopsin, diacylglycerol kinase and the potassium channel KcsA, seem to fit within this trend [107]. On the contrary, CopA  does not follow this tendency. In this way, it is worth mentioning that there is a small number of large proteins (none of them a membrane protein), for which thermodynamic stability was assessed and only in a few cases they unfold following a two-state process. This set of large soluble proteins also show unusually low values of
does not follow this tendency. In this way, it is worth mentioning that there is a small number of large proteins (none of them a membrane protein), for which thermodynamic stability was assessed and only in a few cases they unfold following a two-state process. This set of large soluble proteins also show unusually low values of  , e.g., human serum albumin for which
, e.g., human serum albumin for which  is a quarter of the value expected according its molecular mass [108].
is a quarter of the value expected according its molecular mass [108]. values [110].
values [110].5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Creighton, T.E. Proteins: Structures and Molecular Properties, 2nd ed.; W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Uversky, V.N.; Gillespie, J.R.; Fink, A.L. Why are “natively unfolded” proteins unstructured under physiologic conditions? Proteins 2000, 41, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N. Natively unfolded proteins: A point where biology waits for physics. Protein Sci. 2002, 11, 739–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N. A decade and a half of protein intrinsic disorder: Biology still waits for physics. Protein Sci. 2013, 22, 693–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Li, L.; Meroueh, S.O.; Uversky, V.N.; Dunker, A.K. Analysis of structured and intrinsically disordered regions of transmembrane proteins. Mol. Biosyst. 2009, 5, 1688–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Brown, C.J.; Dunker, A.K.; Uversky, V.N. Intrinsically disordered regions of p53 family are highly diversified in evolution. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1834, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, E.; von Heijne, G. Genome-wide analysis of integral membrane proteins from eubacterial, archaean, and eukaryotic organisms. Protein Sci. 1998, 7, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almén, M.S.; Nordstrom, K.J.V.; Fredriksson, R.; Schioth, H.B. Mapping the human membrane proteome: A majority of the human membrane proteins can be classified according to function and evolutionary origin. BMC Biol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, M.A.; Goh, K.-I.; Cusick, M.E.; Barabasi, A.-L.; Vidal, M. Drug-target network. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Heijne, G. Membrane proteins: From sequence to structure. Ann. Rev. Biophys. 1994, 23, 167–192. [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava, I.H.; Durell, S.R.; Robert Guy, H. A model of voltage gating developed using the KvAP channel crystal structure. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 2255–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfinsen, C.B.; Haber, E.; Sela, M.; White, F.H., Jr. The kinetics of formation of native ribonuclease during oxidation of the reduced polypeptide chain. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 1961, 47, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalgin, I.V.; Caflisch, A.; Chekmarev, S.F.; Karplus, M. New insights into the folding of a β-sheet miniprotein in a reduced space of collective hydrogen bond variables: Application to a hydrodynamic analysis of the folding flow. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 6092–6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, M.; Liu, H.; Messer, B.; Warshel, A. On the relationship between thermal stability and catalytic power of enzyme. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 15076–15088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teilum, K.; Olsen, J.G.; Kragelund, B.B. Protein stability, flexibility and function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1814, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bill, R.M.; Henderson, P.J.F.; Iwata, S.; Kunji, E.R.S.; Michel, H.; Neutze, R.; Newstead, S.; Poolman, B.; Tate, C.G.; Vogel, H. Overcoming barriers to membrane protein structure determination. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowie, J.U. Stabilizing membrane proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2001, 11, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, A.V.; Galzitskaya, O.V. Physics of protein folding. Phys. Life Rev. 2004, 1, 23–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, N.K.; Dao, T.P.; Stanley, A.M.; Fleming, K.G. β-Barrel proteins that reside in the Escherichia coli outer membrane in vivo demonstrate varied folding behavior in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 26748–26758. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, W.A.; Muñoz, V.; Hagen, S.J.; Jas, G.S.; Lapidus, L.J.; Henry, E.R.; Hofrichter, J. Fast kinetics and mechanisms in protein folding. Ann. Rev. Biophys. 2000, 29, 327–359. [Google Scholar]
- Otzen, D.E.; Andersen, K.K. Folding of outer membrane proteins. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 531, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, K.R. Folding and stability of α-helical integral membrane proteins. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 1931–1977. [Google Scholar]
- Palmgren, M.G.; Nissen, P. P-type ATPases. Ann. Rev. Biophys. 2011, 40, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thogersen, L.; Nissen, P. Flexible P-type ATPases interacting with the membrane. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2012, 22, 491–499. [Google Scholar]
- Traian, M.M.; Cattoni, D.I.; Levi, V.; González-Flecha, F.L. A two-stage model for lipid modulation of the activity of integral membrane proteins. PLoS One 2012, 7, e39255. [Google Scholar]
- Møeller, J.V.; Olesen, C.; Winther, A.-M.L.; Nissen, P. The sarcoplasmic Ca2+-ATPase: Design of a perfect chemi-osmotic pump. Rev. Biophys. 2010, 43, 501–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellman, J.A. The thermodynamic stability of proteins. Ann. Rev. Biophys. 1987, 16, 115–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanford, C. Protein denaturation. Adv. Prot. Chem. 1968, 23, 121–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privalov, P.L. Stability of proteins small globular proteins. Adv. Prot. Chem. 1979, 33, 167–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.K.; Pace, C.N.; Scholtz, J.M. Denaturant m values and heat capacity changes: Relation to changes in accessible surface areas of protein unfolding. Protein Sci. 1995, 4, 2138–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, R.F.; Pace, C.N. Urea and guanidine hydrochloride denaturation of ribonuclease, lysozyme, α-chymotrypsin, and β-lactoglobulin. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 5388–5393. [Google Scholar]
- Courtenay, E.S.; Capp, M.W.; Record, M.T. Thermodynamics of interactions of urea and guanidinium salts with protein surface: Relationship between solute effects on protein processes and changes in water-accessible surface area. Protein Sci. 2001, 10, 2485–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canchi, D.R.; García, A.E. Cosolvent effects on protein stability. Ann. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2013, 63, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinn, E.J.; Pegram, L.M.; Capp, M.W.; Pollock, M.N.; Record, M.T. Quantifying why urea is a protein denaturant, whereas glycine betaine is a protein stabilizer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16932–16937. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, E.P.; Dima, R.I.; Brooks, B.; Thirumalai, D. Interactions between hydrophobic and ionic solutes in aqueous guanidinium chloride and urea solutions: Lessons for protein denaturation mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7346–7353. [Google Scholar]
- Shortle, D.; Ackerman, M.S. Persistence of native-like topology in a denatured protein in 8 M urea. Science 2001, 293, 487–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otzen, D. Protein-surfactant interactions: A tale of many states. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1814, 562–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otzen, D.E.; Sehgal, P.; Westh, P. α-Lactalbumin is unfolded by all classes of surfactants but by different mechanisms. J. Coll. Int. Sci. 2009, 329, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, E.A.; Rosi, P.; González Lebrero, M.C.; Wuilloud, R.; González-Flecha, F.L.; Delfino, J.M.; Santos, J. Gain of local structure in an amphipathic peptide does not require a specific tertiary framework. Proteins 2010, 78, 2757–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.A.; Tanford, C. The gross conformation of protein-sodium dodecyl sulfate complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 1970, 245, 5161–5165. [Google Scholar]
- Ibel, K.; May, R.P.; Kirschner, K.; Szadkowski, H.; Mascher, E.; Lundahl, P. Protein-decorated micelle structure of sodium-dodecyl-sulfate-protein complexes as determined by neutron scattering. Eur. J. Biochem. 1990, 190, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turro, N.J.; Lei, X.-G.; Ananthapadmanabhan, K.P.; Aronson, M. Spectroscopic probe analysis of protein-surfactant interactions: The BSA/SDS system. Langmuir 1995, 11, 2525–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, K.K.; Oliveira, C.L.; Larsen, K.L.; Poulsen, F.M.; Callisen, T.H.; Westh, P.; Pedersen, J.S.; Otzen, D. The role of decorated SDS micelles in sub-CMC protein denaturation and association. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 391, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.H.; Zhao, N.M.; Chen, S.H.; Teixeira, J. Small-angle neutron scattering study of the structure of protein/detergent complexes. Biopolymers 1990, 29, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelamo, E.L.; Itri, R.; Alonso, A.; da Silva, J.V.; Tabak, M. Small-angle X-ray scattering and electron paramagnetic resonance study of the interaction of bovine serum albumin with ionic surfactants. J. Coll. Int. Sci. 2004, 277, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popot, J.L.; Engelman, D.M. Helical membrane protein folding, stability, and evolution. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 881–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, A.M.; Fleming, K.G. The process of folding proteins into membranes: Challenges and progress. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2008, 469, 46–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nury, S.; Meunier, J.C. Molecular mechanisms of the irreversible thermal denaturation of guinea-pig liver transglutaminase. Biochem. J. 1990, 266, 487–490. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.B.; Wang, Q.; He, H.W.; Zhou, H.M. Protein thermal aggregation involves distinct regions: Sequential Events in the heat-induced unfolding and aggregation of hemoglobin. Biophys. J. 2004, 86, 1682–1690. [Google Scholar]
- Ahern, T.J.; Klibanov, A.M. The mechanism of irreversible enzyme inactivation at 100 °C. Science 1985, 228, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Lau, F.W.; Nauli, S.; Yang, D.; Bowie, J.U. Inactivation mechanism of the membrane protein diacylglycerol kinase in detergent solution. Protein Sci. 2001, 10, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, E.A.; Santos, J.; González-Flecha, F.L. The use of circular dichroism methods to monitor unfolding transitions in peptides, globular and membrane proteins. In Circular Dichroism, Theory and Spectroscopy; Rodgers, D.S., Ed.; Nova: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 217–254. [Google Scholar]
- Eftink, M.R. The use of fluorescence methods to monitor unfolding transitions in proteins. Biophys. J. 1994, 66, 482–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattoni, D.I.; Kaufman, S.B.; González Flecha, F.L. Kinetics and thermodynamics of the interaction of 1-anilino-naphthalene-8-sulfonate with proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1794, 1700–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Cattoni, D.I.; González-Flecha, F.L.; Argüello, J.M. Thermal stability of CopA, a polytopic membrane protein from the hyperthermophile Archaeoglobus fulgidus. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2008, 471, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, V.; Rossi, J.P.F.C.; Echarte, M.M.; Castello, P.R.; González Flecha, F.L. Thermal stability of the plasma membrane Calcium pump. Quantitative analysis of its dependence on lipid-protein interactions. J. Memb. Biol. 2000, 173, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, S.B.; González-Flecha, F.L.; González-Lebrero, R.M. Opposing effects of Na+ and K+ on the thermal stability of Na+,K+-ATPase. J. Phys. Chem. 2012, 116, 3421–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haltia, T.; Freire, E. Forces and factors that contribute to the structural stability of membrane proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1228, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.V.; Rees, P.; Heathcote, P.; Jones, M.R. Kinetic analysis of the thermal stability of the photosynthetic reaction center from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Biophys. J. 2006, 90, 4155–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, G.A.; Berman, M.C. Mechanism of thermal uncoupling of Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum as revealed by thapsigargin stabilization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1289, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, V.; Villamil-Giraldo, A.M.; Castello, P.R.; Rossi, J.P.F.C.; González Flecha, F.L. Effects of phosphatidylethanolamine glycation on lipid-protein interactions and membrane protein thermal stability. Biochem. J. 2008, 416, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, P.C.; Griffith, O.H.; Capaldi, R.A.; Vanderkooi, G. Evidence for boundary lipid in membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1973, 70, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbuzynskiy, S.O.; Ivankov, D.N.; Bogatyreva, N.S.; Finkelstein, A.V. Golden triangle for folding rates of globular proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein, A.V.; Bogatyreva, N.S.; Garbuzynskiy, S.O. Restrictions to protein folding determined by the protein size. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 1884–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawson, T.; Nash, P. Assembly of cell regulatory systems through protein interaction domains. Science 2003, 300, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musacchio, A.; Noble, M.; Pauptit, R.; Wierenga, R.; Saraste, M. Crystal structure of a Src-homology 3 (SH3) domain. Nature 1992, 359, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantcharova, V.P.; Baker, D. Folding dynamics of the src SH3 domain. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 15685–15692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikary, R.; Zimmermann, J.; Liu, J.; Dawson, P.E.; Romesberg, F.E. Experimental characterization of electrostatic and conformational heterogeneity in an SH3 domain. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 13082–13089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koebnik, R.; Locher, K.P.; van Gelder, P. Structure and function of bacterial outer membrane proteins: Barrels in a nutshell. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 37, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimley, W.C. Toward genomic identification of β-barrel membrane proteins: Composition and architecture of known structures. Protein Sci. 2002, 11, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, A.; Abildgaard, F.; Bushweller, J.H.; Tamm, L.K. Structure of outer membrane protein A transmembrane domain by NMR spectroscopy. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2001, 8, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surrey, T.; Schmid, A.; Jahnig, F. Folding and membrane insertion of the trimeric β-barrel protein OmpF. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 2283–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, S.K.; Yamashita, S.; Fleming, K.G. Structure and folding of outer membrane proteins. Comp. Biophys. 2012, 5, 139–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surrey, T.; Jahnig, F. Refolding and oriented insertion of a membrane protein into a lipid bilayer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 7457–7461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmidt, J.H.; Wiener, M.C.; Tamm, L.K. Outer membrane protein A of E. coli folds into detergent micelles, but not in the presence of monomeric detergent. Protein Sci. 1999, 8, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamm, L.K.; Hong, H.; Liang, B. Folding and assembly of β-barrel membrane proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1666, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surrey, T.; Jahnig, F. Kinetics of folding and membrane insertion of a β-barrel membrane protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 28199–28203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamm, L.K. Characterization of two membrane-bound forms of OmpA. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmidt, J.H.; Tamm, L.K. Time-resolved distance determination by tryptophan fluorescence quenching: Probing intermediates in membrane protein folding. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 4996–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmidt, J.H.; den Blaauwen, T.; Driessen, A.J.M.; Tamm, L.K. Outer membrane protein A of Escherichia coli inserts and folds into lipid bilayers by a concerted mechanism. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 5006–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles in Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Popot, J.L.; Engelman, D.M. Membrane protein folding and oligomerization: The two-stage model. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 4031–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmidt, J.H.; Tamm, L.K. Secondary and tertiary structure formation of the β-barrel membrane protein OmpA is synchronized and depends on membrane thickness. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 324, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Tamm, L.K. Elastic coupling of integral membrane protein stability to lipid bilayer forces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4065–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, D.; Nielsen, K.L.; Otzen, D.E. In vitro association of fragments of a β-sheet membrane protein. Biophys. Chem. 2010, 148, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorieff, N.; Ceska, T.A.; Downing, K.H.; Baldwin, J.M.; Henderson, R. Electron-crystallographic refinement of the structure of bacteriorhodopsin. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 259, 393–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowie, J.U. Membrane protein twists and turns. Science 2013, 339, 398–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faham, S.; Yang, D.; Bare, E.; Yohannan, S.; Whitelegge, J.P.; Bowie, J.U. Side-chain contributions to membrane protein structure and stability. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 335, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curnow, P.; Booth, P.J. Combined kinetic and thermodynamic analysis of alpha-helical membrane protein unfolding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18970–18975. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, F.W.; Bowie, J.U. A method for assessing the stability of a membrane protein. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 5884–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, F.N.; Renart, M.L.; Molina, M.L.; Poveda, J.A.; Encinar, J.A.; Fernández, A.M.; Neira, J.L.; González-Ros, J.M. Unfolding and refolding in vitro of a tetrameric, α-helical membrane protein: The prokaryotic potassium channel KcsA. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 14344–14352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otzen, D.E. Folding of DsbB in mixed micelles: A kinetic analysis of the stability of a bacterial membrane protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 330, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, E.A.; Argüello, J.M.; González-Flecha, F.L. Reversible unfolding of a thermophilic membrane protein in phospholipid/detergent mixed micelles. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 397, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Joh, N.H.; Bowie, J.U.; Tamm, L.K. Methods for measuring the thermodynamic stability of membrane proteins. Methods Enzymol. 2009, 455, 213–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKibbin, C.; Farmer, N.A.; Edwards, P.C.; Villa, C.; Booth, P.J. Urea unfolding of opsin in phospholipid bicelles. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009, 85, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.J.; Booth, P.J. Folding and stability of membrane transport proteins in vitro. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curnow, P.; Booth, P.J. The transition state for integral membrane protein folding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, E.; Khorana, H.G. Denaturation and renaturation of bacteriorhodopsin in detergents and lipid-detergent mixtures. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 7003–7011. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, M.L.; Wallace, B.A.; Flitsch, S.L.; Booth, P.J. Slow α-helix formation during folding of a membrane protein. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, P.J.; Farooq, A. Intermediates in the assembly of bacteriorhodopsin investigated by time-resolved absorption spectroscopy. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 246, 674–680. [Google Scholar]
- Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Røgen, P.; Paci, E.; Vendruscolo, M.; Dobson, C.M. Protein folding and the organization of the protein topology universe. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005, 30, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curnow, P.; di Bartolo, N.D.; Moreton, K.M.; Ajoje, O.O.; Saggese, N.P.; Booth, P.J. Stable folding core in the folding transition state of an α-helical integral membrane protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14133–14138. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamani, V.; Hegde, B.G.; Langen, R.; Lanyi, J.K. Secondary and tertiary structure of bacteriorhodopsin in the SDS denatured state. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.J.; Han, S.K.; Bowie, J.U.; Kim, S. Rampant exchange of the structure and function of extramembrane domains between membrane and water soluble proteins. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourdon, P.; Liu, X.Y.; Skjorringe, T.; Morth, J.P.; Møller, L.B.; Pedersen, B.P.; Nissen, P. Crystal structure of a copper-transporting PIB-type ATPase. Nature 2011, 475, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Mattle, D.; Sitsel, O.; Klymchuk, T.; Nielsen, A.M.; Møller, L.B.; White, S.H.; Nissen, P.; Gourdon, P. Copper-transporting P-type ATPases use a unique ion-release pathway. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Booth, P.J.; Curnow, P. Folding scene investigation: Membrane proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2009, 19, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzammil, S.; Kumar, Y.; Tayyab, S. Anion-induced stabilization of human serum albumin prevents the formation of intermediate during urea denaturation. Proteins 2000, 40, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, A.C.; Argüello, J.M. Toward a molecular understanding of metal transport by P1B-Type ATPases. Curr. Top. Memb. 2012, 69, 113–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulages, J.L. Chemical denaturation: Potential impact of undetected intermediates in the free energy of unfolding and m-values obtained from a two-state assumption. Biophys. J. 1998, 75, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Roman, E.A.; González Flecha, F.L. Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Membrane Protein Folding. Biomolecules 2014, 4, 354-373. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom4010354
Roman EA, González Flecha FL. Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Membrane Protein Folding. Biomolecules. 2014; 4(1):354-373. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom4010354
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoman, Ernesto A., and F. Luis González Flecha. 2014. "Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Membrane Protein Folding" Biomolecules 4, no. 1: 354-373. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom4010354
APA StyleRoman, E. A., & González Flecha, F. L. (2014). Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Membrane Protein Folding. Biomolecules, 4(1), 354-373. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom4010354