Protective Effect of Low 2-O, 3-O Desulfated Heparin (ODSH) Against LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
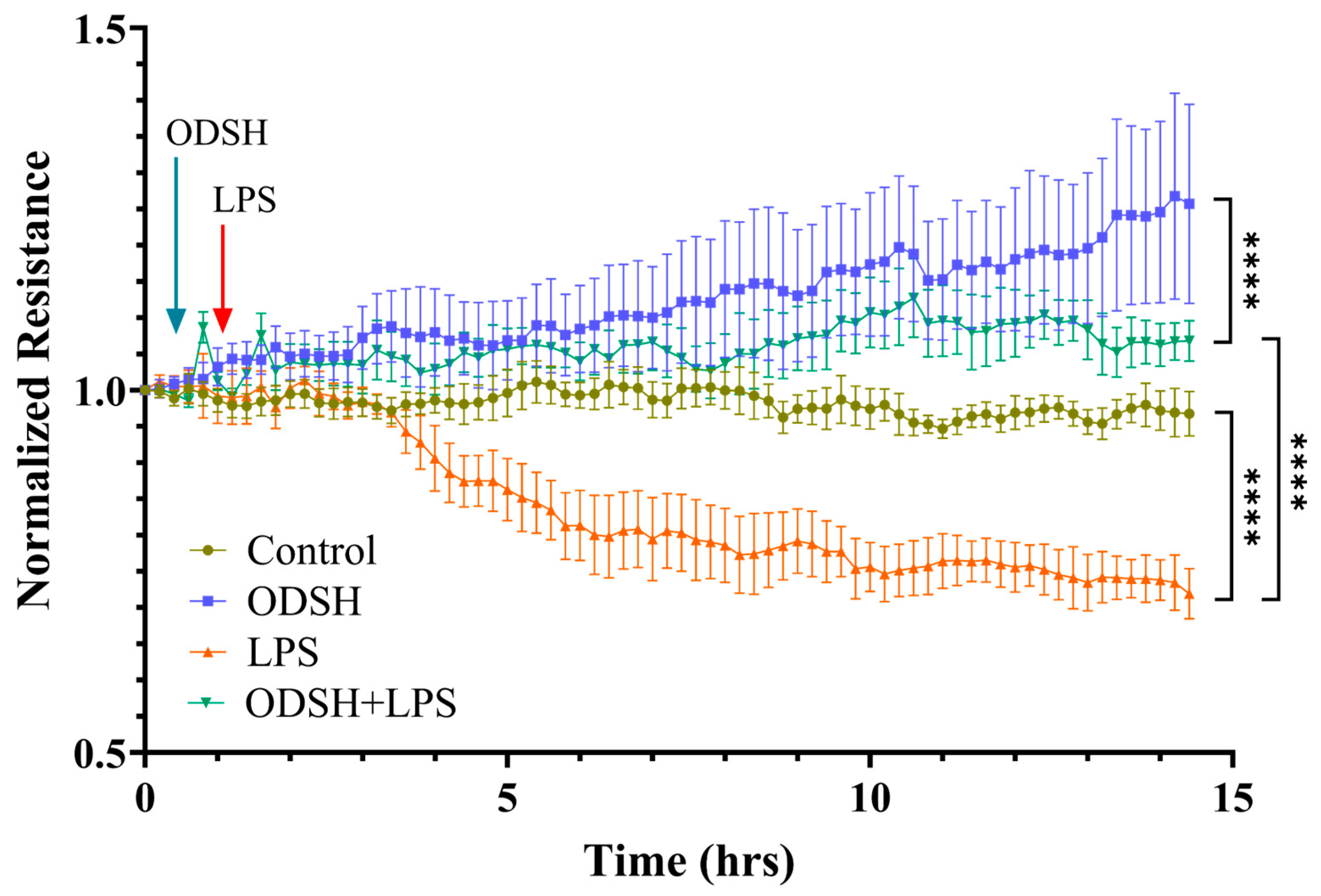
2.2. Transendothelial Electrical Resistance Measurement
2.3. Animal Experiments
2.4. Animal Surgical Procedure
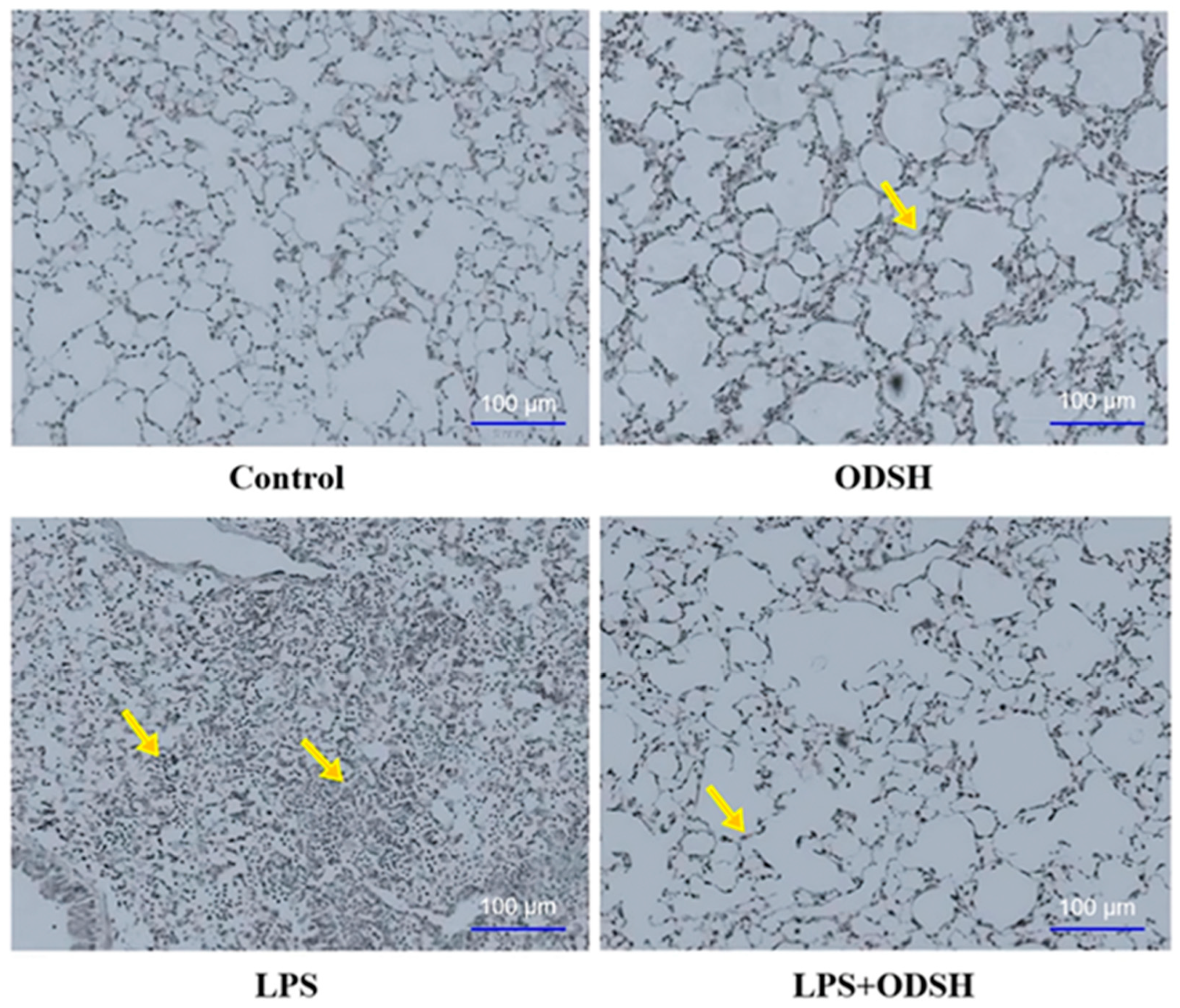
2.5. Lung Histology
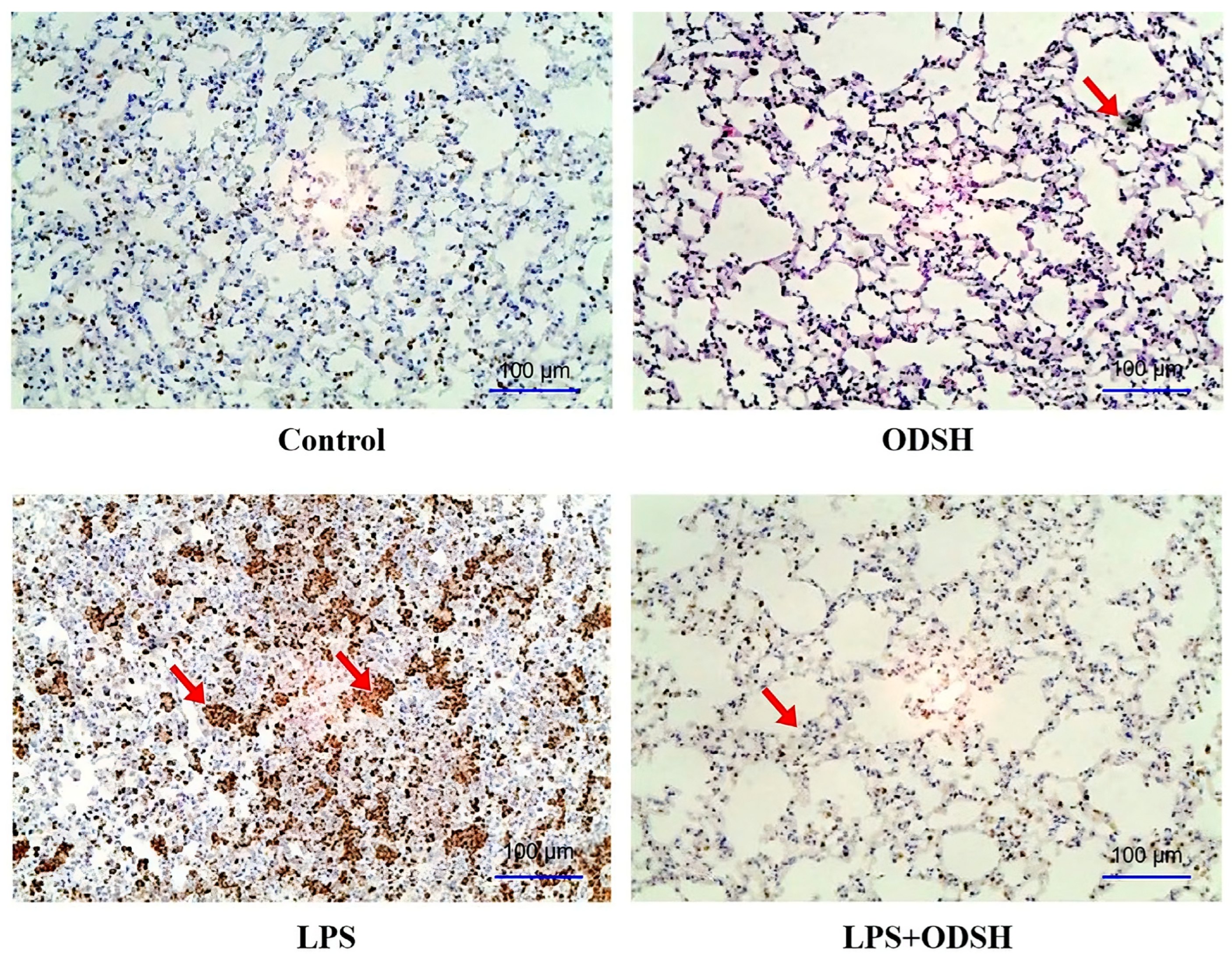
2.6. Immunohistochemistry: Myeloperoxidase (MPO)
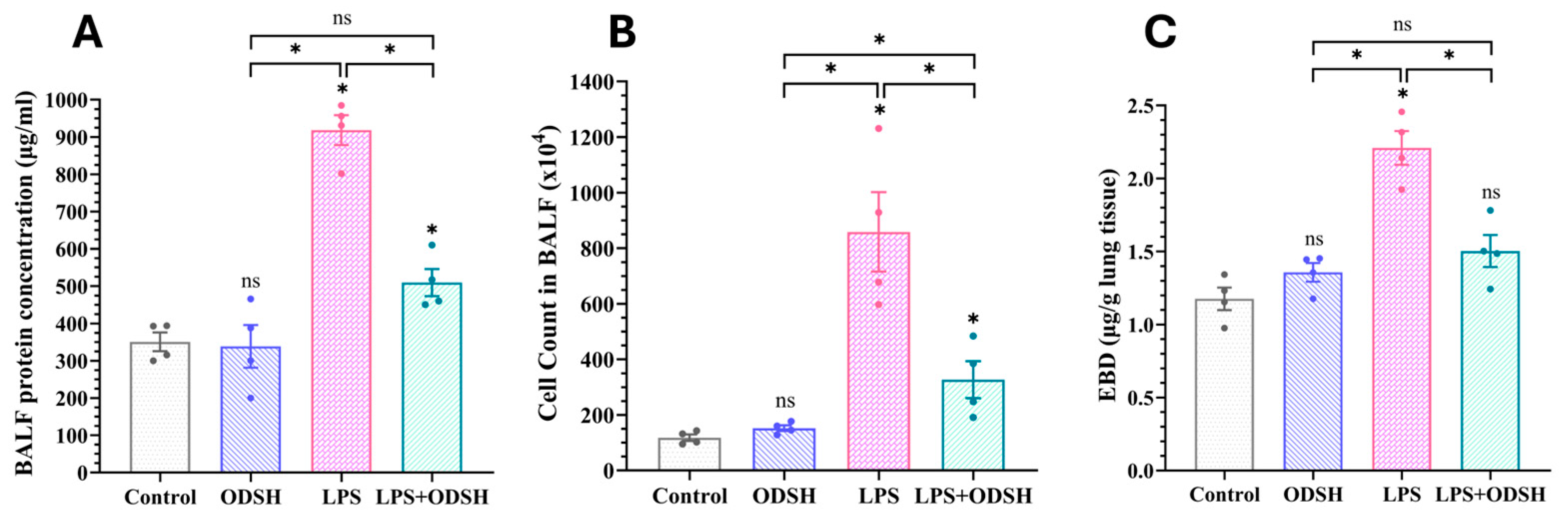
2.7. Lung Permeability Measurement Using Evans Blue Dye Albumin
2.8. Protein Estimation and Cell Count from the BALF
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis (RT-qPCR)
2.10. Protein Extraction and Immunoblotting
2.11. Quantification of Cytokines and Chemokines in BALF
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. ODSH Treatment Significantly Attenuates LPS-Induced Capillary Leak in a Murine Model of LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury
3.2. ODSH Mitigates LPS-Induced Endothelial Permeability in HLMVECs
3.3. Histological Evaluation of ODSH Effect on LPS-Induced Lung Inflammation
3.4. Immunohistochemical Analysis of ODSH Effect on LPS-Induced Neutrophil Activation
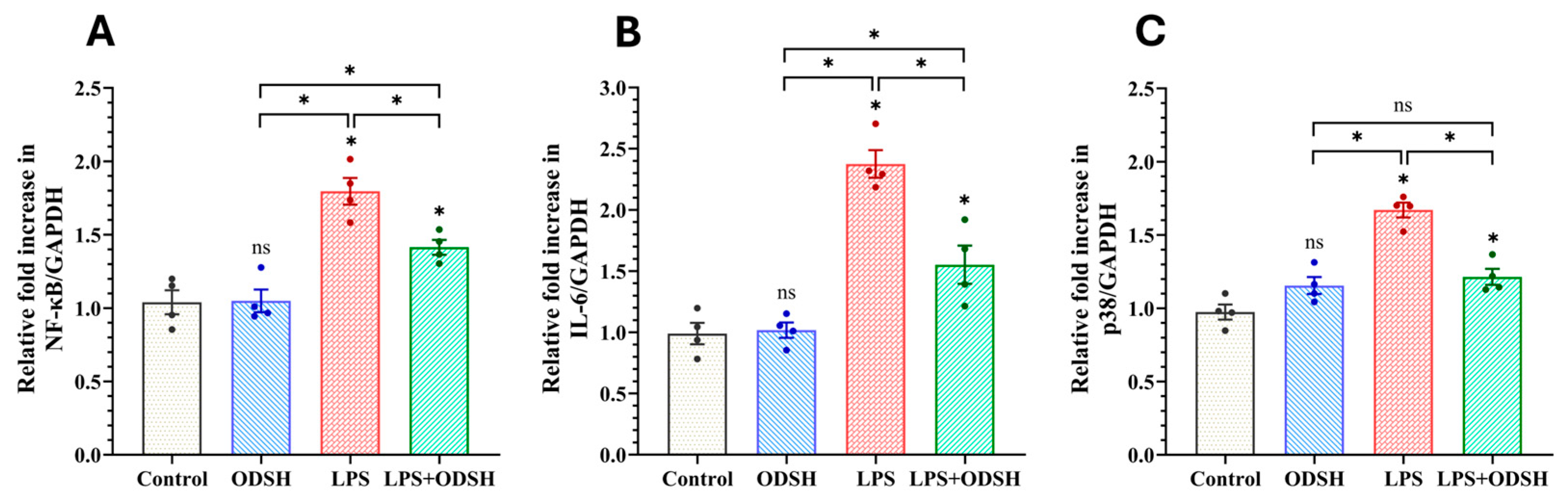
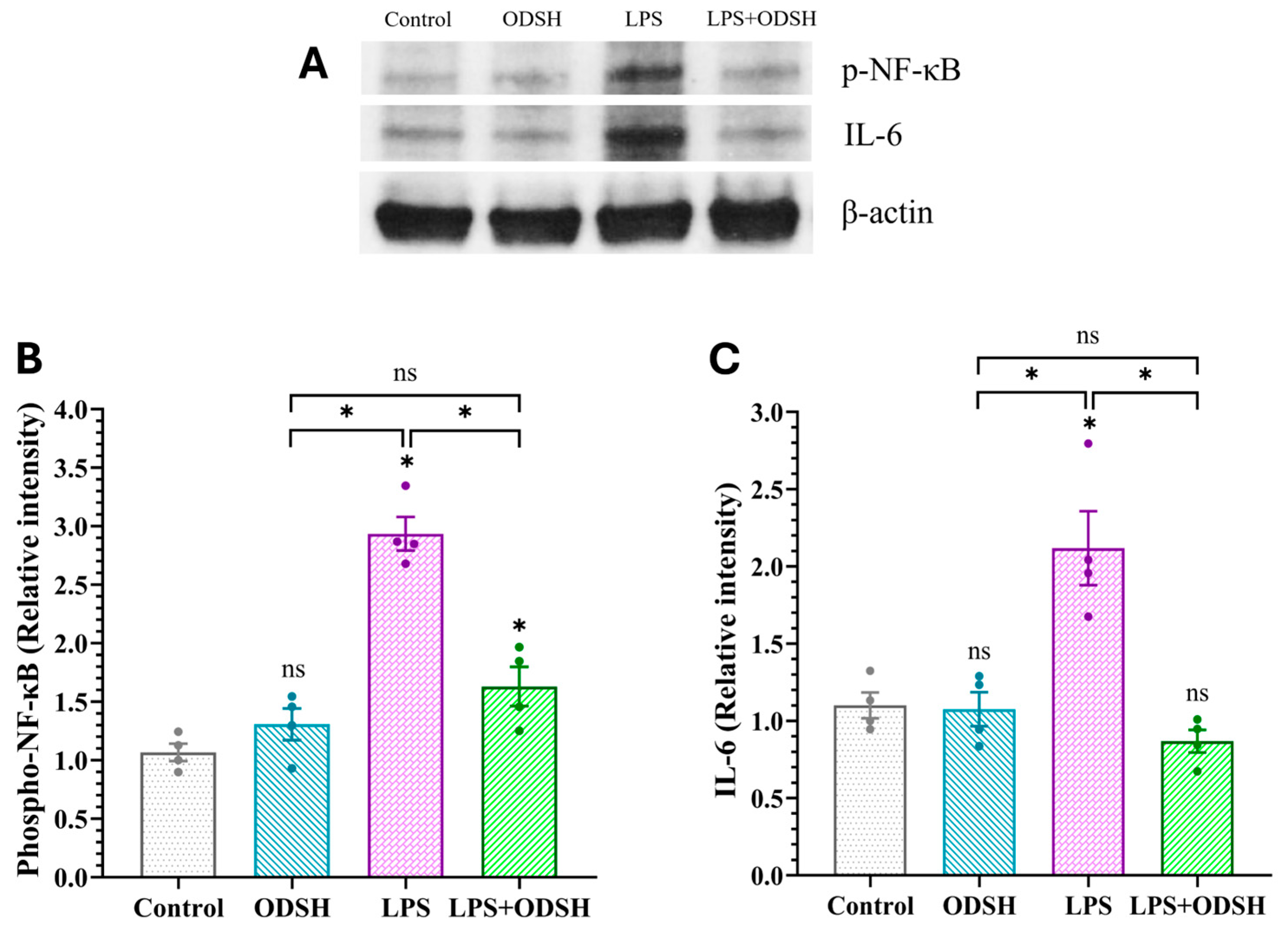
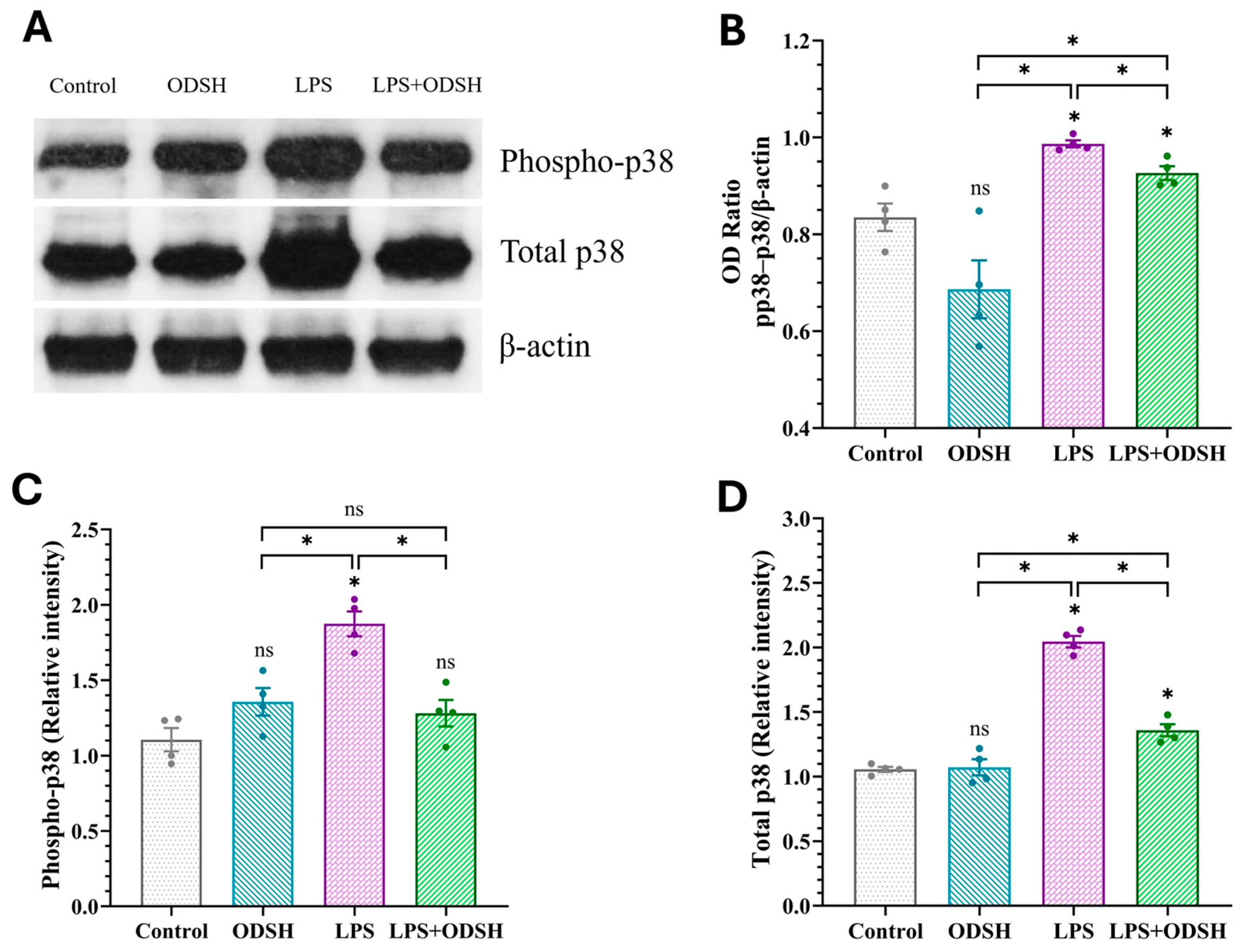
3.5. ODSH Suppresses the Activation of Pro-Inflammatory Signaling Induced by LPS in Murine Lung Tissue
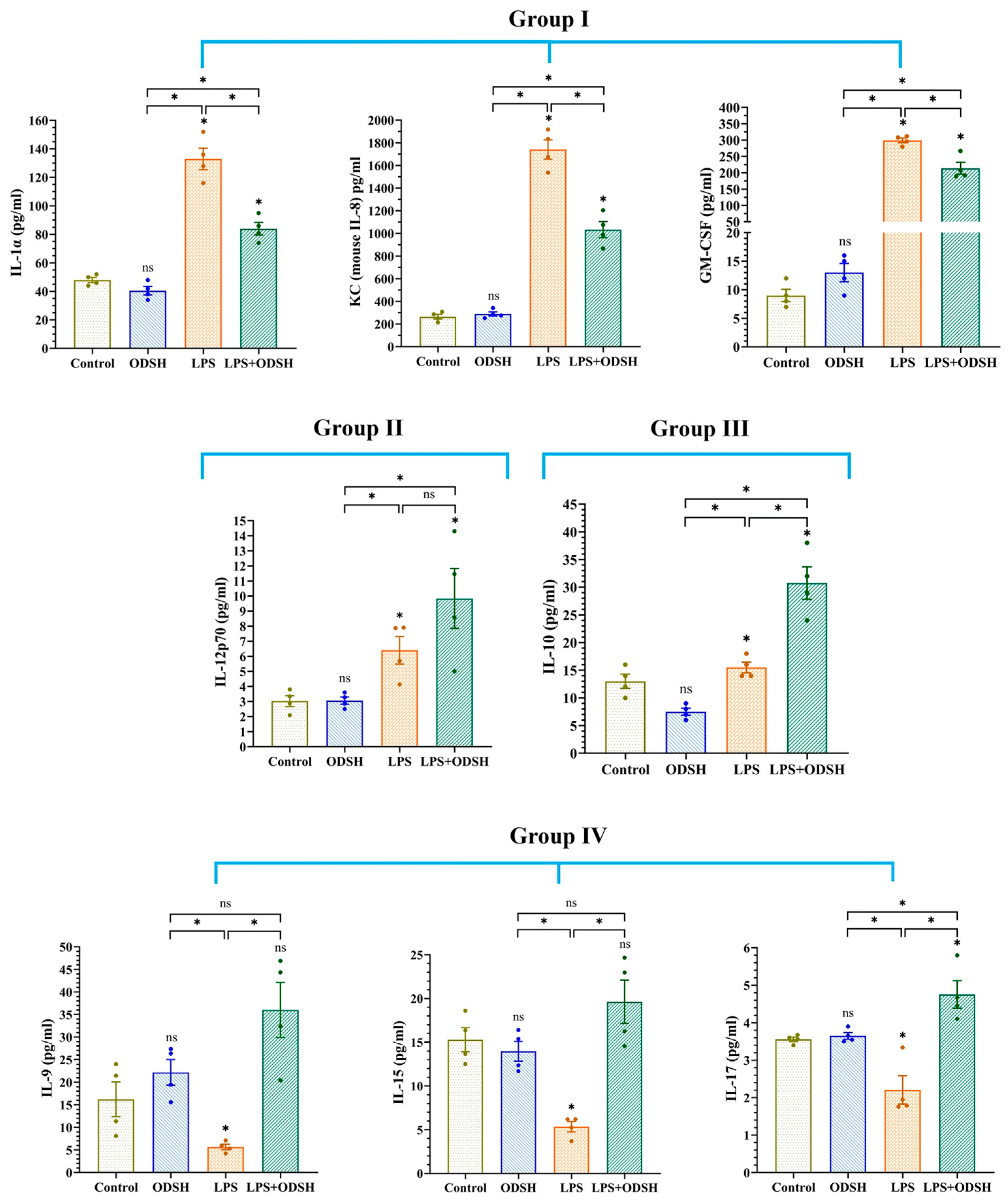
3.6. Effect of LPS and ODSH on the Levels of Cytokines in BALF
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACK | Ammonium–chloride–potassium |
| ALI | Acute lung injury |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| ARDS | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| BAL | Bronchoalveolar lavage |
| BALF | Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid |
| BCA | Bicinchoninic acid |
| CD14 | Cluster of differentiation 14 |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| DAB | 3,3′-diaminobenzidine |
| EBDA | Evans blue dye albumin |
| EC | Endothelial cell |
| ECIS | Electric cell-substrate impedance sensing |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| F(ab)2 | Fragment antigen binding (divalent antibody fragment) |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| HBSS | Hanks balanced salt solution |
| HIT | Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia |
| HLMVEC | Human lung microvascular endothelial cell |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| IJV | Internal jugular vein |
| IL | Interleukin |
| INF-γ | Interferon gamma |
| IT | Intratracheal |
| KC | Keratinocyte-derived chemokine |
| LBP | Lipopolysaccharide binding protein |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MCYTOMAG | Multiplex cytokine magnetic bead panel |
| MPO | Myeloperoxidase |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NK | Natural killer |
| OD | Optical density |
| ODSH | 2-O, 3-O desulfated heparin |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PEEP | Positive end-expiratory pressure |
| p38 | p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| RAGE | Receptor for advanced glycation end-products |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| SE | Standard error |
| TER | Transendothelial electrical resistance |
| Th17 | T helper 17 |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
References
- Bellani, G.; Laffey, J.G.; Pham, T.; Fan, E.; Brochard, L.; Esteban, A.; Gattinoni, L.; van Haren, F.; Larsson, A.; McAuley, D.F.; et al. Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care units in 50 countries. JAMA 2016, 315, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, J.N.; Lucas, R.; Verin, A.D. The acute respiratory distress syndrome: Mechanisms and perspective therapeutic approaches. Austin J. Vasc. Med. 2015, 2, 1009. [Google Scholar]
- Umapathy, N.S.; Gonzales, J.; Fulzele, S.; Kim, K.; Lucas, R.; Verin, A.D. β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory effects in a murine model of acute lung injury. Exp. Lung Res. 2012, 38, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinzelmann, M.; Bosshart, H. Heparin binds to lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein, facilitates the transfer of LPS to CD14, and enhances LPS-induced activation of peripheral blood monocytes. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 2280–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Espliguero, R.; Avanzas, P.; Jeffery, S.; Kaski, J.C. CD14 and toll-like receptor 4: A link between infection and acute coronary events? Heart 2004, 90, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummarapurugu, A.B.; Afosah, D.K.; Sankaranarayanan, N.V.; Gangji, R.N.; Zheng, S.; Kennedy, T.P.; Rubin, B.K.; Voynow, J.A.; Desai, U.R. Molecular principles for heparin oligosaccharide-based inhibition of neutrophil elastase in cystic fibrosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 12480–12490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, N.V.; Argyle, B.; Xu, X.; Reynolds, P.R.; Walenga, J.M.; Prechel, M.; Prestwich, G.D.; MacArthur, R.B.; Walters, B.B.; Hoidal, J.R.; et al. Low anticoagulant heparin targets multiple sites of inflammation, suppresses heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, and inhibits interaction of RAGE with its ligands. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 299, C97–C110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanam, V.D.; Prestwich, G.D.; Hoidal, J.R.; Kennedy, T.P. Low-Anticoagulant heparins in the treatment of Metastasis. In Research on Melanoma—A Glimpse into Current Directions and Future Trends [Internet]; Murph, M., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Gauthier, A.G.; Kennedy, T.P.; Wang, H.; Velagapudi, U.K.; Talele, T.T.; Lin, M.; Wu, J.; Daley, L.; Yang, X.; et al. 2-O, 3-O desulfated heparin (ODSH) increases bacterial clearance and attenuates lung injury in cystic fibrosis by restoring HMGB1-compromised macrophage function. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, J.N.; Kim, K.M.; Zemskova, M.A.; Rafikov, R.; Heeke, B.; Varn, M.N.; Black, S.; Kennedy, T.P.; Verin, A.D.; Zemskov, E.A. Low anticoagulant heparin blocks thrombin-induced endothelial permeability in a PAR-dependent manner. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2014, 62, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matute-Bello, G.; Downey, G.; Moore, B.B.; Groshong, S.D.; Matthay, M.A.; Slutsky, A.S.; Kuebler, W.M. An official American Thoracic Society workshop report: Features and measurements of experimental acute lung injury in animals. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2011, 44, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, J.N.; Gorshkov, B.; Varn, M.N.; Zemskova, M.A.; Zemskov, E.A.; Sridhar, S.; Lucas, R.; Verin, A.D. Protective effect of adenosine receptors against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L497–L507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hu, J.; He, T.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, X.; Lan, X.; Zhang, D.; Mei, H.; Chen, B.; Huang, Y. P38/MAPK contributes to endothelial barrier dysfunction via MAP4 phosphorylation-dependent microtubule disassembly in inflammation-induced acute lung injury. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Li, M.; Lan, E.; Ding, W.; Gao, L.; Tang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; et al. GSK3179106 ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and acute lung injury by targeting P38 MAPK. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannon, P.G.; Kim, M.J.; Dean, R.T.; Dawes, J. Augmentation of vascular endothelial barrier function by heparin and low molecular weight heparin. Thromb. Haemost. 1995, 73, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Ji, Y.; Su, N.; Mei, X.; Wang, Y.; Du, S.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Y.; Xing, X.H. Non-anticoagulant effects of low molecular weight heparins in inflammatory disorders: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 160, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauova, L.; Bdeir, K.; Rux, A.H.; Kalathottukaren, M.T.; Oberg, J.; La, C.C.; Lim, D.T.E.; Hayes, V.M.; Koma, G.T.; Sarkar, A.; et al. Destabilization of PF4-antigenic complexes in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood 2025, 145, 3030–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauova, L.; Zhai, L.; Kowalska, M.A.; Arepally, G.M.; Cines, D.B.; Poncz, M. Role of platelet surface PF4 antigenic complexes in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia pathogenesis: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Blood 2006, 107, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joglekar, M.V.; Quintana Diez, P.M.; Marcus, S.; Qi, R.; Espinasse, B.; Wiesner, M.R.; Pempe, E.; Liu, J.; Monroe, D.M.; Arepally, G.M. Disruption of PF4/H multimolecular complex formation with a minimally anticoagulant heparin (ODSH). Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 107, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, L.; Wu, J.; Patel, V.; Sitapara, R.; Rao, N.V.; Kennedy, T.P.; Mantell, L.L. Partially-desulfated heparin improves survival in Pseudomonas pneumonia by enhancing bacterial clearance and ameliorating lung injury. J. Immunotoxicol. 2014, 11, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, L.B.; Matthay, M.A. Clinical practice. Acute pulmonary edema. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 2788–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malle, E.; Furtmüller, P.G.; Sattler, W.; Obinger, C. Myeloperoxidase: A target for new drug development? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 152, 838–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, L.B.; Matthay, M.A. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1334–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Ai, Q.; Bao, L.; Shi, Y. Protective effect of unfractionated heparin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome in neonatal mice via the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed). 2023, 28, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, S.T.; Tang, J.; Ma, J.Q.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, H.Z.; Ma, X.C.; Zheng, Z. Unfractionated heparin attenuates endothelial barrier dysfunction via the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/serine/threonine kinase/nuclear factor kappa-B pathway. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 1815–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, T.; Cheang, I.; Liu, P.; Zhao, L.; He, X.; Jin, Y.; Tang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Sheng, C.; et al. Macrophage A2aR alleviates LPS-induced vascular endothelial injury and inflammation via inhibiting M1 polarisation and oxidative stress. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2025, 29, e70458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, T.; Wang, K.; Liang, X.; Zong, X.; Yang, H.; Li, Z. Effect of imatinib on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury and endothelial dysfunction through the P38 MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways in vivo and in vitro. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2025, 333, 104388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-S.; Han, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, H.-Y.; Jeon, D.; Lee, K. Polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate induces IL-6 and TNF-α expression through JNK-dependent pathway in human lung epithelial cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 43, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittirsch, D.; Flierl, M.A.; Day, D.E.; Nadeau, B.A.; McGuire, S.R.; Hoesel, L.M.; Ipaktchi, K.; Zetoune, F.S.; Sarma, J.V.; Leng, L.; et al. Acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide is independent of complement activation. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 7664–7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janga, H.; Cassidy, L.; Wang, F.; Spengler, D.; Oestern-Fitschen, S.; Krause, M.F.; Seekamp, A.; Tholey, A.; Fuchs, S. Site-specific and endothelial-mediated dysfunction of the alveolar-capillary barrier in response to lipopolysaccharides. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 982–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korb, A.; Tohidast-Akrad, M.; Cetin, E.; Axmann, R.; Smolen, J.; Schett, G. Differential tissue expression and activation of p38 MAPK alpha, beta, gamma, and delta isoforms in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2745–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, G.W.; Ju, M.J.; Zheng, Y.J.; Hao, G.W.; Ma, G.G.; Hou, J.Y.; Zhang, X.P.; Luo, Z.; Lu, L.M. CXCL16/CXCR6 is involved in LPS-induced acute lung injury via P38 signalling. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 5380–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xia, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; He, W.; Ye, H.; Yuan, X. Dexmedetomidine alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the p38/HO-1 pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 2442–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.; Romero, F.; Zhu, Y.; Duong, M.; Sun, J.; Walsh, K.; Summer, R. C1q deficiency promotes pulmonary vascular inflammation and enhances the susceptibility of the lung endothelium to injury. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 29642–29651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, N.; Kurrer, M.; Bachmann, M.F.; Kopf, M. Interleukin-1 is responsible for acute lung immunopathology but increases survival of respiratory influenza virus infection. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 6441–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Tan, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, W. Mechanism of IL-8-induced acute lung injury through pulmonary surfactant proteins A and B. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupa, A.; Kato, H.; Matthay, M.A.; Kurdowska, A.K. Proinflammatory activity of anti-IL-8 autoantibody:IL-8 complexes in alveolar edema fluid from patients with acute lung injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2004, 286, L1105–L1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blot, P.L.; Chousterman, B.G.; Santafè, M.; Cartailler, J.; Pacheco, A.; Magret, M.; Masclans, J.R.; Artigas, A.; Roca, O.; García-de-Acilu, M. Subphenotypes in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome treated with high-flow oxygen. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudlak, K.; Demuro, J.P.; Hanna, A.F.; Brem, H. Acute lung injury following the use of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Int. J. Crit. Illn. Inj. Sci. 2013, 3, 279–281. [Google Scholar]
- Parajuli, B.; Sonobe, Y.; Kawanokuchi, J.; Doi, Y.; Noda, M.; Takeuchi, H.; Mizuno, T.; Suzumura, A. GM-CSF increases LPS-induced production of proinflammatory mediators via upregulation of TLR4 and CD14 in murine microglia. J. Neuroinflammation 2012, 9, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiomi, A.; Usui, T.; Mimori, T. GM-CSF as a therapeutic target in autoimmune diseases. Inflamm. Regen. 2016, 36, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attanasio, M.; Gori, A.M.; Giusti, B.; Pepe, G.; Comeglio, P.; Brunelli, T.; Prisco, D.; Abbate, R.; Gensini, G.F.; Neri Serneri, G.G. Cytokine gene expression in human LPS- and IFNgamma-stimulated mononuclear cells is inhibited by heparin. Thromb. Haemost. 1998, 79, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yang, Y.C. Heparin inhibits the expression of interleukin-11 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in primate bone marrow stromal fibroblasts through mRNA destabilization. Blood 1995, 86, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Feng, D.; Zhou, B.; Bai, L.; Zhou, S.; Du, J.; Xu, G.; Yin, Y. Melatonin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced immune dysfunction in dendritic cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 120, 110282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.A.H.A.; Kang, B.-H.; Kim, J.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Choi, I.-W.; Cha, G.-H.; Yuk, J.-M.; Lee, Y.-H. IL-12 and IL-23 production in Toxoplasma gondii- or LPS-treated Jurkat T Cells via PI3K and MAPK signaling pathways. Korean J. Parasitol. 2017, 55, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, K.; Guzzo, C.; Che Mat, N.F.; Ma, W.; Kumar, A. The IL-12 family of cytokines in infection, inflammation and autoimmune disorders. Inflamm. Allergy - Drug Targets. 2009, 8, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackstein, H.; Lippitsch, A.; Krug, P.; Schevtschenko, I.; Kranz, S.; Hecker, M.; Dietert, K.; Gruber, A.D.; Bein, G.; Brendel, C.; et al. Prospectively defined murine mesenchymal stem cells inhibit Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced acute lung injury and improve pneumonia survival. Respir. Res. 2015, 16, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.G.; Gillam, F.B.; Hopkins, J.J.; Jayanthi, S.; Gundampati, R.K.; Su, G.; Bear, J.; Pilkington, G.R.; Jalah, R.; Felber, B.K.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of heparin-induced modulation of human interleukin 12 bioactivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 4412–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aass, H.C.D.; Hellum, M.; Trøseid, A.-M.S.; Brandtzaeg, P.; Berg, J.P.; Øvstebø, R.; Henriksson, C.E. Whole-blood incubation with the Neisseria meningitidis lpxL1 mutant induces less pro-inflammatory cytokines than the wild type, and IL-10 reduces the MyD88-dependent cytokines. Innate Immun. 2018, 24, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandtzaeg, P.; Osnes, L.; Ovstebø, R.; Joø, G.B.; Westvik, A.B.; Kierulf, P. Net inflammatory capacity of human septic shock plasma evaluated by a monocyte-based target cell assay: Identification of interleukin-10 as a major functional deactivator of human monocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 184, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.S.; Cheng, G. Role of interleukin 10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune disease. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 32, 23–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbadi, A.; Loftis, J.; Wang, A.; Yu, M.; Wang, Y.; Shakya, S.; Li, X.; Maytin, E.; Hascall, V. Heparin inhibits proinflammatory and promotes anti-inflammatory macrophage polarization under hyperglycemic stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 4849–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.; Moradi, M.; Khorshidahmad, T.; Motamedi, M. Anti-inflammatory effects of heparin and its derivatives: A systematic review. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 2015, 507151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, E. The anti-inflammatory effects of heparin and related compounds. Thromb. Res. 2008, 122, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosmann, M.; Russkamp, N.F.; Ward, P.A. Fingerprinting of the TLR4-induced acute inflammatory response. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2012, 93, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.F.; Aden, J.; Lyons, C.R.; Tesfaigzi, Y. Resolution of LPS-induced airway inflammation and goblet cell hyperplasia is independent of IL-18. Respir. Res. 2007, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.C.; Pang, L.L.; Mao, Q.S.; Wu, S.Y.; Xiao, Q.F. IL-9 exacerbates the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease through oxidative stress. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 8877–8884. [Google Scholar]
- Sadhu, S.; Dalal, R.; Dandotiya, J.; Binayke, A.; Singh, V.; Tripathy, M.R.; Das, V.; Goswami, S.; Kumar, S.; Rizvi, Z.A.; et al. IL-9 aggravates SARS-CoV-2 infection and exacerbates associated airway inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arras, M.; Louahed, J.; Heilier, J.F.; Delos, M.; Brombacher, F.; Renauld, J.C.; Lison, D.; Huaux, F. IL-9 protects against bleomycin-induced lung injury: Involvement of prostaglandins. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Jin, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Ren, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Fang, S.; Lin, N.; et al. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells derived IL-9 reduces macrophage apoptosis and attenuates acute lung injury in sepsis. Inflamm. Res. 2025, 74, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamford, R.N.; DeFilippis, A.P.; Azimi, N.; Kurys, G.; Waldmann, T.A. The 5′ untranslated region, signal peptide, and the coding sequence of the carboxyl terminus of IL-15 participate in its multifaceted translational control. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 4418–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valkenburg, S.A.; Li, O.T.W.; Mak, P.W.Y.; Mok, C.K.P.; Nicholls, J.M.; Guan, Y.; Waldmann, T.A.; Peiris, J.S.; Perera, L.P.; Poon, L.L. IL-15 adjuvanted multivalent vaccinia-based universal influenza vaccine requires CD4+ T cells for heterosubtypic protection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5676–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Sun, Q.; Yu, X.; Zhao, L. Rescue of nonlytic Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) expressing IL-15 for cancer immunotherapy. Virus Res. 2017, 233, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, R.; Maeda, N.; Shibata, K.; Yamada, H.; Kase, T.; Yoshikai, Y. Interleukin-15 is critical in the pathogenesis of influenza a virus-induced acute lung injury. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5574–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, W.E.; Ross, M.E.; Baiocchi, R.A.; Marien, M.J.; Boiani, N.; Grabstein, K.; Caligiuri, M.A. Endogenous production of interleukin 15 by activated human monocytes is critical for optimal production of interferon-gamma by natural killer cells in vitro. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 2578–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Gu, C.; Li, D.; Zhu, L. Depletion of circulating monocytes suppresses IL-17 and HMGB1 expression in mice with LPS-induced acute lung injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 312, L231–L242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-C.; Velichko, S.; Hung, L.-Y.; Wu, R. IL-17A and Th17 cells in lung inflammation: An update on the role of Th17 cell differentiation and IL-17R signaling in host defense against infection. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 267971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Martin, R.J.; Rino, J.G.; Breed, R.; Torres, R.M.; Chu, H.W. IL-23-dependent IL-17 production is essential in neutrophil recruitment and activity in mouse lung defense against respiratory Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Microbes Infect. 2007, 9, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonzales, J.; Patil, R.S.; Kennedy, T.P.; Umapathy, N.S.; Lucas, R.; Verin, A.D. Protective Effect of Low 2-O, 3-O Desulfated Heparin (ODSH) Against LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091232
Gonzales J, Patil RS, Kennedy TP, Umapathy NS, Lucas R, Verin AD. Protective Effect of Low 2-O, 3-O Desulfated Heparin (ODSH) Against LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(9):1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091232
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzales, Joyce, Rahul S. Patil, Thomas P. Kennedy, Nagavedi S. Umapathy, Rudolf Lucas, and Alexander D. Verin. 2025. "Protective Effect of Low 2-O, 3-O Desulfated Heparin (ODSH) Against LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice" Biomolecules 15, no. 9: 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091232
APA StyleGonzales, J., Patil, R. S., Kennedy, T. P., Umapathy, N. S., Lucas, R., & Verin, A. D. (2025). Protective Effect of Low 2-O, 3-O Desulfated Heparin (ODSH) Against LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice. Biomolecules, 15(9), 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091232






