Comparative Analysis of Aggregation of β- and γ-Synucleins in Vertebrates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cloning and Production of Recombinant Proteins
2.2. Aggregation Kinetics
2.3. Amino Acid Sequence Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
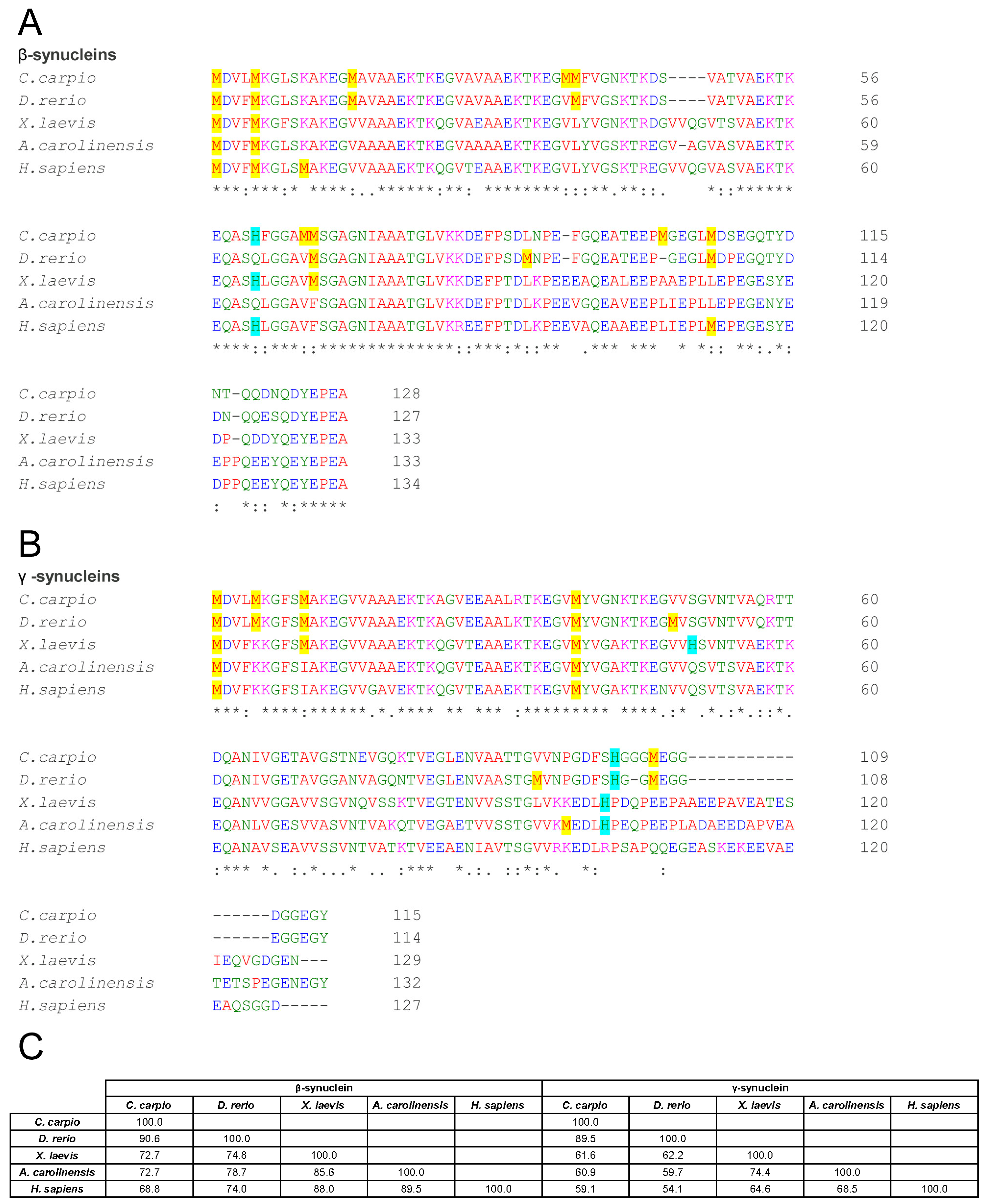
3.1. Sequence Variation and Predicted Structural Features of Vertebrate β- and γ-Synucleins
3.2. β-Synucleins: Human β-Syn Aggregates Under In Vitro Conditions, Whereas Non-Mammalian Orthologues Remain Stable

3.3. γ-Synucleins: All Orthologues Undergo β-Sheet Transitions with Species-Specific Aggregation Dynamics

3.4. Copper (CuSO4) Reduces Human β-Syn Aggregation and Modulates γ-Syn Dynamics in a Species-Specific Manner


4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| CD | Circular dichroism |
| AFM | Atomic force microscopy |
| DLB | Dementia with Lewy bodies |
| ITC | Isothermal titration calorimetry |
| MSA | Multiple system atrophy |
| MST | Microscale thermophoresis |
| NAC | Non-amyloid component |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| ThT | Thioflavin T |
References
- George, J.M. The synucleins. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, REVIEWS3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavedan, C.; Leroy, E.; Dehejia, A.; Buchholtz, S.; Dutra, A.; Nussbaum, R.L.; Polymeropoulos, M.H. Identification, localization and characterization of the human gamma-synuclein gene. Hum. Genet. 1998, 103, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campion, D.; Martin, C.; Heilig, R.; Charbonnier, F.; Moreau, V.; Flaman, J.M.; Petit, J.L.; Hannequin, D.; Brice, A.; Frebourg, T. The NACP/synuclein gene: Chromosomal assignment and screening for alterations in Alzheimer disease. Genomics 1995, 26, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; de Silva, H.A.; Pettenati, M.J.; Rao, P.N.; George-Hyslop, P.S.; Roses, A.D.; Xia, Y.; Horsburgh, K.; Ueda, K.; Saitoh, T. The human NACP/alpha-synuclein gene: Chromosome assignment to 4q21.3-q22 and TaqI RFLP analysis. Genomics 1995, 26, 425–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibasaki, Y.; Baillie, D.A.; St Clair, D.; Brookes, A.J. High-resolution mapping of SNCA encoding alpha-synuclein, the non-A beta component of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid precursor, to human chromosome 4q21.3→q22 by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1995, 71, 54–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavedan, C.; Dehejia, A.; Pike, B.; Dutra, A.; Leroy, E.; Ide, S.E.; Root, H.; Rubenstein, J.; Boyer, R.L.; Chandrasekharappa, S.; et al. Contig map of the Parkinson’s disease region on 4q21-q23. DNA Res. Int. J. Rapid Publ. Rep. Genes Genomes 1998, 5, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nakajo, S.; Tsukada, K.; Omata, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Nakaya, K. A new brain-specific 14-kDa protein is a phosphoprotein. Its complete amino acid sequence and evidence for phosphorylation. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 217, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Fukushima, H.; Masliah, E.; Xia, Y.; Iwai, A.; Yoshimoto, M.; Otero, D.A.; Kondo, J.; Ihara, Y.; Saitoh, T. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding an unrecognized component of amyloid in Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 11282–11286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakes, R.; Spillantini, M.G.; Goedert, M. Identification of two distinct synucleins from human brain. FEBS Lett. 1994, 345, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajo, S.; Shioda, S.; Nakai, Y.; Nakaya, K. Localization of phosphoneuroprotein 14 (PNP 14) and its mRNA expression in rat brain determined by immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization. Mol. Brain Res. 1994, 27, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, A.; Masliah, E.; Yoshimoto, M.; Ge, N.; Flanagan, L.; de Silva, H.A.; Kittel, A.; Saitoh, T. The precursor protein of non-A beta component of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid is a presynaptic protein of the central nervous system. Neuron 1995, 14, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akopian, A.N.; Wood, J.N. Peripheral nervous system-specific genes identified by subtractive cDNA cloning. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 21264–21270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Liu, Y.E.; Jia, T.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Xiao, G.; Joseph, B.K.; Rosen, C.; Shi, Y.E. Identification of a breast cancer-specific gene, BCSG1, by direct differential cDNA sequencing. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buchman, V.L.; Hunter, H.J.; Pinon, L.G.; Thompson, J.; Privalova, E.M.; Ninkina, N.N.; Davies, A.M. Persyn, a member of the synuclein family, has a distinct pattern of expression in the developing nervous system. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 9335–9341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenz Verca, M.S.; Bahi, A.; Boyer, F.; Wagner, G.C.; Dreyer, J.L. Distribution of alpha- and gamma-synucleins in the adult rat brain and their modification by high-dose cocaine treatment. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 18, 1923–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Zhao, Y. Evolutionary aspects of the synuclein super-family and sub-families based on large-scale phylogenetic and group-discrimination analysis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.H.; Eliezer, D. Secondary structure and dynamics of micelle bound beta- and gamma-synuclein. Protein Sci. A Publ. Protein Soc. 2006, 15, 1162–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giasson, B.I.; Murray, I.V.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. A hydrophobic stretch of 12 amino acid residues in the middle of alpha-synuclein is essential for filament assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 2380–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowall, J.S.; Brown, D.R. Alpha-synuclein: Relating metals to structure, function and inhibition. Met. Integr. Biometal Sci. 2016, 8, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Rockenstein, E.; Mante, M.; Mallory, M.; Masliah, E. beta-Synuclein inhibits alpha-synuclein aggregation: A possible role as an anti-parkinsonian factor. Neuron 2001, 32, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Paik, S.R.; Choi, K.Y. Beta-synuclein exhibits chaperone activity more efficiently than alpha-synuclein. FEBS Lett. 2004, 576, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Limprasert, P.; Murray, I.V.; Smith, A.C.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Sopher, B.L.; La Spada, A.R. Beta-synuclein modulates alpha-synuclein neurotoxicity by reducing alpha-synuclein protein expression. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 3002–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Lansbury, P.T., Jr. Beta-synuclein inhibits formation of alpha-synuclein protofibrils: A possible therapeutic strategy against Parkinson’s disease. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 3696–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N.; Li, J.; Souillac, P.; Millett, I.S.; Doniach, S.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M.; Fink, A.L. Biophysical properties of the synucleins and their propensities to fibrillate: Inhibition of alpha-synuclein assembly by beta- and gamma-synucleins. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 11970–11978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.K.; Yang, X.; Atieh, T.B.; Olson, M.P.; Khare, S.D.; Baum, J. Multi-Pronged Interactions Underlie Inhibition of alpha-Synuclein Aggregation by beta-Synuclein. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 2360–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitao, A.; Bhumkar, A.; Hunter, D.J.B.; Gambin, Y.; Sierecki, E. Unveiling a Selective Mechanism for the Inhibition of alpha-Synuclein Aggregation by beta-Synuclein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, M.; Li, J.; Liu, T.; Hou, K.; Sun, L.; Wei, J. beta-Synuclein Intermediates alpha-Synuclein Neurotoxicity in Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2024, 15, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N.; Oldfield, C.J.; Dunker, A.K. Intrinsically disordered proteins in human diseases: Introducing the D2 concept. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2008, 37, 215–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, W.S.; Jonas, A.; Clayton, D.F.; George, J.M. Stabilization of alpha-synuclein secondary structure upon binding to synthetic membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 9443–9449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohaupt, P.; Pons, M.L.; Vialaret, J.; Delaby, C.; Hirtz, C.; Lehmann, S. beta-Synuclein as a candidate blood biomarker for synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2022, 14, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, K.H.; Kang, M.J.; Youn, Y.C.; An, S.S.A.; Kim, S. Alpha-synuclein: A pathological factor with Abeta and tau and biomarker in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2022, 14, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaribash, S.; Mohammadi, K.; Sani, M.A. Alpha-Synuclein Pathophysiology in Neurodegenerative Disorders: A Review Focusing on Molecular Mechanisms and Treatment Advances in Parkinson’s Disease. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 45, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Rahman, T.; Herrera-Calderon, R.E.; Ahluwalia, A.; Wireko, A.A.; Ferreira, T.; Tan, J.K.; Wolfson, M.; Ghosh, S.; Horbas, V.; Garg, V.; et al. The potential of phosphorylated alpha-synuclein as a biomarker for the diagnosis and monitoring of multiple system atrophy. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e14678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, F.; Nishie, M.; Yoshimoto, M.; Takahashi, H.; Wakabayashi, K. Reciprocal accumulation of beta-synuclein in alpha-synuclein lesions in multiple system atrophy. Neuroreport 2003, 14, 1783–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M. Alpha-synuclein and neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toni, M.; Massimino, M.L.; De Mario, A.; Angiulli, E.; Spisni, E. Metal Dyshomeostasis and Their Pathological Role in Prion and Prion-Like Diseases: The Basis for a Nutritional Approach. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusiner, S.B.; Woerman, A.L.; Mordes, D.A.; Watts, J.C.; Rampersaud, R.; Berry, D.B.; Patel, S.; Oehler, A.; Lowe, J.K.; Kravitz, S.N.; et al. Evidence for alpha-synuclein prions causing multiple system atrophy in humans with parkinsonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5308–E5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, D.R.; Li, B.; Sun, C.; Fan, W.; Sawaya, M.R.; Jiang, L.; Eisenberg, D.S. Structures of fibrils formed by alpha-synuclein hereditary disease mutant H50Q reveal new polymorphs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, K.A.; Lee, S.J.; Rochet, J.C.; Ding, T.T.; Williamson, R.E.; Lansbury, P.T., Jr. Acceleration of oligomerization, not fibrillization, is a shared property of both alpha-synuclein mutations linked to early-onset Parkinson’s disease: Implications for pathogenesis and therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro, D.F.; Rodrigues, E.F.; Langohr, R.; Shahpasandzadeh, H.; Ribeiro, T.; Guerreiro, P.; Gerhardt, E.; Krohnert, K.; Klucken, J.; Pereira, M.D.; et al. Systematic comparison of the effects of alpha-synuclein mutations on its oligomerization and aggregation. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherford, N.J.; Giasson, B.I. The A53E alpha-synuclein pathological mutation demonstrates reduced aggregation propensity in vitro and in cell culture. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 597, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Sekigawa, A.; Sekiyama, K.; Takamatsu, Y.; Hashimoto, M. Possible alterations in beta-Synuclein, the non-amyloidogenic homologue of alpha-Synuclein, during progression of sporadic alpha-synucleinopathies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 11584–11592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubrey, L.D.; Ninkina, N.; Ulamec, S.M.; Abramycheva, N.Y.; Vasili, E.; Devine, O.M.; Wilkinson, M.; Mackinnon, E.; Limorenko, G.; Walko, M.; et al. Substitution of Met-38 to Ile in gamma-synuclein found in two patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis induces aggregation into amyloid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2309700120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.K.; Yang, X.; Baum, J. Interactions between the Intrinsically Disordered Proteins beta-Synuclein and alpha-Synuclein. Proteomics 2018, 18, e1800109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirak, Y.; Furuncuoglu, Y.; Yapicier, O.; Alici, S.; Argon, A. Predictive and prognostic values of BubR1 and synuclein-gamma expression in breast cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 5345–5353. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, M.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X. Suppression of synuclein gamma inhibits the movability of endometrial carcinoma cells by PI3K/AKT/ERK signaling pathway. Genes Genom. 2021, 43, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Ren, Z.; Wang, F.; Zheng, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Zeng, Y. gamma-Synuclein promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma via JAK2/STAT5b signaling pathway. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2024, 14, 2408–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemura, Y.; Ojima, H.; Oshima, G.; Shinoda, M.; Hasegawa, Y.; Kitago, M.; Yagi, H.; Abe, Y.; Hori, S.; Fujii-Nishimura, Y.; et al. Gamma-synuclein is a novel prognostic marker that promotes tumor cell migration in biliary tract carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 5599–5613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchman, V.L.; Adu, J.; Pinon, L.G.; Ninkina, N.N.; Davies, A.M. Persyn, a member of the synuclein family, influences neurofilament network integrity. Nat. Neurosci. 1998, 1, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, S.R.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Chang, C.S.; Kim, J. Copper(II)-induced self-oligomerization of alpha-synuclein. Biochem. J. 1999, 340 Pt 3, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N.; Li, J.; Fink, A.L. Metal-triggered structural transformations, aggregation, and fibrillation of human alpha-synuclein. A possible molecular NK between Parkinson’s disease and heavy metal exposure. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 44284–44296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, F. Redox reactions of the alpha-synuclein-Cu2+ complex and their effects on neuronal cell viability. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 8134–8142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, A.L. The aggregation and fibrillation of alpha-synuclein. Acc. Chem. Res. 2006, 39, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binolfi, A.; Lamberto, G.R.; Duran, R.; Quintanar, L.; Bertoncini, C.W.; Souza, J.M.; Cervenansky, C.; Zweckstetter, M.; Griesinger, C.; Fernandez, C.O. Site-specific interactions of Cu(II) with alpha and beta-synuclein: Bridging the molecular gap between metal binding and aggregation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 11801–11812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binolfi, A.; Rodriguez, E.E.; Valensin, D.; D’Amelio, N.; Ippoliti, E.; Obal, G.; Duran, R.; Magistrato, A.; Pritsch, O.; Zweckstetter, M.; et al. Bioinorganic chemistry of Parkinson’s disease: Structural determinants for the copper-mediated amyloid formation of alpha-synuclein. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 10668–10679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deas, E.; Cremades, N.; Angelova, P.R.; Ludtmann, M.H.; Yao, Z.; Chen, S.; Horrocks, M.H.; Banushi, B.; Little, D.; Devine, M.J.; et al. Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers Interact with Metal Ions to Induce Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Death in Parkinson’s Disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 24, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenschlager, J.; Stephens, A.D.; Fusco, G.; Strohl, F.; Curry, N.; Zacharopoulou, M.; Michel, C.H.; Laine, R.; Nespovitaya, N.; Fantham, M.; et al. C-terminal calcium binding of alpha-synuclein modulates synaptic vesicle interaction. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Garcia, M.; Fusco, G.; De Simone, A. Metal interactions of alpha-synuclein probed by NMR amide-proton exchange. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1167766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N.; Li, J.; Fink, A.L. Evidence for a partially folded intermediate in alpha-synuclein fibril formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 10737–10744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Drakulic, S.; Deas, E.; Ouberai, M.; Aprile, F.A.; Arranz, R.; Ness, S.; Roodveldt, C.; Guilliams, T.; De-Genst, E.J.; et al. Structural characterization of toxic oligomers that are kinetically trapped during alpha-synuclein fibril formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1994–E2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heise, H.; Hoyer, W.; Becker, S.; Andronesi, O.C.; Riedel, D.; Baldus, M. Molecular-level secondary structure, polymorphism, and dynamics of full-length alpha-synuclein fibrils studied by solid-state NMR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15871–15876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulatskaya, A.I.; Rodina, N.P.; Sulatsky, M.I.; Povarova, O.I.; Antifeeva, I.A.; Kuznetsova, I.M.; Turoverov, K.K. Investigation of alpha-Synuclein Amyloid Fibrils Using the Fluorescent Probe Thioflavin T. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wordehoff, M.M.; Bannach, O.; Shaykhalishahi, H.; Kulawik, A.; Schiefer, S.; Willbold, D.; Hoyer, W.; Birkmann, E. Single fibril growth kinetics of alpha-synuclein. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.; Meuvis, J.; Hendrix, J.; Carl, S.A.; Engelborghs, Y. Early aggregation steps in alpha-synuclein as measured by FCS and FRET: Evidence for a contagious conformational change. Biophys. J. 2010, 98, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, T.; Matveyenka, M.; Kurouski, D. Elucidation of Secondary Structure and Toxicity of alpha-Synuclein Oligomers and Fibrils Grown in the Presence of Phosphatidylcholine and Phosphatidylserine. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 3183–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, T.; Kumar, R.; Horvath, I.; Scheers, N.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Abundant fish protein inhibits alpha-synuclein amyloid formation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreau, H.S.; Krol, K.M.; Eibl, J.K.; Williams, L.D.; Rossiter, J.P.; Palace, V.P.; Ross, G.M. The association of metal ion exposure with alpha-synuclein-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of fish, Catostomus commersoni. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 92, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toni, M.; Cioni, C. Fish Synucleins: An Update. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6665–6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, H.; Kenmochi, N.; Namikawa, K. Age- and alpha-Synuclein-Dependent Degeneration of Dopamine and Noradrenaline Neurons in the Annual Killifish Nothobranchius furzeri. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 1727–1733.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, R.; Toni, M.; Casini, A.; Vivacqua, G.; Yu, S.; D’Este, L.; Cioni, C. Localization of alpha-synuclein in teleost central nervous system: Immunohistochemical and Western blot evidence by 3D5 monoclonal antibody in the common carp, Cyprinus carpio. J. Comp. Neurol. 2015, 523, 1095–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorsi di Patti, M.C.; Angiulli, E.; Casini, A.; Vaccaro, R.; Cioni, C.; Toni, M. Synuclein Analysis in Adult Xenopus laevis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Chan, W.Y.; Chan, S.O.; Grunz, H.; Zhao, H. Characterization of three synuclein genes in Xenopus laevis. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 2011, 240, 2028–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toni, M.; Cioni, C.; De Angelis, F.; di Patti, M.C. Synuclein expression in the lizard Anolis carolinensis. J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 2016, 202, 577–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seleem, A.A. Expression of alpha-synuclein during eye development of mice (Mus musculus), chick (Gallus gallus domisticus) and fish (Ctenopharyngodon idella) in a comparison study. Tissue Cell 2015, 47, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartman, V.N.; Miller, M.A.; Clayton, D.F.; Liu, W.C.; Kroodsma, D.E.; Brenowitz, E.A. Testosterone regulates alpha-synuclein mRNA in the avian song system. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, V.; Modarres Mousavi, S.M.; Annadurai, N.; Sukur, S.; Mehrnejad, F.; Moradi, S.; Malina, L.; Kolarikova, M.; Ranc, V.; Frydrych, I.; et al. Hydrophobic residues in the alpha-synuclein NAC domain drive seed-competent fibril formation and are targeted by peptide inhibitors. FEBS J. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, N.J.; Jaafar, A.K.; Gambin, Y.; Sierecki, E. Divalent and Trivalent Metallic Ions Differentially Affect Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, C.; Kjaer, L.; Christensen, M.S.; Pedersen, J.N.; Christiansen, G.; Perez, A.W.; Moller, I.M.; Enghild, J.J.; Pedersen, J.S.; Larsen, K.; et al. Alpha-Synucleins from Animal Species Show Low Fibrillation Propensities and Weak Oligomer Membrane Disruption. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 5145–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampomah, G.B.; Hard, E.R.; Pratt, M.R. Alpha-Synuclein Sequences from Long-Lived Animals Display Generally Diminished Aggregation Compared to Shorter-Lived Animals Including Humans. ChemBioChem A Eur. J. Chem. Biol. 2025, 26, e202500340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffioli, E.; Angiulli, E.; Nonnis, S.; Grassi Scalvini, F.; Negri, A.; Tedeschi, G.; Arisi, I.; Frabetti, F.; D’Aniello, S.; Alleva, E.; et al. Brain Proteome and Behavioural Analysis in Wild Type, BDNF+/− and BDNF−/− Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Exposed to Two Different Temperatures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.T. Protein secondary structure prediction based on position-specific scoring matrices. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 292, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psol, M.; Darvas, S.G.; Leite, K.; Mahajani, S.U.; Bahr, M.; Kugler, S. Dementia with Lewy bodies-associated ss-synuclein mutations V70M and P123H cause mutation-specific neuropathological lesions. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 30, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Mehra, S.; Sawner, A.S.; Markam, P.S.; Panigrahi, R.; Navalkar, A.; Chatterjee, D.; Kumar, R.; Kadu, P.; Patel, K.; et al. Effect of Disease-Associated P123H and V70M Mutations on beta-Synuclein Fibrillation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 2836–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.K.; Singh, P.; Roy, S.; Bhat, R. Comparative Analysis of the Conformation, Aggregation, Interaction, and Fibril Morphologies of Human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-Synuclein Proteins. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 3830–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, U.; Lee, J.C. Membrane Interactions of alpha-Synuclein Probed by Neutrons and Photons. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidovic, M.; Rikalovic, M.G. Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation Pathway in Parkinson’s Disease: Current Status and Novel Therapeutic Approaches. Cells 2022, 11, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Cheng, C.H.; Chen, G.D.; Hung, C.C.; Yang, C.H.; Hwang, S.P.; Kawakami, K.; Wu, B.K.; Huang, C.J. Recapitulation of zebrafish sncga expression pattern and labeling the habenular complex in transgenic zebrafish using green fluorescent protein reporter gene. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 2009, 238, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milanese, C.; Sager, J.J.; Bai, Q.; Farrell, T.C.; Cannon, J.R.; Greenamyre, J.T.; Burton, E.A. Hypokinesia and reduced dopamine levels in zebrafish lacking beta- and gamma1-synucleins. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 2971–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, J.M.; Croll, R.P. A Critical Review of Zebrafish Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 835827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biere, A.L.; Wood, S.J.; Wypych, J.; Steavenson, S.; Jiang, Y.; Anafi, D.; Jacobsen, F.W.; Jarosinski, M.A.; Wu, G.M.; Louis, J.C.; et al. Parkinson’s disease-associated alpha-synuclein is more fibrillogenic than beta- and gamma-synuclein and cannot cross-seed its homologs. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 34574–34579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bost, M.; Houdart, S.; Oberli, M.; Kalonji, E.; Huneau, J.F.; Margaritis, I. Dietary copper and human health: Current evidence and unresolved issues. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. Organ Soc. Miner. Trace Elem. 2016, 35, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, P.; Wang, X.; Sarell, C.J.; Drewett, A.; Marken, F.; Viles, J.H.; Brown, D.R. The synucleins are a family of redox-active copper binding proteins. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.E.; Rios, A.; Trujano-Ortiz, L.G.; Villegas, A.; Castaneda-Hernandez, G.; Fernandez, C.O.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Quintanar, L. Comparing the copper binding features of alpha and beta synucleins. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2022, 229, 111715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miotto, M.C.; Pavese, M.D.; Quintanar, L.; Zweckstetter, M.; Griesinger, C.; Fernandez, C.O. Bioinorganic Chemistry of Parkinson’s Disease: Affinity and Structural Features of Cu(I) Binding to the Full-Length beta-Synuclein Protein. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 10387–10395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamin, G.; Glaser, C.B.; Uversky, V.N.; Fink, A.L. Certain metals trigger fibrillation of methionine-oxidized alpha-synuclein. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 27630–27635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villar-Pique, A.; Lopes da Fonseca, T.; Sant’Anna, R.; Szego, E.M.; Fonseca-Ornelas, L.; Pinho, R.; Carija, A.; Gerhardt, E.; Masaracchia, C.; Abad Gonzalez, E.; et al. Environmental and genetic factors support the dissociation between alpha-synuclein aggregation and toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6506–E6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- do Amaral, M.J.; Mohapatra, S.; Passos, A.R.; Lopes da Silva, T.S.; Carvalho, R.S.; da Silva Almeida, M.; Pinheiro, A.S.; Wegmann, S.; Cordeiro, Y. Copper drives prion protein phase separation and modulates aggregation. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadi7347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasia, R.M.; Bertoncini, C.W.; Marsh, D.; Hoyer, W.; Cherny, D.; Zweckstetter, M.; Griesinger, C.; Jovin, T.M.; Fernandez, C.O. Structural characterization of copper(II) binding to alpha-synuclein: Insights into the bioinorganic chemistry of Parkinson’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4294–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamin, G.; Munishkina, L.A.; Karymov, M.A.; Lyubchenko, Y.L.; Uversky, V.N.; Fink, A.L. Forcing nonamyloidogenic beta-synuclein to fibrillate. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 9096–9107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonaccorsi di Patti, M.C.; Meoni, M.; Toni, M. Comparative Analysis of Aggregation of β- and γ-Synucleins in Vertebrates. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091231
Bonaccorsi di Patti MC, Meoni M, Toni M. Comparative Analysis of Aggregation of β- and γ-Synucleins in Vertebrates. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(9):1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091231
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonaccorsi di Patti, Maria Carmela, Martina Meoni, and Mattia Toni. 2025. "Comparative Analysis of Aggregation of β- and γ-Synucleins in Vertebrates" Biomolecules 15, no. 9: 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091231
APA StyleBonaccorsi di Patti, M. C., Meoni, M., & Toni, M. (2025). Comparative Analysis of Aggregation of β- and γ-Synucleins in Vertebrates. Biomolecules, 15(9), 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15091231






