Targeting Focal Adhesion Kinase in Lung Diseases: Current Progress and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Systemic Review
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
- Research on FAK inhibitors in lung diseases.
- Peer-reviewed articles.
- Reviews, clinical trials.
- Provide complete data that can be accessed.
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
- Publications related to FAK inhibitors but not pulmonary diseases.
- Publications not in the English language.
- Lack of full-text availability.
3. FAK and Inhibitors
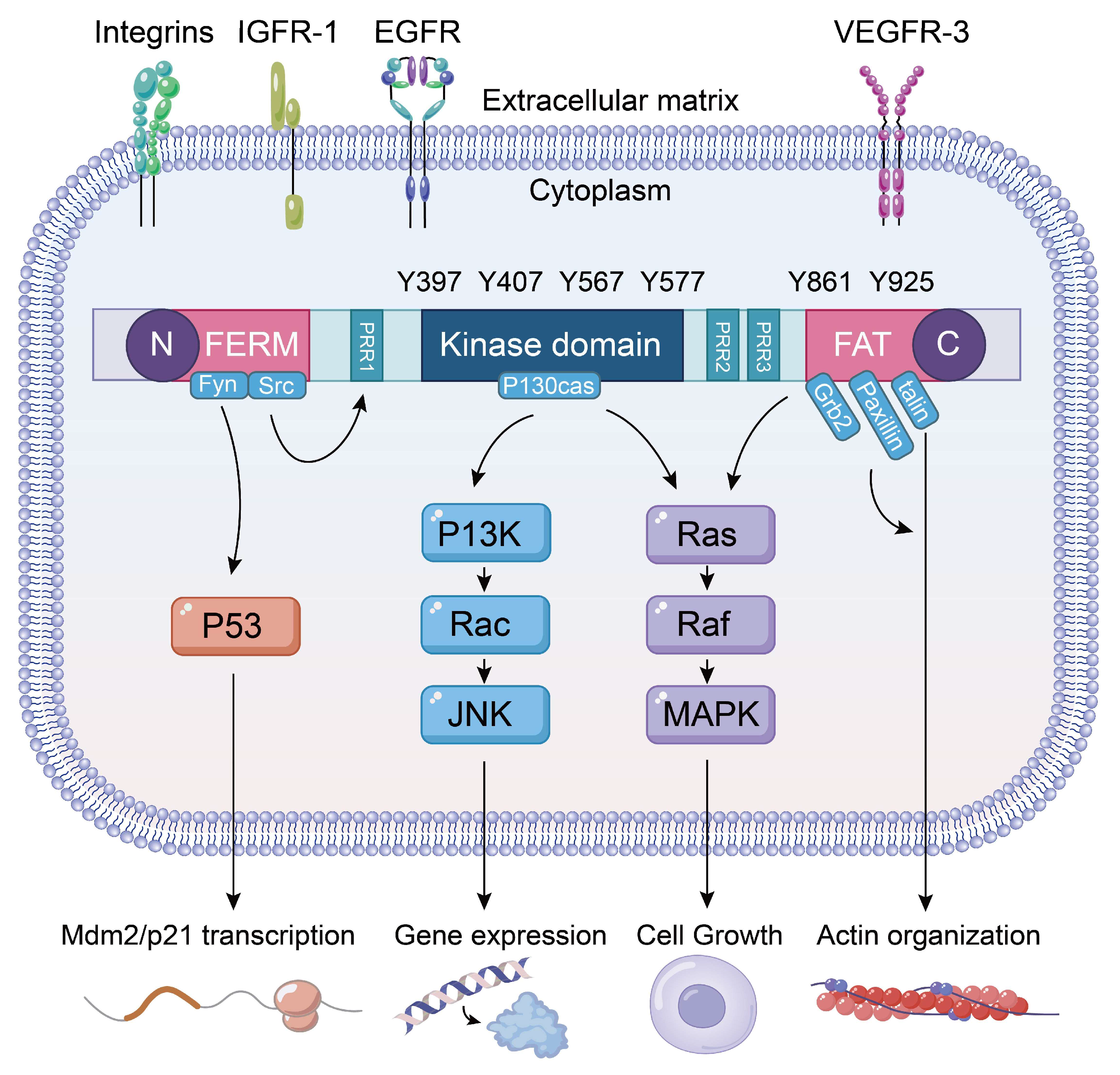
3.1. FAK Phosphorylation and Signaling Pathways
3.2. FAK Inhibitor
4. FAK and Inhibitors in Lung Cancer
5. FAK and Inhibitors in ALI/ARDS
6. FAK and Inhibitors in Pulmonary Fibrosis
7. FAK and Inhibitors in Asthma and COPD
8. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADCs | Antibody–drug conjugates |
| ALI | Acute lung injury |
| ALK | Anaplastic lymphoma kinase |
| ARDS | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| ASM | Airway smooth muscle |
| ASMCs | Airway smooth muscle cells |
| BSMCs | Bronchial smooth muscle cells |
| CLP | Cecal ligation and puncture |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CTGF | Connective tissue growth factor |
| CSE | Cigarette smoke extract |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| ECs | Endothelial cells |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| ERK | Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase |
| ET-1 | Endothelin-1 |
| FAK | Focal adhesion kinase |
| FAs | Focal adhesions |
| ILD | Interstitial lung disease |
| IPDI | Isophorone diisocyanate |
| IPF | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| OVA | Ovalbumin |
| PF | Pulmonary fibrosis |
| Poly (I:C) | Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid |
| PTK2 | Protein tyrosine kinase 2 |
| Pyk2 | Proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SCLC | Small cell lung cancer |
| TKIs | Tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
| EGFR-TKIs | Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| TRALI | Transfusion-related acute lung injury |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Kratzer, T.B.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2025. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2025, 75, 10–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.L.; Peters, S.; Mok, T.S.; Lam, S.; Yang, P.C.; Aggarwal, C.; Brahmer, J.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Felip, E.; Ferris, A.; et al. Lung cancer research and treatment: Global perspectives and strategic calls to action. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2024, 35, 1088–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koudstaal, T.; Funke-Chambour, M.; Kreuter, M.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Wijsenbeek, M.S. Pulmonary fibrosis: From pathogenesis to clinical decision-making. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Bu, W.; Wang, X.; Ruan, J.; Shi, W.; Yu, S.; Huang, L.; Xue, P.; Tang, J.; Zhao, X.; et al. Pulmonary fibrosis: From mechanisms to therapies. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.L.; Fitzgerald, B.G.; Paz-Ares, L.; Cappuzzo, F.; Jänne, P.A.; Peters, S.; Hirsch, F.R. New promises and challenges in the treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet 2024, 404, 803–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Selman, M. Nintedanib and pirfenidone. New antifibrotic treatments indicated for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis offer hopes and raises questions. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, F.; Hong, Y.; Luo, F. Bibliometric analysis of the pirfenidone and nintedanib in interstitial lung diseases. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, M.; Screm, G.; Salton, F.; Confalonieri, P.; Trotta, L.; Barbieri, M.; Ruggero, L.; Mari, M.; Reccardini, N.; Geri, P.; et al. Pirfenidone and Nintedanib in Pulmonary Fibrosis: Lights and Shadows. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.L.; Trevithick, J.E.; Hynes, R.O. Fibronectin/integrin interaction induces tyrosine phosphorylation of a 120-kDa protein. Cell Regul. 1991, 2, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapial Martínez, P.; López Navajas, P.; Lietha, D. FAK Structure and Regulation by Membrane Interactions and Force in Focal Adhesions. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzizacharias, N.A.; Kouraklis, G.P.; Theocharis, S.E. Focal adhesion kinase: A promising target for anticancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2007, 11, 1315–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spallarossa, A.; Tasso, B.; Russo, E.; Villa, C.; Brullo, C. The Development of FAK Inhibitors: A Five-Year Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geijerman, E.; Terrana, F.; Peters, G.J.; Deng, D.; Diana, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Xu, G. Targeting a key FAK-tor: The therapeutic potential of combining focal adhesion kinase (FAK) inhibitors and chemotherapy for chemoresistant non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2024, 33, 1103–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagares, D.; Kapoor, M. Targeting focal adhesion kinase in fibrotic diseases. BioDrugs 2013, 27, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, D.E.; Camidge, D.R.; Morgensztern, D.; Cetnar, J.; Kelly, R.J.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Spigel, D.R.; Jeong, W.; Scaglioni, P.P.; Zhang, S.; et al. Phase 2 study of the focal adhesion kinase inhibitor defactinib (VS-6063) in previously treated advanced KRAS mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2020, 139, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagares, D.; Busnadiego, O.; García-Fernández, R.A.; Kapoor, M.; Liu, S.; Carter, D.E.; Abraham, D.; Xu, S.-W.; Carreira, P.; Fontaine, B.A.; et al. Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase prevents experimental lung fibrosis and myofibroblast formation. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, G.; Soria, J.C.; Blagden, S.P.; Plummer, R.; Fleming, R.A.; Nebot, N.; Zhang, J.; Mazumdar, J.; Rogan, D.; Gazzah, A.; et al. A phase Ib dose-finding, pharmacokinetic study of the focal adhesion kinase inhibitor GSK2256098 and trametinib in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.P.; Willey, C.D.; Anderson, J.C.; Welaya, K.; Chen, D.; Mehta, A.; Ghatalia, P.; Madan, A.; Naik, G.; Sudarshan, S.; et al. Kinomic profiling identifies focal adhesion kinase 1 as a therapeutic target in advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 29220–29232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanapprapasr, D.; Previs, R.A.; Hu, W.; Ivan, C.; Armaiz-Pena, G.N.; Dorniak, P.L.; Hansen, J.M.; Rupaimoole, R.; Huang, J.; Dalton, H.J.; et al. PTEN Expression as a Predictor of Response to Focal Adhesion Kinase Inhibition in Uterine Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekkers, B.G.; Spanjer, A.I.; van der Schuyt, R.D.; Kuik, W.J.; Zaagsma, J.; Meurs, H. Focal adhesion kinase regulates collagen I-induced airway smooth muscle phenotype switching. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 346, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, W. PTP1B Attenuates the Progression of COPD by Suppressing the SHP-2/Src/ERK1/2/NLRP3 Signaling Pathway. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2024. ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, S.K.; Hanson, D.A.; Schlaepfer, D.D. Focal adhesion kinase: In command and control of cell motility. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Coq, J.; Acebrón, I.; Rodrigo Martin, B.; López Navajas, P.; Lietha, D. New insights into FAK structure and function in focal adhesions. J. Cell Sci. 2022, 135, jcs259089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaller, M.D.; Hildebrand, J.D.; Shannon, J.D.; Fox, J.W.; Vines, R.R.; Parsons, J.T. Autophosphorylation of the focal adhesion kinase, pp125FAK, directs SH2-dependent binding of pp60src. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrier, A.L.; Mastrangelo, A.M.; Downward, J.; Ginsberg, M.; LaFlamme, S.E. Activated R-ras, Rac1, PI 3-kinase and PKCepsilon can each restore cell spreading inhibited by isolated integrin beta1 cytoplasmic domains. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 151, 1549–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, L.; Wozniak, M.A.; Collins, A.S.; Wilson, S.D.; Keely, P.J. R-Ras promotes focal adhesion formation through focal adhesion kinase and p130(Cas) by a novel mechanism that differs from integrins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calalb, M.B.; Polte, T.R.; Hanks, S.K. Tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase at sites in the catalytic domain regulates kinase activity: A role for Src family kinases. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arold, S.T.; Hoellerer, M.K.; Noble, M.E. The structural basis of localization and signaling by the focal adhesion targeting domain. Structure 2002, 10, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cary, L.A.; Han, D.C.; Polte, T.R.; Hanks, S.K.; Guan, J.L. Identification of p130Cas as a mediator of focal adhesion kinase-promoted cell migration. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 140, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemke, R.L.; Leng, J.; Molander, R.; Brooks, P.C.; Vuori, K.; Cheresh, D.A. CAS/Crk coupling serves as a “molecular switch” for induction of cell migration. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 140, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, J.D.; Ruest, P.J.; Fry, D.W.; Hanks, S.K. Induced focal adhesion kinase (FAK) expression in FAK-null cells enhances cell spreading and migration requiring both auto- and activation loop phosphorylation sites and inhibits adhesion-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Pyk2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 4806–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieg, D.J.; Hauck, C.R.; Schlaepfer, D.D. Required role of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) for integrin-stimulated cell migration. J. Cell Sci. 1999, 112 Pt 16, 2677–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuori, K.; Hirai, H.; Aizawa, S.; Ruoslahti, E. Introduction of p130cas signaling complex formation upon integrin-mediated cell adhesion: A role for Src family kinases. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 2606–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Yao, J.F.; Deng, X.F.; Zheng, X.D.; Jia, M.; Wang, Y.Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, J.H. 14, 15-EET induces breast cancer cell EMT and cisplatin resistance by up-regulating integrin αvβ3 and activating FAK/PI3K/AKT signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2018, 37, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Han, Q.; Rong, X.Z.; Guo, Y.X.; Liu, Y. PLEKHH2 binds β-arrestin1 through its FERM domain, activates FAK/PI3K/AKT phosphorylation, and promotes the malignant phenotype of non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.F.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Hua, S.N.; Qu, H.Y.; Dong, S.W.; Li, R.L.; Zhao, M.Y.; Zhen, Y.; Yu, X.L.; et al. Alpha-enolase promotes cell glycolysis, growth, migration, and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer through FAK-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Ye, B.; Liu, H.; Bi, R.; Zhang, N.; Hu, J.; Luo, E. Fak-Mapk, Hippo and Wnt signalling pathway expression and regulation in distraction osteogenesis. Cell Prolif. 2018, 51, e12453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llinàs-Arias, P.; Esteller, M. Epigenetic inactivation of tumour suppressor coding and non-coding genes in human cancer: An update. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 170152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar, M.E.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.R. Targeting the RAS/RAF/MAPK pathway for cancer therapy: From mechanism to clinical studies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubovskaya, V.M.; Finch, R.; Cance, W.G. Direct interaction of the N-terminal domain of focal adhesion kinase with the N-terminal transactivation domain of p53. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 25008–25021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipuk, J.E.; Green, D.R. Cytoplasmic p53: Bax and forward. Cell Cycle 2004, 3, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, M.; Zachary, I. Nuclear localization and apoptotic regulation of an amino-terminal domain focal adhesion kinase fragment in endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 276, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.; Ham, C.; Zachary, I. The focal adhesion kinase amino-terminal domain localises to nuclei and intercellular junctions in HEK 293 and MDCK cells independently of tyrosine 397 and the carboxy-terminal domain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 299, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beviglia, L.; Golubovskaya, V.; Xu, L.; Yang, X.; Craven, R.J.; Cance, W.G. Focal adhesion kinase N-terminus in breast carcinoma cells induces rounding, detachment and apoptosis. Biochem. J. 2003, 373, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Stewart, G. Nuclear import of N-terminal FAK by activation of the FcepsilonRI receptor in RBL-2H3 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 314, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Khan, T. Focal adhesion kinase-An emerging viable target in cancer and development of focal adhesion kinase inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2021, 97, 774–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.; Abd El-Hafeez, A.A.; Abdelhafeez, D.A.; Abdelhamid, D.; Mostafa, Y.A.; Ghosh, P.; Hayallah, A.M.; GE, A.A.-R. FAK inhibitors as promising anticancer targets: Present and future directions. Future Med. Chem. 2021, 13, 1559–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.W. Development of focal adhesion kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.C.; Jiang, A.Q.; Zhang, W.M.; Zhu, H.L. FAK inhibitors in Cancer, a patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2018, 28, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brullo, C.; Tasso, B. New Insights on Fak and Fak Inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 3318–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzmaier, F.J.; Jean, C.; Schlaepfer, D.D. FAK in cancer: Mechanistic findings and clinical applications. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.L.; Chen, L.C.; Shen, T.L. Emerging roles of focal adhesion kinase in cancer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 690690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, Z.; Liu, T.; Cai, T.; Wang, A.; Du, W.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Z.; et al. Abnormally activated OPN/integrin αVβ3/FAK signalling is responsible for EGFR-TKI resistance in EGFR mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.L.; Shawe-Taylor, A.J.; Williams, C.M.; Poole, A.W. Characterization of a novel focal adhesion kinase inhibitor in human platelets. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 389, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack-Davis, J.K.; Martin, K.H.; Tilghman, R.W.; Iwanicki, M.; Ung, E.J.; Autry, C.; Luzzio, M.J.; Cooper, B.; Kath, J.C.; Roberts, W.G.; et al. Cellular characterization of a novel focal adhesion kinase inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 14845–14852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, R.A.; Thomas, K.S.; Gutknecht, M.F.; Bouton, A.H. The nonreceptor protein tyrosine kinase Pyk2 promotes the turnover of monocytes at steady state. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 102, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, N.M.; Houtman, J.C. Functions of the FAK family kinases in T cells: Beyond actin cytoskeletal rearrangement. Immunol. Res. 2014, 59, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinamard, R.; Okigaki, M.; Schlessinger, J.; Ravetch, J.V. Absence of marginal zone B cells in Pyk-2-deficient mice defines their role in the humoral response. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosein, A.N.; Brekken, R.A.; Maitra, A. Pancreatic cancer stroma: An update on therapeutic targeting strategies. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 487–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.M.; Lee, B.Y.; Castillo, L.; Spielman, C.; Grogan, J.; Yeung, N.K.; Kench, J.G.; Stricker, P.D.; Haynes, A.M.; Centenera, M.M.; et al. Effect of FAK inhibitor VS-6063 (defactinib) on docetaxel efficacy in prostate cancer. Prostate 2018, 78, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, J.B.; Adair, S.J.; Slack-Davis, J.K.; Walters, D.M.; Tilghman, R.W.; Hershey, E.D.; Lowrey, B.; Thomas, K.S.; Bouton, A.H.; Hwang, R.F.; et al. Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase by PF-562,271 inhibits the growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer concomitant with altering the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.; Pharaon, R.R.; Nam, A.; Salgia, S.; Kulkarni, P.; Massarelli, E. FAK-targeted and combination therapies for the treatment of cancer: An overview of phase I and II clinical trials. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2020, 29, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagi, C.M.; Christensen, J.; Cohen, D.P.; Roberts, W.G.; Wilkie, D.; Swanson, T.; Tuthill, T.; Andresen, C.J. Sunitinib and PF-562,271 (FAK/Pyk2 inhibitor) effectively block growth and recovery of human hepatocellular carcinoma in a rat xenograft model. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, J.R.; Camidge, D.R.; Mileshkin, L.R.; Chen, E.X.; Hicks, R.J.; Rischin, D.; Fingert, H.; Pierce, K.J.; Xu, H.; Roberts, W.G.; et al. Safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic phase I dose-escalation trial of PF-00562271, an inhibitor of focal adhesion kinase, in advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, W.G.; Ung, E.; Whalen, P.; Cooper, B.; Hulford, C.; Autry, C.; Richter, D.; Emerson, E.; Lin, J.; Kath, J.; et al. Antitumor activity and pharmacology of a selective focal adhesion kinase inhibitor, PF-562,271. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, X.; Liang, Y.; Shi, M.; Chen, C.; Lin, F. FAK inhibitor PF-562271 inhibits the migration and proliferation of high-grade serous ovarian cancer cells through FAK and FAK mediated cell cycle arrest. Med. Oncol. 2023, 40, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Han, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Meng, P.; Wang, Y. Breast Cancer Prognosis Prediction and Immune Pathway Molecular Analysis Based on Mitochondria-Related Genes. Genet. Res. 2022, 2022, 2249909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.T.; He, Y.X.; Gang, B.C.; Zhang, M.J.; Kang, H.; Ye, Y.Y.; Liu, G.Q.; Gu, W. Attenuation of Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury by FAK Inhibitor PF-562271. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2023, 37, 6617–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.X.; Gang, B.C.; Zhang, M.J.; Bai, Y.T.; Wan, Z.Y.; Pan, J.S.; Liu, J.; Liu, G.Q.; Gu, W. ACE2 improves endothelial cell function and reduces acute lung injury by downregulating FAK expression. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 128, 111535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.M.; Shaw, A.T. ALK inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: Crizotinib and beyond. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. H O 2014, 12, 429–439. [Google Scholar]
- Golding, B.; Luu, A.; Jones, R.; Viloria-Petit, A.M. The function and therapeutic targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, G.R.; Cheng, M.; Learn, K.S.; Wagner, J.; Gingrich, D.E.; Lisko, J.G.; Curry, M.; Mesaros, E.F.; Ghose, A.K.; Quail, M.R.; et al. Discovery of Clinical Candidate CEP-37440, a Selective Inhibitor of Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) and Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK). J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 7478–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attwa, M.W.; AlRabiah, H.; Abdelhameed, A.S.; Kadi, A.A. Assessment of the in vitro metabolic stability of CEP-37440, a selective FAK/ALK inhibitor, in HLMs using fast UPLC-MS/MS method: In silico metabolic lability and DEREK alerts screening. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1323738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanjoni, I.; Walsh, C.; Uryu, S.; Tomar, A.; Nam, J.O.; Mielgo, A.; Lim, S.T.; Liang, C.; Koenig, M.; Sun, C.; et al. PND-1186 FAK inhibitor selectively promotes tumor cell apoptosis in three-dimensional environments. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 9, 764–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.H.; Wang, S.Q.; Shang, H.L.; Lv, H.F.; Chen, B.B.; Gao, S.G.; Chen, X.B. Roles and inhibitors of FAK in cancer: Current advances and future directions. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1274209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jonge, M.J.A.; Steeghs, N.; Lolkema, M.P.; Hotte, S.J.; Hirte, H.W.; van der Biessen, D.A.J.; Abdul Razak, A.R.; De Vos, F.; Verheijen, R.B.; Schnell, D.; et al. Phase I Study of BI 853520, an Inhibitor of Focal Adhesion Kinase, in Patients with Advanced or Metastatic Nonhematologic Malignancies. Target. Oncol. 2019, 14, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.F.; Siu, L.L.; Bendell, J.C.; Cleary, J.M.; Razak, A.R.; Infante, J.R.; Pandya, S.S.; Bedard, P.L.; Pierce, K.J.; Houk, B.; et al. A phase I study of VS-6063, a second-generation focal adhesion kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Fukuoka, K.; Takeda, M.; Iwasa, T.; Yoshida, T.; Horobin, J.; Keegan, M.; Vaickus, L.; Chavan, A.; Padval, M.; et al. A first-in-Asian phase 1 study to evaluate safety, pharmacokinetics and clinical activity of VS-6063, a focal adhesion kinase (FAK) inhibitor in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Li, R.; Ning, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Jin, Y.; Yin, Y. Discovery of 2,4-diarylaminopyrimidine derivatives bearing dithiocarbamate moiety as novel FAK inhibitors with antitumor and anti-angiogenesis activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 177, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthi, E.; Krishna, M.H.; Arunesh, G.M.; Venkateswara Reddy, K.; Sooriya Kumar, J.; Viswanadhan, V.N. Focal adhesion kinase inhibitors in the treatment of metastatic cancer: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2014, 24, 1077–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirt, U.A.; Waizenegger, I.C.; Schweifer, N.; Haslinger, C.; Gerlach, D.; Braunger, J.; Weyer-Czernilofsky, U.; Stadtmüller, H.; Sapountzis, I.; Bader, G.; et al. Efficacy of the highly selective focal adhesion kinase inhibitor BI 853520 in adenocarcinoma xenograft models is linked to a mesenchymal tumor phenotype. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Singh, P.; Parate, S.; Singh, R.; Ro, H.S.; Song, K.S.; Lee, K.W.; Park, Y.M. Computational insights into allosteric inhibition of focal adhesion kinase: A combined pharmacophore modeling and molecular dynamics approach. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2024, 130, 108789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogoyevitch, M.A.; Fairlie, D.P. A new paradigm for protein kinase inhibition: Blocking phosphorylation without directly targeting ATP binding. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akl, M.R.; Foudah, A.I.; Ebrahim, H.Y.; Meyer, S.A.; El Sayed, K.A. The marine-derived sipholenol A-4-O-3′,4′-dichlorobenzoate inhibits breast cancer growth and motility in vitro and in vivo through the suppression of Brk and FAK signaling. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2282–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubovskaya, V.M.; Nyberg, C.; Zheng, M.; Kweh, F.; Magis, A.; Ostrov, D.; Cance, W.G. A small molecule inhibitor, 1,2,4,5-benzenetetraamine tetrahydrochloride, targeting the y397 site of focal adhesion kinase decreases tumor growth. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 7405–7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, P.; Dutt, N.; Ahirwar, D.K.; Yadav, P. Lung Microbiome in Lung Cancer: A New Horizon in Cancer Study. Cancer Prev. Res. 2024, 17, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, R.; Page, N.; Morgensztern, D.; Read, W.; Tierney, R.; Vlahiotis, A.; Spitznagel, E.L.; Piccirillo, J. Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: Analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 4539–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoda, S.A.; Hoda, R.S. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 154, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.R.; Yang, P.; Cassivi, S.D.; Schild, S.E.; Adjei, A.A. Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agochiya, M.; Brunton, V.G.; Owens, D.W.; Parkinson, E.K.; Paraskeva, C.; Keith, W.N.; Frame, M.C. Increased dosage and amplification of the focal adhesion kinase gene in human cancer cells. Oncogene 1999, 18, 5646–5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carelli, S.; Zadra, G.; Vaira, V.; Falleni, M.; Bottiglieri, L.; Nosotti, M.; Di Giulio, A.M.; Gorio, A.; Bosari, S. Up-regulation of focal adhesion kinase in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2006, 53, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, A.; Horinaka, M.; Yaoi, T.; Ono, H.; Itoh, K.; Yamada, T.; Takayama, K.; Sakai, T. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition status is a remarkable biomarker for the combination treatment with avutometinib and defactinib in KRAS-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2024, 131, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.D.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.B.; Yan, F.J.; Dai, X.Y.; Ying, M.D.; Cao, J.; Ma, J.; Luo, P.H.; Han, Y.X.; et al. CT-707, a Novel FAK Inhibitor, Synergizes with Cabozantinib to Suppress Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Blocking Cabozantinib-Induced FAK Activation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2916–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, P.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Huang, D.; Hu, P.; Sun, Y.; Shi, Y. Conteltinib (CT-707) in patients with advanced ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer: A multicenter, open-label, first-in-human phase 1 study. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.D.; Tao, R.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Xu, C.; Zhai, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Tang, C.; et al. Discovery of a novel ALK/ROS1/FAK inhibitor, APG-2449, in preclinical non-small cell lung cancer and ovarian cancer models. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lietha, D.; Cai, X.; Ceccarelli, D.F.; Li, Y.; Schaller, M.D.; Eck, M.J. Structural basis for the autoinhibition of focal adhesion kinase. Cell 2007, 129, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrano, A.C.; Eytan, E.; Hershko, A.; Pagano, M. SKP2 is required for ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the CDK inhibitor p27. Nat. Cell. Biol. 1999, 1, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Huang, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, G.; Jin, X.; Liu, J.; Kang, F.; Liu, Z. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of coumarin-containing 2,4-diphenylpyrimidine derivatives as novel focal adhesion kinase inhibitors for treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2025, 123, 130240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Dan, M.; Wang, Y.; Shu, C.; Jiao, M.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, J.; et al. Diosmin reduces the stability of Snail and Cyclin D1 by targeting FAK to inhibit NSCLC progression. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2024, 135, 156135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, L.B.; Matthay, M.A. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1334–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Kong, X.; Guo, J. Exploring immune-related pathogenesis in lung injury: Providing new insights Into ALI/ARDS. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikata, Y.; Birukov, K.G.; Garcia, J.G. S1P induces FA remodeling in human pulmonary endothelial cells: Role of Rac, GIT1, FAK, and paxillin. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 94, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usatyuk, P.V.; Natarajan, V. Regulation of reactive oxygen species-induced endothelial cell-cell and cell-matrix contacts by focal adhesion kinase and adherens junction proteins. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2005, 289, L999–L1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usatyuk, P.V.; Parinandi, N.L.; Natarajan, V. Redox regulation of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal-mediated endothelial barrier dysfunction by focal adhesion, adherens, and tight junction proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 35554–35566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirtori, C.R. The pharmacology of statins. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 88, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, S.O.; Budoff, M. Effect of statins on atherosclerotic plaque. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 29, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, J.R.; Dudek, S.M.; Birukov, K.G.; Ye, S.Q.; Grigoryev, D.N.; Girgis, R.E.; Garcia, J.G. Cytoskeletal activation and altered gene expression in endothelial barrier regulation by simvastatin. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 30, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Gang, B.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Gu, W. Protective effect of FAK inhibitor PF-562271 against human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury induced by aging platelets. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2024, 44, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, G.F.; Aimaretti, E.; Einaudi, G.; Mastrocola, R.; de Oliveira, J.G.; Collotta, D.; Porchietto, E.; Aragno, M.; Cifani, C.; Sordi, R.; et al. Pharmacological Inhibition of FAK-Pyk2 Pathway Protects Against Organ Damage and Prolongs the Survival of Septic Mice. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 837180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lederer, P.A.; Zhou, T.; Chen, W.; Epshtein, Y.; Wang, H.; Mathew, B.; Jacobson, J.R. Attenuation of murine acute lung injury by PF-573,228, an inhibitor of focal adhesion kinase. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2018, 110, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wu, D.; Pan, J.; Luo, W.; Wang, Y.; Liang, G. FAK mediates LPS-induced inflammatory lung injury through interacting TAK1 and activating TAK1-NFκB pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, H.; Li, B.L.; Fu, G.; Liu, H.; Cai, J.M.; Zheng, M. CpG-oligodeoxynucleotides may be effective for preventing ionizing radiation induced pulmonary fibrosis. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 292, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouvelekis, A.; Bouros, D. Estrogen Signaling and MicroRNAs in Lung Fibrosis. Sex, Hormones, and Rock Scars. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 1199–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dwyer, D.N.; Ashley, S.L.; Gurczynski, S.J.; Xia, M.; Wilke, C.; Falkowski, N.R.; Norman, K.C.; Arnold, K.B.; Huffnagle, G.B.; Salisbury, M.L.; et al. Lung Microbiota Contribute to Pulmonary Inflammation and Disease Progression in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, A.; Selman, M. The Interplay of the Genetic Architecture, Aging, and Environmental Factors in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 64, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, P.W.; Barkauskas, C.E.; Jiang, D. Pulmonary fibrosis: Patterns and perpetrators. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2756–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, W.J.; Martusewicz-Boros, M.M.; Białas, A.J.; Barczyk, A.; Batko, B.; Błasińska, K.; Boros, P.W.; Górska, K.; Grzanka, P.; Jassem, E.; et al. Guidelines of the Polish Respiratory Society on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases Other than Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Adv. Respir. Med. 2022, 90, 425–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, B.; Collard, H.R.; King, T.E., Jr. Clinical course and prediction of survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryerson, C.J.; Urbania, T.H.; Richeldi, L.; Mooney, J.J.; Lee, J.S.; Jones, K.D.; Elicker, B.M.; Koth, L.L.; King, T.E., Jr.; Wolters, P.J.; et al. Prevalence and prognosis of unclassifiable interstitial lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.; Caro, Y.M.; Gardner, C.; Grischo, G.; Liang, Y.; Wickremasinghe, P.D.; Polmann, M.; Kala, M.; Marlowe, T.; Black, S.M.; et al. PTK2-associated gene signature could predict the prognosis of IPF. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, Y.; Ihn, H.; Jinnin, M.; Asano, Y.; Yamane, K.; Tamaki, K. Constitutive phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase is involved in the myofibroblast differentiation of scleroderma fibroblasts. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serini, G.; Bochaton-Piallat, M.L.; Ropraz, P.; Geinoz, A.; Borsi, L.; Zardi, L.; Gabbiani, G. The fibronectin domain ED-A is crucial for myofibroblastic phenotype induction by transforming growth factor-beta1. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 142, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thannickal, V.J.; Lee, D.Y.; White, E.S.; Cui, Z.; Larios, J.M.; Chacon, R.; Horowitz, J.C.; Day, R.M.; Thomas, P.E. Myofibroblast differentiation by transforming growth factor-beta1 is dependent on cell adhesion and integrin signaling via focal adhesion kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 12384–12389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilić, D.; Furuta, Y.; Kanazawa, S.; Takeda, N.; Sobue, K.; Nakatsuji, N.; Nomura, S.; Fujimoto, J.; Okada, M.; Yamamoto, T. Reduced cell motility and enhanced focal adhesion contact formation in cells from FAK-deficient mice. Nature 1995, 377, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.W.; Rustad, K.C.; Akaishi, S.; Sorkin, M.; Glotzbach, J.P.; Januszyk, M.; Nelson, E.R.; Levi, K.; Paterno, J.; Vial, I.N.; et al. Focal adhesion kinase links mechanical force to skin fibrosis via inflammatory signaling. Nat. Med. 2011, 18, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xu, S.W.; Kennedy, L.; Pala, D.; Chen, Y.; Eastwood, M.; Carter, D.E.; Black, C.M.; Abraham, D.J.; Leask, A. FAK is required for TGFbeta-induced JNK phosphorylation in fibroblasts: Implications for acquisition of a matrix-remodeling phenotype. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 2169–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotsyuk, A.A.; Chen, K.; Hyung, S.; Ma, K.C.; Henn, D.; Mermin-Bunnell, A.M.; Mittal, S.; Padmanabhan, J.; Larson, M.R.; Steele, S.R.; et al. Inhibiting Fibroblast Mechanotransduction Modulates Severity of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Adv. Wound Care 2022, 11, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, K.; Aono, Y.; Azuma, M.; Kishi, J.; Takezaki, A.; Kishi, M.; Makino, H.; Okazaki, H.; Uehara, H.; Izumi, K.; et al. Antifibrotic effects of focal adhesion kinase inhibitor in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, P.; Upagupta, C.; Vierhout, M.; Ayaub, E.; Bellaye, P.S.; Gauldie, J.; Shimbori, C.; Inman, M.; Ask, K.; Kolb, M.R.J. The importance of interventional timing in the bleomycin model of pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aegerter, H.; Lambrecht, B.N. The Pathology of Asthma: What Is Obstructing Our View? Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2023, 18, 387–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoettler, N.; Strek, M.E. Recent Advances in Severe Asthma: From Phenotypes to Personalized Medicine. Chest 2020, 157, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, K.P.; Curtiss, M.L.; Blain, T.J.; Liu, R.M.; Trevor, J.; Deshane, J.S.; Thannickal, V.J. Airway Remodeling in Asthma. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østergaard, C.; Johansen, J.S.; Benfield, T.; Price, P.A.; Lundgren, J.D. YKL-40 is elevated in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with purulent meningitis. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2002, 9, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilmarinen, P.; Tuomisto, L.E.; Niemelä, O.; Tommola, M.; Haanpää, J.; Kankaanranta, H. Cluster Analysis on Longitudinal Data of Patients with Adult-Onset Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 967–978.e963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; van der Grinten, C.P.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, T.; Hirai, K.; Gon, Y.; Maruoka, S.; Mizumura, K.; Hikichi, M.; Holweg, C.; Itoh, K.; Inoue, H.; Hashimoto, S. Combined Assessment of Serum Periostin and YKL-40 May Identify Asthma-COPD Overlap. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 134–145.e131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shi, Z.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Yang, F.; Tang, H. YKL-40 mediates airway remodeling in asthma via activating FAK and MAPK signaling pathway. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 1378–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Ji, J.; Cao, W.; Zhang, H.; Meng, D.; Xie, B.; Xu, S. Cyclic peptide *CRRETAWAC* attenuates fibronectin-induced cytokine secretion of human airway smooth muscle cells by inhibiting FAK and p38 MAPK. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 2535–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.L.; Huang, M.S.; Huang, S.K.; Ni, W.C.; Hung, J.Y.; Ko, Y.C.; Hung, C.H.; Tsai, Y.M.; Duh, T.H.; Hsu, Y.L. Signalling pathway of isophorone diisocyanate-responsive interleukin-8 in airway smooth muscle cells. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Rounds, S. Focal adhesion kinase and endothelial cell apoptosis. Microvasc. Res. 2012, 83, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhatskyy, P.; Gabino Miranda, G.A.; Newton, J.; Lee, C.G.; Choudhary, G.; Vang, A.; Rounds, S.; Lu, Q. Cigarette smoke-induced lung endothelial apoptosis and emphysema are associated with impairment of FAK and eIF2α. Microvasc. Res. 2014, 94, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Hu, W.; Zhang, S.; Ren, C.; Lin, S.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, H.; Yin, J.; Tan, L. Fibroblast growth factor 10 attenuates chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by protecting against glycocalyx impairment and endothelial apoptosis. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzato, C.; Outeiro-Pinho, G.; Galiè, M.; Ramadori, G.; Konstantinidou, G. ERK5 suppression overcomes FAK inhibitor resistance in mutant KRAS-driven non-small cell lung cancer. EMBO Mol. Med. 2024, 16, 2402–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.F.; Yang, L.; Nie, H.J.; Gao, J.; Lei, S.M.; Lai, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wagner, E.; Yu, H.J.; Chen, X.H.; et al. Tumor-targeted PROTAC prodrug nanoplatform enables precise protein degradation and combination cancer therapy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2024, 45, 1740–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xue, L.; Xu, X.; Luo, J.; Zhang, S. FAK-targeting PROTAC demonstrates enhanced antitumor activity against KRAS mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 408, 112868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, R.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Xue, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, T.; Yin, W.; Qin, Q.; Sun, Y.; et al. Identification of novel and potent PROTACs targeting FAK for non-small cell lung cancer: Design, synthesis, and biological study. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 237, 114373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Chemical Compound/Company | Chemical Structure | Molecular Weight | Phase | IC50 on FAK | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Defactinib (VS-6063)/Verastem |  | 510.49 | II | 0.6 nM | [77,78,79] |
| PF-562271/Pfizer |  | 507.49 | I | 1.5 nM | [80] |
| CEP-37440/Cephalon |  | 580.12 | I | 2 nM | [80] |
| VS-4718(PND-1186)/Verastem | 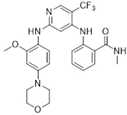 | 501.50 | I | 1.5 nM | [49] |
| GSK-2256098/GlaxoSmithKline | 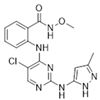 | 414.89 | II | 0.4 nM | [62] |
| BI-853520/Boehringer Ingelhein |  | 588.55 | I | 1 nM | [81] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, P.; Xu, X.; Ma, T.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Qian, F.; Gu, W. Targeting Focal Adhesion Kinase in Lung Diseases: Current Progress and Future Directions. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091233
Wan Z, Zhu Z, Wang P, Xu X, Ma T, Li H, Li L, Qian F, Gu W. Targeting Focal Adhesion Kinase in Lung Diseases: Current Progress and Future Directions. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(9):1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091233
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Ziyu, Zefeng Zhu, Pengbin Wang, Xuan Xu, Tianhao Ma, Huari Li, Lexing Li, Feng Qian, and Wei Gu. 2025. "Targeting Focal Adhesion Kinase in Lung Diseases: Current Progress and Future Directions" Biomolecules 15, no. 9: 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091233
APA StyleWan, Z., Zhu, Z., Wang, P., Xu, X., Ma, T., Li, H., Li, L., Qian, F., & Gu, W. (2025). Targeting Focal Adhesion Kinase in Lung Diseases: Current Progress and Future Directions. Biomolecules, 15(9), 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091233






